MiR-155-5p Attenuates Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell Oxidative Stress and Migration via Inhibiting BACH1 Expression
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. BACH1 Knockdown in VSMCs
2.2. Transfection of miR-155-5p Mimic and Inhibitor
2.3. ROS Measurement
2.4. NAD(P)H Oxidase Activity Assay
2.5. VSMC Migration Assay
2.6. Dual-Luciferase Reporter Assay
2.7. Western Blot Analysis
2.8. Measurement of the miR-155-5p Level
2.9. Real-Time PCR
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
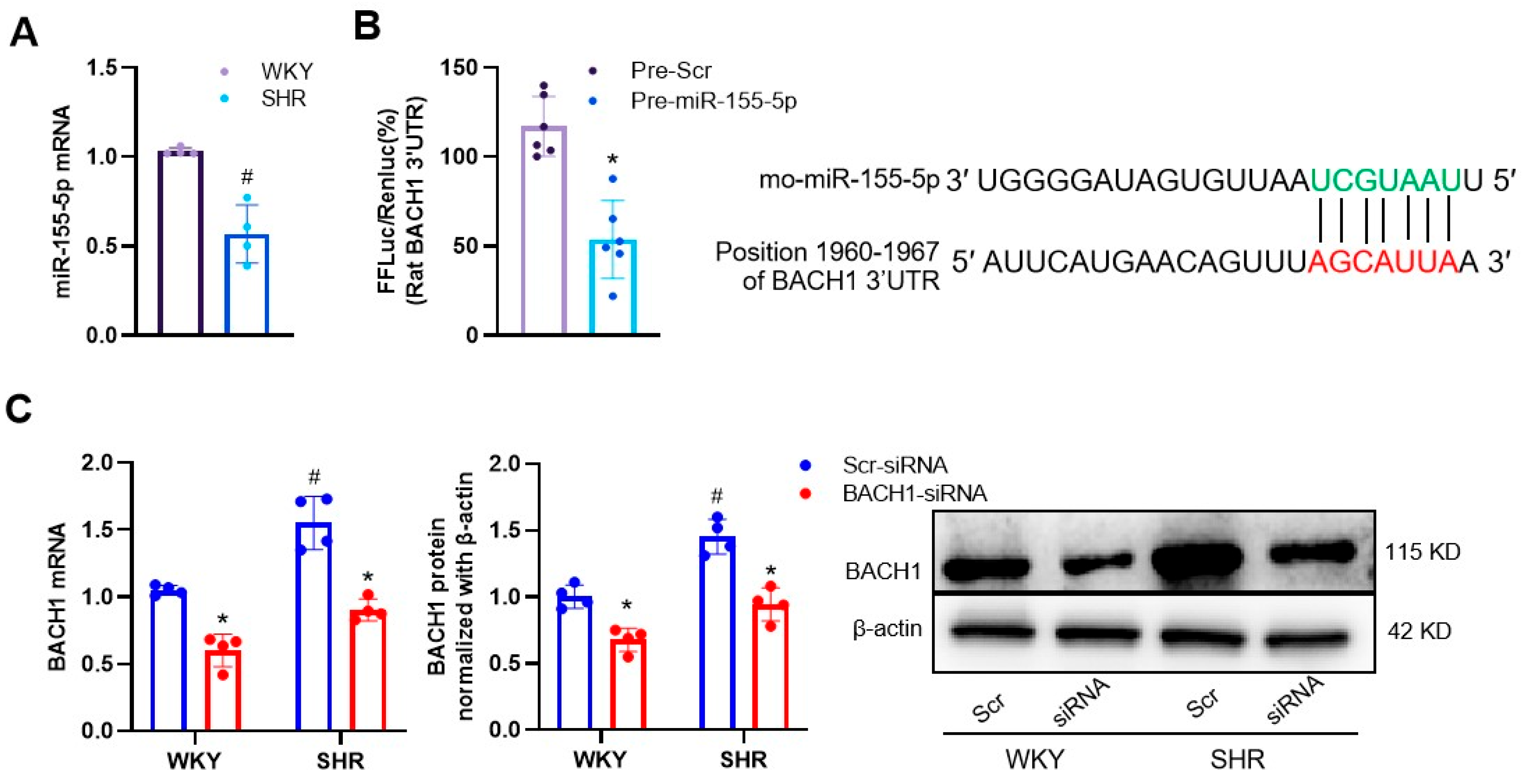
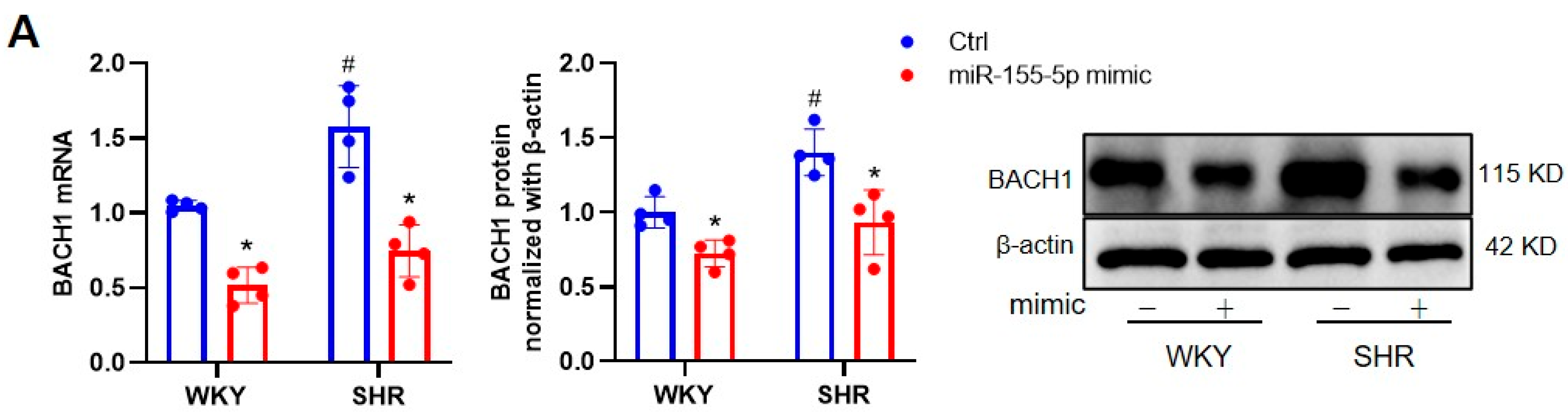
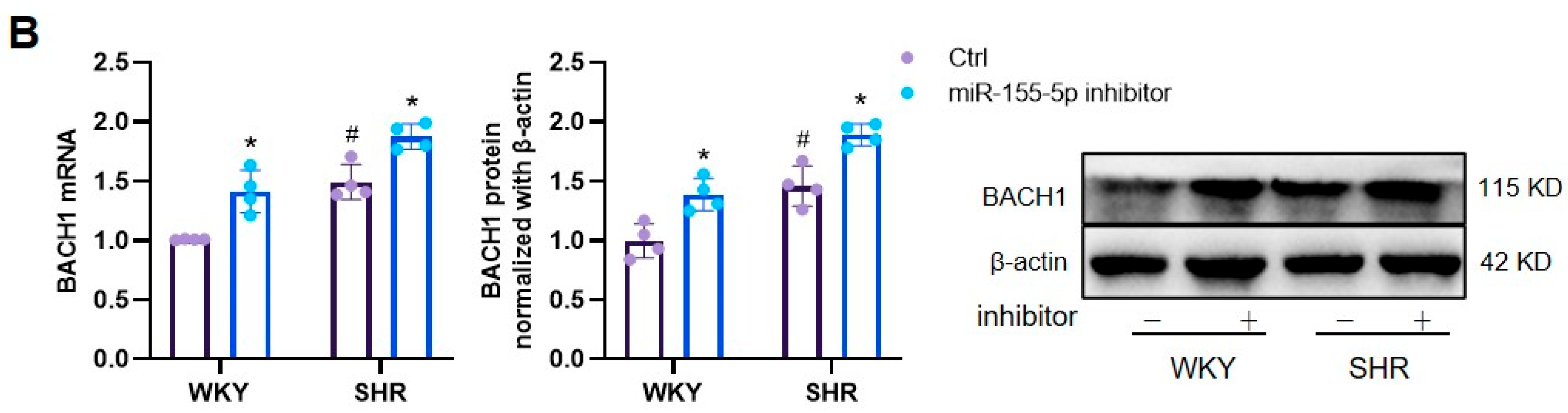
3.1. Effects of miR-155-5p Overexpression on VSMC Oxidative Stress in WKYs and SHRs
3.2. MiR-155-5p Targeted BACH1 in VSMCs
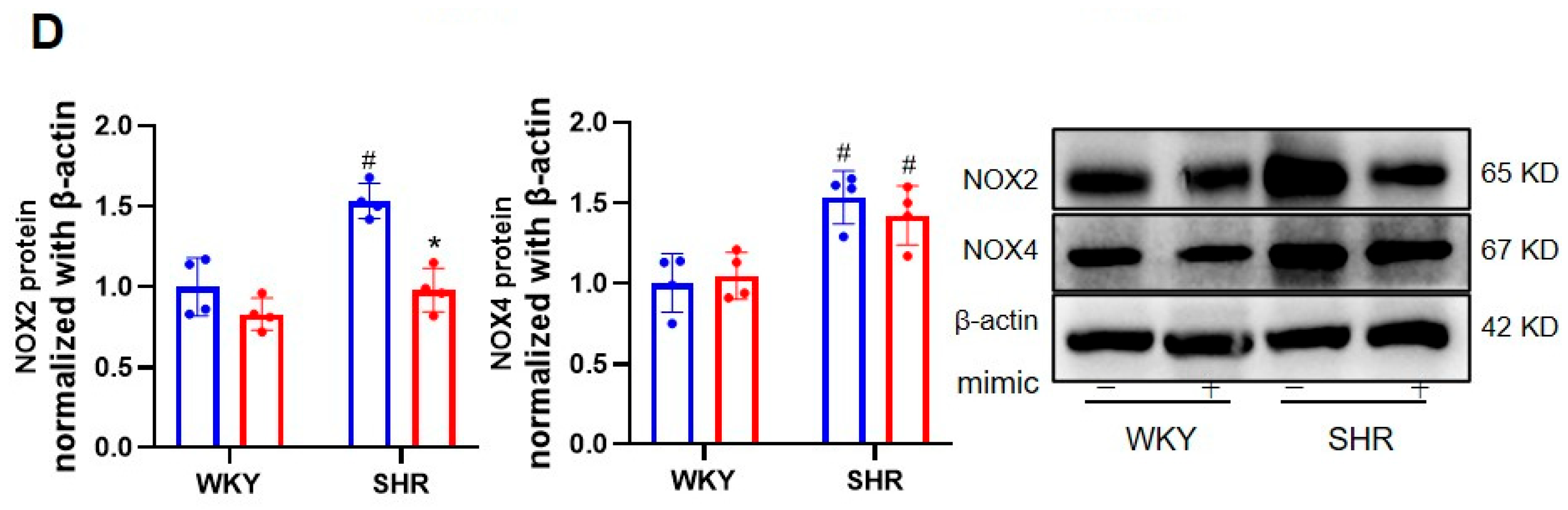
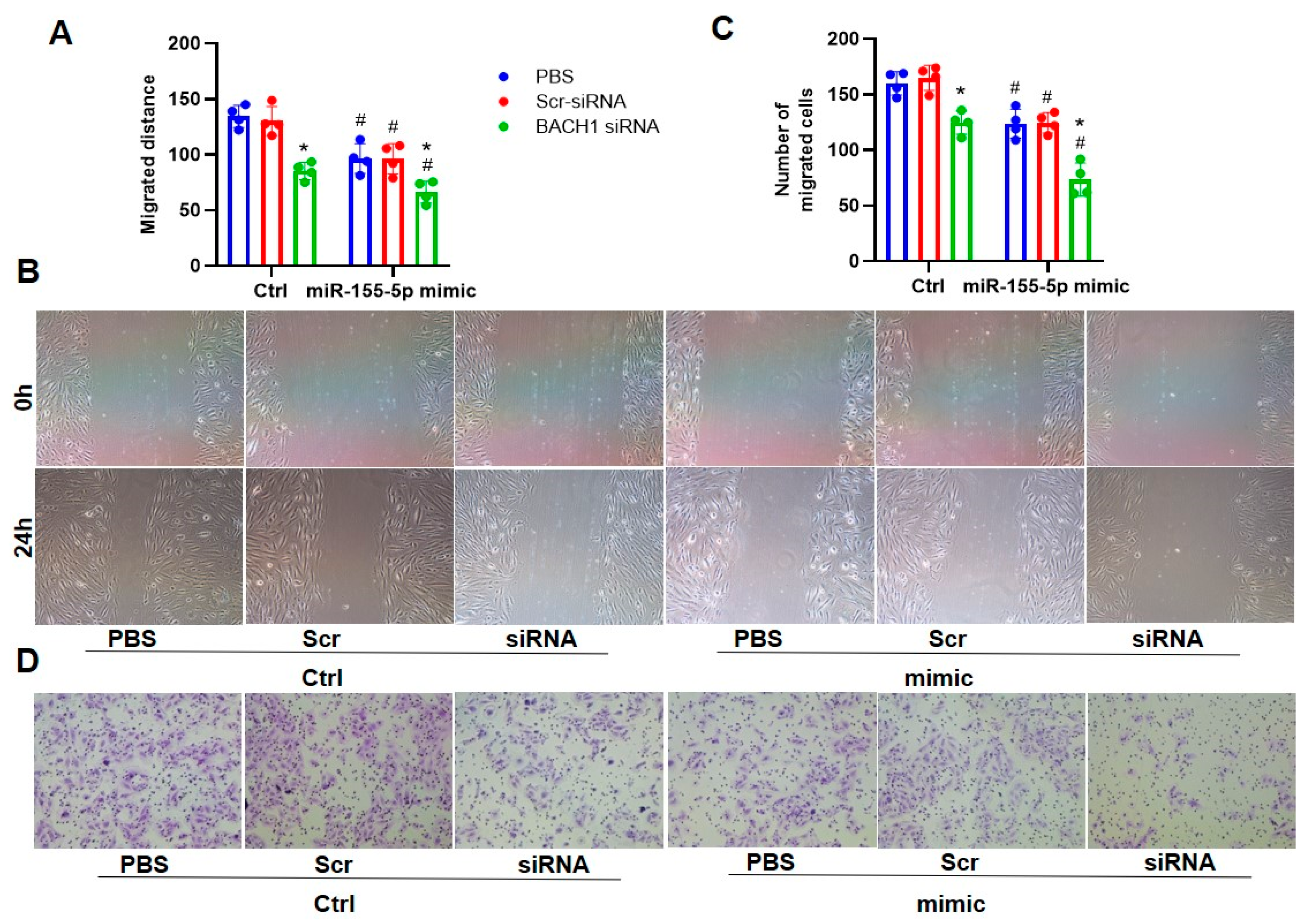
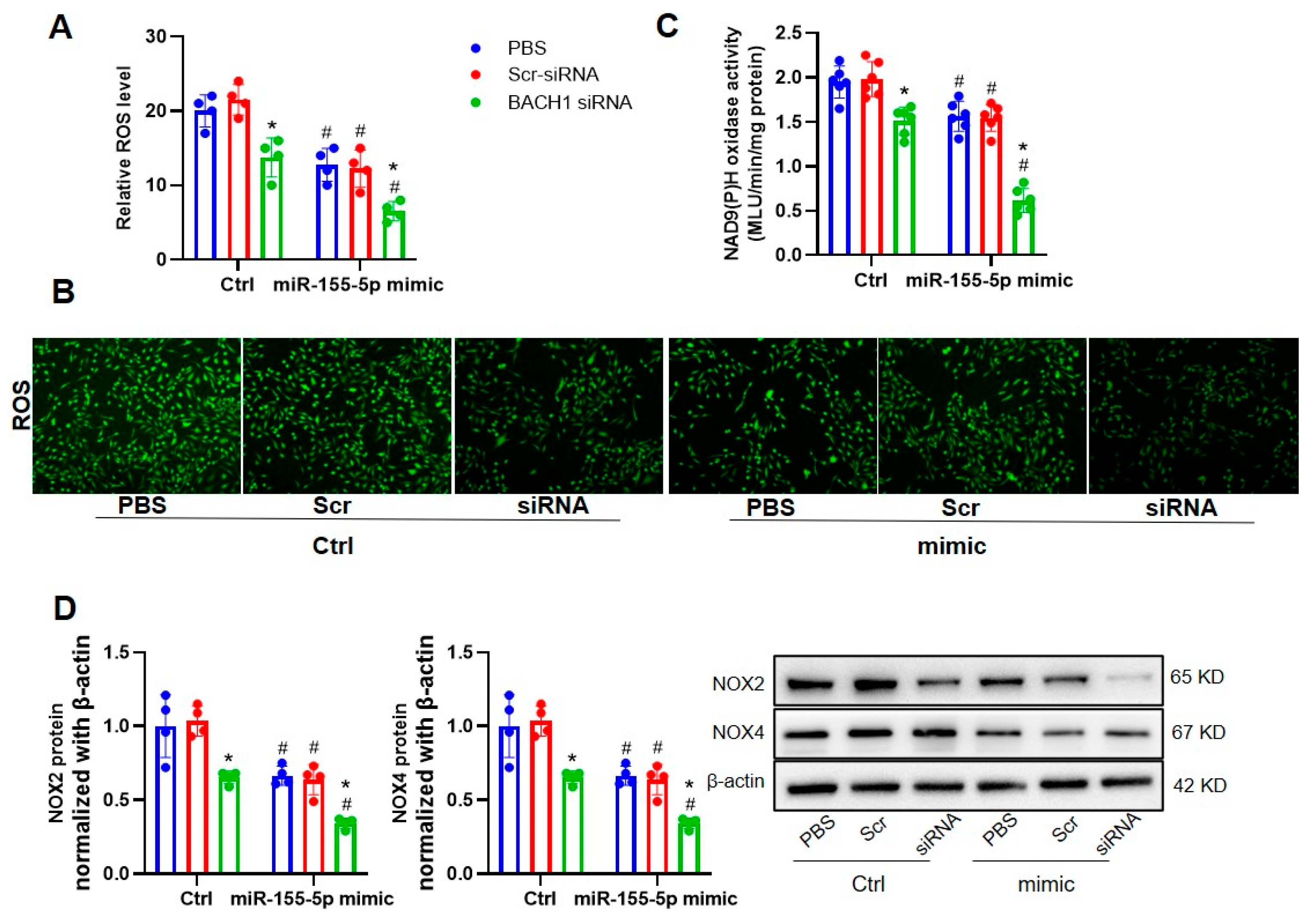
3.3. Ablation of BACH1 on VSMC Migration and Oxidative Damage in WKYs and SHRs
3.4. The Ablation of BACH1 Facilitated the Inhibitory Effects of miR-155-5p Mimics on VSMC Migration and ROS Formation in SHRs
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Limitations
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lacolley, P.; Regnault, V.; Avolio, A.P. Smooth muscle cell and arterial aging: Basic and clinical aspects. Cardiovasc. Res. 2018, 114, 513–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, A.A.R.; Lawrie, A. Targeting Vascular Remodeling to Treat Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension. Trends Mol. Med. 2017, 23, 31–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.J.; Wang, Z.C.; Nie, X.W.; Bian, J.S. Therapeutic potential of carbon monoxide in hypertension-induced vascular smooth muscle cell damage revisited: From physiology and pharmacology. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2022, 199, 115008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.X.; Wang, Z.C.; Machuki, J.O.; Li, M.Z.; Wu, Y.J.; Niu, M.K.; Yu, K.Y.; Lu, Q.B.; Sun, H.J. Benefits of Curcumin in the Vasculature: A Therapeutic Candidate for Vascular Remodeling in Arterial Hypertension and Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension? Front. Physiol. 2022, 13, 848867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.R.; Sun, H.J. MiRNAs, lncRNAs, and circular RNAs as mediators in hypertension-related vascular smooth muscle cell dysfunction. Hypertens. Res. Off. J. Jpn. Soc. Hypertens. 2021, 44, 129–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Ning, Q. Long noncoding RNAs as novel players in the pathogenesis of hypertension. Hypertens. Res. Off. J. Jpn. Soc. Hypertens. 2020, 43, 597–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.R.; Sun, H.J. Extracellular Vesicle-Mediated Vascular Cell Communications in Hypertension: Mechanism Insights and Therapeutic Potential of ncRNAs. Cardiovasc. Drugs Ther. 2022, 36, 157–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, D.; Fiedler, J.; Sonnenschein, K.; Just, A.; Pfanne, A.; Zimmer, K.; Remke, J.; Foinquinos, A.; Butzlaff, M.; Schimmel, K.; et al. MicroRNA-Based Therapy of GATA2-Deficient Vascular Disease. Circulation 2016, 134, 1973–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths-Jones, S. The microRNA Registry. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, D109–D111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Pan, Q.; Zhao, Y.; He, C.; Bi, K.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, B.; Chen, Y.; Ma, X. MicroRNA-155 Regulates ROS Production, NO Generation, Apoptosis and Multiple Functions of Human Brain Microvessel Endothelial Cells Under Physiological and Pathological Conditions. J. Cell. Biochem. 2015, 116, 2870–2881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazari-Jahantigh, M.; Wei, Y.; Schober, A. The role of microRNAs in arterial remodelling. Thromb. Haemost. 2012, 107, 611–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DuPont, J.J.; McCurley, A.; Davel, A.P.; McCarthy, J.; Bender, S.B.; Hong, K.; Yang, Y.; Yoo, J.K.; Aronovitz, M.; Baur, W.E.; et al. Vascular mineralocorticoid receptor regulates microRNA-155 to promote vasoconstriction and rising blood pressure with aging. JCI Insight 2016, 1, e88942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Sun, W.; Saaoud, F.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Hodge, J.; Hui, Y.; Yin, S.; Lessner, S.M.; Kong, X.; et al. MiR155 modulates vascular calcification by regulating Akt-FOXO3a signalling and apoptosis in vascular smooth muscle cells. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2021, 25, 535–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, X.S.; Tong, Y.; Qiu, Y.; Ye, C.; Wu, N.; Xiong, X.Q.; Wang, J.J.; Han, Y.; Zhou, Y.B.; Zhang, F.; et al. MiR155-5p in adventitial fibroblasts-derived extracellular vesicles inhibits vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation via suppressing angiotensin-converting enzyme expression. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2020, 9, 1698795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, N.; Ye, C.; Zheng, F.; Wan, G.W.; Wu, L.L.; Chen, Q.; Li, Y.H.; Kang, Y.M.; Zhu, G.Q. MiR155-5p Inhibits Cell Migration and Oxidative Stress in Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells of Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Ouyang, Y.; Bai, Y.; Gong, J.; Liao, H. miR-155-5p inhibits the viability of vascular smooth muscle cell via targeting FOS and ZIC3 to promote aneurysm formation. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2019, 853, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q.B.; Wan, M.Y.; Wang, P.Y.; Zhang, C.X.; Xu, D.Y.; Liao, X.; Sun, H.J. Chicoric acid prevents PDGF-BB-induced VSMC dedifferentiation, proliferation and migration by suppressing ROS/NFκB/mTOR/P70S6K signaling cascade. Redox Biol. 2018, 14, 656–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badran, A.; Nasser, S.A. Reactive Oxygen Species: Modulators of Phenotypic Switch of Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Zhang, F.; Xu, Y.; Sun, S.; Wang, H.; Du, Q.; Gu, C.; Black, S.M.; Han, Y.; Tang, H. Salusin-β Promotes Vascular Calcification via Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide Phosphate/Reactive Oxygen Species-Mediated Klotho Downregulation. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2019, 31, 1352–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almajdoob, S.; Hossain, E.; Anand-Srivastava, M.B. Resveratrol attenuates hyperproliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells from spontaneously hypertensive rats: Role of ROS and ROS-mediated cell signaling. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2018, 101, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omura, S.; Suzuki, H.; Toyofuku, M.; Ozono, R.; Kohno, N.; Igarashi, K. Effects of genetic ablation of bach1 upon smooth muscle cell proliferation and atherosclerosis after cuff injury. Genes Cells 2005, 10, 277–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hromadnikova, I.; Kotlabova, K.; Hympanova, L.; Krofta, L. Cardiovascular and Cerebrovascular Disease Associated microRNAs Are Dysregulated in Placental Tissues Affected with Gestational Hypertension, Preeclampsia and Intrauterine Growth Restriction. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0138383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klimczak, D.; Kuch, M.; Pilecki, T.; Żochowska, D.; Wirkowska, A.; Pączek, L. Plasma microRNA-155-5p is increased among patients with chronic kidney disease and nocturnal hypertension. J. Am. Soc. Hypertens. JASH 2017, 11, 831–841.e834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.; Park, M.; Kim, J.; Park, W.; Kim, S.; Lee, D.K.; Hwang, J.Y.; Choe, J.; Won, M.H.; Ryoo, S.; et al. TNF-α elicits phenotypic and functional alterations of vascular smooth muscle cells by miR-155-5p-dependent down-regulation of cGMP-dependent kinase 1. J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 14812–14822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, C.; Chen, B.; Chen, C.; Li, H.; Wang, D.; Tan, Y.; Weng, H. CircNr1h4 regulates the pathological process of renal injury in salt-sensitive hypertensive mice by targeting miR-155-5p. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 1700–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Gloria, J.L.; Carbó, R.; Buelna-Chontal, M.; Osorio-Alonso, H.; Henández-Díazcouder, A.; de la Fuente-León, R.L.; Sandoval, J.; Sánchez, F.; Rubio-Gayosso, I.; Sánchez-Muñoz, F. Cold exposure aggravates pulmonary arterial hypertension through increased miR-146a-5p, miR-155-5p and cytokines TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6. Life Sci. 2021, 287, 120091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Tao, X.; Peng, L. miR-155-5p regulates hypoxia-induced pulmonary artery smooth muscle cell function by targeting PYGL. Bioengineered 2022, 13, 12985–12997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.R.; Sun, H.J. LncRNAs and circular RNAs as endothelial cell messengers in hypertension: Mechanism insights and therapeutic potential. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2020, 47, 5535–5547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NandyMazumdar, M.; Paranjapye, A. BACH1, the master regulator of oxidative stress, has a dual effect on CFTR expression. Biochem. J. 2021, 478, 3741–3756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishizawa, H.; Yamanaka, M.; Igarashi, K. Ferroptosis: Regulation by competition between NRF2 and BACH1 and propagation of the death signal. FEBS J. 2022, 290, 1688–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Hoshino, H.; Takaku, K.; Nakajima, O.; Muto, A.; Suzuki, H.; Tashiro, S.; Takahashi, S.; Shibahara, S.; Alam, J.; et al. Hemoprotein Bach1 regulates enhancer availability of heme oxygenase-1 gene. EMBO J. 2002, 21, 5216–5224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Igarashi, K.; Nishizawa, H.; Saiki, Y.; Matsumoto, M. The transcription factor BACH1 at the crossroads of cancer biology: From epithelial-mesenchymal transition to ferroptosis. J. Biol. Chem. 2021, 297, 101032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weber, G.J.; Purkayastha, B.; Ren, L.; Pushpakumar, S.; Sen, U. Hypertension exaggerates renovascular resistance via miR-122-associated stress response in aging. J. Hypertens. 2018, 36, 2226–2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tong, Y.; Zhou, M.-H.; Li, S.-P.; Zhao, H.-M.; Zhang, Y.-R.; Chen, D.; Wu, Y.-X.; Pang, Q.-F. MiR-155-5p Attenuates Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell Oxidative Stress and Migration via Inhibiting BACH1 Expression. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 1679. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11061679
Tong Y, Zhou M-H, Li S-P, Zhao H-M, Zhang Y-R, Chen D, Wu Y-X, Pang Q-F. MiR-155-5p Attenuates Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell Oxidative Stress and Migration via Inhibiting BACH1 Expression. Biomedicines. 2023; 11(6):1679. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11061679
Chicago/Turabian StyleTong, Ying, Mei-Hui Zhou, Sheng-Peng Li, Hui-Min Zhao, Ya-Ru Zhang, Dan Chen, Ya-Xian Wu, and Qing-Feng Pang. 2023. "MiR-155-5p Attenuates Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell Oxidative Stress and Migration via Inhibiting BACH1 Expression" Biomedicines 11, no. 6: 1679. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11061679
APA StyleTong, Y., Zhou, M.-H., Li, S.-P., Zhao, H.-M., Zhang, Y.-R., Chen, D., Wu, Y.-X., & Pang, Q.-F. (2023). MiR-155-5p Attenuates Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell Oxidative Stress and Migration via Inhibiting BACH1 Expression. Biomedicines, 11(6), 1679. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11061679






