Nanotechnology as a Promising Approach to Combat Multidrug Resistant Bacteria: A Comprehensive Review and Future Perspectives
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Development of Antibiotic Resistance
- 1.
- Production of inactivating enzymes: The bacterium produces particular enzymes that precisely inactivate the antibiotic, causing it to lose its biological function. For instance, when β-lactam drugs are digested by β-lactamases, this occurs. Extended-spectrum β-lactamases (ESBLs), which have the same inactivating activity, are produced by some bacteria, making them challenging to eradicate. The enzymes acetyltransferase, phosphotransferase, and adenyl transferase are additional ones that can render certain antibiotics inactive [66,67,68,69].
- 2.
- Changes and alterations in the antibiotic target: In the case of erythromycin resistance, for instance, methylation of an adenine residue in the peptidyl-transferase of r-RNA 23S reduces the enzyme’s affinity for the antibiotic without impairing protein synthesis. The alteration of penicillin-binding proteins (PBPs) by MRSA is another significant instance [70].
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- Activation of alternative metabolic pathways: The sulfonamides case serves as an explanation. In fact, bacteria exposed to sulfonamides are still able to produce folic acid through a different metabolic pathway [77].
- 6.
- 7.
- Inactive metabolic state of microorganism: The metabolically inert bacterial subpopulations known as persister cells have a lower antibacterial susceptibility than active ones [79].
- 8.
3. Spread of MDR and XDR Bacteria
4. Types and Formulations of Nanoparticles
4.1. Organic NPs
4.2. Inorganic NPs
4.3. Hybrid NPs
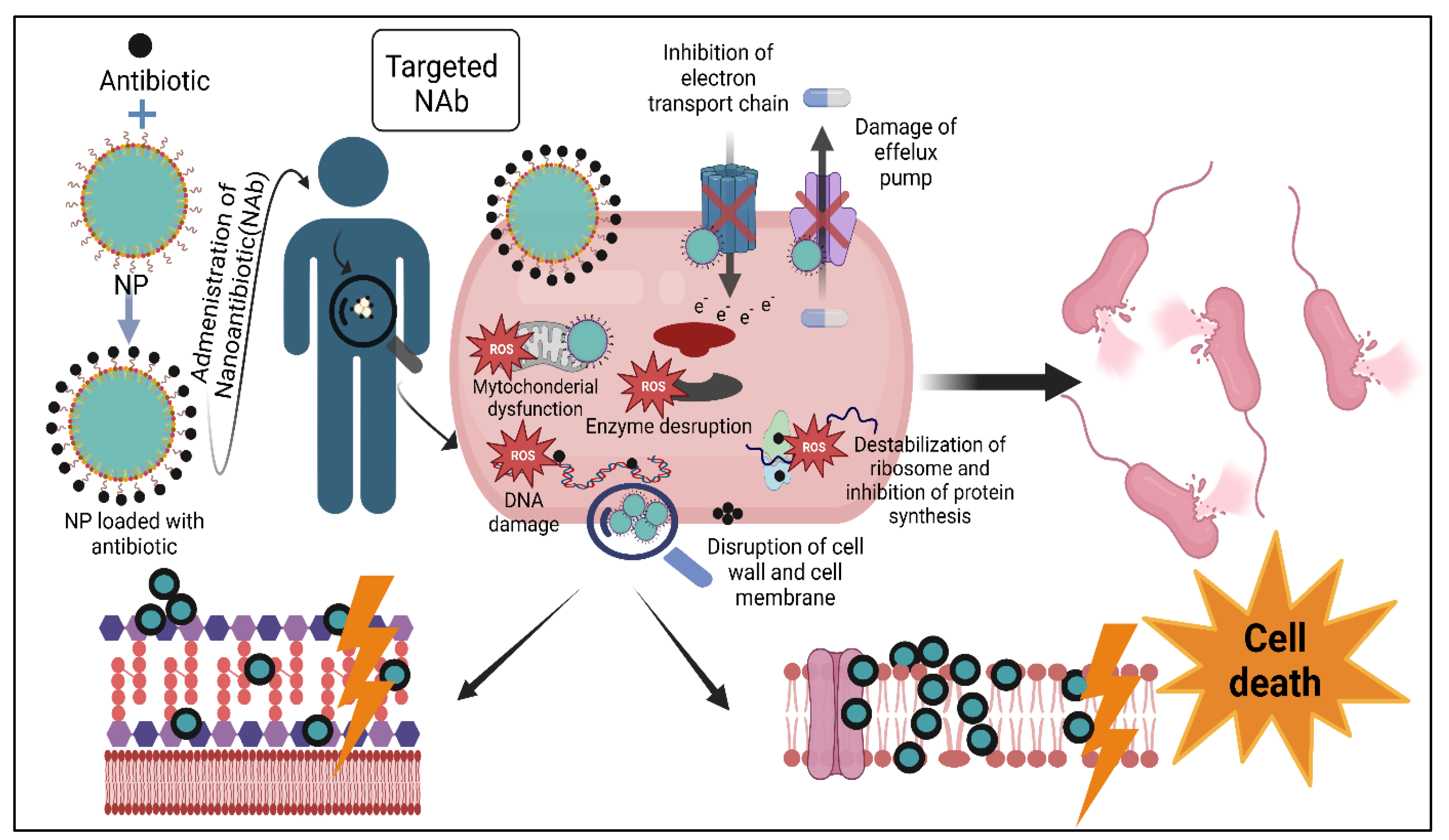
5. Free Antibiotic VS Nanoantibiotic
6. Mechanisms of Action of Nanoparticles (NPs)
6.1. Destruction of Cell Wall and Cell Membrane
6.2. Production of Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS)
6.3. Binding to and Damaging Intracellular Component
6.4. Destruction of Biofilm Architecture
7. Synergistic Activity of Nanoantibiotics
7.1. Effect on Planktonic Bacteria
7.2. Effect on Intracellular Bacteria
7.3. Effect on Bacterial Biofilm
8. Strengths and Challenges in the Application of NPs against MDR Infection
9. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- CDC. Antimicrobial (AR) Threats Report. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/drugresistance/biggest-threats.html (accessed on 1 December 2022).
- Nageeb, W.M.; Hetta, H.F. The predictive potential of different molecular markers linked to amikacin susceptibility phenotypes in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0267396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Algammal, A.M.; Alfifi, K.J.; Mabrok, M.; Alatawy, M.; Abdel-Moneam, D.A.; Alghamdi, S.; Azab, M.M.; Ibrahim, R.A.; Hetta, H.F.; El-Tarabili, R.M. Newly Emerging MDR B. cereus in Mugil seheli as the First Report Commonly Harbor nhe, hbl, cytK, and pc-plc Virulence Genes and bla1, bla2, tetA, and ermA Resistance Genes. Infect. Drug Resist. 2022, 15, 2167–2185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamad, A.A.; Sharaf, M.; Hamza, M.A.; Selim, S.; Hetta, H.F.; El-Kazzaz, W. Investigation of the Bacterial Contamination and Antibiotic Susceptibility Profile of Bacteria Isolated from Bottled Drinking Water. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e0151621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Algammal, A.M.; Abo Hashem, M.E.; Alfifi, K.J.; Al-Otaibi, A.S.; Alatawy, M.; ElTarabili, R.M.; Abd El-Ghany, W.A.; Hetta, H.F.; Hamouda, A.M.; Elewa, A.A. Sequence Analysis, Antibiogram Profile, Virulence and Antibiotic Resistance Genes of XDR and MDR Gallibacterium anatis Isolated from Layer Chickens in Egypt. Infect. Drug Resist. 2022, 15, 4321–4334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meshaal, A.K.; Hetta, H.F.; Yahia, R.; Abualnaja, K.M.; Mansour, A.T.; Al-Kadmy, I.M.; Alghamdi, S.; Dablool, A.S.; Emran, T.B.; Sedky, H. In Vitro Antimicrobial Activity of Medicinal Plant Extracts against Some Bacterial Pathogens Isolated from Raw and Processed Meat. Life 2021, 11, 1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangel-López, L.; Zaragoza-Bastida, A.; Valladares-Carranza, B.; Peláez-Acero, A.; Sosa-Gutiérrez, C.G.; Hetta, H.F.; Batiha, G.E.-S.; Alqahtani, A.; Rivero-Perez, N. In Vitro Antibacterial Potential of Salix babylonica Extract against Bacteria that Affect Oncorhynchus mykiss and Oreochromis spp. Animals 2020, 10, 1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ventola, C.L. The antibiotic resistance crisis: Part 1: Causes and threats. Pharm. Ther. 2015, 40, 277. [Google Scholar]
- Pelgrift, R.Y.; Friedman, A.J. Nanotechnology as a therapeutic tool to combat microbial resistance. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2013, 65, 1803–1815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, M.; Sanchez-Lopez, E.; Espina, M.; Calpena, A.; Silva, A.M.; Veiga, F.; Garcia, M.; Souto, E.B. Advances in antibiotic nanotherapy: Overcoming antimicrobial resistance. Emerg. Nanotechnologies Immunol. 2018, 21, 233–259. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.; Ye, W.; Qi, Y.; Ying, Y.; Xia, Z. Overcoming Multidrug Resistance in Bacteria Through Antibiotics Delivery in Surface-Engineered Nano-Cargos: Recent Developments for Future Nano-Antibiotics. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 696514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donadu, M.G.; Mazzarello, V.; Cappuccinelli, P.; Zanetti, S.; Madléna, M.; Nagy, Á.L.; Stájer, A.; Burián, K.; Gajdács, M. Relationship between the Biofilm-Forming Capacity and Antimicrobial Resistance in Clinical Acinetobacter baumannii Isolates: Results from a Laboratory-Based In Vitro Study. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 2384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usai, D.; Donadu, M.; Bua, A.; Molicotti, P.; Zanetti, S.; Piras, S.; Corona, P.; Ibba, R.; Carta, A. Enhancement of antimicrobial activity of pump inhibitors associating drugs. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries 2019, 13, 162–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spengler, G.; Gajdács, M.; Donadu, M.G.; Usai, M.; Marchetti, M.; Ferrari, M.; Mazzarello, V.; Zanetti, S.; Nagy, F.; Kovács, R. Evaluation of the Antimicrobial and Antivirulent Potential of Essential Oils Isolated from Juniperus oxycedrus L. ssp. macrocarpa Aerial Parts. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinna, A.; Donadu, M.G.; Usai, D.; Dore, S.; Boscia, F.; Zanetti, S. In Vitro Antimicrobial Activity of a New Ophthalmic Solution Containing Hexamidine Diisethionate 0.05% (Keratosept). Cornea 2020, 39, 1415–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Algammal, A.M.; Elsayed, M.E.; Hashem, H.R.; Ramadan, H.; Sheraba, N.S.; El-Diasty, E.M.; Abbas, S.M.; Hetta, H.F. Molecular and HPLC-based approaches for detection of aflatoxin B1 and ochratoxin A released from toxigenic Aspergillus species in processed meat. BMC Microbiol. 2021, 21, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horikoshi, S.; Serpone, N. Microwaves in Nanoparticle Synthesis: Fundamentals and Applications; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Abd El-Aziz, F.E.-Z.A.; Hetta, H.F.; Abdelhamid, B.N.; Abd Ellah, N.H. Antibacterial and wound-healing potential of PLGA/spidroin nanoparticles: A study on earthworms as a human skin model. Nanomedicine 2022, 17, 353–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdellatif, A.A.; Tawfeek, H.M.; Abdelfattah, A.; Batiha, G.E.-S.; Hetta, H.F. Recent updates in COVID-19 with emphasis on inhalation therapeutics: Nanostructured and targeting systems. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2021, 63, 102435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wasef, L.; Nassar, A.M.; El-Sayed, Y.S.; Samak, D.; Noreldin, A.; Elshony, N.; Saleh, H.; Elewa, Y.H.; Hassan, S.; Saati, A.A. The potential ameliorative impacts of cerium oxide nanoparticles against fipronil-induced hepatic steatosis. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eid, A.M.; Fouda, A.; Niedbała, G.; Hassan, S.E.-D.; Salem, S.S.; Abdo, A.M.; Hetta, F.H.; Shaheen, T.I. Endophytic Streptomyces laurentii mediated green synthesis of Ag-NPs with antibacterial and anticancer properties for developing functional textile fabric properties. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mubeen, B.; Ansar, A.N.; Rasool, R.; Ullah, I.; Imam, S.S.; Alshehri, S.; Ghoneim, M.M.; Alzarea, S.I.; Nadeem, M.S.; Kazmi, I. Nanotechnology as a Novel Approach in Combating Microbes Providing an Alternative to Antibiotics. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, N.; Goshisht, M.K. Recent Advances and Mechanistic Insights into Antibacterial Activity, Antibiofilm Activity, and Cytotoxicity of Silver Nanoparticles. ACS Appl. Bio. Mater. 2022, 5, 1391–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tawre, M.S.; Shiledar, A.; Satpute, S.K.; Ahire, K.; Ghosh, S.; Pardesi, K. Synergistic and antibiofilm potential of Curcuma aromatica derived silver nanoparticles in combination with antibiotics against multidrug-resistant pathogens. Front. Chem. 2022, 10, 1029056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hetta, H.F.; Al-Kadmy, I.; Khazaal, S.S.; Abbas, S.; Suhail, A.; El-Mokhtar, M.A.; Ellah, N.H.A.; Ahmed, E.A.; Abd-Ellatief, R.B.; El-Masry, E.A. Antibiofilm and antivirulence potential of silver nanoparticles against multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 10751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelraheem, W.M.; Khairy, R.M.; Zaki, A.I.; Zaki, S.H. Effect of ZnO nanoparticles on methicillin, vancomycin, linezolid resistance and biofilm formation in Staphylococcus aureus isolates. Ann. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob. 2021, 20, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashem, A.H.; Al Abboud, M.A.; Alawlaqi, M.M.; Abdelghany, T.M.; Hasanin, M. Synthesis of nanocapsules based on biosynthesized nickel nanoparticles and potato starch: Antimicrobial, antioxidant, and anticancer activity. Starch Stärke 2022, 74, 2100165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashem, A.H.; Salem, S.S. Green and ecofriendly biosynthesis of selenium nanoparticles using Urtica dioica (stinging nettle) leaf extract: Antimicrobial and anticancer activity. Biotechnol. J. 2022, 17, 2100432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abu-Elghait, M.; Hasanin, M.; Hashem, A.H.; Salem, S.S. Ecofriendly novel synthesis of tertiary composite based on cellulose and myco-synthesized selenium nanoparticles: Characterization, antibiofilm and biocompatibility. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 175, 294–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.-W.; Patel, K.D.; Kwak, J.-H.; Jun, S.-K.; Jang, T.-S.; Lee, S.-H.; Knowles, J.C.; Kim, H.-W.; Lee, H.-H.; Lee, J.-H. Selenium nanoparticles as candidates for antibacterial substitutes and supplements against multidrug-resistant bacteria. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elbahnasawy, M.A.; Shehabeldine, A.M.; Khattab, A.M.; Amin, B.H.; Hashem, A.H. Green biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using novel endophytic Rothia endophytica: Characterization and anticandidal activity. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2021, 62, 102401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Batal, A.I.; Mosallam, F.M.; El-Sayyad, G.S. Synthesis of metallic silver nanoparticles by fluconazole drug and gamma rays to inhibit the growth of multidrug-resistant microbes. J. Clust. Sci. 2018, 29, 1003–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Liu, P.; Liu, X.; Wang, Y.; Wei, H.; Zhang, J.; Yu, L.; Yan, X.; He, Z. Dealing with MDR bacteria and biofilm in the post-antibiotic era: Application of antimicrobial peptides-based nano-formulation. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2021, 128, 112318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalid, M.; El-Sawy, H.S. Polymeric nanoparticles: Promising platform for drug delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 528, 675–691. [Google Scholar]
- Qayyum, S.; Khan, A.U. Nanoparticles vs. biofilms: A battle against another paradigm of antibiotic resistance. MedChemComm 2016, 7, 1479–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Cui, Q.; Wu, Q.; Li, X.; Song, K.; Ge, D.; Guan, S. Mechanism study of bacteria killed on nanostructures. J. Phys. Chem. B 2019, 123, 8686–8696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.-Y.; Van der Mei, H.C.; Ren, Y.; Busscher, H.J.; Shi, L. Lipid-based antimicrobial delivery-systems for the treatment of bacterial infections. Front. Chem. 2020, 7, 872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, H.; Nassar, A.M.; Noreldin, A.E.; Samak, D.; Elshony, N.; Wasef, L.; Elewa, Y.H.; Hassan, S.M.; Saati, A.A.; Hetta, H.F. Chemo-protective potential of cerium oxide nanoparticles against fipronil-induced oxidative stress, apoptosis, inflammation and reproductive dysfunction in male white albino rats. Molecules 2020, 25, 3479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeyemi, O.S.; Arowolo, A.T.; Hetta, H.F.; Al-Rejaie, S.; Rotimi, D.; Batiha, G.E.-S. Apoferritin and Apoferritin-Capped Metal Nanoparticles Inhibit Arginine Kinase of Trypanosoma brucei. Molecules 2020, 25, 3432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaturvedi, V.K.; Yadav, N.; Rai, N.K.; Ellah, N.H.A.; Bohara, R.A.; Rehan, I.F.; Marraiki, N.; Batiha, G.E.-S.; Hetta, H.F.; Singh, M. Pleurotus sajor-caju-mediated synthesis of silver and gold nanoparticles active against colon cancer cell lines: A new era of herbonanoceutics. Molecules 2020, 25, 3091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hetta, H.F.; Ahmed, E.A.; Hemdan, A.G.; El-Deek, H.E.; Abd-Elregal, S.; Abd Ellah, N.H. Modulation of rifampicin-induced hepatotoxicity using poly (lactic-co-glycolic acid) nanoparticles: A study on rat and cell culture models. Nanomedicine 2020, 15, 1375–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd Ellah, N.H.; Ahmed, E.A.; Abd-Ellatief, R.B.; Ali, M.F.; Zahran, A.M.; Hetta, H.F. Metoclopramide nanoparticles modulate immune response in a diabetic rat model: Association with regulatory T cells and proinflammatory cytokines. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, E.; Shen, H.; Ferrari, M. Principles of nanoparticle design for overcoming biological barriers to drug delivery. Nat. Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 941–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, D.; Misba, L.; Khan, A.U. Antibiotics versus biofilm: An emerging battleground in microbial communities. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control. 2019, 8, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramasamy, M.; Lee, J. Recent nanotechnology approaches for prevention and treatment of biofilm-associated infections on medical devices. BioMed Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 1851242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, N.-Y.; Ko, W.-C.; Hsueh, P.-R. Nanoparticles in the treatment of infections caused by multidrug-resistant organisms. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, L.; Li, R.; Liu, G.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, X.; Wang, J.; Liu, H.; Qin, Y. Potential antibacterial mechanism of silver nanoparticles and the optimization of orthopedic implants by advanced modification technologies. Int. J. Nanomed. 2018, 13, 3311. [Google Scholar]
- Shobha, G.; Moses, V.; Ananda, S. Biological synthesis of copper nanoparticles and its impact. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Invent 2014, 3, 6–28. [Google Scholar]
- Jaworski, S.; Wierzbicki, M.; Sawosz, E.; Jung, A.; Gielerak, G.; Biernat, J.; Jaremek, H.; Łojkowski, W.; Woźniak, B.; Wojnarowicz, J. Graphene oxide-based nanocomposites decorated with silver nanoparticles as an antibacterial agent. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anselmo, A.C.; Mitragotri, S. Nanoparticles in the clinic. Bioeng. Transl. Med. 2016, 1, 10–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yetisgin, A.A.; Cetinel, S.; Zuvin, M.; Kosar, A.; Kutlu, O. Therapeutic nanoparticles and their targeted delivery applications. Molecules 2020, 25, 2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abd Ellah, N.H.; Gad, S.F.; Muhammad, K.; E Batiha, G.; Hetta, H.F. Nanomedicine as a promising approach for diagnosis, treatment and prophylaxis against COVID-19. Nanomedicine 2020, 15, 2085–2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mba, I.E.; Nweze, E.I. The use of nanoparticles as alternative therapeutic agents against Candida infections: An up-to-date overview and future perspectives. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 36, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mba, I.E.; Sharndama, H.C.; Osondu-Chuka, G.O.; Okeke, O.P. Immunobiology and nanotherapeutics of severe acute respiratory syndrome 2 (SARS-CoV-2): A current update. Infect. Dis. 2021, 53, 559–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd Ellah, N.H.; Tawfeek, H.M.; John, J.; Hetta, H.F. Nanomedicine as a future therapeutic approach for Hepatitis C virus. Nanomedicine 2019, 14, 1471–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sayad, R.; Abdelsabour, H.A.; Farhat, S.M.; Omer, N.G.; Ahmed, M.M.; Elsayh, I.K.; Ibrahim, I.H.; Algammal, A.M.; AL-Kadmy, I.M.S.; Batiha, G.E.-S.; et al. Applications of nanotechnology in the fight against coronavirus disease 2019. Rev. Res. Med. Microbiol. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abid, S.A.; Muneer, A.A.; Al-Kadmy, I.M.; Sattar, A.A.; Beshbishy, A.M.; Batiha, G.E.-S.; Hetta, H.F. Biosensors as a future diagnostic approach for COVID-19. Life Sci. 2021, 273, 119117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, S.; Zhang, Y.; Pan, X.; Zhu, F.; Jiang, C.; Liu, Q.; Cheng, Z.; Dai, G.; Wu, G.; Wang, L. Antibacterial activity and mechanism of silver nanoparticles against multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Möhler, J.S.; Sim, W.; Blaskovich, M.A.; Cooper, M.A.; Ziora, Z.M. Silver bullets: A new lustre on an old antimicrobial agent. Biotechnol. Adv. 2018, 36, 1391–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merrifield, R.C.; Stephan, C.; Lead, J.R. Single-particle inductively coupled plasma mass spectroscopy analysis of size and number concentration in mixtures of monometallic and bimetallic (core-shell) nanoparticles. Talanta 2017, 162, 130–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajeshkumar, S.; Bharath, L. Mechanism of plant-mediated synthesis of silver nanoparticles–a review on biomolecules involved, characterisation and antibacterial activity. Chem. -Biol. Interact. 2017, 273, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacGowan, A.; Macnaughton, E. Antibiotic resistance. Medicine 2017, 45, 622–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Mokhtar, M.A.; Hetta, H.F. Ambulance vehicles as a source of multidrug-resistant infections: A multicenter study in Assiut City, Egypt. Infect. Drug Resist. 2018, 11, 587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munita, J.M.; Arias, C.A. Mechanisms of antibiotic resistance. Microbiol. Spectr. 2016, 4, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alekshun, M.N.; Levy, S.B. Molecular mechanisms of antibacterial multidrug resistance. Cell 2007, 128, 1037–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Kazzaz, W.; Metwally, L.; Yahia, R.; Al-Harbi, N.; El-Taher, A.; Hetta, H.F. Antibiogram, prevalence of OXA carbapenemase encoding genes, and RAPD-genotyping of multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii incriminated in hidden community-acquired infections. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd El-Baky, R.M.; Farhan, S.M.; Ibrahim, R.A.; Mahran, K.M.; Hetta, H.F. Antimicrobial resistance pattern and molecular epidemiology of ESBL and MBL producing Acinetobacter baumannii isolated from hospitals in Minia, Egypt. Alex. J. Med. 2020, 56, 4–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makharita, R.R.; El-Kholy, I.; Hetta, H.F.; Abdelaziz, M.H.; Hagagy, F.I.; Ahmed, A.A.; Algammal, A.M. Antibiogram and genetic characterization of carbapenem-resistant gram-negative pathogens incriminated in healthcare-associated infections. Infect. Drug Resist. 2020, 13, 3991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farhan, S.M.; Ibrahim, R.A.; Mahran, K.M.; Hetta, H.F.; Abd El-Baky, R.M. Antimicrobial resistance pattern and molecular genetic distribution of metallo-β-lactamases producing Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolated from hospitals in Minia, Egypt. Infect. Drug Resist. 2019, 12, 2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Algammal, A.M.; Hetta, H.F.; Elkelish, A.; Alkhalifah, D.H.H.; Hozzein, W.N.; Batiha, G.E.-S.; El Nahhas, N.; Mabrok, M.A. Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA): One health perspective approach to the bacterium epidemiology, virulence factors, antibiotic-resistance, and zoonotic impact. Infect. Drug Resist. 2020, 13, 3255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kareem, S.M.; Al-Kadmy, I.M.; Kazaal, S.S.; Ali, A.N.M.; Aziz, S.N.; Makharita, R.R.; Algammal, A.M.; Al-Rejaie, S.; Behl, T.; Batiha, G.E.-S. Detection of gyra and parc mutations and prevalence of plasmid-mediated quinolone resistance genes in Klebsiella pneumoniae. Infect. Drug Resist. 2021, 14, 555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Kadmy, I.M.; Ibrahim, S.A.; Al-Saryi, N.; Aziz, S.N.; Besinis, A.; Hetta, H.F. Prevalence of genes involved in colistin resistance in Acinetobacter baumannii: First report from Iraq. Microb. Drug Resist. 2020, 26, 616–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd El-Baky, R.M.; Masoud, S.M.; Mohamed, D.S.; Waly, N.G.; Shafik, E.A.; Mohareb, D.A.; Elkady, A.; Elbadr, M.M.; Hetta, H.F. Prevalence and some possible mechanisms of colistin resistance among multidrug-resistant and extensively drug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect. Drug Resist. 2020, 13, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Saleh, N.M.; Das, R.; Landis, R.F.; Bigdeli, A.; Motamedchaboki, K.; Campos, A.R.; Pomeroy, K.; Mahmoudi, M.; Rotello, V.M. Synergistic antimicrobial therapy using nanoparticles and antibiotics for the treatment of multidrug-resistant bacterial infection. Nano Futures 2017, 1, 015004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, D.; Singh, A.; Khan, A.U. Nanoparticles as efflux pump and biofilm inhibitor to rejuvenate bactericidal effect of conventional antibiotics. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2017, 12, 454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abd El-Baky, R.M.; Sandle, T.; John, J.; Abuo-Rahma, G.E.-D.A.; Hetta, H.F. A novel mechanism of action of ketoconazole: Inhibition of the NorA efflux pump system and biofilm formation in multidrug-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Infect. Drug Resist. 2019, 12, 1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ovung, A.; Bhattacharyya, J. Sulfonamide drugs: Structure, antibacterial property, toxicity, and biophysical interactions. Biophys. Rev. 2021, 13, 259–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blair, J.; Webber, M.A.; Baylay, A.J.; Ogbolu, D.O.; Piddock, L.J. Molecular mechanisms of antibiotic resistance. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2015, 13, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurdle, J.G.; O’neill, A.J.; Chopra, I.; Lee, R.E. Targeting bacterial membrane function: An underexploited mechanism for treating persistent infections. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2011, 9, 62–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, B.S.; Zhang, W.; Harrison, J.J.; Quach, T.P.; Song, J.L.; Penterman, J.; Singh, P.K.; Chopp, D.L.; Packman, A.I.; Parsek, M.R. The extracellular matrix protects P seudomonas aeruginosa biofilms by limiting the penetration of tobramycin. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 15, 2865–2878. [Google Scholar]
- Khalil, M.A.; Ahmed, F.A.; Elkhateeb, A.F.; Mahmoud, E.E.; Ahmed, M.I.; Ahmed, R.I.; Hosni, A.; Alghamdi, S.; Kabrah, A.; Dablool, A.S. Virulence characteristics of biofilm-forming acinetobacter baumannii in clinical isolates using a Galleria Mellonella Model. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 2365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Gefen, O.; Ronin, I.; Bar-Meir, M.; Balaban, N.Q. Effect of tolerance on the evolution of antibiotic resistance under drug combinations. Science 2020, 367, 200–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torky, H.A.; Saad, H.M.; Khaliel, S.A.; Kassih, A.T.; Sabatier, J.-M.; Batiha, G.E.-S.; Hetta, H.F.; Elghazaly, E.M.; De Waard, M. Isolation and Molecular Characterization of Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis: Association with Proinflammatory Cytokines in Caseous Lymphadenitis Pyogranulomas. Animals 2023, 13, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mabrok, M.; Algammal, A.; Sivaramasamy, E.; Hetta, H.F.; Atwah, B.; Alghamdi, S.; Fawzy, A.; Avendaño-Herrera, R.; Rodkhum, C. Tenacibaculosis caused by Tenacibaculum maritimum: Updated knowledge of this marine bacterial fish pathogen. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2023, 1862, 1068000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salah, M.; Badr, G.; Hetta, H.F.; Khalifa, W.A.; Shoreit, A.A. Fig latex inhibits the growth of pathogenic bacteria invading human diabetic wounds and accelerates wound closure in diabetic mice. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 21852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgan, D.J.; Okeke, I.N.; Laxminarayan, R.; Perencevich, E.N.; Weisenberg, S. Non-prescription antimicrobial use worldwide: A systematic review. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2011, 11, 692–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Antibiotic Resistance: Multi-Country Public Awareness Survey; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Algammal, A.M.; Mabrok, M.; Sivaramasamy, E.; Youssef, F.M.; Atwa, M.H.; El-Kholy, A.W.; Hetta, H.F.; Hozzein, W.N. Emerging MDR-Pseudomonas aeruginosa in fish commonly harbor oprL and toxA virulence genes and blaTEM, blaCTX-M, and tetA antibiotic-resistance genes. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 15961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roca, I.; Akova, M.; Baquero, F.; Carlet, J.; Cavaleri, M.; Coenen, S.; Cohen, J.; Findlay, D.; Gyssens, I.; Heure, O. The global threat of antimicrobial resistance: Science for intervention. New Microbes New Infect. 2015, 6, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Algammal, A.M.; Hashem, H.R.; Alfifi, K.J.; Hetta, H.F.; Sheraba, N.S.; Ramadan, H.; El-Tarabili, R.M. atpD gene sequencing, multidrug resistance traits, virulence-determinants, and antimicrobial resistance genes of emerging XDR and MDR-Proteus mirabilis. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 9476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Algammal, A.M.; Hetta, H.F.; Batiha, G.E.; Hozzein, W.N.; El Kazzaz, W.M.; Hashem, H.R.; Tawfik, A.M.; El-Tarabili, R.M. Virulence-determinants and antibiotic-resistance genes of MDR-E. coli isolated from secondary infections following FMD-outbreak in cattle. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 19779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkhawaga, A.A.; Hetta, H.F.; Osman, N.S.; Hosni, A.; El-Mokhtar, M.A. Emergence of Cronobacter sakazakii in cases of neonatal sepsis in upper Egypt: First report in North Africa. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebeaux, D.; Chauhan, A.; Rendueles, O.; Beloin, C. From in vitro to in vivo models of bacterial biofilm-related infections. Pathogens 2013, 2, 288–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saginur, R.; StDenis, M.; Ferris, W.; Aaron, S.D.; Chan, F.; Lee, C.; Ramotar, K. Multiple combination bactericidal testing of staphylococcal biofilms from implant-associated infections. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2006, 50, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall-Stoodley, L.; Costerton, J.W.; Stoodley, P. Bacterial biofilms: From the natural environment to infectious diseases. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2004, 2, 95–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, C.W.; Mah, T.-F. Molecular mechanisms of biofilm-based antibiotic resistance and tolerance in pathogenic bacteria. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2017, 41, 276–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanwar, J.; Das, S.; Fatima, Z.; Hameed, S. Multidrug Resistance: An Emerging Crisis. Interdiscip. Perspect. Infect. Dis. 2014, 2014, 541340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, M.; Yang, M.; Yan, D.; Yang, L.; Wan, X.; Xiao, J.; Yao, Y.; Luo, J. Surface-Charge-Switchable and Size-Transformable Thermosensitive Nanocomposites for Chemo-Photothermal Eradication of Bacterial Biofilms in Vitro and in Vivo. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 8847–8864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, B.; Hu, E.; Xie, R.; Yu, K.; Lu, F.; Bao, R.; Wang, C.; Lan, G.; Dai, F. Magnetically Guided Nanoworms for Precise Delivery to Enhance In Situ Production of Nitric Oxide to Combat Focal Bacterial Infection In Vivo. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 22225–22239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zylberberg, C.; Matosevic, S. Pharmaceutical liposomal drug delivery: A review of new delivery systems and a look at the regulatory landscape. Drug Deliv. 2016, 23, 3319–3329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemière, J.; Carvalho, K.; Sykes, C. Cell-Sized Liposomes That Mimic Cell Motility and the Cell Cortex. In Methods in Cell Biology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; Volume 128, pp. 271–285. [Google Scholar]
- Shek, P.; Yung, B.; Stanacev, N. Comparison between multilamellar and unilamellar liposomes in enhancing antibody formation. Immunology 1983, 49, 37. [Google Scholar]
- Bassetti, M.; Vena, A.; Russo, A.; Peghin, M. Inhaled Liposomal Antimicrobial Delivery in Lung Infections. Drugs 2020, 80, 1309–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amreddy, N.; Babu, A.; Muralidharan, R.; Panneerselvam, J.; Srivastava, A.; Ahmed, R.; Mehta, M.; Munshi, A.; Ramesh, R. Recent advances in nanoparticle-based cancer drug and gene delivery. Adv. Cancer Res. 2018, 137, 115–170. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sánchez, A.; Mejía, S.P.; Orozco, J. Recent Advances in Polymeric Nanoparticle-Encapsulated Drugs against Intracellular Infections. Molecules 2020, 25, 3760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saneja, A.; Kumar, R.; Mintoo, M.J.; Dubey, R.D.; Sangwan, P.L.; Mondhe, D.M.; Panda, A.K.; Gupta, P.N. Gemcitabine and betulinic acid co-encapsulated PLGA− PEG polymer nanoparticles for improved efficacy of cancer chemotherapy. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 98, 764–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahlool, A.Z.; Fattah, S.; O’Sullivan, A.; Cavanagh, B.; MacLoughlin, R.; Keane, J.; O’Sullivan, M.P.; Cryan, S.A. Development of Inhalable ATRA-Loaded PLGA Nanoparticles as Host-Directed Immunotherapy against Tuberculosis. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherje, A.P.; Jadhav, M.; Dravyakar, B.R.; Kadam, D. Dendrimers: A versatile nanocarrier for drug delivery and targeting. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 548, 707–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghezzi, M.; Pescina, S.; Padula, C.; Santi, P.; Del Favero, E.; Cantù, L.; Nicoli, S. Polymeric micelles in drug delivery: An insight of the techniques for their characterization and assessment in biorelevant conditions. J. Control. Release Off. J. Control. Release Soc. 2021, 332, 312–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ameh, T.; Gibb, M.; Stevens, D.; Pradhan, S.H.; Braswell, E.; Sayes, C.M. Silver and Copper Nanoparticles Induce Oxidative Stress in Bacteria and Mammalian Cells. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 2402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haidari, H.; Bright, R.; Kopecki, Z.; Zilm, P.S.; Garg, S.; Cowin, A.J.; Vasilev, K.; Goswami, N. Polycationic Silver Nanoclusters Comprising Nanoreservoirs of Ag+ Ions with High Antimicrobial and Antibiofilm Activity. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 14, 390–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Hagbani, T.; Rizvi, S.M.D.; Hussain, T.; Mehmood, K.; Rafi, Z.; Moin, A.; Abu Lila, A.S.; Alshammari, F.; Khafagy, E.S.; Rahamathulla, M.; et al. Cefotaxime Mediated Synthesis of Gold Nanoparticles: Characterization and Antibacterial Activity. Polymers 2022, 14, 771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zheng, W.; Li, S.; Zhong, L.; Jiang, X. Aminophenol-Decorated Gold Nanoparticles for Curing Bacterial Infections. Nano Lett. 2022, 22, 3576–3582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Periakaruppan, R.; S, M.P.; C, P.; P, R.; S, G.R.; Danaraj, J. Biosynthesis of Silica Nanoparticles Using the Leaf Extract of Punica granatum and Assessment of Its Antibacterial Activities Against Human Pathogens. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2022, 194, 5594–5605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnamoorthy, R.; Athinarayanan, J.; Periyasamy, V.S.; Alshuniaber, M.A.; Alshammari, G.; Hakeem, M.J.; Ahmed, M.A.; Alshatwi, A.A. Antibacterial Mechanisms of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticle against Bacterial Food Pathogens Resistant to Beta-Lactam Antibiotics. Molecules 2022, 27, 2489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaghubi Kalurazi, T.; Jafari, A. Evaluation of magnesium oxide and zinc oxide nanoparticles against multi-drug-resistance Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Indian J. Tuberc. 2021, 68, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.; Liu, X.; Liu, Z.; Xu, Y. Visible-Light-Driven Photocatalysis-Enhanced Nanozyme of TiO2 Nanotubes@ MoS2 Nanoflowers for Efficient Wound Healing Infected with Multidrug-Resistant Bacteria. Small 2021, 17, 2103348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eymard-Vernain, E.; Luche, S.; Rabilloud, T.; Lelong, C. ZnO and TiO2 nanoparticles alter the ability of Bacillus subtilis to fight against a stress. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0240510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younis, A.B.; Haddad, Y.; Kosaristanova, L.; Smerkova, K. Titanium dioxide nanoparticles: Recent progress in antimicrobial applications. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Nanomed. Nanobiotechnology 2022, e1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilbertson, L.M.; Albalghiti, E.M.; Fishman, Z.S.; Perreault, F.; Corredor, C.; Posner, J.D.; Elimelech, M.; Pfefferle, L.D.; Zimmerman, J.B. Shape-Dependent Surface Reactivity and Antimicrobial Activity of Nano-Cupric Oxide. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 3975–3984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca, S.; Cayer, M.P.; Ahmmed, K.M.T.; Khadem-Mohtaram, N.; Charette, S.J.; Brouard, D. Characterization of the Antibacterial Activity of an SiO(2) Nanoparticular Coating to Prevent Bacterial Contamination in Blood Products. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Huo, S.; Hardie, J.; Liang, X.-J.; Rotello, V.M. Progress and perspective of inorganic nanoparticle-based siRNA delivery systems. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2016, 13, 547–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcato, P.D.; Durán, N. New aspects of nanopharmaceutical delivery systems. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2008, 8, 2216–2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kassem, A.; Ayoub, G.M.; Malaeb, L. Antibacterial activity of chitosan nano-composites and carbon nanotubes: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 668, 566–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noor, M.M.; Santana-Pereira, A.L.R.; Liles, M.R.; Davis, V.A. Dispersant Effects on Single-Walled Carbon Nanotube Antibacterial Activity. Molecules 2022, 27, 1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ang, C.W.; Tan, L.; Qu, Z.; West, N.P.; Cooper, M.A.; Popat, A.; Blaskovich, M.A.T. Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles Improve Oral Delivery of Antitubercular Bicyclic Nitroimidazoles. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2022, 8, 4196–4206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alandiyjany, M.N.; Abdelaziz, A.S.; Abdelfattah-Hassan, A.; Hegazy, W.A.H.; Hassan, A.A.; Elazab, S.T.; Mohamed, E.A.A.; El-Shetry, E.S.; Saleh, A.A.; ElSawy, N.A.; et al. Novel In Vivo Assessment of Antimicrobial Efficacy of Ciprofloxacin Loaded Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles against Salmonella typhimurium Infection. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-Salcedo, S.; García, A.; González-Jiménez, A.; Vallet-Regí, M. Antibacterial effect of 3D printed mesoporous bioactive glass scaffolds doped with metallic silver nanoparticles. Acta Biomater. 2022, 155, 654–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zafar, A.; Alruwaili, N.K.; Imam, S.S.; Alsaidan, O.A.; Ahmed, M.M.; Yasir, M.; Warsi, M.H.; Alquraini, A.; Ghoneim, M.M.; Alshehri, S. Development and Optimization of Hybrid Polymeric Nanoparticles of Apigenin: Physicochemical Characterization, Antioxidant Activity and Cytotoxicity Evaluation. Sensors 2022, 22, 1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalili, L.; Dehghan, G.; Sheibani, N.; Khataee, A. Smart active-targeting of lipid-polymer hybrid nanoparticles for therapeutic applications: Recent advances and challenges. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 213, 166–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elhassan, E.; Devnarain, N.; Mohammed, M.; Govender, T.; Omolo, C.A. Engineering hybrid nanosystems for efficient and targeted delivery against bacterial infections. J. Control. Release Off. J. Control. Release Soc. 2022, 351, 598–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.X.; Ahmed, T.; Li, L.Y.; Li, J.; Abbasi, A.Z.; Wu, X.Y. Design of nanocarriers for nanoscale drug delivery to enhance cancer treatment using hybrid polymer and lipid building blocks. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 1334–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Dai, L.; Ye, L.; Sun, X.; Enoch, O.; Hu, R.; Zan, X.; Lin, F.; Shen, J. A Vehicle-Free Antimicrobial Polymer Hybrid Gold Nanoparticle as Synergistically Therapeutic Platforms for Staphylococcus aureus Infected Wound Healing. Adv. Sci. 2022, 9, e2105223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, H.; Zeng, X.; Fan, S.; Cai, R.; Wang, Z.; Yuan, Y.; Yue, T. Silver nanoparticles anchored magnetic self-assembled carboxymethyl cellulose-ε-polylysine hybrids with synergetic antibacterial activity for wound infection therapy. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 210, 703–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cascioferro, S.; Carbone, D.; Parrino, B.; Pecoraro, C.; Giovannetti, E.; Cirrincione, G.; Diana, P. Therapeutic strategies to counteract antibiotic resistance in MRSA biofilm-associated infections. ChemMedChem 2021, 16, 65–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makabenta, J.M.V.; Nabawy, A.; Li, C.-H.; Schmidt-Malan, S.; Patel, R.; Rotello, V.M. Nanomaterial-based therapeutics for antibiotic-resistant bacterial infections. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 19, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohanski, M.A.; Dwyer, D.J.; Collins, J.J. How antibiotics kill bacteria: From targets to networks. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2010, 8, 423–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mamun, M.M.; Sorinolu, A.J.; Munir, M.; Vejerano, E.P. Nanoantibiotics: Functions and properties at the nanoscale to combat antibiotic resistance. Front. Chem. 2021, 9, 687660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeh, Y.-C.; Huang, T.-H.; Yang, S.-C.; Chen, C.-C.; Fang, J.-Y. Nano-based drug delivery or targeting to eradicate bacteria for infection mitigation: A review of recent advances. Front. Chem. 2020, 8, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaidi, S.; Misba, L.; Khan, A.U. Nano-therapeutics: A revolution in infection control in post antibiotic era. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2017, 13, 2281–2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, H.S.; Yao, Z.; Goehring, N.W.; Kishony, R.; Beckwith, J.; Kahne, D. Rapid beta-lactam-induced lysis requires successful assembly of the cell division machinery. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 21872–21877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.M.; Rock, C.O. Membrane lipid homeostasis in bacteria. Nat. Reviews. Microbiol. 2008, 6, 222–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nel, A.E.; Mädler, L.; Velegol, D.; Xia, T.; Hoek, E.M.; Somasundaran, P.; Klaessig, F.; Castranova, V.; Thompson, M. Understanding biophysicochemical interactions at the nano-bio interface. Nat. Mater. 2009, 8, 543–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Tian, Y.; Cui, Y.; Liu, W.; Ma, W.; Jiang, X. Small molecule-capped gold nanoparticles as potent antibacterial agents that target gram-negative bacteria. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 12349–12356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Tian, Y.; Zhang, W.; Lü, X.; Jiang, X. The molecular mechanism of action of bactericidal gold nanoparticles on Escherichia coli. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 2327–2333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemire, J.A.; Harrison, J.J.; Turner, R.J. Antimicrobial activity of metals: Mechanisms, molecular targets and applications. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2013, 11, 371–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarrat, N.; Benoit, M.; Giraud, M.; Ponchet, A.; Casanove, M.-J. The gold/ampicillin interface at the atomic scale. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 14515–14524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.; Kwon, S.J.; Wu, X.; Sauve, J.; Lee, I.; Nam, J.; Kim, J.; Dordick, J.S. Selective Killing of Pathogenic Bacteria by Antimicrobial Silver Nanoparticle-Cell Wall Binding Domain Conjugates. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 13317–13324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jijie, R.; Barras, A.; Teodorescu, F.; Boukherroub, R.; Szunerits, S. Advancements on the molecular design of nanoantibiotics: Current level of development and future challenges. Mol. Syst. Des. Eng. 2017, 2, 349–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheeseman, S.; Christofferson, A.J.; Kariuki, R.; Cozzolino, D.; Daeneke, T.; Crawford, R.J.; Truong, V.K.; Chapman, J.; Elbourne, A. Antimicrobial metal nanomaterials: From passive to stimuli-activated applications. Adv. Sci. 2020, 7, 1902913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochvaldová, L.; Večeřová, R.; Kolář, M.; Prucek, R.; Kvítek, L.; Lapčík, L.; Panáček, A. Antibacterial nanomaterials: Upcoming hope to overcome antibiotic resistance crisis. Nanotechnol. Rev. 2022, 11, 1115–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Mumtaz, S.; Li, C.-H.; Hussain, I.; Rotello, V.M. Combatting antibiotic-resistant bacteria using nanomaterials. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2019, 48, 415–427. [Google Scholar]
- Muthukrishnan, L.; Chellappa, M.; Nanda, A. Bio-engineering and cellular imaging of silver nanoparticles as weaponry against multidrug resistant human pathogens. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2019, 194, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Hu, C.; Shao, L. The antimicrobial activity of nanoparticles: Present situation and prospects for the future. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slavin, Y.N.; Asnis, J.; Häfeli, U.O.; Bach, H. Metal nanoparticles: Understanding the mechanisms behind antibacterial activity. J. Nanobiotechnology 2017, 15, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Du, Y.; Fan, L.; Liu, H.; Hu, Y. Chitosan-metal complexes as antimicrobial agent: Synthesis, characterization and Structure-activity study. Polym. Bull. 2005, 55, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natan, M.; Banin, E. From nano to micro: Using nanotechnology to combat microorganisms and their multidrug resistance. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2017, 41, 302–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fenoglio, I.; Corazzari, I.; Francia, C.; Bodoardo, S.; Fubini, B. The oxidation of glutathione by cobalt/tungsten carbide contributes to hard metal-induced oxidative stress. Free. Radic. Res. 2008, 42, 437–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quinteros, M.; Aristizábal, V.C.; Dalmasso, P.R.; Paraje, M.G.; Páez, P.L. Oxidative stress generation of silver nanoparticles in three bacterial genera and its relationship with the antimicrobial activity. Toxicol. Vitr. 2016, 36, 216–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hailan, W.A.; Al-Anazi, K.M.; Farah, M.A.; Ali, M.A.; Al-Kawmani, A.A.; Abou-Tarboush, F.M. Reactive Oxygen Species-Mediated Cytotoxicity in Liver Carcinoma Cells Induced by Silver Nanoparticles Biosynthesized Using Schinus molle Extract. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, S.; Vishakha, K.; Das, S.; Sangma, P.D.; Mondal, S.; Ganguli, A. Oxidative stress, DNA, and membranes targets as modes of antibacterial and antibiofilm activity of facile synthesized biocompatible keratin-copper nanoparticles against multidrug resistant uro-pathogens. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2022, 38, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahimmunisha, B.A.; Ishwarya, R.; AlSalhi, M.S.; Devanesan, S.; Govindarajan, M.; Vaseeharan, B. Green fabrication, characterization and antibacterial potential of zinc oxide nanoparticles using Aloe socotrina leaf extract: A novel drug delivery approach. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2020, 55, 101465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathakoti, K.; Manubolu, M.; Hwang, H.M. Effect of Size and Crystalline Phase of TiO₂ Nanoparticles on Photocatalytic Inactivation of Escherichia coli. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2019, 19, 8172–8179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bardestani, A.; Ebrahimpour, S.; Esmaeili, A.; Esmaeili, A. Quercetin attenuates neurotoxicity induced by iron oxide nanoparticles. J. Nanobiotechnology 2021, 19, 327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaithawiwat, K.; Vangnai, A.; McEvoy, J.M.; Pruess, B.; Krajangpan, S.; Khan, E. Role of oxidative stress in inactivation of Escherichia coli BW25113 by nanoscale zero-valent iron. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 565, 857–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ševců, A.; El-Temsah, Y.S.; Joner, E.J.; Černík, M. Oxidative stress induced in microorganisms by zero-valent iron nanoparticles. Microbes Environ. 2011, 26, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shamaila, S.; Zafar, N.; Riaz, S.; Sharif, R.; Nazir, J.; Naseem, S. Gold nanoparticles: An efficient antimicrobial agent against enteric bacterial human pathogen. Nanomaterials 2016, 6, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatterjee, A.K.; Chakraborty, R.; Basu, T. Mechanism of antibacterial activity of copper nanoparticles. Nanotechnology 2014, 25, 135101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutherland, I.W. The biofilm matrix--an immobilized but dynamic microbial environment. Trends Microbiol. 2001, 9, 222–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosnedlova, B.; Kabanov, D.; Kepinska, M.; VH, B.N.; Parikesit, A.A.; Fernandez, C.; Bjørklund, G.; Nguyen, H.V.; Farid, A.; Sochor, J.; et al. Effect of Biosynthesized Silver Nanoparticles on Bacterial Biofilm Changes in S. aureus and E. coli. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 2183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, A.N.; Smith, K.; Samuels, T.A.; Lu, J.; Obare, S.O.; Scott, M.E. Nanoparticles functionalized with ampicillin destroy multiple-antibiotic-resistant isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Enterobacter aerogenes and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 78, 2768–2774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.-H.; Chen, X.; Landis, R.F.; Geng, Y.; Makabenta, J.M.; Lemnios, W.; Gupta, A.; Rotello, V.M. Phytochemical-based nanocomposites for the treatment of bacterial biofilms. ACS Infect. Dis. 2019, 5, 1590–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abo-Shama, U.H.; El-Gendy, H.; Mousa, W.S.; Hamouda, R.A.; Yousuf, W.E.; Hetta, H.F.; Abdeen, E.E. Synergistic and antagonistic effects of metal nanoparticles in combination with antibiotics against some reference strains of pathogenic microorganisms. Infect. Drug Resist. 2020, 13, 351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bera, S.M.D. Drug Targeting and Stimuli Sensitive Drug Delivery Systems; William Andrew Publishing: Norwich, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 271–302. [Google Scholar]
- Li, P.; Li, J.; Wu, C.; Wu, Q.; Li, J. Synergistic antibacterial effects of β-lactam antibiotic combined with silver nanoparticles. Nanotechnology 2005, 16, 1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamundeeswari, M.; Sobhana, S.L.; Jacob, J.P.; Kumar, M.G.; Devi, M.P.; Sastry, T.P.; Mandal, A.B. Preparation, characterization and evaluation of a biopolymeric gold nanocomposite with antimicrobial activity. Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 2010, 55, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelghany, S.M.; Quinn, D.J.; Ingram, R.J.; Gilmore, B.F.; Donnelly, R.F.; Taggart, C.C.; Scott, C.J. Gentamicin-loaded nanoparticles show improved antimicrobial effects towards Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection. Int. J. Nanomed. 2012, 7, 4053. [Google Scholar]
- Hazime, N.; Belguesmia, Y.; Kempf, I.; Barras, A.; Drider, D.; Boukherroub, R. Enhancing Colistin Activity against Colistin-Resistant Escherichia coli through Combination with Alginate Nanoparticles and Small Molecules. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hada, A.M.; Potara, M.; Astilean, S.; Cordaro, A.; Neri, G.; Malanga, M.; Nostro, A.; Mazzaglia, A.; Scala, A.; Piperno, A. Linezolid nanoAntiobiotics and SERS-nanoTags based on polymeric cyclodextrin bimetallic core-shell nanoarchitectures. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 293, 119736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rumbaugh, K.P.; Sauer, K. Biofilm dispersion. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2020, 18, 571–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michael, C.A.; Dominey-Howes, D.; Labbate, M. The antimicrobial resistance crisis: Causes, consequences, and management. Front. Public Health 2014, 2, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cassandra, W. The drug-resistant bacteria that pose the greatest health threats. Nature 2017, 543, 15. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, C.-M.; Chen, C.-H.; Pornpattananangkul, D.; Zhang, L.; Chan, M.; Hsieh, M.-F.; Zhang, L. Eradication of drug resistant Staphylococcus aureus by liposomal oleic acids. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, C.; Wang, X.; Dai, J.; Ju, Y. Metal and Metal Oxide Nanomaterials for Fighting Planktonic Bacteria and Biofilms: A Review Emphasizing on Mechanistic Aspects. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Guo, L.; Fu, Y.; Huo, M.; Qi, Q.; Zhao, G. Bacterial protein acetylation and its role in cellular physiology and metabolic regulation. Biotechnol. Adv. 2021, 53, 107842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Zhang, C.; Wang, X.; Liu, D. Release strategies of silver ions from materials for bacterial killing. ACS Appl. Bio. Mater. 2021, 4, 3985–3999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, T.; Huang, B.; Cao, J.; Li, C.; Jiao, J.; Xiao, Z.; Wei, L.; Ma, J.; Du, X.; Wang, S. Ni Nanocrystals Supported on Graphene Oxide: Antibacterial Agents for Synergistic Treatment of Bacterial Infections. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 18339–18349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sondi, I.; Salopek-Sondi, B. Silver nanoparticles as antimicrobial agent: A case study on E. coli as a model for Gram-negative bacteria. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2004, 275, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Short, F.L.; Lee, V.; Mamun, R.; Malmberg, R.; Li, L.; Espinosa, M.I.; Abbu, K.-I.; Algie, J.; Callaghan, A.; Cenderawasih-Nere, P. Benzalkonium chloride antagonises aminoglycoside antibiotics and promotes evolution of resistance. EBioMedicine 2021, 73, 103653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Shu, Q.; Xu, C.; Zheng, Q.; Guo, Z.; Wang, C.; Hao, Z.; Liu, X.; Wang, G. Copper clusters: An effective antibacterial for eradicating multidrug-resistant bacterial infection in vitro and in vivo. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2008720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emmanuel, R.; Palanisamy, S.; Chen, S.-M.; Chelladurai, K.; Padmavathy, S.; Saravanan, M.; Prakash, P.; Ali, M.A.; Al-Hemaid, F.M. Antimicrobial efficacy of green synthesized drug blended silver nanoparticles against dental caries and periodontal disease causing microorganisms. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2015, 56, 374–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, C.; Wang, W.; Sun, X.; Chu, W.; Yang, J.; Dai, J.; Ju, Y. An intrinsically thermogenic nanozyme for synergistic antibacterial therapy. Biomater. Sci. 2021, 9, 8323–8334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, B.; Su, Y.-b.; Li, H.; Han, Y.; Guo, C.; Tian, Y.-m.; Peng, X.-x. Exogenous alanine and/or glucose plus kanamycin kills antibiotic-resistant bacteria. Cell Metab. 2015, 21, 249–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marambio-Jones, C.; Hoek, E. A review of the antibacterial effects of silver nanomaterials and potential implications for human health and the environment. J. Nanoparticle Res. 2010, 12, 1531–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzello, L.; Pompa, P.P. Nanosilver-based antibacterial drugs and devices: Mechanisms, methodological drawbacks, and guidelines. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 1501–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eng, S.-K.; Pusparajah, P.; Ab Mutalib, N.-S.; Ser, H.-L.; Chan, K.-G.; Lee, L.-H. Salmonella: A review on pathogenesis, epidemiology and antibiotic resistance. Front. Life Sci. 2015, 8, 284–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hetta, H.F.; Meshaal, A.K.; Algammal, A.M.; Yahia, R.; Makharita, R.R.; Marraiki, N.; Shah, M.A.; Hassan, H.-A.M.; Batiha, G.E.-S. In-vitro antimicrobial activity of essential oils and spices powder of some medicinal plants against bacillus species isolated from raw and processed meat. Infect. Drug Resist. 2020, 13, 4367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibarra, J.A.; Steele-Mortimer, O. Salmonella–the ultimate insider. Salmonella virulence factors that modulate intracellular survival. Cell. Microbiol. 2009, 11, 1579–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamaruzzaman, N.F.; Kendall, S.; Good, L. Targeting the hard to reach: Challenges and novel strategies in the treatment of intracellular bacterial infections. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2017, 174, 2225–2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, D.G. Mycobacterium tuberculosis: Here today, and here tomorrow. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2001, 2, 569–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Masry, E.A.; Taher, I.; Hetta, H.F.; Eldahdouh, S.S. Pulmonary tuberculosis susceptibility and association with Toll-Like receptor 2 Arg753Gln polymorphism. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries. 2022, 16, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Algammal, A.M.; Hashem, H.R.; Al-Otaibi, A.S.; Alfifi, K.J.; El-Dawody, E.M.; Mahrous, E.; Hetta, H.F.; El-Kholy, A.W.; Ramadan, H.; El-Tarabili, R.M. Emerging MDR-Mycobacterium avium subsp. avium in house-reared domestic birds as the first report in Egypt. BMC Microbiol. 2021, 21, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dar, H.A.; Ismail, S.; Waheed, Y.; Ahmad, S.; Jamil, Z.; Aziz, H.; Hetta, H.F.; Muhammad, K. Designing a multi-epitope vaccine against Mycobacteroides abscessus by pangenome-reverse vaccinology. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 11197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, T.; Chiappi, M.; Garcia-Trenco, A.; Al-Ejji, M.; Sarkar, S.; Georgiou, T.K.; Shaffer, M.S.; Tetley, T.D.; Schwander, S.; Ryan, M.P. Multimetallic microparticles increase the potency of rifampicin against intracellular Mycobacterium tuberculosis. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 5228–5240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Li, X.; Xing, Z.; Niu, Q.; Xu, J. Intracellular Activity of Poly (DL-lactide-co-glycolide) Nanoparticles Encapsulated with Prothionamide, Pyrazinamide, Levofloxacin, Linezolid or Ethambutol on Multidrug-Resistant Mycobacterium Tuberculosis. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2022. online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Du, X.; Li, K.; Chen, Y.; Guan, Y.; Zhao, X.; Niu, G.; Luan, Y.; Zhang, D.; Sun, C.; et al. Construction of engineered corpus cavernosum with primary mesenchymal stem cells in vitro. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 18053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menina, S.; Eisenbeis, J.; Kamal, M.A.M.; Koch, M.; Bischoff, M.; Gordon, S.; Loretz, B.; Lehr, C.M. Bioinspired liposomes for oral delivery of colistin to combat intracellular infections by Salmonella enterica. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2019, 8, 1900564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mu, H.; Tang, J.; Liu, Q.; Sun, C.; Wang, T.; Duan, J. Potent antibacterial nanoparticles against biofilm and intracellular bacteria. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 18877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Wang, J.; Li, B.; Geng, M.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, J.; Jin, B.; Li, Y. Response of extracellular polymeric substances and microbial community structures on resistance genes expression in wastewater treatment containing copper oxide nanoparticles and humic acid. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 340, 125741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costerton, J.W.; Stewart, P.S.; Greenberg, E.P. Bacterial biofilms: A common cause of persistent infections. Science 1999, 284, 1318–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geesey, G.; Richardson, W.; Yeomans, H.; Irvin, R.; Costerton, J. Microscopic examination of natural sessile bacterial populations from an alpine stream. Can. J. Microbiol. 1977, 23, 1733–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flemming, H.-C.; Wingender, J.; Szewzyk, U.; Steinberg, P.; Rice, S.A.; Kjelleberg, S. Biofilms: An emergent form of bacterial life. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2016, 14, 563–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnaouteli, S.; Bamford, N.C.; Stanley-Wall, N.R.; Kovács, Á.T. Bacillus subtilis biofilm formation and social interactions. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 19, 600–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flemming, H.-C.; Wingender, J. The biofilm matrix. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2010, 8, 623–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, R. Biofilms and antimicrobial resistance. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2005, 437, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Acker, H.; Van Dijck, P.; Coenye, T. Molecular mechanisms of antimicrobial tolerance and resistance in bacterial and fungal biofilms. Trends Microbiol. 2014, 22, 326–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauer, K.; Stoodley, P.; Goeres, D.M.; Hall-Stoodley, L.; Burmølle, M.; Stewart, P.S.; Bjarnsholt, T. The biofilm life cycle: Expanding the conceptual model of biofilm formation. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2022, 20, 608–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciofu, O.; Moser, C.; Jensen, P.; Høiby, N. Tolerance and resistance of microbial biofilms. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2022, 20, 621–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morales-Ubaldo, A.L.; Rivero-Perez, N.; Avila-Ramos, F.; Aquino-Torres, E.; Prieto-Méndez, J.; Hetta, H.F.; El-Saber Batiha, G.; Zaragoza-Bastida, A. Bactericidal activity of Larrea tridentata hydroalcoholic extract against phytopathogenic bacteria. Agronomy 2021, 11, 957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Bian, Z.; Wang, Y. Biofilm formation and inhibition mediated by bacterial quorum sensing. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2022, 106, 6365–6381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fulaz, S.; Vitale, S.; Quinn, L.; Casey, E. Nanoparticle–biofilm interactions: The role of the EPS matrix. Trends Microbiol. 2019, 27, 915–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikuma, K.; Decho, A.W.; Lau, B.L. When nanoparticles meet biofilms—Interactions guiding the environmental fate and accumulation of nanoparticles. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birk, S.E.; Boisen, A.; Nielsen, L.H. Polymeric nano- and microparticulate drug delivery systems for treatment of biofilms. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2021, 174, 30–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, S.; Vishakha, K.; Das, S.; Dutta, M.; Mukherjee, D.; Mondal, J.; Mondal, S.; Ganguli, A. Antibacterial, anti-biofilm activity and mechanism of action of pancreatin doped zinc oxide nanoparticles against methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2020, 190, 110921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, N.; Thorn, C.; Richter, K.; Thierry, B.; Prestidge, C. Efficacy of Poly-Lactic-Co-Glycolic Acid Micro- and Nanoparticles of Ciprofloxacin Against Bacterial Biofilms. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 105, 3115–3122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zazo, H.; Colino, C.I.; Lanao, J.M. Current applications of nanoparticles in infectious diseases. J. Control. Release 2016, 224, 86–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huh, A.J.; Kwon, Y.J. “Nanoantibiotics”: A new paradigm for treating infectious diseases using nanomaterials in the antibiotics resistant era. J. Control. Release 2011, 156, 128–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baptista, P.V.; McCusker, M.P.; Carvalho, A.; Ferreira, D.A.; Mohan, N.M.; Martins, M.; Fernandes, A.R. Nano-strategies to fight multidrug resistant bacteria—“A Battle of the Titans”. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandhiya, S.; Dkhar, S.A.; Surendiran, A. Emerging trends of nanomedicine--an overview. Fundam. Clin. Pharmacol. 2009, 23, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Ansary, A.; Al-Daihan, S. On the Toxicity of Therapeutically Used Nanoparticles: An Overview. J. Toxicol. 2009, 2009, 754810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagens, W.I.; Oomen, A.G.; de Jong, W.H.; Cassee, F.R.; Sips, A.J.A.M. What do we (need to) know about the kinetic properties of nanoparticles in the body? Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2007, 49, 217–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Jong, W.H.; Borm, P.J. Drug delivery and nanoparticles:applications and hazards. Int. J. Nanomed. 2008, 3, 133–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyazaki, T.; Chen, S.; Florinas, S.; Igarashi, K.; Matsumoto, Y.; Yamasoba, T.; Xu, Z.-Q.; Wu, H.; Gao, C.; Kataoka, K. A Hoechst Reporter Enables Visualization of Drug Engagement In Vitro and In Vivo: Toward Safe and Effective Nanodrug Delivery. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 12290–12304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, R.; Gaspar, R. Nanomedicine(s) under the microscope. Mol. Pharm. 2011, 8, 2101–2141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hetta, H.F.; Ramadan, Y.N.; Al-Harbi, A.I.; A. Ahmed, E.; Battah, B.; Abd Ellah, N.H.; Zanetti, S.; Donadu, M.G. Nanotechnology as a Promising Approach to Combat Multidrug Resistant Bacteria: A Comprehensive Review and Future Perspectives. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 413. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11020413
Hetta HF, Ramadan YN, Al-Harbi AI, A. Ahmed E, Battah B, Abd Ellah NH, Zanetti S, Donadu MG. Nanotechnology as a Promising Approach to Combat Multidrug Resistant Bacteria: A Comprehensive Review and Future Perspectives. Biomedicines. 2023; 11(2):413. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11020413
Chicago/Turabian StyleHetta, Helal F., Yasmin N. Ramadan, Alhanouf I. Al-Harbi, Esraa A. Ahmed, Basem Battah, Noura H. Abd Ellah, Stefania Zanetti, and Matthew Gavino Donadu. 2023. "Nanotechnology as a Promising Approach to Combat Multidrug Resistant Bacteria: A Comprehensive Review and Future Perspectives" Biomedicines 11, no. 2: 413. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11020413
APA StyleHetta, H. F., Ramadan, Y. N., Al-Harbi, A. I., A. Ahmed, E., Battah, B., Abd Ellah, N. H., Zanetti, S., & Donadu, M. G. (2023). Nanotechnology as a Promising Approach to Combat Multidrug Resistant Bacteria: A Comprehensive Review and Future Perspectives. Biomedicines, 11(2), 413. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11020413







