Specific and Polyfunctional T Cell Response Against N-Methyl-d-aspartate Receptor in an Autoantibody-Mediated Encephalitis Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Active Immunization
2.3. Isolation of Spleen and Meninges
2.4. Cell Culture of Leukocytes from Spleen and Meninges
2.5. Cell Proliferation Assay by Carbofluorescein Succinimidyl Ester (CFSE) Dilution
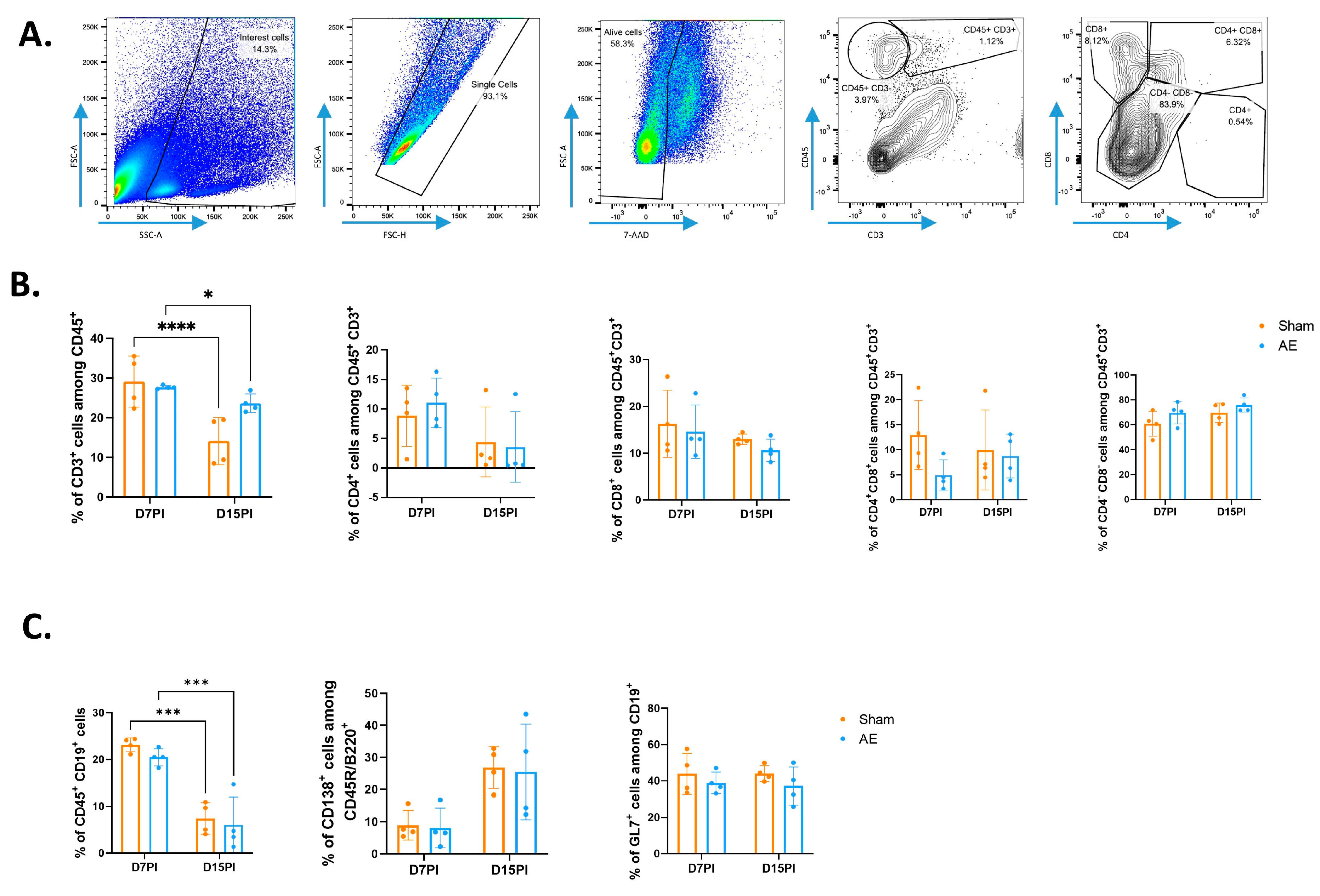
2.6. Flow Cytometry
2.7. Cytokine Assays
2.8. Preparation of Protein Samples for Proteomics Analysis
2.9. Identification of Proteins Using MS/MS Analysis
2.10. Differential Gene Expression Analysis
2.11. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Immunization with GluN1 Peptide Did Not Modify the Adaptive Immune Cell Repartition in Both Spleen and Meninges of NMDAR AE Mice
3.2. An Anti-GluN1-Specific T Cell Response Is Elicited Both in Periphery and in CNS of NMDAR AE Mice
3.3. Anti-GluN1-Specific T Cells Preferentially Display a Th1, Th2/Tfh, and Th17 Profile
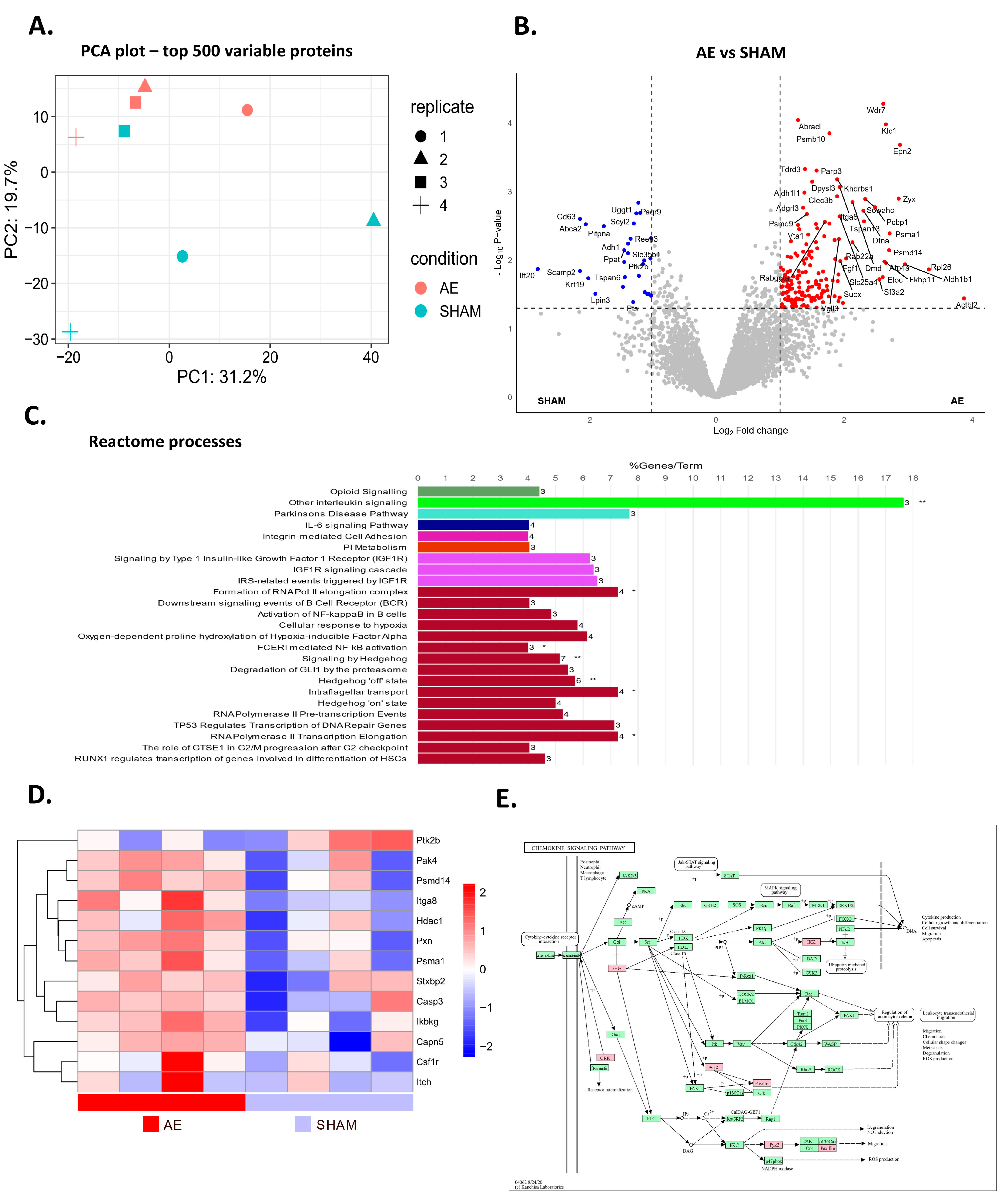
3.4. AE Alters Protein Profile Related to B Cell Activation and Cytokine Production in Meninges
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dalmau, J.; Armangué, T.; Pl anagumà, J.; Radosevic, M.; Mannara, F.; Leypoldt, F.; Geis, C.; Lancaster, E.; Titulaer, M.J.; Rosenfeld, M.R.; et al. An update on anti-NMDA receptor encephalitis for neurologists and psychiatrists: Mechanisms and models. Lancet Neurol. 2019, 18, 1045–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moscato, E.H.; Peng, X.; Jain, A.; Parsons, T.D.; Dalmau, J.; Balice-Gordon, R.J. Acute mechanisms underlying antibody effects in anti-N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor encephalitis. Ann. Neurol. 2014, 76, 108–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Planagumà, J.; Leypoldt, F.; Mannara, F.; Gutiérrez-Cuesta, J.; Martín-García, E.; Aguilar, E.; Titulaer, M.J.; Petit-Pedrol, M.; Jain, A.; Balice-Gordon, R.; et al. Human N-methyl d-aspartate receptor antibodies alter memory and behaviour in mice. Brain 2015, 138, 94–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crotty, S. T Follicular Helper Cell Biology: A Decade of Discovery and Diseases. Immunity 2019, 50, 1132–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Hernandez, E.; Horvath, J.; Shiloh-Malawsky, Y.; Sangha, N.; Martinez-Lage, M.; Dalmau, J. Analysis of complement and plasma cells in the brain of patients with anti-NMDAR encephalitis. Neurology 2011, 77, 589–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, B.E.; Tovar, K.R.; Goehring, A.; Jalali-Yazdi, F.; Okada, N.J.; Gouaux, E.; Westbrook, G.L. Autoimmune receptor encephalitis in mice induced by active immunization with conformationally stabilized holoreceptors. Sci. Transl. Med. 2019, 11, eaaw0044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagnon, I.; Hélie, P.; Bardou, I.; Regnauld, C.; Lesec, L.; Leprince, J.; Naveau, M.; Delaunay, B.; Toutirais, O.; Lemauff, B.; et al. Autoimmune encephalitis mediated by B-cell response against N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor. Brain 2020, 143, 2957–2972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Chen, J.; Peng, Y.; Wang, H.; Qiu, W.; Xie, W.; Zhang, J.; Wang, H. Anti-NMDAR encephalitis induced in mice by active immunization with a peptide from the amino-terminal domain of the GluN1 subunit. J. Neuroinflamm. 2021, 18, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linnoila, J.; Jalali Motlagh, N.; Jachimiec, G.; Lin, C.-C.J.; Küllenberg, E.; Wojtkiewicz, G.; Tanzi, R.; Chen, J.W. Optimizing animal models of autoimmune encephalitis using active immunization. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1177672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böhmer, R.M.; Bandala-Sanchez, E.; Harrison, L.C. Forward light scatter is a simple measure of T-cell activation and proliferation but is not universally suited for doublet discrimination. Cytometry A 2011, 79, 646–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lind Enoksson, S.; Bergman, P.; Klingström, J.; Boström, F.; Da Silva Rodrigues, R.; Winerdal, M.E.; Marits, P. A flow cytometry-based proliferation assay for clinical evaluation of T-cell memory against SARS-CoV-2. J. Immunol. Methods 2021, 499, 113159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hughes, E.G.; Peng, X.; Gleichman, A.J.; Lai, M.; Zhou, L.; Tsou, R.; Parsons, T.D.; Lynch, D.R.; Dalmau, J.; Balice-Gordon, R.J. Cellular and synaptic mechanisms of anti-NMDA receptor encephalitis. J. Neurosci. 2010, 30, 5866–5875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.-G.; Lee, J.-U.; Kim, D.-H.; Lim, S.; Kang, I.; Choi, J.-M. Pathogenic function of bystander-activated memory-like CD4+ T cells in autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, M.; Zhang, Z.; Cui, Y. Unconventional T cells in brain homeostasis, injury and neurodegeneration. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1273459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonobe, Y.; Jin, S.; Wang, J.; Kawanokuchi, J.; Takeuchi, H.; Mizuno, T.; Suzumura, A. Chronological changes of CD4+ and CD8+ T cell subsets in the experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis, a mouse model of multiple sclerosis. Tohoku J. Exp. Med. 2007, 213, 329–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Martinez-Pasamar, S.; Abad, E.; Moreno, B.; Velez de Mendizabal, N.; Martinez-Forero, I.; Garcia-Ojalvo, J.; Villoslada, P. Dynamic cross-regulation of antigen-specific effector and regulatory T cell subpopulations and microglia in brain autoimmunity. BMC Syst. Biol. 2013, 7, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steckner, C.; Weber, A.; Mausberg, A.K.; Heininger, M.; Opdenhövel, F.; Kieseier, B.C.; Hartung, H.P.; Hofstetter, H.H. Alteration of the cytokine signature by various TLR ligands in different T cell populations in MOG37-50 and MOG35-55-induced EAE in C57BL/6 mice. Clin. Immunol. 2016, 170, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofstetter, H.H.; Ibrahim, S.M.; Koczan, D.; Kruse, N.; Weishaupt, A.; Toyka, K.V.; Gold, R. Therapeutic efficacy of IL-17 neutralization in murine experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Cell. Immunol. 2005, 237, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dao, L.-M.; Machule, M.-L.; Bacher, P.; Hoffmann, J.; Ly, L.-T.; Wegner, F.; Scheffold, A.; Prüss, H. Decreased inflammatory cytokine production of antigen-specific CD4+ T cells in NMDA receptor encephalitis. J. Neurol. 2021, 268, 2123–2131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, M.S.; Prod’homme, T.; Patarroyo, J.C.; Molnarfi, N.; Karnezis, T.; Lehmann-Horn, K.; Danilenko, D.M.; Eastham-Anderson, J.; Slavin, A.J.; Linington, C.; et al. B-cell activation influences T-cell polarization and outcome of anti-CD20 B-cell depletion in central nervous system autoimmunity. Ann. Neurol. 2010, 68, 369–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molnarfi, N.; Schulze-Topphoff, U.; Weber, M.S.; Patarroyo, J.C.; Prod’homme, T.; Varrin-Doyer, M.; Shetty, A.; Linington, C.; Slavin, A.J.; Hidalgo, J.; et al. MHC class II-dependent B cell APC function is required for induction of CNS autoimmunity independent of myelin-specific antibodies. J. Exp. Med. 2013, 210, 2921–2937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lino, A.C.; Dörner, T.; Bar-Or, A.; Fillatreau, S. Cytokine-producing B cells: A translational view on their roles in human and mouse autoimmune diseases. Immunol. Rev. 2016, 269, 130–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malmeström, C.; Andersson, B.A.; Haghighi, S.; Lycke, J. IL-6 and CCL2 levels in CSF are associated with the clinical course of MS: Implications for their possible immunopathogenic roles. J. Neuroimmunol. 2006, 175, 176–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Pierson, E.R.; Stromnes, I.M.; Goverman, J.M. B cells promote induction of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis by facilitating reactivation of T cells in the central nervous system. J. Immunol. 2014, 192, 929–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitsdoerffer, M.; Lee, Y.; Jäger, A.; Kim, H.-J.; Korn, T.; Kolls, J.K.; Cantor, H.; Bettelli, E.; Kuchroo, V.K. Proinflammatory T helper type 17 cells are effective B-cell helpers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 14292–14297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, A.; Pitcher, L.A.; Sullivan, J.M.; Mitsdoerffer, M.; Acton, S.E.; Franz, B.; Wucherpfennig, K.; Turley, S.; Carroll, M.C.; Sobel, R.A.; et al. Th17 cells induce ectopic lymphoid follicles in central nervous system tissue inflammation. Immunity 2011, 35, 986–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Zhao, C.; Wu, F.; Tao, L.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, D.; Yang, S.; Jiang, D.; Wang, J.; Sun, Y.; et al. T Follicular Helper-Like Cells Are Involved in the Pathogenesis of Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinn, J.L.; Kumar, G.; Agasing, A.; Ko, R.M.; Axtell, R.C. Role of TFH Cells in Promoting T Helper 17-Induced Neuroinflammation. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moffitt, J.R.; Lundberg, E.; Heyn, H. The emerging landscape of spatial profiling technologies. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2022, 23, 741–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pohl, M.; Fischer, M.-T.; Mader, S.; Schanda, K.; Kitic, M.; Sharma, R.; Wimmer, I.; Misu, T.; Fujihara, K.; Reindl, M.; et al. Pathogenic T cell responses against aquaporin 4. Acta Neuropathol. 2011, 122, 21–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; Whitaker, J.N.; Huang, Z.; Liu, D.; Coleclough, C.; Wekerle, H.; Raine, C.S. Myelin antigen-specific CD8+ T cells are encephalitogenic and produce severe disease in C57BL/6 mice. J. Immunol. 2001, 166, 7579–7587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bettini, M.; Rosenthal, K.; Evavold, B.D. Pathogenic MOG-reactive CD8+ T cells require MOG-reactive CD4+ T cells for sustained CNS inflammation during chronic EAE. J. Neuroimmunol. 2009, 213, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagner, C.A.; Roqué, P.J.; Mileur, T.R.; Liggitt, D.; Goverman, J.M. Myelin-specific CD8+ T cells exacerbate brain inflammation in CNS autoimmunity. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 130, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lesec, L.; Serrier, J.; Seillier, C.; Bernay, B.; Regnauld, C.; Furon, J.; Leprince, J.; Lefranc, B.; Vivien, D.; Docagne, F.; et al. Specific and Polyfunctional T Cell Response Against N-Methyl-d-aspartate Receptor in an Autoantibody-Mediated Encephalitis Model. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 2458. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12112458
Lesec L, Serrier J, Seillier C, Bernay B, Regnauld C, Furon J, Leprince J, Lefranc B, Vivien D, Docagne F, et al. Specific and Polyfunctional T Cell Response Against N-Methyl-d-aspartate Receptor in an Autoantibody-Mediated Encephalitis Model. Biomedicines. 2024; 12(11):2458. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12112458
Chicago/Turabian StyleLesec, Léonie, Julien Serrier, Célia Seillier, Benoit Bernay, Caroline Regnauld, Jonathane Furon, Jérôme Leprince, Benjamin Lefranc, Denis Vivien, Fabian Docagne, and et al. 2024. "Specific and Polyfunctional T Cell Response Against N-Methyl-d-aspartate Receptor in an Autoantibody-Mediated Encephalitis Model" Biomedicines 12, no. 11: 2458. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12112458
APA StyleLesec, L., Serrier, J., Seillier, C., Bernay, B., Regnauld, C., Furon, J., Leprince, J., Lefranc, B., Vivien, D., Docagne, F., Le Mauff, B., & Toutirais, O. (2024). Specific and Polyfunctional T Cell Response Against N-Methyl-d-aspartate Receptor in an Autoantibody-Mediated Encephalitis Model. Biomedicines, 12(11), 2458. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12112458






