Synthetic Cationic Lipopeptide Can Effectively Treat Mouse Mastitis Caused by Staphylococcus aureus
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Strains
2.2. Animals and Cells
2.3. Lipopeptide Synthesis
2.4. Determination of MICs
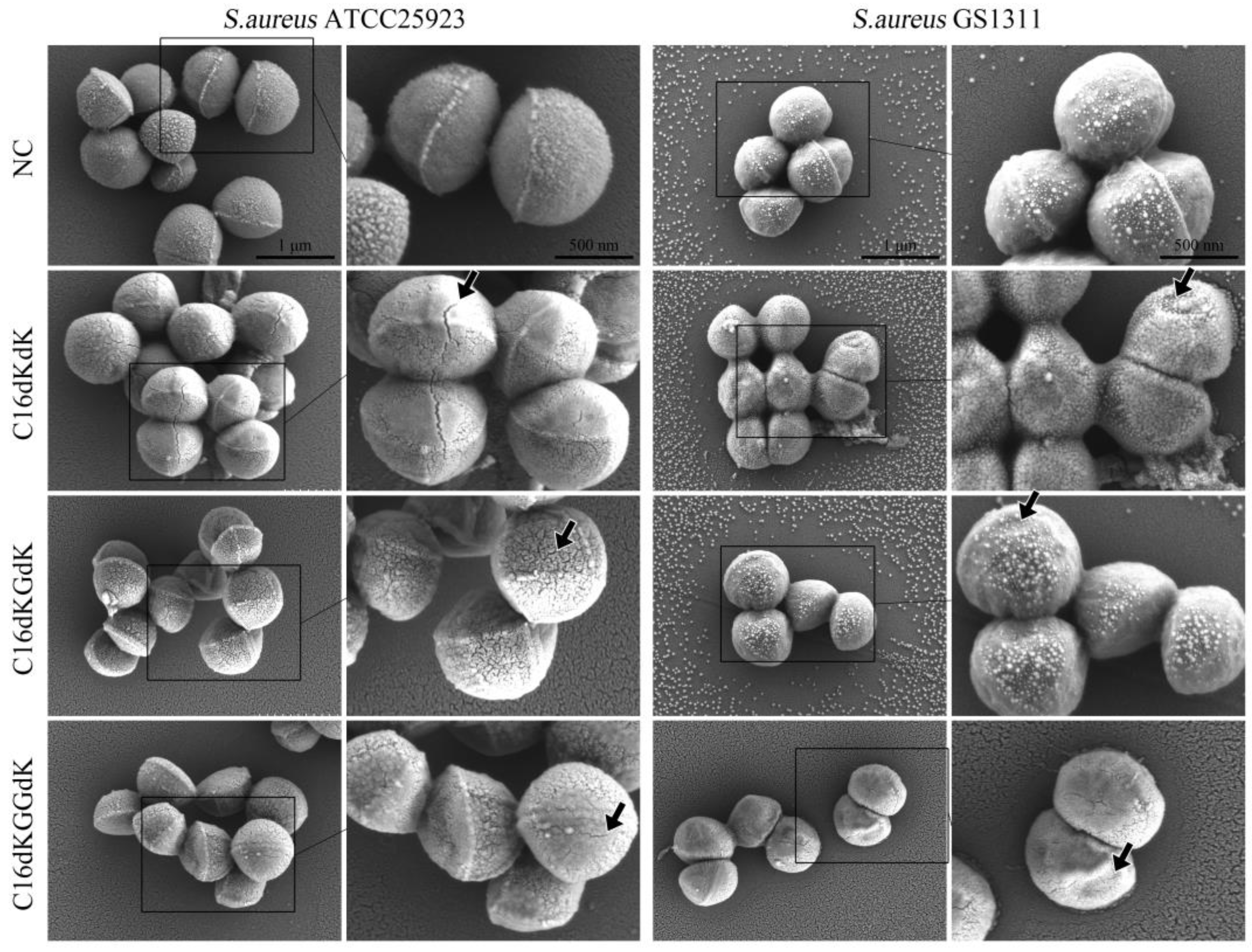
2.5. Electron Microscopy Observation
2.6. Hemolytic Assay
2.7. Cytotoxicity Assay
2.8. In Vivo Mouse Experiment
2.9. Bacterial Load Determination in Breast Tissue
2.10. Inflammatory Factor Expression Assay
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Lipopeptide Design
3.2. Antibacterial Effect of Synthetic Lipopeptide
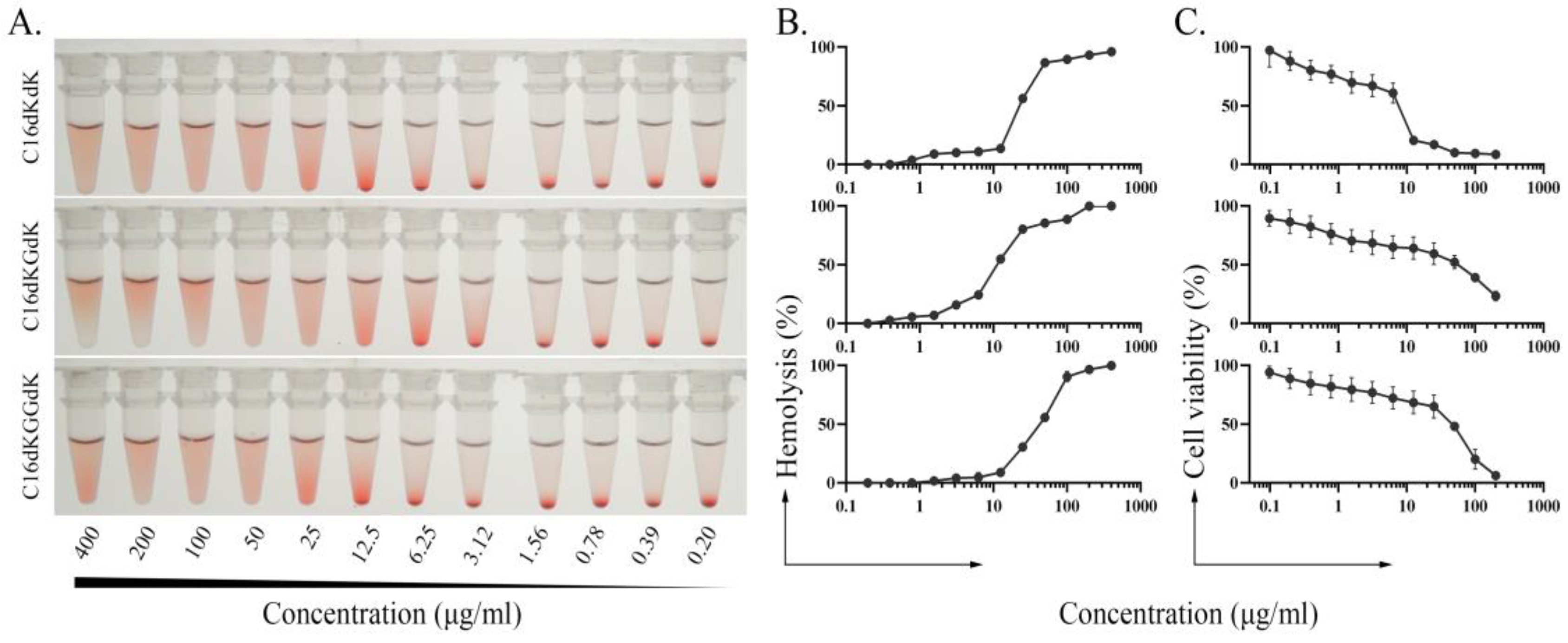
3.3. Hemolytic Analysis
3.4. Cytotoxicity
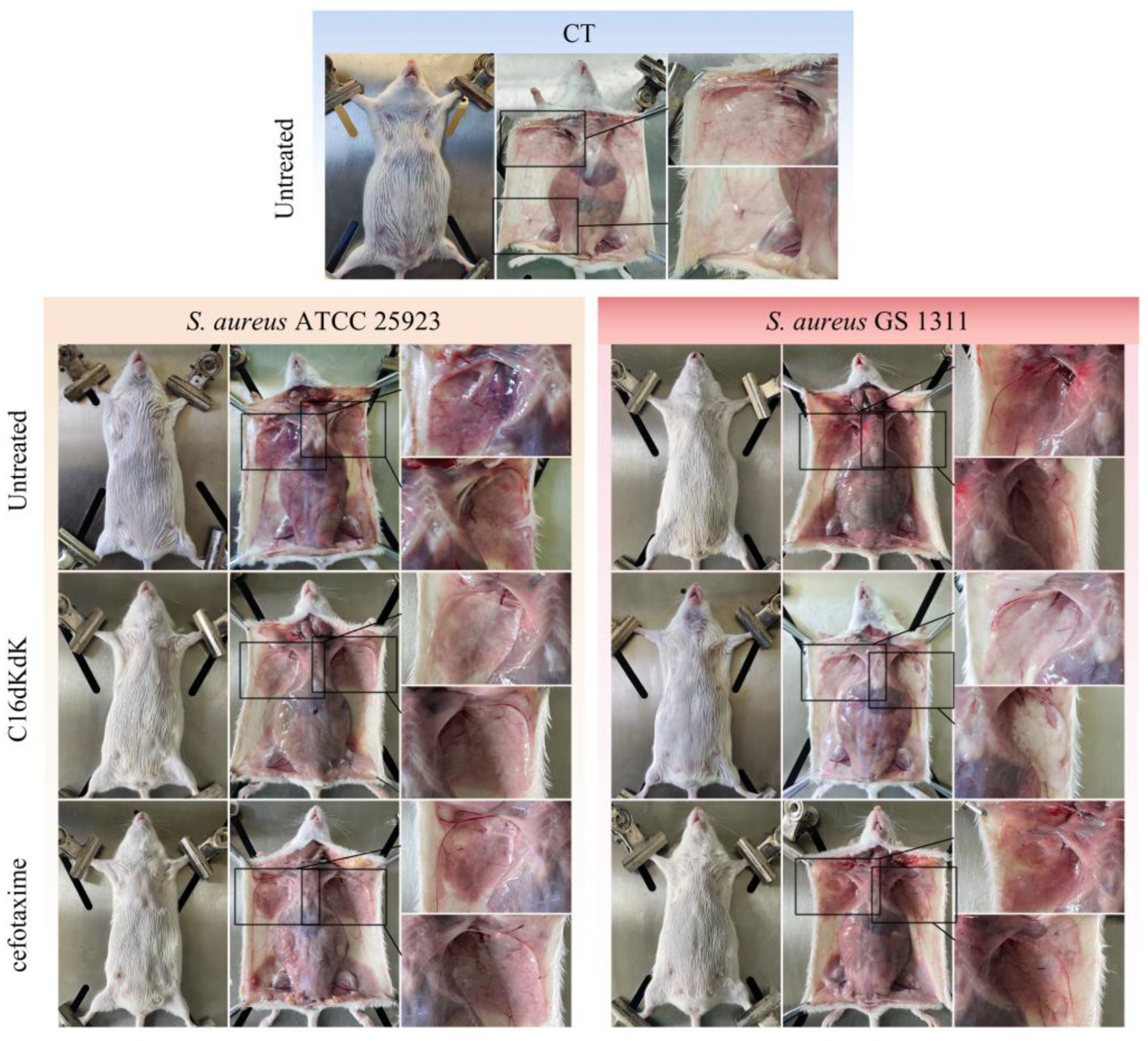
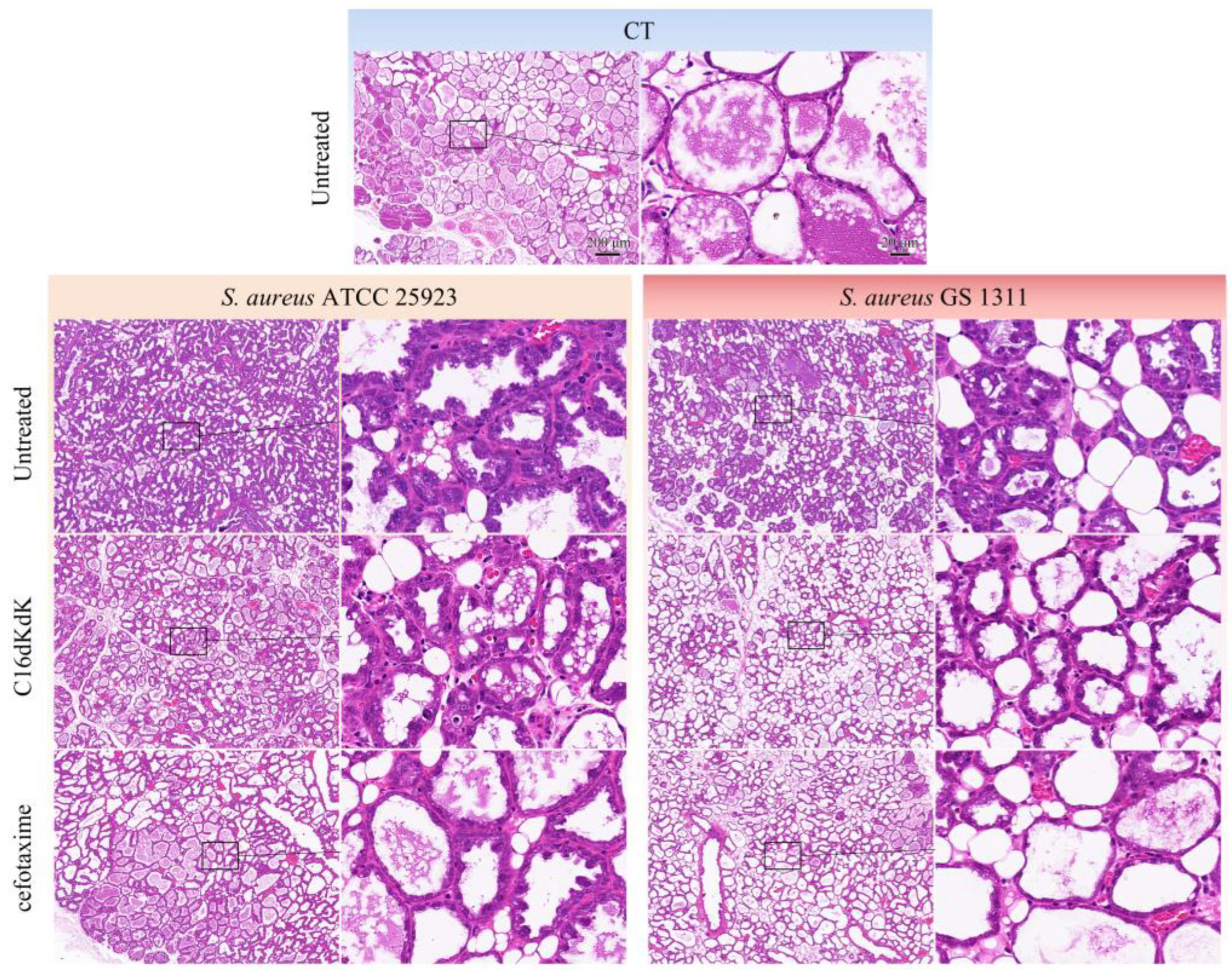
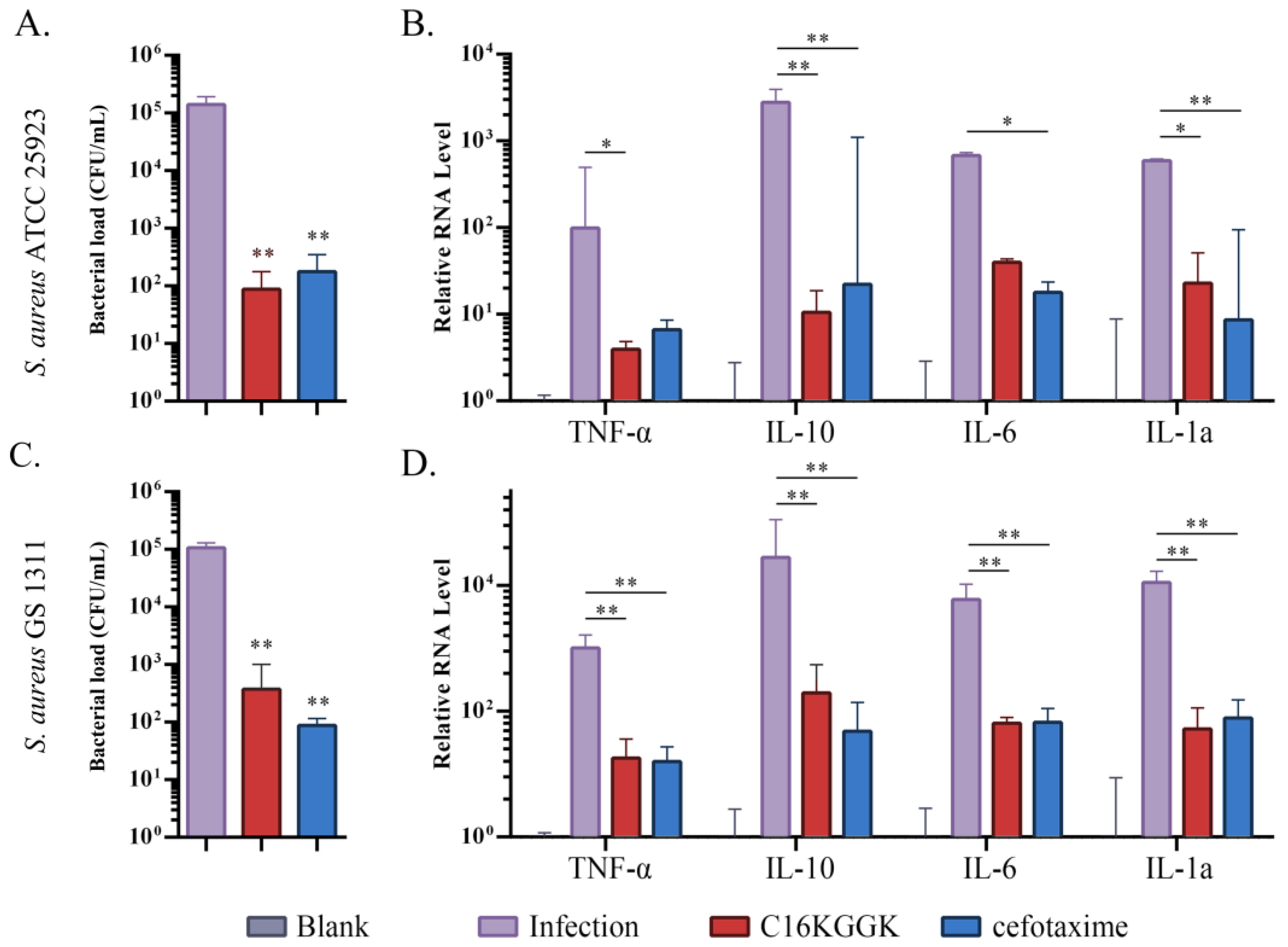
3.5. Therapeutic Trial
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ren, Q.; Liao, G.; Wu, Z.; Lv, J.; Chen, W. Prevalence and characterization of Staphylococcus aureus isolates from subclinical bovine mastitis in southern Xinjiang, China. J. Dairy Sci. 2020, 103, 3368–3380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhou, M.; Yang, G.; Liu, H.; Yang, W.; Yue, J.; Chen, D. Shifted T Helper Cell Polarization in a Murine Staphylococcus aureus Mastitis Model. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0134797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotzamanidis, C.; Vafeas, G.; Giantzi, V.; Anastasiadou, S.; Mygdalias, S.; Malousi, A.; Loukia, E.; Daniel, S.; Zdragas, A. Staphylococcus aureus Isolated from Ruminants with Mastitis in Northern Greece Dairy Herds: Genetic Relatedness and Phenotypic and Genotypic Characterization. Toxins 2021, 13, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rainard, P.; Foucras, G.; Fitzgerald, J.R.; Watts, J.L.; Koop, G.; Middleton, J.R. Knowledge gaps and research priorities in Staphylococcus aureus mastitis control. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2018, 65 (Suppl. S1), 149–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, Y.; Zhao, H.; Nobrega, D.B.; Cobo, E.R.; Han, B.; Zhao, Z.; Li, S.; Li, M.; Barkema, H.W.; Gao, J. Molecular epidemiology and distribution of antimicrobial resistance genes of Staphylococcus species isolated from Chinese dairy cows with clinical mastitis. J. Dairy Sci. 2019, 102, 1571–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makovitzki, A.; Avrahami, D.; Shai, Y. Ultrashort antibacterial and antifungal lipopeptides. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 15997–16002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munusamy, S.; Conde, R.; Bertrand, B.; Munoz-Garay, C. Biophysical approaches for exploring lipopeptide-lipid interactions. Biochimie 2020, 170, 173–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, C.; Zhang, F.; Zhu, N.; Zhu, Y.; Yao, J.; Gou, S.; Xie, J.; Ni, J. Ultra-short lipopeptides against gram-positive bacteria while alleviating antimicrobial resistance. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 212, 113138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahane, G.; Ding, W.; Palaiokostas, M.; Azevedo, H.S.; Orsi, M. Interaction of Antimicrobial Lipopeptides with Bacterial Lipid Bilayers. J. Membr. Biol. 2019, 252, 317–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, M.D.T.; Sothiselvam, S.; Lu, T.K.; Fuente-Nunez, C.D.L. Peptide Design Principles for Antimicrobial Applications. J. Mol. Biol. 2019, 431, 3547–3567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laverty, G.; Gorman, S.P.; Gilmore, B.F. The Potential of Antimicrobial Peptides as Biocides. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2011, 12, 6566–6596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosen, M.J.; Kunjappu, J.T. Surfactants and Interfacial Phenomena; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Andrews, J.M. Determination of minimum inhibitory concentrations. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2001, 48, 5–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Yang, N.; Teng, D.; Mao, R.; Hao, Y.; Ma, X.; Wang, X.; Wang, J. Fatty acid modified-antimicrobial peptide analogues with potent antimicrobial activity and topical therapeutic efficacy against Staphylococcus hyicus. Appl. Microbiol. Blot. 2021, 105, 5845–5859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, L.; Zhang, S.; Peng, J.; Li, Y.; Yang, Q. Synthetic surfactin analogues have improved anti-PEDV properties. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0215227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandler, R.L. Experimental Bacterial Mastitis In The Mouse. J. Med. Microbiol. 1970, 3, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greco, I.; Molchanova, N.; Holmedal, E.; Jenssen, H.; Hummel, B.D.; Watts, J.L.; Hakansson, J.; Hansen, P.R.; Svenson, J. Correlation between hemolytic activity, cytotoxicity and systemic in vivo toxicity of synthetic antimicrobial peptides. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 13206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; Guoyan, Z.; Tianbi, W.; Yinglin, L.; Tao, Z. Resent research progress on mastitis in dairy cows in China. Dis. Prev. 2022, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yafei, L.; Yan, G.; Bo, Y.; Lin, W.; Xianming, L.; Shuzhen, Z.; Zhenling, Z. Study on the effectiveness of cefquinoxime sulfate udder injection for the control of dry-lactation mastitis in dairy cows. Prog. Vet. Med. 2020, 41, 125–132. [Google Scholar]
- Laverty, G.; McLaughlin, M.; Shaw, C.; Gorman, S.P.; Gilmore, B.F. Antimicrobial activity of short, synthetic cationic lipopeptides. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2010, 75, 563–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, J.-J.; Lin, S.; Beuerman, R.W.; Liu, S. Recent advances in synthetic lipopeptides as anti-microbial agents: Designs and synthetic approaches. Amino Acids 2017, 49, 1653–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huaiqiu, X.; Yuzhen, L.; Qinlu, L.; Mouming, Z.; Jun, L.; Quan, Z. Advances on structural optimization and reformation strategies of antimicrobial peptides. China Brew. 2021, 40, 12–18. [Google Scholar]
- Roman, J. Synthetic lipopeptides: A novel class of anti-infectives. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2007, 16, 1159. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, J.; Lu, Q.; Liu, X.; Deng, Y.; Shang, T.; Yuan, L.; Zhang, H.; Zeng, Q. Antibacterial effect of synthetic ultra-short lipopeptide on Streptococcus agalactiae and its active on bacterial mastitis in mice. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2022, 601, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fillion, M.; Valois-Paillard, G.V.; Lorin, A.L.; Noe¨l, M.; Voyer, N.; Auger, M. Membrane Interactions of Synthetic Peptides with Antimicrobial Potential: Effect of Electrostatic Interactions and Amphiphilicity. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2015, 7, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, C.; Zhu, N.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, T.; Gou, S.; Xie, J.; Yao, J.; Ni, J. Antimicrobial peptides conjugated with fatty acids on the side chain of D-amino acid promises antimicrobial potency against multidrug-resistant bacteria. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 141, 105123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Hong, T.; Cui, P.; Wang, J.; Xia, J. Antimicrobial peptides towards clinical application: Delivery and formulation. Adv. Drug Deliver. Rev. 2021, 175, 113818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Notebaert, S.; Meyer, E. Mouse models to study the pathogenesis and control of bovine mastitis. A review. Vet. Q. 2006, 28, 2–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DuoYao, C. Dynamics of γδT Lyphocytes and Their Associated Cytokines in C57BL/6J Mouse Model of Mastitis Challenged with Staphylococcus aureus. Master’s Thesis, Northwest A&F University, Xian Yang, China, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Suresh, S.; Sankar, P.; Telang, A.G.; Kesavan, M.; Sarkar, S.N. Nanocurcumin ameliorates Staphylococcus aureus-induced mastitis in mouse by suppressing NFκB signaling and inflammation. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2018, 65, 408–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Shang, T.; Peng, S.; Lu, Q.; Zeng, Q.; Peng, J. Isolation of Streptococcus agalactiae from dairy cattle and construction of its induced mastitis mouse model. Anim. Husb. Vet. Med. 2021, 53, 117–122. [Google Scholar]
- Sharun, K.; Dhama, K.; Tiwari, R.; Gugjoo, M.B.; IqbalYatoo, M.; Patel, S.K.; Pathak, M.; Karthik, K.; KumarKhurana, S.; Singh, R.; et al. Advances in therapeutic and managemental approaches of bovine mastitis: A comprehensive review. Vet. Q. 2021, 41, 107–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Fu, X.; Jiang, J.; Han, S. C16 Peptide Promotes Vascular Growth and Reduces Inflammation in a Neuromyelitis Optica Model. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riollet, C.; Rainard, P.; Poutrel, B. Differential Induction of Complement Fragment C5a and Inflammatory Cytokines during Intramammary Infections with Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus. Clin. Diagn. Lab. Immunol. 2000, 7, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vitenberga-Verza, Z.; Pilmane, M.; Serstnova, K.; Melderis, I.; Gontar, L.; Kochanski, M.; Drutowska, A.; Maroti, G.; Prieto-Simon, B. Identification of Inflammatory and Regulatory Cytokines IL-1alpha-, IL-4-, IL-6-, IL-12-, IL-13-, IL-17A-, TNF-alpha-, and IFN-gamma-Producing Cells in the Milk of Dairy Cows with Subclinical and Clinical Mastitis. Pathogens 2022, 11, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulanger, D.; Brouillette, E.; Jaspar, F.; Malouin, F.; Mainil, J.; Bureau, F.; Lekeux, P. Helenalin reduces Staphylococcus aureus infection in vitro and in vivo. Vet. Microbiol. 2007, 119, 330–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Yang, J.; Huang, Z.; Yin, B.; Umar, T.; Yang, C.; Zhang, X.; Jing, H.; Guo, S.; Guo, M.; et al. Vitexin Mitigates Staphylococcus aureus-Induced Mastitis via Regulation of ROS/ER Stress/NF-kappaB/MAPK Pathway. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2022, 2022, 7977433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.-T.; Ke, C.-Y.; Wu, W.-T.; Lee, R.-P.; Tseng, Y.-H. Effective Treatment of Bovine Mastitis with Intramammary Infusion of Angelica dahurica and Rheum officinale Extracts. Evid. -Based Complement. Altern. Med. eCAM 2019, 2019, 7242705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, W.; O’Garra, A. IL-10 Family Cytokines IL-10 and IL-22: From Basic Science to Clinical Translation. Immunity 2019, 50, 871–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, K.W.; Malefyt, R.d.W.; Coffman, R.L.; O’Garra, A. Interleukin-10 andthe interleukin-10 receptor. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2001, 19, 683–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leech, J.M.; Lacey, K.A.; Mulcahy, M.E.; Medina, E.; McLoughlin, R.M. IL-10 Plays Opposing Roles during Staphylococcus aureus Systemic and Localized Infections. J. Immunol. 2017, 198, 2352–2365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
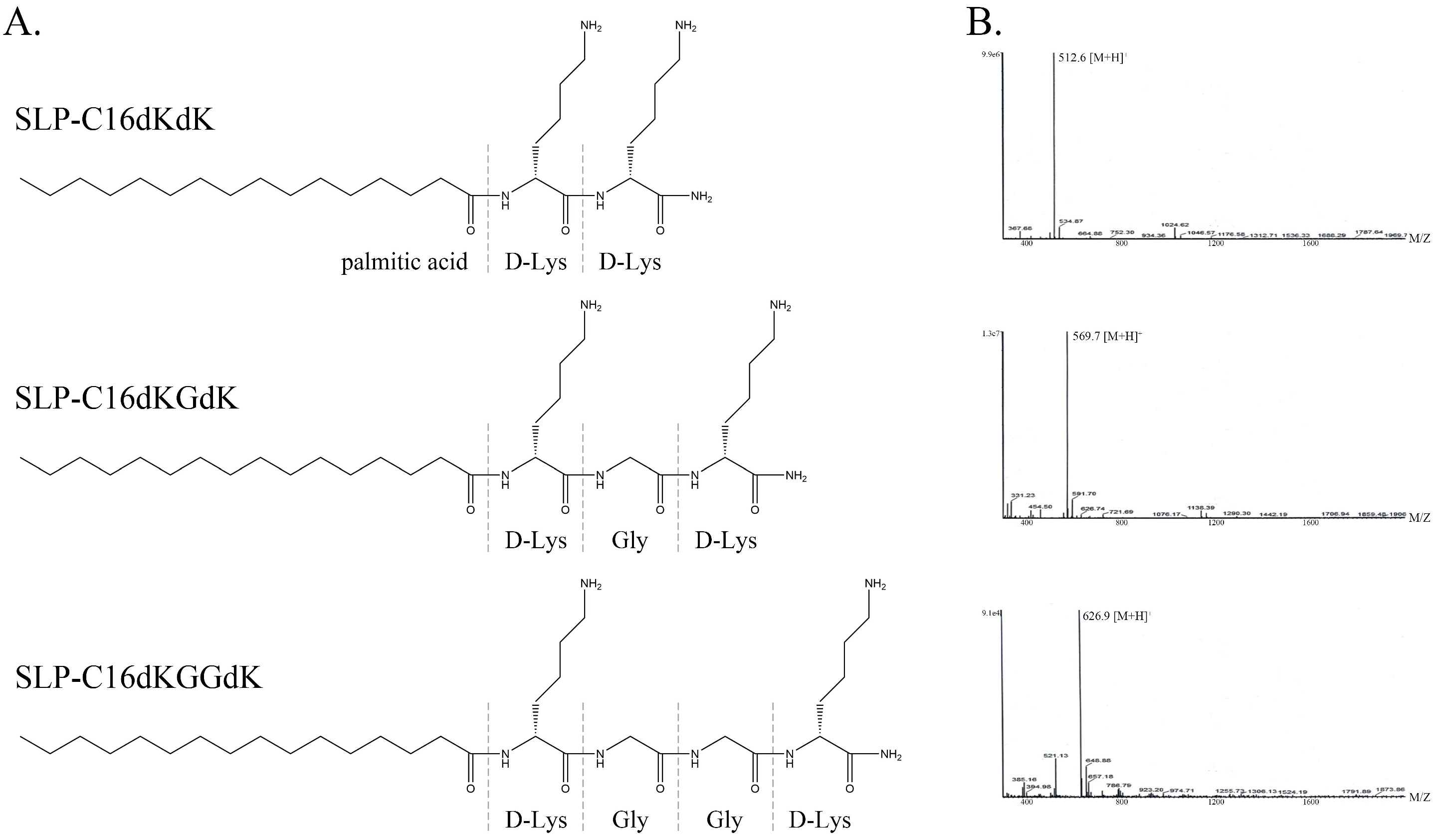

| Name | Sequence |
|---|---|
| C16dKdK | C16-(D)Lys-(D)Lys-NH2 |
| C16dKGdK | C16-(D)Lys-Gly-(D)Lys-NH2 |
| C16dKGGdK | C16-(D)Lys-Gly-Gly-(D)Lys-NH2 |
| Inflammatory Factors | Primer | Primer Sequence |
|---|---|---|
| IL-1α | m * -il1α-qF | ACCCAGATCAGCACCTTACACC |
| m-il1α-qR | CTCCTCCCGACGAGTAGGCAT | |
| IL-6 | m-il6-qF | TCTGGAGCCCACCAAGAACGA |
| m-il6-qR | ACATGTGTAATTAAGCCTCCGAC | |
| IL-10 | m-il10-qF | CTGCACCCACTTCCCAGTCG |
| m-il10-qR | ACTGGATCATTTCCGATAAGGC | |
| TNF-α | m-tnf-qF | AGCACAGAAAGCATGATCCG |
| m-tnf-qR | AGCTGCTCCTCCACTTGGT | |
| GAPDH | m-gapdh-qF | GCGACTTCAACAGCAACTCCC |
| m-gapdh-qR | CACCCTGTTGCTGTAGCCGTA |
| MIC (μg/mL) | C16dKdK | C16dKGdK | C16dKGGdK |
|---|---|---|---|
| ATCC25923 | 0.39 | 25 | 12.5 |
| GS1311 | 1.56 | 50 | 100 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Peng, J.; Lu, Q.; Yuan, L.; Zhang, H. Synthetic Cationic Lipopeptide Can Effectively Treat Mouse Mastitis Caused by Staphylococcus aureus. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 1188. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11041188
Peng J, Lu Q, Yuan L, Zhang H. Synthetic Cationic Lipopeptide Can Effectively Treat Mouse Mastitis Caused by Staphylococcus aureus. Biomedicines. 2023; 11(4):1188. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11041188
Chicago/Turabian StylePeng, Jie, Qiangsheng Lu, Lvfeng Yuan, and Hecheng Zhang. 2023. "Synthetic Cationic Lipopeptide Can Effectively Treat Mouse Mastitis Caused by Staphylococcus aureus" Biomedicines 11, no. 4: 1188. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11041188
APA StylePeng, J., Lu, Q., Yuan, L., & Zhang, H. (2023). Synthetic Cationic Lipopeptide Can Effectively Treat Mouse Mastitis Caused by Staphylococcus aureus. Biomedicines, 11(4), 1188. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11041188







