Complement Activation in Nephrotic Glomerular Diseases
Abstract
1. Introduction
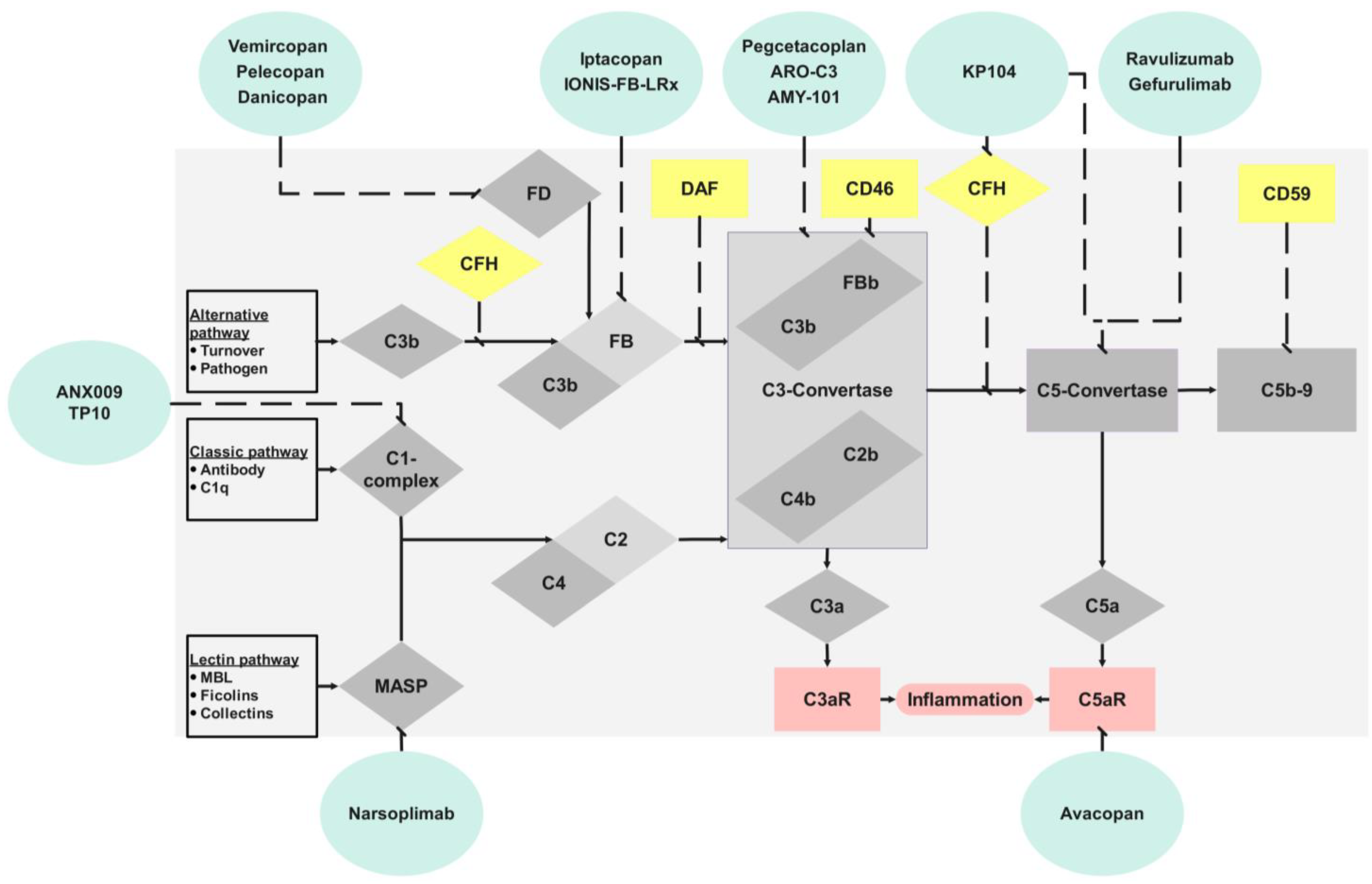
2. Complement
3. Renal Complement Activation
4. Nephrotic Glomerular Diseases
4.1. Membranous Nephropathy (MN)
4.2. Membranoproliferative Glomerulonephritis (MPGN)
4.3. Lupus Nephritis (LN)
4.4. Focal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis (FSGS)
4.5. Minimal Change Disease (MCD)
5. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Claudio:, P.; Gabriella, M. Nephrotic Syndrome: Pathophysiology and Consequences. J. Nephrol. 2023, 36, 2179–2190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benzing, T.; Salant, D. Insights into Glomerular Filtration and Albuminuria. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 1437–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinrichs, G.R.; Jensen, B.L.; Svenningsen, P. Mechanisms of Sodium Retention in Nephrotic Syndrome. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 2020, 29, 207–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larionov, A.; Dahlke, E.; Kunke, M.; Zanon Rodriguez, L.; Schiessl, I.M.; Magnin, J.; Kern, U.; Alli, A.A.; Mollet, G.; Schilling, O.; et al. Cathepsin B Increases ENaC Activity Leading to Hypertension Early in Nephrotic Syndrome. J. Cell. Mol. Medi 2019, 23, 6543–6553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddall, E.C.; Radhakrishnan, J. The Pathophysiology of Edema Formation in the Nephrotic Syndrome. Kidney Int. 2012, 82, 635–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gyamlani, G.; Molnar, M.Z.; Lu, J.L.; Sumida, K.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K.; Kovesdy, C.P. Association of Serum Albumin Level and Venous Thromboembolic Events in a Large Cohort of Patients with Nephrotic Syndrome. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2017, 32, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, H.; Bao, W.; Shi, S. Innate Immune Activity in Glomerular Podocytes. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Liu, Y.; He, Y.; Rong, W.; Zhang, M.; Li, L.; Liu, Z.; Zen, K. Podocytes Present Antigen to Activate Specific T Cell Immune Responses in Inflammatory Renal Disease. J. Pathol. 2020, 252, 165–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhargava, R.; Tsokos, G.C. The Immune Podocyte. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2019, 31, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zoshima, T.; Hara, S.; Yamagishi, M.; Pastan, I.; Matsusaka, T.; Kawano, M.; Nagata, M. Possible Role of Complement Factor H in Podocytes in Clearing Glomerular Subendothelial Immune Complex Deposits. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 7857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mühlig, A.K.; Keir, L.S.; Abt, J.C.; Heidelbach, H.S.; Horton, R.; Welsh, G.I.; Meyer-Schwesinger, C.; Licht, C.; Coward, R.J.; Fester, L.; et al. Podocytes Produce and Secrete Functional Complement C3 and Complement Factor H. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borza, D.-B. Glomerular Basement Membrane Heparan Sulfate in Health and Disease: A Regulator of Local Complement Activation. Matrix Biol. 2017, 57–58, 299–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petr, V.; Thurman, J.M. The Role of Complement in Kidney Disease. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2023, 19, 771–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Kimura, Y.; Fang, C.; Zhou, L.; Sfyroera, G.; Lambris, J.D.; Wetsel, R.A.; Miwa, T.; Song, W.-C. Regulation of Toll-like Receptor–Mediated Inflammatory Response by Complement in Vivo. Blood 2007, 110, 228–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arbore, G.; West, E.E.; Spolski, R.; Robertson, A.A.B.; Klos, A.; Rheinheimer, C.; Dutow, P.; Woodruff, T.M.; Yu, Z.X.; O’Neill, L.A.; et al. T Helper 1 Immunity Requires Complement-Driven NLRP3 Inflammasome Activity in CD4 + T Cells. Science 2016, 352, aad1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huber-Lang, M.; Sarma, J.V.; Zetoune, F.S.; Rittirsch, D.; Neff, T.A.; McGuire, S.R.; Lambris, J.D.; Warner, R.L.; Flierl, M.A.; Hoesel, L.M.; et al. Generation of C5a in the Absence of C3: A New Complement Activation Pathway. Nat. Med. 2006, 12, 682–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vandendriessche, S.; Cambier, S.; Proost, P.; Marques, P.E. Complement Receptors and Their Role in Leukocyte Recruitment and Phagocytosis. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 624025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serna, M.; Giles, J.L.; Morgan, B.P.; Bubeck, D. Structural Basis of Complement Membrane Attack Complex Formation. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 10587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastellos, D.C.; Hajishengallis, G.; Lambris, J.D. A Guide to Complement Biology, Pathology and Therapeutic Opportunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2023, 24, 118–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garred, P.; Genster, N.; Pilely, K.; Bayarri-Olmos, R.; Rosbjerg, A.; Ma, Y.J.; Skjoedt, M. A Journey through the Lectin Pathway of Complement—MBL and Beyond. Immunol. Rev. 2016, 274, 74–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Boer, E.C.; Thielen, A.J.; Langereis, J.D.; Kamp, A.; Brouwer, M.C.; Oskam, N.; Jongsma, M.L.; Baral, A.J.; Spaapen, R.M.; Zeerleder, S.; et al. The Contribution of the Alternative Pathway in Complement Activation on Cell Surfaces Depends on the Strength of Classical Pathway Initiation. Clin. Trans. Immunol. 2023, 12, e1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lachmann, P.J.; Lay, E.; Seilly, D.J. Experimental Confirmation of the C3 Tickover Hypothesis by Studies with an Ab (S77) That Inhibits Tickover in Whole Serum. FASEB J. 2018, 32, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zipfel, P.F.; Skerka, C. Complement Regulators and Inhibitory Proteins. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2009, 9, 729–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucientes-Continente, L.; Márquez-Tirado, B.; Goicoechea De Jorge, E. The Factor H Protein Family: The Switchers of the Complement Alternative Pathway. Immunol. Rev. 2023, 313, 25–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Servais, A.; Noël, L.-H.; Roumenina, L.T.; Le Quintrec, M.; Ngo, S.; Dragon-Durey, M.-A.; Macher, M.-A.; Zuber, J.; Karras, A.; Provot, F.; et al. Acquired and Genetic Complement Abnormalities Play a Critical Role in Dense Deposit Disease and Other C3 Glomerulopathies. Kidney Int. 2012, 82, 454–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín Merinero, H.; Zhang, Y.; Arjona, E.; Del Angel, G.; Goodfellow, R.; Gomez-Rubio, E.; Ji, R.-R.; Michelena, M.; Smith, R.J.H.; Rodríguez De Córdoba, S. Functional Characterization of 105 Factor H Variants Associated with aHUS: Lessons for Variant Classification. Blood 2021, 138, 2185–2201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blom, A.M. A Cluster of Positively Charged Amino Acids in the Alpha-Chain of C4b-Binding Protein (C4BP) Is Pivotal for the Regulation of the Complement System and the Interaction with Bacteria. Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Investig. Suppl. 2000, 233, 37–49. [Google Scholar]
- Degn, S.E.; Hansen, A.G.; Steffensen, R.; Jacobsen, C.; Jensenius, J.C.; Thiel, S. MAp44, a Human Protein Associated with Pattern Recognition Molecules of the Complement System and Regulating the Lectin Pathway of Complement Activation. J. Immunol. 2009, 183, 7371–7378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Post, T.W.; Liszewski, M.K.; Adams, E.M.; Tedja, I.; Miller, E.A.; Atkinson, J.P. Membrane Cofactor Protein of the Complement System: Alternative Splicing of Serine/Threonine/Proline-Rich Exons and Cytoplasmic Tails Produces Multiple Isoforms That Correlate with Protein Phenotype. J. Exp. Med. 1991, 174, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaefer, F.; Ardissino, G.; Ariceta, G.; Fakhouri, F.; Scully, M.; Isbel, N.; Lommelé, Å.; Kupelian, V.; Gasteyger, C.; Greenbaum, L.A.; et al. Clinical and Genetic Predictors of Atypical Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome Phenotype and Outcome. Kidney Int. 2018, 94, 408–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angeletti, A.; Cantarelli, C.; Petrosyan, A.; Andrighetto, S.; Budge, K.; D’Agati, V.D.; Hartzell, S.; Malvi, D.; Donadei, C.; Thurman, J.M.; et al. Loss of Decay-Accelerating Factor Triggers Podocyte Injury and Glomerulosclerosis. J. Exp. Med. 2020, 217, e20191699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lake, B.B.; Menon, R.; Winfree, S.; Hu, Q.; Melo Ferreira, R.; Kalhor, K.; Barwinska, D.; Otto, E.A.; Ferkowicz, M.; Diep, D.; et al. An Atlas of Healthy and Injured Cell States and Niches in the Human Kidney. Nature 2023, 619, 585–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodship, T.H.J.; Cook, H.T.; Fakhouri, F.; Fervenza, F.C.; Frémeaux-Bacchi, V.; Kavanagh, D.; Nester, C.M.; Noris, M.; Pickering, M.C.; Rodríguez de Córdoba, S.; et al. Atypical Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome and C3 Glomerulopathy: Conclusions from a “Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes” (KDIGO) Controversies Conference. Kidney Int. 2017, 91, 539–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawachi, H.; Fukusumi, Y. New Insight into Podocyte Slit Diaphragm, a Therapeutic Target of Proteinuria. Clin. Exp. Nephrol. 2020, 24, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schell, C.; Huber, T.B. The Evolving Complexity of the Podocyte Cytoskeleton. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. JASN 2017, 28, 3166–3174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blaine, J.; Dylewski, J. Regulation of the Actin Cytoskeleton in Podocytes. Cells 2020, 9, 1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butt, L.; Unnersjö-Jess, D.; Höhne, M.; Edwards, A.; Binz-Lotter, J.; Reilly, D.; Hahnfeldt, R.; Ziegler, V.; Fremter, K.; Rinschen, M.M.; et al. A Molecular Mechanism Explaining Albuminuria in Kidney Disease. Nat. Metab. 2020, 2, 461–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banas, M.C.; Banas, B.; Hudkins, K.L.; Wietecha, T.A.; Iyoda, M.; Bock, E.; Hauser, P.; Pippin, J.W.; Shankland, S.J.; Smith, K.D.; et al. TLR4 Links Podocytes with the Innate Immune System to Mediate Glomerular Injury. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2008, 19, 704–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srivastava, T.; Sharma, M.; Yew, K.-H.; Sharma, R.; Duncan, R.S.; Saleem, M.A.; McCarthy, E.T.; Kats, A.; Cudmore, P.A.; Alon, U.S.; et al. LPS and PAN-Induced Podocyte Injury in an in Vitro Model of Minimal Change Disease: Changes in TLR Profile. J. Cell Commun. Signal. 2013, 7, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, R.D.; Beresford, M.W. Podocytes Contribute, and Respond, to the Inflammatory Environment in Lupus Nephritis. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2018, 315, F1683–F1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coers, W.; Brouwer, L.; Vos, J.T.W.M.; Chand, A.; Huitema, S.; Heeringa, P.; Kallenberg, C.G.M.; Weening, J.J. Podocyte Expression of MHC Class I and II and Intercellular Adhesion Molecule-1 (ICAM-1) in Experimental Pauci-Immune Crescentic Glomerulonephritis. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2008, 98, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dylewski, J.; Dobrinskikh, E.; Lewis, L.; Tonsawan, P.; Miyazaki, M.; Jat, P.S.; Blaine, J. Differential Trafficking of Albumin and IgG Facilitated by the Neonatal Fc Receptor in Podocytes in Vitro and in Vivo. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0209732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagata, M. Podocyte Injury and Its Consequences. Kidney Int. 2016, 89, 1221–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takano, T.; Elimam, H.; Cybulsky, A.V. Complement-Mediated Cellular Injury. Semin. Nephrol. 2013, 33, 586–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cybulsky, A.V. The Intersecting Roles of Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress, Ubiquitin–Proteasome System, and Autophagy in the Pathogenesis of Proteinuric Kidney Disease. Kidney Int. 2013, 84, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greka, A.; Mundel, P. Balancing Calcium Signals through TRPC5 and TRPC6 in Podocytes. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2011, 22, 1969–1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, Q.; Yang, F.; Chen, K.; Zhang, Y. Autophagy Protects Podocytes from Sublytic Complement Induced Injury. Exp. Cell Res. 2016, 341, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.J.; Li, Z.; Chen, X.; Zhao, X.; Zhong, Z.; Yang, C.; Wu, H.; An, N.; Li, W.; Liu, H. Blockage of the Lysosome-Dependent Autophagic Pathway Contributes to Complement Membrane Attack Complex-Induced Podocyte Injury in Idiopathic Membranous Nephropathy. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 8643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abe, K.; Miyazaki, M.; Koji, T.; Furusu, A.; Nakamura-Kurashige, T.; Nishino, T.; Ozono, Y.; Harada, T.; Sakai, H.; Kohno, S. Enhanced Expression of Complement C5a Receptor mRNA in Human Diseased Kidney Assessed by in Situ Hybridization. Kidney Int. 2001, 60, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keir, L.S.; Firth, R.; Aponik, L.; Feitelberg, D.; Sakimoto, S.; Aguilar, E.; Welsh, G.I.; Richards, A.; Usui, Y.; Satchell, S.C.; et al. VEGF Regulates Local Inhibitory Complement Proteins in the Eye and Kidney. J. Clin. Investig. 2016, 127, 199–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Jiang, Z.; Chen, D.; Wang, S.; Zhao, W.; Li, L. Pathological Significance of Urinary Complement Activation in Diabetic Nephropathy: A Full View from the Development of the Disease. J. Diabetes Investig. 2019, 10, 738–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wörn, M.; Bohnert, B.N.; Alenazi, F.; Boldt, K.; Klose, F.; Junger, K.; Ueffing, M.; Birkenfeld, A.L.; Kalbacher, H.; Artunc, F. Proteasuria in Nephrotic Syndrome–Quantification and Proteomic Profiling. J. Proteom. 2021, 230, 103981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medica, D.; Franzin, R.; Stasi, A.; Castellano, G.; Migliori, M.; Panichi, V.; Figliolini, F.; Gesualdo, L.; Camussi, G.; Cantaluppi, V. Extracellular Vesicles Derived from Endothelial Progenitor Cells Protect Human Glomerular Endothelial Cells and Podocytes from Complement- and Cytokine-Mediated Injury. Cells 2021, 10, 1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maisonneuve, P.; Agodoa, L.; Gellert, R.; Stewart, J.H.; Buccianti, G.; Lowenfels, A.B.; Wolfe, R.A.; Jones, E.; Disney, A.P.S.; Briggs, D.; et al. Distribution of Primary Renal Diseases Leading to End-Stage Renal Failure in the United States, Europe, and Australia/New Zealand: Results from an International Comparative Study. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2000, 35, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, L.H.; Bonegio, R.G.B.; Lambeau, G.; Beck, D.M.; Powell, D.W.; Cummins, T.D.; Klein, J.B.; Salant, D.J. M-Type Phospholipase A 2 Receptor as Target Antigen in Idiopathic Membranous Nephropathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 361, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomas, N.M.; Beck, L.H.; Meyer-Schwesinger, C.; Seitz-Polski, B.; Ma, H.; Zahner, G.; Dolla, G.; Hoxha, E.; Helmchen, U.; Dabert-Gay, A.-S.; et al. Thrombospondin Type-1 Domain-Containing 7A in Idiopathic Membranous Nephropathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 2277–2287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vidarsson, G.; Dekkers, G.; Rispens, T. IgG Subclasses and Allotypes: From Structure to Effector Functions. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5, 520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiech, T.; Stahl, R.A.K.; Hoxha, E. Diagnostic Role of Renal Biopsy in PLA2R1-Antibody-Positive Patients with Nephrotic Syndrome. Mod. Pathol. 2019, 32, 1320–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayashi, N.; Okada, K.; Matsui, Y.; Fujimoto, K.; Adachi, H.; Yamaya, H.; Matsushita, M.; Yokoyama, H. Glomerular Mannose-Binding Lectin Deposition in Intrinsic Antigen-Related Membranous Nephropathy. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2018, 33, 832–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoxha, E.; Harendza, S.; Pinnschmidt, H.; Panzer, U.; Stahl, R.A.K. PLA2R Antibody Levels and Clinical Outcome in Patients with Membranous Nephropathy and Non-Nephrotic Range Proteinuria under Treatment with Inhibitors of the Renin-Angiotensin System. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e110681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bally, S.; Debiec, H.; Ponard, D.; Dijoud, F.; Rendu, J.; Fauré, J.; Ronco, P.; Dumestre-Perard, C. Phospholipase A2 Receptor–Related Membranous Nephropathy and Mannan-Binding Lectin Deficiency. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. JASN 2016, 27, 3539–3544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seifert, L.; Zahner, G.; Meyer-Schwesinger, C.; Hickstein, N.; Dehde, S.; Wulf, S.; Köllner, S.M.S.; Lucas, R.; Kylies, D.; Froembling, S.; et al. The Classical Pathway Triggers Pathogenic Complement Activation in Membranous Nephropathy. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manral, P.; Caza, T.N.; Storey, A.J.; Beck, L.H.; Borza, D.-B. The Alternative Pathway Is Necessary and Sufficient for Complement Activation by Anti-THSD7A Autoantibodies, Which Are Predominantly IgG4 in Membranous Nephropathy. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 952235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sethi, S.; Fervenza, F.C. Membranoproliferative Glomerulonephritis—A New Look at an Old Entity. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 1119–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sethi, S.; Fervenza, F.C. Membranoproliferative Glomerulonephritis: Pathogenetic Heterogeneity and Proposal for a New Classification. Semin. Nephrol. 2011, 31, 341–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, R.J.H.; Appel, G.B.; Blom, A.M.; Cook, H.T.; D’Agati, V.D.; Fakhouri, F.; Fremeaux-Bacchi, V.; Józsi, M.; Kavanagh, D.; Lambris, J.D.; et al. C3 Glomerulopathy—Understanding a Rare Complement-Driven Renal Disease. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2019, 15, 129–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickering, M.C.; D’Agati, V.D.; Nester, C.M.; Smith, R.J.; Haas, M.; Appel, G.B.; Alpers, C.E.; Bajema, I.M.; Bedrosian, C.; Braun, M.; et al. C3 Glomerulopathy: Consensus Report. Kidney Int. 2013, 84, 1079–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zipfel, P.F.; Wiech, T.; Gröne, H.-J.; Skerka, C. Complement Catalyzing Glomerular Diseases. Cell Tissue Res. 2021, 385, 355–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zipfel, P.F.; Wiech, T.; Stea, E.D.; Skerka, C. CFHR Gene Variations Provide Insights in the Pathogenesis of the Kidney Diseases Atypical Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome and C3 Glomerulopathy. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. JASN 2020, 31, 241–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iatropoulos, P.; Noris, M.; Mele, C.; Piras, R.; Valoti, E.; Bresin, E.; Curreri, M.; Mondo, E.; Zito, A.; Gamba, S.; et al. Complement Gene Variants Determine the Risk of Immunoglobulin-Associated MPGN and C3 Glomerulopathy and Predict Long-Term Renal Outcome. Mol. Immunol. 2016, 71, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donadelli, R.; Pulieri, P.; Piras, R.; Iatropoulos, P.; Valoti, E.; Benigni, A.; Remuzzi, G.; Noris, M. Unraveling the Molecular Mechanisms Underlying Complement Dysregulation by Nephritic Factors in C3G and IC-MPGN. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega, L.M.; Schultz, D.R.; Lenz, O.; Pardo, V.; Contreras, G.N. Review: Lupus Nephritis: Pathologic Features, Epidemiology and a Guide to Therapeutic Decisions. Lupus 2010, 19, 557–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markowitz, G.S.; D’Agati, V.D. Classification of Lupus Nephritis. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 2009, 18, 220–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birmingham, D.; Irshaid, F.; Nagaraja, H.; Zou, X.; Tsao, B.; Wu, H.; Yu, C.; Hebert, L.; Rovin, B. The Complex Nature of Serum C3 and C4 as Biomarkers of Lupus Renal Flare. Lupus 2010, 19, 1272–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, A.H.J.; Strand, V.; Sen, D.P.; Fu, Q.; Mathis, N.L.; Schmidt, M.J.; Bruchas, R.R.; Staten, N.R.; Olson, P.K.; Stiening, C.M.; et al. Association of Blood Concentrations of Complement Split Product iC 3b and Serum C3 With Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Disease Activity. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019, 71, 420–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, M.; Trattner, R.; Nilsson, S.C.; Björk, A.; Zickert, A.; Blom, A.M.; Gunnarsson, I. Plasma C4d Correlates with C4d Deposition in Kidneys and With Treatment Response in Lupus Nephritis Patients. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 582737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sethi, S.; Palma, L.M.P.; Theis, J.D.; Fervenza, F.C. Proteomic Analysis of Complement Proteins in Glomerular Diseases. Kidney Int. Rep. 2023, 8, 827–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drachenberg, C.B.; Papadimitriou, J.C.; Chandra, P.; Haririan, A.; Mendley, S.; Weir, M.R.; Rubin, M.F. Epidemiology and Pathophysiology of Glomerular C4d Staining in Native Kidney Biopsies. Kidney Int. Rep. 2019, 4, 1555–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.; Haas, M.; Glassock, R.; Zhao, M.-H. Redefining Lupus Nephritis: Clinical Implications of Pathophysiologic Subtypes. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2017, 13, 483–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaya Da Costa, M.; Poppelaars, F.; Berger, S.P.; Daha, M.R.; Seelen, M.A. The Lectin Pathway in Renal Disease: Old Concept and New Insights. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2018, 33, 2073–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asanuma, Y.; Nozawa, K.; Matsushita, M.; Kusaoi, M.; Abe, Y.; Yamaji, K.; Tamura, N. Critical Role of Lectin Pathway Mediated by MBL-Associated Serine Proteases in Complement Activation for the Pathogenesis in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Heliyon 2023, 9, e19072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Agati, V.D.; Kaskel, F.J.; Falk, R.J. Focal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 365, 2398–2411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van De Lest, N.A.; Zandbergen, M.; Wolterbeek, R.; Kreutz, R.; Trouw, L.A.; Dorresteijn, E.M.; Bruijn, J.A.; Bajema, I.M.; Scharpfenecker, M.; Chua, J.S. Glomerular C4d Deposition Can Precede the Development of Focal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis. Kidney Int. 2019, 96, 738–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Cui, Z.; Gu, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Qu, Z.; Wang, X.; Wang, F.; Cheng, X.; Meng, L.; Liu, G.; et al. Complement Activation Profile of Patients with Primary Focal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0234934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thurman, J.M.; Wong, M.; Renner, B.; Frazer-Abel, A.; Giclas, P.C.; Joy, M.S.; Jalal, D.; Radeva, M.K.; Gassman, J.; Gipson, D.S.; et al. Complement Activation in Patients with Focal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0136558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Xie, J.; Zhang, X.; Tong, J.; Hao, X.; Ren, H.; Wang, W.; Chen, N. Serum C3 and Renal Outcome in Patients with Primary Focal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 4095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tato, A.M.; Carrera, N.; García-Murias, M.; Shabaka, A.; Ávila, A.; Mora Mora, M.T.; Rabasco, C.; Soto, K.; de la Prada Alvarez, F.J.; Fernández-Lorente, L.; et al. Genetic Testing in Focal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis: In Whom and When? Clin. Kidney J. 2023, 16, 2011–2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trachtman, H.; Laskowski, J.; Lee, C.; Renner, B.; Feemster, A.; Parikh, S.; Panzer, S.E.; Zhong, W.; Cravedi, P.; Cantarelli, C.; et al. Natural Antibody and Complement Activation Characterize Patients with Idiopathic Nephrotic Syndrome. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2021, 321, F505–F516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koopman, J.J.E.; Van Essen, M.F.; Rennke, H.G.; De Vries, A.P.J.; Van Kooten, C. Deposition of the Membrane Attack Complex in Healthy and Diseased Human Kidneys. Front. Immunol. 2021, 11, 599974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chugh, S.S.; Clement, L.C. “Idiopathic” Minimal Change Nephrotic Syndrome: A Podocyte Mystery Nears the End. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2023, 325, F685–F694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muruve, D.A.; Debiec, H.; Dillon, S.T.; Gu, X.; Plaisier, E.; Can, H.; Otu, H.H.; Libermann, T.A.; Ronco, P. Serum Protein Signatures Using Aptamer-Based Proteomics for Minimal Change Disease and Membranous Nephropathy. Kidney Int. Rep. 2022, 7, 1539–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wendt, R.; Siwy, J.; He, T.; Latosinska, A.; Wiech, T.; Zipfel, P.F.; Tserga, A.; Vlahou, A.; Rupprecht, H.; Catanese, L.; et al. Molecular Mapping of Urinary Complement Peptides in Kidney Diseases. Proteomes 2021, 9, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legendre, C.M.; Licht, C.; Muus, P.; Greenbaum, L.A.; Babu, S.; Bedrosian, C.; Bingham, C.; Cohen, D.J.; Delmas, Y.; Douglas, K.; et al. Terminal Complement Inhibitor Eculizumab in Atypical Hemolytic–Uremic Syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 368, 2169–2181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruggenenti, P.; Daina, E.; Gennarini, A.; Carrara, C.; Gamba, S.; Noris, M.; Rubis, N.; Peraro, F.; Gaspari, F.; Pasini, A.; et al. C5 Convertase Blockade in Membranoproliferative Glomerulonephritis: A Single-Arm Clinical Trial. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2019, 74, 224–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sethi, S.; Fervenza, F.C.; Zhang, Y.; Zand, L.; Meyer, N.C.; Borsa, N.; Nasr, S.H.; Smith, R.J.H. Atypical Postinfectious Glomerulonephritis Is Associated with Abnormalities in the Alternative Pathway of Complement. Kidney Int. 2013, 83, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, E.; Nester, C.; Cavero, T.; Karras, A.; Le Quintrec, M.; Lightstone, L.; Eisenberger, U.; Soler, M.J.; Kavanagh, D.; Daina, E.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Iptacopan in Patients with C3 Glomerulopathy. Kidney Int. Rep. 2023, 8, 2754–2764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarragon Estebanez, B.; Bomback, A.S. C3 Glomerulopathy: Novel Treatment Paradigms. Kidney Int. Rep. 2023, 93, 977–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fervenza, F.C.; Appel, G.B.; Barbour, S.J.; Rovin, B.H.; Lafayette, R.A.; Aslam, N.; Jefferson, J.A.; Gipson, P.E.; Rizk, D.V.; Sedor, J.R.; et al. Rituximab or Cyclosporine in the Treatment of Membranous Nephropathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kistler, A.D.; Salant, D.J. Complement Activation and Effector Pathways in Membranous Nephropathy. Kidney Int. 2023, 5, 572–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickering, M.C.; Botto, M.; Taylor, P.R.; Lachmann, P.J.; Walport, M.J. Systemic Lupus Erythematosus, Complement Deficiency, and Apoptosis. In Advances in Immunology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2001; Volume 76, pp. 227–324. ISBN 978-0-12-022476-0. [Google Scholar]
- McGrogan, A.; Franssen, C.F.M.; de Vries, C.S. The Incidence of Primary Glomerulonephritis Worldwide: A Systematic Review of the Literature. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2011, 26, 414–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, H.; Kiryluk, K.; Novak, J.; Moldoveanu, Z.; Herr, A.B.; Renfrow, M.B.; Wyatt, R.J.; Scolari, F.; Mestecky, J.; Gharavi, A.G.; et al. The Pathophysiology of IgA Nephropathy. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2011, 22, 1795–1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caravaca-Fontán, F.; Gutiérrez, E.; Sevillano, Á.M.; Praga, M. Targeting Complement in IgA Nephropathy. Clin. Kidney J. 2023, 16, ii28–ii39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Rizk, D.V.; Perkovic, V.; Maes, B.; Kashihara, N.; Rovin, B.; Trimarchi, H.; Sprangers, B.; Meier, M.; Kollins, D.; et al. Results of a Randomized Double-Blind Placebo-Controlled Phase 2 Study Propose Iptacopan as an Alternative Complement Pathway Inhibitor for IgA Nephropathy. Kidney Int. 2024, 105, 189–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Broder, A.; Shao, D.; Kesarwani, V.; Boderman, B.; Aguilan, J.; Sidoli, S.; Suzuki, M.; Greally, J.M.; Saenger, Y.M.; et al. Urine Proteomics Link Complement Activation with Interstitial Fibrosis/Tubular Atrophy in Lupus Nephritis Patients. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2023, 63, 152263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, T.; Afonso, S.; Perie, L.; Heidenreich, K.; Wulf, S.; Krebs, C.F.; Zipfel, P.F.; Wiech, T. An Interdisciplinary Diagnostic Approach to Guide Therapy in C3 Glomerulopathy. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 826513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Person, F.; Petschull, T.; Wulf, S.; Buescheck, F.; Biniaminov, S.; Fehrle, W.; Oh, J.; Skerka, C.; Zipfel, P.F.; Wiech, T. In Situ Visualization of C3/C5 Convertases to Differentiate Complement Activation. Kidney Int. Rep. 2020, 5, 927–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Disease | Inhibitor | Pathway | Phase | NCT-Number |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Primary membranous nephropathy | Iptacopan | Alternative (factor B) | II | NCT04154787 |
| Pelecopan | Alternative (factor D) | II | NCT05162066 | |
| Narsoplimab | Lectin (MASP2) | II | NCT02682407 | |
| Pegcetacoplan | Central (C3) | II | NCT03453619 | |
| Gefurulimab | Terminal (C5) | I | NCT05314231 | |
| C3G | Iptacopan | Alternative (factor B) | II, III, OLE | NCT03832114, NCT04817618, NCT03955445 |
| NM8074 | Alternative (factor Bb) | Ib | NCT05647811 | |
| Pelecopan | Alternative (factor D) | II | NCT05162066 | |
| Danicopan | Alternative (factor D) | IIa, IIb | NCT03124368, NCT03369236, NCT03459443, NCT03723512 | |
| Narsoplimab | Lectin (MASP2) | II | NCT02682407 | |
| TP10 | Inhibition (scR1) | IIa | NCT02302755 | |
| Pegcetacoplan | Central (C3) | II, III, OLE | NCT04572854, NCT03453619, NCT05067127, NCT05809531 | |
| ARO-C3 | Central (C3) | I/II | NCT05083364 | |
| AMY-101 | Central (C3) | I | NCT03316521 | |
| KP104 | Inhibition (CFH/C5) | II | NCT05517980 | |
| Avacopan | Inflammation (C5aR) | II | NCT03301467 | |
| IC-MPGN | Iptacopan | Alternative (factor B) | III | NCT05755386 |
| Danicopan | Alternative (factor D) | IIa, IIb | NCT03124368, NCT03459443, NCT03723512, NCT03369236 | |
| Pegcetacoplan | Central (C3) | II, III, OLE | NCT04572854, NCT05067127, NCT05809531 | |
| Lupus Nephritis | Iptacopan | Alternative (factor B) | II | NCT05268289 |
| Vemircopan | Alternative (factor D) | II | NCT05097989 | |
| Narsoplimab | Lectin (MASP2) | II | NCT02682407 | |
| ANX009 | Classical (C1q) | I | NCT05780515 | |
| Pegcetacoplan | Central (C3) | II | NCT03453619 | |
| Gefurulimab | Terminal (C5) | I | NCT05314231 | |
| Ravulizumab | Terminal (C5) | II | NCT04564339 | |
| IgA Nephropathy | IONIS-FB-LRx | Alternative (factor B) | II, III | NCT04014335, NCT05797610 |
| Iptacopan | Alternative (factor B) | II, III | NCT03373461, NCT04557462, NCT04578834 | |
| Vemircopan | Alternative (factor D) | II | NCT05097989 | |
| Pelecopan | Alternative (factor D) | II | NCT05162066 | |
| Narsoplimab | Lectin (MASP2) | II, III | NCT02682407, NCT03608033 | |
| ARO-C3 | Central (C3) | I | NCT05083364 | |
| KP104 | Inhibition (CFH/C5) | II | NCT05517980 | |
| Ravulizumab | Terminal (C5) | II | NCT04564339 | |
| Avacopan | Inflammation (C5aR) | I | NCT06004947 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nell, D.; Wolf, R.; Podgorny, P.M.; Kuschnereit, T.; Kuschnereit, R.; Dabers, T.; Stracke, S.; Schmidt, T. Complement Activation in Nephrotic Glomerular Diseases. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 455. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12020455
Nell D, Wolf R, Podgorny PM, Kuschnereit T, Kuschnereit R, Dabers T, Stracke S, Schmidt T. Complement Activation in Nephrotic Glomerular Diseases. Biomedicines. 2024; 12(2):455. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12020455
Chicago/Turabian StyleNell, Dominik, Robert Wolf, Przemyslaw Marek Podgorny, Tobias Kuschnereit, Rieke Kuschnereit, Thomas Dabers, Sylvia Stracke, and Tilman Schmidt. 2024. "Complement Activation in Nephrotic Glomerular Diseases" Biomedicines 12, no. 2: 455. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12020455
APA StyleNell, D., Wolf, R., Podgorny, P. M., Kuschnereit, T., Kuschnereit, R., Dabers, T., Stracke, S., & Schmidt, T. (2024). Complement Activation in Nephrotic Glomerular Diseases. Biomedicines, 12(2), 455. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12020455






