Aberrantly Expressed Hsa_circ_0060762 and CSE1L as Potential Peripheral Blood Biomarkers for ALS
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Samples
2.2. RNA Extraction
2.3. Microarray Analysis
2.4. QPCR
2.5. Statistical Analysis
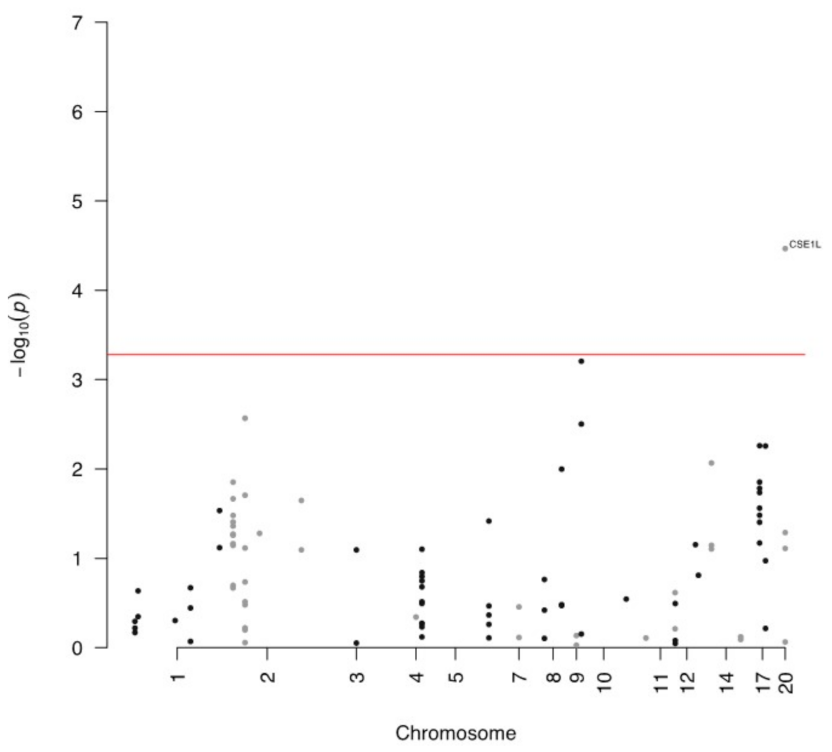
3. Results
4. Expression of circRNA and Host Gene
5. Associations between Clinical Variables and circRNA Expression
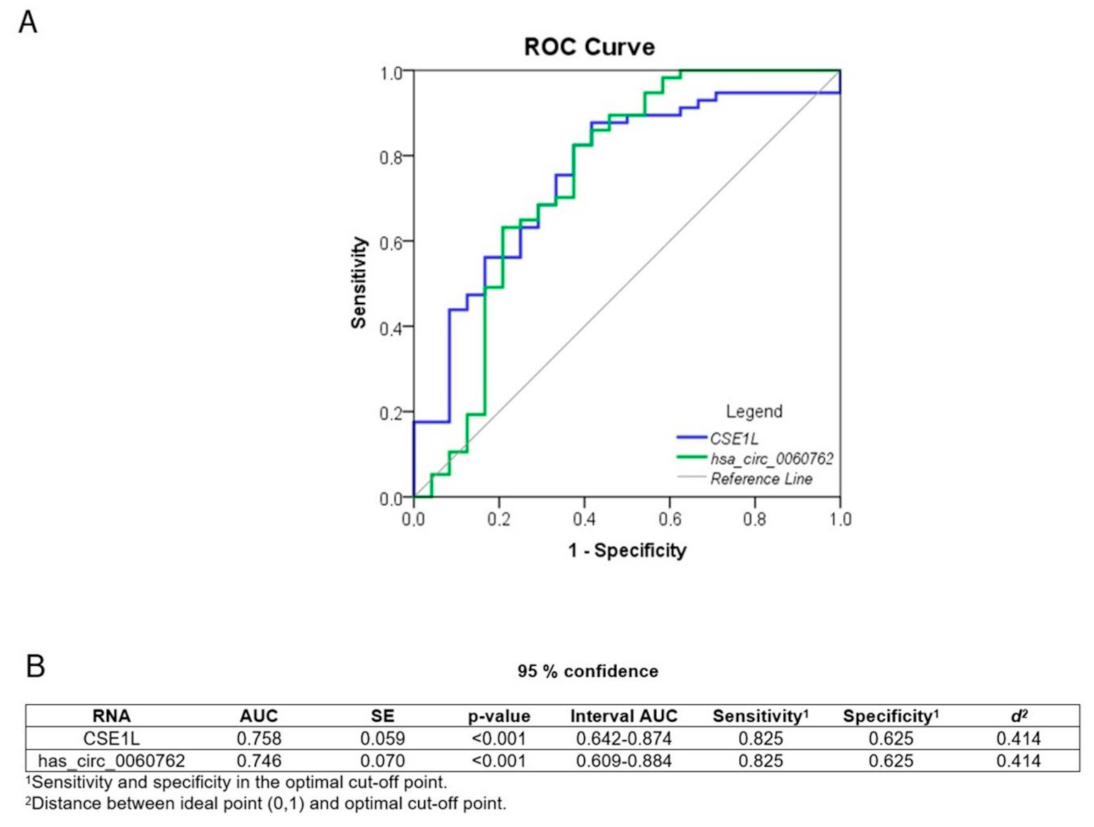
6. Diagnostic Potential
7. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Turner, M.R.; Swash, M. The expanding syndrome of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: A clinical and molecular odyssey. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2015, 86, 667–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardiman, O.; Al-Chalabi, A.; Brayne, C.; Beghi, E.; van den Berg, L.H.; Chio, A.; Martin, S.; Logroscino, G.; Rooney, J. The changing picture of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: Lessons from European registers. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2017, 88, 557–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brooks, B.R.; Miller, R.G.; Swash, M.; Munsat, T.L. El Escorial revisited: Revised criteria for the diagnosis of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Amyotroph. Lateral Scler. Other Mot. Neuron Disord. 2000, 1, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Carvalho, M.; Dengler, R.; Eisen, A.; England, J.D.; Kaji, R.; Kimura, J.; Mills, K.; Mitsumoto, H.; Nodera, H.; Shefner, J.; et al. Electrodiagnostic criteria for diagnosis of ALS. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2008, 119, 497–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geevasinga, N.; Howells, J.; Menon, P.; van den Bos, M.; Shibuya, K.; Matamala, J.M.; Park, S.B.; Byth, K.; Kiernan, M.C.; Vucic, S. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis diagnostic index. Towar. A Pers. Diagn. ALS 2019, 92, e536–e547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richards, D.; Morren, J.A.; Pioro, E.P. Time to diagnosis and factors affecting diagnostic delay in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J. Neurol. Sci. 2020, 417, 117054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagliardi, D.; Bresolin, N.; Comi, G.P.; Corti, S. Extracellular vesicles and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: From misfolded protein vehicles to promising clinical biomarkers. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2021, 78, 561–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhasmana, S.; Dhasmana, A.; Narula, A.S.; Jaggi, M.; Yallapu, M.M.; Chauhan, S.C. The panoramic view of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: A fatal intricate neurological disorder. Life Sci. 2022, 288, 120156. [Google Scholar]
- Querin, G.; Bede, P.; El Mendili, M.M.; Li, M.; Pélégrini-Issac, M.; Rinaldi, D.; Catala, M.; Saracino, D.; Salachas, F.; Camuzat, A.; et al. Presymptomatic spinal cord pathology in c9orf72 mutation carriers: A longitudinal neuroimaging study. Ann. Neurol. 2019, 86, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chipika, R.H.; Siah, W.F.; McKenna, M.C.; Li, H.; Shing, S.; Hardiman, O.; Bede, P. The presymptomatic phase of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: Are we merely scratching the surface? J. Neurol. 2021, 268, 4607–4629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayakumar, U.G.; Milla, V.; Cynthia Stafford, M.Y.; Bjourson, A.J.; Duddy, W.; Duguez, S.M. A Systematic Review of Suggested Molecular Strata, Biomarkers and Their Tissue Sources in ALS. Front. Neurol. 2019, 10, 400. [Google Scholar]
- Dolinar, A.; Koritnik, B.; Glavač, D.; Ravnik-Glavač, M. Circular RNAs as potential blood biomarkers in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Mol. Neurobiol. 2019, 56, 8052–8062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeck, W.R.; Sorrentino, J.A.; Wang, K.; Slevin, M.K.; Burd, C.E.; Liu, J.; Marzluff, W.F.; Sharpless, N.E. Circular RNAs are abundant, conserved, and associated with ALU repeats. RNA 2013, 19, 141–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, Z. CircRNAs: A new perspective of biomarkers in the nervous system. Biomed. Pharm. 2020, 128, 110251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sang, Q.; Liu, X.; Wang, L.; Qi, L.; Sun, W.; Wang, W.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, H. CircSNCA downregulation by pramipexole treatment mediates cell apoptosis and autophagy in Parkinson’s disease by targeting miR-7. Aging 2018, 10, 1281–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, L.; Shamsuzzama Jadiya, P.; Haque, R.; Shukla, S.; Nazir, A. Functional Characterization of Novel Circular RNA Molecule, circzip-2 and Its Synthesizing Gene zip-2 in C. elegans Model of Parkinson’s Disease. Mol. Neurobiol. 2018, 55, 6914–6926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Alexandrov, P.; Jaber, V.; Lukiw, W. Deficiency in the ubiquitin conjugating enzyme UBE2A in Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is linked to deficits in a natural circular miRNA-7 Sponge (circRNA; ciRS-7). Genes 2016, 7, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dube, U.; Del-Aguila, J.L.; Li, Z.; Budde, J.P.; Jiang, S.; Hsu, S.; Ibanez, L.; Victoria Fernandez, M.; Farias, F.; Norton, J.; et al. An atlas of cortical circular RNA expression in Alzheimer disease brains demonstrates clinical and pathological associations. Nat. Neurosci. 2019, 22, 1903–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Huang, N.; Yang, X.; Luo, J.; Yan, S.; Xiao, F.; Chen, W.; Gao, X.; Zhao, K.; Zhou, H.; et al. A novel protein encoded by the circular form of the SHPRH gene suppresses glioma tumorigenesis. Oncogene 2018, 37, 1805–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Gao, X.; Zhang, M.; Yan, S.; Sun, C.; Xiao, F.; Huang, N.; Yang, X.; Zhao, K.; Zhou, H.; et al. Novel Role of FBXW7 Circular RNA in Repressing Glioma Tumorigenesis. JNCI J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2018, 110, 304–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iparraguirre, L.; Muñoz-Culla, M.; Prada-Luengo, I.; Castillo-Triviño, T.; Olascoaga, J.; Otaegui, D. Circular RNA profiling reveals that circular RNAs from ANXA2 can be used as new biomarkers for multiple sclerosis. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2017, 26, 3564–3572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, G.H.; An, F.M.; Wang, Y.; Bian, M.; Wang, D.; Wei, C.X. Comprehensive Circular RNA Profiling Reveals the Regulatory Role of the CircRNA-0067835/miR-155 Pathway in Temporal Lobe Epilepsy. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 51, 1399–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Havrilla, J.M.; Pedersen, B.S.; Layer, R.M.; Quinlan, A.R. A map of constrained coding regions in the human genome. Nat. Genet. 2019, 51, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrovski, S.; Gussow, A.B.; Wang, Q.; Halvorsen, M.; Han, Y.; Weir, W.H.; Allen, A.S.; Goldstein, D.B. The Intolerance of Regulatory Sequence to Genetic Variation Predicts Gene Dosage Sensitivity. PLoS Genet. 2015, 11, e1005492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lek, M.; Karczewski, K.J.; Minikel, E.V.; Samocha, K.E.; Banks, E.; Fennell, T.; O’Donnell-Luria, A.H.; Ware, J.S.; Hill, A.J.; Cummings, B.B.; et al. Analysis of protein-coding genetic variation in 60,706 humans. Nature 2016, 536, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mezzavilla, M.; Cocca, M.; Guidolin, F.; Gasparini, P. A population-based approach for gene prioritization in understanding complex traits. Hum. Genet. 2020, 139, 647–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. 2020. Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 20 March 2023).
- Chakraborty, A.; Diwan, A. Biomarkers and molecular mechanisms of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. AIMS Neurosci. 2022, 9, 423–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Fan, H.; Sun, J.; Ni, M.; Zhang, L.; Chen, C.; Hong, X.; Fang, F.; Zhang, W.; Ma, P. Circular RNA expression profile of Alzheimer’s disease and its clinical significance as biomarkers for the disease risk and progression. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2020, 123, 105747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, X.; Niu, W.; Kong, L.; He, M.; Jiang, K.; Chen, S.; Zhong, A.; Li, W.; Lu, J.; Zhang, L. hsa_circRNA_103636: Potential novel diagnostic and therapeutic biomarker in Major depressive disorder. Biomark. Med. 2016, 10, 943–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.-D.; Jiang, L.-H.; Sun, D.-W.; Hou, J.-C.; Ji, Z.-L. CircRNA: A novel type of biomarker for cancer. Breast Cancer 2018, 25, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsitsipatis, D.; Mazan-Mamczarz, K.; Si, Y.; Herman, A.B.; Yang, J.H.; Guha, A.; Piao, Y.; Fan, J.; Martindale, J.L.; Munk, R.; et al. Transcriptomic analysis of human ALS skeletal muscle reveals a disease-specific pattern of dysregulated circRNAs. Aging 2022, 14, 9832–9859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutay, U.; Bischoff, F.R.; Kostka, S.; Kraft, R.; Görlich, D. Export of importin alpha from the nucleus is mediated by a specific nuclear transport factor. Cell 1997, 90, 1061–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinoshita, Y.; Ito, H.; Hirano, A.; Fujita, K.; Wate, R.; Nakamura, M.; Kaneko, S.; Nakano, S.; Kusaka, H. Nuclear Contour Irregularity and Abnormal Transporter Protein Distribution in Anterior Horn Cells in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2009, 68, 1184–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishimura, A.L.; Zupunski, V.; Troakes, C.; Kathe, C.; Fratta, P.; Howell, M.; Gallo, J.-M.; Hortobágyi, T.; Shaw, C.E.; Rogelj, B. Nuclear import impairment causes cytoplasmic trans-activation response DNA-binding protein accumulation and is associated with frontotemporal lobar degeneration. Brain 2010, 133, 1763–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prpar Mihevc, S.; Darovic, S.; Kovanda, A.; Bajc Česnik, A.; Župunski, V.; Rogelj, B. Nuclear trafficking in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and frontotemporal lobar degeneration. Brain 2017, 140, 13–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fallini, C.; Khalil, B.; Smith, C.L.; Rossoll, W. Traffic jam at the nuclear pore: All roads lead to nucleocytoplasmic transport defects in ALS/FTD. Neurobiol. Dis. 2020, 140, 104835. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dormann, D.; Rodde, R.; Edbauer, D.; Bentmann, E.; Fischer, I.; Hruscha, A.; Than, E.; Mackenzie, I.R.A.; Capell, A.; Schmid, B.; et al. ALS-associated fused in sarcoma (FUS) mutations disrupt Transportin-mediated nuclear import. EMBO J. 2010, 29, 2841–2857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kino, Y.; Washizu, C.; Aquilanti, E.; Okuno, M.; Kurosawa, M.; Yamada, M.; Doi, H.; Nukina, N. Intracellular localization and splicing regulation of FUS/TLS are variably affected by amyotrophic lateral sclerosis-linked mutations. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, 2781–2798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamaki, Y.; Urushitani, M. Molecular Dissection of TDP-43 as a Leading Cause of ALS/FTLD. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 12508. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Doll, S.G.; Cingolani, G. Importin α/β and the tug of war to keep TDP-43 in solution: Quo vadis? Bioessays 2022, 44, e2200181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dormann, D.; Haass, C. TDP-43 and FUS: A nuclear affair. Trends Neurosci. 2011, 34, 339–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Rossum, D.; Verheijen, B.M.; Pasterkamp, R.J. Circular RNAs: Novel Regulators of Neuronal Development. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2016, 9, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrabec, K.; Boštjančič, E.; Koritnik, B.; Leonardis, L.; Dolenc Grošelj, L.; Zidar, J.; Rogelj, B.; Glavač, D.; Ravnik-Glavač, M. Differential Expression of Several miRNAs and the Host Genes AATK and DNM2 in Leukocytes of Sporadic ALS Patients. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2018, 11, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saucier, D.; Wajnberg, G.; Roy, J.; Beauregard, A.P.; Chacko, S.; Crapoulet, N.; Fournier, S.; Ghosh, A.; Lewis, S.M.; Marrero, A.; et al. Identification of a circulating miRNA signature in extracellular vesicles collected from amyotrophic lateral sclerosis patients. Brain Res. 2019, 1708, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Felice, B.; Manfellotto, F.; Fiorentino, G.; Annunziata, A.; Biffali, E.; Pannone, R.; Federico, A. Wide-Ranging Analysis of MicroRNA Profiles in Sporadic Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Using Next-Generation Sequencing. Front. Genet. 2018, 9, 310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheinerman, K.S.; Toledo, J.B.; Tsivinsky, V.G.; Irwin, D.; Grossman, M.; Weintraub, D.; Hurtig, H.I.; Chen-Plotkin, A.; Wolk, D.A.; McCluskey, L.F.; et al. Circulating brain-enriched microRNAs as novel biomarkers for detection and differentiation of neurodegenerative diseases. Alzheimers Res. Ther. 2017, 9, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raheja, R.; Regev, K.; Healy, B.C.; Mazzola, M.A.; Beynon, V.; Von Glehn, F.; Paul, A.; Diaz-Cruz, C.; Gholipour, T.; Glanz, B.I.; et al. Correlating serum micrornas and clinical parameters in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Muscle Nerve 2018, 58, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freischmidt, A.; Müller, K.; Zondler, L.; Weydt, P.; Volk, A.E.; Božič, A.L.; Walter, M.; Bonin, M.; Mayer, B.; von Arnim, C.A.F.; et al. Serum microRNAs in patients with genetic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and pre-manifest mutation carriers. Brain 2014, 137, 2938–2950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Felice, B.; Guida, M.; Guida, M.; Coppola, C.; De Mieri, G.; Cotrufo, R. A miRNA signature in leukocytes from sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Gene 2012, 508, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parisi, C.; Napoli, G.; Amadio, S.; Spalloni, A.; Apolloni, S.; Longone, P.; Volonté, C. MicroRNA-125b regulates microglia activation and motor neuron death in ALS. Cell Death Differ. 2016, 23, 531–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hawley, Z.C.E.; Campos-Melo, D.; Strong, M.J. MiR-105 and miR-9 regulate the mRNA stability of neuronal intermediate filaments. Implications for the pathogenesis of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). Brain Res. 2019, 1706, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zecca, C.; Dell’Abate, M.T.; Pasculli, G.; Capozzo, R.; Barone, R.; Arima, S.; Pollice, A.; Brescia, V.; Tortelli, R.; Logroscino, G. Role of plasma phosphorylated neurofilament heavy chain (pNfH) in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2022, 26, 3608–3615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Samples | ||
|---|---|---|
| Characteristics | ALS (n = 60) | Healthy Controls (n = 25) |
| Sex (M/F) | 30/30 | 15/10 |
| Age (years) a | 67 (35–92) | 56 (47–73) |
| Age at onset (years) | 65 (35–92) | / |
| ALS onset (spinal/bulbar/mixed) | 45/13/2 | / |
| Disease duration (years) b | 1.5 (0.0–5.5) | / |
| Survival time (years) c | 2.0 (0.5–5.0) n = 27 | / |
| Level of functional impairment d | 34 (20–48) | / |
| Rate of progression e | −1.11 (−0.03–−4.19) | / |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ravnik Glavač, M.; Mezzavilla, M.; Dolinar, A.; Koritnik, B.; Glavač, D. Aberrantly Expressed Hsa_circ_0060762 and CSE1L as Potential Peripheral Blood Biomarkers for ALS. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 1316. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11051316
Ravnik Glavač M, Mezzavilla M, Dolinar A, Koritnik B, Glavač D. Aberrantly Expressed Hsa_circ_0060762 and CSE1L as Potential Peripheral Blood Biomarkers for ALS. Biomedicines. 2023; 11(5):1316. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11051316
Chicago/Turabian StyleRavnik Glavač, Metka, Massimo Mezzavilla, Ana Dolinar, Blaž Koritnik, and Damjan Glavač. 2023. "Aberrantly Expressed Hsa_circ_0060762 and CSE1L as Potential Peripheral Blood Biomarkers for ALS" Biomedicines 11, no. 5: 1316. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11051316
APA StyleRavnik Glavač, M., Mezzavilla, M., Dolinar, A., Koritnik, B., & Glavač, D. (2023). Aberrantly Expressed Hsa_circ_0060762 and CSE1L as Potential Peripheral Blood Biomarkers for ALS. Biomedicines, 11(5), 1316. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11051316








