Use of a Novel Whole Blood Separation and Transport Device for Targeted and Untargeted Proteomics
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Samples
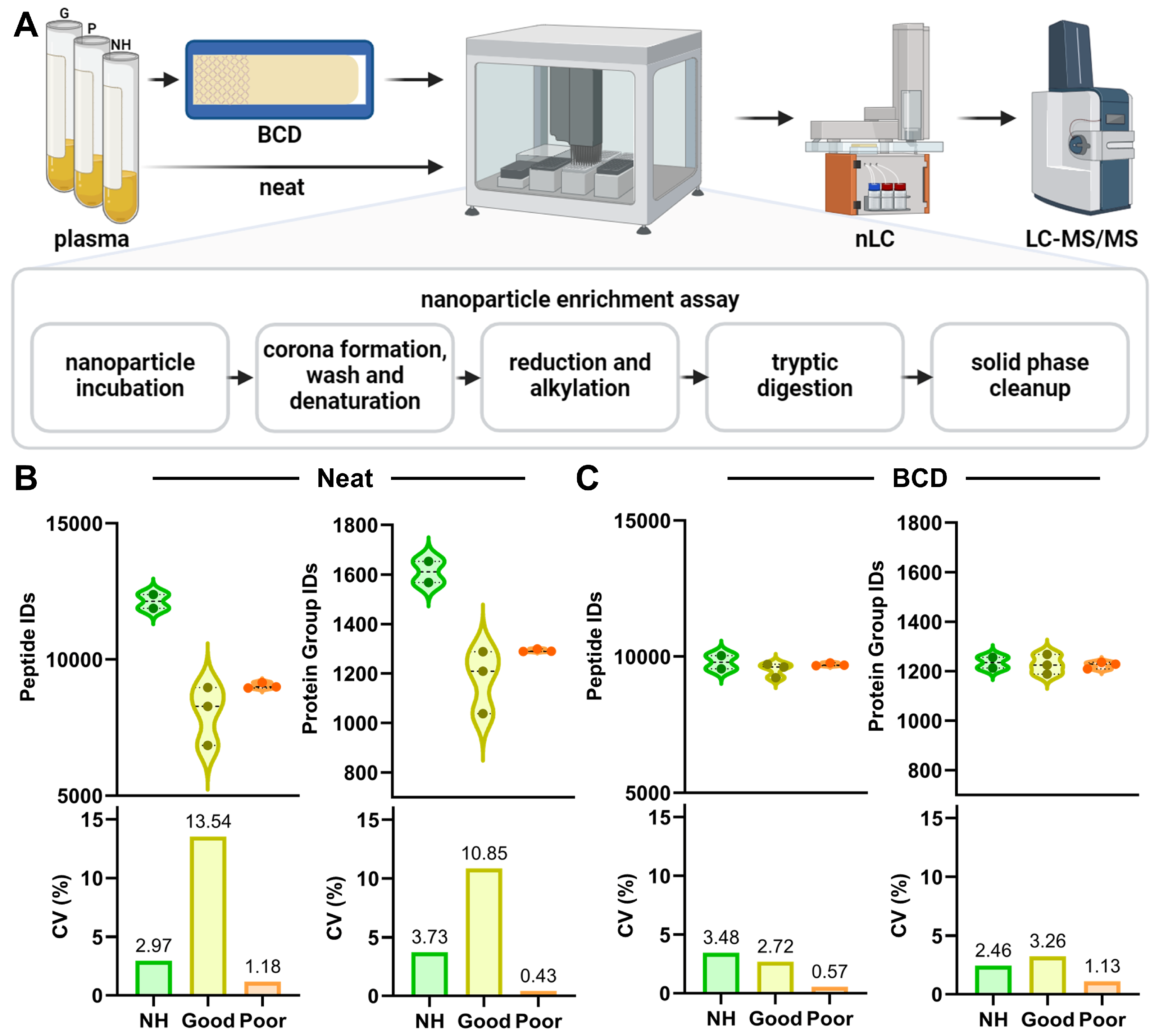
2.2. Proteomic Preparation
2.3. Untargeted LC-MS/MS
2.4. Targeted LC-MS/MS
2.5. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Untargeted Proteomics with the Blood Collection Device
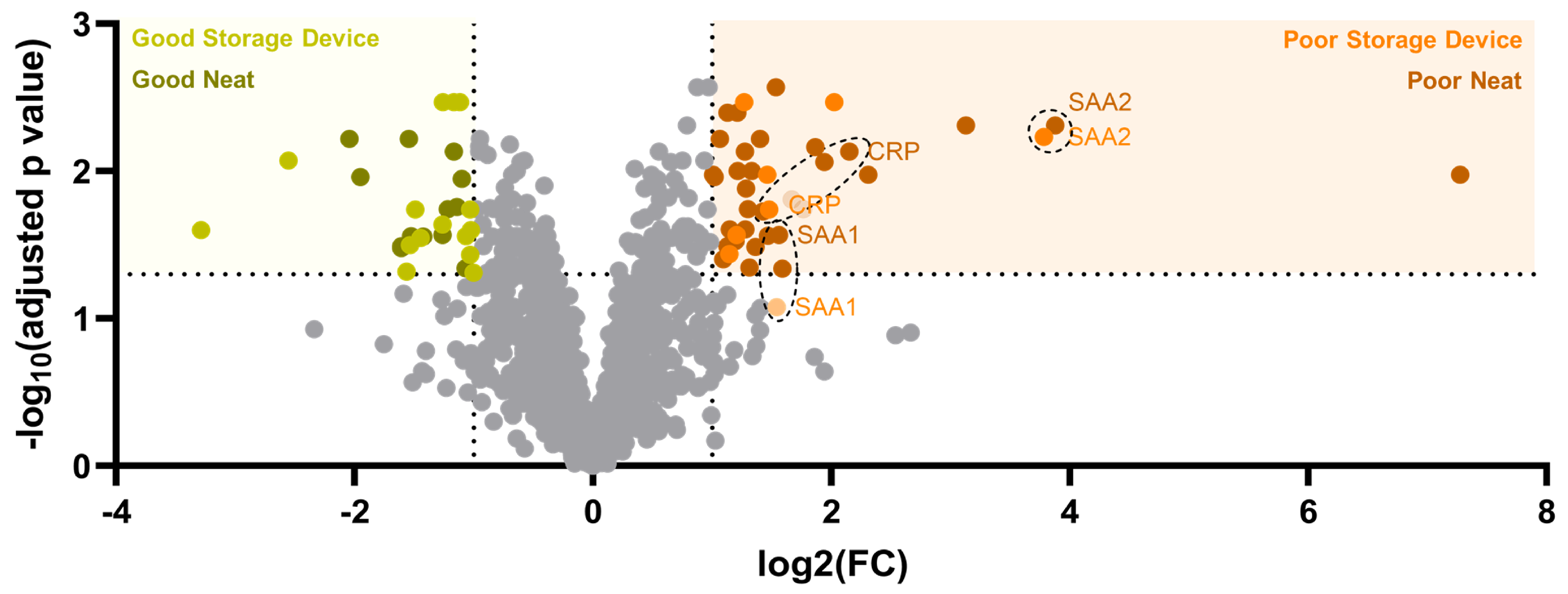
3.2. Effect of the BCD on the Plasma Proteome
3.3. Use of the BCD for a Clinical Immune Classifier
3.4. Targeted Proteomics with the Blood Collection Device
3.5. Protein Abundance Measurements Between the BCD and Neat Plasma
3.6. Device Protein Migration Gradient
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Patents
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Anderson, N.L. The Clinical Plasma Proteome: A Survey of Clinical Assays for Proteins in Plasma and Serum. Clin. Chem. 2010, 56, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, N.L.; Anderson, N.G. The Human Plasma Proteome: History, Character, and Diagnostic Prospects. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2002, 1, 845–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chambers, A.G.; Percy, A.J.; Yang, J.; Borchers, C.H. Multiple Reaction Monitoring Enables Precise Quantification of 97 Proteins in Dried Blood Spots. Mol. Cell Proteom. 2015, 14, 3094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Tse, F.L.S. Dried Blood Spot Sampling in Combination with LC-MS/MS for Quantitative Analysis of Small Molecules. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2010, 24, 49–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, M.; Tonoli, D.; Varesio, E.; Hopfgartner, G. The Use of Mass Spectrometry to Analyze Dried Blood Spots. Mass. Spectrom. Rev. 2016, 35, 361–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakaria, R.; Allen, K.J.; Koplin, J.J.; Roche, P.; Greaves, R.F. Advantages and Challenges of Dried Blood Spot Analysis by Mass Spectrometry Across the Total Testing Process. EJIFCC 2016, 27, 288. [Google Scholar]
- Demirev, P.A. Dried Blood Spots: Analysis and Applications. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 779–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eshghi, A.; Pistawka, A.J.; Liu, J.; Chen, M.; Sinclair, N.J.T.; Hardie, D.B.; Elliott, M.; Chen, L.; Newman, R.; Mohammed, Y.; et al. Concentration Determination of >200 Proteins in Dried Blood Spots for Biomarker Discovery and Validation. Mol. Cell Proteom. 2020, 19, 540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, C.M.; Bollinger, J.G.; Becker, J.O.; Wallace, J.M.; Laha, T.J.; MacCoss, M.J.; Hoofnagle, A.N. Quantification by Nano Liquid Chromatography-Parallel Reaction Monitoring-Mass Spectrometry of Human Apolipoprotein A-I, Apolipoprotein B, and Hemoglobin A1c in Dried Blood Spots. Proteom. Clin. Appl. 2017, 11, 1600103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razavi, M.; Anderson, N.L.; Yip, R.; Pope, M.E.; Pearson, T.W. Multiplexed Longitudinal Measurement of Protein Biomarkers in DBS Using an Automated SISCAPA Workflow. Bioanalysis 2016, 8, 1597–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozcan, S.; Cooper, J.D.; Lago, S.G.; Kenny, D.; Rustogi, N.; Stocki, P.; Bahn, S. Towards Reproducible MRM Based Biomarker Discovery Using Dried Blood Spots. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 45178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chambers, A.G.; Percy, A.J.; Hardie, D.B.; Borchers, C.H. Comparison of Proteins in Whole Blood and Dried Blood Spot Samples by LC/MS/MS. J. Am. Soc. Mass. Spectrom. 2013, 24, 1338–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velghe, S.; Delahaye, L.; Stove, C.P. Is the Hematocrit Still an Issue in Quantitative Dried Blood Spot Analysis? J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2019, 163, 188–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Kesel, P.M.M.; Sadones, N.; Capiau, S.; Lambert, W.E.; Stove, C.P. Hemato-Critical Issues in Quantitative Analysis of Dried Blood Spots: Challenges and Solutions. Bioanalysis 2013, 5, 2023–2041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Rabie, P.; Denniff, P.; Spooner, N.; Chowdhry, B.Z.; Pullen, F.S. Investigation of Different Approaches to Incorporating Internal Standard in DBS Quantitative Bioanalytical Workflows and Their Effect on Nullifying Hematocrit-Based Assay Bias. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 4996–5003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vries, R.; Barfield, M.; Van De Merbel, N.; Schmid, B.; Siethoff, C.; Ortiz, J.; Verheij, E.; Van Baar, B.; Cobb, Z.; White, S.; et al. The Effect of Hematocrit on Bioanalysis of DBS: Results from The EBF DBS-Microsampling Consortium. Bioanalysis 2013, 5, 2147–2160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sturm, R.; Henion, J.; Abbott, R.; Wang, P. Novel Membrane Devices and Their Potential Utility in Blood Sample Collection Prior to Analysis of Dried Plasma Spots. Bioanalysis 2015, 7, 1987–2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Woenker, T.; Adamec, J.; Regnier, F.E. Simple, Miniaturized Blood Plasma Extraction Method. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 11501–11508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaiser, N.K.; Steers, M.; Nichols, C.M.; Mellert, H.; Pestano, G.A. Design and Characterization of a Novel Blood Collection and Transportation Device for Proteomic Applications. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crawford, M.L.; Collier, B.B.; Bradley, M.N.; Holland, P.L.; Shuford, C.M.; Grant, R.P. Empiricism in Microsampling: Utilizing a Novel Lateral Flow Device and Intrinsic Normalization to Provide Accurate and Precise Clinical Analysis from a Finger Stick. Clin. Chem. 2020, 66, 821–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forchelet, D.; Béguin, S.; Sajic, T.; Bararpour, N.; Pataky, Z.; Frias, M.; Grabherr, S.; Augsburger, M.; Liu, Y.; Charnley, M.; et al. Separation of Blood Microsamples by Exploiting Sedimentation at the Microscale. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 14101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koc, M.A.; Wiles, T.A.; Weinhold, D.C.; Rightmyer, S.; Weaver, A.L.; McDowell, C.T.; Roder, J.; Asmellash, S.; Pestano, G.A.; Roder, H.; et al. Molecular and Translational Biology of the Blood-Based VeriStrat® Proteomic Test Used in Cancer Immunotherapy Treatment Guidance. J. Mass. Spectrom. Adv. Clin. Lab. 2023, 30, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rich, P.; Mitchell, R.B.; Schaefer, E.; Walker, P.R.; Dubay, J.W.; Boyd, J.; Oubre, D.; Page, R.; Khalil, M.; Sinha, S.; et al. Real-World Performance of Blood-Based Proteomic Profiling in First-Line Immunotherapy Treatment in Advanced Stage Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. J. Immunother. Cancer 2021, 9, e002989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leal, T.A.; Argento, A.C.; Bhadra, K.; Hogarth, D.K.; Grigorieva, J.; Hartfield, R.M.; McDonald, R.C.; Bonomi, P.D. Prognostic Performance of Proteomic Testing in Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Systematic Literature Review and Meta-Analysis. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 2020, 1497–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaither, C.; Popp, R.; Borchers, S.P.; Skarphedinsson, K.; Eiriksson, F.F.; Thorsteinsdóttir, M.; Mohammed, Y.; Borchers, C.H. Performance Assessment of a 125 Human Plasma Peptide Mixture Stored at Room Temperature for Multiple Reaction Monitoring-Mass Spectrometry. J. Proteome Res. 2021, 20, 4292–4302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demichev, V.; Messner, C.B.; Vernardis, S.I.; Lilley, K.S.; Ralser, M. DIA-NN: Neural Networks and Interference Correction Enable Deep Proteome Coverage in High Throughput. Nat. Methods 2020, 17, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashburner, M.; Ball, C.A.; Blake, J.A.; Botstein, D.; Butler, H.; Cherry, J.M.; Davis, A.P.; Dolinski, K.; Dwight, S.S.; Eppig, J.T.; et al. Gene Ontology: Tool for the Unification of Biology. Nat. Genet. 2000, 25, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, P.D.; Campbell, M.J.; Kejariwal, A.; Mi, H.; Karlak, B.; Daverman, R.; Diemer, K.; Muruganujan, A.; Narechania, A. PANTHER: A Library of Protein Families and Subfamilies Indexed by Function. Genome Res. 2003, 13, 2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, H.; Muruganujan, A.; Casagrande, J.T.; Thomas, P.D. Large-Scale Gene Function Analysis with PANTHER Classification System. Nat. Protoc. 2013, 8, 1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasteiger, E.; Hoogland, C.; Gattiker, A.; Duvaud, S.; Wilkins, M.R.; Appel, R.D.; Bairoch, A. Protein Identification and Analysis Tools on the ExPASy Server. In The Proteomics Protocols Handbook; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005; pp. 571–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacLean, B.; Tomazela, D.M.; Shulman, N.; Chambers, M.; Finney, G.L.; Frewen, B.; Kern, R.; Tabb, D.L.; Liebler, D.C.; MacCoss, M.J. Skyline: An Open Source Document Editor for Creating and Analyzing Targeted Proteomics Experiments. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blume, J.E.; Manning, W.C.; Troiano, G.; Hornburg, D.; Figa, M.; Hesterberg, L.; Platt, T.L.; Zhao, X.; Cuaresma, R.A.; Everley, P.A.; et al. Rapid, Deep and Precise Profiling of the Plasma Proteome with Multi-Nanoparticle Protein Corona. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guruprasad, K.; Reddy, B.V.B.; Pandit, M.W. Correlation between Stability of a Protein and Its Dipeptide Composition: A Novel Approach for Predicting in Vivo Stability of a Protein from Its Primary Sequence. Protein Eng. 1990, 4, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kyte, J.; Doolittle, R.F. A Simple Method for Displaying the Hydropathic Character of a Protein. J. Mol. Biol. 1982, 157, 105–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parida, S.K.; Dash, S.; Patel, S.; Mishra, B.K. Adsorption of Organic Molecules on Silica Surface. Adv. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2006, 121, 77–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaut, R.A.; Bakaev, V.A.; Pantano, C.G. Surface Chemistry and Adsorption on Glass Fibers. In Fiberglass Science and Technology: Chemistry, Characterization, Processing, Modeling, Application, and Sustainability; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; pp. 217–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, B.; Shin, Y.K.; Hassanali, A.A.; Singer, S.J. DNA Binding to the Silica Surface. J. Phys. Chem. B 2015, 119, 11030–11040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bag, S.; Rauwolf, S.; Schwaminger, S.P.; Wenzel, W.; Berensmeier, S. DNA Binding to the Silica: Cooperative Adsorption in Action. Langmuir 2021, 37, 5902–5908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.P.; Chen, Y.C.; Chen, W.Y. Improve Sample Preparation Process for MiRNA Isolation from the Culture Cells by Using Silica Fiber Membrane. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 21132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taguchi, F.; Solomon, B.; Gregorc, V.; Roder, H.; Gray, R.; Kasahara, K.; Nishio, M.; Brahmer, J.; Spreafico, A.; Ludovini, V.; et al. Mass Spectrometry to Classify Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer Patients for Clinical Outcome After Treatment with Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors: A Multicohort Cross-Institutional Study. JNCI J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2007, 99, 838–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harlan, R.; Zhang, H. Targeted Proteomics: A Bridge between Discovery and Validation. Expert. Rev. Proteom. 2014, 11, 657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakayasu, E.S.; Gritsenko, M.; Piehowski, P.D.; Gao, Y.; Orton, D.J.; Schepmoes, A.A.; Fillmore, T.L.; Frohnert, B.I.; Rewers, M.; Krischer, J.P.; et al. Tutorial: Best Practices and Considerations for Mass-Spectrometry-Based Protein Biomarker Discovery and Validation. Nat. Protoc. 2021, 16, 3737–3760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffin, N.M.; Yu, J.; Long, F.; Oh, P.; Shore, S.; Li, Y.; Koziol, J.A.; Schnitzer, J.E. Label-Free, Normalized Quantification of Complex Mass Spectrometry Data for Proteomics Analysis. Nat. Biotechnol. 2010, 28, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Välikangas, T.; Suomi, T.; Elo, L.L. A Systematic Evaluation of Normalization Methods in Quantitative Label-Free Proteomics. Brief. Bioinform. 2018, 19, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.J.; Lee, L.W.; Hayward, C.; Brusniak, M.Y.; Fong, P.Y.; McLean, M.; Mulligan, J.; Spicer, D.; Fang, K.C.; Hunsucker, S.W.; et al. An Integrated Quantification Method to Increase the Precision, Robustness, and Resolution of Protein Measurement in Human Plasma Samples. Clin. Proteom. 2015, 12, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bioanalytical Method. Validation Guidance for Industry. 2018. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/files/drugs/published/Bioanalytical-Method-Validation-Guidance-for-Industry.pdf (accessed on 3 October 2024).
- Wei, A.A.J.; Joshi, A.; Chen, Y.; McIndoe, J.S. Strategies for Avoiding Saturation Effects in ESI-MS. Int. J. Mass. Spectrom. 2020, 450, 116306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norde, W.; Favier, J.P. Structure of Adsorbed and Desorbed Proteins. Colloids Surf. 1992, 64, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakanishi, K.; Sakiyama, T.; Imamura, K. On the Adsorption of Proteins on Solid Surfaces, a Common but Very Complicated Phenomenon. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2001, 91, 233–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poeckh, T.; Lopez, S.; Fuller, A.O.; Solomon, M.J.; Larson, R.G. Adsorption and Elution Characteristics of Nucleic Acids on Silica Surfaces and Their Use in Designing a Miniaturized Purification Unit. Anal. Biochem. 2008, 373, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, S.C.; Yiap, B.C. DNA, RNA, and Protein Extraction: The Past and The Present. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2009, 2009, 574398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dederich, D.A.; Okwuonu, G.; Garner, T.; Denn, A.; Sutton, A.; Escotto, M.; Martindale, A.; Delgado, O.; Muzny, D.M.; Gibbs, R.A.; et al. Glass Bead Purification of Plasmid Template DNA for High Throughput Sequencing of Mammalian Genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, e32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- March, D.; Bianco, V.; Franzese, G. Protein Unfolding and Aggregation near a Hydrophobic Interface. Polymers 2021, 13, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabe, M.; Verdes, D.; Seeger, S. Understanding Protein Adsorption Phenomena at Solid Surfaces. Adv. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2011, 162, 87–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schvartz, M.; Saudrais, F.; Devineau, S.; Aude, J.C.; Chédin, S.; Henry, C.; Millán-Oropeza, A.; Perrault, T.; Pieri, L.; Pin, S.; et al. A Proteome Scale Study Reveals How Plastic Surfaces and Agitation Promote Protein Aggregation. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duncan, M.W.; Roder, H.; Hunsucker, S.W. Quantitative Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption/Ionization Mass Spectrometry. Brief. Funct. Genom. Proteomic 2008, 7, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Alessandro, A.; Righetti, P.G.; Zolla, L. The Red Blood Cell Proteome and Interactome: An Update. J. Proteome Res. 2010, 9, 144–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, K.; Li, Z.; Zhang, L.; Shen, W. Understanding Haemolysis in Polysulfone and Glass Fibre Membranes for Blood Separation. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2023, 396, 134566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenn, W.O. Hemolysis of erythrocytes in contact with glass. J. Exp. Med. 1922, 35, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




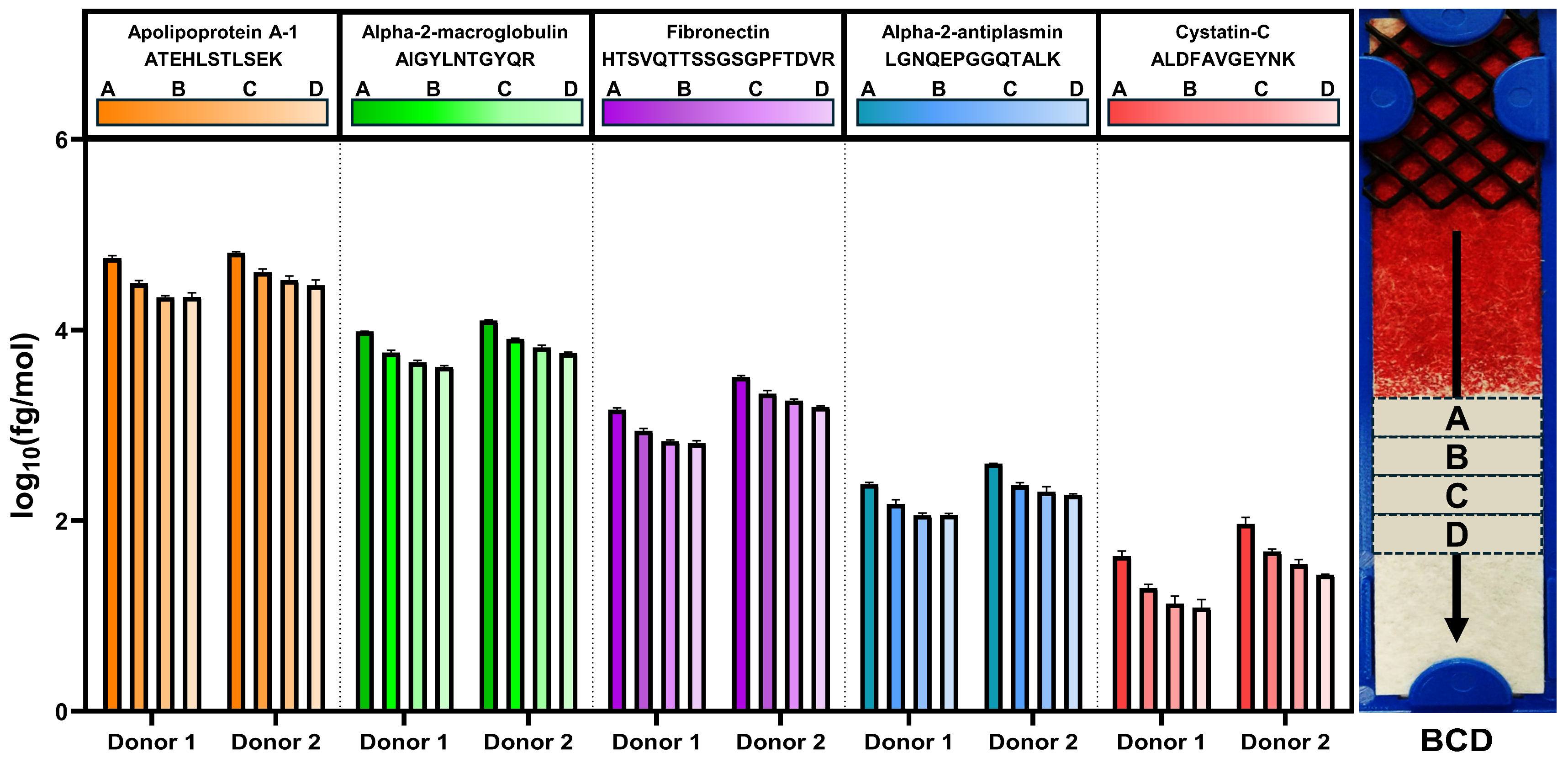
| Section | Sum (fmol/μL) | Average (fmol/μL) | Standard Deviation (fmol/μL) |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | 1,644,948 | 18,691 | 516 |
| B | 1,040,229 | 11,820 | 313 |
| C | 879,382 | 9991 | 350 |
| D | 800,815 | 9099 | 258 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
McDowell, C.T.; Weaver, A.L.; Vargas-Cruz, N.; Kaiser, N.K.; Nichols, C.M.; Pestano, G.A. Use of a Novel Whole Blood Separation and Transport Device for Targeted and Untargeted Proteomics. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 2318. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12102318
McDowell CT, Weaver AL, Vargas-Cruz N, Kaiser NK, Nichols CM, Pestano GA. Use of a Novel Whole Blood Separation and Transport Device for Targeted and Untargeted Proteomics. Biomedicines. 2024; 12(10):2318. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12102318
Chicago/Turabian StyleMcDowell, Colin T., Amanda L. Weaver, Nylev Vargas-Cruz, Nathan K. Kaiser, Charles M. Nichols, and Gary A. Pestano. 2024. "Use of a Novel Whole Blood Separation and Transport Device for Targeted and Untargeted Proteomics" Biomedicines 12, no. 10: 2318. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12102318
APA StyleMcDowell, C. T., Weaver, A. L., Vargas-Cruz, N., Kaiser, N. K., Nichols, C. M., & Pestano, G. A. (2024). Use of a Novel Whole Blood Separation and Transport Device for Targeted and Untargeted Proteomics. Biomedicines, 12(10), 2318. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12102318







