Advancing Osteoarthritis Treatment: The Therapeutic Potential of Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes and Biomaterial Integration
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Biological Properties and Mechanisms of Exosomes
2.1. Biogenesis of Exosomes
2.2. Exosome Cargo and Its Functional Implications
2.2.1. Proteins
2.2.2. Ribonucleic Acids
2.2.3. Lipids
2.3. Mechanisms of Intercellular Communication
2.4. Therapeutic Potential in OA
3. Therapeutic Potential of Exosomes in Osteoarthritis
3.1. Anti-Inflammatory Effects
3.2. Cartilage Regeneration and Repair
3.3. Advantages over Traditional and Stem Cell Therapies
4. Integration of Exosome Therapy with Biomaterials for Enhanced Delivery
4.1. Hydrogels and Scaffolds for Exosome Delivery
4.2. Nanoparticles for Targeted Delivery
4.3. Controlled Release and Bioavailability
5. Challenges in the Clinical Application of Exosome-Based Therapies
5.1. Standardization of Exosome Isolation and Characterization
5.2. Scalability of Exosome Production
5.3. Regulatory Challenges
6. Future Directions and Opportunities for Exosome-Based Therapies
6.1. Mechanistic Understanding
6.2. Bioengineering and Integration with Biomaterials
6.3. Long-Term Safety and Personalized Medicine
7. Discussion
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Poole, A.R. Osteoarthritis as a whole joint disease. HSS J. 2012, 8, 4–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katz, J.N.; Arant, K.R.; Loeser, R.F. Diagnosis and Treatment of Hip and Knee Osteoarthritis: A Review. JAMA 2021, 325, 568–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safiri, S.; Kolahi, A.A.; Smith, E.; Hill, C.; Bettampadi, D.; Mansournia, M.A.; Hoy, D.; Ashrafi-Asgarabad, A.; Sepidarkish, M.; Almasi-Hashiani, A.; et al. Global, regional and national burden of osteoarthritis 1990–2017: A systematic analysis of the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2020, 79, 819–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheuing, W.J.; Reginato, A.M.; Deeb, M.; Acer Kasman, S. The burden of osteoarthritis: Is it a rising problem? Best Pract. Res. Clin. Rheumatol. 2023, 37, 101836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Li, Z.; Alexander, P.G.; Ocasio-Nieves, B.D.; Yocum, L.; Lin, H.; Tuan, R.S. Pathogenesis of Osteoarthritis: Risk Factors, Regulatory Pathways in Chondrocytes, and Experimental Models. Biology 2020, 9, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvanova, D.; Matejova, J.; Slovinska, L.; Lacko, M.; Gulova, S.; Fecskeova, L.K.; Janockova, J.; Spakova, T.; Rosocha, J. The Role of Synovial Membrane in the Development of a Potential In Vitro Model of Osteoarthritis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, Q.; Wu, X.; Tao, C.; Gong, W.; Chen, M.; Qu, M.; Zhong, Y.; He, T.; Chen, S.; Xiao, G. Osteoarthritis: Pathogenic signaling pathways and therapeutic targets. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berteau, J.P. Knee Pain from Osteoarthritis: Pathogenesis, Risk Factors, and Recent Evidence on Physical Therapy Interventions. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 3252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckwalter, J.A.; Anderson, D.D.; Brown, T.D.; Tochigi, Y.; Martin, J.A. The Roles of Mechanical Stresses in the Pathogenesis of Osteoarthritis: Implications for Treatment of Joint Injuries. Cartilage 2013, 4, 286–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aubourg, G.; Rice, S.J.; Bruce-Wootton, P.; Loughlin, J. Genetics of osteoarthritis. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2022, 30, 636–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macchi, V.; Stocco, E.; Stecco, C.; Belluzzi, E.; Favero, M.; Porzionato, A.; De Caro, R. The infrapatellar fat pad and the synovial membrane: An anatomo-functional unit. J. Anat. 2018, 233, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.G.; Seale, P.; Furman, D. The infrapatellar fat pad in inflammaging, knee joint health, and osteoarthritis. NPJ Aging 2024, 10, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, N.; Yan, Z.P.; Chen, X.Y.; Ni, G.X. Infrapatellar Fat Pad and Knee Osteoarthritis. Aging Dis. 2020, 11, 1317–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belluzzi, E.; Stocco, E.; Pozzuoli, A.; Granzotto, M.; Porzionato, A.; Vettor, R.; De Caro, R.; Ruggieri, P.; Ramonda, R.; Rossato, M.; et al. Contribution of Infrapatellar Fat Pad and Synovial Membrane to Knee Osteoarthritis Pain. Biomed Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 6390182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bannuru, R.R.; Schmid, C.H.; Kent, D.M.; Vaysbrot, E.E.; Wong, J.B.; McAlindon, T.E. Comparative effectiveness of pharmacologic interventions for knee osteoarthritis: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. Ann. Intern. Med. 2015, 162, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, A.; Chen, Y.; Rong, X.; You, X.; Wu, D.; Zhou, X.; Zeng, W.; Zhou, Z. The application of exosomes in the early diagnosis and treatment of osteoarthritis. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1154135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.; Lin, J.; Wu, H.; Yu, J.; Tu, M.; Cheang, L.H.; Zhang, J. Effect of conditioned medium from human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stromal cells on rejuvenation of nucleus pulposus derived stem/progenitor cells from degenerated intervertebral disc. Int. J. Stem Cells 2020, 13, 257–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, D.; Kwong, J.; Yang, Z.; Hou, Y.; Zhang, W.; Ma, B.; Lin, J. Intra-articular injection of mesenchymal stem cells in treating knee osteoarthritis: A systematic review of animal studies. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2018, 26, 445–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aithal, A.P.; Bairy, L.K.; Seetharam, R.N. Safety and therapeutic potential of human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stromal cells in regenerative medicine. Stem Cell Investig. 2021, 8, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; He, T.; Xing, J.; Zhou, Q.; Fan, L.; Liu, C.; Chen, Y.; Wu, D.; Tian, Z.; Liu, B.; et al. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes protect cartilage damage and relieve knee osteoarthritis pain in a rat model of osteoarthritis. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2020, 11, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Gupta, P.; Sgaglione, N.A.; Grande, D.A. Exosomes derived from non-classic sources for treatment of post-traumatic osteoarthritis and cartilage injury of the knee: In vivo review. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, J.; Sun, Y.; Ma, Y.; Ao, Y.; Hu, X.; Meng, Q. Engineering of MSC-derived exosomes: A promising cell-free therapy for osteoarthritis. Membranes 2022, 12, 739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welsh, J.A.; Goberdhan, D.C.I.; O’Driscoll, L.; Buzas, E.I.; Blenkiron, C.; Bussolati, B.; Cai, H.; Di Vizio, D.; Driedonks, T.A.P.; Erdbrügger, U.; et al. Minimal information for studies of extracellular vesicles (MISEV2023): From basic to advanced approaches. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2024, 13, e12404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kordelas, L.; Rebmann, V.; Ludwig, A.K.; Radtke, S.; Ruesing, J.; Doeppner, T.R.; Epple, M.; Horn, P.A.; Beelen, D.W. MSC-derived exosomes: A novel tool to treat therapy-refractory graft-versus-host disease. Leukemia 2014, 28, 970–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, S.C.; Yuan, T.; Zhang, Y.L.; Yin, W.J.; Guo, S.C.; Zhang, C.Q. Exosomes derived from miR-140-5p-overexpressing human synovial mesenchymal stem cells enhance cartilage tissue regeneration and prevent osteoarthritis of the knee in a rat model. Theranostics 2017, 7, 180–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitag, J.; Bates, D.; Wickham, J.; Shah, K.; Huguenin, L.; Tenen, A.; Paterson, K.; Boyd, R. Adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cell therapy in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis: A randomized controlled trial. Regen. Med. 2019, 14, 213–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, L.; Xu, X.; Xu, L.; Chen, H.; Li, X.; Alahdal, M.; Xiao, Y.; Liang, Y.; Xia, J. Exosome-mediated drug delivery for cell-free therapy of osteoarthritis. Curr. Med. Chem. 2021, 28, 6458–6483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Fan, Y.; Zhang, X. Biomaterials-assisted exosomes therapy in osteoarthritis. Biomed. Mater. 2022, 17, 022001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maehara, M.; Toyoda, E.; Takahashi, T.; Watanabe, M.; Sato, M. Potential of exosomes for diagnosis and treatment of joint disease: Towards a point-of-care therapy for osteoarthritis of the knee. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yu, D.; Liu, Z.; Zhou, F.; Dai, J.; Wu, B.; Zhou, J.; Heng, B.C.; Zou, X.H.; Ouyang, H.; et al. Exosomes from embryonic mesenchymal stem cells alleviate osteoarthritis through balancing synthesis and degradation of cartilage extracellular matrix. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2017, 8, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.; Xu, X.; Wang, R.; Chen, W.; Qin, K.; Yan, J. Chondroprotective effects of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes in osteoarthritis. J. Bioenerg. Biomembr. 2024, 56, 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, D.; Zhu, H.; Li, S.; Wang, Z.; Xiao, J. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes as a promising cell-free therapy for knee osteoarthritis. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2024, 12, 1309946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Zhou, Y.; Ying, B.; Dong, X.; Qian, Q.; Gao, S. Effects of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes in the rat osteoarthritis models. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2024, 13, 803–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vadhan, A.; Gupta, T.; Hsu, W.L. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes as a treatment option for osteoarthritis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 9149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalluri, R.; LeBleu, V.S. The biology, function, and biomedical applications of exosomes. Science 2020, 367, eaau6977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Liu, Y.; Wang, C.; Xiang, W.; Wang, N.; Peng, L.; Jiang, X.; Zhang, X.; Fu, Z. Strategies for Cartilage Repair in Osteoarthritis Based on Diverse Mesenchymal Stem Cells-Derived Extracellular Vesicles. Orthop. Surg. 2023, 15, 2749–2765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Z.; Zhou, S.; Li, S.; Kuang, L.; Chen, H.; Luo, X.; Ouyang, J.; He, M.; Du, X.; Chen, L. Exosomes: Roles and therapeutic potential in osteoarthritis. Bone Res. 2020, 8, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, G.B.; Shon, O.J.; Seo, M.S.; Choi, Y.; Park, W.T.; Lee, G.W. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes and Their Therapeutic Potential for Osteoarthritis. Biology 2021, 10, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhaskara, M.; Anjorin, O.; Wang, M. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomal microRNAs in Cardiac Regeneration. Cells 2023, 12, 2815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amsar, R.M.; Wijaya, C.H.; Ana, I.D.; Hidajah, A.C.; Notobroto, H.B.; Kencana Wungu, T.D.; Barlian, A. Extracellular vesicles: A promising cell-free therapy for cartilage repair. Future Sci. OA 2021, 8, FSO774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foo, J.B.; Looi, Q.H.; Chong, P.P.; Hassan, N.H.; Yeo, G.E.C.; Ng, C.Y.; Koh, B.; How, C.W.; Lee, S.H.; Law, J.X. Comparing the Therapeutic Potential of Stem Cells and their Secretory Products in Regenerative Medicine. Stem Cells Int. 2021, 2021, 2616807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Lin, Y.; Zhang, X.; Shan, C. Research progress of exosomes in orthopedics. Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 915141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurunathan, S.; Kang, M.H.; Jeyaraj, M.; Qasim, M.; Kim, J.H. Review of the Isolation, Characterization, Biological Function, and Multifarious Therapeutic Approaches of Exosomes. Cells 2019, 8, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Waheed, S.; Wang, C.; Shekh, M.; Li, Z.; Wu, J. Exosomes and Their Bioengineering Strategies in the Cutaneous Wound Healing and Related Complications: Current Knowledge and Future Perspectives. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2023, 19, 1430–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.Z.; Ma, Z.J.; Kang, X.W. Current status and outlook of advances in exosome isolation. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2022, 414, 7123–7141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Liu, D. Bioengineered mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes: Emerging strategies for diabetic wound healing. Burn. Trauma 2024, 12, tkae030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.K.; Tsai, T.H.; Lee, C.H. Regulation of exosomes as biologic medicines: Regulatory challenges faced in exosome development and manufacturing processes. Clin. Transl. Sci. 2024, 17, e13904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaie, J.; Feghhi, M.; Etemadi, T. A review on exosomes application in clinical trials: Perspective, questions, and challenges. Cell Commun. Signal. 2022, 20, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, J.; Shojaee, M.; Mitchell Crow, J.; Khanabdali, R. From Mesenchymal Stromal Cells to Engineered Extracellular Vesicles: A New Therapeutic Paradigm. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 705676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Wang, X.; Lin, X.; Wu, C. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles: A regulator and carrier for targeting bone-related diseases. Cell Death. Discov. 2024, 10, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muralikumar, M.; Manoj Jain, S.; Ganesan, H.; Duttaroy, A.K.; Pathak, S.; Banerjee, A. Current understanding of the mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes in cancer and aging. Biotechnol. Rep. 2021, 31, e00658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dilsiz, N. A comprehensive review on recent advances in exosome isolation and characterization: Toward clinical applications. Transl. Oncol. 2024, 50, 102121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molnar, V.; Pavelić, E.; Vrdoljak, K.; Čemerin, M.; Klarić, E.; Matišić, V.; Bjelica, R.; Brlek, P.; Kovačić, I.; Tremolada, C.; et al. Mesenchymal stem cell mechanisms of action and clinical effects in osteoarthritis: A narrative review. Genes 2022, 13, 949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isaac, R.; Reis, F.C.G.; Ying, W.; Olefsky, J.M. Exosomes as mediators of intercellular crosstalk in metabolism. Cell Metab. 2021, 33, 1744–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stawarska, A.; Bamburowicz-Klimkowska, M.; Runden-Pran, E.; Dusinska, M.; Cimpan, M.R.; Rios-Mondragon, I.; Grudzinski, I.P. Extracellular Vesicles as Next-Generation Diagnostics and Advanced Therapy Medicinal Products. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 6533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Author (year) | Title | Focus Area | Key Findings |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chen et al., 2023 [16] | The Application of Exosomes in Early Diagnosis and Treatment of Osteoarthritis | Exosome application in early OA diagnosis | Discussed how exosomes in the synovial fluid can serve as biomarkers and therapeutic agents for early-stage OA |
| He et al., 2020 [20] | Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes Protect Cartilage Damage | MSC-derived exosomes in OA | Demonstrated how BMSC-derived exosomes protect the cartilage from degeneration and reduce pain in OA models |
| Li et al., 2021 [21] | Exosomes Derived from Non-Classic Sources for Treatment of Post-Traumatic OA | Nonclassical exosome sources | Explored the use of exosomes from nontraditional sources, such as plant-derived exosomes, to treat post-traumatic OA |
| Cheng et al., 2022 [22] | Engineering of MSC-Derived Exosomes: A Promising Cell-Free Therapy for OA | MSC exosome engineering for cell-free therapy | Discussed MSC-derived exosome modifications to enhance therapeutic efficacy in OA treatment through improved targeting and potency |
| Tao et al., 2017 [25] | Exosomes from miR-140-5p Overexpressing Human Synovial MSCs Enhance Cartilage Tissue Regeneration | miR-140-5p in exosome-mediated therapy | Showed that exosomes enriched with miR-140-5p from MSCs can inhibit OA progression and promote cartilage regeneration |
| Duan et al., 2021 [27] | Exosome-Mediated Drug Delivery for Cell-Free Therapy of Osteoarthritis | Exosome-mediated drug delivery | Analyzed the effectiveness of exosome-mediated drug delivery systems as cell-free alternatives to traditional OA therapies |
| Chen et al., 2022 [28] | Biomaterials-Assisted Exosomes Therapy in Osteoarthritis | Biomaterials in exosome therapy | Investigated the role of biomaterials in enhancing exosome delivery, stability, and therapeutic efficacy for OA treatment |
| Maehara et al., 2021 [29] | Potential of Exosomes for Diagnosis and Treatment of Joint Disease | Exosome biology and therapeutic potential | Highlighted the diagnostic potential of exosomes in joint disease and their promising role in OA therapy |
| Wang et al., 2017 [30] | Exosomes from Embryonic MSCs Alleviate Osteoarthritis | ESC-derived exosomes in OA | Demonstrated how exosomes derived from embryonic stem cells reduce OA symptoms and aid cartilage repair in animal models |
| Cheng et al., 2024 [31] | Chondroprotective Effects of Bone Marrow MSC-Derived Exosomes in OA | MSC-derived exosomes in cartilage repair | Highlighted chondroprotective effects of MSC-derived exosomes and their ability to modulate inflammation and cartilage regeneration in OA |
| Luo et al., 2024 [32] | Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes: A Cell-Free Therapy for Knee OA | MSC-derived exosomes and immune modulation | Focused on the immune-modulatory properties of exosomes and their therapeutic potential in OA treatment, particularly in reducing inflammation and modulating immune responses |
| Yang et al., 2024 [33] | Effects of Human Umbilical Cord MSC-Derived Exosomes in Rat OA Models | Umbilical cord MSC-derived exosomes in OA | Showed the therapeutic potential of umbilical cord-derived exosomes in animal models, emphasizing their ability to reduce OA-related inflammation and promote cartilage repair |
| Vadhan et al., 2024 [34] | MSC-Derived Exosomes as a Treatment Option for OA | MSC-derived exosomes for inflammation reduction | Examined MSC-derived exosomes’ potential to reduce inflammation and promote cartilage repair in OA |
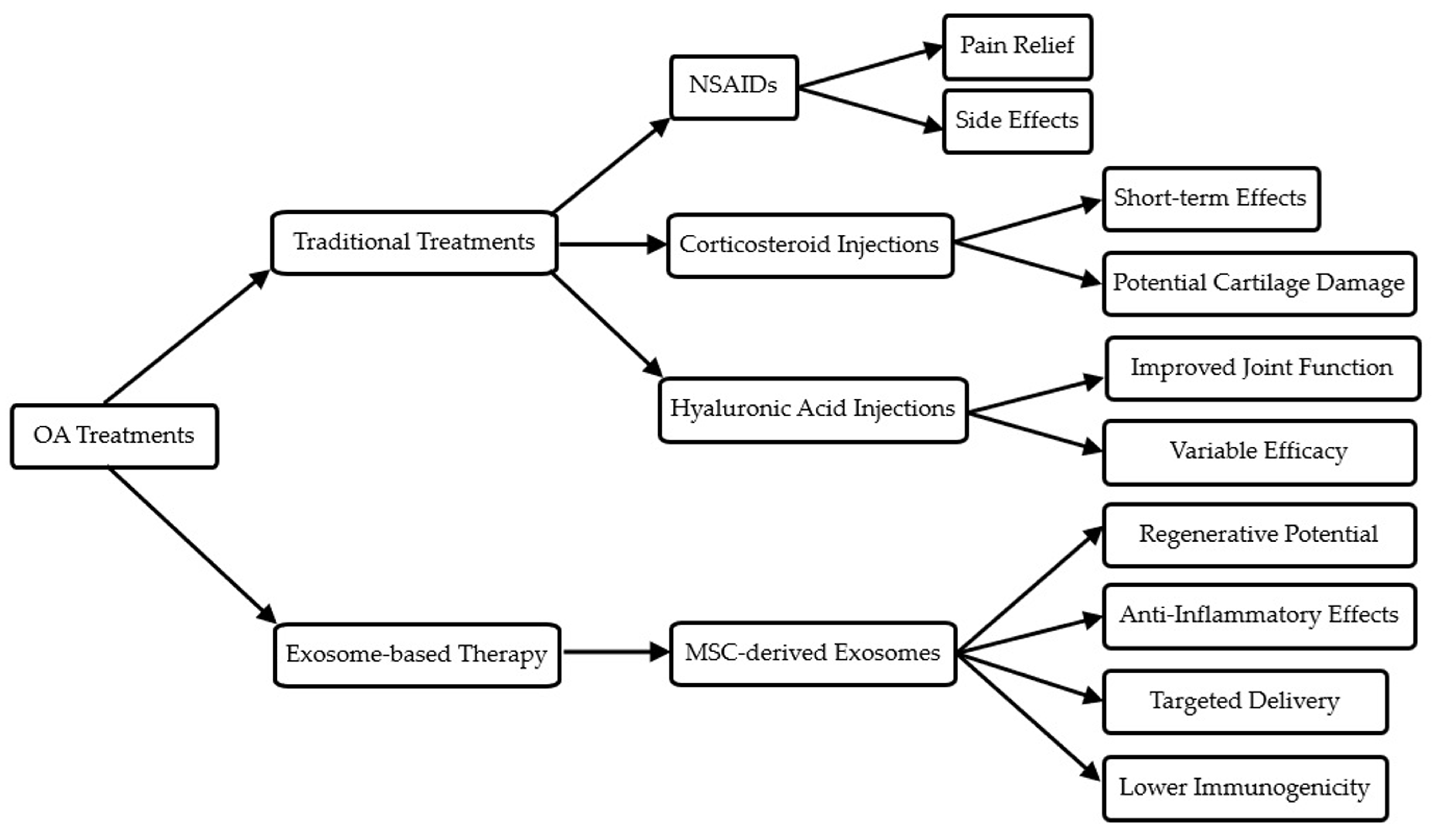
| Treatment Type | Mechanism of Action | Advantages | Limitations | Current Stage of Development/Use |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NSAIDs | Inhibit cyclooxygenase enzymes, reduce inflammation | Easily accessible, effective for pain relief | Gastrointestinal side effects, cardiovascular risks with long-term use | Widely used, first-line treatment |
| Intra-articular corticosteroid injections | Suppress inflammation and pain | Rapid pain relief, can be repeated | Short-term effects, potential cartilage damage with repeated use | Commonly used in clinical practice |
| Hyaluronic acid injections | Improve joint lubrication and shock absorption | Improve joint function, longer-lasting effects than steroids | Variable efficacy, multiple injections needed | Approved and used clinically |
| MSC-based cell therapy | Differentiate into chondrocytes, secrete paracrine factors | Potential for cartilage regeneration, anti-inflammatory effects | Invasive, potential for immune rejection, variability in cell quality | Clinical trials ongoing, limited approved uses |
| Exosome-based therapy | Deliver bioactive molecules (miRNAs, proteins, lipids) to target cells | Cell-free, easier to store and handle, potentially more consistent than cell therapy | Still in early stages of research, optimal dosing and administration to be determined | Preclinical and early clinical trials |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chu, C.-H.; Lee, R.-P.; Wu, W.-T.; Chen, I.-H.; Yeh, K.-T.; Wang, C.-C. Advancing Osteoarthritis Treatment: The Therapeutic Potential of Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes and Biomaterial Integration. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 2478. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12112478
Chu C-H, Lee R-P, Wu W-T, Chen I-H, Yeh K-T, Wang C-C. Advancing Osteoarthritis Treatment: The Therapeutic Potential of Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes and Biomaterial Integration. Biomedicines. 2024; 12(11):2478. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12112478
Chicago/Turabian StyleChu, Chung-Hua, Ru-Ping Lee, Wen-Tien Wu, Ing-Ho Chen, Kuang-Ting Yeh, and Chen-Chie Wang. 2024. "Advancing Osteoarthritis Treatment: The Therapeutic Potential of Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes and Biomaterial Integration" Biomedicines 12, no. 11: 2478. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12112478
APA StyleChu, C.-H., Lee, R.-P., Wu, W.-T., Chen, I.-H., Yeh, K.-T., & Wang, C.-C. (2024). Advancing Osteoarthritis Treatment: The Therapeutic Potential of Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes and Biomaterial Integration. Biomedicines, 12(11), 2478. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12112478










