Advances in the Early Diagnosis of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma and Premalignant Pancreatic Lesions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Current Approaches to Diagnosing and Predicting Pancreatic Cancer
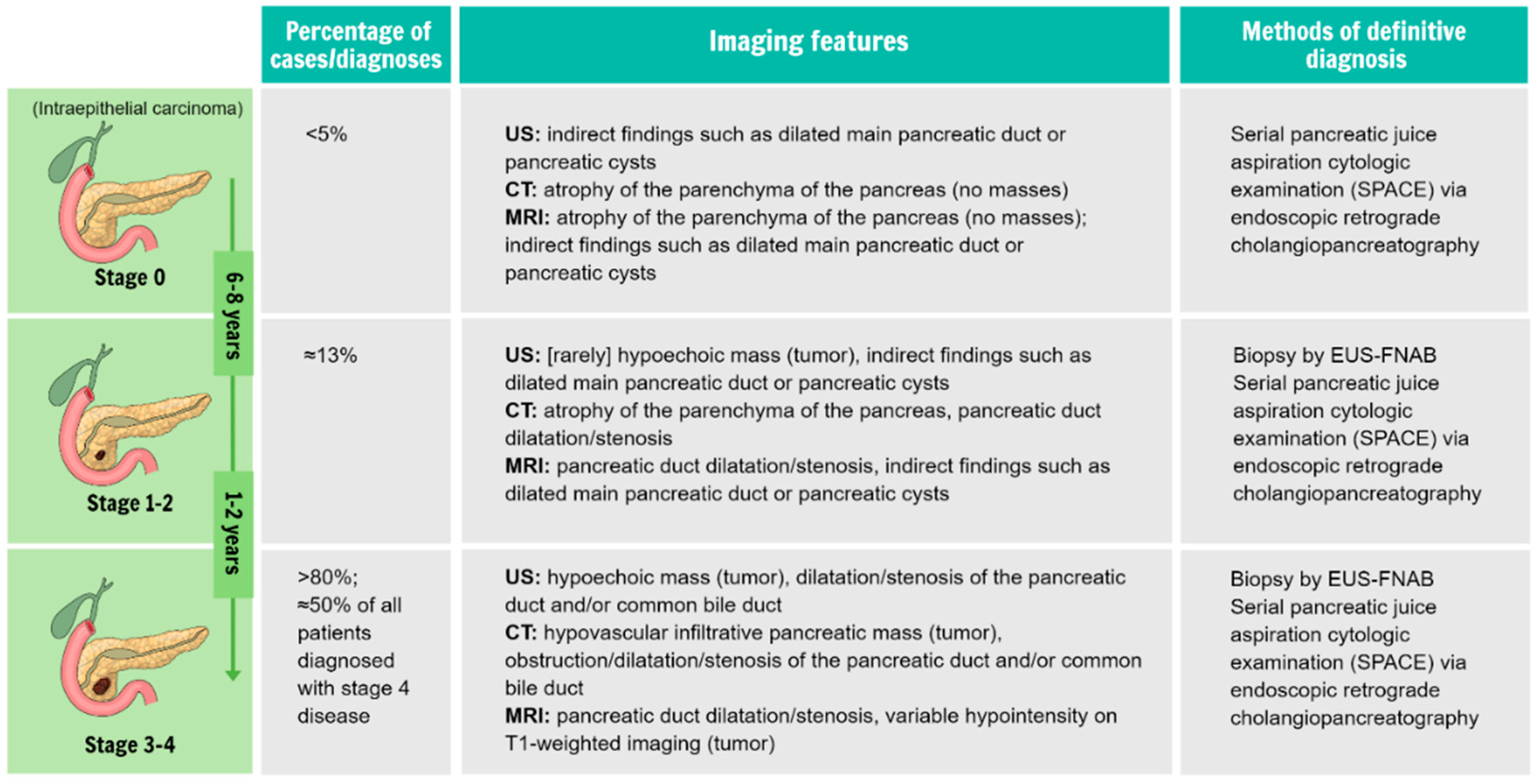
2.1. Current Approaches to Diagnosing Pancreatic Cancer
2.2. Current Approaches for Identifying Individuals at High Risk of Developing Pancreatic Cancer
3. Improvements to Current Diagnostic Approaches
3.1. Innovations in Interpreting Radiomics and Imaging Findings
3.2. Innovations in Biomarkers and Biopsy Techniques
4. Improvements to Current Surveillance Approaches
4.1. Insight into Indicators of Early Stage Pancreatic Cancer from Population-Based Analyses
4.2. Familial Pancreatic Cancer and Genetic Predispositions
5. Future Directions
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Badheeb, M.; Abdelrahim, A.; Esmail, A.; Umoru, G.; Abboud, K.; Al-Najjar, E.; Rasheed, G.; Alkhulaifawi, M.; Abudayyeh, A.; Abdelrahim, M. Pancreatic tumorigenesis: Precursors, genetic risk factors and screening. Curr. Oncol. 2022, 29, 8693–8719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osei-Bordom, D.C.; Serifis, N.; Brown, Z.J.; Hewitt, D.B.; Lawal, G.; Sachdeva, G.; Cloonan, D.J.; Pawlik, T.M. Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: Emerging therapeutic strategies. Surg. Oncol. 2022, 43, 101803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naffouje, S.A.; Pointer, D.T., Jr.; Satyadi, M.A.; Hodul, P.; Anaya, D.A.; Pimiento, J.; Malafa, M.; Kim, D.W.; Fleming, J.B.; Denbo, J.W. Surgical approach to pancreaticoduodenectomy for pancreatic adenocarcinoma: Uncomplicated ends justify the means. Surg. Endosc. 2022, 36, 4912–4922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egawa, S.; Toma, H.; Ohigashi, H.; Okusaka, T.; Nakao, A.; Hatori, T.; Maguchi, H.; Yanagisawa, A.; Tanaka, M. Japan Pancreatic Cancer Registry; 30th year anniversary: Japan Pancreas Society. Pancreas 2012, 41, 985–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singhi, A.D.; Koay, E.J.; Chari, S.T.; Maitra, A. Early Detection of pancreatic cancer: Opportunities and challenges. Gastroenterology 2019, 156, 2024–2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ryan, D.P.; Hong, T.S.; Bardeesy, N. Pancreatic adenocarcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 1039–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleeff, J.; Korc, M.; Apte, M.; La Vecchia, C.; Johnson, C.D.; Biankin, A.V.; Neale, R.E.; Tempero, M.; Tuveson, D.A.; Hruban, R.H.; et al. Pancreatic cancer. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2016, 2, 16022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, N.R.M.; Matrisian, L.M.; Shrader, E.E.; Feng, Z.; Chari, S.; Roth, J.A. Potential cost-effectiveness of risk-based pancreatic cancer screening in patients with new-onset diabetes. J. Natl. Compr. Canc. Netw. 2021, 20, 451–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2019, 69, 7–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hruban, R.H.; Adsay, N.V.; Albores-Saavedra, J.; Compton, C.; Garrett, E.S.; Goodman, S.N.; Kern, S.E.; Klimstra, D.S.; Klöppel, G.; Longnecker, D.S.; et al. Pancreatic intraepithelial neoplasia: A new nomenclature and classification system for pancreatic duct lesions. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2001, 25, 579–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Storz, P. Acinar cell plasticity and development of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 14, 296–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Guideline Alliance (UK). Pancreatic Cancer in Adults: Diagnosis and Management; National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE): London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Hawary, M.M.; Francis, I.R.; Chari, S.T.; Fishman, E.K.; Hough, D.M.; Lu, D.S.; Macari, M.; Megibow, A.J.; Miller, F.H.; Mortele, K.J.; et al. Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma radiology reporting template: Consensus statement of the Society of Abdominal Radiology and the American Pancreatic Association. Radiology 2014, 270, 248–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Treadwell, J.R.; Zafar, H.M.; Mitchell, M.D.; Tipton, K.; Teitelbaum, U.; Jue, J. Imaging tests for the diagnosis and staging of pancreatic adenocarcinoma: A meta-analysis. Pancreas 2016, 45, 789–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nakahodo, J.; Kikuyama, M.; Nojiri, S.; Chiba, K.; Yoshimoto, K.; Kamisawa, T.; Horiguchi, S.I.; Honda, G. Focal parenchymal atrophy of pancreas: An important sign of underlying high-grade pancreatic intraepithelial neoplasia without invasive carcinoma, i.e., carcinoma in situ. Pancreatology 2020, 20, 1689–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miura, S.; Takikawa, T.; Kikuta, K.; Hamada, S.; Kume, K.; Yoshida, N.; Tanaka, Y.; Matsumoto, R.; Ikeda, M.; Kataoka, F.; et al. Focal Parenchymal Atrophy of the Pancreas Is Frequently Observed on Pre-Diagnostic Computed Tomography in Patients with Pancreatic Cancer: A Case-Control Study. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikemoto, J.; Serikawa, M.; Hanada, K.; Eguchi, N.; Sasaki, T.; Fujimoto, Y.; Sugiyama, S.; Yamaguchi, A.; Noma, B.; Kamigaki, M.; et al. Clinical analysis of early-stage pancreatic cancer and proposal for a new diagnostic algorithm: A multicenter observational study. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakamoto, H.; Kitano, M.; Suetomi, Y.; Maekawa, K.; Takeyama, Y.; Kudo, M. Utility of contrast-enhanced endoscopic ultrasonography for diagnosis of small pancreatic carcinomas. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2008, 34, 525–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasuda, I.; Iwashita, T.; Doi, S.; Nakashima, M.; Moriwaki, H. Role of EUS in the early detection of small pancreatic cancer. Dig. Endosc. 2011, 23 (Suppl. S1), 22–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okusaka, T.; Nakamura, M.; Yoshida, M.; Kitano, M.; Uesaka, K.; Ito, Y.; Furuse, J.; Hanada, K.; Okazaki, K.; Committee for Revision of Clinical Guidelines for Pancreatic Cancer of the Japan Pancreas Society. Clinical practice guidelines for pancreatic cancer 2019 from the Japan Pancreas Society: A synopsis. Pancreas 2020, 49, 326–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puli, S.R.; Bechtold, M.L.; Buxbaum, J.L.; Eloubeidi, M.A. How good is endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration in diagnosing the correct etiology for a solid pancreatic mass?: A meta-analysis and systematic review. Pancreas 2013, 42, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, G.M.; Laporte, L.; Paquin, S.C.; Menard, C.; Sahai, A.V.; Mâsse, B.; Trottier, H. Endoscopic ultrasound guided fine needle aspiration versus endoscopic ultrasound guided fine needle biopsy for pancreatic cancer diagnosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 2951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirabayashi, K.; Saika, T.; Nakamura, N. Background features in the cytology of pancreatic neoplasms. DEN Open 2022, 2, e105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US Preventive Services Task Force; Owens, D.K.; Davidson, K.W.; Krist, A.H.; Barry, M.J.; Cabana, M.; Caughey, A.B.; Curry, S.J.; Doubeni, C.A.; Epling, J.W., Jr.; et al. Screening for pancreatic cancer: US Preventive Services Task Force reaffirmation recommendation statement. JAMA 2019, 322, 438–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Canto, M.I.; Almario, J.A.; Schulick, R.D.; Yeo, C.J.; Klein, A.; Blackford, A.; Shin, E.J.; Sanyal, A.; Yenokyan, G.; Lennon, A.M.; et al. Risk of neoplastic progression in individuals at high risk for pancreatic cancer undergoing long-term surveillance. Gastroenterology 2018, 155, 740–751.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Canto, M.I.; Hruban, R.H.; Fishman, E.K.; Kamel, I.R.; Schulick, R.; Zhang, Z.; Topazian, M.; Takahashi, N.; Fletcher, J.; Petersen, G.; et al. Frequent detection of pancreatic lesions in asymptomatic high-risk individuals. Gastroenterology 2012, 142, 796–804, quiz e14–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Naudin, S.; Viallon, V.; Hashim, D.; Freisling, H.; Jenab, M.; Weiderpass, E.; Perrier, F.; McKenzie, F.; Bueno-de-Mesquita, H.B.; Olsen, A.; et al. Healthy lifestyle and the risk of pancreatic cancer in the EPIC study. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2020, 35, 975–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aslanian, H.R.; Lee, J.H.; Canto, M.I. AGA Clinical practice update on pancreas cancer screening in high-risk individuals: Expert review. Gastroenterology 2020, 159, 358–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norris, A.L.; Roberts, N.J.; Jones, S.; Wheelan, S.J.; Papadopoulos, N.; Vogelstein, B.; Kinzler, K.W.; Hruban, R.H.; Klein, A.P.; Eshleman, J.R. Familial and sporadic pancreatic cancer share the same molecular pathogenesis. Fam. Cancer. 2015, 14, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oyama, H.; Tada, M.; Takagi, K.; Tateishi, K.; Hamada, T.; Nakai, Y.; Hakuta, R.; Ijichi, H.; Ishigaki, K.; Kanai, S.; et al. Long-term risk of malignancy in branch-duct intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms. Gastroenterology 2020, 158, 226–237.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prizment, A.E.; Gross, M.; Rasmussen-Torvik, L.; Peacock, J.M.; Anderson, K.E. Genes related to diabetes may be associated with pancreatic cancer in a population-based case-control study in Minnesota. Pancreas 2012, 41, 50–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xing, H.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Tong, M.; Hu, H.; Huang, C.; Li, D. Diagnostic value of CA 19-9 and carcinoembryonic antigen for pancreatic cancer: A meta-analysis. Gastroenterol. Res. Pract. 2018, 2018, 8704751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hasan, S.; Jacob, R.; Manne, U.; Paluri, R. Advances in pancreatic cancer biomarkers. Oncol. Rev. 2019, 13, 410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Teng, D.; Wu, K.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, M.; Wang, D.; Wu, J.; Yin, T.; Gong, W.; Ding, Y.; Xiao, W.; et al. Significant increased CA199 levels in acute pancreatitis patients predicts the presence of pancreatic cancer. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 12745–12753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Uygur-Bayramicli, O.; Dabak, R.; Orbay, E.; Dolapcioglu, C.; Sargin, M.; Kilicoglu, G.; Guleryuzlu, Y.; Mayadagli, A. Type 2 diabetes mellitus and CA 19-9 levels. World J. Gastroenterol. 2007, 13, 5357–5359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ćwik, G.; Wallner, G.; Skoczylas, T.; Ciechański, A.; Zinkiewicz, K. Cancer antigens 19-9 and 125 in the differential diagnosis of pancreatic mass lesions. Arch. Surg. 2006, 141, 968–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Engle, D.D.; Tiriac, H.; Rivera, K.D.; Pommier, A.; Whalen, S.; Oni, T.E.; Alagesan, B.; Lee, E.J.; Yao, M.A.; Lucito, M.S.; et al. The glycan CA19-9 promotes pancreatitis and pancreatic cancer in mice. Science 2019, 364, 1156–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qureshi, T.A.; Gaddam, S.; Wachsman, A.M.; Wang, L.; Azab, L.; Asadpour, V.; Chen, W.; Xie, Y.; Wu, B.; Pandol, S.J.; et al. Predicting pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma using artificial intelligence analysis of pre-diagnostic computed tomography images. Cancer Biomark. 2022, 33, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukherjee, S.; Patra, A.; Khasawneh, H.; Korfiatis, P.; Rajamohan, N.; Suman, G.; Majumder, S.; Panda, A.; Johnson, M.P.; Larson, N.B.; et al. Radiomics-based machine-learning models can detect pancreatic cancer on prediagnostic computed tomography scans at a substantial lead time before clinical diagnosis. Gastroenterology 2022, 163, 1435–1446.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tikhonova, V.S.; Karmazanovsky, G.G.; Kondratyev, E.V.; Gruzdev, I.S.; Mikhaylyuk, K.A.; Sinelnikov, M.Y.; Revishvili, A.S. Radiomics model-based algorithm for preoperative prediction of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma grade. Eur. Radiol. 2023, 33, 1152–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, H.; Hao, Z.; Zhu, W.; Sun, D.; Ding, J.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Y.; Huo, L. Preoperative prediction of pathological grade in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma based on 18F-FDG PET/CT radiomics. EJNMMI Res. 2021, 11, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, R.; Nakane, K.; Kadoya, N.; Matsuda, C.; Imai, H.; Tsuboi, J.; Hamada, Y.; Tanaka, K.; Tawara, I.; Nakagawa, H. Development of “mathematical technology for cytopathology,” an image analysis algorithm for pancreatic cancer. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, J.; Lundberg, E.; Jonsson, P.; Nyström, H.; Franklin, O.; Lundin, C.; Naredi, P.; Antti, H.; Sund, M.; Öhlund, D. A cross-sectional and longitudinal analysis of pre-diagnostic blood plasma biomarkers for early detection of pancreatic cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 12969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuang, L.; Huang, C.; Ning, Z.; Yang, L.; Zou, W.; Wang, P.; Cheng, C.S.; Meng, Z. Circulating tumor-associated autoantibodies as novel diagnostic biomarkers in pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Int. J. Cancer 2023, 152, 1013–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suehiro, Y.; Suenaga, S.; Kunimune, Y.; Yada, S.; Hamamoto, K.; Tsuyama, T.; Amano, S.; Matsui, H.; Higaki, S.; Fujii, I.; et al. CA19-9 in combination with methylated HOXA1 and SST is useful to diagnose stage I pancreatic cancer. Oncology 2022, 100, 674–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.Y.; Lin, R.T.; Chen, C.Y.; Yeh, C.C.; Tseng, C.M.; Huang, W.H.; Lee, T.Y.; Chu, C.S.; Lin, J.T. Accuracy of simultaneous measurement of serum biomarkers: Carbohydrate antigen 19-9, pancreatic elastase-1, amylase, and lipase for diagnosing pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. J. Formos. Med. Assoc. 2022, 121, 2601–2607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vikramdeo, K.S.; Anand, S.; Khan, M.A.; Khushman, M.; Heslin, M.J.; Singh, S.; Singh, A.P.; Dasgupta, S. Detection of mitochondrial DNA mutations in circulating mitochondria-originated extracellular vesicles for potential diagnostic applications in pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 18455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuzhat, Z.; Kinhal, V.; Sharma, S.; Rice, G.E.; Joshi, V.; Salomon, C. Tumour-derived exosomes as a signature of pancreatic cancer—Liquid biopsies as indicators of tumour progression. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 17279–17291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Inoue, H.; Eguchi, A.; Kobayashi, Y.; Usugi, E.; Yamada, R.; Tsuboi, J.; Akuta, T.; Horiki, N.; Iwasa, M.; Takei, Y. Extracellular vesicles from pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma endoscopic ultrasound-fine needle aspiration samples contain a protein barcode. J. Hepatobiliary Pancreat. Sci. 2022, 29, 394–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bararia, A.; Chakraborty, P.; Roy, P.; Chattopadhay, B.K.; Das, A.; Chatterjee, A.; Sikdar, N. Emerging role of non-invasive and liquid biopsy biomarkers in pancreatic cancer. World J. Gastroenterol. 2023, 29, 2241–2260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ak, C.; Sayar, S.; Kilic, E.T.; Kahraman, R.; Ozturk, O.; Zemheri, I.E.; Ozdil, K. EUS-FNA and ROSE in solid lesions of the pancreas; have the same diagnostic efficacy compared to pancreatic sites? North. Clin. Istanb. 2022, 9, 464–469. [Google Scholar]
- Yamashita, Y.; Shimokawa, T.; Ashida, R.; Napoléon, B.; Lisotti, A.; Fusaroli, P.; Gincul, R.; Dietrich, C.F.; Omoto, S.; Kitano, M. Comparison of endoscopic ultrasonography with and without contrast enhancement for characterization of pancreatic tumors: A meta-analysis. Endosc. Int. Open 2022, 10, E369–E377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bunganič, B.; Laclav, M.; Dvořáková, T.; Bradáč, O.; Traboulsi, E.; Suchánek, Š.; Frič, P.; Zavoral, M. Accuracy of EUS and CEH EUS for the diagnosis of pancreatic tumours. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 53, 1411–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rimbas, M.; Crino, S.F.; Gasbarrini, A.; Costamagna, G.; Scarpa, A.; Larghi, A. EUS-guided fine-needle tissue acquisition for solid pancreatic lesions: Finally moving from fine-needle aspiration to fine-needle biopsy? Endosc. Ultrasound 2018, 7, 137–140. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.I.; Chatterjee, A.; Berger, R.; Kanber, Y.; Wyse, J.M.; Lam, E.; Gan, I.; Auger, M.; Kenshil, S.; Telford, J.; et al. Endoscopic ultrasound (EUS)-guided fine needle biopsy alone vs. EUS-guided fine needle aspiration with rapid onsite evaluation in pancreatic lesions: A multicenter randomized trial. Endoscopy 2022, 54, 4–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crinò, S.F.; Di Mitri, R.; Nguyen, N.Q.; Tarantino, I.; de Nucci, G.; Deprez, P.H.; Carrara, S.; Kitano, M.; Shami, V.M.; Fernández-Esparrach, G.; et al. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle biopsy with or without rapid on-site evaluation for diagnosis of solid pancreatic lesions: A randomized controlled non-inferiority trial. Gastroenterology 2021, 16, 899–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crinò, S.F.; Le Grazie, M.; Manfrin, E.; Bellocchi, M.C.C.; Bernardoni, L.; Granato, A.; Locatelli, F.; Parisi, A.; Di Stefano, S.; Frulloni, L.; et al. Randomized trial comparing fork-tip and side-fenestrated needles for EUS-guided fine-needle biopsy of solid pancreatic lesions. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2020, 92, 648–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gkolfakis, P.; Crinò, S.F.; Tziatzios, G.; Ramai, D.; Papaefthymiou, A.; Papanikolaou, I.S.; Triantafyllou, K.; Arvanitakis, M.; Lisotti, A.; Fusaroli, P.; et al. Comparative diagnostic performance of end-cutting fine-needle biopsy needles for endoscopic ultrasound tissue sampling of solid pancreatic masses: A network meta-analysis. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2022, 95, 1067–1077.e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mie, T.; Sasaki, T.; Kanata, R.; Furukawa, T.; Takeda, T.; Kasuga, A.; Matsuyama, M.; Ozaka, M.; Sasahira, N. Diagnostic yield of endoscopic ultrasound-guided tissue acquisition for small solid pancreatic lesions. Endosc. Int. Open 2020, 8, E1359–E1364. [Google Scholar]
- Fitzpatrick, M.J.; Hernandez-Barco, Y.G.; Krishnan, K.; Casey, B.; Pitman, M.B. Evaluating triage protocols for endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine needle biopsies of the pancreas. J. Am. Soc. Cytopathol. 2020, 9, 396–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naito, Y.; Tsuneki, M.; Fukushima, N.; Koga, Y.; Higashi, M.; Notohara, K.; Aishima, S.; Ohike, N.; Tajiri, T.; Yamaguchi, H.; et al. A deep learning model to detect pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma on endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle biopsy. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 8454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oshima, M.; Okano, K.; Kamada, H.; Suto, H.; Ando, Y.; Ibuki, E.; Ishikawa, R.; Masaki, T.; Haba, R.; Suzuki, Y. P53 immunolabeling in EUS-FNA biopsy can predict low resection rate and early recurrence in resectable or borderline resectable pancreatic cancer treated with neoadjuvant therapy. J. Hepatobiliary Pancreat. Sci. 2022. online ahead of print. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, R.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Chen, Q.; Duan, Y.; Xiong, S.; Luan, Z.; Wang, J.; Cheng, B. Diagnostic and prognostic values of KRAS mutations on EUS-FNA specimens and circulating tumor DNA in patients with pancreatic cancer. Clin. Transl. Gastroenterol. 2022, 13, e00487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanno, A.; Masamune, A.; Hanada, K.; Maguchi, H.; Shimizu, Y.; Ueki, T.; Hasebe, O.; Ohtsuka, T.; Nakamura, M.; Takenaka, M.; et al. Multicenter study of early pancreatic cancer in Japan. Pancreatology 2018, 18, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, R.; Isaji, S.; Fujii, T.; Mizuno, S.; Kishiwada, M.; Murata, Y.; Hayasaki, A.; Inoue, H.; Umeda, Y.; Tanaka, K.; et al. Improving the prognosis of pancreatic cancer through early detection: Protocol for a prospective observational study. JMIR Res. Protoc. 2021, 10, e26898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chari, S.T.; Leibson, C.L.; Rabe, K.G.; Timmons, L.J.; Ransom, J.; de Andrade, M.; Petersen, G.M. Pancreatic cancer-associated diabetes mellitus: Prevalence and temporal association with diagnosis of cancer. Gastroenterology 2008, 134, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tada, M.; Kawabe, T.; Arizumi, M.; Togawa, O.; Matsubara, S.; Yamamoto, N.; Nakai, Y.; Sasahira, N.; Hirano, K.; Tsujino, T.; et al. Pancreatic cancer in patients with pancreatic cystic lesions: A prospective study in 197 patients. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2006, 4, 1265–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaguchi, K.; Kanemitsu, S.; Hatori, T.; Maguchi, H.; Shimizu, Y.; Tada, M.; Nakagohri, T.; Hanada, K.; Osanai, M.; Noda, Y.; et al. Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma derived from IPMN and pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma concomitant with IPMN. Pancreas 2011, 40, 571–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, M.; Fernández-Del Castillo, C.; Kamisawa, T.; Jang, J.Y.; Levy, P.; Ohtsuka, T.; Salvia, R.; Shimizu, Y.; Tada, M.; Wolfgang, C.L. Revisions of international consensus Fukuoka guidelines for the management of IPMN of the pancreas. Pancreatology 2017, 17, 738–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, X.; Zhao, X.; Su, J.; Xu, M.; Zhang, W.; Sheng, H.; Li, Z.; Wang, J. Malignant transformation and overall survival of morphological subtypes of intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms of the pancreas: A network meta-analysis. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2015, 26, 652–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vege, S.S.; Ziring, B.; Jain, R.; Moayyedi, P.; Clinical Guidelines Committee; American Gastroenterology Association. American gastroenterological association institute guideline on the diagnosis and management of asymptomatic neoplastic pancreatic cysts. Gastroenterology 2015, 148, 819–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tanaka, S.; Nakao, M.; Ioka, T.; Takakura, R.; Takano, Y.; Tsukuma, H.; Uehara, H.; Suzuki, R.; Fukuda, J. Slight dilatation of the main pancreatic duct and presence of pancreatic cysts as predictive signs of pancreatic cancer: A prospective study. Radiology. 2010, 254, 965–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.S.; Chae, W.; Sung, M.J.; Keum, J.; Jo, J.H.; Chung, M.J.; Park, J.Y.; Park, S.W.; Song, S.Y.; Park, E.C.; et al. Difference of risk of pancreatic cancer in new-onset diabetes and long-standing diabetes: Population-based cohort study. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2022. online ahead of print. [Google Scholar]
- Goggins, M.; Overbeek, K.A.; Brand, R.; Syngal, S.; Del Chiaro, M.; Bartsch, D.K.; Bassi, C.; Carrato, A.; Farrell, J.; Fishman, E.; et al. Management of patients with increased risk for familial pancreatic cancer: Updated recommendations from the International Cancer of the Pancreas Screening (CAPS) Consortium. Gut 2020, 69, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Overbeek, K.A.; Levink, I.J.M.; Koopmann, B.D.M.; Harinck, F.; Konings, I.C.A.W.; Ausems, M.G.E.M.; Wagner, A.; Fockens, P.; van Eijck, C.H.; Groot Koerkamp, B.; et al. Long-term yield of pancreatic cancer surveillance in high-risk individuals. Gut 2022, 71, 1152–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porter, N.; Laheru, D.; Lau, B.; He, J.; Zheng, L.; Narang, A.; Roberts, N.J.; Canto, M.I.; Lennon, A.M.; Goggins, M.G.; et al. Risk of pancreatic cancer in the long-term prospective follow-up of familial pancreatic cancer kindreds. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2022, 114, 1681–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riquelme, E.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Montiel, M.; Zoltan, M.; Dong, W.; Quesada, P.; Sahin, I.; Chandra, V.; San Lucas, A.; et al. Tumor microbiome diversity and composition influence pancreatic cancer outcomes. Cell 2019, 178, 795–806.e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herremans, K.M.; Riner, A.N.; Cameron, M.E.; McKinley, K.L.; Triplett, E.W.; Hughes, S.J.; Trevino, J.G. The oral microbiome, pancreatic cancer and human diversity in the age of precision medicine. Microbiome 2022, 10, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binda, C.; Gibiino, G.; Sbrancia, M.; Coluccio, C.; Cazzato, M.; Carloni, L.; Cucchetti, A.; Ercolani, G.; Sambri, V.; Fabbri, C. Microbiota in the natural history of pancreatic cancer: From predisposition to therapy. Cancers 2022, 15, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Zhang, H.; Lu, L.; Li, X.; Zhang, C.; Zhu, J.; Li, C.; Wang, Q.; Chen, K. Research progress in intestinal microecology in pancreatic cancer diagnosis and treatment. J. Oncol. 2022, 6069403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Z.; Sha, G.; Wang, D.; Tang, D. Intratumoral microbiota: A new force in diagnosing and treating pancreatic cancer. Cancer Lett. 2023, 554, 216031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahmani, H.; Mansouri Majd, S.; Salimi, A.; Ghasemi, F. Ultrasensitive immunosensor for monitoring of CA 19-9 pancreatic cancer marker using electrolyte-gated TiS3 nanoribbons field-effect transistor. Talanta 2023, 257, 124336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurudatt, N.G.; Gwak, H.; Hyun, K.A.; Jeong, S.E.; Lee, K.; Park, S.; Chung, M.J.; Kim, S.E.; Jo, J.H.; Jung, H.I. Electrochemical detection and analysis of tumor-derived extracellular vesicles to evaluate malignancy of pancreatic cystic neoplasm using integrated microfluidic device. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2023, 226, 115124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauer, A.; Elamurugan, S.; Tolba, S.A.; Fatima; Nega, E.; Lima, I.T., Jr.; Xia, W.; Sun, D. A portable elliptical dichroism spectrometer targeting secondary structural features of tumorous protein for pancreatic cancer detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2023, 222, 114934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ajgaonkar, R.; Lee, B.; Valimukhametova, A.; Nguyen, S.; Gonzalez-Rodriguez, R.; Coffer, J.; Akkaraju, G.R.; Naumov, A.V. Detection of pancreatic cancer miRNA with biocompatible nitrogen-doped graphene quantum dots. Materials 2022, 15, 5760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Name | Associated Risk | Gene(s) Involved | Associated Pancreatic Cancer | References | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Conditions | Branch-duct intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms | 19–30% of cases progress to malignancy | KRAS/BRAF PI3K/AKT TP53 SHH (hypermethylation) | Mucin-producing neoplasms | [31] |
| Obesity | ≈20% increased lifetime risk | KRAS TP53 | PDAC | [25] | |
| Diabetes | ≈82% increased lifetime risk | KRAS GCKR | PDAC | [23,32] | |
| Hereditary diseases | Peutz–Jeghers syndrome | ≈36% increased lifetime risk | STK11 (LKB1) | PDAC | [1] |
| Hereditary pancreatitis | ≈50% increased lifetime risk | PRSS1 | PDAC | [1] | |
| Ataxia telangiectasia | ≈10% increased lifetime risk | ATM | PDAC | [1] | |
| Fanconi anemia (DNA repair pathway) | At least 50-fold higher lifetime risk | RAD51 BRCA2 etc. | PDAC | [25] | |
| Lynch II syndrome | <5% increased lifetime risk | MLHL MSH2/MSH6, PMS2 EPCAM | PDAC | [25] |
| Factors | Risk | |
|---|---|---|
| Hereditary disease | Peutz–Jeghers syndrome | 132–140× (RR), incidence: 11–29% |
| Hereditary pancreatitis | 87× (SIR), incidence: 10% (50 y.o.), 50% (75 y.o.) | |
| Familial atypical multiple nevi melanoma syndrome | Incidence: 17% (75 y.o.) | |
| Hereditary breast cancer/ovarian | BRCA1 mutation: 2.3–2.8× (RR) BRCA2 mutation: 3.5× (RR), incidence: 4% | |
| Lynch syndrome | 8.6× (RR), 4.5–11× (SIR), incidence: 4% | |
| Familial adenomatous syndrome of the colon | 4.5× (RR) | |
| Family history | Sporadic pancreatic cancer | 1st degree relative with pancreatic cancer (1 person): 1.5–1.7× (RR) |
| Familial pancreatic cancer | 1st degree relative with pancreatic cancer (1 person): 4.5×; (2 persons): 6.4×; (3 persons): 32× (RR) | |
| Lifestyle | Smoking | 1.7–1.8× (RR) |
| Alcohol use | 1.1–1.3× (RR) (alcoholic consumption >24–50 g/day) | |
| Medical history | Diabetes | 1.6–2.0× (onset <1 year: 6.7×, 1–4 years: 1.9×, 5–9 years: 1.7×, >10 years: 1.4×) (RR) |
| Obesity | 1.3–1.4× (RR) | |
| Pancreatic disease/imaging findings | Chronic pancreatitis | 13.3–16.2× (EEs) (especially within 2 years of diagnosis) |
| Pancreatic cysts | 22.5× (SIR) | |
| IPMN | Cancer derived from IPMN: annual rate 0.2–3.0%, coexisting cancer with IPMN: annual rate 0–1.1% | |
| Dilation of main pancreatic duct | 6.4× (main pancreatic duct ≥2.5 mm) (HR) | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yamada, R.; Tsuboi, J.; Murashima, Y.; Tanaka, T.; Nose, K.; Nakagawa, H. Advances in the Early Diagnosis of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma and Premalignant Pancreatic Lesions. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 1687. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11061687
Yamada R, Tsuboi J, Murashima Y, Tanaka T, Nose K, Nakagawa H. Advances in the Early Diagnosis of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma and Premalignant Pancreatic Lesions. Biomedicines. 2023; 11(6):1687. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11061687
Chicago/Turabian StyleYamada, Reiko, Junya Tsuboi, Yumi Murashima, Takamitsu Tanaka, Kenji Nose, and Hayato Nakagawa. 2023. "Advances in the Early Diagnosis of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma and Premalignant Pancreatic Lesions" Biomedicines 11, no. 6: 1687. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11061687
APA StyleYamada, R., Tsuboi, J., Murashima, Y., Tanaka, T., Nose, K., & Nakagawa, H. (2023). Advances in the Early Diagnosis of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma and Premalignant Pancreatic Lesions. Biomedicines, 11(6), 1687. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11061687





