Sulforaphane-Induced Cell Mitotic Delay and Inhibited Cell Proliferation via Regulating CDK5R1 Upregulation in Breast Cancer Cell Lines
Abstract
:1. Background
2. Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Cells
2.3. Cell Proliferation Assay
2.4. Apoptosis Measurement
2.5. Caspase-3 Activity Assay
2.6. Cell Cycle Analysis
2.7. Evaluation of Mitochondrial Membrane Potential
2.8. Measurement of Intracellular Reactive Oxygen Species Generation
2.9. Mitotic Index Analysis
2.10. Confocal Microscopy
2.11. Western Blot Analysis
2.12. Co-Immunoprecipitation (Co-IP)
2.13. Gene Expression Profiling (GEP)
2.14. Quantitative Real-Time PCR
2.15. Small-Interfering RNA
2.16. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Non-SFN-Induced Apoptosis/Necrosis of Breast Cancer Cell Lines
3.2. Assessment of Changes in Mitochondrial Membrane Potential
3.3. SFN Reduced ROS Accumulation in Cells
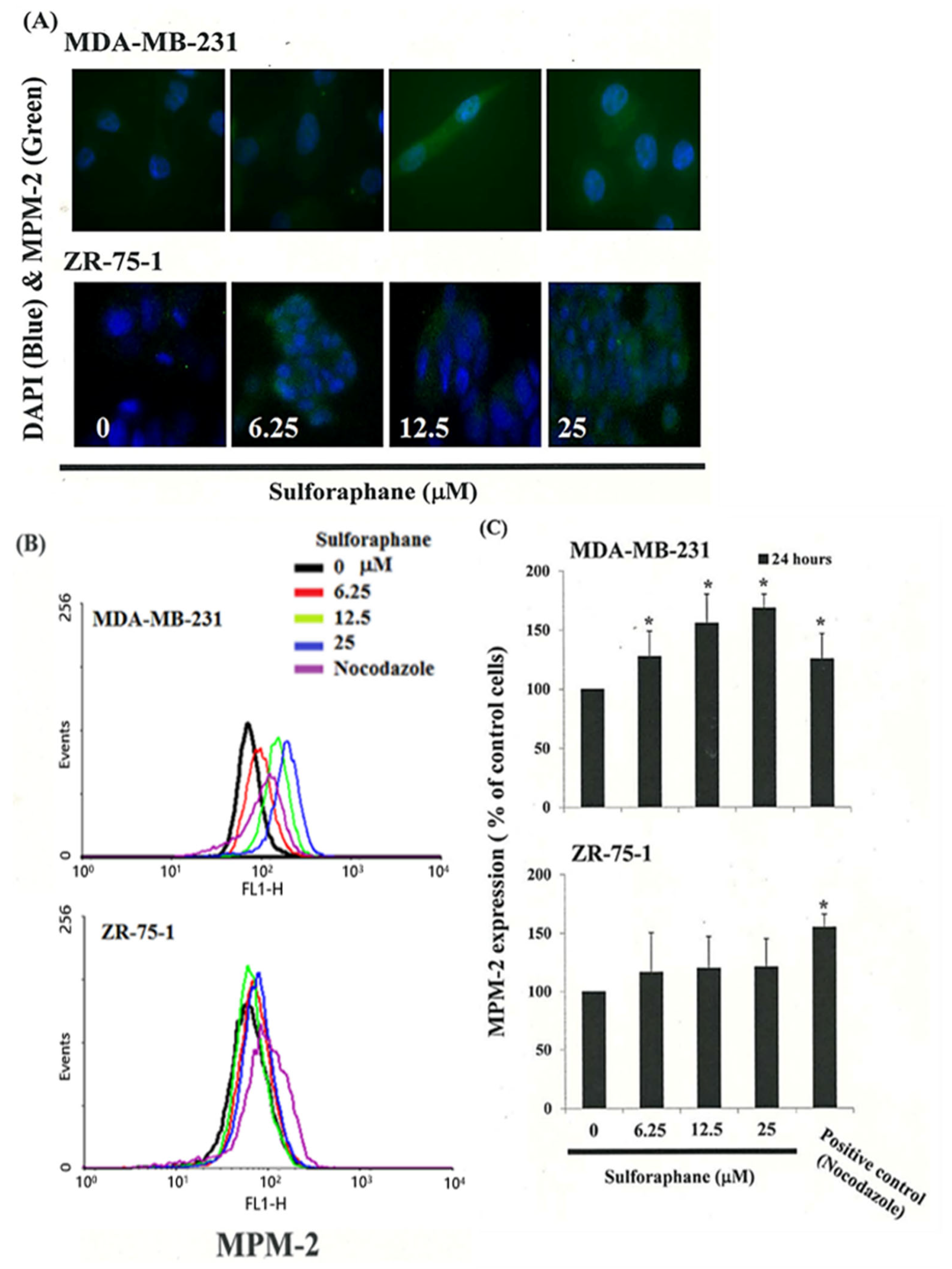
3.4. Effects of SFN on the Mitotic Index
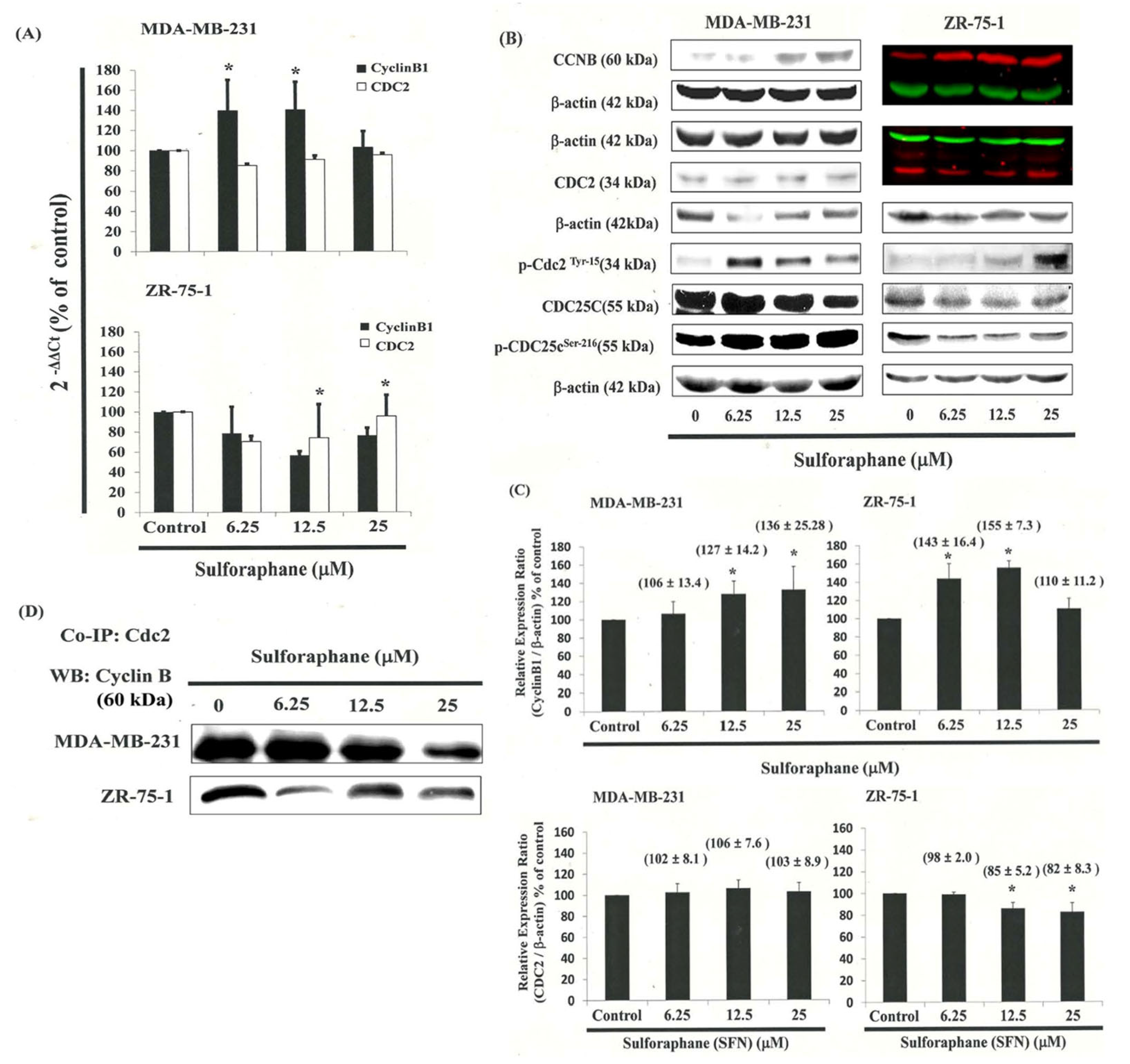
3.5. G2/M-Phase Cell Cycle Arrest by SFN in the MDA-MB-231 Cells through CDC2 and Cyclin B1 Disassociation
3.6. Effects of SFN on CDC25C in MDA-MB-231 and ZR-75-1 Cells
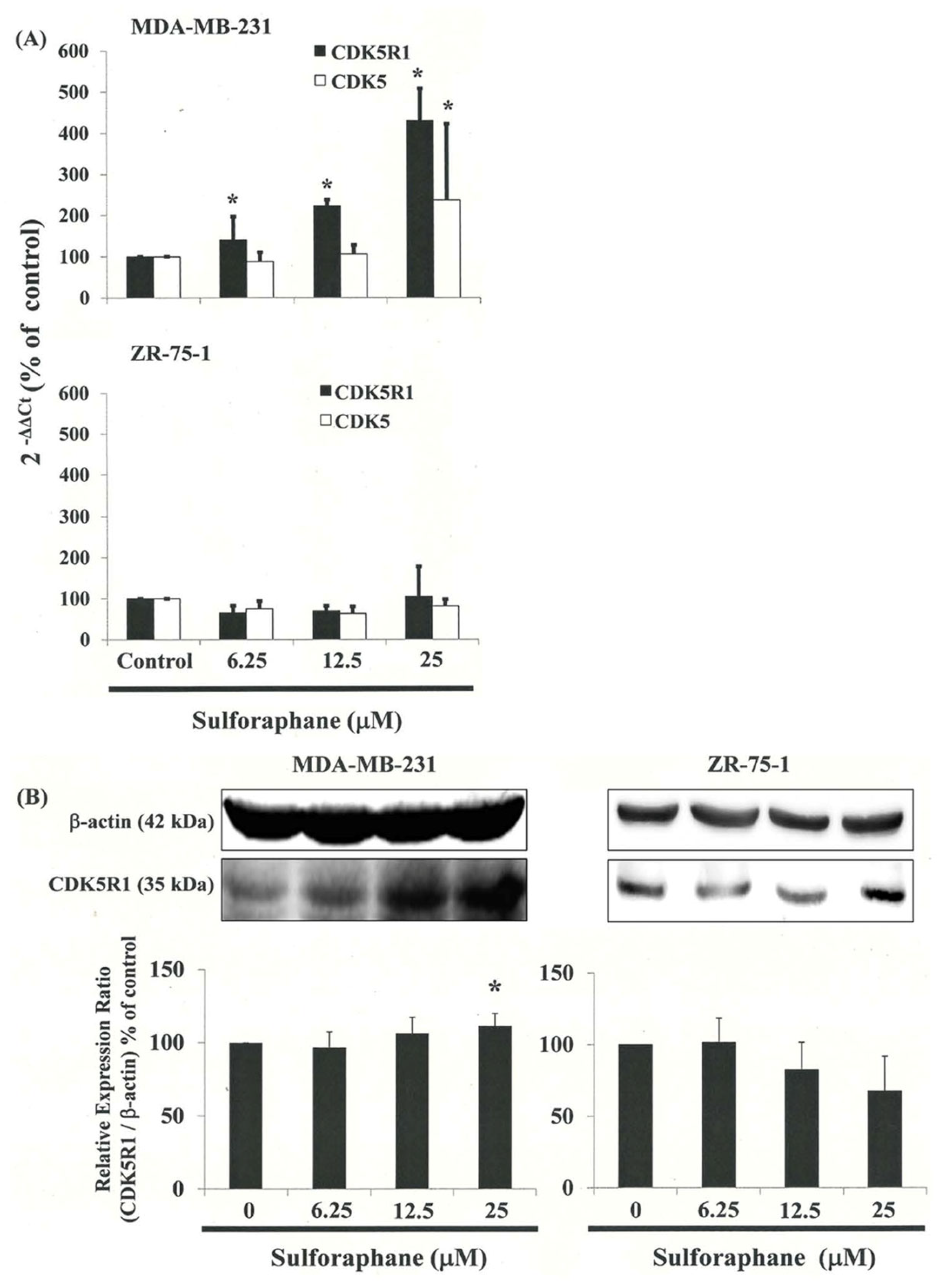
3.7. Gene Expression Profile of Cells following Exposure to SFN
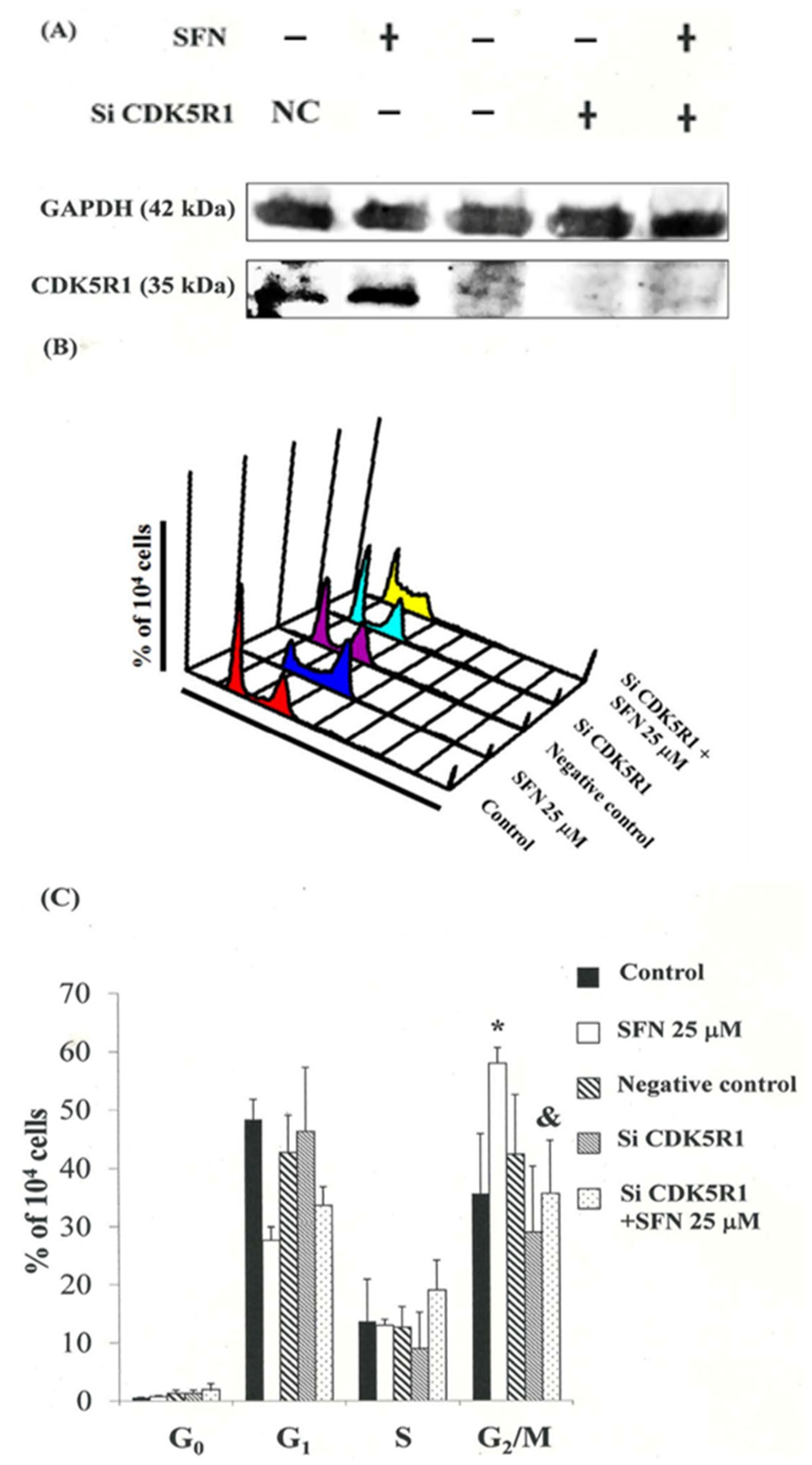
3.8. Down-Regulation of the CDK5R1 in MDA-MB-231 and ZR-75-1 Cells by Silencing CDK5R1 Was Reversed by SFN Induced G2/M Arrest
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Morris, E.V.; Edwards, C.M. Bone marrow adipose tissue: A new player in cancer metastasis to bone. Front. Endocrinol. 2016, 7, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chakraborty, C.; Chin, K.Y.; Das, S. miRNA-regulated cancer stem cells: Understanding the property and the role of miRNA in carcinogenesis. Tumour Biol. 2016, 37, 13039–13048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gradishar, W.J. Treatment challenges for community oncologists treating postmenopausal women with endocrine-resistant, hormone receptor-positive, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-negative advanced breast cancer. Cancer Manag. Res. 2016, 8, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shrivastava, S.R.; Shrivastava, P.S.; Ramasamy, J. Therapeutics. Exploring the role of dietary factors in the development of breast cancer. J. Cancer Res. Ther. 2016, 12, 493–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krohe, M.; Hao, Y.; Lamoureux, R.E.; Galipeau, N.; Globe, D.; Foley, C.; Mazar, I.; Solomon, J.; Shields, A.L. Patient-Reported Outcomes in Metastatic Breast Cancer: A Review of Industry-Sponsored Clinical Trials. Breast Cancer 2016, 10, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hashem, S.; Ali, T.A.; Akhtar, S.; Nisar, S.; Sageena, G.; Ali, S.; Al-Mannai, S.; Therachiyil, L.; Mir, R.; Elfaki, I.; et al. Targeting cancer signaling pathways by natural products: Exploring promising anti-cancer agents. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 150, 113054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganai, S.A. Histone deacetylase inhibitor sulforaphane: The phytochemical with vibrant activity against prostate cancer. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2016, 81, 250–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Palliyaguru, D.L.; Kensler, T.W. Frugal chemoprevention: Targeting Nrf2 with foods rich in sulforaphane. Semin. Oncol. 2016, 43, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tuorkey, M.J. Cancer therapy with phytochemicals: Present and future perspectives. Biomed. Environ. Sci. 2015, 28, 808–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gali-Muhtasib, H.; Hmadi, R.; Kareh, M.; Tohme, R.; Darwiche, N. Cell death mechanisms of plant-derived anticancer drugs: Beyond apoptosis. Apoptosis 2015, 20, 1531–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; McArthur, G. Cell Cycle Regulation and Melanoma. Curr. Oncol. Rep. 2016, 18, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pecoraro, C.; Parrino, B.; Cascioferro, S.; Puerta, A.; Avan, A.; Peters, G.J.; Diana, P.; Giovannetti, E.; Carbone, D. A new oxadiazole-based topsentin derivative modulates cyclin-dependent kinase 1 expression and exerts cytotoxic effects on pancreatic cancer cells. Molecules 2021, 27, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DiPippo, A.J.; Patel, N.K.; Barnett, C.M. Cyclin-Dependent Kinase Inhibitors for the Treatment of Breast Cancer: Past, Present, and Future. Pharmacotherapy 2016, 36, 652–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sørensen, C.S.; Syljuåsen, R.G. Safeguarding genome integrity: The checkpoint kinases ATR, CHK1 and WEE1 restrain CDK activity during normal DNA replication. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, 477–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sur, S.; Agrawal, D.K. Phosphatases and kinases regulating CDC25 activity in the cell cycle: Clinical implications of CDC25 overexpression and potential treatment strategies. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2016, 416, 33–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, S.; Li, R.; Yu-jia, L.; Lü, M.; Wang, H.; Wang, Z. Progress on Correlation between the Expression of CDK5 and Brain Injury Time. Fa Yi Xue Za Zhi 2016, 32, 58–60. [Google Scholar]
- Izawa, I.; Goto, H.; Kasahara, K.; Inagaki, M. Current topics of functional links between primary cilia and cell cycle. Cilia 2015, 4, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wilkaniec, A.; Czapski, G.A.; Adamczyk, A. Cdk5 at crossroads of protein oligomerization in neurodegenerative diseases: Facts and hypotheses. J. Neurochem. 2016, 136, 222–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Malumbres, M. Cyclin-dependent kinases. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arif, A. Extraneuronal activities and regulatory mechanisms of the atypical cyclin-dependent kinase Cdk5. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2012, 84, 985–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelo, M.; Plattner, F.; Giese, K.P. Cyclin-dependent kinase 5 in synaptic plasticity, learning and memory. J. Neurochem. 2006, 99, 353–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moncini, S.; Lunghi, M.; Valmadre, A.; Grasso, M.; Del Vescovo, V.; Riva, P.; Denti, M.A.; Venturin, M. The miR-15/107 family of microRNA genes regulates CDK5R1/p35 with implications for Alzheimer’s disease pathogenesis. Mol. Neurobiol. 2017, 54, 4329–4342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luo, F.; Zhang, J.; Burke, K.; Miller, R.H.; Yang, Y. The Activators of Cyclin-Dependent Kinase 5 p35 and p39 Are Essential for Oligodendrocyte Maturation, Process Formation, and Myelination. J. Neurosci. 2016, 36, 3024–3037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, S.S.; Zhou, X.; Huang, Y.Y.; Kong, L.-P.; Mei, M.; Guo, W.Y.; Zhao, M.H.; Ren, Y.; Shen, Q.; Zhang, L.; et al. Targeting STAT3/miR-21 axis inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition via regulating CDK5 in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Mol. Cancer 2015, 14, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hung, C.M.; Chang, C.C.; Lin, C.W.; Chen, C.C.; Hsu, Y.C. GADD45γ induces G2/M arrest in human pharynx and nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells by cucurbitacin E. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 6454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chang, C.C.; Hung, C.M.; Yang, Y.R.; Lee, M.J.; Hsu, Y.C. Sulforaphane induced cell cycle arrest in the G2/M phase via the blockade of cyclin B1/CDC2 in human ovarian cancer cells. J. Ovarian Res. 2013, 6, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rao, P.C.; Begum, S.; Jahromi, M.A.F.; Jahromi, Z.H.; Sriram, S.; Sahai, M. Cytotoxicity of withasteroids: Withametelin induces cell cycle arrest at G2/M phase and mitochondria-mediated apoptosis in non-small cell lung cancer A549 cells. Tumour Biol. 2016, 37, 12579–12587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Teng, W.; Qu, Y.; Wang, H.; Yuan, Q. Sulforaphene inhibits triple negative breast cancer through activating tumor suppressor Egr1. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2016, 158, 277–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aressy, B.; Ducommun, B. Cell cycle control by the CDC25 phosphatases. Anticancer Agents Med. Chem. 2008, 8, 818–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiyokawa, H.; Ray, D. In vivo roles of CDC25 phosphatases: Biological insight into the anti-cancer therapeutic targets. Anticancer Agents Med. Chem. 2008, 8, 832–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lam, M.H.; Rosen, J.M. Chk1 versus Cdc25: Chking one’s levels of cellular proliferation. Cell Cycle 2004, 3, 1355–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Jiang, Z.; Zhou, C.; Chen, K.; Li, X.; Wang, Z.; Wu, Z.; Ma, J.; Ma, Q.; Duan, W. Activation of Nrf2 by Sulforaphane Inhibits High Glucose-Induced Progression of Pancreatic Cancer via AMPK Dependent Signaling. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 50, 1201–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hung, C.-M.; Tsai, T.-H.; Lee, K.-T.; Hsu, Y.-C. Sulforaphane-Induced Cell Mitotic Delay and Inhibited Cell Proliferation via Regulating CDK5R1 Upregulation in Breast Cancer Cell Lines. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 996. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11040996
Hung C-M, Tsai T-H, Lee K-T, Hsu Y-C. Sulforaphane-Induced Cell Mitotic Delay and Inhibited Cell Proliferation via Regulating CDK5R1 Upregulation in Breast Cancer Cell Lines. Biomedicines. 2023; 11(4):996. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11040996
Chicago/Turabian StyleHung, Chao-Ming, Tai-Hsin Tsai, Kuan-Ting Lee, and Yi-Chiang Hsu. 2023. "Sulforaphane-Induced Cell Mitotic Delay and Inhibited Cell Proliferation via Regulating CDK5R1 Upregulation in Breast Cancer Cell Lines" Biomedicines 11, no. 4: 996. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11040996
APA StyleHung, C.-M., Tsai, T.-H., Lee, K.-T., & Hsu, Y.-C. (2023). Sulforaphane-Induced Cell Mitotic Delay and Inhibited Cell Proliferation via Regulating CDK5R1 Upregulation in Breast Cancer Cell Lines. Biomedicines, 11(4), 996. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11040996







