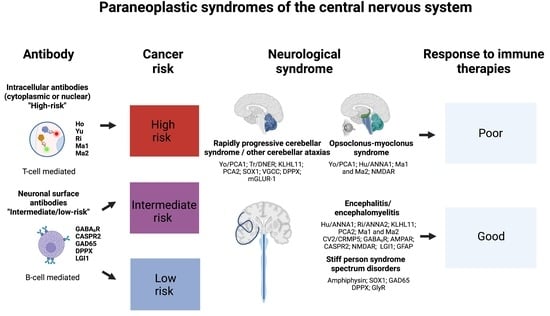
Paraneoplastic Neurological Syndromes of the Central Nervous System: Pathophysiology, Diagnosis, and Treatment
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Rapidly Progressive Cerebellar Syndrome
3. Opsoclonus–Myoclonus Syndrome
4. Paraneoplastic Encephalitides
5. Stiff-Person Spectrum Disorders
6. Immune-Checkpoint Inhibitors, CAR T-Cell Therapies, and Related Syndromes
7. Diagnosis
8. Treatment
9. Discussion
10. Conclusions and Next Steps
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chirra, M.; Marsili, L.; Gallerini, S.; Keeling, E.G.; Marconi, R.; Colosimo, C. Paraneoplastic movement disorders: Phenomenology, diagnosis, and treatment. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2019, 67, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalmau, J.; Rosenfeld, M.R. Paraneoplastic syndromes of the CNS. Lancet Neurol. 2008, 7, 327–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darnell, R.B.; Posner, J.B. Paraneoplastic syndromes involving the nervous system. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 349, 1543–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pittock, S.J.; Lucchinetti, C.F.; Parisi, J.E.; Benarroch, E.E.; Mokri, B.; Stephan, C.L.; Kim, K.K.; Kilimann, M.W.; Lennon, V.A. Amphiphysin autoimmunity: Paraneoplastic accompaniments. Ann. Neurol. 2005, 58, 96–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giometto, B.; Grisold, W.; Vitaliani, R.; Graus, F.; Honnorat, J.; Bertolini, G. Paraneoplastic neurologic syndrome in the PNS Euronetwork database: A European study from 20 centers. Arch. Neurol. 2010, 67, 330–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graus, F.; Delattre, J.Y.; Antoine, J.C.; Dalmau, J.; Giometto, B.; Grisold, W.; Honnorat, J.; Smitt, P.S.; Vedeler, C.; Verschuuren, J.J.; et al. Recommended diagnostic criteria for paraneoplastic neurological syndromes. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2004, 75, 1135–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, A.M.; Baehring, J.M. Paraneoplastic neurological syndromes: A single institution 10-year case series. J. Neurooncol. 2019, 141, 431–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubey, D.; Pittock, S.J.; Kelly, C.R.; McKeon, A.; Lopez-Chiriboga, A.S.; Lennon, V.A.; Gadoth, A.; Smith, C.Y.; Bryant, S.C.; Klein, C.J.; et al. Autoimmune encephalitis epidemiology and a comparison to infectious encephalitis. Ann. Neurol. 2018, 83, 166–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flanagan, E.P.; McKeon, A.; Lennon, V.A.; Boeve, B.F.; Trenerry, M.R.; Tan, K.M.; Drubach, D.A.; Josephs, K.A.; Britton, J.W.; Mandrekar, J.N.; et al. Autoimmune dementia: Clinical course and predictors of immunotherapy response. Mayo. Clin. Proc. 2010, 85, 881–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flanagan, E.P.; Geschwind, M.D.; Lopez-Chiriboga, A.S.; Blackburn, K.M.; Turaga, S.; Binks, S.; Zitser, J.; Gelfand, J.M.; Day, G.S.; Dunham, S.R.; et al. Autoimmune Encephalitis Misdiagnosis in Adults. JAMA Neurol. 2023, 80, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogrig, A.; Muñiz-Castrillo, S.; Desestret, V.; Joubert, B.; Honnorat, J. Pathophysiology of paraneoplastic and autoimmune encephalitis: Genes, infections, and checkpoint inhibitors. Ther. Adv. Neurol. Disord. 2020, 13, 1756286420932797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Honorat, J.A.; Komorowski, L.; Josephs, K.A.; Fechner, K.; St Louis, E.K.; Hinson, S.R.; Lederer, S.; Kumar, N.; Gadoth, A.; Lennon, V.A.; et al. IgLON5 antibody: Neurological accompaniments and outcomes in 20 patients. Neurol. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2017, 4, e385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, C.; Allen, E.; Umoru, G. Paraneoplastic syndromes: A focus on pathophysiology and supportive care. Am. J. Health Syst. Pharm. 2022, 79, 1988–2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ippolito, G.; Bertaccini, R.; Tarasi, L.; Di Gregorio, F.; Trajkovic, J.; Battaglia, S.; Romei, V. The Role of Alpha Oscillations among the Main Neuropsychiatric Disorders in the Adult and Developing Human Brain: Evidence from the Last 10 Years of Research. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 3189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Battaglia, S.; Nazzi, C.; Thayer, J.F. Fear-induced bradycardia in mental disorders: Foundations, current advances, future perspectives. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2023, 149, 105163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graus, F.; Vogrig, A.; Muñiz-Castrillo, S.; Antoine, J.G.; Desestret, V.; Dubey, D.; Giometto, B.; Irani, S.R.; Joubert, B.; Leypoldt, F.; et al. Updated Diagnostic Criteria for Paraneoplastic Neurologic Syndromes. Neurol. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2021, 8, e1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Storstein, A.; Krossnes, B.K.; Vedeler, C.A. Morphological and immunohistochemical characterization of paraneoplastic cerebellar degeneration associated with Yo antibodies. Acta Neurol. Scand. 2009, 120, 64–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenlee, J.E.; Brashear, H.R. Antibodies to cerebellar Purkinje cells in patients with paraneoplastic cerebellar degeneration and ovarian carcinoma. Ann. Neurol. 1983, 14, 609–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogrig, A.; Bernardini, A.; Gigli, G.L.; Corazza, E.; Marini, A.; Segatti, S.; Fabris, M.; Honnorat, J.; Valente, M. Stroke-Like Presentation of Paraneoplastic Cerebellar Degeneration: A Single-Center Experience and Review of the Literature. Cerebellum 2019, 18, 976–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, M.; Truh, L.I.; O’Neill, B.P.; Lennon, V.A. Autoimmune paraneoplastic cerebellar degeneration: Ultrastructural localization of antibody-binding sites in Purkinje cells. Neurology 1988, 38, 1380–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKeon, A.; Tracy, J.A.; Pittock, S.J.; Parisi, J.E.; Klein, C.J.; Lennon, V.A. Purkinje cell cytoplasmic autoantibody type 1 accompaniments: The cerebellum and beyond. Arch. Neurol. 2011, 68, 1282–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendes, N.T.; Ronchi, N.R.; Silva, G.D. A Systematic Review on Anti-Yo/PCA-1 Antibody: Beyond Cerebellar Ataxia in Middle-Aged Women with Gynecologic Cancer. Cerebellum 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatham, M.; Niravath, P. Anti-Yo-Associated Paraneoplastic Cerebellar Degeneration: Case Series and Review of Literature. Cureus 2021, 13, e20203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Graaff, E.; Maat, P.; Hulsenboom, E.; van den Berg, R.; van den Bent, M.; Demmers, J.; Lugtenburg, P.J.; Hoogenraad, C.C.; Sillevis Smitt, P. Identification of delta/notch-like epidermal growth factor-related receptor as the Tr antigen in paraneoplastic cerebellar degeneration. Ann. Neurol. 2012, 71, 815–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernal, F.; Shams’ili, S.; Rojas, I.; Sanchez-Valle, R.; Saiz, A.; Dalmau, J.; Honnorat, J.; Sillevis Smitt, P.; Graus, F. Anti-Tr antibodies as markers of paraneoplastic cerebellar degeneration and Hodgkin’s disease. Neurology 2003, 60, 230–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simard, C.; Vogrig, A.; Joubert, B.; Muñiz-Castrillo, S.; Picard, G.; Rogemond, V.; Ducray, F.; Berzero, G.; Psimaras, D.; Antoine, J.C.; et al. Clinical spectrum and diagnostic pitfalls of neurologic syndromes with Ri antibodies. Neurol. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2020, 7, e699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, D.; Wilson, M.R.; Clarkson, B.; Giannini, C.; Gandhi, M.; Cheville, J.; Lennon, V.A.; Eggers, S.; Devine, M.F.; Mandel-Brehm, C.; et al. Expanded Clinical Phenotype, Oncological Associations, and Immunopathologic Insights of Paraneoplastic Kelch-like Protein-11 Encephalitis. JAMA Neurol. 2020, 77, 1420–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maudes, E.; Landa, J.; Muñoz-Lopetegi, A.; Armangue, T.; Alba, M.; Saiz, A.; Graus, F.; Dalmau, J.; Sabater, L. Clinical significance of Kelch-like protein 11 antibodies. Neurol. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2020, 7, e666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammami, M.B.; Rezk, M.; Dubey, D. Validation of MATCH score: A predictive tool for identification of patients with kelch-like protein-11 autoantibodies. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2023, 94, 171–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winklehner, M.; Bauer, J.; Endmayr, V.; Schwaiger, C.; Ricken, G.; Motomura, M.; Yoshimura, S.; Shintaku, H.; Ishikawa, K.; Tsuura, Y.; et al. Paraneoplastic Cerebellar Degeneration with P/Q-VGCC vs Yo Autoantibodies. Neurol. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2022, 9, e200006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Titulaer, M.J.; Lang, B.; Verschuuren, J.J. Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome: From clinical characteristics to therapeutic strategies. Lancet Neurol. 2011, 10, 1098–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, H.B. The Neuropathology of Autoimmune Ataxias. Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taraghikhah, N.; Ashtari, S.; Asri, N.; Shahbazkhani, B.; Al-Dulaimi, D.; Rostami-Nejad, M.; Rezaei-Tavirani, M.; Razzaghi, M.R.; Zali, M.R. An updated overview of spectrum of gluten-related disorders: Clinical and diagnostic aspects. BMC Gastroenterol. 2020, 20, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thapa, S.; Shah, S.; Chand, S.; Sah, S.K.; Gyawali, P.; Paudel, S.; Khanal, P. Ataxia due to vitamin E deficiency: A case report and updated review. Clin. Case Rep. 2022, 10, e6303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grahn, A.; Studahl, M. Varicella-zoster virus infections of the central nervous system—Prognosis, diagnostics and treatment. J. Infect. 2015, 71, 281–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, U.; Panwar, A.; Pandit, A.; Das, S.K.; Joshi, B. Clinical and Neuroradiological Spectrum of Metronidazole Induced Encephalopathy: Our Experience and the Review of Literature. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2016, 10, Oe01–Oe09. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liampas, A.; Nteveros, A.; Parperis, K.; Akil, M.; Dardiotis, E.; Andreadou, E.; Hadjivassiliou, M.; Zis, P. Primary Sjögren’s syndrome (pSS)-related cerebellar ataxia: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Acta Neurol. Belg. 2022, 122, 457–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manto, M.; Hadjivassiliou, M.; Baizabal-Carvallo, J.F.; Hampe, C.S.; Honnorat, J.; Joubert, B.; Mitoma, H.; Muñiz-Castrillo, S.; Shaikh, A.G.; Vogrig, A. Consensus Paper: Latent Autoimmune Cerebellar Ataxia (LACA). Cerebellum 2023, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallerini, S.; Marsili, L.; Marconi, R. Opsoclonus-Myoclonus Syndrome in the Era of Neuronal Cell Surface Antibodies: A Message for Clinicians. JAMA Neurol. 2016, 73, 891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armangué, T.; Sabater, L.; Torres-Vega, E.; Martínez-Hernández, E.; Ariño, H.; Petit-Pedrol, M.; Planagumà, J.; Bataller, L.; Dalmau, J.; Graus, F. Clinical and Immunological Features of Opsoclonus-Myoclonus Syndrome in the Era of Neuronal Cell Surface Antibodies. JAMA Neurol. 2016, 73, 417–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graus, F.; Ariño, H.; Dalmau, J. Opsoclonus-Myoclonus Syndrome in the Era of Neuronal Cell Surface Antibodies-Reply. JAMA Neurol. 2016, 73, 891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.Y.; Kim, J.S.; Dieterich, M. Update on opsoclonus-myoclonus syndrome in adults. J. Neurol. 2019, 266, 1541–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krug, P.; Schleiermacher, G.; Michon, J.; Valteau-Couanet, D.; Brisse, H.; Peuchmaur, M.; Sarnacki, S.; Martelli, H.; Desguerre, I.; Tardieu, M. Opsoclonus-myoclonus in children associated or not with neuroblastoma. Eur. J. Paediatr. Neurol. 2010, 14, 400–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallerini, S.; Marsili, L. Pediatric opsoclonus-myoclonus syndrome: The role of functional brain connectivity studies. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2017, 59, 14–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhatia, P.; Heim, J.; Cornejo, P.; Kane, L.; Santiago, J.; Kruer, M.C. Opsoclonus-myoclonus-ataxia syndrome in children. J. Neurol. 2022, 269, 750–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dale, R.C. Childhood opsoclonus myoclonus. Lancet Neurol. 2003, 2, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, H.; Cai, W. Opsoclonus-myoclonus syndrome associated with neuroblastoma: Insights into antitumor immunity. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2022, 69, e29949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emamikhah, M.; Babadi, M.; Mehrabani, M.; Jalili, M.; Pouranian, M.; Daraie, P.; Mohaghegh, F.; Aghavali, S.; Zaribafian, M.; Rohani, M. Opsoclonus-myoclonus syndrome, a post-infectious neurologic complication of COVID-19: Case series and review of literature. J. Neurovirol. 2021, 27, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santoro, J.D.; Kerr, L.M.; Codden, R.; Casper, T.C.; Greenberg, B.M.; Waubant, E.; Kong, S.W.; Mandl, K.D.; Gorman, M.P. Increased Prevalence of Familial Autoimmune Disease in Children With Opsoclonus-Myoclonus Syndrome. Neurol. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2021, 8, e1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alburaiky, S.; Dale, R.C.; Crow, Y.J.; Jones, H.F.; Wassmer, E.; Melki, I.; Boespflug-Tanguy, O.; Do Cao, J.; Gras, D.; Sharpe, C. Opsoclonus-myoclonus in Aicardi-Goutières syndrome. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2021, 63, 1483–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graus, F. Towards a better recognition of paraneoplastic brainstem encephalitis. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2021, 92, 1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.T.; Baek, S.H.; Lee, S.U.; Kim, J.B.; Kim, J.S. Clinical Reasoning: A 48-Year-Old Woman Presenting With Vertigo, Ptosis, and Red Eyes. Neurology 2022, 98, 678–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutton, I.J.; Barnett, M.H.; Watson, J.D.; Ell, J.J.; Dalmau, J. Paraneoplastic brainstem encephalitis and anti-Ri antibodies. J. Neurol. 2002, 249, 1597–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohyagi, M.; Ishibashi, S.; Ohkubo, T.; Kobayashi, Z.; Mizusawa, H.; Yokota, T.; Emoto, H.; Kiyosawa, M. Subacute Supranuclear Palsy in anti-Hu Paraneoplastic Encephalitis. Can. J. Neurol. Sci. 2017, 44, 444–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Najjar, M.; Taylor, A.; Agrawal, S.; Fojo, T.; Merkler, A.E.; Rosenblum, M.K.; Lennihan, L.; Kluger, M.D. Anti-Hu paraneoplastic brainstem encephalitis caused by a pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor presenting with central hypoventilation. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2017, 40, 72–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berger, B.; Bischler, P.; Dersch, R.; Hottenrott, T.; Rauer, S.; Stich, O. “Non-classical” paraneoplastic neurological syndromes associated with well-characterized antineuronal antibodies as compared to “classical” syndromes—More frequent than expected. J. Neurol. Sci. 2015, 352, 58–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandel-Brehm, C.; Dubey, D.; Kryzer, T.J.; O’Donovan, B.D.; Tran, B.; Vazquez, S.E.; Sample, H.A.; Zorn, K.C.; Khan, L.M.; Bledsoe, I.O.; et al. Kelch-like Protein 11 Antibodies in Seminoma-Associated Paraneoplastic Encephalitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Schino, C.; Nunzi, M.; Colosimo, C. Subacute axial parkinsonism associated with anti-Ri antibodies. Neurol. Sci. 2021, 42, 1155–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalmau, J.; Graus, F.; Villarejo, A.; Posner, J.B.; Blumenthal, D.; Thiessen, B.; Saiz, A.; Meneses, P.; Rosenfeld, M.R. Clinical analysis of anti-Ma2-associated encephalitis. Brain 2004, 127, 1831–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, T.; Tsuji, S. Anti-Ma2-associated encephalitis and paraneoplastic limbic encephalitis. Brain Nerve 2010, 62, 838–851. [Google Scholar]
- Adams, C.; McKeon, A.; Silber, M.H.; Kumar, R. Narcolepsy, REM sleep behavior disorder, and supranuclear gaze palsy associated with Ma1 and Ma2 antibodies and tonsillar carcinoma. Arch. Neurol. 2011, 68, 521–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, F.; Marsili, L.; Truong, D.D. Parkinsonism in Viral, Paraneoplastic, and Autoimmune Diseases. J. Neurol. Sci. 2022, 433, e120014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogrig, A.; Joubert, B.; Maureille, A.; Thomas, L.; Bernard, E.; Streichenberger, N.; Cotton, F.; Ducray, F.; Honnorat, J. Motor neuron involvement in anti-Ma2-associated paraneoplastic neurological syndrome. J. Neurol. 2019, 266, 398–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomar, L.R.; Agarwal, U.; Shah, D.J.; Jain, S.; Agrawal, C.S. Jaw Dystonia and Myelopathy: Paraneoplastic Manifestations of Breast Malignancy with anti-Ri/ANNA-2 Antibody. Ann. Indian Acad. Neurol. 2021, 24, 826–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega Suero, G.; Sola-Valls, N.; Escudero, D.; Saiz, A.; Graus, F. Anti-Ma and anti-Ma2-associated paraneoplastic neurological syndromes. Neurologia 2018, 33, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunchok, A.; McKeon, A. Opsoclonus in Anti-Ma2 Brain-Stem Encephalitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, e84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orozco, E.; Valencia-Sanchez, C.; Britton, J.; Dubey, D.; Flanagan, E.P.; Lopez-Chiriboga, A.S.; Zalewski, N.; Zekeridou, A.; Pittock, S.J.; McKeon, A. Autoimmune Encephalitis Criteria in Clinical Practice. Neurol. Clin. Pract. 2023, 13, e200151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghimire, P.; Khanal, U.P.; Gajurel, B.P.; Karn, R.; Rajbhandari, R.; Paudel, S.; Gautam, N.; Ojha, R. Anti-LGI1, anti-GABABR, and Anti-CASPR2 encephalitides in Asia: A systematic review. Brain Behav. 2020, 10, e01793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alamowitch, S.; Graus, F.; Uchuya, M.; Reñé, R.; Bescansa, E.; Delattre, J.Y. Limbic encephalitis and small cell lung cancer. Clinical and immunological features. Brain 1997, 120 Pt 6, 923–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graus, F.; Keime-Guibert, F.; Reñe, R.; Benyahia, B.; Ribalta, T.; Ascaso, C.; Escaramis, G.; Delattre, J.Y. Anti-Hu-associated paraneoplastic encephalomyelitis: Analysis of 200 patients. Brain 2001, 124, 1138–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steriade, C.; Britton, J.; Dale, R.C.; Gadoth, A.; Irani, S.R.; Linnoila, J.; McKeon, A.; Shao, X.Q.; Venegas, V.; Bien, C.G. Acute symptomatic seizures secondary to autoimmune encephalitis and autoimmune-associated epilepsy: Conceptual definitions. Epilepsia 2020, 61, 1341–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, K.J.; Ji, Y.I. Anti-Hu antibody-mediated limbic encephalitis associated with cervical cancer: A case report. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. Res. 2018, 44, 1181–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silsby, M.; Clarke, C.J.; Lee, K.; Sharpe, D. Anti-Hu limbic encephalitis preceding the appearance of mediastinal germinoma by 9 years. Neurol. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2020, 7, e685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honnorat, J.; Didelot, A.; Karantoni, E.; Ville, D.; Ducray, F.; Lambert, L.; Deiva, K.; Garcia, M.; Pichit, P.; Cavillon, G.; et al. Autoimmune limbic encephalopathy and anti-Hu antibodies in children without cancer. Neurology 2013, 80, 2226–2232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalmau, J.; Tüzün, E.; Wu, H.Y.; Masjuan, J.; Rossi, J.E.; Voloschin, A.; Baehring, J.M.; Shimazaki, H.; Koide, R.; King, D.; et al. Paraneoplastic anti-N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor encephalitis associated with ovarian teratoma. Ann. Neurol. 2007, 61, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Titulaer, M.J.; McCracken, L.; Gabilondo, I.; Armangué, T.; Glaser, C.; Iizuka, T.; Honig, L.S.; Benseler, S.M.; Kawachi, I.; Martinez-Hernandez, E.; et al. Treatment and prognostic factors for long-term outcome in patients with anti-NMDA receptor encephalitis: An observational cohort study. Lancet Neurol. 2013, 12, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bost, C.; Chanson, E.; Picard, G.; Meyronet, D.; Mayeur, M.E.; Ducray, F.; Rogemond, V.; Psimaras, D.; Antoine, J.C.; Delattre, J.Y.; et al. Malignant tumors in autoimmune encephalitis with anti-NMDA receptor antibodies. J. Neurol. 2018, 265, 2190–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakraborty, A.P.; Pandit, A.; Ray, B.K.; Mukherjee, A.; Dubey, S. Capgras syndrome and confabulation unfurling anti NMDAR encephalitis with classical papillary thyroid carcinoma: First reported case. J. Neuroimmunol. 2021, 357, 577611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Li, B.; Li, X.; Lai, Z. Anti-N-Methyl-D-Aspartate Receptor Encephalitis Associated with Clear Cell Renal Carcinoma: A Case Report. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalhout, S.Z.; Emerick, K.S.; Sadow, P.M.; Linnoila, J.J.; Miller, D.M. Regionally Metastatic Merkel Cell Carcinoma Associated with Paraneoplastic Anti-N-methyl-D-aspartate Receptor Encephalitis. Case Rep. Oncol. Med. 2020, 2020, 1257587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prüss, H.; Finke, C.; Höltje, M.; Hofmann, J.; Klingbeil, C.; Probst, C.; Borowski, K.; Ahnert-Hilger, G.; Harms, L.; Schwab, J.M.; et al. N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor antibodies in herpes simplex encephalitis. Ann. Neurol. 2012, 72, 902–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leypoldt, F.; Titulaer, M.J.; Aguilar, E.; Walther, J.; Bönstrup, M.; Havemeister, S.; Teegen, B.; Lütgehetmann, M.; Rosenkranz, M.; Magnus, T.; et al. Herpes simplex virus-1 encephalitis can trigger anti-NMDA receptor encephalitis: Case report. Neurology 2013, 81, 1637–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salovin, A.; Glanzman, J.; Roslin, K.; Armangue, T.; Lynch, D.R.; Panzer, J.A. Anti-NMDA receptor encephalitis and nonencephalitic HSV-1 infection. Neurol. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2018, 5, e458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Lan, T.; Bai, R.; Jiang, S.; Cai, J.; Ren, L. HSV encephalitis triggered anti-NMDAR encephalitis: A case report. Neurol. Sci. 2021, 42, 857–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Yan, B.; Wang, R.; Li, C.; Chen, C.; Zhou, D.; Hong, Z. Seizure outcomes in patients with anti-NMDAR encephalitis: A follow-up study. Epilepsia 2017, 58, 2104–2111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmitt, S.E.; Pargeon, K.; Frechette, E.S.; Hirsch, L.J.; Dalmau, J.; Friedman, D. Extreme delta brush: A unique EEG pattern in adults with anti-NMDA receptor encephalitis. Neurology 2012, 79, 1094–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moise, A.M.; Karakis, I.; Herlopian, A.; Dhakar, M.; Hirsch, L.J.; Cotsonis, G.; LaRoche, S.; Cabrera Kang, C.M.; Westover, B.; Rodriguez, A. Continuous EEG Findings in Autoimmune Encephalitis. J. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2021, 38, 124–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalmau, J.; Armangué, T.; Planagumà, J.; Radosevic, M.; Mannara, F.; Leypoldt, F.; Geis, C.; Lancaster, E.; Titulaer, M.J.; Rosenfeld, M.R.; et al. An update on anti-NMDA receptor encephalitis for neurologists and psychiatrists: Mechanisms and models. Lancet Neurol. 2019, 18, 1045–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irani, S.R.; Alexander, S.; Waters, P.; Kleopa, K.A.; Pettingill, P.; Zuliani, L.; Peles, E.; Buckley, C.; Lang, B.; Vincent, A. Antibodies to Kv1 potassium channel-complex proteins leucine-rich, glioma inactivated 1 protein and contactin-associated protein-2 in limbic encephalitis, Morvan’s syndrome and acquired neuromyotonia. Brain 2010, 133, 2734–2748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irani, S.R.; Pettingill, P.; Kleopa, K.A.; Schiza, N.; Waters, P.; Mazia, C.; Zuliani, L.; Watanabe, O.; Lang, B.; Buckley, C.; et al. Morvan syndrome: Clinical and serological observations in 29 cases. Ann. Neurol. 2012, 72, 241–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benoit, J.; Muñiz-Castrillo, S.; Vogrig, A.; Farina, A.; Pinto, A.L.; Picard, G.; Rogemond, V.; Guery, D.; Alentorn, A.; Psimaras, D.; et al. Early-Stage Contactin-Associated Protein-like 2 Limbic Encephalitis: Clues for Diagnosis. Neurol. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2023, 10, e200041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Sonderen, A.; Thijs, R.D.; Coenders, E.C.; Jiskoot, L.C.; Sanchez, E.; de Bruijn, M.A.; van Coevorden-Hameete, M.H.; Wirtz, P.W.; Schreurs, M.W.; Sillevis Smitt, P.A.; et al. Anti-LGI1 encephalitis: Clinical syndrome and long-term follow-up. Neurology 2016, 87, 1449–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffith, S.P.; Malpas, C.B.; Alpitsis, R.; O’Brien, T.J.; Monif, M. The neuropsychological spectrum of anti-LGI1 antibody mediated autoimmune encephalitis. J. Neuroimmunol. 2020, 345, 577271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, A.; Klein, C.J.; Sechi, E.; Alden, E.; Basso, M.R.; Pudumjee, S.; Pittock, S.J.; McKeon, A.; Britton, J.W.; Lopez-Chiriboga, A.S.; et al. LGI1 antibody encephalitis: Acute treatment comparisons and outcome. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry. 2022, 93, 309–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, N.; Hao, H.; Guan, H.; Sun, H.; Liu, Q.; Lu, Q.; Jin, L.; Ren, H.; Huang, Y. Sleep Disorders in Leucine-Rich Glioma-Inactivated Protein 1 and Contactin Protein-Like 2 Antibody-Associated Diseases. Front. Neurol. 2020, 11, 696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piffer, S.; Cantalupo, G.; Filipponi, S.; Poretto, V.; Pellegrini, M.; Tanel, R.; Buganza, M.; Giometto, B. Agrypnia excitata as the main feature in anti-leucine-rich glioma-inactivated 1 encephalitis: A detailed clinical and polysomnographic semiological analysis. Eur. J. Neurol. 2022, 29, 890–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldelli, L.; Provini, F. Differentiating Oneiric Stupor in Agrypnia Excitata From Dreaming Disorders. Front. Neurol. 2020, 11, 565694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graus, F.; Titulaer, M.J.; Balu, R.; Benseler, S.; Bien, C.G.; Cellucci, T.; Cortese, I.; Dale, R.C.; Gelfand, J.M.; Geschwind, M.; et al. A clinical approach to diagnosis of autoimmune encephalitis. Lancet Neurol. 2016, 15, 391–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhang, M.; Wei, M.; Huang, Z.; Ye, J.; Liu, A.; Wang, Y. LGI1 antibody-associated encephalitis without evidence of inflammation in CSF and brain MRI. Acta Neurol. Belg. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abgrall, G.; Demeret, S.; Rohaut, B.; Leu-Semenescu, S.; Arnulf, I. Status dissociatus and disturbed dreaming in a patient with Morvan syndrome plus myasthenia gravis. Sleep Med. 2015, 16, 894–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagappa, M.; Mahadevan, A.; Sinha, S.; Bindu, P.S.; Mathuranath, P.S.; Bineesh, C.; Bharath, R.D.; Taly, A.B. Fatal Morvan Syndrome Associated With Myasthenia Gravis. Neurologist 2017, 22, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyko, M.; Au, K.L.K.; Casault, C.; de Robles, P.; Pfeffer, G. Systematic review of the clinical spectrum of CASPR2 antibody syndrome. J. Neurol. 2020, 267, 1137–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lancaster, E.; Lai, M.; Peng, X.; Hughes, E.; Constantinescu, R.; Raizer, J.; Friedman, D.; Skeen, M.B.; Grisold, W.; Kimura, A.; et al. Antibodies to the GABA(B) receptor in limbic encephalitis with seizures: Case series and characterisation of the antigen. Lancet Neurol. 2010, 9, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Höftberger, R.; Titulaer, M.J.; Sabater, L.; Dome, B.; Rózsás, A.; Hegedus, B.; Hoda, M.A.; Laszlo, V.; Ankersmit, H.J.; Harms, L.; et al. Encephalitis and GABAB receptor antibodies: Novel findings in a new case series of 20 patients. Neurology 2013, 81, 1500–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Bruijn, M.; van Sonderen, A.; van Coevorden-Hameete, M.H.; Bastiaansen, A.E.M.; Schreurs, M.W.J.; Rouhl, R.P.W.; van Donselaar, C.A.; Majoie, M.; Neuteboom, R.F.; Sillevis Smitt, P.A.E.; et al. Evaluation of seizure treatment in anti-LGI1, anti-NMDAR, and anti-GABA(B)R encephalitis. Neurology 2019, 92, e2185–e2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Fan, S.; Ren, H.; Zhou, L.; Guan, H. Clinical characteristics and prognosis of anti-alpha-Amino-3-Hydroxy-5-Methyl-4-Isoxazolepropionic acid receptor encephalitis. BMC Neurol. 2021, 21, 490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joubert, B.; Kerschen, P.; Zekeridou, A.; Desestret, V.; Rogemond, V.; Chaffois, M.O.; Ducray, F.; Larrue, V.; Daubail, B.; Idbaih, A.; et al. Clinical Spectrum of Encephalitis Associated With Antibodies Against the α-Amino-3-Hydroxy-5-Methyl-4-Isoxazolepropionic Acid Receptor: Case Series and Review of the Literature. JAMA Neurol. 2015, 72, 1163–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Höftberger, R.; van Sonderen, A.; Leypoldt, F.; Houghton, D.; Geschwind, M.; Gelfand, J.; Paredes, M.; Sabater, L.; Saiz, A.; Titulaer, M.J.; et al. Encephalitis and AMPA receptor antibodies: Novel findings in a case series of 22 patients. Neurology 2015, 84, 2403–2412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKeon, A.; Robinson, M.T.; McEvoy, K.M.; Matsumoto, J.Y.; Lennon, V.A.; Ahlskog, J.E.; Pittock, S.J. Stiff-man syndrome and variants: Clinical course, treatments, and outcomes. Arch. Neurol. 2012, 69, 230–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Hernandez, E.; Ariño, H.; McKeon, A.; Iizuka, T.; Titulaer, M.J.; Simabukuro, M.M.; Lancaster, E.; Petit-Pedrol, M.; Planagumà, J.; Blanco, Y.; et al. Clinical and Immunologic Investigations in Patients With Stiff-Person Spectrum Disorder. JAMA Neurol. 2016, 73, 714–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budhram, A.; Sechi, E.; Flanagan, E.P.; Dubey, D.; Zekeridou, A.; Shah, S.S.; Gadoth, A.; Naddaf, E.; McKeon, A.; Pittock, S.J.; et al. Clinical spectrum of high-titre GAD65 antibodies. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2021, 92, 645–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasaki, A.; Kato, T.; Ujiie, H.; Wakasa, S.; Otake, S.; Kikuchi, K.; Ohno, K. Thymoma-Related Stiff-Person Syndrome with Successfully Treated by Surgery. Ann. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2022, 28, 448–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murinson, B.B.; Guarnaccia, J.B. Stiff-person syndrome with amphiphysin antibodies: Distinctive features of a rare disease. Neurology 2008, 71, 1955–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKeon, A.; Pittock, S.J.; Lennon, V.A. Stiff-person syndrome with amphiphysin antibodies: Distinctive features of a rare disease. Neurology 2009, 73, 2132–2133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvajal-González, A.; Leite, M.I.; Waters, P.; Woodhall, M.; Coutinho, E.; Balint, B.; Lang, B.; Pettingill, P.; Carr, A.; Sheerin, U.M.; et al. Glycine receptor antibodies in PERM and related syndromes: Characteristics, clinical features and outcomes. Brain 2014, 137, 2178–2192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balint, B.; Jarius, S.; Nagel, S.; Haberkorn, U.; Probst, C.; Blöcker, I.M.; Bahtz, R.; Komorowski, L.; Stöcker, W.; Kastrup, A.; et al. Progressive encephalomyelitis with rigidity and myoclonus: A new variant with DPPX antibodies. Neurology 2014, 82, 1521–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobin, W.O.; Lennon, V.A.; Komorowski, L.; Probst, C.; Clardy, S.L.; Aksamit, A.J.; Appendino, J.P.; Lucchinetti, C.F.; Matsumoto, J.Y.; Pittock, S.J.; et al. DPPX potassium channel antibody: Frequency, clinical accompaniments, and outcomes in 20 patients. Neurology 2014, 83, 1797–1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKeon, A.; Martinez-Hernandez, E.; Lancaster, E.; Matsumoto, J.Y.; Harvey, R.J.; McEvoy, K.M.; Pittock, S.J.; Lennon, V.A.; Dalmau, J. Glycine receptor autoimmune spectrum with stiff-man syndrome phenotype. JAMA Neurol. 2013, 70, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, P.W.; Chang, J.W. Immune checkpoint inhibitors win the 2018 Nobel Prize. Biomed. J. 2019, 42, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guidon, A.C.; Burton, L.B.; Chwalisz, B.K.; Hillis, J.; Schaller, T.H.; Amato, A.A.; Betof Warner, A.; Brastianos, P.K.; Cho, T.A.; Clardy, S.L.; et al. Consensus disease definitions for neurologic immune-related adverse events of immune checkpoint inhibitors. J. Immunother. Cancer 2021, 9, e002890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marini, A.; Bernardini, A.; Gigli, G.L.; Valente, M.; Muñiz-Castrillo, S.; Honnorat, J.; Vogrig, A. Neurologic Adverse Events of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors: A Systematic Review. Neurology 2021, 96, 754–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marsili, L.; Vogrig, A.; Colosimo, C. Movement Disorders in Oncology: From Clinical Features to Biomarkers. Biomedicines 2021, 10, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graus, F.; Dalmau, J. Paraneoplastic neurological syndromes in the era of immune-checkpoint inhibitors. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 16, 535–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogrig, A.; Fouret, M.; Joubert, B.; Picard, G.; Rogemond, V.; Pinto, A.L.; Muñiz-Castrillo, S.; Roger, M.; Raimbourg, J.; Dayen, C.; et al. Increased frequency of anti-Ma2 encephalitis associated with immune checkpoint inhibitors. Neurol. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2019, 6, e604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zekeridou, A.; Kryzer, T.; Guo, Y.; Hassan, A.; Lennon, V.; Lucchinetti, C.F.; Pittock, S.; McKeon, A. Phosphodiesterase 10A IgG: A novel biomarker of paraneoplastic neurologic autoimmunity. Neurology 2019, 93, e815–e822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giommoni, E.; Giorgione, R.; Paderi, A.; Pellegrini, E.; Gambale, E.; Marini, A.; Antonuzzo, A.; Marconcini, R.; Roviello, G.; Matucci-Cerinic, M.; et al. Eosinophil Count as Predictive Biomarker of Immune-Related Adverse Events (irAEs) in Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors (ICIs) Therapies in Oncological Patients. Immuno 2021, 1, 253–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrinjaquet, C.; Desbaillets, N.; Hottinger, A.F. Neurotoxicity associated with cancer immunotherapy: Immune checkpoint inhibitors and chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2019, 32, 500–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santomasso, B.D.; Park, J.H.; Salloum, D.; Riviere, I.; Flynn, J.; Mead, E.; Halton, E.; Wang, X.; Senechal, B.; Purdon, T.; et al. Clinical and Biological Correlates of Neurotoxicity Associated with CAR T-cell Therapy in Patients with B-cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Cancer Discov. 2018, 8, 958–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torre, M.; Solomon, I.H.; Sutherland, C.L.; Nikiforow, S.; DeAngelo, D.J.; Stone, R.M.; Vaitkevicius, H.; Galinsky, I.A.; Padera, R.F.; Trede, N.; et al. Neuropathology of a Case With Fatal CAR T-Cell-Associated Cerebral Edema. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2018, 77, 877–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neelapu, S.S.; Tummala, S.; Kebriaei, P.; Wierda, W.; Gutierrez, C.; Locke, F.L.; Komanduri, K.V.; Lin, Y.; Jain, N.; Daver, N.; et al. Chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy—Assessment and management of toxicities. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 15, 47–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gövert, F.; Leypoldt, F.; Junker, R.; Wandinger, K.P.; Deuschl, G.; Bhatia, K.P.; Balint, B. Antibody-related movement disorders—A comprehensive review of phenotype-autoantibody correlations and a guide to testing. Neurol. Res. Pract. 2020, 2, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balint, B.; Vincent, A.; Meinck, H.M.; Irani, S.R.; Bhatia, K.P. Movement disorders with neuronal antibodies: Syndromic approach, genetic parallels and pathophysiology. Brain 2018, 141, 13–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, T.T. Paraneoplastic autoimmune movement disorders. Park. Relat. Disord. 2017, 44, 106–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Budhram, A.; Dubey, D.; Sechi, E.; Flanagan, E.P.; Yang, L.; Bhayana, V.; McKeon, A.; Pittock, S.J.; Mills, J.R. Neural Antibody Testing in Patients with Suspected Autoimmune Encephalitis. Clin. Chem. 2020, 66, 1496–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayo Clinic Laboratories. Available online: https://www.mayocliniclabs.com (accessed on 1 January 2023).
- Dubey, D.; Pittock, S.J.; McKeon, A. Antibody Prevalence in Epilepsy and Encephalopathy score: Increased specificity and applicability. Epilepsia 2019, 60, 367–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalmau, J.; Graus, F. Autoimmune Encephalitis-Misdiagnosis, Misconceptions, and How to Avoid Them. JAMA Neurol. 2023, 80, 12–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valencia-Sanchez, C.; Pittock, S.J.; Mead-Harvey, C.; Dubey, D.; Flanagan, E.P.; Lopez-Chiriboga, S.; Trenerry, M.R.; Zalewski, N.L.; Zekeridou, A.; McKeon, A. Brain dysfunction and thyroid antibodies: Autoimmune diagnosis and misdiagnosis. Brain Commun. 2021, 3, fcaa233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoccarato, M.; Valeggia, S.; Zuliani, L.; Gastaldi, M.; Mariotto, S.; Franciotta, D.; Ferrari, S.; Lombardi, G.; Zagonel, V.; De Gaspari, P.; et al. Conventional brain MRI features distinguishing limbic encephalitis from mesial temporal glioma. Neuroradiology 2019, 61, 853–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, R.M.; Vandenberghe, R.; Garcia-Merino, A.; Yamamoto, T.; Landolfi, J.C.; Rosenfeld, M.R.; Rossi, J.E.; Thiessen, B.; Dropcho, E.J.; Dalmau, J. Orchiectomy for suspected microscopic tumor in patients with anti-Ma2-associated encephalitis. Neurology 2007, 68, 900–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas-Marcos, I.; Graus, F.; Sanz, G.; Robledo, A.; Diaz-Espejo, C. Hypersomnia as presenting symptom of anti-Ma2-associated encephalitis: Case study. Neuro Oncol. 2007, 9, 75–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, F. Autoimmune choreas. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2017, 88, 412–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Titulaer, M.J.; Soffietti, R.; Dalmau, J.; Gilhus, N.E.; Giometto, B.; Graus, F.; Grisold, W.; Honnorat, J.; Sillevis Smitt, P.A.; Tanasescu, R.; et al. Screening for tumours in paraneoplastic syndromes: Report of an EFNS task force. Eur. J. Neurol. 2011, 18, 19.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zoccarato, M.; Gastaldi, M.; Zuliani, L.; Biagioli, T.; Brogi, M.; Bernardi, G.; Corsini, E.; Bazzigaluppi, E.; Fazio, R.; Giannotta, C.; et al. Diagnostics of paraneoplastic neurological syndromes. Neurol. Sci. 2017, 38, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalakas, M.C.; Fujii, M.; Li, M.; Lutfi, B.; Kyhos, J.; McElroy, B. High-dose intravenous immune globulin for stiff-person syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001, 345, 1870–1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubey, D.; Britton, J.; McKeon, A.; Gadoth, A.; Zekeridou, A.; Lopez Chiriboga, S.A.; Devine, M.; Cerhan, J.H.; Dunlay, K.; Sagen, J.; et al. Randomized Placebo-Controlled Trial of Intravenous Immunoglobulin in Autoimmune LGI1/CASPR2 Epilepsy. Ann. Neurol. 2020, 87, 313–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Comprehensive Cancer Network. Available online: https://www.nccn.org/login?ReturnURL=https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/immunotherapy.pdf (accessed on 29 September 2021).
- Vogrig, A.; Muñiz-Castrillo, S.; Joubert, B.; Picard, G.; Rogemond, V.; Marchal, C.; Chiappa, A.M.; Chanson, E.; Skowron, F.; Leblanc, A.; et al. Central nervous system complications associated with immune checkpoint inhibitors. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2020, 91, 772–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimura, M.; Yamamoto, T.; Iso-o, N.; Imafuku, I.; Momose, T.; Shirouzu, I.; Kwak, S.; Kanazawa, I. Hemiparkinsonism associated with a mesencephalic tumor. J. Neurol. Sci. 2002, 197, 89–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hébert, J.; Riche, B.; Vogrig, A.; Muñiz-Castrillo, S.; Joubert, B.; Picard, G.; Rogemond, V.; Psimaras, D.; Alentorn, A.; Berzero, G.; et al. Epidemiology of paraneoplastic neurologic syndromes and autoimmune encephalitides in France. Neurol. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2020, 7, e883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthew, J.E.; Shih-Hon, L.; Evan, R.; James, F.B.; Ben, R.C.; Anna, G.; Mousumi, B.; Brian, C.C. Unintended consequences of Mayo paraneoplastic evaluations. Neurology 2018, 91, e2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seluk, L.; Taliansky, A.; Yonath, H.; Gilburd, B.; Amital, H.; Shoenfeld, Y.; Kivity, S. A large screen for paraneoplastic neurological autoantibodies; diagnosis and predictive values. Clin. Immunol. 2019, 199, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaig, C.; Graus, F.; Compta, Y.; Högl, B.; Bataller, L.; Brüggemann, N.; Giordana, C.; Heidbreder, A.; Kotschet, K.; Lewerenz, J.; et al. Clinical manifestations of the anti-IgLON5 disease. Neurology 2017, 88, 1736–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Escudero, D.; Guasp, M.; Ariño, H.; Gaig, C.; Martínez-Hernández, E.; Dalmau, J.; Graus, F. Antibody-associated CNS syndromes without signs of inflammation in the elderly. Neurology 2017, 89, 1471–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hébert, J.; Gros, P.; Lapointe, S.; Amtashar, F.S.; Steriade, C.; Maurice, C.; Wennberg, R.A.; Day, G.S.; Tang-Wai, D.F. Searching for autoimmune encephalitis: Beware of normal CSF. J. Neuroimmunol. 2020, 345, 577285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabater, L.; Gaig, C.; Gelpi, E.; Bataller, L.; Lewerenz, J.; Torres-Vega, E.; Contreras, A.; Giometto, B.; Compta, Y.; Embid, C.; et al. A novel non-rapid-eye movement and rapid-eye-movement parasomnia with sleep breathing disorder associated with antibodies to IgLON5: A case series, characterisation of the antigen, and post-mortem study. Lancet Neurol. 2014, 13, 575–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grüter, T.; Möllers, F.E.; Tietz, A.; Dargvainiene, J.; Melzer, N.; Heidbreder, A.; Strippel, C.; Kraft, A.; Höftberger, R.; Schöberl, F.; et al. Clinical, serological and genetic predictors of response to immunotherapy in anti-IgLON5 disease. Brain 2023, 146, 600–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadoth, A.; Pittock, S.J.; Dubey, D.; McKeon, A.; Britton, J.W.; Schmeling, J.E.; Smith, A.; Kotsenas, A.L.; Watson, R.E.; Lachance, D.H.; et al. Expanded phenotypes and outcomes among 256 LGI1/CASPR2-IgG-positive patients. Ann. Neurol. 2017, 82, 79–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannoccaro, M.P.; Gastaldi, M.; Rizzo, G.; Jacobson, L.; Vacchiano, V.; Perini, G.; Capellari, S.; Franciotta, D.; Costa, A.; Liguori, R.; et al. Antibodies to neuronal surface antigens in patients with a clinical diagnosis of neurodegenerative disorder. Brain Behav. Immun. 2021, 96, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannoccaro, M.P.; Crisp, S.J.; Vincent, A. Antibody-mediated central nervous system diseases. Brain Neurosci. Adv. 2018, 2, 2398212818817497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Li, L. Autoantibodies in Alzheimer’s disease: Potential biomarkers, pathogenic roles, and therapeutic implications. J. Biomed. Res. 2016, 30, 361–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannoccaro, M.P.; Verde, F.; Morelli, L.; Rizzo, G.; Ricciardiello, F.; Liguori, R. Neural Surface Antibodies and Neurodegeneration: Clinical Commonalities and Pathophysiological Relationships. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espay, A.J. Is Pathology Always the Diagnostic Gold Standard in Neurodegeneration? Mov. Disord. Clin. Pract. 2022, 9, 1152–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



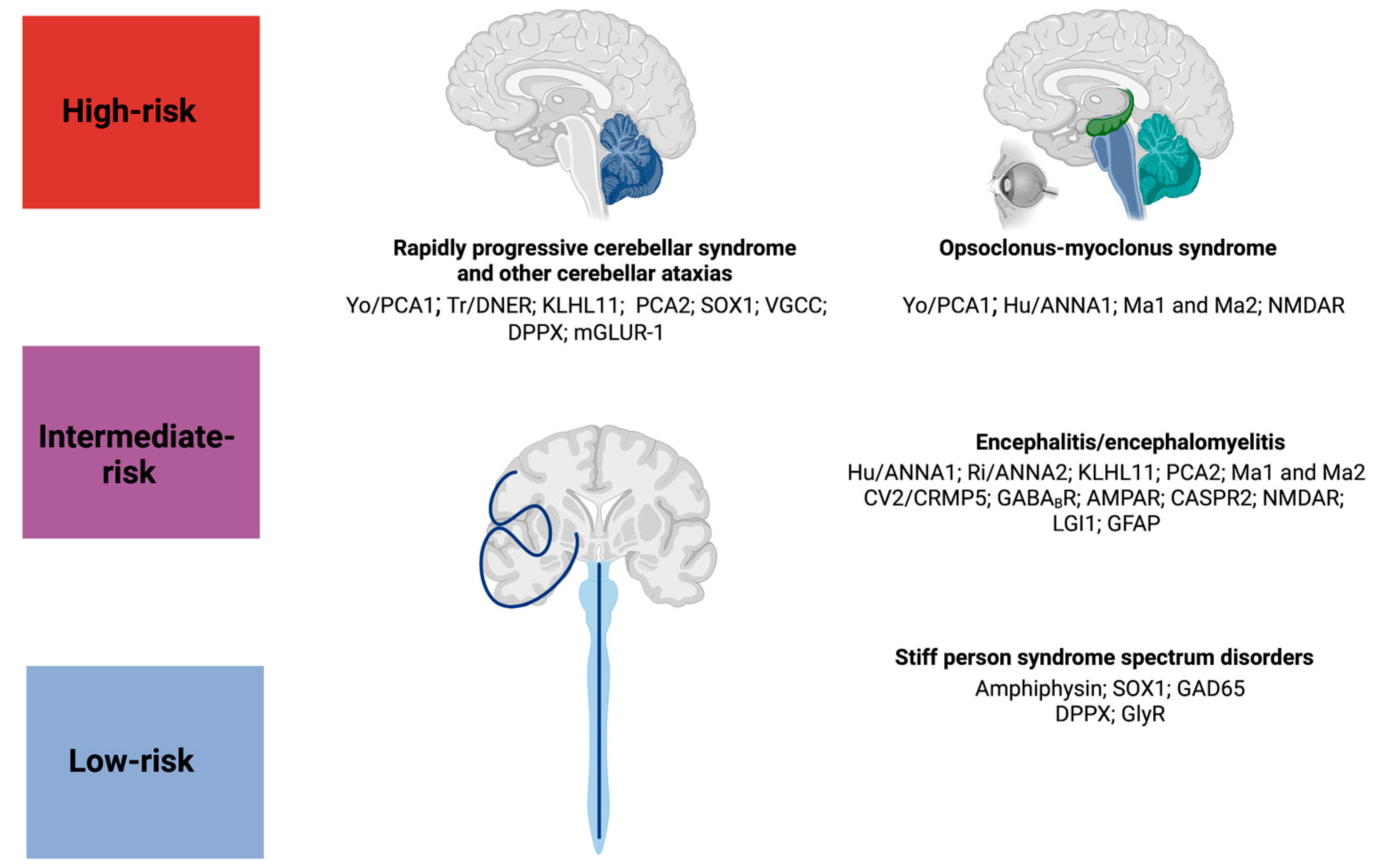
| Antibody | Cancer Type | Paraneoplastic Neurological Syndrome |
|---|---|---|
| High-Risk | ||
| Anti-Yo/PCA1 | Breast cancer, ovarian cancer | Rapidly progressive cerebellar syndrome, OMS |
| Anti-Hu/ANNA1 | SCLC, NSCLC | Limbic encephalitis, encephalomyelitis, OMS |
| Anti-Ri/ANNA2 | Breast cancer in women, lung cancer in men | Brainstem encephalitis |
| Anti-Tr/DNER | Hodgkin lymphoma | Rapidly progressive cerebellar syndrome |
| Anti- KLHL11 | Testicular germ cell cancer | Brainstem encephalitis, rapidly progressive cerebellar syndrome |
| Anti-PCA2 | SCLC, NSCLC, breast cancer | Rapidly progressive cerebellar syndrome, encephalitis |
| Anti-Ma1 and Ma2 | Testicular cancer and NSCLC | Limbic and brainstem encephalitis, OMS |
| Anti-CV2/CRMP5 | SCLC and thymoma | Encephalitis, encephalomyelitis |
| Anti-Amphiphysin | SCLC and breast cancer | SPSD |
| Anti-SOX1 | SCLC | Rapidly progressive cerebellar syndrome, SPSD |
| Intermediate-risk | ||
| Anti-GABABR | SCLC | Limbic encephalitis |
| Anti-AMPAR | SCLC and thymoma | Limbic encephalitis |
| Anti-CASPR2 | Thymoma | Morvan syndrome, Limbic encephalitis |
| Anti-NMDAR | Ovarian or extra-ovarian teratoma | Encephalitis, OMS |
| Anti-VGCC | SCLC | Rapidly progressive cerebellar syndrome |
| Low-risk | ||
| Anti-LGI1 | Thymoma | Limbic encephalitis |
| Anti-GAD65 | SCLC and thymoma (rare) | SPSD |
| Anti-DPPX | Lymphoma | SPSD, PERM, cerebellar ataxia |
| Anti-GFAP | Ovarian teratoma and adenocarcinoma | Meningoencephalitis |
| Anti-GlyR | Lymphoma, thymoma, and lung cancer | SPSD, PERM |
| Anti-mGLUR-1 | Lymphoma | Cerebellar ataxia |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Marsili, L.; Marcucci, S.; LaPorta, J.; Chirra, M.; Espay, A.J.; Colosimo, C. Paraneoplastic Neurological Syndromes of the Central Nervous System: Pathophysiology, Diagnosis, and Treatment. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 1406. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11051406
Marsili L, Marcucci S, LaPorta J, Chirra M, Espay AJ, Colosimo C. Paraneoplastic Neurological Syndromes of the Central Nervous System: Pathophysiology, Diagnosis, and Treatment. Biomedicines. 2023; 11(5):1406. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11051406
Chicago/Turabian StyleMarsili, Luca, Samuel Marcucci, Joseph LaPorta, Martina Chirra, Alberto J. Espay, and Carlo Colosimo. 2023. "Paraneoplastic Neurological Syndromes of the Central Nervous System: Pathophysiology, Diagnosis, and Treatment" Biomedicines 11, no. 5: 1406. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11051406
APA StyleMarsili, L., Marcucci, S., LaPorta, J., Chirra, M., Espay, A. J., & Colosimo, C. (2023). Paraneoplastic Neurological Syndromes of the Central Nervous System: Pathophysiology, Diagnosis, and Treatment. Biomedicines, 11(5), 1406. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11051406