Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy and Left Atrial Remodeling: A Novel Insight?
Abstract
:1. Background
2. LA Remodeling: From Physiology to Pathophysiology
3. The Contemporary Role of CRT in Modern Cardiology
3.1. Technical Aspects of CRT
3.2. Current Indications for CRT
3.3. Evaluating the Efficacy of CRT
4. Assessment of LA Function by Cardiac Functional Imaging
4.1. Echocardiography
4.2. CMR
5. The Impact of CRT on LA Remodeling Evaluated by Cardiac Functional Imaging
5.1. LA Volume
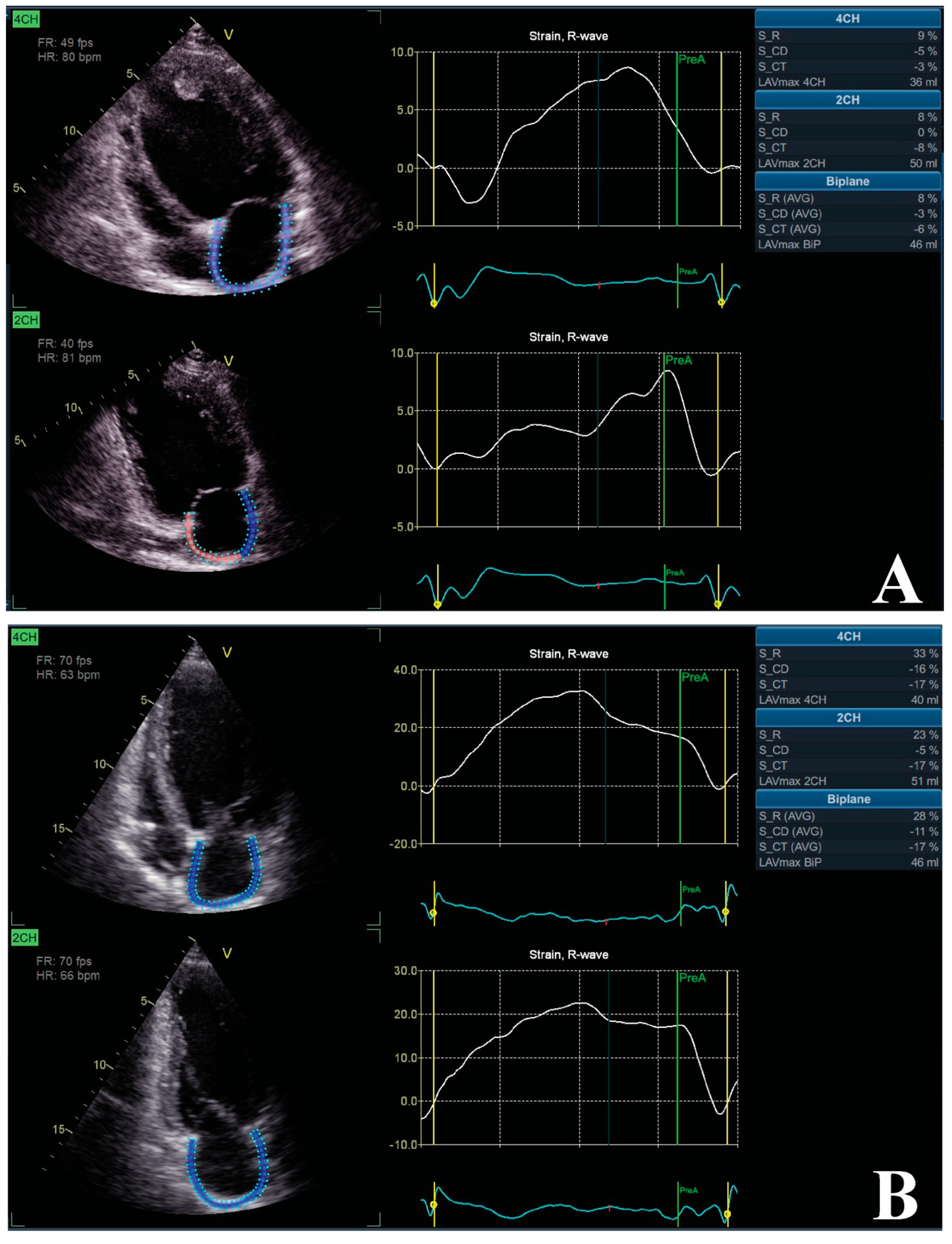
5.2. LA Phasic Function and Strain
6. Future Perspectives
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Boros, A.M.; Perge, P.; Merkely, B.; Széplaki, G. Risk scores in cardiac resynchronization therapy—A review of the literature. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2023, 9, 1048673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bax, J.J.; van der Bijl, P. Apical Rocking and Septal Flash. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2022, 15, 221–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aalen, J.M.; Donal, E.; Larsen, C.K.; Duchenne, J.; Lederlin, M.; Cvijic, M.; Hubert, A.; Voros, G.; Leclercq, C.; Bogaert, J.; et al. Imaging predictors of response to cardiac resynchronization therapy: Left ventricular work asymmetry by echocardiography and septal viability by cardiac magnetic resonance. Eur. Heart J. 2020, 41, 3813–3823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malagoli, A.; Rossi, L.; Bursi, F.; Zanni, A.; Sticozzi, C.; Piepoli, M.F.; Villani, G.Q. Left Atrial Function Predicts Cardiovascular Events in Patients With Chronic Heart Failure With Reduced Ejection Fraction. J. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr. 2019, 32, 248–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blume, G.G.; Mcleod, C.J.; Barnes, M.E.; Seward, J.B.; Pellikka, P.A.; Bastiansen, P.M.; Tsang, T.S.M. Left atrial function: Physiology, assessment, and clinical implications. Eur. J. Echocardiogr. 2011, 12, 421–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, J.H.; Shapiro, W. Atrial function and the hemodynamic consequences of atrial fibrillation in man. Am. J. Cardiol. 1969, 23, 556–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pagel, P.S.; Kehl, F.; Gare, M.; Hettrick, D.A.; Kersten, J.R.; Warltier, D.C. Mechanical Function of the Left Atrium. Anesthesiology 2003, 98, 975–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toutouzas, K.; Trikas, A.; Pitsavos, C.; Barbetseas, J.; Androulakis, A.; Stefanadis, C.; Toutouzas, P. Echocardiographic features of left atrium in elite male athletes. Am. J. Cardiol. 1996, 78, 1314–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozzoli, M.; Capomolla, S.; Sanarico, M.; Pinna, G.; Cobelli, F.; Tavazzi, L. Doppler evaluations of left ventricular diastolic filling and pulmonary wedge pressure provide similar prognostic information in patients with systolic dysfunction after myocardial infarction. Am. Heart J. 1995, 129, 716–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, N.; Okamoto, M.; Makita, Y.; Nanba, K.; Yoshizumi, M. Determinants of Enhanced Left Atrial Active Emptying with Aging: Left Atrial Preload, Contractility or Both? Intern. Med. 2009, 48, 987–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakao, T.; Shimizu, M.; Sugihara, N.; Kita, Y.; Shimizu, K.; Takeda, R. Preload dependency of left atrial pump function in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Jpn. Circ. J. 1993, 57, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blondheim, D.S.; Osipov, A.; Meisel, S.R.; Frimerman, A.; Shochat, M.; Shotan, A. Relation of Left Atrial Size to Function as Determined by Transesophageal Echocardiography. Am. J. Cardiol. 2005, 96, 457–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujimoto, N.; Hastings, J.L.; Bhella, P.S.; Shibata, S.; Gandhi, N.K.; Carrick-Ranson, G.; Palmer, D.; Levine, B.D. Effect of ageing on left ventricular compliance and distensibility in healthy sedentary humans. J. Physiol. 2012, 590, 1871–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerstenblith, G.; Frederiksen, J.; Yin, F.C.; Fortuin, N.J.; Lakatta, E.G.; Weisfeldt, M.L. Echocardiographic assessment of a normal adult aging population. Circulation 1977, 56, 273–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erol, M.K.; Ugur, M.; Yilmaz, M.; Acikel, M.; Sevimli, S.; Alp, N. Left atrial mechanical functions in elite male athletes. Am. J. Cardiol. 2001, 88, 915–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrzad, R.; Rajab, M.; Spodick, D. The Three Integrated Phases of Left Atrial Macrophysiology and Their Interactions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 15146–15160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoit, B.D. Left Atrial Size and Function. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2014, 63, 493–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goette, A.; Kalman, J.M.; Aguinaga, L.; Akar, J.; Cabrera, J.A.; Chen, S.A.; Chugh, S.S.; Corradi, D.; D’Avila, A.; Dobrev, D.; et al. EHRA/HRS/APHRS/SOLAECE expert consensus on atrial cardiomyopathies: Definition, characterization, and clinical implication. Heart Rhythm 2017, 14, e3–e40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoit, B.D. Left Atrial Remodeling. Circ. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2017, 10, e006036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiao, S.-H.; Huang, W.-C.; Lin, K.-L.; Chiou, K.-R.; Kuo, F.-Y.; Lin, S.-K.; Cheng, C.-C. Left Atrial Distensibility and Left Ventricular Filling Pressure in Acute Versus Chronic Severe Mitral Regurgitation. Am. J. Cardiol. 2010, 105, 709–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietz, J. Mechanisms of atrial natriuretic peptide secretion from the atrium. Cardiovasc. Res. 2005, 68, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, H.D.; Fuchs, S.; Campbell, D.J.; Lewis, W.; Dudley, S.C.; Kasi, V.S.; Hoit, B.D.; Keshelava, G.; Zhao, H.; Capecchi, M.R.; et al. Mice with Cardiac-Restricted Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme (ACE) Have Atrial Enlargement, Cardiac Arrhythmia, and Sudden Death. Am. J. Pathol. 2004, 165, 1019–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stockand, J.D.; Meszaros, J.G. Aldosterone stimulates proliferation of cardiac fibroblasts by activating Ki-RasA and MAPK1/2 signaling. Am. J. Physiol.-Heart Circ. Physiol. 2003, 284, H176–H184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Psychari, S.N.; Apostolou, T.S.; Sinos, L.; Hamodraka, E.; Liakos, G.; Kremastinos, D.T. Relation of elevated C-reactive protein and interleukin-6 levels to left atrial size and duration of episodes in patients with atrial fibrillation. Am. J. Cardiol. 2005, 95, 764–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, L.; Abhayaratna, W.P. Left Atrial Reverse Remodeling. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2017, 10, 65–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgan, J.M.; Delgado, V. Lead positioning for cardiac resynchronization therapy: Techniques and priorities. Europace 2009, 11, v22–v28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gras, D.; Böcker, D.; Lunati, M.; Wellens, H.J.J.; Calvert, M.; Freemantle, N.; Gervais, R.; Kappenberger, L.; Tavazzi, L.; Erdmann, E.; et al. Implantation of cardiac resynchronization therapy systems in the CARE-HF trial: Procedural success rate and safety. EP Europace 2007, 9, 516–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambiase, P.D. Non-contact left ventricular endocardial mapping in cardiac resynchronisation therapy. Heart 2004, 90, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansalone, G.; Giannantoni, P.; Ricci, R.; Trambaiolo, P.; Fedele, F.; Santini, M. Doppler myocardial imaging to evaluate the effectiveness of pacing sites in patients receiving biventricular pacing. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2002, 39, 489–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fung, J.W.-H. Variable left ventricular activation pattern in patients with heart failure and left bundle branch block. Heart 2004, 90, 17–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BLEEKER, G.B.; SCHALIJ, M.J.; van der WALL, E.E.; BAX, J.J. Postero-Lateral Scar Tissue Resulting in Non-Response to Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2006, 17, 899–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forleo, G.B.; Schiavone, M.; Della Rocca, D.; Solimene, F.; Schillaci, V.; Covino, G.; Sassara, M.; Savarese, G.; Donzelli, S.; Badolati, S.; et al. Effective nonapical left ventricular pacing with quadripolar leads for cardiac resynchronization therapy. Kardiol. Pol. 2021, 79, 442–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keene, D.; Whinnett, Z.I. Advances in cardiac resynchronisation therapy: Review of indications and delivery options. Heart 2022, 108, 889–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glikson, M.; Nielsen, J.C.; Kronborg, M.B.; Michowitz, Y.; Auricchio, A.; Barbash, I.M.; Barrabés, J.A.; Boriani, G.; Braunschweig, F.; Brignole, M.; et al. 2021 ESC Guidelines on cardiac pacing and cardiac resynchronization therapy. Eur. Heart J. 2021, 42, 3427–3520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponikowski, P.; Voors, A.A.; Anker, S.D.; Bueno, H.; Cleland, J.G.F.; Coats, A.J.S.; Falk, V.; González-Juanatey, J.R.; Harjola, V.-P.; Jankowska, E.A.; et al. 2016 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure: The Task Force for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) Developed with the special contribution of the Heart Failure Association (HFA) of the ESC. Eur. Heart J. 2016, 37, 2129–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baumgartner, H.; Falk, V.; Bax, J.J.; de Bonis, M.; Hamm, C.; Holm, P.J.; Iung, B.; Lancellotti, P.; Lansac, E.; Rodriguez Muñoz, D.; et al. 2017 ESC/EACTS Guidelines for the management of valvular heart disease. Eur. Heart J. 2017, 38, 2739–2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruschitzka, F.; Abraham, W.T.; Singh, J.P.; Bax, J.J.; Borer, J.S.; Brugada, J.; Dickstein, K.; Ford, I.; Gorcsan, J., III; Gras, D. Cardiac-resynchronization therapy in heart failure with a narrow QRS complex. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 1395–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beshai, J.F.; Grimm, R.A.; Nagueh, S.F.; Baker, J.H.; Beau, S.L.; Greenberg, S.M.; Pires, L.A.; Tchou, P.J. Cardiac-Resynchronization Therapy in Heart Failure with Narrow QRS Complexes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 357, 2461–2471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ploux, S.; Eschalier, R.; Whinnett, Z.I.; Lumens, J.; Derval, N.; Sacher, F.; Hocini, M.; Jaïs, P.; Dubois, R.; Ritter, P.; et al. Electrical dyssynchrony induced by biventricular pacing: Implications for patient selection and therapy improvement. Heart Rhythm 2015, 12, 782–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, W.T.; Young, J.B.; León, A.R.; Adler, S.; Bank, A.J.; Hall, S.A.; Lieberman, R.; Liem, L.B.; O’Connell, J.B.; Schroeder, J.S.; et al. Effects of Cardiac Resynchronization on Disease Progression in Patients with Left Ventricular Systolic Dysfunction, an Indication for an Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillator, and Mildly Symptomatic Chronic Heart Failure. Circulation 2004, 110, 2864–2868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thibault, B.; Harel, F.; Ducharme, A.; White, M.; Ellenbogen, K.A.; Frasure-Smith, N.; Roy, D.; Philippon, F.; Dorian, P.; Talajic, M.; et al. Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy in Patients With Heart Failure and a QRS Complex <120 Milliseconds. Circulation 2013, 127, 873–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salden, O.A.E.; Vernooy, K.; van Stipdonk, A.M.W.; Cramer, M.J.; Prinzen, F.W.; Meine, M. Strategies to Improve Selection of Patients Without Typical Left Bundle Branch Block for Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy. JACC Clin. Electrophysiol. 2020, 6, 129–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Stipdonk, A.M.W.; Vanbelle, S.; ter Horst, I.A.H.; Luermans, J.G.; Meine, M.; Maass, A.H.; Auricchio, A.; Prinzen, F.W.; Vernooy, K. Large variability in clinical judgement and definitions of left bundle branch block to identify candidates for cardiac resynchronisation therapy. Int. J. Cardiol. 2019, 286, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cleland, J.G.; Abraham, W.T.; Linde, C.; Gold, M.R.; Young, J.B.; Claude Daubert, J.; Sherfesee, L.; Wells, G.A.; Tang, A.S. An individual patient meta-analysis of five randomized trials assessing the effects of cardiac resynchronization therapy on morbidity and mortality in patients with symptomatic heart failure. Eur. Heart J. 2013, 34, 3547–3556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eschalier, R.; Ploux, S.; Ritter, P.; Haïssaguerre, M.; Ellenbogen, K.A.; Bordachar, P. Nonspecific intraventricular conduction delay: Definitions, prognosis, and implications for cardiac resynchronization therapy. Heart Rhythm 2015, 12, 1071–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henin, M.; Ragy, H.; Mannion, J.; David, S.; Refila, B.; Boles, U. Indications of Cardiac Resynchronization in Non-Left Bundle Branch Block: Clinical Review of Available Evidence. Cardiol. Res. 2020, 11, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullens, W.; Auricchio, A.; Martens, P.; Witte, K.; Cowie, M.R.; Delgado, V.; Dickstein, K.; Linde, C.; Vernooy, K.; Leyva, F.; et al. Optimized implementation of cardiac resynchronization therapy: A call for action for referral and optimization of care. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2020, 22, 2349–2369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gold, M.R.; Rickard, J.; Daubert, J.C.; Zimmerman, P.; Linde, C. Redefining the Classifications of Response to Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy. JACC Clin. Electrophysiol. 2021, 7, 871–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakai, T.; Ikeya, Y.; Kogawa, R.; Otsuka, N.; Wakamatsu, Y.; Kurokawa, S.; Ohkubo, K.; Nagashima, K.; Okumura, Y. What Are the Expectations for Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy? A Validation of Two Response Definitions. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cazeau, S.; Leclercq, C.; Lavergne, T.; Walker, S.; Varma, C.; Linde, C.; Garrigue, S.; Kappenberger, L.; Haywood, G.A.; Santini, M.; et al. Effects of Multisite Biventricular Pacing in Patients with Heart Failure and Intraventricular Conduction Delay. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001, 344, 873–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, W.T.; Fisher, W.G.; Smith, A.L.; Delurgio, D.B.; Leon, A.R.; Loh, E.; Kocovic, D.Z.; Packer, M.; Clavell, A.L.; Hayes, D.L.; et al. Cardiac Resynchronization in Chronic Heart Failure. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002, 346, 1845–1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Auricchio, A.; Stellbrink, C.; Sack, S.; Block, M.; Vogt, J.Ü.; Bakker, P.; Huth, C.; Schöndube, F.; Wolfhard, U.; Böcker, D.; et al. Long-term clinical effect of hemodynamically optimized cardiac resynchronization therapy in patients with heart failure and ventricular conduction delay. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2002, 39, 2026–2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, J.B. Combined Cardiac Resynchronization and Implantable Cardioversion Defibrillation in Advanced Chronic Heart Failure. JAMA 2003, 289, 2685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higgins, S.L.; Hummel, J.D.; Niazi, I.K.; Giudici, M.C.; Worley, S.J.; Saxon, L.A.; Boehmer, J.P.; Higginbotham, M.B.; De Marco, T.; Foster, E.; et al. Cardiac resynchronization therapy for the treatment of heart failure in patients with intraventricular conduction delay and malignant ventricular tachyarrhythmias. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2003, 42, 1454–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brenyo, A.; Link, M.S.; Barsheshet, A.; Moss, A.J.; Zareba, W.; Wang, P.J.; McNitt, S.; Huang, D.; Foster, E.; Estes, M.; et al. Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy Reduces Left Atrial Volume and the Risk of Atrial Tachyarrhythmias in MADIT-CRT (Multicenter Automatic Defibrillator Implantation Trial with Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy). J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2011, 58, 1682–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bristow, M.R.; Saxon, L.A.; Boehmer, J.; Krueger, S.; Kass, D.A.; De Marco, T.; Carson, P.; DiCarlo, L.; DeMets, D.; White, B.G.; et al. Cardiac-Resynchronization Therapy with or without an Implantable Defibrillator in Advanced Chronic Heart Failure. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 350, 2140–2150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleland, J.G.F.; Daubert, J.-C.; Erdmann, E.; Freemantle, N.; Gras, D.; Kappenberger, L.; Kappenberger, L.; Tavazzi, L. The Effect of Cardiac Resynchronization on Morbidity and Mortality in Heart Failure. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 352, 1539–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linde, C.; Abraham, W.T.; Gold, M.R.; St. John Sutton, M.; Ghio, S.; Daubert, C. Randomized Trial of Cardiac Resynchronization in Mildly Symptomatic Heart Failure Patients and in Asymptomatic Patients with Left Ventricular Dysfunction and Previous Heart Failure Symptoms. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2008, 52, 1834–1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kheiri, B.; Przybylowicz, R.; Simpson, T.F.; Merrill, M.; Osman, M.; Dalouk, K.; Rahmouni, H.; Stecker, E.; Nazer, B.; Henrikson, C.A. Imaging—guided cardiac resynchronization therapy: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. 2021, 44, 1570–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borgquist, R.; Carlsson, M.; Markstad, H.; Werther-Evaldsson, A.; Ostenfeld, E.; Roijer, A.; Bakos, Z. Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy Guided by Echocardiography, MRI, and CT Imaging. JACC Clin. Electrophysiol. 2020, 6, 1300–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, L.; Marwick, T.H.; Popescu, B.A.; Donal, E.; Badano, L.P. Left Atrial Structure and Function, and Left Ventricular Diastolic Dysfunction. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2019, 73, 1961–1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhatt, A.; Flink, L.; Lu, D.-Y.; Fang, Q.; Bibby, D.; Schiller, N.B. Exercise physiology of the left atrium: Quantity and timing of contribution to cardiac output. Am. J. Physiol.-Heart Circ. Physiol. 2021, 320, H575–H583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsang, T.S.; Abhayaratna, W.P.; Barnes, M.E.; Miyasaka, Y.; Gersh, B.J.; Bailey, K.R.; Cha, S.S.; Seward, J.B. Prediction of Cardiovascular Outcomes with Left Atrial Size: Is Volume Superior to Area or Diameter? J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2006, 47, 1018–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fatema, K.; Barnes, M.E.; Bailey, K.R.; Abhayaratna, W.P.; Cha, S.; Seward, J.B.; Tsang, T.S. Minimum vs. maximum left atrial volume for prediction of first atrial fibrillation or flutter in an elderly cohort: A prospective study. Eur. J. Echocardiogr. 2009, 10, 282–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russo, C.; Jin, Z.; Homma, S.; Rundek, T.; Elkind, M.S.; Sacco, R.L.; Di Tullio, M.R. LA Phasic Volumes and Reservoir Function in the Elderly by Real-Time 3D Echocardiography. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2016, 10, 976–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thadani, S.R.; Shaw, R.E.; Fang, Q.; Whooley, M.A.; Schiller, N.B. Left Atrial End-Diastolic Volume Index as a Predictor of Cardiovascular Outcomes. Circ. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2020, 13, e009746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, V.C.-C.; Takeuchi, M.; Kuwaki, H.; Iwataki, M.; Nagata, Y.; Otani, K.; Haruki, N.; Yoshitani, H.; Tamura, M.; Abe, H.; et al. Prognostic Value of LA Volumes Assessed by Transthoracic 3D Echocardiography. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2013, 6, 1025–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caselli, S.; Canali, E.; Foschi, M.L.; Santini, D.; Di Angelantonio, E.; Pandian, N.G.; De Castro, S. Long-term prognostic significance of three-dimensional echocardiographic parameters of the left ventricle and left atrium. Eur. J. Echocardiogr. 2009, 11, 250–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugimoto, T.; Robinet, S.; Dulgheru, R.; Bernard, A.; Ilardi, F.; Contu, L.; Addetia, K.; Caballero, L.; Kacharava, G.; Athanassopoulos, G.D.; et al. Echocardiographic reference ranges for normal left atrial function parameters: Results from the EACVI NORRE study. Eur. Heart J.—Cardiovasc. Imaging 2018, 19, 630–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, V.; Ghosh, R.; Gupta, M.; Saijo, Y.; Bansal, A.; Farwati, M.; Marcus, R.; Klein, A.; Xu, B. Contemporary narrative review on left atrial strain mechanics in echocardiography: Cardiomyopathy, valvular heart disease and beyond. Cardiovasc. Diagn. Ther. 2021, 11, 924–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cameli, M. Left Atrial Strain Predicts Pro-Thrombotic State in Patients with Non-Valvular Atrial Fibrillation. J. Atr. Fibrillation 2017, 10, 1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lacalzada-Almeida, J.; Izquierdo-Gómez, M.M.; García-Niebla, J.; Elosua, R.; Jiménez-Sosa, A.; Baranchuk, A.; Bayes de Luna, A. Advanced interatrial block is a surrogate for left atrial strain reduction which predicts atrial fibrillation and stroke. Ann. Noninvasive Electrocardiol. 2019, 24, e12632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, Y.E.; Oh, I.-Y.; Kim, S.-A.; Park, K.-H.; Kim, S.H.; Park, J.-H.; Kim, J.E.; Lee, S.P.; Kim, H.K.; Kim, Y.J.; et al. Echocardiographic Predictors of Progression to Persistent or Permanent Atrial Fibrillation in Patients with Paroxysmal Atrial Fibrillation (E6P Study). J. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr. 2015, 28, 709–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carluccio, E.; Biagioli, P.; Mengoni, A.; Cerasa, M.F.; Lauciello, R.; Zuchi, C.; Bardelli, G.; Alunni, G.; Coiro, S.; Gronda, E.G.; et al. Left Atrial Reservoir Function and Outcome in Heart Failure With Reduced Ejection Fraction. Circ. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2018, 11, e007696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurt, M.; Tanboga, I.H.; Aksakal, E.; Kaya, A.; Isik, T.; Ekinci, M.; Bilen, E. Relation of left ventricular end-diastolic pressure and N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide level with left atrial deformation parameters. Eur. Heart J.—Cardiovasc. Imaging 2011, 13, 524–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Wan, K.; Han, Y.; Liu, H.; Cheng, W.; Sun, J.; Luo, Y.; Yang, D.; Chung, Y.-C.; Chen, Y. Reference value of left and right atrial size and phasic function by SSFP CMR at 3.0 T in healthy Chinese adults. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habibi, M.; Samiei, S.; Venkatesh, B.A.; Opdahl, A.; Helle-Valle, T.M.; Zareian, M.; Almeida, A.L.; Choi, E.-Y.; Wu, C.; Alonso, A.; et al. Cardiac Magnetic Resonance–Measured Left Atrial Volume and Function and Incident Atrial Fibrillation. Circ. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2016, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.A.; Yang, E.Y.; Zhan, Y.; Judd, R.M.; Chan, W.; Nabi, F.; Heitner, J.F.; Kim, R.J.; Klem, I.; Nagueh, S.F.; et al. Association of left atrial volume index and all-cause mortality in patients referred for routine cardiovascular magnetic resonance: A multicenter study. J. Cardiovasc. Magn. Reson. 2019, 21, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chirinos, J.A.; Sardana, M.; Ansari, B.; Satija, V.; Kuriakose, D.; Edelstein, I.; Oldland, G.; Miller, R.; Gaddam, S.; Lee, J.; et al. Left Atrial Phasic Function by Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Feature Tracking Is a Strong Predictor of Incident Cardiovascular Events. Circ. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2018, 11, e007512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, J.; Weber, J.; Hsu, B.; Mulyala, R.R.; Wang, L.; Cao, J.J. Comparing left atrial indices by CMR in association with left ventricular diastolic dysfunction and adverse clinical outcomes. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 21331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mojica-Pisciotti, M.L.; Panovský, R.; Masárová, L.; Pešl, M.; Stárek, Z.; Holeček, T.; Feitová, V.; Opatřil, L.; Doležalová, K.; Kincl, V. Left atrium phasic impairments in paroxysmal atrial fibrillation patients assessed by cardiovascular magnetic resonance feature tracking. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 7539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kowallick, J.T.; Kutty, S.; Edelmann, F.; Chiribiri, A.; Villa, A.; Steinmetz, M.; Sohns, J.M.; Staab, W.; Bettencourt, N.; Unterberg-Buchwald, C.; et al. Quantification of left atrial strain and strain rate using Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance myocardial feature tracking: A feasibility study. J. Cardiovasc. Magn. Reson. 2014, 16, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Truong, V.T.; Palmer, C.; Wolking, S.; Sheets, B.; Young, M.; Ngo, T.N.M.; Taylor, M.; Nagueh, S.F.; Zareba, K.M.; Raman, S.; et al. Normal left atrial strain and strain rate using cardiac magnetic resonance feature tracking in healthy volunteers. Eur. Heart J.—Cardiovasc. Imaging 2019, 21, 446–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raafs, A.G.; Vos, J.L.; Henkens, M.T.H.M.; Verdonschot, J.A.J.; Gerretsen, S.; Knackstedt, C.; Hazebroek, M.R.; Nijveldt, R.; Heymans, S.R.B. Left atrial strain at CMR is a strong independent prognostic predictor in DCM, superior to LV-GLS, LVEF and LAVI, and incremental to LGE. Eur. Heart J. 2022, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayyar, D.; Nguyen, T.; Pathan, F.; Vo, G.; Richards, D.; Thomas, L.; Dimitri, H.; Otton, J. Cardiac magnetic resonance derived left atrial strain after ST-elevation myocardial infarction: An independent prognostic indicator. Cardiovasc. Diagn. Ther. 2021, 11, 383–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjamin, M.M.; Moulki, N.; Waqar, A.; Ravipati, H.; Schoenecker, N.; Wilber, D.; Kinno, M.; Rabbat, M.; Sanagala, T.; Syed, M.A. Association of left atrial strain by cardiovascular magnetic resonance with recurrence of atrial fibrillation following catheter ablation. J. Cardiovasc. Magn. Reson. 2022, 24, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuperstein, R.; Goldenberg, I.; Moss, A.J.; Solomon, S.; Bourgoun, M.; Shah, A.; McNitt, S.; Zareba, W.; Klempfner, R. Left Atrial Volume and the Benefit of Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy in the MADIT-CRT Trial. Circ. Heart Fail. 2014, 7, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bytyçi, I.; Bajraktari, G.; Henein, M. Left atrial volume index predicts response to cardiac resynchronisation therapy: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch. Med. Sci. 2020, 18, 930–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badran, H.A.; Abdelhamid, M.; Ibrahim, M.T.; Abdelmoteleb, A.M.; Zarif, J.K. Left atrium in cardiac resynchronization therapy: Active participant or innocent bystander. J. Saudi Heart Assoc. 2017, 29, 259–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, L.; Malagoli, A.; Piepoli, M.; Franchi, F.; Malavasi, V.; Casali, E.; Rusticali, G.; Villani, G.Q. Indexed maximal left atrial volume predicts response to cardiac resynchronization therapy. Int. J. Cardiol. 2013, 168, 3629–3633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koruth, J.; Shen, X.; Holmberg, M.J.; Li, H.; Nair, C.K.; Hee, T.; Hunter, C.; Koster, N.; Mooss, A.N.; Esterbrooks, D.J. The predictive value of left atrial volume in patients with wide QRS, left ventricular Dyssynchrony and cardiac resynchronization therapy. Chest 2007, 132, 579A. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupu, S.; Mitre, A.; Sus, I.; Rudzik, R.; Beke, I.; Dobreanu, D. Changes in left atrial size and function early after cardiac resynchronization therapy as assessed by conventional two-dimensional echocardiography. Med. Ultrason. 2018, 20, 362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donal, E.; Tan, K.; Leclercq, C.; Ollivier, R.; Derumeaux, G.; Bernard, M.; de Place, C.; Mabo, P.; Daubert, J.-C. Left Atrial Reverse Remodeling and Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy for Chronic Heart Failure Patients in Sinus Rhythm. J. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr. 2009, 22, 1152–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stassen, J.; Galloo, X.; Chimed, S.; Hirasawa, K.; Marsan, N.A.; Delgado, V.; van der Bijl, P.; Bax, J.J. Clinical implications of left atrial reverse remodelling after cardiac resynchronization therapy. Eur. Heart J.—Cardiovasc. Imaging 2022, 23, 730–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dokuni, K.; Matsumoto, K.; Tatsumi, K.; Suto, M.; Tanaka, H.; Fukuzawa, K.; Hirata, K.I. Cardiac resynchronization therapy improves left atrial reservoir function through resynchronization of the left atrium in patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction. Int. J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2020, 36, 1203–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feneon, D.; Behaghel, A.; Bernard, A.; Fournet, M.; Mabo, P.; Daubert, J.-C.; Leclercq, C.; Donal, E. Left atrial function, a new predictor of response to cardiac resynchronization therapy? Heart Rhythm 2015, 12, 1800–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valzania, C.; Gadler, F.; Boriani, G.; Rapezzi, C.; Eriksson, M.J. Effect of Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy on Left Atrial Size and Function as Expressed by Speckle Tracking 2-Dimensional Strain. Am. J. Cardiol. 2016, 118, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huntjens, P.; Sugahara, M.; Soyama, Y.; Lumens, J.; Faddis, M.N.; Gorcsan, J. Abstract 15815: Left Atrial Strain Characterizes the Atrio-ventricular Substrate Responsive to Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy in Patients with Intermediate Electrocardiographic Criteria. Circulation 2020, 142, A15815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, E.; Russo, G.; Cassese, M.; Braccio, M.; Carella, M.; Compagnucci, P.; Russo, A.D.; Casella, M. The Role of Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy for the Management of Functional Mitral Regurgitation. Cells 2022, 11, 2407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Clinical Trial | n | Year | NYHA Class | QRS Interval | LVEF | Follow-Up |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Multisite stimulation in cardiomyopathy (MUSTIC) | 67 | 2001 | III | >150 ms | <35% | 6 Mo |
| Multicenter inSync randomized clinical evaluation (MIRACLE) | 453 | 2002 | III, IV | >130 ms | <35% | >6 Mo |
| Pacing Therapies for Congestive Heart Failure (PATH-CHF) | 42 | 2002 | III, IV | >120 ms | <35% | >6 Mo |
| Multicenter InSync Implantable Cardioversion Defibrillation Randomized Clinical Evaluation (MIRACLE ICD) | 639 | 2003 | III, IV | >130 ms | <35% | 6 Mo |
| Safety and Effectiveness of Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy with Defibrillation (CONTAK CD) | 333 | 2003 | III, IV | >120 ms | <35% | 6 Mo |
| Multicenter InSync Implantable Cardioversion Defibrillation Randomized Clinical Evaluation II (MIRACLE ICD II) | 186 | 2004 | II | >130 ms | <35% | 6 Mo |
| Pacing Therapies for Congestive Heart Failure II (PATH-CHF II) | 89 | 2004 | III, IV | >120 ms | <35% | 6 Mo |
| Cardiac Resynchronization Heart Failure Study (CARE-HF) | 813 | 2006 | III, IV | >120 ms | <35% | 29.4 Mo |
| Comparison of Medical Therapy, Pacing and Defibrillation in Heart Failure (COMPANION) | 1520 | 2009 | III, IV | >120 ms | <35% | 14.4 Mo |
| Resynchronization reverses Remodeling in Systolic left ventricular dysfunction (REVERSE) | 610 | 2013 | I, II | >120 ms | <40% | 12 Mo |
| Multicenter Automatic Defibrillator Implantation Trial–Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy (MADIT–CRT) | 1820 | 2014 | I, II | >130 ms | <30% | 24 Mo |
| Resynchronization-Defibrillation for Ambulatory Heart Failure Trial (RAFT) | 1798 | 2014 | I, II | >130 ms | <30% | 60 Mo |
| Authors | Ref | Year | n | Data | Follow-Up | Findings |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Donal et al. | [83] | 2009 | 46 | LAPF LAVmax LAS-r | 6 Mo for the impact of CRT on LA remodeling | CRT significantly improved LAVmax, LAVmin, LAS-r, LAPF inducing LA reverse remodeling |
| Brenyo et al. | [77] | 2011 | 1785 | LAVmax | 6 Mo for the risk to develop atrial tachyarrhythmias | Lower LAV is correlated with lower incidence of atrial tachyarrhythmias and lower outcome |
| Rossi et al. | [80] | 2013 | 52 | LAVmax LAVmin LAVpre-A | 6 Mo for the ability of LAVmax to predict CRT responsiveness | Lower LAVmax, LAVmin, and LAVpre-A were significantly associated with higher rate of CRT response |
| Kuperstein et al. | [76] | 2014 | 1785 | LAVmax | 6 Mo for all-cause mortality and HF | Higher LAVmax is associated with outcome Each 1% reduction in LAV = 4% reduction in hazard for HF/death |
| Feneon et al. | [86] | 2015 | 79 | LAS-r LA pre-ejection index | 6 Mo to evaluate the impact of CRT on LA strain | LAS-r was a good predictor for CRT responsiveness, regardless of cardiac pathology |
| Valzania et al. | [87] | 2016 | 30 | LAS-r | 12 Mo for the impact of CRT on LA strain and the relationship with some parameters | CRT responsiveness had beneficial impact on LA size and LAS-r. LV function, filling pressures, and mitral regurgitation significantly influenced LA remodeling |
| Badran et al. | [79] | 2017 | 37 | LAVmax LAVmin LAVpre-A; LATF LAS-r; LAS-cd | 3 Mo for evaluating LA remodeling | LAVmax, LAVmin, LAS-r, LAS-cd, LATF were significantly improved in those who were responders to CRT |
| Lupu et al. | [82] | 2018 | 28 | LAVmax LAVmin LAVpre-A; LATF, LAPF, LAAF | 3 Mo for the impact of CRT on LA volumes and phasic functions | CRT has beneficial effects on LAVmax, LAVmin, and LAVpre-A, even within first days of implant |
| Dokuni et al. | [85] | 2020 | 90 | LAS-r LAPF | 6 Mo for the role of CRT on LA strain function | CRT reduced LA dyssynchrony, which in turn improved LAS-r and LAPF |
| Stassen et al. | [84] | 2022 | 923 | LAS-r GLS | 6 Mo for the impact of CRT on both LA and LV remodeling | Patients who exerted both LA and LV remodeling had lowest mortality risk |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Radu, A.D.; Zlibut, A.; Scarlatescu, A.; Cojocaru, C.; Bogdan, S.; Scafa-Udriște, A.; Dorobantu, M. Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy and Left Atrial Remodeling: A Novel Insight? Biomedicines 2023, 11, 1156. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11041156
Radu AD, Zlibut A, Scarlatescu A, Cojocaru C, Bogdan S, Scafa-Udriște A, Dorobantu M. Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy and Left Atrial Remodeling: A Novel Insight? Biomedicines. 2023; 11(4):1156. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11041156
Chicago/Turabian StyleRadu, Andrei Dan, Alexandru Zlibut, Alina Scarlatescu, Cosmin Cojocaru, Stefan Bogdan, Alexandru Scafa-Udriște, and Maria Dorobantu. 2023. "Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy and Left Atrial Remodeling: A Novel Insight?" Biomedicines 11, no. 4: 1156. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11041156
APA StyleRadu, A. D., Zlibut, A., Scarlatescu, A., Cojocaru, C., Bogdan, S., Scafa-Udriște, A., & Dorobantu, M. (2023). Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy and Left Atrial Remodeling: A Novel Insight? Biomedicines, 11(4), 1156. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11041156






