Sex Differences in Intestinal Microbiota and Their Association with Some Diseases in a Japanese Population Observed by Analysis Using a Large Dataset
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
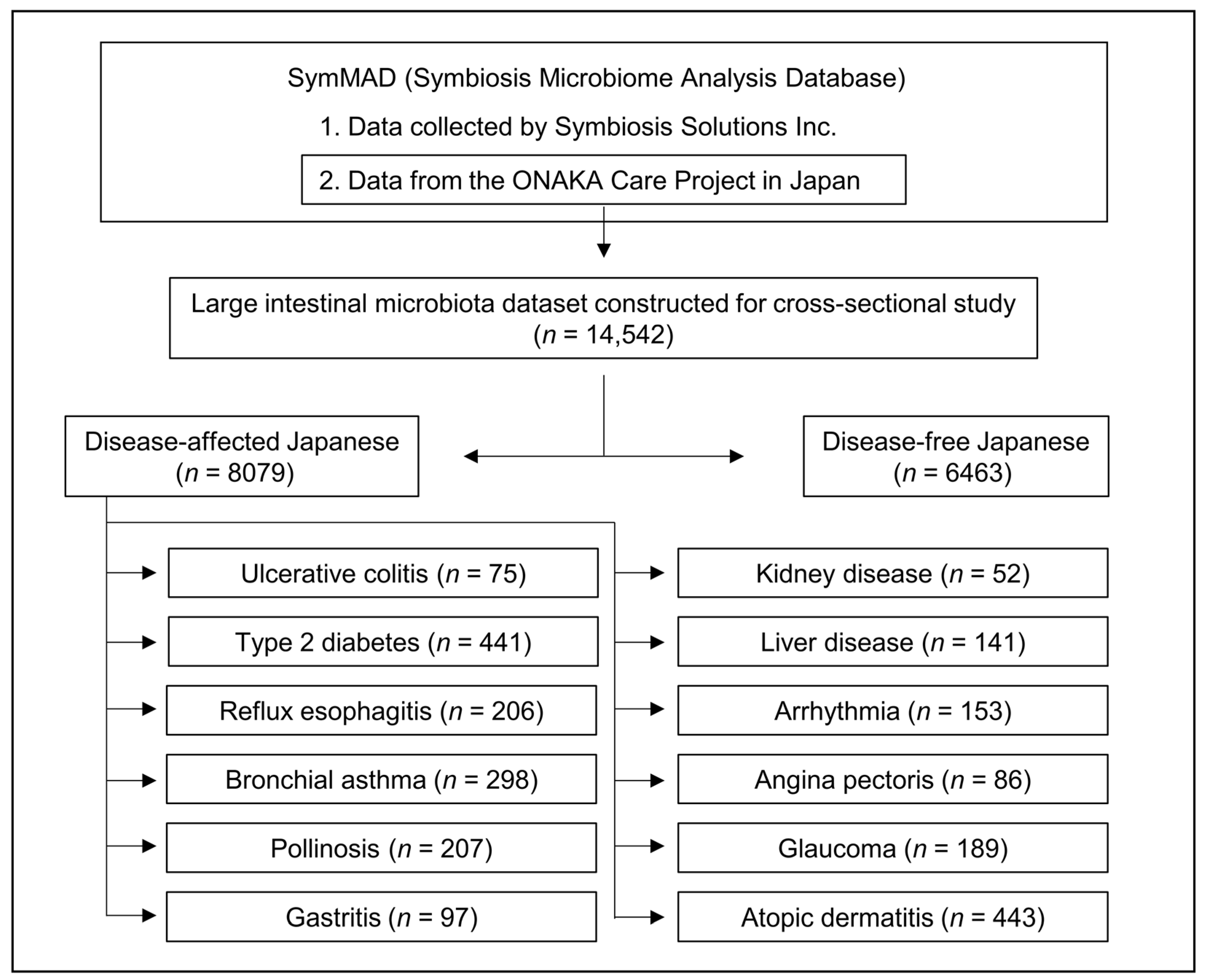
2.1. Database, Dataset, and Study Populations
2.2. Ethical Considerations
2.3. Questionnaire Survey
2.4. Collection of Stool Samples
2.5. DNA Extraction
2.6. DNA Sequencing
2.7. 16S rRNA Data Analysis
2.8. Intestinal Microbiota Analysis
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Sex Differences in the Intestinal Microbiota of a Disease-Free Japanese Population
3.2. Differences in Intestinal Bacteria Potentially Associated with Disease between Japanese Males and Females
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nishijima, S.; Suda, W.; Oshima, K.; Kim, S.-W.; Hirose, Y.; Morita, H.; Hattori, M. The Gut Microbiome of Healthy Japanese and Its Microbial and Functional Uniqueness. DNA Res. 2016, 23, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Odamaki, T.; Kato, K.; Sugahara, H.; Hashikura, N.; Takahashi, S.; Xiao, J.; Abe, F.; Osawa, R. Age-Related Changes in Gut Microbiota Composition from Newborn to Centenarian: A Cross-Sectional Study. BMC Microbiol. 2016, 16, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, Y.S.; Unno, T.; Kim, B.-Y.; Park, M.-S. Sex Differences in Gut Microbiota. World J. Men’s Health 2020, 38, 48–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oki, K.; Toyama, M.; Banno, T.; Chonan, O.; Benno, Y.; Watanabe, K. Comprehensive Analysis of the Fecal Microbiota of Healthy Japanese Adults Reveals a New Bacterial Lineage Associated with a Phenotype Characterized by a High Frequency of Bowel Movements and a Lean Body Type. BMC Microbiol. 2016, 16, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Park, J.; Kato, K.; Murakami, H.; Hosomi, K.; Tanisawa, K.; Nakagata, T.; Ohno, H.; Konishi, K.; Kawashima, H.; Chen, Y.-A.; et al. Comprehensive Analysis of Gut Microbiota of a Healthy Population and Covariates Affecting Microbial Variation in Two Large Japanese Cohorts. BMC Microbiol. 2021, 21, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takagi, T.; Naito, Y.; Inoue, R.; Kashiwagi, S.; Uchiyama, K.; Mizushima, K.; Tsuchiya, S.; Dohi, O.; Yoshida, N.; Kamada, K.; et al. Differences in Gut Microbiota Associated with Age, Sex, and Stool Consistency in Healthy Japanese Subjects. J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 54, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larabi, A.; Barnich, N.; Nguyen, H.T.T. New Insights into the Interplay between Autophagy, Gut Microbiota and Inflammatory Responses in IBD. Autophagy 2020, 16, 38–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harata, G.; Kumar, H.; He, F.; Miyazawa, K.; Yoda, K.; Kawase, M.; Kubota, A.; Hiramatsu, M.; Rautava, S.; Salminen, S. Probiotics Modulate Gut Microbiota and Health Status in Japanese Cedar Pollinosis Patients during the Pollen Season. Eur. J. Nutr. 2017, 56, 2245–2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nomura, A.; Matsubara, A.; Goto, S.; Takahata, J.; Sawada, K.; Ihara, K.; Nakaji, S. Relationship between Gut Microbiota Composition and Sensitization to Inhaled Allergens. Allergol. Int. 2020, 69, 437–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Luca, F.; Shoenfeld, Y. The Microbiome in Autoimmune Diseases. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2019, 195, 74–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, H.; Liu, M.; Cao, J.; Li, X.; Fan, D.; Xia, Y.; Lu, X.; Li, J.; Ju, D.; Zhao, H. The Dynamic Interplay between the Gut Microbiota and Autoimmune Diseases. J. Immunol. Res. 2019, 2019, 7546047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Patterson, E.; Ryan, P.M.; Cryan, J.F.; Dinan, T.G.; Ross, R.P.; Fitzgerald, G.F.; Stanton, C. Gut Microbiota, Obesity and Diabetes. Postgrad. Med. J. 2016, 92, 286–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gurung, M.; Li, Z.; You, H.; Rodrigues, R.; Jump, D.B.; Morgun, A.; Shulzhenko, N. Role of Gut Microbiota in Type 2 Diabetes Pathophysiology. EBioMedicine 2020, 51, 102590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gérard, P. Gut Microbiota and Obesity. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2016, 73, 147–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albhaisi, S.A.M.; Bajaj, J.S.; Sanyal, A.J. Role of Gut Microbiota in Liver Disease. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2020, 318, G84–G98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bajaj, J.S. Alcohol, Liver Disease and the Gut Microbiota. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 16, 235–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safari, Z.; Gérard, P. The Links between the Gut Microbiome and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD). Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2019, 76, 1541–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.-J.; Ni, Y.-H. Gut Microbiota and Pediatric Obesity/Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. J. Formos. Med. Assoc. 2019, 118 (Suppl. S1), S55–S61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonsson, A.L.; Bäckhed, F. Role of Gut Microbiota in Atherosclerosis. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2017, 14, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagatomo, Y.; Tang, W.H.W. Intersections Between Microbiome and Heart Failure: Revisiting the Gut Hypothesis. J. Card. Fail. 2015, 21, 973–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Garrett, W.S. Cancer and the Microbiota. Science 2015, 348, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dai, Z.; Zhang, J.; Wu, Q.; Chen, J.; Liu, J.; Wang, L.; Chen, C.; Xu, J.; Zhang, H.; Shi, C.; et al. The Role of Microbiota in the Development of Colorectal Cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2019, 145, 2032–2041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cenit, M.C.; Sanz, Y.; Codoñer-Franch, P. Influence of Gut Microbiota on Neuropsychiatric Disorders. World J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 23, 5486–5498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Naseribafrouei, A.; Hestad, K.; Avershina, E.; Sekelja, M.; Linløkken, A.; Wilson, R.; Rudi, K. Correlation between the Human Fecal Microbiota and Depression. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2014, 26, 1155–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.-F.; Shen, Y.-Q. Dysbiosis of Gut Microbiota and Microbial Metabolites in Parkinson’s Disease. Ageing Res. Rev. 2018, 45, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kono, K.; Murakami, Y.; Ebara, A.; Okuma, K.; Tokuno, H.; Odachi, A.; Ogasawara, K.; Hidaka, E.; Mori, T.; Satoh, K.; et al. Fluctuations in Intestinal Microbiota Following Ingestion of Natto Powder Containing Bacillus Subtilis Var. Natto SONOMONO Spores: Considerations Using a Large-Scale Intestinal Microflora Database. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayashi, H.; Sakamoto, M.; Benno, Y. Evaluation of Three Different Forward Primers by Terminal Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism Analysis for Determination of Fecal Bifidobacterium Spp. in Healthy Subjects. Microbiol. Immunol. 2004, 48, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Holmes, S.P. Exact Sequence Variants Should Replace Operational Taxonomic Units in Marker-Gene Data Analysis. ISME J. 2017, 11, 2639–2643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yurkovetskiy, L.; Burrows, M.; Khan, A.A.; Graham, L.; Volchkov, P.; Becker, L.; Antonopoulos, D.; Umesaki, Y.; Chervonsky, A.V. Gender Bias in Autoimmunity Is Influenced by Microbiota. Immunity 2013, 39, 400–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ohno, Y.; Ohtsubo, Y.; Izawa, M.; Oshitani, N.; Kishimoto, M.; Nagata, K.; Tamura, T.; Ishizu, H.; Kasai, Y. Studies on Consciousness of Health and Dietary Style among Young Adults. J. Integr. Study Diet. Habits 2003, 14, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagendra, H. Opposite Trends in Response for the Shannon and Simpson Indices of Landscape Diversity. Appl. Geogr. 2002, 22, 175–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.L.; Madak-Erdogan, Z. Estrogen and Microbiota Crosstalk: Should We Pay Attention? Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2016, 27, 752–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores, R.; Shi, J.; Fuhrman, B.; Xu, X.; Veenstra, T.D.; Gail, M.H.; Gajer, P.; Ravel, J.; Goedert, J.J. Fecal Microbial Determinants of Fecal and Systemic Estrogens and Estrogen Metabolites: A Cross-Sectional Study. J. Transl. Med. 2012, 10, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bischoff, S.C. Microbiota and Aging. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2016, 19, 26–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salles, N. Basic Mechanisms of the Aging Gastrointestinal Tract. Dig. Dis. 2007, 25, 112–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de la Cuesta-Zuluaga, J.; Kelley, S.T.; Chen, Y.; Escobar, J.S.; Mueller, N.T.; Ley, R.E.; McDonald, D.; Huang, S.; Swafford, A.D.; Knight, R.; et al. Age- and Sex-Dependent Patterns of Gut Microbial Diversity in Human Adults. mSystems 2019, 4, e00261-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]








| Age Group (Age) | Male | Female | p-Value 1 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | Age (Mean ± SD) | n | Age (Mean ± SD) | ||
| 20s (20–29) | 194 | 24.8 ± 3.0 | 377 | 24.6 ± 3.0 | 0.626 |
| 30s (30–39) | 382 | 35.3 ± 2.8 | 741 | 35.1 ± 2.9 | 0.315 |
| 40s (40–49) | 569 | 44.5 ± 2.8 | 1298 | 44.7 ± 2.8 | 0.073 |
| 50s (50–59) | 505 | 54.2 ± 2.9 | 1117 | 53.9 ± 2.8 | 0.062 |
| 60s (60–69) | 360 | 64.2 ± 2.9 | 625 | 64.1 ± 2.8 | 0.713 |
| 70s (70–79) | 126 | 72.8 ± 2.7 | 169 | 72.8 ± 2.8 | 0.975 |
| Disease | Sex | Number of Disease-Affected Participants by Age Groups | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20s | 30s | 40s | 50s | 60s | 70s | ||
| Ulcerative colitis | Male | - | - | 9 | 13 | 10 | - |
| Female | - | - | 23 | 12 | 8 | - | |
| Type 2 diabetes | Male | - | - | 17 | 49 | 120 | 84 |
| Female | - | - | 17 | 29 | 65 | 60 | |
| Reflux esophagitis | Male | - | - | - | 19 | 33 | 27 |
| Female | - | - | - | 41 | 49 | 37 | |
| Bronchial asthma | Male | - | 11 | 17 | 22 | 27 | 24 |
| Female | - | 32 | 50 | 39 | 44 | 32 | |
| Pollinosis | Male | - | 8 | 17 | 10 | 8 | - |
| Female | - | 17 | 60 | 49 | 38 | - | |
| Gastritis | Male | - | - | - | 9 | 15 | 12 |
| Female | - | - | - | 18 | 20 | 23 | |
| Kidney disease | Male | - | - | - | 8 | 14 | - |
| Female | - | - | - | 16 | 14 | - | |
| Liver disease | Male | - | - | 8 | 23 | 16 | 10 |
| Female | - | - | 21 | 23 | 20 | 20 | |
| Arrhythmia | Male | - | - | - | 12 | 36 | 43 |
| Female | - | - | - | 10 | 30 | 22 | |
| Angina pectoris | Male | - | - | - | - | 26 | 25 |
| Female | - | - | - | - | 15 | 20 | |
| Glaucoma | Male | - | - | - | 24 | 39 | 33 |
| Female | - | - | - | 40 | 33 | 20 | |
| Atopic dermatitis | Male | 13 | 35 | 41 | 17 | 9 | 11 |
| Female | 46 | 87 | 91 | 62 | 17 | 14 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hatayama, K.; Kono, K.; Okuma, K.; Hasuko, K.; Masuyama, H.; Benno, Y. Sex Differences in Intestinal Microbiota and Their Association with Some Diseases in a Japanese Population Observed by Analysis Using a Large Dataset. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 376. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11020376
Hatayama K, Kono K, Okuma K, Hasuko K, Masuyama H, Benno Y. Sex Differences in Intestinal Microbiota and Their Association with Some Diseases in a Japanese Population Observed by Analysis Using a Large Dataset. Biomedicines. 2023; 11(2):376. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11020376
Chicago/Turabian StyleHatayama, Kouta, Kanako Kono, Kana Okuma, Kazumi Hasuko, Hiroaki Masuyama, and Yoshimi Benno. 2023. "Sex Differences in Intestinal Microbiota and Their Association with Some Diseases in a Japanese Population Observed by Analysis Using a Large Dataset" Biomedicines 11, no. 2: 376. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11020376
APA StyleHatayama, K., Kono, K., Okuma, K., Hasuko, K., Masuyama, H., & Benno, Y. (2023). Sex Differences in Intestinal Microbiota and Their Association with Some Diseases in a Japanese Population Observed by Analysis Using a Large Dataset. Biomedicines, 11(2), 376. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11020376






