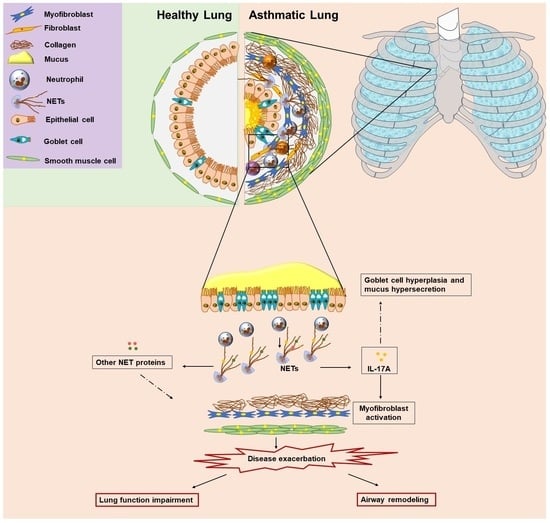
Ιnterleukin-17A-Enriched Neutrophil Extracellular Traps Promote Immunofibrotic Aspects of Childhood Asthma Exacerbation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients and Sample Collection
2.2. Neutrophil Isolation
2.3. Human Embryonic Lung Fibroblast (HELF) Culture
2.4. Stimulation and Inhibition Studies
2.4.1. Neutrophils
2.4.2. HELFs
2.5. NET Structure Generation and Collection
2.6. Collagen Measurement
2.7. Migration/Wound Healing Assay
2.8. H3Cit ELISA
2.9. IL-17A ELISA
2.10. RNA Extraction, cDNA Synthesis and qPCR
2.11. Immunofluorescence
2.11.1. Neutrophils
2.11.2. HELFs
2.12. MGG Stain
2.13. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
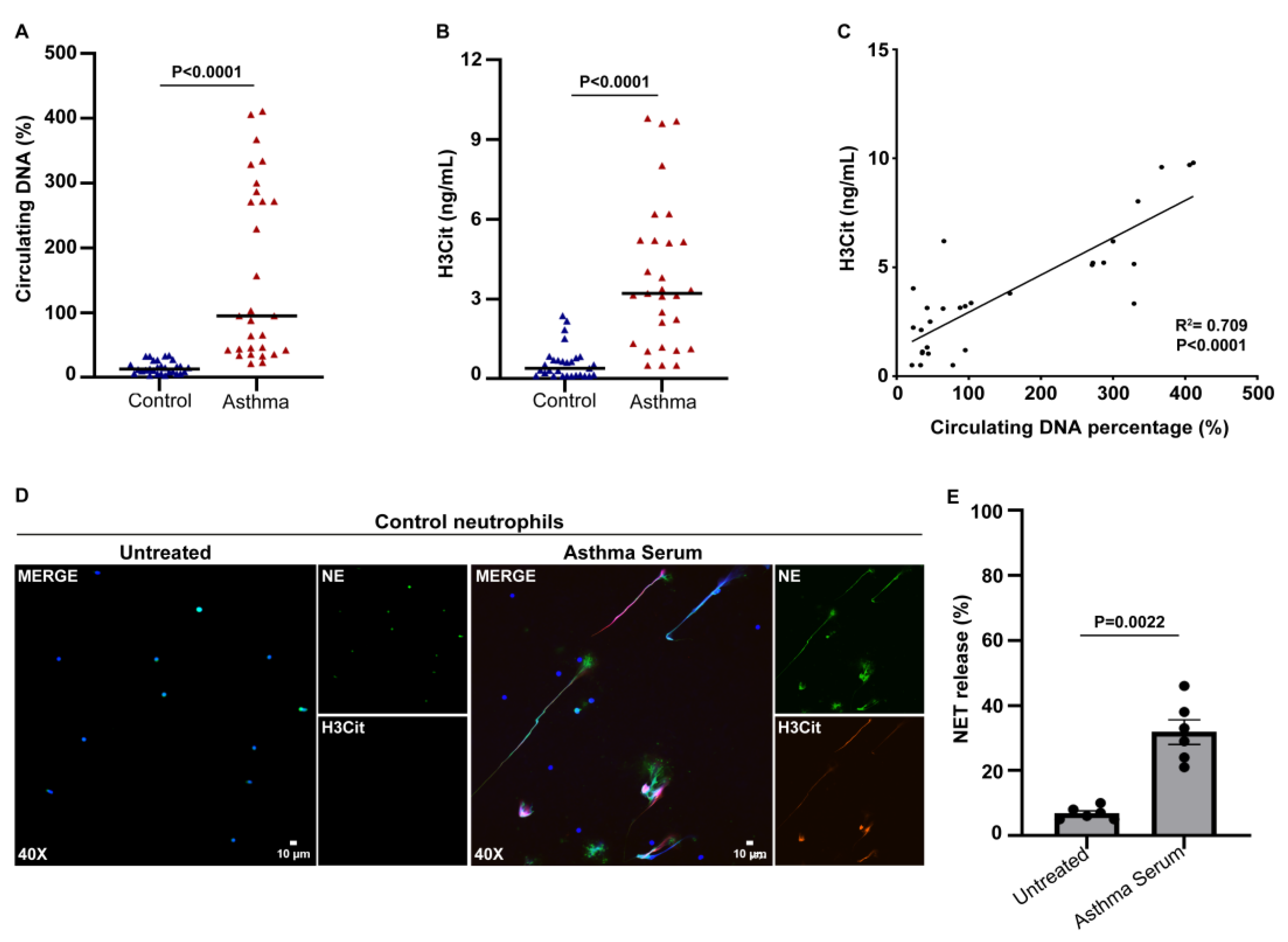
3.1. Increased Levels of Circulating NETs in Patients with Asthma Exacerbation
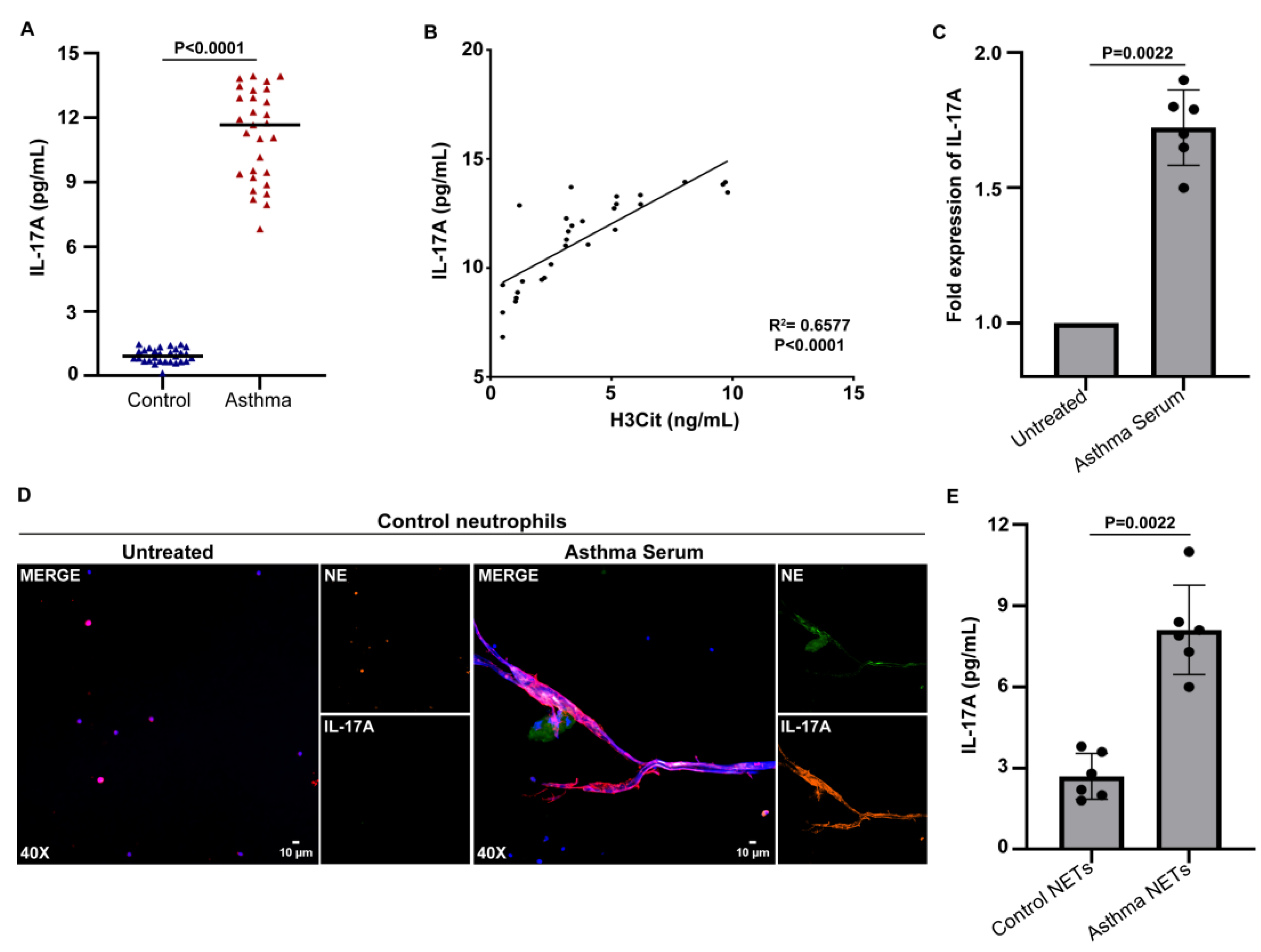
3.2. Serum from Asthma Patients during Exacerbation Induces the Release of NETs Carrying IL-17A
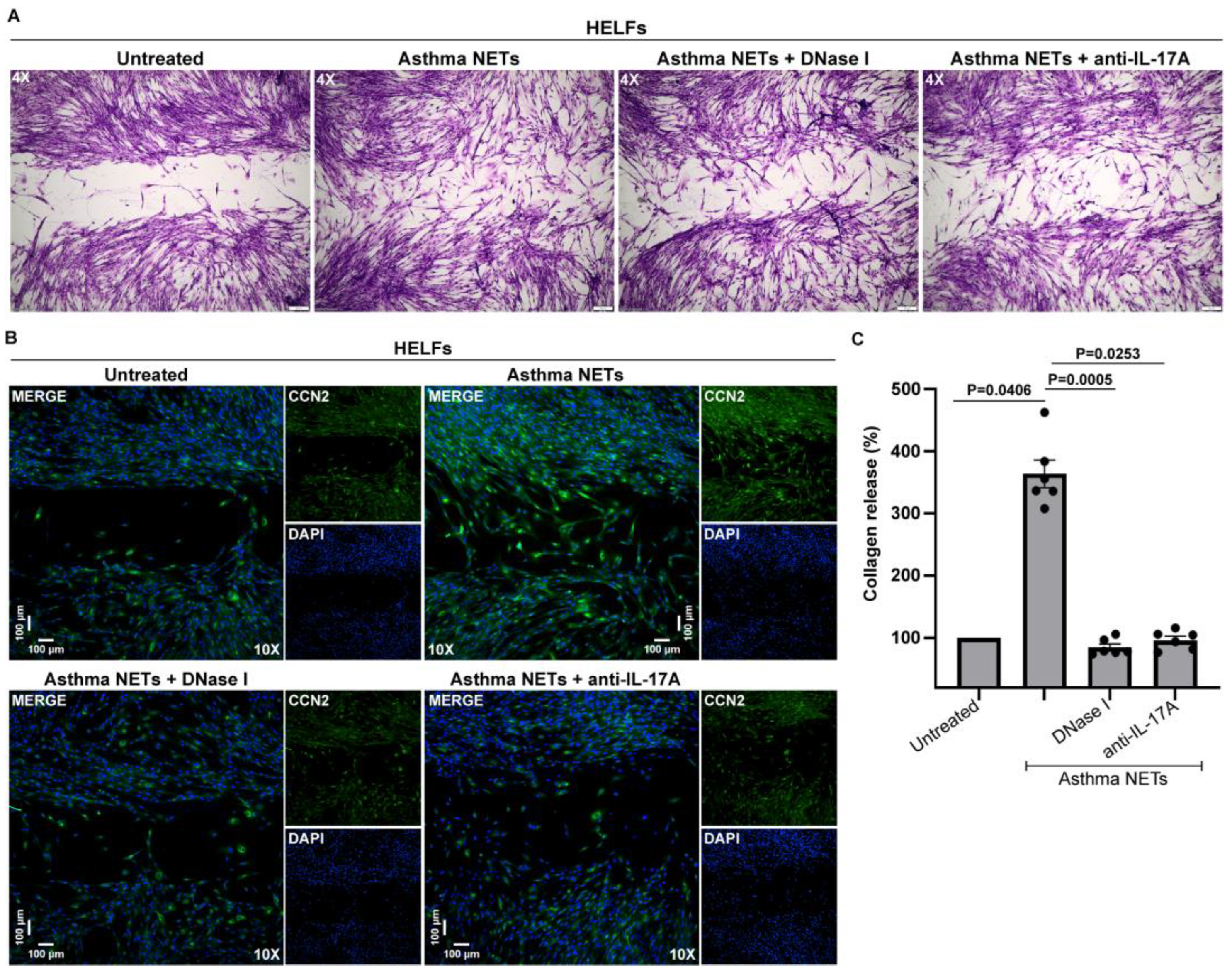
3.3. IL-17A-Enriched NETs Activate Human Lung Fibroblasts toward Collagen Production
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Serebrisky, D.; Wiznia, A. Pediatric Asthma: A Global Epidemic. Ann. Glob. Health 2019, 85, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komlósi, Z.I.; van de Veen, W.; Kovács, N.; Szűcs, G.; Sokolowska, M.; O’Mahony, L.; Akdis, M.; Akdis, C.A. Cellular and Molecular Mechanisms of Allergic Asthma. Mol. Asp. Med. 2022, 85, 100995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abrams, E.M.; Becker, A.B.; Szefler, S.J. Current State and Future of Biologic Therapies in the Treatment of Asthma in Children. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. Pulmonol. 2018, 31, 119–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, W.C.; Hastie, A.T.; Li, X.; Li, H.; Busse, W.W.; Jarjour, N.N.; Wenzel, S.E.; Peters, S.P.; Meyers, D.A.; Bleecker, E.R.; et al. Sputum Neutrophil Counts Are Associated with More Severe Asthma Phenotypes Using Cluster Analysis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2014, 133, 1557–1563.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norzila, M.Z.; Fakes, K.; Henry, R.L.; Simpson, J.; Gibson, P.G. Interleukin-8 Secretion and Neutrophil Recruitment Accompanies Induced Sputum Eosinophil Activation in Children with Acute Asthma. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2000, 161, 769–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grunwell, J.R.; Stephenson, S.T.; Tirouvanziam, R.; Brown, L.A.S.; Brown, M.R.; Fitzpatrick, A.M. Children with Neutrophil-Predominant Severe Asthma Have Proinflammatory Neutrophils with Enhanced Survival and Impaired Clearance. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2019, 7, 516–525.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hough, K.P.; Curtiss, M.L.; Blain, T.J.; Liu, R.-M.; Trevor, J.; Deshane, J.S.; Thannickal, V.J. Airway Remodeling in Asthma. Front. Med. 2020, 7, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makinde, T.; Murphy, R.F.; Agrawal, D.K. The Regulatory Role of TGF-Beta in Airway Remodeling in Asthma. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2007, 85, 348–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohno, I.; Nitta, Y.; Yamauchi, K.; Hoshi, H.; Honma, M.; Woolley, K.; O’Byrne, P.; Tamura, G.; Jordana, M.; Shirato, K. Transforming Growth Factor Beta 1 (TGF Beta 1) Gene Expression by Eosinophils in Asthmatic Airway Inflammation. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 1996, 15, 404–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molet, S.; Hamid, Q.; Davoine, F.; Nutku, E.; Taha, R.; Pagé, N.; Olivenstein, R.; Elias, J.; Chakir, J. IL-17 Is Increased in Asthmatic Airways and Induces Human Bronchial Fibroblasts to Produce Cytokines. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2001, 108, 430–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Zhang, Y.; Yao, C.; Li, B.; Li, S.; Liu, W.; Chen, R.; Shi, F. Increased Levels of Serum IL-17 and Induced Sputum Neutrophil Percentage Are Associated with Severe Early-Onset Asthma in Adults. Allergy Asthma Clin. Immunol. 2021, 17, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Yao, W. Sputum Interleukin-17 Is Increased and Associated with Airway Neutrophilia in Patients with Severe Asthma. Chin. Med. J. 2005, 118, 953–956. [Google Scholar]
- Mansour, A.I.; Abd Almonaem, E.R.; Behairy, O.G.; Gouda, T.M. Predictive Value of IL-35 and IL-17 in Diagnosis of Childhood Asthma. Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Investig. 2017, 77, 373–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosales, C. Neutrophil: A Cell with Many Roles in Inflammation or Several Cell Types? Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrero-Cervera, A.; Soehnlein, O.; Kenne, E. Neutrophils in Chronic Inflammatory Diseases. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2022, 19, 177–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumagin, R. Emerging Neutrophil Plasticity: Terminally Differentiated Cells No More. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2021, 109, 473–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatfield, S.M.; Thieblemont, N.; Witko-Sarsat, V. Expanding Neutrophil Horizons: New Concepts in Inflammation. J. Innate Immun. 2018, 10, 422–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvestre-Roig, C.; Fridlender, Z.G.; Glogauer, M.; Scapini, P. Neutrophil Diversity in Health and Disease. Trends Immunol. 2019, 40, 565–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frangou, E.; Chrysanthopoulou, A.; Mitsios, A.; Kambas, K.; Arelaki, S.; Angelidou, I.; Arampatzioglou, A.; Gakiopoulou, H.; Bertsias, G.K.; Verginis, P.; et al. REDD1/Autophagy Pathway Promotes Thromboinflammation and Fibrosis in Human Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) through NETs Decorated with Tissue Factor (TF) and Interleukin-17A (IL-17A). Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2019, 78, 238–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skendros, P.; Mitsios, A.; Chrysanthopoulou, A.; Mastellos, D.C.; Metallidis, S.; Rafailidis, P.; Ntinopoulou, M.; Sertaridou, E.; Tsironidou, V.; Tsigalou, C.; et al. Complement and Tissue Factor-Enriched Neutrophil Extracellular Traps Are Key Drivers in COVID-19 Immunothrombosis. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 130, 6151–6157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsourouktsoglou, T.-D.; Warnatsch, A.; Ioannou, M.; Hoving, D.; Wang, Q.; Papayannopoulos, V. Histones, DNA, and Citrullination Promote Neutrophil Extracellular Trap Inflammation by Regulating the Localization and Activation of TLR4. Cell Rep. 2020, 31, 107602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herster, F.; Bittner, Z.; Archer, N.K.; Dickhöfer, S.; Eisel, D.; Eigenbrod, T.; Knorpp, T.; Schneiderhan-Marra, N.; Löffler, M.W.; Kalbacher, H.; et al. Neutrophil Extracellular Trap-Associated RNA and LL37 Enable Self-Amplifying Inflammation in Psoriasis. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chrysanthopoulou, A.; Gkaliagkousi, E.; Lazaridis, A.; Arelaki, S.; Pateinakis, P.; Ntinopoulou, M.; Mitsios, A.; Antoniadou, C.; Argyriou, C.; Georgiadis, G.S.; et al. Angiotensin II Triggers Release of Neutrophil Extracellular Traps, Linking Thromboinflammation with Essential Hypertension. JCI Insight 2021, 6, e148668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, F.; Yu, M.; Zhong, Y.; Wang, L.; Huang, H. Characteristics and Role of Neutrophil Extracellular Traps in Asthma. Inflammation 2022, 45, 6–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chrysanthopoulou, A.; Mitroulis, I.; Apostolidou, E.; Arelaki, S.; Mikroulis, D.; Konstantinidis, T.; Sivridis, E.; Koffa, M.; Giatromanolaki, A.; Boumpas, D.T.; et al. Neutrophil Extracellular Traps Promote Differentiation and Function of Fibroblasts. J. Pathol. 2014, 233, 294–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papagoras, C.; Chrysanthopoulou, A.; Mitsios, A.; Ntinopoulou, M.; Tsironidou, V.; Batsali, A.K.; Papadaki, H.A.; Skendros, P.; Ritis, K. IL-17A Expressed on Neutrophil Extracellular Traps Promotes Mesenchymal Stem Cell Differentiation toward Bone-Forming Cells in Ankylosing Spondylitis. Eur. J. Immunol. 2021, 51, 930–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.; Luu, Q.Q.; Park, H.-S. Extracellular Traps: A Novel Therapeutic Target for Severe Asthma. J. Asthma Allergy 2022, 15, 803–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultz, B.M.; Acevedo, O.A.; Kalergis, A.M.; Bueno, S.M. Role of Extracellular Trap Release During Bacterial and Viral Infection. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 798853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wittig, H.J.; Belloit, J.; Fillippi, I.D.; Royal, G. Age-Related Serum Immunoglobulin E Levels in Healthy Subjects and in Patients with Allergic Disease. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1980, 66, 305–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csorba, S.; Jezerniczky, J.; Ilyés, I.; Nagy, B.; Dvorácsek, E.; Szabó, B. Immunoglobulin E in the Sera of Infants and Children. Acta Paediatr. Acad. Sci. Hung. 1976, 17, 207–214. [Google Scholar]
- Ferrante, A.; Thong, Y.H. Optimal Conditions for Simultaneous Purification of Mononuclear and Polymorphonuclear Leucocytes from Human Blood by the Hypaque-Ficoll Method. J. Immunol. Methods 1980, 36, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavriilidis, E.; Antoniadou, C.; Chrysanthopoulou, A.; Ntinopoulou, M.; Smyrlis, A.; Fotiadou, I.; Zioga, N.; Kogias, D.; Natsi, A.-M.; Pelekoudas, C.; et al. Combined Administration of Inhaled DNase, Baricitinib and Tocilizumab as Rescue Treatment in COVID-19 Patients with Severe Respiratory Failure. Clin. Immunol. 2022, 238, 109016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chrysanthopoulou, A.; Antoniadou, C.; Natsi, A.-M.; Gavriilidis, E.; Papadopoulos, V.; Xingi, E.; Didaskalou, S.; Mikroulis, D.; Tsironidou, V.; Kambas, K.; et al. Down-Regulation of KLF2 in Lung Fibroblasts Is Linked with COVID-19 Immunofibrosis and Restored by Combined Inhibition of NETs, JAK-1/2 and IL-6 Signaling. Clin. Immunol. 2023, 247, 109240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saffarzadeh, M.; Juenemann, C.; Queisser, M.A.; Lochnit, G.; Barreto, G.; Galuska, S.P.; Lohmeyer, J.; Preissner, K.T. Neutrophil Extracellular Traps Directly Induce Epithelial and Endothelial Cell Death: A Predominant Role of Histones. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e32366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoimenou, M.; Tzoros, G.; Skendros, P.; Chrysanthopoulou, A. Methods for the Assessment of NET Formation: From Neutrophil Biology to Translational Research. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 15823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chrysanthopoulou, A.; Mitroulis, I.; Kambas, K.; Skendros, P.; Kourtzelis, I.; Vradelis, S.; Kolios, G.; Aslanidis, S.; Doumas, M.; Ritis, K. Tissue Factor-Thrombin Signaling Enhances the Fibrotic Activity of Myofibroblasts in Systemic Sclerosis through up-Regulation of Endothelin Receptor A. Arthritis Rheum. 2011, 63, 3586–3597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stakos, D.A.; Kambas, K.; Konstantinidis, T.; Mitroulis, I.; Apostolidou, E.; Arelaki, S.; Tsironidou, V.; Giatromanolaki, A.; Skendros, P.; Konstantinides, S.; et al. Expression of Functional Tissue Factor by Neutrophil Extracellular Traps in Culprit Artery of Acute Myocardial Infarction. Eur. Heart J. 2015, 36, 1405–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of Relative Gene Expression Data Using Real-Time Quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schindelin, J.; Arganda-Carreras, I.; Frise, E.; Kaynig, V.; Longair, M.; Pietzsch, T.; Preibisch, S.; Rueden, C.; Saalfeld, S.; Schmid, B.; et al. Fiji: An Open-Source Platform for Biological-Image Analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lachowicz-Scroggins, M.E.; Dunican, E.M.; Charbit, A.R.; Raymond, W.; Looney, M.R.; Peters, M.C.; Gordon, E.D.; Woodruff, P.G.; Lefrançais, E.; Phillips, B.R.; et al. Extracellular DNA, Neutrophil Extracellular Traps, and Inflammasome Activation in Severe Asthma. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2019, 199, 1076–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, M.; Watz, H.; Malmgren, A.; Pedersen, F. NETopathic Inflammation in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease and Severe Asthma. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boeltz, S.; Amini, P.; Anders, H.-J.; Andrade, F.; Bilyy, R.; Chatfield, S.; Cichon, I.; Clancy, D.M.; Desai, J.; Dumych, T.; et al. To NET or Not to NET: Current Opinions and State of the Science Regarding the Formation of Neutrophil Extracellular Traps. Cell Death Differ. 2019, 26, 395–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorch, S.K.; Kubes, P. An Emerging Role for Neutrophil Extracellular Traps in Noninfectious Disease. Nat. Med. 2017, 23, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murdoch, J.R.; Lloyd, C.M. Chronic Inflammation and Asthma. Mutat. Res. 2010, 690, 24–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Royce, S.G.; Cheng, V.; Samuel, C.S.; Tang, M.L.K. The Regulation of Fibrosis in Airway Remodeling in Asthma. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 2012, 351, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chesné, J.; Braza, F.; Mahay, G.; Brouard, S.; Aronica, M.; Magnan, A. IL-17 in Severe Asthma. Where Do We Stand? Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2014, 190, 1094–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitsios, A.; Arampatzioglou, A.; Arelaki, S.; Mitroulis, I.; Ritis, K. NETopathies? Unraveling the Dark Side of Old Diseases through Neutrophils. Front. Immunol. 2016, 7, 678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherzer, R.; Grayson, M.H. Heterogeneity and the Origins of Asthma. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2018, 121, 400–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papi, A.; Brightling, C.; Pedersen, S.E.; Reddel, H.K. Asthma. Lancet 2018, 391, 783–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzpatrick, A.M.; Teague, W.G.; Meyers, D.A.; Peters, S.P.; Li, X.; Li, H.; Wenzel, S.E.; Aujla, S.; Castro, M.; Bacharier, L.B.; et al. Heterogeneity of Severe Asthma in Childhood: Confirmation by Cluster Analysis of Children in the National Institutes of Health/National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute Severe Asthma Research Program. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2011, 127, 382–389.e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddad, A.; Gaudet, M.; Plesa, M.; Allakhverdi, Z.; Mogas, A.K.; Audusseau, S.; Baglole, C.J.; Eidelman, D.H.; Olivenstein, R.; Ludwig, M.S.; et al. Neutrophils from Severe Asthmatic Patients Induce Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition in Healthy Bronchial Epithelial Cells. Respir. Res. 2019, 20, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ray, A.; Kolls, J.K. Neutrophilic Inflammation in Asthma and Association with Disease Severity. Trends Immunol. 2017, 38, 942–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambrecht, B.N.; Hammad, H.; Fahy, J.V. The Cytokines of Asthma. Immunity 2019, 50, 975–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, W.; Lv, Z.; Li, Y.; Chen, Y.; Huang, K.; Corrigan, C.J.; Ying, S. Elevated Expression of IL-33 and TSLP in the Airways of Human Asthmatics In Vivo: A Potential Biomarker of Severe Refractory Disease. J. Immunol. 2018, 200, 2253–2262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalik, M.; Wójcik-Pszczoła, K.; Paw, M.; Wnuk, D.; Koczurkiewicz, P.; Sanak, M.; Pękala, E.; Madeja, Z. Fibroblast-to-Myofibroblast Transition in Bronchial Asthma. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2018, 75, 3943–3961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phelan, P.D.; Robertson, C.F.; Olinsky, A. The Melbourne Asthma Study: 1964–1999. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2002, 109, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuge, M.; Ikeda, M.; Tsukahara, H. Novel Lung Growth Strategy with Biological Therapy Targeting Airway Remodeling in Childhood Bronchial Asthma. Children 2022, 9, 1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagome, K.; Nagata, M. Innate Immune Responses by Respiratory Viruses, Including Rhinovirus, During Asthma Exacerbation. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 865973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakiela, B.; Rebane, A.; Soja, J.; Bazan-Socha, S.; Laanesoo, A.; Plutecka, H.; Surmiak, M.; Sanak, M.; Sladek, K.; Bochenek, G. Remodeling of Bronchial Epithelium Caused by Asthmatic Inflammation Affects Its Response to Rhinovirus Infection. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 12821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamasaki, A.; Okazaki, R.; Harada, T. Neutrophils and Asthma. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagome, K.; Matsushita, S.; Nagata, M. Neutrophilic Inflammation in Severe Asthma. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2012, 158 (Suppl. S1), 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dworski, R.; Simon, H.-U.; Hoskins, A.; Yousefi, S. Eosinophil and Neutrophil Extracellular DNA Traps in Human Allergic Asthmatic Airways. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2011, 127, 1260–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delgado-Rizo, V.; Martínez-Guzmán, M.A.; Iñiguez-Gutierrez, L.; García-Orozco, A.; Alvarado-Navarro, A.; Fafutis-Morris, M. Neutrophil Extracellular Traps and Its Implications in Inflammation: An Overview. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, A.M.; Rubin, C.J.; Khandpur, R.; Wang, J.Y.; Riblett, M.; Yalavarthi, S.; Villanueva, E.C.; Shah, P.; Kaplan, M.J.; Bruce, A.T. Mast Cells and Neutrophils Release IL-17 through Extracellular Trap Formation in Psoriasis. J. Immunol. 2011, 187, 490–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reyes-Castillo, Z.; Palafox-Sánchez, C.A.; Parra-Rojas, I.; Martínez-Bonilla, G.E.; del Toro-Arreola, S.; Ramírez-Dueñas, M.G.; Ocampo-Bermudes, G.; Muñoz-Valle, J.F. Comparative Analysis of Autoantibodies Targeting Peptidylarginine Deiminase Type 4, Mutated Citrullinated Vimentin and Cyclic Citrullinated Peptides in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Associations with Cytokine Profiles, Clinical and Genetic Features. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2015, 182, 119–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindén, A.; Dahlén, B. Interleukin-17 Cytokine Signalling in Patients with Asthma. Eur. Respir. J. 2014, 44, 1319–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saglani, S.; Molyneux, C.; Gong, H.; Rogers, A.; Malmström, K.; Pelkonen, A.; Mäkelä, M.; Adelroth, E.; Bush, A.; Payne, D.N.R.; et al. Ultrastructure of the Reticular Basement Membrane in Asthmatic Adults, Children and Infants. Eur. Respir. J. 2006, 28, 505–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazan-Socha, S.; Buregwa-Czuma, S.; Jakiela, B.; Zareba, L.; Zawlik, I.; Myszka, A.; Soja, J.; Okon, K.; Zarychta, J.; Kozlik, P.; et al. Reticular Basement Membrane Thickness Is Associated with Growth- and Fibrosis-Promoting Airway Transcriptome Profile-Study in Asthma Patients. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiam, F.; Yazeedi, S.A.; Feng, K.; Phogat, S.; Demirsoy, E.; Brussow, J.; Abokor, F.A.; Osei, E.T. Understanding Fibroblast-Immune Cell Interactions via Co-Culture Models and Their Role in Asthma Pathogenesis. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1128023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wnuk, D.; Paw, M.; Ryczek, K.; Bochenek, G.; Sładek, K.; Madeja, Z.; Michalik, M. Enhanced Asthma-Related Fibroblast to Myofibroblast Transition Is the Result of Profibrotic TGF-β/Smad2/3 Pathway Intensification and Antifibrotic TGF-β/Smad1/5/(8)9 Pathway Impairment. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 16492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Jia, X.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, L.; Yang, J.; Hu, C.; Shi, J.; Jiang, X.; Lu, J.; Shen, H. Neutrophil Extracellular Traps Activate Lung Fibroblast to Induce Polymyositis-related Interstitial Lung Diseases via TLR9-miR-7-Smad2 Pathway. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 1658–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osei, E.T.; Mostaço-Guidolin, L.B.; Hsieh, A.; Warner, S.M.; AL-Fouadi, M.; Wang, M.; Cole, D.J.; Maksym, G.N.S.; Hallstrand, T.; Timens, W.; et al. Epithelial-Interleukin-1 Inhibits Collagen Formation by Airway Fibroblasts: Implications for Asthma. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 8721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, D.R.; Pijnenburg, M.W.; Smith, A.D.; De Jongste, J.C. Exhaled Nitric Oxide Measurements: Clinical Application and Interpretation. Thorax 2006, 61, 817–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petsky, H.L.; Kew, K.M.; Chang, A.B. Exhaled Nitric Oxide Levels to Guide Treatment for Children with Asthma. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2016, 11, CD011439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Licari, A.; Castagnoli, R.; Brambilla, I.; Marseglia, A.; Tosca, M.A.; Marseglia, G.L.; Ciprandi, G. Asthma Endotyping and Biomarkers in Childhood Asthma. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. Pulmonol. 2018, 31, 44–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quoc, Q.L.; Choi, Y.; Thi Bich, T.C.; Yang, E.-M.; Shin, Y.S.; Park, H.-S. S100A9 in Adult Asthmatic Patients: A Biomarker for Neutrophilic Asthma. Exp. Mol. Med. 2021, 53, 1170–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bich, T.C.T.; Quoc, Q.L.; Choi, Y.; Yang, E.-M.; Trinh, H.K.T.; Shin, Y.S.; Park, H.-S. Serum Amyloid A1: A Biomarker for Neutrophilic Airway Inflammation in Adult Asthmatic Patients. Allergy Asthma Immunol. Res. 2022, 14, 40–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirra, V.; Montella, S.; Santamaria, F. Pediatric Severe Asthma: A Case Series Report and Perspectives on Anti-IgE Treatment. BMC Pediatr. 2018, 18, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, P.G.; Yang, I.A.; Upham, J.W.; Reynolds, P.N.; Hodge, S.; James, A.L.; Jenkins, C.; Peters, M.J.; Marks, G.B.; Baraket, M.; et al. Effect of Azithromycin on Asthma Exacerbations and Quality of Life in Adults with Persistent Uncontrolled Asthma (AMAZES): A Randomised, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Lancet 2017, 390, 659–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; McAlees, J.W.; Bischoff, L.J.; Kaur, D.; Houshel, L.K.; Gray, J.; Hargis, J.; Davis, X.; Dudas, P.L.; Deshmukh, H.; et al. Combined Administration of Anti-IL-13 and Anti-IL-17A at Individually Sub-Therapeutic Doses Limits Asthma-like Symptoms in a Mouse Model of Th2/Th17 High Asthma. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2019, 49, 317–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busse, W.W.; Holgate, S.; Kerwin, E.; Chon, Y.; Feng, J.; Lin, J.; Lin, S.-L. Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study of Brodalumab, a Human Anti-IL-17 Receptor Monoclonal Antibody, in Moderate to Severe Asthma. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2013, 188, 1294–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koga, H.; Miyahara, N.; Fuchimoto, Y.; Ikeda, G.; Waseda, K.; Ono, K.; Tanimoto, Y.; Kataoka, M.; Gelfand, E.W.; Tanimoto, M.; et al. Inhibition of Neutrophil Elastase Attenuates Airway Hyperresponsiveness and Inflammation in a Mouse Model of Secondary Allergen Challenge: Neutrophil Elastase Inhibition Attenuates Allergic Airway Responses. Respir. Res. 2013, 14, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boogaard, R.; Smit, F.; Schornagel, R.; Vaessen-Verberne, A.A.P.H.; Kouwenberg, J.M.; Hekkelaan, M.; Hendriks, T.; Feith, S.W.W.; Hop, W.C.J.; de Jongste, J.C.; et al. Recombinant Human Deoxyribonuclease for the Treatment of Acute Asthma in Children. Thorax 2008, 63, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hull, J.H.K.; Castle, N.; Knight, R.K.; Ho, T.B.L. Nebulised DNase in the Treatment of Life Threatening Asthma. Resuscitation 2007, 74, 175–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Asthma n = 29 | Controls n = 29 | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sex male, (%) | 18 (62%) | 16 (55.2%) | 0.182 |
| Age (years), mean (±SD) | 8.9 ± 4.7 | 10.9 ± 5.7 | 0.071 |
| Comorbidities | - | ||
| AD n (%) | 12 (41.4%) | - | |
| FA n (%) | 6 (20.7%) | - | |
| AR n (%) | 14 (48.3%) | - | |
| Laboratory data | |||
| Ig E IU/mL mean (±SD) | 582.7 ± 188.4 | 103.13 ± 16.7 | 0.0001 |
| WBC count (1000/mm3) | 8.9 | 7.4 | 0.21 |
| Neutrophil count | 62% | 58.4% | 0.59 |
| Eosinophil count | 8.4% | 3.2% | 0.0001 |
| CRP mg/dL mean (±SD) | 0.95 (±0.84) | 0.65 (±0.41) | 0.44 |
| Asthma medication | |||
| Inhaled SABA frequency n (%) | |||
| None | 2 (6.9%) | - | |
| <1/month | 20 (68.9%) | - | |
| ≥1/month | 7 (24.1%) | - | |
| Asthma severity n (%) | |||
| Intermittent | 8 (27.5%) | - | |
| Mild persistent | 9 (31%) | - | |
| Moderate or severe persistent | 12 (41.4%) | - | |
| Inhaled corticosteroid grade | |||
| None | 4 (13.8) | - | |
| Low dose | 13 (44.8%) | - | |
| Medium or high dose | 12 (41.4%) | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ntinopoulou, M.; Cassimos, D.; Roupakia, E.; Kolettas, E.; Panopoulou, M.; Mantadakis, E.; Konstantinidis, T.; Chrysanthopoulou, A. Ιnterleukin-17A-Enriched Neutrophil Extracellular Traps Promote Immunofibrotic Aspects of Childhood Asthma Exacerbation. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 2104. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11082104
Ntinopoulou M, Cassimos D, Roupakia E, Kolettas E, Panopoulou M, Mantadakis E, Konstantinidis T, Chrysanthopoulou A. Ιnterleukin-17A-Enriched Neutrophil Extracellular Traps Promote Immunofibrotic Aspects of Childhood Asthma Exacerbation. Biomedicines. 2023; 11(8):2104. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11082104
Chicago/Turabian StyleNtinopoulou, Maria, Dimitrios Cassimos, Eugenia Roupakia, Evangelos Kolettas, Maria Panopoulou, Elpis Mantadakis, Theocharis Konstantinidis, and Akrivi Chrysanthopoulou. 2023. "Ιnterleukin-17A-Enriched Neutrophil Extracellular Traps Promote Immunofibrotic Aspects of Childhood Asthma Exacerbation" Biomedicines 11, no. 8: 2104. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11082104
APA StyleNtinopoulou, M., Cassimos, D., Roupakia, E., Kolettas, E., Panopoulou, M., Mantadakis, E., Konstantinidis, T., & Chrysanthopoulou, A. (2023). Ιnterleukin-17A-Enriched Neutrophil Extracellular Traps Promote Immunofibrotic Aspects of Childhood Asthma Exacerbation. Biomedicines, 11(8), 2104. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11082104