Urinary Collectrin as Promising Biomarker for Acute Kidney Injury in Patients Undergoing Cardiac Surgery
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Population
2.2. Urine Collection
- Baseline: 60 min after anesthesia induction, before skin incision;
- Thirty minutes after initiating cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB);
- End of surgery;
- Postoperative day (POD) one (i.e., 6:00 am the day after surgery).
2.3. Collectrin (TMEM27) ELISA
2.4. AKI Diagnosis
2.5. Data Processing and Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Study Population
3.2. Urinary Collectrin Levels during Perioperative Course
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Uchino, S.; Bellomo, R.; Goldsmith, D.; Bates, S.; Ronco, C. An assessment of the RIFLE criteria for acute renal failure in hospitalized patients. Crit. Care Med. 2006, 34, 1913–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrier, R.W.; Wang, W.; Poole, B.; Mitra, A. Acute renal failure: Definitions, diagnosis, pathogenesis, and therapy. J. Clin. Investig. 2004, 114, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lameire, N.; Van Biesen, W.; Vanholder, R. Acute renal failure. Lancet 2005, 365, 417–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouchard, J.; Acharya, A.; Cerda, J.; Maccariello, E.R.; Madarasu, R.C.; Tolwani, A.J.; Liang, X.; Fu, P.; Liu, Z.H.; Mehta, R.L. A Prospective International Multicenter Study of AKI in the Intensive Care Unit. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2015, 10, 1324–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostermann, M.; Zarbock, A.; Goldstein, S.; Kashani, K.; Macedo, E.; Murugan, R.; Bell, M.; Forni, L.; Guzzi, L.; Joannidis, M.; et al. Recommendations on Acute Kidney Injury Biomarkers From the Acute Disease Quality Initiative Consensus Conference: A Consensus Statement. JAMA Netw. Open 2020, 3, e2019209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanmassenhove, J.; Van Biesen, W.; Vanholder, R.; Lameire, N. Subclinical AKI: Ready for primetime in clinical practice? J. Nephrol. 2019, 32, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boutin, L.; Latosinska, A.; Mischak, H.; Deniau, B.; Asakage, A.; Legrand, M.; Gayat, E.; Mebazaa, A.; Chadjichristos, C.E.; Depret, F. Subclinical and clinical acute kidney injury share similar urinary peptide signatures and prognosis. Intensive Care Med. 2023, 49, 1191–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moledina, D.G.; Parikh, C.R. Phenotyping of Acute Kidney Injury: Beyond Serum Creatinine. Semin. Nephrol. 2018, 38, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menez, S.; Parikh, C.R. Assessing the health of the nephron in acute kidney injury: Biomarkers of kidney function and injury. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 2019, 28, 560–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srisawat, N.; Kellum, J.A. The Role of Biomarkers in Acute Kidney Injury. Crit. Care Clin. 2020, 36, 125–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulvichit, W.; Kellum, J.A.; Srisawat, N. Biomarkers in Acute Kidney Injury. Crit. Care Clin. 2021, 37, 385–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kashani, K.; Al-Khafaji, A.; Ardiles, T.; Artigas, A.; Bagshaw, S.M.; Bell, M.; Bihorac, A.; Birkhahn, R.; Cely, C.M.; Chawla, L.S.; et al. Discovery and validation of cell cycle arrest biomarkers in human acute kidney injury. Crit. Care 2013, 17, R25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zou, Z.; Jin, J.; Teng, J.; Xu, J.; Shen, B.; Jiang, W.; Zhuang, Y.; Liu, L.; Luo, Z.; et al. Urinary TIMP-2 and IGFBP7 for the prediction of acute kidney injury following cardiac surgery. BMC Nephrol. 2017, 18, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, W.K.; Bailly, V.; Abichandani, R.; Thadhani, R.; Bonventre, J.V. Kidney Injury Molecule-1 (KIM-1): A novel biomarker for human renal proximal tubule injury. Kidney Int. 2002, 62, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Huang, Y.; Shang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Xu, G. The Predictive Value of Urinary Kidney Injury Molecular 1 for the Diagnosis of Contrast-Induced Acute Kidney Injury after Cardiac Catheterization: A Meta-Analysis. J. Interv. Cardiol. 2020, 2020, 4982987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bennett, M.; Dent, C.L.; Ma, Q.; Dastrala, S.; Grenier, F.; Workman, R.; Syed, H.; Ali, S.; Barasch, J.; Devarajan, P. Urine NGAL Predicts Severity of Acute Kidney Injury After Cardiac Surgery: A Prospective Study. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2008, 3, 665–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parikh, C.R.; Abraham, E.; Ancukiewicz, M.; Edelstein, C.L. Urine IL-18 is an early diagnostic marker for acute kidney injury and predicts mortality in the intensive care unit. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2005, 16, 3046–3052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pajenda, S.; Mechtler, K.; Wagner, L. Urinary neprilysin in the critically ill patient. BMC Nephrol. 2017, 18, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardi, M.H.; Wagner, L.; Ryz, S.; Puchinger, J.; Nixdorf, L.; Edlinger-Stanger, M.; Geilen, J.; Kainz, M.; Hiesmayr, M.J.; Lassnigg, A. Urinary neprilysin for early detection of acute kidney injury after cardiac surgery: A prospective observational study. Eur. J. Anaesthesiol. EJA 2021, 38, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khorashadi, M.; Beunders, R.; Pickkers, P.; Legrand, M. Proenkephalin: A New Biomarker for Glomerular Filtration Rate and Acute Kidney Injury. Nephron 2020, 144, 655–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bullen, A.L.; Fregoso, A.; Ascher, S.B.; Shlipak, M.G.; Ix, J.H.; Rifkin, D.E. Markers of Kidney Tubule Dysfunction and MAKE. Nephron 2023, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, K.M.; Morgan, D.J.R. The Proximal Tubule as the Pathogenic and Therapeutic Target in Acute Kidney Injury. Nephron 2022, 146, 494–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villa, G.; Katz, N.; Ronco, C. Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation and the Kidney. Cardiorenal Med. 2015, 6, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thiele, R.H.; Isbell, J.M.; Rosner, M.H. AKI Associated with Cardiac Surgery. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2015, 10, 500–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmussen, S.B.; Boyko, Y.; Ranucci, M.; de Somer, F.; Ravn, H.B. Cardiac surgery-Associated acute kidney injury—A narrative review. Perfusion 2023, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massoth, C.; Zarbock, A.; Meersch, M. Acute Kidney Injury in Cardiac Surgery. Crit. Care Clin. 2021, 37, 267–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danilczyk, U.; Sarao, R.; Remy, C.; Benabbas, C.; Stange, G.; Richter, A.; Arya, S.; Pospisilik, J.A.; Singer, D.; Camargo, S.M.; et al. Essential role for collectrin in renal amino acid transport. Nature 2006, 444, 1088–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pajenda, S.; Wagner, L.; Gerges, D.; Herkner, H.; Tevdoradze, T.; Mechtler, K.; Schmidt, A.; Winnicki, W. Urinary Collectrin (TMEM27) as Novel Marker for Acute Kidney Injury. Life 2022, 12, 1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kellum, J.A.; Lameire, N.; KDIGO AKI Guideline Work Group. Diagnosis, evaluation, and management of acute kidney injury: A KDIGO summary (Part 1). Crit. Care 2013, 17, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostermann, M.; Kunst, G.; Baker, E.; Weerapolchai, K.; Lumlertgul, N. Cardiac Surgery Associated AKI Prevention Strategies and Medical Treatment for CSA-AKI. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 5285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.-Y.; Chen, Y.-C.; Tsai, F.-C.; Tian, Y.-C.; Jenq, C.-C.; Fang, J.-T.; Yang, C.-W. RIFLE classification is predictive of short-term prognosis in critically ill patients with acute renal failure supported by extracorporeal membrane oxygenation. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2006, 21, 2867–2873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Jia, S.; Meng, X.; Dong, P.; Jia, M.; Wan, J.; Hou, X. Acute kidney injury in adult postcardiotomy patients with extracorporeal membrane oxygenation: Evaluation of the RIFLE classification and the Acute Kidney Injury Network criteria. Eur. J. Cardio-Thorac. Surg. 2010, 37, 334–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Bellomo, R. Cardiac surgery-associated acute kidney injury: Risk factors, pathophysiology and treatment. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2017, 13, 697–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.; Chen, R.; Liu, S.; Yu, X.; Zou, J.; Ding, X. Global Incidence and Outcomes of Adult Patients With Acute Kidney Injury After Cardiac Surgery: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Cardiothorac. Vasc. Anesth. 2016, 30, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lannemyr, L.; Bragadottir, G.; Krumbholz, V.; Redfors, B.; Sellgren, J.; Ricksten, S.E. Effects of Cardiopulmonary Bypass on Renal Perfusion, Filtration, and Oxygenation in Patients Undergoing Cardiac Surgery. Anesthesiology 2017, 126, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronco, C.; Haapio, M.; House, A.A.; Anavekar, N.; Bellomo, R. Cardiorenal Syndrome. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2008, 52, 1527–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinze, C.; Schmidt-Ott, K.M. Acute kidney injury biomarkers in the single-cell transcriptomic era. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2022, 323, C1430–C1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.; Parikh, C.R. Current concepts and advances in biomarkers of acute kidney injury. Crit. Rev. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2021, 58, 354–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poudel, N.; Zheng, S.; Schinderle, C.M.; Sun, N.; Hu, S.; Okusa, M.D. Peritubular Capillary Oxygen Consumption in Sepsis-Induced AKI: Multi-Parametric Photoacoustic Microscopy. Nephron 2020, 144, 621–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, P.L.; Gigliotti, J.C.; Cechova, S.; Bodonyi-Kovacs, G.; Wang, Y.T.; Chen, L.J.; Smoller, S.W.; Cai, J.W.; Isakson, B.E.; Franceschini, N.; et al. Collectrin (Tmem27) deficiency in proximal tubules causes hypertension in mice and a TMEM27 variant associates with blood pressure in males in a Latino cohort. Am. J. Physiol.-Ren. Physiol. 2023, 324, F30–F42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malakauskas, S.M.; Quan, H.; Fields, T.A.; McCall, S.J.; Yu, M.J.; Kourany, W.M.; Frey, C.W.; Le, T.H. Aminoaciduria and altered renal expression of luminal amino acid transporters in mice lacking novel gene collectrin. Am. J. Physiol.-Ren. Physiol. 2007, 292, F533–F544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esterházy, D.; Akpinar, P.; Stoffel, M. Tmem27 dimerization, deglycosylation, plasma membrane depletion, and the extracellular Phe-Phe motif are negative regulators of cleavage by Bace2. Biol. Chem. 2012, 393, 473–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wada, J.; Yasuhara, A.; Iseda, I.; Eguchi, J.; Fukui, K.; Yang, Q.; Yamagata, K.; Hiesberger, T.; Igarashi, P.; et al. The role for HNF-1beta-targeted collectrin in maintenance of primary cilia and cell polarity in collecting duct cells. PLoS ONE 2007, 2, e414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udzik, J.; Pacholewicz, J.; Biskupski, A.; Walerowicz, P.; Januszkiewicz, K.; Kwiatkowska, E. Alterations to Kidney Physiology during Cardiopulmonary Bypass-A Narrative Review of the Literature and Practical Remarks. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 6894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaiao, S.M.; Paiva, J. Biomarkers of renal recovery after acute kidney injury. Rev. Bras. Ter. Intensiv. 2017, 29, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meersch, M.; Schmidt, C.; Hoffmeier, A.; Van Aken, H.; Wempe, C.; Gerss, J.; Zarbock, A. Prevention of cardiac surgery-associated AKI by implementing the KDIGO guidelines in high risk patients identified by biomarkers: The PrevAKI randomized controlled trial. Intensive Care Med. 2017, 43, 1551–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moon, S.J.; Park, H.B.; Yoon, S.Y.; Lee, S.C. Urinary Biomarkers for Early Detection of Recovery in Patients with Acute Kidney Injury. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2013, 28, 1181–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aregger, F.; Uehlinger, D.E.; Witowski, J.; Brunisholz, R.A.; Hunziker, P.; Frey, F.J.; Jorres, A. Identification of IGFBP-7 by urinary proteomics as a novel prognostic marker in early acute kidney injury. Kidney Int. 2014, 85, 909–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srisawat, N.; Murugan, R.; Lee, M.; Kong, L.; Carter, M.; Angus, D.C.; Kellum, J.A.; Genetic and Inflammatory Markers of Sepsis (GenIMS) Study Investigators. Plasma neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin predicts recovery from acute kidney injury following community-acquired pneumonia. Kidney Int. 2011, 80, 545–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollinger, A.; Wittebole, X.; Francois, B.; Pickkers, P.; Antonelli, M.; Gayat, E.; Chousterman, B.G.; Lascarrou, J.B.; Dugernier, T.; Di Somma, S.; et al. Proenkephalin A 119-159 (Penkid) Is an Early Biomarker of Septic Acute Kidney Injury: The Kidney in Sepsis and Septic Shock (Kid-SSS) Study. Kidney Int. Rep. 2018, 3, 1424–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
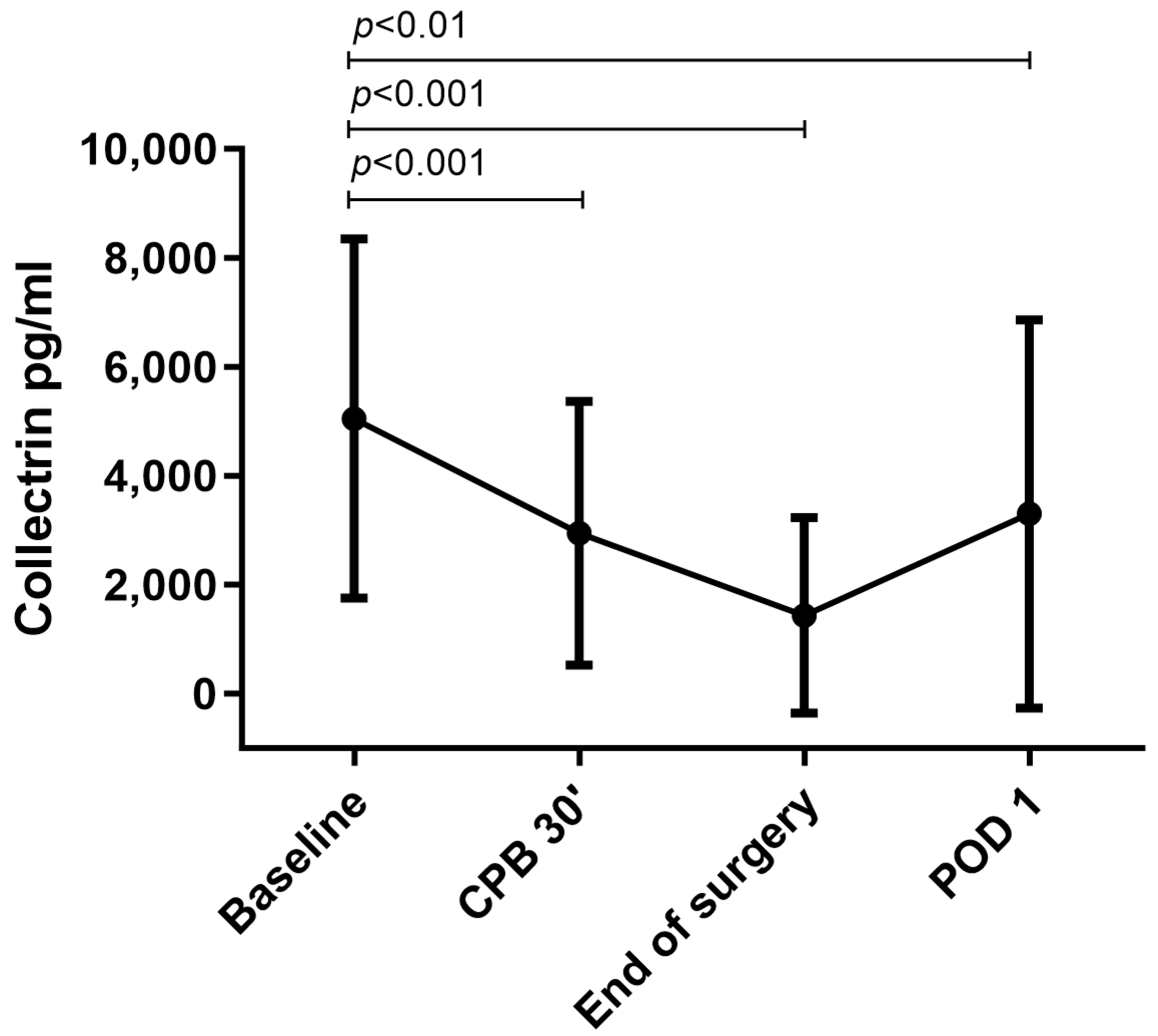
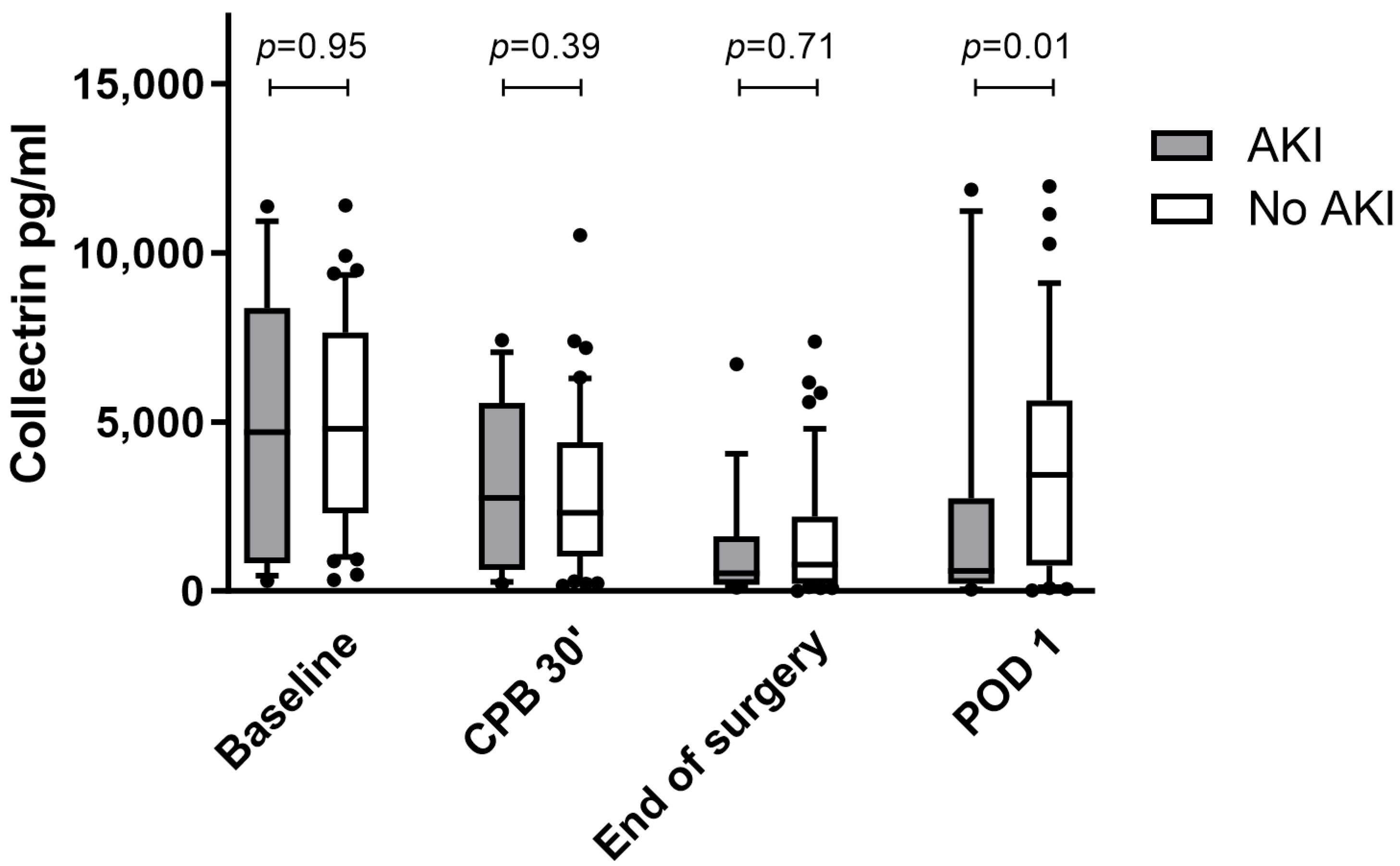
| AKI (N = 19) | No AKI (N = 44) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 70.0 [61.0; 75.0] | 69.0 [55.8; 76.0] | 0.759 |
| Male | 13 (68.4%) | 25 (56.8%) | 0.560 |
| Female | 6 (31.6%) | 19 (43.2%) | |
| BMI | 28.0 ± 6.1 | 26.5 ± 4.7 | 0.36 |
| Baseline SCr (mg/dL) | 0.90 [0.79; 1.04] | 0.86 [0.71; 0.97] | 0.467 |
| Comorbidities | |||
| Asthma | 2 (10.5%) | 1 (2.27%) | 0.214 |
| COPD | 3 (15.8%) | 6 (13.6%) | 0.999 |
| NIDDM | 3 (15.8%) | 5 (11.4%) | 0.688 |
| IDDM | 0 (0.00%) | 4 (9.09%) | 0.306 |
| Chronic kidney disease | 2 (10.5%) | 2 (4.55%) | 0.578 |
| Cardiac decompensation | 0 (0.00%) | 1 (2.27%) | 0.999 |
| PAOD | 1 (5.26%) | 3 (6.98%) | 0.999 |
| Angina pectoris | |||
| Absent | 14 (73.7%) | 30 (69.8%) | 0.999 |
| Stable | 5 (26.3%) | 11 (25.6%) | |
| Unstable | 0 (0.00%) | 2 (4.65%) | |
| LVEF | |||
| >50% | 12 (66.7%) | 30 (68.2%) | 0.882 |
| 30–50% | 6 (33.3%) | 12 (27.3%) | |
| <30% | 0 (0.00%) | 2 (4.55%) | |
| Procedure | |||
| CABG | 2 (10.5%) | 6 (13.6%) | 0.999 |
| Valve | 11 (57.9%) | 26 (59.1%) | |
| Combined | 6 (31.6%) | 12 (27.3%) | |
| Surgical characteristics | |||
| Anesthesia duration (minutes) | 376 [322; 450] | 389 [332; 457] | 0.747 |
| Surgery (minutes) | 309 ± 94.6 | 303 ± 74.6 | 0.830 |
| CPB (minutes) | 148 [112; 188] | 135 [106; 179] | 0.782 |
| AoCC (minutes) | 89.6 ± 43.9 | 99.1 ± 43.3 | 0.435 |
| Reoperation | 2 (10.5%) | 9 (20.5%) | 0.480 |
| Crystalloids (mL) | 5000 [3750; 5525] | 4225 [3500; 5125] | 0.392 |
| Intraoperative urinary output (mL) | 403 [403; 628] | 403 [403; 672] | 0.445 |
| Balance intraoperative (mL) | 4718 [3510; 5936] | 4458 [3704; 5922] | 0.999 |
| PRBC (units) | 0.00 [0.00; 1.00] | 0.00 [0.00; 1.00] | 0.874 |
| Platelets (received) | 4 (21.1%) | 8 (18.2%) | 0.999 |
| Fresh frozen plasma (received) | 3 (15.8%) | 3 (6.8) | 0.5185 |
| Fibrinogen (g) | 0.00 [0.00; 2.00] | 0.00 [0.00; 2.00] | 0.724 |
| Coagulation factors (I.U.) | 0.00 [0.00; 131.6] | 0.00 [0.00; 204.5] | 0.6224 |
| Postoperative complications | |||
| SAPS 3 | 45.7 ± 10.8 | 42.5 ± 7.6 | 0.2513 |
| no AKI | 0 (0.00%) | 44 (100%) | <0.001 |
| AKI KDIGO Stage 1 | 17 (89.5%) | 0 (0.00%) | |
| AKI KDIGO Stage 2 | 2 (10.5%) | 0 (0.00%) | |
| AKI KDIGO Stage 3 | 0 (0.00%) | 0 (0.00%) | |
| Renal replacement therapy | 0 (0.00%) | 0 (0.00%) | 0.999 |
| Length of stay on ICU (days) | 1.00 [1.00; 5.00] | 2.00 [1.00; 3.00] | 0.956 |
| Variable | Coefficient (95% CI) Units Collectrin Change | p-Value |
|---|---|---|
| AKI crude | −3058 (−5411 to −705) | 0.01 |
| AKI-adjusted | −1567 (−4401 to 1266) | 0.27 |
| Age (years) | −86 (−214 to 42) | 0.18 |
| Sex (male) | −699 (−3371 to 1973) | 0.60 |
| Extracorporeal circulation time (per minute) | 16 (−7 to 38) | 0.17 |
| Baseline serum creatinine (per mg/dL) | −635 (−5161 to 3891) | 0.78 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tichy, J.; Pajenda, S.; Bernardi, M.H.; Wagner, L.; Ryz, S.; Aiad, M.; Gerges, D.; Schmidt, A.; Lassnigg, A.; Herkner, H.; et al. Urinary Collectrin as Promising Biomarker for Acute Kidney Injury in Patients Undergoing Cardiac Surgery. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 3244. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11123244
Tichy J, Pajenda S, Bernardi MH, Wagner L, Ryz S, Aiad M, Gerges D, Schmidt A, Lassnigg A, Herkner H, et al. Urinary Collectrin as Promising Biomarker for Acute Kidney Injury in Patients Undergoing Cardiac Surgery. Biomedicines. 2023; 11(12):3244. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11123244
Chicago/Turabian StyleTichy, Johanna, Sahra Pajenda, Martin H. Bernardi, Ludwig Wagner, Sylvia Ryz, Monika Aiad, Daniela Gerges, Alice Schmidt, Andrea Lassnigg, Harald Herkner, and et al. 2023. "Urinary Collectrin as Promising Biomarker for Acute Kidney Injury in Patients Undergoing Cardiac Surgery" Biomedicines 11, no. 12: 3244. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11123244
APA StyleTichy, J., Pajenda, S., Bernardi, M. H., Wagner, L., Ryz, S., Aiad, M., Gerges, D., Schmidt, A., Lassnigg, A., Herkner, H., & Winnicki, W. (2023). Urinary Collectrin as Promising Biomarker for Acute Kidney Injury in Patients Undergoing Cardiac Surgery. Biomedicines, 11(12), 3244. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11123244







