Role of Microbiota-Derived Hydrogen Sulfide (H2S) in Modulating the Gut–Brain Axis: Implications for Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s Disease Pathogenesis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
3. Results
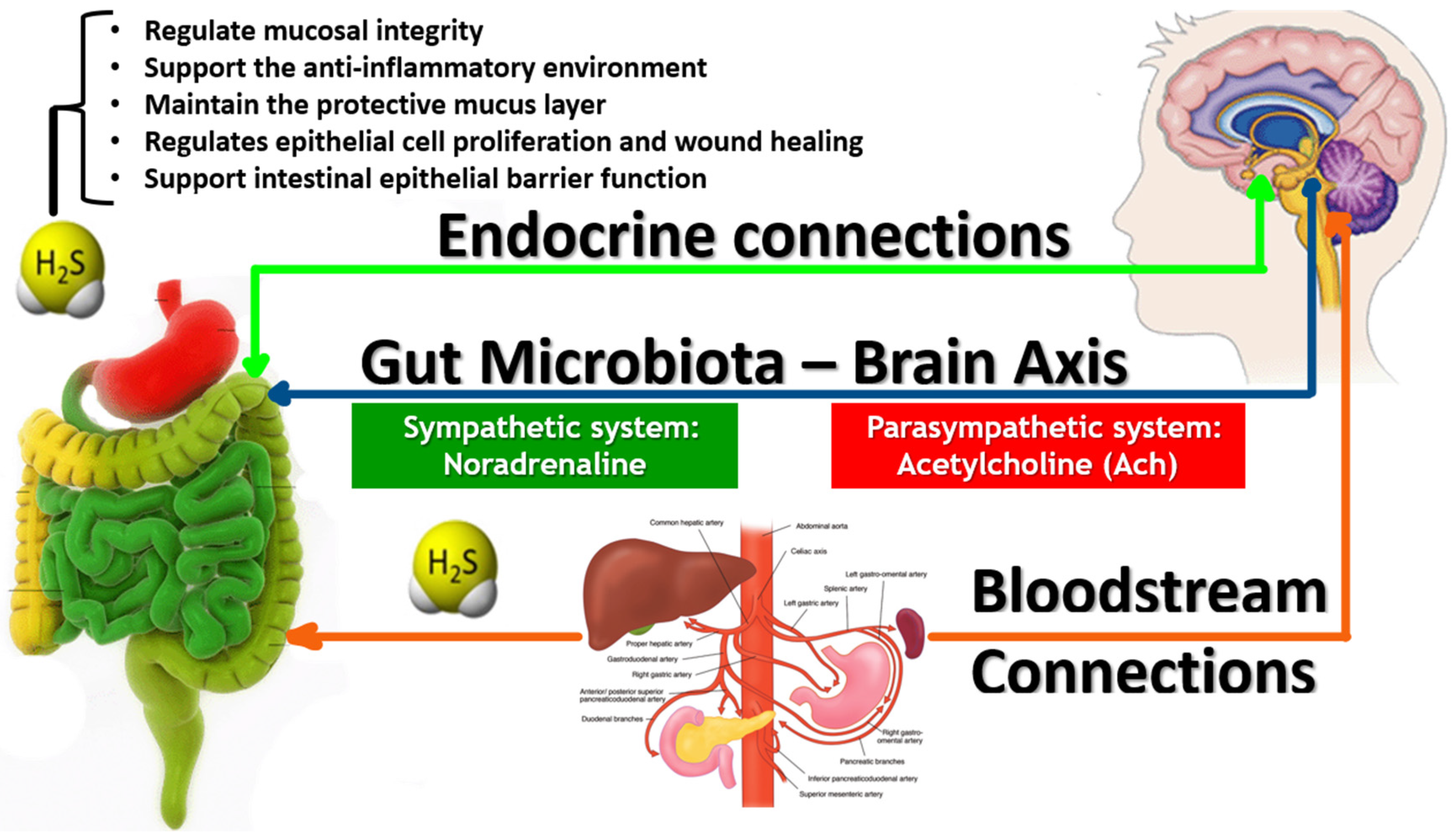
3.1. H2S as a Protective Agent in Gut Homeostasis
3.2. Dichotomous Nature of H2S in Inflammation and Gut Permeability
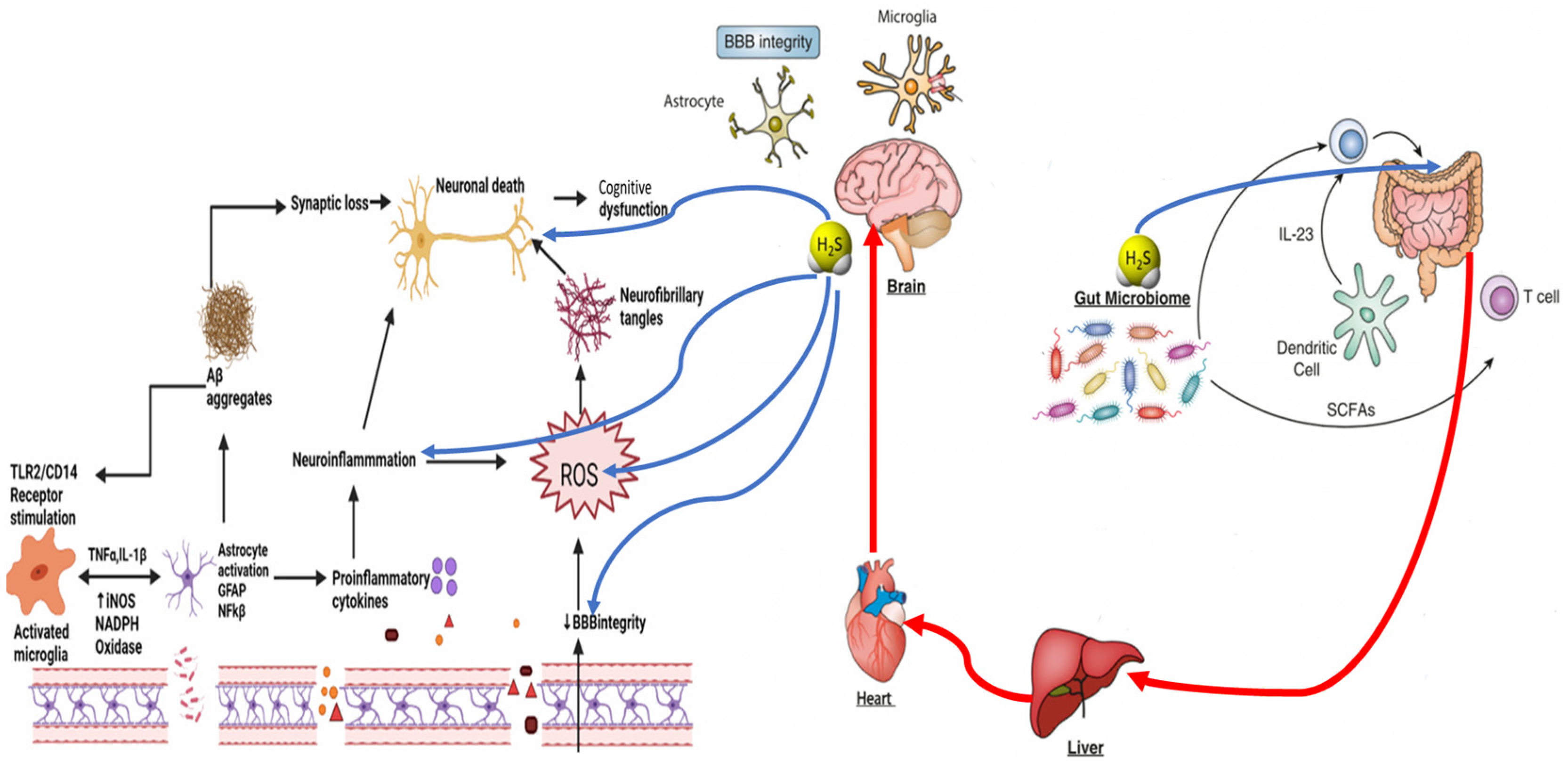
3.3. Impact of H2S on Neuroinflammation and the Gut–Brain Axis
3.4. H2S and Blood–Brain Barrier Dysfunction
3.5. H2S and Glial Cell Dysfunction in Neurodegeneration
3.6. Interaction with Neural Signaling via the Vagus Nerve
3.7. Modulation of Mitochondrial Function and Oxidative Stress
3.8. Microbial Metabolite Interactions and Neurotransmitter Regulation
4. Age, Gender, and Comorbidities in Gut Microbiota Composition and H2S Production
4.1. Age-Related Changes in Gut Microbiota Composition and H2S Production
4.2. Gender Differences in Gut Microbiota Composition and H2S Production
4.3. Other Comorbidities, Gut Microbiota Composition and H2S Production
5. Therapeutic Targets and Interventions Related to H2S Modulation
5.1. Probiotics and Prebiotics
5.2. Dietary Modifications
5.3. Fecal Microbiota Transplantation (FMT)
5.4. Pharmacological Inhibitors of H2S Production
5.5. Antioxidants and Anti-Inflammatory Agents
5.6. Combination Therapies
6. Limitations and Gaps in Current Research
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Thursby, E.; Juge, N. Introduction to the human gut microbiota. Biochem. J. 2017, 474, 1823–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pessemier, B.; De Grine, L.; Debaere, M.; Maes, A.; Paetzold, B.; Callewaert, C. Gut–skin axis: Current knowledge of the interrelationship between microbial dysbiosis and skin conditions. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jandhyala, S.M.; Talukdar, R.; Subramanyam, C.; Vuyyuru, H.; Sasikala, M.; Reddy, D.N. Role of the normal gut microbiota. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 8836–8847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carabotti, M.; Scirocco, A.; Antonietta Maselli, M.; Severi, C. The gut-brain axis: Interactions between enteric microbiota, central and enteric nervous systems. Ann. Gastroenterol. 2015, 28, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Andrés, C.M.C.; Pérez de la Lastra, J.M.; Andrés Juan, C.; Plou, F.J.; Pérez-Lebeña, E. Chemistry of Hydrogen Sulfide—Pathological and Physiological Functions in Mammalian Cells. Cells 2023, 12, 2684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgakopoulou, V.; Lempesis, I.; Sklapani, P.; Trakas, N.; Spandidos, D. Exploring the pathogenetic mechanisms of Mycoplasma pneumoniae (Review). Exp. Ther. Med. 2024, 28, 424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Saadony, M.T.; Yang, T.; Korma, S.A.; Sitohy, M.; El-Mageed, T.A.A.; Selim, S.; Al Jaouni, S.K.; Salem, H.M.; Mahmmod, Y.; Soliman, S.M.; et al. Impacts of turmeric and its principal bioactive curcumin on human health: Pharmaceutical, medicinal, and food applications: A comprehensive review. Front. Nutr. 2023, 9, 1040259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breijyeh, Z.; Karaman, R. Comprehensive Review on Alzheimer’s Disease: Causes and Treatment. Molecules 2020, 25, 5789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostafavi Abdolmaleky, H.; Zhou, J.R. Gut Microbiota Dysbiosis, Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, and Epigenetic Alterations in Metabolic Diseases. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bicknell, B.; Liebert, A.; Borody, T.; Herkes, G.; McLachlan, C.; Kiat, H. Neurodegenerative and Neurodevelopmental Diseases and the Gut-Brain Axis: The Potential of Therapeutic Targeting of the Microbiome. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 9577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, J.Y.; Groer, M.; Dutra, S.V.O.; Sarkar, A.; McSkimming, D.I. Gut microbiota and immune system interactions. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Figliuolo, V.R.; dos Santos, L.M.; Abalo, A.; Nanini, H.; Santos, A.; Brittes, N.M.; Bernardazzi, C.; de Souza, H.S.P.; Vieira, L.Q.; Coutinho-Silva, R.; et al. Sulfate-reducing bacteria stimulate gut immune responses and contribute to inflammation in experimental colitis. Life Sci. 2017, 189, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonaz, B.; Bazin, T.; Pellissier, S. The vagus nerve at the interface of the microbiota-gut-brain axis. Front. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, C.R.; Osadchiy, V.; Kalani, A.; Mayer, E.A. The Brain-Gut-Microbiome Axis. Cell. Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 6, 133–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breit, S.; Kupferberg, A.; Rogler, G.; Hasler, G. Vagus nerve as modulator of the brain-gut axis in psychiatric and inflammatory disorders. Front. Psychiatry 2018, 9, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, M.; Chen, N.; Yang, Y.; Cheng, L.; He, H.; Cai, Y.; Liu, Y.; Liu, H.; Hong, G. The gut microbiota–brain axis in neurological disorders. MedComm 2024, 5, e656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, H.S.; Koh, S.H. Neuroinflammation in neurodegenerative disorders: The roles of microglia and astrocytes. Transl. Neurodegener. 2020, 9, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uriarte Huarte, O.; Richart, L.; Mittelbronn, M.; Michelucci, A. Microglia in Health and Disease: The Strength to Be Diverse and Reactive. Front. Cell Neurosci. 2021, 15, 660523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrabi, S.M.; Sharma, N.S.; Karan, A.; Shahriar, S.M.S.; Cordon, B.; Ma, B.; Xie, J. Nitric Oxide: Physiological Functions, Delivery, and Biomedical Applications. Adv. Sci. 2023, 10, e2303259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hills, R.D.; Pontefract, B.A.; Mishcon, H.R.; Black, C.A.; Sutton, S.C.; Theberge, C.R. Gut microbiome: Profound implications for diet and disease. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bidell, M.R.; Hobbs, A.L.V.; Lodise, T.P. Gut microbiome health and dysbiosis: A clinical primer. Pharmacotherapy 2022, 42, 849–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, K.; Wu, Z.X.; Chen, X.Y.; Wang, J.Q.; Zhang, D.; Xiao, C.; Zhu, D.; Koya, J.B.; Wei, L.; Li, J.; et al. Microbiota in health and diseases. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merlo, G.; Bachtel, G.; Sugden, S.G. Gut microbiota, nutrition, and mental health. Front. Nutr. 2024, 11, 1337889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Deng, H.; Cui, H.; Fang, J.; Zuo, Z.; Deng, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhao, L. Inflammatory responses and inflammation-associated diseases in organs. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 7204–7218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumaresan, M.; Khan, S. Spectrum of Non-Motor Symptoms in Parkinson’s Disease. Cureus 2021, 13, e13275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Song, Y.; Xu, Y.; Xu, H. Manipulating Microbiota in Inflammatory Bowel Disease Treatment: Clinical and Natural Product Interventions Explored. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 11004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buret, A.G.; Allain, T.; Motta, J.P.; Wallace, J.L. Effects of Hydrogen Sulfide on the Microbiome: From Toxicity to Therapy. Antioxid. Redox Signal 2022, 36, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahindru, A.; Patil, P.; Agrawal, V. Role of Physical Activity on Mental Health and Well-Being: A Review. Cureus 2023, 15, e33475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jäkel, S.; Dimou, L. Glial cells and their function in the adult brain: A journey through the history of their ablation. Front. Cell Neurosci. 2017, 11, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamu, A.; Li, S.; Gao, F.; Xue, G. The role of neuroinflammation in neurodegenerative diseases: Current understanding and future therapeutic targets. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2024, 16, 1347987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siracusa, R.; Fusco, R.; Cuzzocrea, S. Astrocytes: Role and functions in brain pathologies. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Araújo, B.; Caridade-Silva, R.; Soares-Guedes, C.; Martins-Macedo, J.; Gomes, E.D.; Monteiro, S.; Teixeira, F.G. Neuroinflammation and Parkinson’s Disease—From Neurodegeneration to Therapeutic Opportunities. Cells 2022, 11, 2908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azam, S.; Haque, M.E.; Balakrishnan, R.; Kim, I.S.; Choi, D.K. The Ageing Brain: Molecular and Cellular Basis of Neurodegeneration. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 683459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alahmari, A. Blood-Brain Barrier Overview: Structural and Functional Correlation. Neural Plast. 2021, 2021, 6564585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hrncir, T. Gut Microbiota Dysbiosis: Triggers, Consequences, Diagnostic and Therapeutic Options. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latif, A.; Shehzad, A.; Niazi, S.; Zahid, A.; Ashraf, W.; Iqbal, M.W.; Rehman, A.; Riaz, T.; Aadil, R.M.; Khan, I.M.; et al. Probiotics: Mechanism of action, health benefits and their application in food industries. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1216674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kesika, P.; Sivamaruthi, B.S.; Chaiyasut, C. Do Probiotics Improve the Health Status of Individuals with Diabetes Mellitus? A Review on Outcomes of Clinical Trials. BioMed Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 1531567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Allen-Vercoe, E.; Petrof, E.O. Fecal microbiota transplantation: In perspective. Ther. Adv. Gastroenterol. 2016, 9, 229–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cronin, P.; Joyce, S.A.; O’toole, P.W.; O’connor, E.M. Dietary fibre modulates the gut microbiota. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.K.; Cabral, C.; Kumar, R.; Ganguly, R.; Rana, H.K.; Gupta, A.; Rosaria Lauro, M.; Carbone, C.; Reis, F.; Pandey, A.K. Beneficial effects of dietary polyphenols on gut microbiota and strategies to improve delivery efficiency. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Liang, Q.; Balakrishnan, B.; Belobrajdic, D.P.; Feng, Q.J.; Zhang, W. Role of dietary nutrients in the modulation of gut microbiota: A narrative review. Nutrients 2020, 12, 381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chelakkot, C.; Ghim, J.; Ryu, S.H. Mechanisms regulating intestinal barrier integrity and its pathological implications. Exp. Mol. Med. 2018, 50, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farré, R.; Fiorani, M.; Rahiman, S.A.; Matteoli, G. Intestinal permeability, inflammation and the role of nutrients. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vancamelbeke, M.; Vermeire, S. The intestinal barrier: A fundamental role in health and disease. Expert. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 11, 821–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randeni, N.; Bordiga, M.; Xu, B. A Comprehensive Review of the Triangular Relationship among Diet–Gut Microbiota–Inflammation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 9366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munteanu, C.; Turnea, M.A.; Rotariu, M. Hydrogen Sulfide: An Emerging Regulator of Oxidative Stress and Cellular Homeostasis—A Comprehensive One-Year Review. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barathan, M.; Ng, S.L.; Lokanathan, Y.; Ng, M.H.; Law, J.X. The Profound Influence of Gut Microbiome and Extracellular Vesicles on Animal Health and Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 4024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.; Wan, H.; Cong, P.; Huang, X.; Wu, T.; He, M.; Zhang, Q.; Xiong, L.; Tian, L. Targeting neuroinflammation as a preventive and therapeutic approach for perioperative neurocognitive disorders. J. Neuroinflammation 2022, 19, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Liu, X.; Jiang, R.; Yan, X.; Ling, Z. Roles and Mechanisms of Gut Microbiota in Patients with Alzheimer’s Disease. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2021, 13, 650047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, R.P.; Easson, C.; Lyle, S.M.; Kapoor, R.; Donnelly, C.P.; Davidson, E.J.; Parikh, E.; Lopez, J.V.; Tartar, J.L. Gut microbiome diversity is associated with sleep physiology in humans. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0222394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutsch, A.; Kantsjö, J.B.; Ronchi, F. The Gut-Brain Axis: How Microbiota and Host Inflammasome Influence Brain Physiology and Pathology. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 604179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sui, Y.; Feng, X.; Ma, Y.; Zou, Y.; Liu, Y.; Huang, J.; Zhu, X.; Wang, J. BHBA attenuates endoplasmic reticulum stress-dependent neuroinflammation via the gut–brain axis in a mouse model of heat stress. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2024, 30, e14840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munteanu, C.; Iordan, D.A.; Hoteteu, M.; Popescu, C.; Postoiu, R.; Onu, I.; Onose, G. Mechanistic Intimate Insights into the Role of Hydrogen Sulfide in Alzheimer’s Disease: A Recent Systematic Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 15481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sen, N. Functional and Molecular Insights of Hydrogen Sulfide Signaling and Protein Sulfhydration. J. Mol. Biol. 2017, 429, 543–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rose, P.; Moore, P.K.; Zhu, Y.Z. H2S biosynthesis and catabolism: New insights from molecular studies. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2017, 74, 1391–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, K.; Kotzur, R.; Richter, F. Blood–brain barrier alterations and their impact on Parkinson’s disease pathogenesis and therapy. Transl. Neurodegener. 2024, 13, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweeney, M.D.; Zhao, Z.; Montagne, A.; Nelson, A.R.; Zlokovic, B.V. Blood-Brain Barrier: From Physiology to Disease and Back. Physiol. Rev. 2019, 99, 21–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorini, F.; Del Turco, S.; Sabatino, L.; Gaggini, M.; Vassalle, C. H2S as a bridge linking inflammation, oxidative stress and endothelial biology: A possible defense in the fight against SARS-CoV-2 infection? Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, K.N.; Nguyen, I.D.; Islam, R.; Pirzadah, H.; Malik, H. Roles of Hydrogen Sulfide (H2S) as a Potential Therapeutic Agent in Cardiovascular Diseases: A Narrative Review. Cureus 2024, 16, e64913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.Q.; Yuan, H.; Liu, Y.F.; Zhu, Y.W.; Wang, Y.; Liang, X.Y.; Gao, W.; Ren, Z.G.; Ji, X.Y.; Wu, D.D. Role of hydrogen sulfide in health and disease. MedComm 2024, 5, e661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cirino, G.; Szabo, C.; Papapetropoulos, A. Physiological roles of hydrogen sulfide in mammalian cells, tissues, and organs. Physiol. Rev. 2023, 103, 31–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Y.; Chu, S.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Pang, Z.; Chen, N. Neuroinflammatory In Vitro Cell Culture Models and the Potential Applications for Neurological Disorders. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 671734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCook, O.; Denoix, N.; Radermacher, P.; Waller, C.; Merz, T. H2S and oxytocin systems in early life stress and cardiovascular disease. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 3484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, C.D.; Xu, Q.J.; Chang, R.B. Vagal sensory neurons and gut-brain signaling. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2020, 62, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, P.A.; Schneeberger, M.; Matheis, F.; Wang, P.; Kerner, Z.; Ilanges, A.; Pellegrino, K.; Del Mármol, J.; Castro, T.B.R.; Furuichi, M.; et al. Microbiota modulate sympathetic neurons via a gut–brain circuit. Nature 2020, 583, 441–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, J.; Yang, K.; Nie, H.; Yuan, L.; Wang, S.; Zeng, L.; Ge, A.; Ge, J. The mechanism of intestinal microbiota regulating immunity and inflammation in ischemic stroke and the role of natural botanical active ingredients in regulating intestinal microbiota: A review. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 157, 114026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Wang, B.; Gao, H.; He, C.; Hua, R.; Liang, C.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Y.; Xin, S.; Xu, J. Vagus Nerve and Underlying Impact on the Gut Microbiota-Brain Axis in Behavior and Neurodegenerative Diseases. J. Inflamm. Res. 2022, 15, 6213–6230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogaru, B.G.; Munteanu, C. The Role of Hydrogen Sulfide (H2S) in Epigenetic Regulation of Neurodegenerative Diseases: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 12555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Tian, M.; Han, Y. Hydrogen sulfide: A multi-tasking signal molecule in the regulation of oxidative stress responses. J. Exp. Bot. 2020, 71, 2862–2869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, V.K.; Bandyopadhyay, P.; Singh, A. Hydrogen sulfide in physiology and pathogenesis of bacteria and viruses. IUBMB Life 2018, 70, 393–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.B.; Lin, H.C. Hydrogen sulfide in physiology and diseases of the digestive tract. Microorganisms 2015, 3, 866–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olas, B. Hydrogen sulfide in signaling pathways. Clin. Chim. Acta 2015, 439, 212–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munteanu, C.; Popescu, C.; Vlădulescu-Trandafir, A.-I.; Onose, G. Signaling Paradigms of H2S-Induced Vasodilation: A Comprehensive Review. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munteanu, C.; Galaction, A.I.; Turnea, M.; Blendea, C.D.; Rotariu, M.; Poștaru, M. Redox Homeostasis, Gut Microbiota, and Epigenetics in Neurodegenerative Diseases: A Systematic Review. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popescu, C.; Munteanu, C.; Anghelescu, A.; Ciobanu, V.; Spînu, A.; Andone, I.; Mandu, M.; Bistriceanu, R.; Băilă, M.; Postoiu, R.L.; et al. Novelties on Neuroinflammation in Alzheimer’s Disease–Focus on Gut and Oral Microbiota Involvement. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 11272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Tan, Y.; Cheng, H.; Zhang, D.; Feng, W.; Peng, C. Functions of Gut Microbiota Metabolites, Current Status and Future Perspectives. Aging Dis. 2022, 13, 1106–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perridon, B.W.; van Ghbem, L. The role of hydrogen sulfide in aging and age-related pathologies. Aging 2016, 8, 2264–2289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pataky, M.W.; Young, W.F.; Nair, K.S. Hormonal and Metabolic Changes of Aging and the Influence of Lifestyle Modifications. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2021, 96, 788–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camilleri, M. Leaky gut: Mechanisms, measurement and clinical implications in humans. Gut 2019, 68, 1516–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Jin, L.; Huang, W. Bile Acids, Intestinal Barrier Dysfunction, and Related Diseases. Cells 2023, 12, 1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martel, J.; Chang, S.H.; Ko, Y.F.; Hwang, T.L.; Young, J.D.; Ojcius, D.M. Gut barrier disruption and chronic disease. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2022, 33, 247–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donertas Ayaz, B.; Zubcevic, J. Gut microbiota and neuroinflammation in pathogenesis of hypertension: A potential role for hydrogen sulfide. Pharmacol. Res. 2020, 153, 104677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rinninella, E.; Raoul, P.; Cintoni, M.; Franceschi, F.; Miggiano, G.A.D.; Gasbarrini, A.; Mele, M.C. What is the healthy gut microbiota composition? A changing ecosystem across age, environment, diet, and diseases. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Postal, B.G.; Ghezzal, S.; Aguanno, D.; André, S.; Garbin, K.; Genser, L.; Brot-Laroche, E.; Poitou, C.; Soula, H.; Leturque, A.; et al. AhR activation defends gut barrier integrity against damage occurring in obesity. Mol. Metab. 2020, 39, 101007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takiishi, T.; Fenero, C.I.M.; Câmara, N.O.S. Intestinal barrier and gut microbiota: Shaping our immune responses throughout life. Tissue Barriers 2017, 5, e1373208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Małkiewicz, M.A.; Szarmach, A.; Sabisz, A.; Cubała, W.J.; Szurowska, E.; Winklewski, P.J. Blood-brain barrier permeability and physical exercise. J. Neuroinflammation 2019, 16, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villa, A.; Vegeto, E.; Poletti, A.; Maggi, A. Estrogens, neuroinflammation, and neurodegeneration. Endocr. Rev. 2016, 37, 372–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vegeto, E.; Benedusi, V.; Maggi, A. Estrogen anti-inflammatory activity in brain: A therapeutic opportunity for menopause and neurodegenerative diseases. Front. Neuroendocr. Neuroendocrinol. 2008, 29, 507–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foster, J.A.; Rinaman, L.; Cryan, J.F. Stress & the gut-brain axis: Regulation by the microbiome. Neurobiol. Stress. 2017, 7, 124–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fasano, A. All disease begins in the (leaky) gut: Role of zonulin-mediated gut permeability in the pathogenesis of some chronic inflammatory diseases. F1000Res 2020, 9, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stolfi, C.; Maresca, C.; Monteleone, G.; Laudisi, F. Implication of Intestinal Barrier Dysfunction in Gut Dysbiosis and Diseases. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hägg, S.; Jylhävä, J. Sex differences in biological aging with a focus on human studies. Elife 2021, 10, e63425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manor, O.; Dai, C.L.; Kornilov, S.A.; Smith, B.; Price, N.D.; Lovejoy, J.C.; Gibbons, S.M.; Magis, A.T. Health and disease markers correlate with gut microbiome composition across thousands of people. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iorga, A.; Cunningham, C.M.; Moazeni, S.; Ruffenach, G.; Umar, S.; Eghbali, M. The protective role of estrogen and estrogen receptors in cardiovascular disease and the controversial use of estrogen therapy. Biol. Sex. Differ. 2017, 8, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Anders, S.M.; Steiger, J.; Goldey, K.L. Effects of gendered behavior on testosterone in women and men. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 13805–13810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semo, D.; Reinecke, H.; Godfrey, R. Gut microbiome regulates inflammation and insulin resistance: A novel therapeutic target to improve insulin sensitivity. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2024, 9, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wadden, T.A.; Tronieri, J.S.; Butryn, M.L. Lifestyle modification approaches for the treatment of obesity in adults. Am. Psychol. 2020, 75, 235–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.T.; Li, H.; Yang, L.; Mao, C.Y. Role of hydrogen sulfide in cognitive deficits: Evidences and mechanisms. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2019, 849, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassamal, S. Chronic stress, neuroinflammation, and depression: An overview of pathophysiological mechanisms and emerging anti-inflammatories. Front. Psychiatry 2023, 14, 1130989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santiago, J.A.; Potashkin, J.A. The Impact of Disease Comorbidities in Alzheimer’s Disease. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2021, 13, 631770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, B.D.; Pieper, A.A. Protective Roles of Hydrogen Sulfide in Alzheimer’s Disease and Traumatic Brain Injury. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanmiguel, C.; Gupta, A.; Mayer, E.A. Gut Microbiome and Obesity: A Plausible Explanation for Obesity. Curr. Obes. Rep. 2015, 4, 250–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uranga, R.M.; Keller, J.N. The complex interactions between obesity, metabolism and the brain. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.; Zhang, L.; Yang, L.; Chu, H. The critical role of gut microbiota in obesity. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 1025706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petraroli, M.; Castellone, E.; Patianna, V.; Esposito, S. Gut Microbiota and Obesity in Adults and Children: The State of the Art. Front. Pediatr. 2021, 9, 657020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malone Rubright, S.L.; Pearce, L.L.; Peterson, J. Environmental toxicology of hydrogen sulfide. Nitric Oxide 2017, 71, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.J.; Wu, Z.Y.; Nie, X.W.; Bian, J.S. Role of endothelial dysfunction in cardiovascular diseases: The link between inflammation and hydrogen sulfide. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 10, 1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munteanu, C. Hydrogen Sulfide and Oxygen Homeostasis in Atherosclerosis: A Systematic Review from Molecular Biology to Therapeutic Perspectives. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 8376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munteanu, C.; Galaction, A.I.; Poștaru, M.; Rotariu, M.; Turnea, M.; Blendea, C.D. Hydrogen Sulfide Modulation of Matrix Metalloproteinases and CD147/EMMPRIN: Mechanistic Pathways and Impact on Atherosclerosis Progression. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, L. Irritable bowel syndrome: Pathogenesis, diagnosis, treatment, and evidence-based medicine. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 6759–6773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quaglio, A.E.V.; Grillo, T.G.; De Oliveira, E.C.S.; Di Stasi, L.C.; Sassaki, L.Y. Gut microbiota, inflammatory bowel disease and colorectal cancer. World J. Gastroenterol. 2022, 28, 4053–4060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cresci, G.A.; Bawden, E. Gut microbiome: What we do and don’t know. Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2015, 30, 734–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mccutcheon, R.A.; Krystal, J.H.; Howes, O.D. Dopamine and glutamate in schizophrenia: Biology, symptoms and treatment. World Psychiatry 2020, 19, 15–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisetsky, D.S. Pathogenesis of autoimmune disease. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2023, 19, 509–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, K.F.; Isaacs, J.D. Novel therapies for immune-mediated inflammatory diseases: What can we learn from their use in rheumatoid arthritis, spondyloarthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, psoriasis, Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis? Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2018, 77, 175–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Pan, J. Immunopathogenic mechanisms of rheumatoid arthritis and the use of anti-inflammatory drugs. Intractable Rare Dis. Res. 2021, 10, 154–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Yu, Y.; Yue, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Su, K. Microbial Infection and Rheumatoid Arthritis. J. Clin. Cell Immunol. 2013, 4, 000174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, M.Y.; Inohara, N.; Nuñez, G. Mechanisms of inflammation-driven bacterial dysbiosis in the gut. Mucosal Immunol. 2017, 10, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ameer, M.A.; Chaudhry, H.; Mushtaq, J.; Khan, O.S.; Babar, M.; Hashim, T.; Zeb, S.; Tariq, M.A.; Patlolla, S.R.; Ali, J.; et al. An Overview of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) Pathogenesis, Classification, and Management. Cureus 2022, 14, e30330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.; Kim, S.T.; Craft, J. The pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus-an update. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2012, 24, 651–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katarzyna, P.B.; Wiktor, S.; Ewa, D.; Piotr, L. Current treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus: A clinician’s perspective. Rheumatol. Int. 2023, 43, 1395–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maeng, S.H.; Hong, H. Inflammation as the potential basis in depression. Int. Neurourol. J. 2019, 23, S63–S71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammar, Å.; Ronold, E.H.; Rekkedal, G.Å. Cognitive Impairment and Neurocognitive Profiles in Major Depression—A Clinical Perspective. Front. Psychiatry 2022, 13, 764374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popa, S.-L.; Dumitrascu, D.L. Anxiety and IBS Revisited: Ten years later. Med. Pharm. Rep. 2015, 88, 253–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murros, K.E. Hydrogen Sulfide Produced by Gut Bacteria May Induce Parkinson’s Disease. Cells 2022, 11, 978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petschow, B.; Doré, J.; Hibberd, P.; Dinan, T.; Reid, G.; Blaser, M.; Cani, P.D.; Degnan, F.H.; Foster, J.; Gibson, G.; et al. Probiotics, prebiotics, and the host microbiome: The science of translation. Ann. N. Y Acad. Sci. 2013, 1306, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pichette, J.; Fynn-Sackey, N.; Gagnon, J. Hydrogen sulfide and sulfate prebiotic stimulates the secretion of GLP-1 and improves glycemia in male mice. Endocrinology 2017, 158, 3416–3425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fijan, S. Microorganisms with claimed probiotic properties: An overview of recent literature. Int. J. Env. Environ. Res. Public Health 2014, 11, 4745–4767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zommiti, M.; Feuilloley, M.G.J.; Connil, N. Update of probiotics in human world: A nonstop source of benefactions till the end of time. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gul, S.; Durante-Mangoni, E. Unraveling the Puzzle: Health Benefits of Probiotics—A Comprehensive Review. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, R.K.; Samak, G. Protection and Restitution of Gut Barrier by Probiotics: Nutritional and Clinical Implications. Curr. Nutr. Food Sci. 2013, 9, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, S.; Whitley, C.S.; Haribabu, B.; Jala, V.R. Regulation of Intestinal Barrier Function by Microbial Metabolites. Cell. Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 11, 1463–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Portincasa, P.; Bonfrate, L.; Vacca, M.; De Angelis, M.; Farella, I.; Lanza, E.; Khalil, M.; Wang, D.Q.; Sperandio, M.; Di Ciaula, A. Gut Microbiota and Short Chain Fatty Acids: Implications in Glucose Homeostasis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, S.; Jung, S.C.; Kwak, K.; Kim, J.S. The Role of Prebiotics in Modulating Gut Microbiota: Implications for Human Health. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 4834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guarino, M.P.L.; Altomare, A.; Emerenziani, S.; Di Rosa, C.; Ribolsi, M.; Balestrieri, P.; Iovino, P.; Rocchi, G.; Cicala, M. Mechanisms of action of prebiotics and their effects on gastro-intestinal disorders in adults. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.K.; Chang, H.W.; Yan, D.; Lee, K.M.; Ucmak, D.; Wong, K.; Abrouk, M.; Farahnik, B.; Nakamura, M.; Zhu, T.H.; et al. Influence of diet on the gut microbiome and implications for human health. J. Transl. Med. 2017, 15, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romaní-Pérez, M.; Bullich-Vilarrubias, C.; López-Almela, I.; Liébana-García, R.; Olivares, M.; Sanz, Y. The microbiota and the gut-brain axis in controlling food intake and energy homeostasis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinninella, E.; Cintoni, M.; Raoul, P.; Lopetuso, L.R.; Scaldaferri, F.; Pulcini, G.; Miggiano, G.A.D.; Gasbarrini, A.; Mele, M.C. Food components and dietary habits: Keys for a healthy gut microbiota composition. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, P.G.; Cowley, E.S.; Breister, A.; Matatov, S.; Lucio, L.; Polak, P.; Ridlon, J.M.; Gaskins, H.R.; Anantharaman, K. Diversity and distribution of sulfur metabolic genes in the human gut microbiome and their association with colorectal cancer. Microbiome 2022, 10, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ioniță-Mîndrican, C.B.; Ziani, K.; Mititelu, M.; Oprea, E.; Neacșu, S.M.; Moroșan, E.; Dumitrescu, D.E.; Roșca, A.C.; Drăgănescu, D.; Negrei, C. Therapeutic Benefits and Dietary Restrictions of Fiber Intake: A State of the Art Review. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, B.A.; Grant, L.J.; Gidley, M.J.; Mikkelsen, D. Gut fermentation of dietary fibres: Physico-chemistry of plant cell walls and implications for health. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolluru, G.K.; Shackelford, R.E.; Shen, X.; Dominic, P.; Kevil, C.G. Sulfide regulation of cardiovascular function in health and disease. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2023, 20, 109–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borody, T.J.; Paramsothy, S.; Agrawal, G. Fecal microbiota transplantation: Indications, methods, evidence, and future directions. Curr. Gastroenterol. Rep. 2013, 15, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, F.; Li, N.; Wang, C.; Xing, H.; Chen, D.; Wei, Y. Clinical efficacy of fecal microbiota transplantation for patients with small intestinal bacterial overgrowth: A randomized, placebo-controlled clinic study. BMC Gastroenterol. 2021, 21, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belotserkovsky, I.; Stabryla, L.M.; Hunter, M.; Allegretti, J.; Callahan, B.J.; Carlson, P.E.; Daschner, P.J.; Goudarzi, M.; Guyard, C.; Jackson, S.A.; et al. Standards for fecal microbiota transplant: Tools and therapeutic advances. Biologicals 2024, 86, 101758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartle, M.D.; Pluth, M.D. A practical guide to working with H2S at the interface of chemistry and biology. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 6108–6117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merz, T.; McCook, O.; Brucker, C.; Waller, C.; Calzia, E.; Radermacher, P.; Datzmann, T. H2S in Critical Illness—A New Horizon for Sodium Thiosulfate? Biomolecules 2022, 12, 543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mora-Ochomogo, M.; Lohans, C.T. β-Lactam antibiotic targets and resistance mechanisms: From covalent inhibitors to substrates. RSC Med. Chem. 2021, 12, 1623–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bull, M.J.; Plummer, N.T. Part 1: The Human Gut Microbiome in Health and Disease. Integr. Med. 2014, 13, 17–22. [Google Scholar]
- Kerksick, C.; Willoughby, D. The Antioxidant Role of Glutathione and N-Acetyl-Cysteine Supplements and Exercise-Induced Oxidative Stress. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2005, 2, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurutas, E.B. The importance of antioxidants which play the role in cellular response against oxidative/nitrosative stress: Current state. Nutr. J. 2016, 15, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yahfoufi, N.; Alsadi, N.; Jambi, M.; Matar, C. The immunomodulatory and anti-inflammatory role of polyphenols. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabil, O.; Motl, N.; Banerjee, R. H2S and its role in redox signaling. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Proteins Proteom. 2014, 1844, 1355–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kashfi, K.; Olson, K.R. Biology and therapeutic potential of hydrogen sulfide and hydrogen sulfide-releasing chimeras. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2013, 85, 689–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szabõ, C. Hydrogen sulphide and its therapeutic potential. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2007, 6, 917–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohajeri, M.H.; Brummer, R.J.M.; Rastall, R.A.; Weersma, R.K.; Harmsen, H.J.M.; Faas, M.; Eggersdorfer, M. The role of the microbiome for human health: From basic science to clinical applications. Eur. J. Nutr. 2018, 57, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, D.; Hu, Q.; Zhu, D. An update on hydrogen sulfide and nitric oxide interactions in the cardiovascular system. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2018, 2018, 4579140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.; Yi, B.; Zhong, R.; Wang, M.; Zhang, S.; Ma, J.; Yin, Y.; Yin, J.; Chen, L.; Zhang, H. From gut microbiota to host appetite: Gut microbiota-derived metabolites as key regulators. Microbiome 2021, 9, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Munteanu, C.; Onose, G.; Rotariu, M.; Poștaru, M.; Turnea, M.; Galaction, A.I. Role of Microbiota-Derived Hydrogen Sulfide (H2S) in Modulating the Gut–Brain Axis: Implications for Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s Disease Pathogenesis. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 2670. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12122670
Munteanu C, Onose G, Rotariu M, Poștaru M, Turnea M, Galaction AI. Role of Microbiota-Derived Hydrogen Sulfide (H2S) in Modulating the Gut–Brain Axis: Implications for Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s Disease Pathogenesis. Biomedicines. 2024; 12(12):2670. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12122670
Chicago/Turabian StyleMunteanu, Constantin, Gelu Onose, Mariana Rotariu, Mădălina Poștaru, Marius Turnea, and Anca Irina Galaction. 2024. "Role of Microbiota-Derived Hydrogen Sulfide (H2S) in Modulating the Gut–Brain Axis: Implications for Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s Disease Pathogenesis" Biomedicines 12, no. 12: 2670. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12122670
APA StyleMunteanu, C., Onose, G., Rotariu, M., Poștaru, M., Turnea, M., & Galaction, A. I. (2024). Role of Microbiota-Derived Hydrogen Sulfide (H2S) in Modulating the Gut–Brain Axis: Implications for Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s Disease Pathogenesis. Biomedicines, 12(12), 2670. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12122670






