A Holistic Perspective on How Photobiomodulation May Influence Fatigue, Pain, and Depression in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Beyond Molecular Mechanisms
Abstract
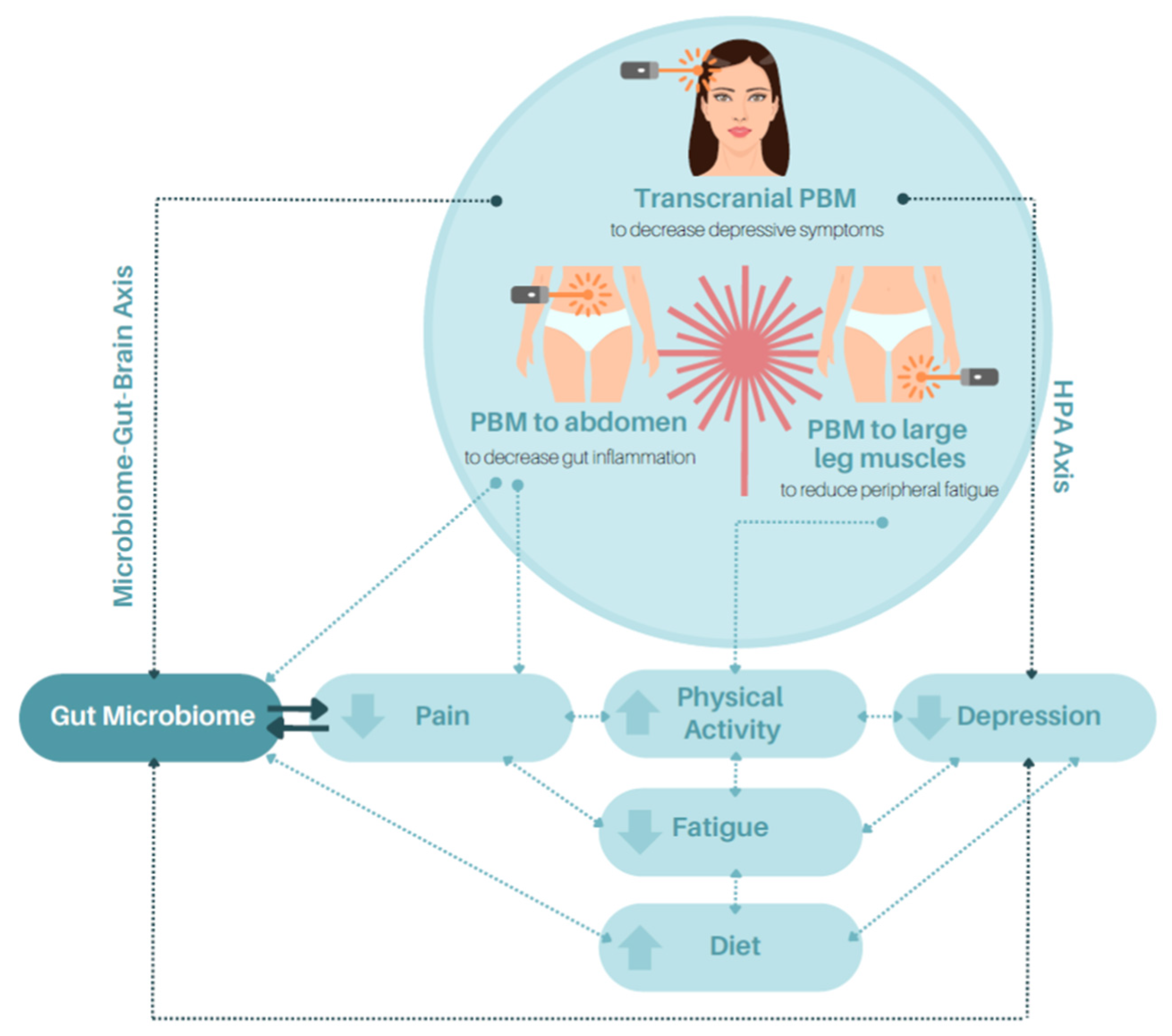
:1. Background
2. PBM and the Microbiome
3. PBM, the Microbiome–Gut–Brain Axis and Hypothalamic–Pituitary–Adrenal Axis
4. PBM and the Attenuation of Inflammation (Inflammasome) in IBD
5. PBM and IBD-Related Pain
6. PBM, Fatigue, and Depression
6.1. The Potential Role of PBM in Mitigating Peripheral Fatigue
6.2. Impact of PBM in Alleviating Central Fatigue and Depression
7. PBM, Quality of Life, and Well-Being
8. PBM Adverse Reactions
9. Summary and Implications
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cronshaw, M.; Parker, S.; Arany, P. Feeling the heat: Evolutionary and microbial basis for the analgesic mechanisms of photobiomodulation therapy. Photobiomodul. Photomed. Laser Surg. 2019, 37, 517–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Freitas, L.D.; Hamblin, M.R. Proposed mechanisms of photobiomodulation or low-level light therapy. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum. Electron. 2016, 22, 7000417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamblin, M.R. Mechanisms and mitochondrial redox signaling in photobiomodulation. Photochem. Photobiol. 2018, 94, 199–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liebert, A.D.; Bicknell, B.T.; Adams, R.D. Protein conformational modulation by photons: A mechanism for laser treatment effects. Med. Hypotheses 2014, 82, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommer, A.P. Mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase is not the primary acceptor for near infrared light—It is mitochondrial bound water: The principles of low-level light therapy. Ann. Transl. Med. 2019, 7 (Suppl. S1), S13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, R.T.; David, M.A.; Armati, P.J. 830 nm laser irradiation induces varicosity formation, reduces mitochondrial membrane potential and blocks fast axonal flow in small and medium diameter rat dorsal root ganglion neurons: Implications for the analgesic effects of 830 nm laser. J. Peripher. Nerv. Syst. 2007, 2, 28–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walski, T.; Dąbrowska, K.; Drohomirecka, A.; Jędruchniewicz, N.; Trochanowska-Pauk, N.; Witkiewicz, W.; Komorowska, M. The effect of red-to-near-infrared (R/NIR) irradiation on inflammatory processes. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2019, 95, 1326–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liebert, A.D.; Chow, R.T.; Bicknell, B.T.; Varigos, E. Neuroprotective effects against POCD by photobiomodulation: Evidence from assembly/disassembly of the cytoskeleton. J. Exp. Neurosci. 2016, 10, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholson, D.J. The concept of mechanism in biology. Stud. Hist Philos. Biol. Biomed. Sci. 2012, 43, 152–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camolesi, G.C.V.; Marichalar-Mendía, X.; Padín-Iruegas, M.E.; Spanemberg, J.C.; López-López, J.; Blanco-Carrión, A.; Gándara-Vila, P.; Gallas-Torreira, M.; Pérez-Sayáns, M. Efficacy of photobiomodulation in reducing pain and improving the quality of life in patients with idiopathic burning mouth syndrome. A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lasers Med. Sci. 2022, 37, 2123–2133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, D.B.; Xavier, R.J. From genetics of inflammatory bowel disease towards mechanistic insights. Trends Immunol. 2013, 34, 371–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Souza, H.S.; Fiocchi, C.; Iliopoulos, D. The IBD interactome: An integrated view of aetiology, pathogenesis and therapy. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 14, 739–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyengar, R. Complex diseases require complex therapies. EMBO Rep. 2013, 14, 1039–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.R.; Rodriguez, J.R. Clinical presentation of Crohn’s, ulcerative colitis, and indeterminate colitis: Symptoms, extraintestinal manifestations, and disease phenotypes. Semin. Pediatr. Surg 2017, 26, 349–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perler, B.K.; Ungaro, R.; Baird, G.; Mallette, M.; Bright, R.; Shah, S.; Shapiro, J.; Sands, B.E. Presenting symptoms in inflammatory bowel disease: Descriptive analysis of a community-based inception cohort. BMC Gastroenterol. 2019, 19, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gracie, D.J.; Ford, A.C. Psychological comorbidity and inflammatory bowel disease activity: Cause or effect? Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 14, 1061–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hindryckx, P.; Laukens, D.; D’Amico, F.; Danese, S. Unmet needs in IBD: The case of fatigue. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2018, 55, 368–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liebert, A.; Bicknell, B.; Johnstone, D.M.; Gordon, L.C.; Kiat, H.; Hamblin, M.R. ‘‘Photobiomics’’: Can light, including photobiomodulation, alter the microbiome? Photobiomodul. Photomed. Laser Surg. 2019, 37, 681–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bicknell, B.; Liebert, A.; McLachlan, C.S.; Kiat, H. Microbiome changes in humans with Parkinson’s disease after photobiomodulation therapy: A retrospective study. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bicknell, B.; Laakso, E.-L.; Liebert, A.D.; Kiat, H. Modifying the microbiome as a mechanism of photobiomodulation: A case report. Photobiomodul. Photomed. Laser Surg. 2022, 40, 88–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnstone, D.M.; Hamilton, C.; Gordon, L.C.; Moro, C.; Torres, N.; Nicklason, F.; Stone, J.; Benabid, A.-L.; Mitrofanis, J. Exploring the use of intracranial and extracranial (remote) photobiomodulation devices in Parkinson’s disease: A comparison of direct and indirect systemic stimulations. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2021, 83, 1399–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borovikova, L.V.; Ivanova, S.; Zhang, M.; Yang, H.; Botchkina, G.I.; Watkins, L.R.; Wang, H.; Abumrad, N.; Eaton, J.W.; Tracey, K.J. Vagus nerve stimulation attenuates the systemic inflammatory response to endotoxin. Nature 2000, 405, 458–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laakso, E.L.; Cramond, T.; Richardson, C.; Galligan, J.P. Plasma ACTH and β-endorphin levels in response to low level laser therapy (LLLT) for myofascial trigger points. Laser Ther. 1994, 6, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKirdy, J. The Effect of Low Level Laser Therapy on Sympathetic Nervous System Activity in Chronic Lateral Epicondylalgia. Ph.D. Dissertation, Griffith University, Gold Coast, Australia, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Laakso, E.-L.; Meppem, P.; Mitchell, G.; White, C. The effect of 780 nm laser treatment on lateral epicondylalgia—A single case study. In Proceedings of the World Association of Laser Therapy Conference, Limassol, Cypress, 25–28 October 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Laakso, E.-L.; Spencer, S.; King, K.; Preston, E.; Borg, M.; Diminic, L. Effect of combining laser and magnet therapy to induce sympathoexcitation in a subject with lateral epicondylalgia. In Proceedings of the World Association of Laser Therapy Conference, Limassol, Cypress, 25–28 October 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Lindgren, S.; Stewenius, J.; Sjolund, K.; Lilja, B.; Sundkvist, G. Autonomic vagal nerve dysfunction in patients with ulcerative colitis. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 1993, 28, 638–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bankskota, S.; Khan, W.I. Gut-derived serotonin and its emerging roles in immune function, inflammation, metabolism and the gut–brain axis. Curr. Opin. Endocrinol. Diabetes Obes. 2022, 29, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, L.; Korkutata, M.; Vimal, S.K.; Yadav, M.K.; Bhattacharyya, S.; Shiga, T. Therapeutic potential of serotonin 4 receptor for chronic depression and its associated comorbidity in the gut. Neuropharmacology 2020, 166, 107969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellissier, S.; Dantzer, C.; Canini, F.; Mathieu, N.; Bonaz, B. Psychological adjustment and autonomic disturbances in inflammatory bowel diseases and irritable bowel syndrome. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2010, 35, 653–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellissier, S.; Dantzer, C.; Mondillon, L.; Trocme, C.; Gauchez, A.S.; Ducros, V.; Mathieu, N.; Toussaint, B.; Fournier, A.; Canini, F.; et al. Relationship between vagal tone, cortisol, TNF-alpha, epinephrine and negative affects in Crohn’s disease and irritable bowel syndrome. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e105328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Kwon, J.; Cho, M.-L. Immunological pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease. Intest. Res. 2018, 16, 26–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamblin, M.R. Mechanisms and applications of the anti-inflammatory effects of photobiomodulation. AIMS Biophys. 2017, 4, 337–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Docherty, M.J.; Jones, R.C.W.; Wallace, M.S. Managing pain in inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2011, 7, 592–601. [Google Scholar]
- Orchard, T.R. Management of arthritis in patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2012, 8, 327–329. [Google Scholar]
- Cotler, H.B.; Chow, R.T.; Hamblin, M.R.; Carroll, J. The use of low level laser therapy (LLLT) for musculoskeletal pain. MOJ Orthop. Rheumatol. 2015, 2, 00068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holanda, V.M.; Chavantes, M.C.; Wu, X.; Anders, J.J. The mechanistic basis for photobiomodulation therapy of neuropathic pain by near infrared laser light. Lasers Surg. Med. 2017, 49, 516–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, R.T.; Armati, P.; Laakso, E.-L.; Bjordal, J.M.; Baxter, G.D. Inhibitory effects of laser irradiation on peripheral mammalian nerves and relevance to analgesic effects: A systematic review. Photomed. Laser Surg. 2011, 29, 365–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fulop, A.M.; Dhimmer, S.; Deluca, J.R.; Johanson, D.D.; Lenz, R.V.; Patel, K.B.; Douris, P.C.; Enwemeka, C.S. A Meta-analysis of the efficacy of laser phototherapy on pain relief. Clin. J. Pain 2010, 26, 729–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clijsen, R.; Brunner, A.; Barbero, M.; Clarys, P.; Taeymans, J. Effects of low-level laser therapy on pain in patients with musculoskeletal disorders: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2017, 53, 603–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, S.-W.; Hong, C.-H.; Shih, M.-C.; Tam, K.-W.; Huang, Y.-H.; Kuan, Y.-C. Low-level laser therapy for fibromyalgia: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Pain Physician 2019, 22, 241–254. [Google Scholar]
- Stausholm, M.B.; Naterstad, I.F.; Joensen, J.; Lopes-Martins, R.A.B.; Sæbø, H.; Lund, H.; Fersum, K.V.; Bjordal, J.M. Efficacy of low-level laser therapy on pain and disability in knee osteoarthritis: Systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised placebo-controlled trials. BMJ Open 2019, 9, e031142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, R.T.; Johnson, M.I.; Lopes-Martins, R.A.B.; Bjordal, J.M. Efficacy of low-level laser therapy in the management of neck pain: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised placebo or active-treatment controlled trials. Lancet 2009, 374, 1897–1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjordal, J.M.; Lopes-Martins, R.A.B.; Joensen, J.; Couppe, C.; Ljunggren, A.E.; Stergioulas, A.; Johnson, M.I. A systematic review with procedural assessments and meta-analysis of low level laser therapy in lateral elbow tendinopathy (tennis elbow). BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2008, 9, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haslerud, S.; Magnussen, L.H.; Joensen, J.; Lopes-Martins, R.A.B.; Bjordal, J.M. The efficacy of low-level laser therapy for shoulder tendinopathy: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Physiother. Res. Int. 2015, 20, 108–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tumilty, S.; Munn, J.; McDonough, S.; Hurley, D.A.; Basford, J.R.; Baxter, G.D. Low level laser treatment of tendinopathy: A systematic review with meta-analysis. Photomed. Laser Surg. 2010, 28, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dos Santos, S.A.; Sampaio, L.M.; Caires, J.R.; Fernandes, G.H.C.; Marsico, A.; Serra, A.J.; Leal-Junior, E.C.; de Carvalho, P.T.C. Parameters and effects of photobiomodulation in plantar fasciitis: A meta-analysis and systematic review. Photobiomodul. Photomed. Laser Surg. 2019, 37, 327–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tunér, J.; Hosseinpour, S.; Fekrazad, R. Photobiomodulation in temporomandibular disorders. Photobiomodul. Photomed. Laser Surg. 2019, 37, 826–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haldeman, S.; Carroll, L.; Cassidy, J.D.; Schubert, J.; Nygren, Å. The Bone and Joint Decade 2000–2010 Task Force on Neck Pain and Its Associated Disorders. Executive summary. Spine 2008, 33, S5–S7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glazov, G.; Yelland, M.; Emery, J. Low-level laser therapy for chronic non-specific low back pain: A metaanalysis of randomised controlled trials. Acupunct. Med. 2016, 34, 328–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Souza Guimara, L.; da Cunha Menezes Costa, L.; Araujoa, A.C.; Nascimentoa, D.P.; Medeirosa, F.C.; Avanzia, M.A.; Leal-Junior, E.C.P.; Costa, L.O.P.; Tomazoni, S.S. Photobiomodulation therapy is not better than placebo in patients with chronic nonspecific low back pain: A randomised placebo-controlled trial. Pain 2021, 162, 1612–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whelan, H.T.; Smits, R.L.; Buchman, E.V.; Whelan, N.T.; Turner, S.G.; Margolis, D.A.; Cevenini, V.; Stinson, H.; Ignatius, R.; Martin, T.; et al. Effect of NASA light-emitting diode irradiation on wound healing. J. Clin. Laser Med. Surg. 2001, 19, 305–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodruff, L.D.; Bounkeo, J.M.; Brannon, W.M.; Dawes, K.S.; Barham, C.D.; Waddell, D.L.; Enwemeka, C.S. The efficacy of laser therapy in wound repair: A meta-analysis of the literature. Photomed. Laser Surg. 2004, 22, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, A.N.; Fernandes, K.P.S.; Deana, A.M.; Bussadori, S.K.; Mesquita-Ferrari, R.A. Effects of low-level laser therapy on skeletal muscle repair: A systematic review. Am. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2014, 93, 1073–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal-Junior, E.C.P.; Vanin, A.A.; Miranda, E.F.; de Carvalho, P.T.C.; Corso, S.D.; Bjordal, J.M. Effect of phototherapy (low-level laser therapy and light-emitting diode therapy) on exercise performance and markers of exercise recovery: A systematic review with meta-analysis. Lasers Med. Sci. 2015, 30, 925–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laakso, E.-L.; Cabot, P.J. Nociceptive scores and endorphin-containing cells reduced by low-level laser therapy (LLLT) in inflamed paws of Wistar rat. Photomed. Laser Surg. 2005, 23, 32–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagiwara, S.; Iwasaka, H.; Okuda, K.; Noguchi, T. GaAlAs (830 nm) low-level laser enhances peripheral endogenous opioid analgesia in rats. Lasers Surg. Med. 2007, 39, 797–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laakso, E.-L. Tendinopathy: Then, now and where to from here-Laser—A modality for tendon repair. In Proceedings of the ‘Connect’, Australian Physiotherapy Association Conference, Gold Coast, Australia, 3–6 October 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Martin-Subero, M.; Anderson, G.; Kanchanatawan, B.; Berk, M.; Maes, M. Comorbidity between depression and inflammatory bowel disease explained by immune-inflammatory, oxidative, and nitrosative stress; tryptophan catabolite; and gut-brain pathways. CNS Spectr. 2016, 21, 184–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villoria, A.; García, V.; Dosal, A.; Moreno, L.; Montserrat, A.; Figuerola, A.; Horta, D.; Calvet, X.; Ramírez-Lázaro, M.J. Fatigue in out-patients with inflammatory bowel disease: Prevalence and predictive factors. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0181435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikocka-Walus, A.; Pittet, V.; Rossel, J.-B.; Von Känel, R. Symptoms of depression and anxiety are independently associated with clinical recurrence of inflammatory bowel disease. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 14, 829–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regueiro, M.; Greer, J.B.; Szigethy, E. Etiology and treatment of pain and psychosocial issues in patients with inflammatory bowel diseases. Gastroenterology 2017, 152, 430–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.-H.; Giuliana, F. The role of inflammation in depression and fatigue. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, G.; Berk, M.; Galecki, P.; Walder, K.; Maes, M. The neuro-immune pathophysiology of central and peripheral fatigue in systemic immune-inflammatory and neuro-immune diseases. Mol. Neurobiol. 2016, 53, 1195–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ailioaie, L.M.; Litscher, G. Photobiomodulation and sports: Results of a narrative review. Life 2021, 11, 1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nampo, F.K.; Cavalheri, V.; Dos Santos Soares, F.; de Paula Ramos, S.; Camargo, E.A. Low-level phototherapy to improve exercise capacity and muscle performance: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lasers Med. Sci. 2016, 31, 1957–1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanin, A.A.; Verhagen, E.; Barboza, S.D.; Costa, L.O.P.; Leal-Junior, E.C.P. Photobiomodulation therapy for the improvement of muscular performance and reduction of muscular fatigue associated with exercise in healthy people: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lasers Med. Sci. 2018, 33, 181–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, E.F.; de Oliveira, L.V.F.; Antonialli, F.C.; Vanin, A.A.; de Carvalho, P.T.C.; Leal-Junior, E.C.P. Phototherapy with combination of super-pulsed laser and light-emitting diodes is beneficial in improvement of muscular performance (strength and muscular endurance), dyspnea, and fatigue sensation in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Lasers Med. Sci. 2015, 30, 437–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toma, R.L.; Oliveira, M.X.; Renno, A.C.M.; Laakso, E.-L. Photobiomodulation (PBM) therapy at 904 nm mitigates effects of exercise-induced skeletal muscle fatigue in young women. Lasers Med. Sci. 2018, 33, 1197–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, M.X.; Toma, R.L.; Jones, B.J.L.; Cyprien, T.P.; Tier, M.R.; Wallace, C.A.; Renno, A.C.M.; Sabapathy, S.; Laakso, E.-L. Effects of photobiomodulation therapy (pulsed LASER 904 nm) on muscle oxygenation and performance in exercise-induced skeletal muscle fatigue in young women: A pilot study. In Proceedings of the SPIE: Mechanisms of Photobiomodulation Therapy XII, San Francisco, CA, USA, 28 January–2 February 2017; Volume 10048, pp. 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossein-khannazer, N.; Arki, M.K.; Keramatinia, A.; Rezaei-Tavirani, M. The role of low-level laser therapy in the treatment of multiple sclerosis: A review study. J. Lasers Med. Sci. 2021, 12, e88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liebert, A.; Pang, V.; Bicknell, B.; McLachlan, C.; Mitrofanis, J.; Kiat, H. A perspective on the potential of opsins as an integral mechanism of photobiomodulation: It’s not just the eyes. Photobiomodul. Photomed. Laser Surg. 2022, 40, 123–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samoilova, K.A.; Zimin, A.A.; Buinyakova, A.I.; Makela, A.M.; Zhevago, N.A. Regulatory systemic effect of postsurgical polychromatic light (480–3400 nm) irradiation of breast cancer patients on the proliferation of tumor and normal cells in vitro. Photomed. Laser Surg. 2015, 33, 555–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassano, P.; Petrie, S.R.; Mischoulon, D.; Cusin, C.; Katnani, H.; Yeung, A.; De Taboada, L.; Archibald, A.; Bui, E.; Baer, L.; et al. Transcranial photobiomodulation for the treatment of major depressive disorder. The ELATED-2 pilot trial. Photomed. Laser Surg. 2018, 36, 634–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goehler, L.E.; Lyte, M.; Gaykema, R.P.A. Infection-induced viscerosensory signals from the gut enhance anxiety: Implications for psychoneuroimmunology. Brain Behav. Immun. 2007, 21, 721–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reif-Leonhard, C.; Reif, A.; Baune, B.T.; Kavakbasi, E. Vagusnervstimulation bei schwer zu behandelnden depressionen. Nervenarzt 2022, 93, 921–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dodds, K.N.; Travis, L.; Kyloh, M.A.; Jones, L.A.; Keating, D.J.; Spencer, N.J. The gut-brain axis: Spatial relationship between spinal afferent nerves and 5-HT-containing enterochromaffin cells in mucosa of mouse colon. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2022, 322, G523–G533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cassano, P.; Petrie, S.R.; Hamblin, M.R.; Henderson, T.A.; Iosifescu, D.V. Review of transcranial photobiomodulation for major depressive disorder: Targeting brain metabolism, inflammation, oxidative stress, and neurogenesis. Neurophotonics 2016, 3, 031404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salehpour, F.; Mahmoudi, J.; Kamari, F.; Sadigh-Eteghad, S.; Rasta, S.H.; Hamblin, M.R. Brain photobiomodulation therapy: A narrative review. Mol. Neurobiol. 2018, 55, 6601–6636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamilton, C.; El Khoury, H.; Hamilton, D.; Nicklason, F.; Mitrofanis, J. “Buckets”: Early observations on the use of red and infrared light helmets in Parkinson’s disease patients. Photobiomodul. Photomed. Laser Surg. 2019, 37, 615–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liebert, A.; Bicknell, B.; Laakso, E.-L.; Jalilitabaei, P.; Tilley, S.; Kiat, H.; Mitrofanis, J. Remote photobiomodulation treatment for the clinical signs of Parkinson’s disease: A case series conducted during COVID-19. Photobiomodul. Photomed. Laser Surg. 2022, 40, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habibi, F.; Habibi, M.E.; Gharavinia, A.; Mahdavi, S.B.; Akbarpour, M.J.; Baghaei, A.; Emami, M.H. Quality of life in inflammatory bowel disease patients: A cross-sectional study. J. Res. Med. Sci. 2017, 22, 104–110. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, B.; Chae, J.; Kim, E.H.; Yang, H.I.; Cheon, J.H.; Kim, T.I.; Kim, W.H.; Jeon, J.Y.; Park, S.J. Physical activity and quality of life of patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Medicine 2021, 100, e26290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, R.; Mazurak, N.; Fantasia, L.; Fusco, S.; Malek, N.P.; Wehkamp, J.; Enck, P.; Klag, T. Quality of life in inflammatory bowel diseases: It is not all about the bowel. Intest. Res. 2021, 19, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, A.P.; Fernandes, D.J.; Vidyasagar, M.S.; Maiya, A.G.; Nigudgi, S. Effect of low-level laser therapy on patient reported measures of oral mucositis and quality of life in head and neck cancer patients receiving chemoradiotherapy—A randomized controlled trial. Support. Care Cancer 2013, 21, 1421–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehpour, F.; Hamblin, M.R.; DiDuro, J.O. Rapid reversal of cognitive decline, olfactory dysfunction, and quality of life using multi-modality photobiomodulation therapy: Case report. Photobiomodul. Photomed. Laser Surg. 2019, 37, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gür, A.; Karakoc, M.; Nas, K.; Cevik, R.; Sarac, A.J.; Ataoglu, S. Effects of low power laser and low dose amitriptyline therapy on clinical symptoms and quality of life in fibromyalgia: A single-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Rheumatol. Int. 2002, 22, 188–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youssef, E.F.; Muaidi, Q.I.; Shanb, A.A. Effect of laser therapy on chronic osteoarthritis of the knee in older subjects. J. Lasers Med. Sci. 2016, 7, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, J.C.; Jorge, P.; Santos, A. The effect of photobiomodulation therapy on the management of chronic idiopathic large-bowel diarrhea in dogs. Lasers Med. Sci. 2022, 37, 2045–2051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croghan, I.T.; Hurt, R.T.; Schroeder, D.R.; Fokken, S.C.; Jensen, M.D.; Clark, M.M.; Ebbert, J.O. Low-level laser therapy for weight reduction: A randomized pilot study. Lasers Med. Sci. 2020, 35, 663–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liebert, A.; Bicknell, B.; Laakso, E.-L.; Heller, G.; Jalilitabaei, P.; Tilley, S.; Mitrofanis, J.; Kiat, H. Improvements in clinical signs of Parkinson’s disease using photobiomodulation: A prospective proof-of-concept study. BMC Neurol. 2021, 21, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laakso, E.L.; Richardson, C.; Cramond, T. Pain scores and side effects in response to low level laser therapy (LLLT) for myofascial trigger points. Laser Ther. 1997, 9, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassano, P.; Caldieraro, M.A.; Norton, R.; Mischoulon, D.; Trinh, N.-H.; Nyer, M.; Dordin, C.; Hamblin, M.R.; Campbell, B.; Iosifescu, D.V. Reported side effects, weight and blood pressure, after repeated sessions of transcranial photobiomodulation. Photobiomodul. Photomed. Laser Surg. 2019, 37, 651–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moro, C.; Torres, N.; Arvanitakis, K.; Cullen, K.; Chabrol, C.; Agay, D.; Darlot, F.; Benabid, A.-L.; Mitrofanis, J. No evidence for toxicity after long-term photobiomodulation in normal non-human primates. Exp. Brain Res. 2017, 235, 3081–3092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moskvin, S.V.; Khadartsev, A.A. Laser light—Can it be harmful? J. New Med. Technol. 2016, 23, 265–283. [Google Scholar]
- Bullock-Saxton, J.; Lehn, A.; Laakso, E.-L. Exploring the effect of combined transcranial and intra-oral photobiomodulation therapy over a four-week period on physical and cognitive outcome measures for people with Parkinson’s disease: A randomized double-blind placebo-controlled pilot study. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2021, 83, 1499–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Mitochondrial chromophores such as cytochrome C oxidase (CCO) accept photonic energy resulting in dissociation of nitric oxide, production of reactive oxygen species, increased mitochondrial membrane potential, increased intracellular ATP and cyclic AMP, changes in Ca2+ concentration and numerous downstream effects such as transcription factor activation (NF-κB, HIF-1α and RANKL), e.g., [1,2,3]. |
| Hypothesised modulation of ion channels and protein conformational transfer [4] requires further investigation. |
| Interaction of far and near-infrared photons with bound mitochondrial water [2,5] refuting the CCO mechanism noted above. |
| Disruption of the neural cytoskeleton to explain the modulatory effect of PBM in pain [6] with the finding that 830 nm (continuous wave) laser PBM decreased mitochondrial membrane potential, induced reversible varicosity formation in rat dorsal root ganglion neurons blocking fast axonal flow thus explaining clinically observed analgesia via neural blockade. |
| Modulation of genes, neurotrophins, cytokines, and inflammatory processes in conditions expressing inflammation [2,7]. Examples include TNF, BDNF, several interleukins, VEGF, histamine, and prostaglandins. |
| Potential TRPV1 interaction with the cytoskeleton in conditions expressing pain, inflammation, and skin wounds [1,2,8]. |
| Activation of extra-cellular transforming growth factor beta (TGFβ) in tissue healing settings [2]. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Laakso, E.-L.; Ewais, T. A Holistic Perspective on How Photobiomodulation May Influence Fatigue, Pain, and Depression in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Beyond Molecular Mechanisms. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 1497. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11051497
Laakso E-L, Ewais T. A Holistic Perspective on How Photobiomodulation May Influence Fatigue, Pain, and Depression in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Beyond Molecular Mechanisms. Biomedicines. 2023; 11(5):1497. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11051497
Chicago/Turabian StyleLaakso, E-Liisa, and Tatjana Ewais. 2023. "A Holistic Perspective on How Photobiomodulation May Influence Fatigue, Pain, and Depression in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Beyond Molecular Mechanisms" Biomedicines 11, no. 5: 1497. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11051497
APA StyleLaakso, E.-L., & Ewais, T. (2023). A Holistic Perspective on How Photobiomodulation May Influence Fatigue, Pain, and Depression in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Beyond Molecular Mechanisms. Biomedicines, 11(5), 1497. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11051497






