Microplastics: A Matter of the Heart (and Vascular System)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. MP/NP Effects on Aquatic Fauna Vascular System
3. MP/NP Impact on Heart Physiology in Aquatic Organisms
4. MP/NP Effects on Mammalian Circulating Cells and Vascular System
5. MPs/NPs Effects on Cardiac Physiology in Mammals
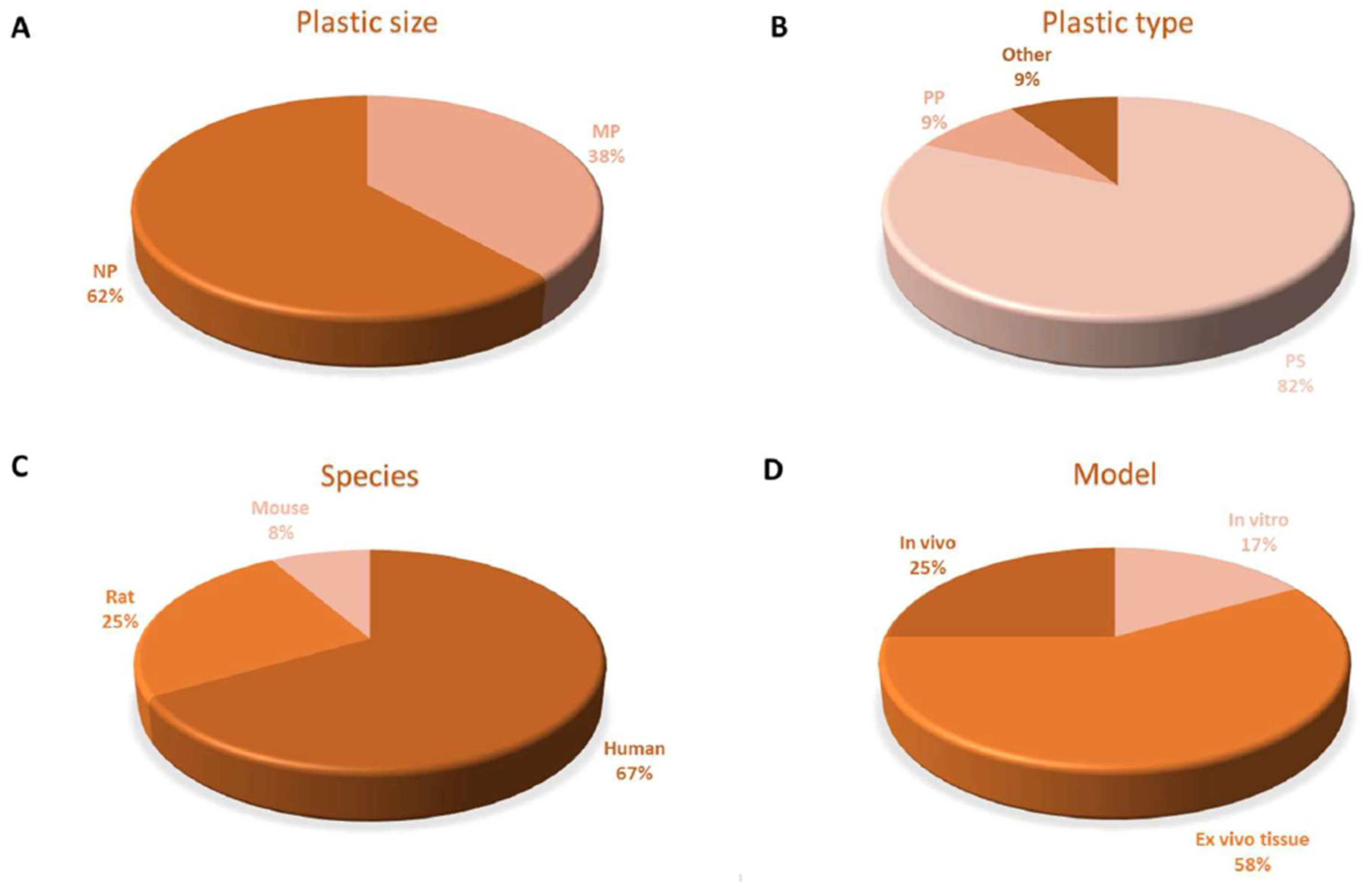
6. Discussion, Conclusions, and Recommendations
- Refinement of techniques to quantify small plastic fragments.
- Identification of plastic type, size, shape, and charge causative of adverse effects mainly in the heart. Weathering/ageing of plastic particles may be considered.
- Realistic time of exposure and quantity of plastic.
- Mechanisms of vascular absorption and transport.
- Cardiac bioaccumulation and pathogenesis.
- Dose and time-dependency of cardiotoxicity.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jambeck, J.R.; Geyer, R.; Wilcox, C.; Siegler, T.R.; Perryman, M.; Andrady, A.; Narayan, R.; Law, K.L. Marine Pollution. Plastic Waste Inputs from Land into the Ocean. Science 2015, 347, 768–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eriksen, M.; Lebreton, L.C.M.; Carson, H.S.; Thiel, M.; Moore, C.J.; Borerro, J.C.; Galgani, F.; Ryan, P.G.; Reisser, J. Plastic Pollution in the World’s Oceans: More than 5 Trillion Plastic Pieces Weighing over 250,000 Tons Afloat at Sea. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e111913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zalasiewicz, J.; Waters, C.N.; Ivar do Sul, J.A.; Corcoran, P.L.; Barnosky, A.D.; Cearreta, A.; Edgeworth, M.; Gałuszka, A.; Jeandel, C.; Leinfelder, R.; et al. The Geological Cycle of Plastics and Their Use as a Stratigraphic Indicator of the Anthropocene. Anthropocene 2016, 13, 4–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gündoğdu, S.; Yeşilyurt, İ.N.; Erbaş, C. Potential Interaction between Plastic Litter and Green Turtle Chelonia Mydas during Nesting in an Extremely Polluted Beach. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 140, 138–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapron, L.; Peru, E.; Engler, A.; Ghiglione, J.F.; Meistertzheim, A.L.; Pruski, A.M.; Purser, A.; Vétion, G.; Galand, P.E.; Lartaud, F. Macro- and Microplastics Affect Cold-Water Corals Growth, Feeding and Behaviour. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 15299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Browne, M.A.; Crump, P.; Niven, S.J.; Teuten, E.; Tonkin, A.; Galloway, T.; Thompson, R. Accumulation of Microplastic on Shorelines Woldwide: Sources and Sinks. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 9175–9179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrady, A.L. Microplastics in the Marine Environment. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2011, 62, 1596–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Costa, J.P.; Santos, P.S.M.; Duarte, A.C.; Rocha-Santos, T. (Nano)Plastics in the Environment - Sources, Fates and Effects. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 566–567, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gigault, J.; Halle, A.T.; Baudrimont, M.; Pascal, P.-Y.; Gauffre, F.; Phi, T.-L.; El Hadri, H.; Grassl, B.; Reynaud, S. Current Opinion: What Is a Nanoplastic? Environ. Pollut. 2018, 235, 1030–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza Machado, A.A.; Kloas, W.; Zarfl, C.; Hempel, S.; Rillig, M.C. Microplastics as an Emerging Threat to Terrestrial Ecosystems. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2018, 24, 1405–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auta, H.S.; Emenike, C.U.; Fauziah, S.H. Distribution and Importance of Microplastics in the Marine Environment: A Review of the Sources, Fate, Effects, and Potential Solutions. Environ. Int. 2017, 102, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galloway, T.S.; Cole, M.; Lewis, C. Interactions of Microplastic Debris throughout the Marine Ecosystem. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2017, 1, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, S.; Scherer, C.; Wagner, M. Ecotoxicity Testing of Microplastics: Considering the Heterogeneity of Physicochemical Properties. Integr. Environ. Assess. Manag. 2017, 13, 470–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adam, V.; Yang, T.; Nowack, B. Toward an Ecotoxicological Risk Assessment of Microplastics: Comparison of Available Hazard and Exposure Data in Freshwaters. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2019, 38, 436–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akdogan, Z.; Guven, B. Microplastics in the Environment: A Critical Review of Current Understanding and Identification of Future Research Needs. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 254, 113011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartmann, N.B.; Rist, S.; Bodin, J.; Jensen, L.H.; Schmidt, S.N.; Mayer, P.; Meibom, A.; Baun, A. Microplastics as Vectors for Environmental Contaminants: Exploring Sorption, Desorption, and Transfer to Biota. Integr. Environ. Assess. Manag. 2017, 13, 488–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caruso, G. Microplastics as Vectors of Contaminants. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 146, 921–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sgier, L.; Freimann, R.; Zupanic, A.; Kroll, A. Flow Cytometry Combined with ViSNE for the Analysis of Microbial Biofilms and Detection of Microplastics. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Pan, J.; Li, M.; Li, Y.; Bartlam, M.; Wang, Y. Selective Enrichment of Bacterial Pathogens by Microplastic Biofilm. Water Res. 2019, 165, 114979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sl, W.; Rc, T.; Ts, G. The Physical Impacts of Microplastics on Marine Organisms: A Review. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattsson, K.; Ekvall, M.T.; Hansson, L.-A.; Linse, S.; Malmendal, A.; Cedervall, T. Altered Behavior, Physiology, and Metabolism in Fish Exposed to Polystyrene Nanoparticles. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 553–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chae, Y.; Kim, D.; Kim, S.W.; An, Y.-J. Trophic Transfer and Individual Impact of Nano-Sized Polystyrene in a Four-Species Freshwater Food Chain. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llorca, M.; Farré, M.; Karapanagioti, H.K.; Barceló, D. Levels and Fate of Perfluoroalkyl Substances in Beached Plastic Pellets and Sediments Collected from Greece. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 87, 286–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cedervall, T.; Hansson, L.-A.; Lard, M.; Frohm, B.; Linse, S. Food Chain Transport of Nanoparticles Affects Behaviour and Fat Metabolism in Fish. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e32254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vethaak, A.D.; Legler, J. Microplastics and Human Health. Science 2021, 371, 672–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Qu, X.; Su, L.; Zhang, W.; Yang, D.; Kolandhasamy, P.; Li, D.; Shi, H. Microplastics in Mussels along the Coastal Waters of China. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 214, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neves, D.; Sobral, P.; Ferreira, J.L.; Pereira, T. Ingestion of Microplastics by Commercial Fish off the Portuguese Coast. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 101, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karami, A.; Golieskardi, A.; Keong Choo, C.; Larat, V.; Galloway, T.S.; Salamatinia, B. The Presence of Microplastics in Commercial Salts from Different Countries. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 46173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liebezeit, G.; Liebezeit, E. Non-Pollen Particulates in Honey and Sugar. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2013, 30, 2136–2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez, L.M.; Xu, E.G.; Larsson, H.C.E.; Tahara, R.; Maisuria, V.B.; Tufenkji, N. Plastic Teabags Release Billions of Microparticles and Nanoparticles into Tea. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 12300–12310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pivokonsky, M.; Cermakova, L.; Novotna, K.; Peer, P.; Cajthaml, T.; Janda, V. Occurrence of Microplastics in Raw and Treated Drinking Water. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 643, 1644–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koelmans, A.A.; Mohamed Nor, N.H.; Hermsen, E.; Kooi, M.; Mintenig, S.M.; De France, J. Microplastics in Freshwaters and Drinking Water: Critical Review and Assessment of Data Quality. Water Res. 2019, 155, 410–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oßmann, B.E.; Sarau, G.; Holtmannspötter, H.; Pischetsrieder, M.; Christiansen, S.H.; Dicke, W. Small-Sized Microplastics and Pigmented Particles in Bottled Mineral Water. Water Res. 2018, 141, 307–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuccarello, P.; Ferrante, M.; Cristaldi, A.; Copat, C.; Grasso, A.; Sangregorio, D.; Fiore, M.; Oliveri Conti, G. Exposure to Microplastics (<10 μm) Associated to Plastic Bottles Mineral Water Consumption: The First Quantitative Study. Water Res. 2019, 157, 365–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rist, S.; Carney Almroth, B.; Hartmann, N.B.; Karlsson, T.M. A Critical Perspective on Early Communications Concerning Human Health Aspects of Microplastics. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 626, 720–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eyles, J.; Alpar, O.; Field, W.N.; Lewis, D.A.; Keswick, M. The Transfer of Polystyrene Microspheres from the Gastrointestinal Tract to the Circulation after Oral Administration in the Rat. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 1995, 47, 561–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jani, P.; Halbert, G.W.; Langridge, J.; Florence, A.T. Nanoparticle Uptake by the Rat Gastrointestinal Mucosa: Quantitation and Particle Size Dependency. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 1990, 42, 821–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Zhang, J.; Qiu, Z.; Cui, Z.; Li, N.; Li, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, C. Effects of Polyethylene Microplastics on Cell Membranes: A Combined Study of Experiments and Molecular Dynamics Simulations. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 429, 128323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forte, M.; Iachetta, G.; Tussellino, M.; Carotenuto, R.; Prisco, M.; De Falco, M.; Laforgia, V.; Valiante, S. Polystyrene Nanoparticles Internalization in Human Gastric Adenocarcinoma Cells. Toxicol. Vitr. 2016, 31, 126–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Wen, Y.; Marshall, M.R.; Zhao, J.; Gui, H.; Yang, Y.; Zeng, Z.; Jones, D.L.; Zang, H. Microplastics as an Emerging Threat to Plant and Soil Health in Agroecosystems. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 787, 147444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, C.-D.; Chen, C.-W.; Chen, Y.-C.; Chen, H.-H.; Lee, J.-S.; Lin, C.-H. Polystyrene Microplastic Particles: In Vitro Pulmonary Toxicity Assessment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 385, 121575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, K.; Lai, K.P.; Stoeger, T.; Ji, S.; Lin, Z.; Lin, X.; Chan, T.F.; Fang, J.K.-H.; Lo, M.; Gao, L.; et al. Detrimental Effects of Microplastic Exposure on Normal and Asthmatic Pulmonary Physiology. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 416, 126069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Zhang, T.; Lv, W.; Wang, H.; Chen, H.; Xu, Q.; Cai, H.; Dai, J. Intratracheal Administration of Polystyrene Microplastics Induces Pulmonary Fibrosis by Activating Oxidative Stress and Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway in Mice. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 232, 113238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Deng, Y.; Jiang, W.; Zhao, Y.; Geng, J.; Ding, L.; Ren, H. Uptake and Accumulation of Polystyrene Microplastics in Zebrafish (Danio Rerio) and Toxic Effects in Liver. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 4054–4060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, J.; Zhang, S.; Razanajatovo, R.M.; Zou, H.; Zhu, W. Accumulation, Tissue Distribution, and Biochemical Effects of Polystyrene Microplastics in the Freshwater Fish Red Tilapia (Oreochromis Niloticus). Environ. Pollut. 2018, 238, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Browne, M.A.; Dissanayake, A.; Galloway, T.S.; Lowe, D.M.; Thompson, R.C. Ingested Microscopic Plastic Translocates to the Circulatory System of the Mussel, Mytilus Edulis (L). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 5026–5031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cajaraville, M.P.; Pal, S.G. Morphofunctional Study of the Haemocytes of the Bivalve Mollusc Mytilus Galloprovincialis with Emphasis on the Endolysosomal Compartment. Cell Struct. Funct. 1995, 20, 355–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banaee, M.; Soltanian, S.; Sureda, A.; Gholamhosseini, A.; Haghi, B.N.; Akhlaghi, M.; Derikvandy, A. Evaluation of Single and Combined Effects of Cadmium and Micro-Plastic Particles on Biochemical and Immunological Parameters of Common Carp (Cyprinus Carpio). Chemosphere 2019, 236, 124335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Lu, L.; Zheng, M.; Zhang, X.; Tian, H.; Wang, W.; Ru, S. Polystyrene Microplastics Cause Tissue Damages, Sex-Specific Reproductive Disruption and Transgenerational Effects in Marine Medaka (Oryzias Melastigma). Environ. Pollut. 2019, 254, 113024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Ding, R.; Ma, Y.; Sun, Q.; Ren, X.; Sun, Z.; Duan, J. Cardiovascular Toxicity Assessment of Polyethylene Nanoplastics on Developing Zebrafish Embryos. Chemosphere 2021, 282, 131124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canesi, L.; Ciacci, C.; Bergami, E.; Monopoli, M.P.; Dawson, K.A.; Papa, S.; Canonico, B.; Corsi, I. Evidence for Immunomodulation and Apoptotic Processes Induced by Cationic Polystyrene Nanoparticles in the Hemocytes of the Marine Bivalve Mytilus. Mar. Environ. Res. 2015, 111, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Incardona, J.P.; Scholz, N.L. The Influence of Heart Developmental Anatomy on Cardiotoxicity-Based Adverse Outcome Pathways in Fish. Aquat. Toxicol. 2016, 177, 515–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pitt, J.A.; Trevisan, R.; Massarsky, A.; Kozal, J.S.; Levin, E.D.; Di Giulio, R.T. Maternal Transfer of Nanoplastics to Offspring in Zebrafish (Danio Rerio): A Case Study with Nanopolystyrene. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 643, 324–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pitt, J.A.; Kozal, J.S.; Jayasundara, N.; Massarsky, A.; Trevisan, R.; Geitner, N.; Wiesner, M.; Levin, E.D.; Di Giulio, R.T. Uptake, Tissue Distribution, and Toxicity of Polystyrene Nanoparticles in Developing Zebrafish (Danio Rerio). Aquat. Toxicol. 2018, 194, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Xiong, H.; Mi, K.; Xue, W.; Wei, W.; Zhang, Y. Toxicity Comparison of Nano-Sized and Micron-Sized Microplastics to Goldfish Carassius Auratus Larvae. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 388, 122058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohr, K.; Sommer, M.; Baier, G.; Schöttler, S.; Okwieka, P.; Tenzer, S.; Landfester, K.; Mailänder, V.; Schmidt, M.; Meyer, R. Aggregation Behavior of Polystyrene-Nanoparticles in Human Blood Serum and Its Impact on the in Vivo Distribution in Mice. J. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. 2014, 05. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballesteros, S.; Domenech, J.; Barguilla, I.; Cortés, C.; Marcos, R.; Hernández, A. Genotoxic and Immunomodulatory Effects in Human White Blood Cells after Ex Vivo Exposure to Polystyrene Nanoplastics. Environ. Sci. Nano 2020, 7, 3431–3446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prietl, B.; Meindl, C.; Roblegg, E.; Pieber, T.R.; Lanzer, G.; Fröhlich, E. Nano-Sized and Micro-Sized Polystyrene Particles Affect Phagocyte Function. Cell Biol. Toxicol. 2014, 30, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundqvist, M.; Stigler, J.; Elia, G.; Lynch, I.; Cedervall, T.; Dawson, K.A. Nanoparticle Size and Surface Properties Determine the Protein Corona with Possible Implications for Biological Impacts. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 14265–14270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pm, G.; V, S.; S, V.; M, M.M.; S, R.; R, K.; A, P.; J, T.; A, M.; N, C. Assessment on Interactive Prospectives of Nanoplastics with Plasma Proteins and the Toxicological Impacts of Virgin, Coronated and Environmentally Released-Nanoplastics. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barshtein, G.; Livshits, L.; Shvartsman, L.D.; Shlomai, N.O.; Yedgar, S.; Arbell, D. Polystyrene Nanoparticles Activate Erythrocyte Aggregation and Adhesion to Endothelial Cells. Cell Biochem. Biophys 2016, 74, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Y, Z.; X, S.; G, Z.; Bg, T.; Ii, S.; Vs, L. Interaction of Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles with Human Red Blood Cell Membranes: Size and Surface Effects. ACS Nano 2011, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J.; Choi, D.; Han, S.; Choi, J.; Hong, J. An Assessment of the Toxicity of Polypropylene Microplastics in Human Derived Cells. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 684, 657–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saravia, J.; You, D.; Thevenot, P.; Lee, G.I.; Shrestha, B.; Lomnicki, S.; Cormier, S.A. Early-Life Exposure to Combustion-Derived Particulate Matter Causes Pulmonary Immunosuppression. Mucosal. Immunol. 2014, 7, 694–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, A.E.; Watts, J.A.; Debelak, J.P.; Thornton, L.R.; Younger, J.G.; Kline, J.A. Inhibition of Prostaglandin Synthesis during Polystyrene Microsphere-Induced Pulmonary Embolism in the Rat. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 2003, 284, L1072-1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.-S.; Amarakoon, D.; Wei, C.-I.; Choi, K.Y.; Smolensky, D.; Lee, S.-H. Adverse Effect of Polystyrene Microplastics (PS-MPs) on Tube Formation and Viability of Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2021, 154, 112356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarnat, S.E.; Suh, H.H.; Coull, B.A.; Schwartz, J.; Stone, P.H.; Gold, D.R. Ambient Particulate Air Pollution and Cardiac Arrhythmia in a Panel of Older Adults in Steubenville, Ohio. Occup. Environ. Med. 2006, 63, 700–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savi, M.; Rossi, S.; Bocchi, L.; Gennaccaro, L.; Cacciani, F.; Perotti, A.; Amidani, D.; Alinovi, R.; Goldoni, M.; Aliatis, I.; et al. Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles Promote Arrhythmias via a Direct Interaction with Rat Cardiac Tissue. Part Fibre Toxicol. 2014, 11, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Zhuan, Q.; Zhang, L.; Meng, L.; Fu, X.; Hou, Y. Polystyrene Microplastics Induced Female Reproductive Toxicity in Mice. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 424, 127629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walczak, A.P.; Hendriksen, P.J.M.; Woutersen, R.A.; van der Zande, M.; Undas, A.K.; Helsdingen, R.; van den Berg, H.H.J.; Rietjens, I.M.C.M.; Bouwmeester, H. Bioavailability and Biodistribution of Differently Charged Polystyrene Nanoparticles upon Oral Exposure in Rats. J. Nanopart Res. 2015, 17, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Zhang, R.; Li, B.; Du, Y.; Li, J.; Tong, X.; Wu, Y.; Ji, X.; Zhang, Y. Tissue Distribution of Polystyrene Nanoplastics in Mice and Their Entry, Transport, and Cytotoxicity to GES-1 Cells. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 280, 116974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stock, V.; Böhmert, L.; Lisicki, E.; Block, R.; Cara-Carmona, J.; Pack, L.K.; Selb, R.; Lichtenstein, D.; Voss, L.; Henderson, C.J.; et al. Uptake and Effects of Orally Ingested Polystyrene Microplastic Particles in Vitro and in Vivo. Arch. Toxicol. 2019, 93, 1817–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fournier, S.B.; D’Errico, J.N.; Adler, D.S.; Kollontzi, S.; Goedken, M.J.; Fabris, L.; Yurkow, E.J.; Stapleton, P.A. Nanopolystyrene Translocation and Fetal Deposition after Acute Lung Exposure during Late-Stage Pregnancy. Part Fibre Toxicol. 2020, 17, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stapleton, P.A.; Minarchick, V.C.; Cumpston, A.M.; McKinney, W.; Chen, B.T.; Sager, T.M.; Frazer, D.G.; Mercer, R.R.; Scabilloni, J.; Andrew, M.E.; et al. Impairment of Coronary Arteriolar Endothelium-Dependent Dilation after Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotube Inhalation: A Time-Course Study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 13781–13803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Zhu, S.; Liu, Q.; Wei, J.; Jin, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, L. Polystyrene Microplastics Cause Cardiac Fibrosis by Activating Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway and Promoting Cardiomyocyte Apoptosis in Rats. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 265, 115025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roshanzadeh, A.; Oyunbaatar, N.-E.; Ganjbakhsh, S.E.; Park, S.; Kim, D.-S.; Kanade, P.P.; Lee, S.; Lee, D.-W.; Kim, E.-S. Exposure to Nanoplastics Impairs Collective Contractility of Neonatal Cardiomyocytes under Electrical Synchronization. Biomaterials 2021, 278, 121175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revel, M.; Châtel, A.; Mouneyrac, C. Micro(Nano)Plastics: A Threat to Human Health? Curr. Opin. Environ. Sci. Health 2018, 1, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marris, C.R.; Kompella, S.N.; Miller, M.R.; Incardona, J.P.; Brette, F.; Hancox, J.C.; Sørhus, E.; Shiels, H.A. Polyaromatic Hydrocarbons in Pollution: A Heart-Breaking Matter. J. Physiol. 2020, 598, 227–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Organism | Type of Particles | Size of Particles | Observed Effects on CV System | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zebrafish (Danio rerio) | PS | 5 μm and 70 nm | Bioaccumulation in gills (transfer to capillaries) | [44] |
| Red tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) | PS | 0.1 μm | Bioaccumulation in gills and transfer to capillaries | [45] |
| Blue mussel (Mytilus edulis) | PS | 3.0 or 9.6 μm | Transfer to capillaries, internalisation into haemocytes | [46] |
| Common carp (Cyprinus carpio) | Mixture (mainly PE) | Mixed | Reduced plasma levels of AChE and GGT, and increased AST, ALT, ALP and LDH, lowered lysozyme and ACH50 activities, lowered total immunoglobulins and complement C3 and C4 factors | [48] |
| Marine medaka (Oryzias melastigma) | PS | 10 μm | Bioaccumulation in gills, ROS production and histopathological changes in loco | [49] |
| Zebrafish (Danio rerio) | PE | Mixed (191.10 ± 3.13 nm) | Vascular endothelium damage and compromised angiogenesis, pro-thrombotic state. Altered hemodynamic | [50] |
| Mediterranean mussel (Mytilus galloprovincialis) | PS | 50 nm | Blood cells apoptosis, compromised immunocompetence | [51] |
| Organism | Type of Particles | Size of Particles | Observed Effects on Heart | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zebrafish (Danio rerio) | PE | Mixed (191.10 ± 3.13 nm) | Pericardial oedema | [50] |
| Zebrafish (Danio rerio) | PS | 42 nm | Bradycardia | [53] |
| Zebrafish (Danio rerio) | PS | 51 nm | Bioaccumulation in pericardium, bradycardia | [54] |
| Marine medaka (Oryzias melastigma) | PS | 10 μm | Bradycardia | [49] |
| Goldfish (Carassius auratus) | PS | 70 nm and 5 μm | Tachycardia | [55] |
| Specimen/Model | Type of Particles | Size of Particles | Observed Effects on Circulating Cells and Vasculature | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Human serum | PS | 80–170 nm | Internalisation into monocytes, granulocytes and myeloid dendritic cells | [56] |
| Human whole blood | PS | 0.04–0.09 μm | Internalisation into white cells and monocytes, genotoxic effects on PMN and monocytes | [57] |
| Human PBMCs, murine macrophages | PS | 20, 100, 200, 500 and 1000 nm | Internalisation into macrophages and phagocytes (for coronated plastics), IL-6 release | [58] |
| Human plasma | PS | 100 nm | Lymphocytes and erythrocytes promoting cytotoxicity and genotoxicity, haemolysis. Escape immune surveillance (corona formation) | [60] |
| Human RBCs | PS | 49.9 ± 6.3; 107.9 ± 1.4; 243 ± 3.0 nm | Aggregation and adhesion to endothelial cells (more pronounced with decreasing size of NPs) | [61] |
| Sheep RBCs, human PBMCs, murine macrophage cell line, human mast cell line, human fibroblasts | PP | 20 or 25–200 μm | Haemolysis, pro-inflammatory cytokines (IL-2, IL-6, TNF-α) release | [63] |
| Sprague-Dawley rats | PS | 24 μm | Vascular occlusion, hypercoagulability, pulmonary embolism | [65] |
| HUVEC | PS | 0.5, 1, and 5 μm | Impaired angiogenesis (through inhibition of VEGF pathway), autophagy and necrosis | [66] |
| Specimen/Model | Type of Particles | Size of Particles | Observed Effects on Heart | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sprague-Dawley rats | PS | 24 μm | Arterial hypotension, increased arterial lactate concentration, hypoxia | [65] |
| Specific pathogen free (SPF) CD-1® mice | PS | 0.7918 ± 0.00273 and 0.7939 ± 0.00282 μm | Particles accumulation | [69] |
| Fischer 344 rats | PS | 50 nm | Particles accumulation | [70] |
| Sprague-Dawley rats | PS | 20 nm | Particles accumulation (for both maternal and foetal heart) | [73] |
| Wistar rats | PS | 0.5 μm | Particles accumulation, internalisation into cardiomyocytes. Myocardium apoptosis, fibrosis. Increased myocardial creatine-kinase MB and cardiac Troponin I, oxidation | [75] |
| Sprague-Dawley rats | PS | 50 nm | Particles internalisation into cardiomyocytes. Inhibition of LTCC and decreased contraction forces | [76] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Persiani, E.; Cecchettini, A.; Ceccherini, E.; Gisone, I.; Morales, M.A.; Vozzi, F. Microplastics: A Matter of the Heart (and Vascular System). Biomedicines 2023, 11, 264. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11020264
Persiani E, Cecchettini A, Ceccherini E, Gisone I, Morales MA, Vozzi F. Microplastics: A Matter of the Heart (and Vascular System). Biomedicines. 2023; 11(2):264. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11020264
Chicago/Turabian StylePersiani, Elisa, Antonella Cecchettini, Elisa Ceccherini, Ilaria Gisone, Maria Aurora Morales, and Federico Vozzi. 2023. "Microplastics: A Matter of the Heart (and Vascular System)" Biomedicines 11, no. 2: 264. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11020264
APA StylePersiani, E., Cecchettini, A., Ceccherini, E., Gisone, I., Morales, M. A., & Vozzi, F. (2023). Microplastics: A Matter of the Heart (and Vascular System). Biomedicines, 11(2), 264. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11020264





