New Insights into Chemoresistance Mediated by Mdm2 Inhibitors: The Benefits of Targeted Therapy over Common Cytostatics
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents, Primers and Antibodies
2.2. Cell Lines
2.3. MTT Test, EC50
2.4. Transport Activity
2.5. qPCR Analysis
2.6. P-glycoprotein ATPase Assay
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
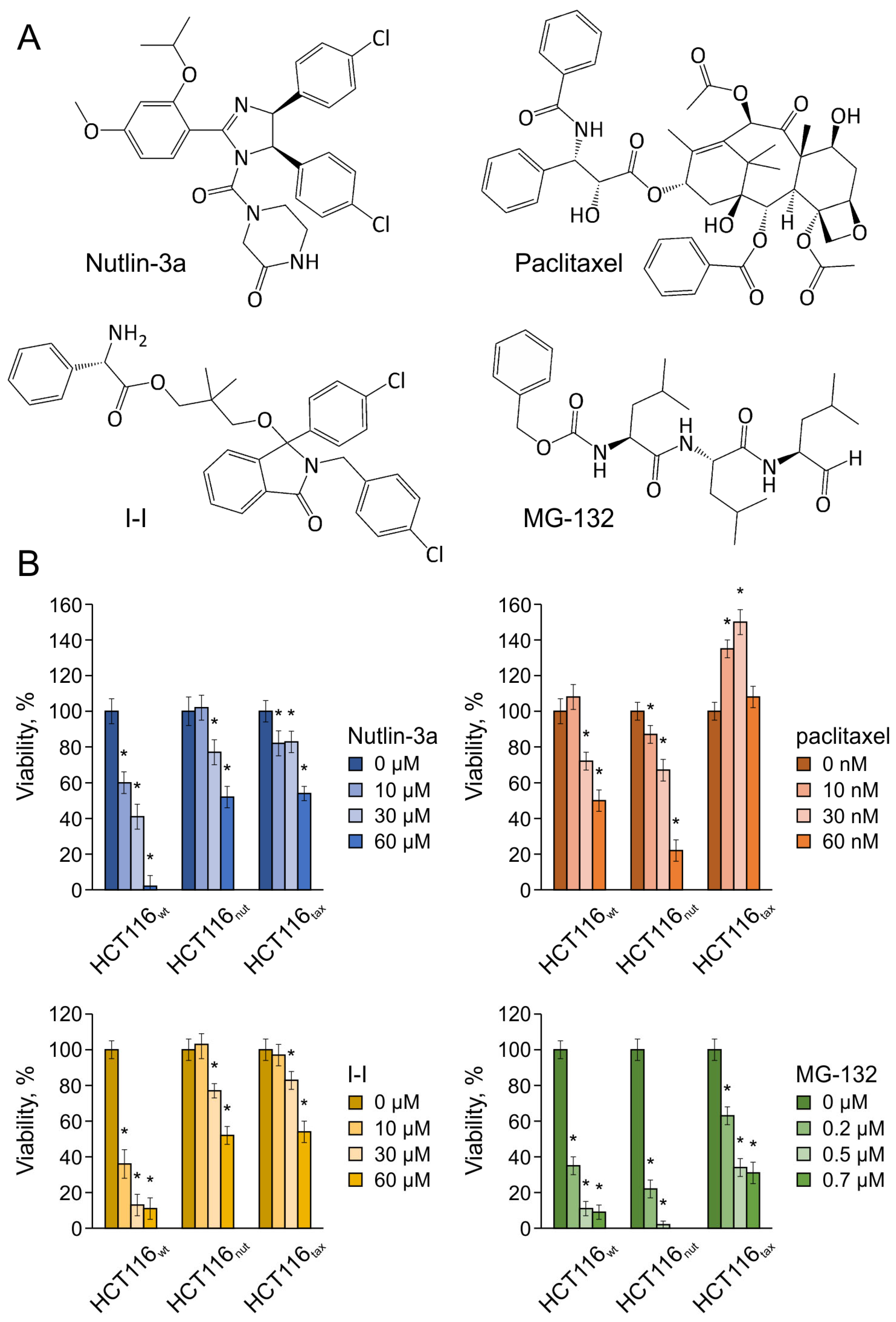
3.1. Tumor Cells Adapt to Nutlin-3a Significantly Worse Than to Paclitaxel
- HCT116nut—HCT116 resistant to Nutlin-3a at a concentration of 30 μM;
- HCT116tax—HCT116 resistant to paclitaxel at a concentration of 0.1 μM.
3.2. Nutlin-3a Sensitizes Cells to Drugs of Other Mechanisms, While Paclitaxel Provokes Multidrug Resistance
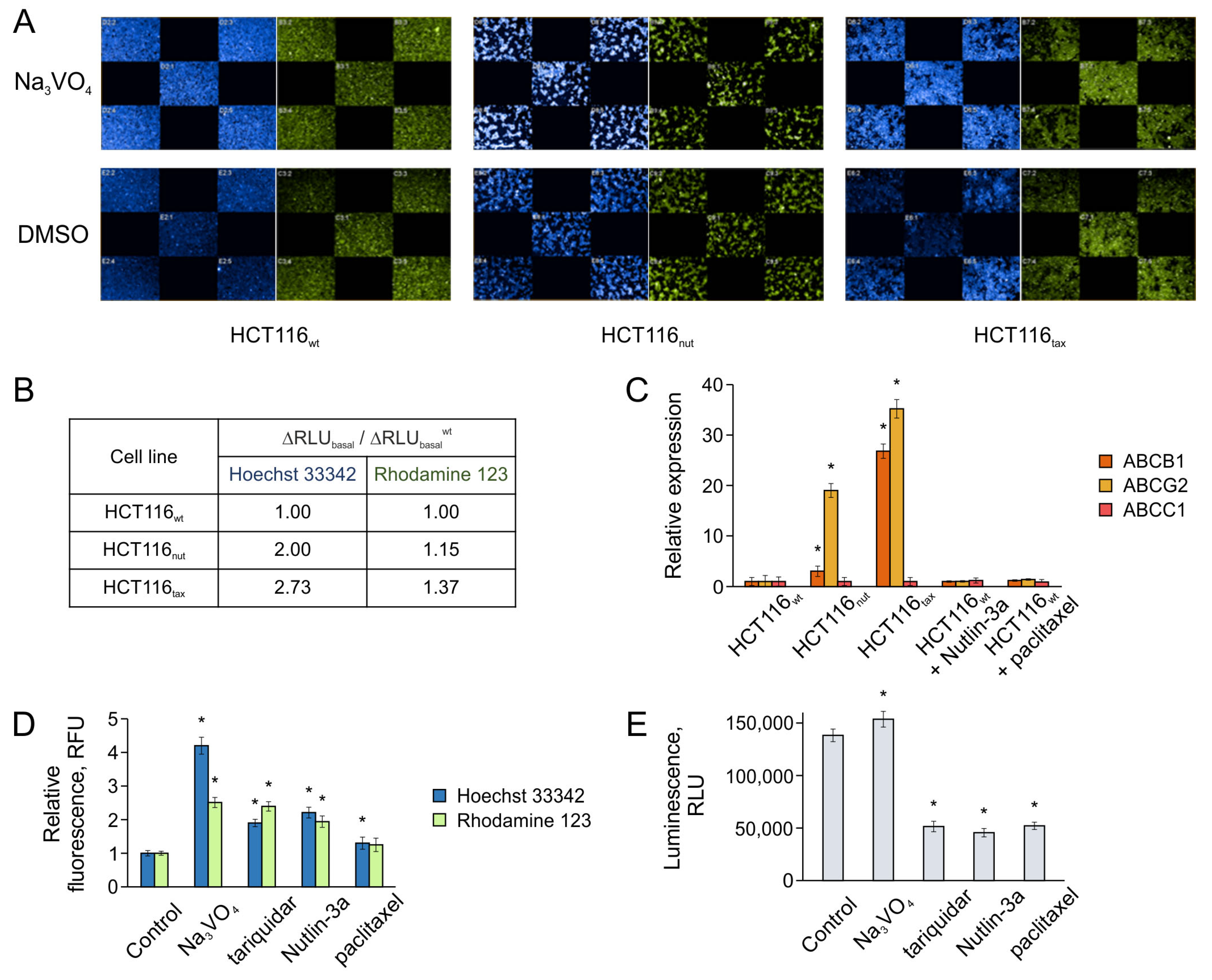
3.3. The Relationship between Adaptation to Nutlin-3a and ABC Transporter-Mediated Efflux Typical for Paclitaxel
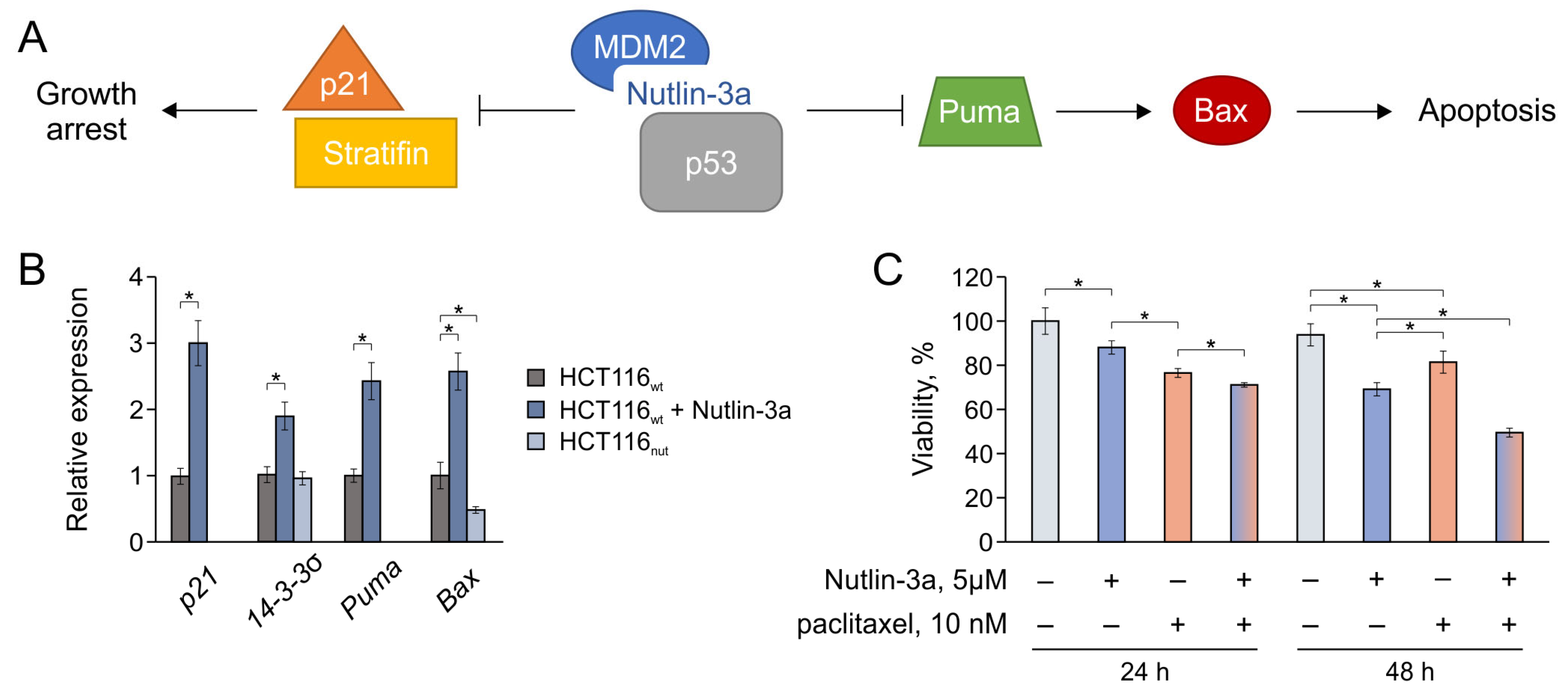
3.4. Nutlin-3a Provokes Changes in p53-Mediated Processes and Promotes the Apoptosis of Tumor Cells during Combined Therapy
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Correction Statement
References
- Konopleva, M.; Martinelli, G.; Daver, N.; Papayannidis, C.; Wei, A.; Higgins, B.; Ott, M.; Mascarenhas, J.; Andreeff, M. MDM2 inhibition: An important step forward in cancer therapy. Leukemia 2020, 34, 2858–2874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haronikova, L.; Bonczek, O.; Zatloukalova, P.; Kokas-Zavadil, F.; Kucerikova, M.; Coates, P.J.; Fahraeus, R.; Vojtesek, B. Resistance mechanisms to inhibitors of p53-MDM2 interactions in cancer therapy: Can we overcome them? Cell Mol. Biol. Lett. 2021, 26, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammond, W.A.; Swaika, A.; Mody, K. Pharmacologic resistance in colorectal cancer: A review. Ther. Adv. Med. Oncol. 2016, 8, 57–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berberich, A.; Kessler, T.; Thome, C.; Pusch, S.; Hielscher, T.; Sahm, F.; Oezen, I.; Schmitt, L.-M.; Ciprut, S.; Hucke, N.; et al. Targeting resistance against the MDM2 inhibitor RG7388 in glioblastoma cells by the MEK inhibitor trametinib. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 253–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drummond, C.J.; Esfandiari, A.; Liu, J.; Lu, X.; Hutton, C.; Jackson, J.; Bennaceur, K.; Xu, Q.; Makimanejavali, A.R.; Del Bello, F.; et al. TP53 mutant MDM2-amplified cell lines selected for resistance to MDM2-p53 binding antagonists retain sensitivity to ionizing radiation. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 46203–46218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapeau, E.A.; Gembarska, A.; Durand, E.Y.; Mandon, E.; Estadieu, C.; Romanet, V.; Wiesmann, M.; Tiedt, R.; Lehar, J.; de Weck, A.; et al. Resistance mechanisms to TP53-MDM2 inhibition identified by in vivo piggyBac transposon mutagenesis screen in an Arf(-/-) mouse model. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 3151–3156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skalniak, L.; Kocik, J.; Polak, J.; Skalniak, A.; Rak, M.; Wolnicka-Glubisz, A.; Holak, T.A. Prolonged idasanutlin (RG7388) treatment leads to the generation of p53-mutated cells. Cancers 2018, 10, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffman-Luca, C.G.; Yang, C.Y.; Lu, J.; Ziazadeh, D.; McEachern, D.; Debussche, L.; Wang, S. Significant differences in the development of acquired resistance to the MDM2 inhibitor SAR405838 between in vitro and in vivo drug treatment. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0128807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aziz, M.H.; Shen, H.; Maki, C.G. Acquisition of p53 mutations in response to the non-genotoxic p53 activator Nutlin-3. Oncogene 2011, 30, 4678–4686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michaelis, M.; Rothweiler, F.; Barth, S.; Cinatl, J.; van Rikxoort, M.; Loschmann, N.; Voges, Y.; Breitling, R.; von Deimling, A.; Rodel, F.; et al. Adaptation of cancer cells from different entities to the MDM2 inhibitor nutlin-3 results in the emergence of p53-mutated multi-drug-resistant cancer cells. Cell Death Dis. 2011, 2, e243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, R.J.; Bjorklund, C.C.; Baladandayuthapani, V.; Kuhn, D.J.; Orlowski, R.Z. Drug resistance to inhibitors of the human double minute-2 E3 ligase is mediated by point mutations of p53, but can be overcome with the p53 targeting agent RITA. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2012, 11, 2243–2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grigoreva, T.A.; Novikova, D.S.; Petukhov, A.V.; Gureev, M.A.; Garabadzhiu, A.V.; Melino, G.; Barlev, N.A.; Tribulovich, V.G. Proapoptotic modification of substituted isoindolinones as MDM2-p53 inhibitors. Bioorg Med. Chem. Lett. 2017, 27, 5197–5202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grigoreva, T.; Sagaidak, A.; Vorona, S.; Novikova, D.; Tribulovich, V. The ATP mimetic attack on the nucleotide-binding domain to overcome ABC transporter mediated chemoresistance. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2022, 13, 1848–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nanayakkara, A.K.; Follit, C.A.; Chen, G.; Williams, N.S.; Vogel, P.D.; Wise, J.G. Targeted inhibitors of P-glycoprotein increase chemotherapeutic-induced mortality of multidrug resistant tumor cells. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grigoreva, T.; Romanova, A.; Sagaidak, A.; Vorona, S.; Novikova, D.; Tribulovich, V. Mdm2 inhibitors as a platform for the design of P-glycoprotein inhibitors. Bioorg Med. Chem. Lett. 2020, 30, 127424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gureev, M.; Novikova, D.; Grigoreva, T.; Vorona, S.; Garabadzhiu, A.; Tribulovich, V. Simulation of MDM2 N-terminal domain conformational lability in the presence of imidazoline based inhibitors of MDM2-p53 protein-protein interaction. J. Comput. Aided Mol. Des. 2020, 34, 55–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.H.; Wang, H.S.; Soong, Y.K. Paclitaxel-induced cell death: Where the cell cycle and apoptosis come together. Cancer 2000, 88, 2619–2628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.; Verdier-Pinard, P.; Fernandez-Fuentes, N.; Burd, B.; Angeletti, R.; Fiser, A.; Horwitz, S.B.; Orr, G.A. Insights into the mechanism of microtubule stabilization by Taxol. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 10166–10173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, H.; Li, L.; Garcia Carcedo, I.; Xu, Z.P.; Monteiro, M.; Gu, W. Synergistic inhibition of colon cancer cell growth with nanoemulsion-loaded paclitaxel and PI3K/mTOR dual inhibitor BEZ235 through apoptosis. Int. J. Nanomed. 2016, 11, 1947–1958. [Google Scholar]
- Saiki, A.Y.; Caenepeel, S.; Cosgrove, E.; Su, C.; Boedigheimer, M.; Oliner, J.D. Identifying the determinants of response to MDM2 inhibition. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 7701–7712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grigoreva, T.; Sagaidak, A.; Romanova, A.; Novikova, D.; Garabadzhiu, A.; Tribulovich, V. Establishment of drug-resistant cell lines under the treatment with chemicals acting through different mechanisms. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2021, 344, 109510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.H.; He, Y.P.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, P.; Qin, H. Establishment and identification of the human multi-drug-resistant cholangiocarcinoma cell line QBC939/ADM. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2011, 38, 3075–3082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemcova-Furstova, V.; Kopperova, D.; Balusikova, K.; Ehrlichova, M.; Brynychova, V.; Vaclavikova, R.; Daniel, P.; Soucek, P.; Kovar, J. Characterization of acquired paclitaxel resistance of breast cancer cells and involvement of ABC transporters. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2016, 310, 215–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hellweg, C.E.; Shinde, V.; Srinivasan, S.P.; Henry, M.; Rotshteyn, T.; Baumstark-Khan, C.; Schmitz, C.; Feles, S.; Spitta, L.F.; Hemmersbach, R.; et al. Radiation response of murine embryonic stem cells. Cells 2020, 9, 1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fox, E.; Bates, S.E. Tariquidar (XR9576): A P-glycoprotein drug efflux pump inhibitor. Expert. Rev. Anticancer. Ther. 2007, 7, 447–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pessoa, J.C.; Etcheverry, S.; Gambino, D. Vanadium compounds in medicine. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2015, 301, 24–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novikova, D.S.; Grigoreva, T.A.; Ivanov, G.S.; Melino, G.; Barlev, N.A.; Tribulovich, V.G. Activating effect of 3-benzylidene oxindoles on AMPK: From computer simulation to high-content screening. ChemMedChem 2020, 15, 2521–2529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosmann, T. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: Application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J. Immunol. Methods 1983, 65, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bukowski, K.; Kciuk, M.; Kontek, R. Mechanisms of multidrug resistance in cancer chemotherapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grigoreva, T.A.; Novikova, D.S.; Gureev, M.A.; Garabadzhiu, A.V.; Tribulovich, V.G. Amino acids as chiral derivatizing agents for antiproliferative substituted N-benzyl isoindolinones. Chirality 2018, 30, 785–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.H.; Goldberg, A.L. Proteasome inhibitors: Valuable new tools for cell biologists. Trends Cell Biol. 1998, 8, 397–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besse, A.; Besse, L.; Kraus, M.; Mendez-Lopez, M.; Bader, J.; Xin, B.T.; de Bruin, G.; Maurits, E.; Overkleeft, H.S.; Driessen, C. Proteasome inhibition in multiple myeloma: Head-to-head comparison of currently available proteasome inhibitors. Cell Chem. Biol. 2019, 26, 340–351 e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Podolski-Renić, A.; Andelković, T.; Banković, J.; Tanić, N.; Ruždijić, S.; Pešić, M. The role of paclitaxel in the development and treatment of multidrug resistant cancer cell lines. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2011, 65, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doganlar, O.; Doganlar, Z.B.; Erdogan, S.; Delen, E. Antineoplastic multi-drug chemotherapy to sensitize tumors triggers multi-drug resistance and inhibits efficiency of maintenance treatment inglioblastoma cells. EXCLI J. 2023, 22, 35–52. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- El-Awady, R.; Saleh, E.; Hashim, A.; Soliman, N.; Dallah, A.; Elrasheed, A.; Elakraa, G. The role of eukaryotic and prokaryotic ABC transporter family in failure of chemotherapy. Front. Pharmacol. 2016, 7, 535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holohan, C.; van Schaeybroeck, S.; Longley, D.B.; Johnston, P.G. Cancer drug resistance: An evolving paradigm. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2013, 13, 714–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Chen, X.Y.; Dong, X.D.; Wang, J.Q.; Feng, W.; Teng, Q.X.; Cui, Q.; Li, J.; Li, X.Q.; Chen, Z.S. NVP-CGM097, an HDM2 inhibitor, antagonizes ATP-binding cassette subfamily B member 1-mediated drug resistance. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donnenberg, V.S.; Meyer, E.M.; Donnenberg, A.D. Measurement of multiple drug resistance transporter activity in putative cancer stem/progenitor cells. Methods Mol. Biol. 2009, 568, 261–279. [Google Scholar]
- Candeil, L.; Gourdier, I.; Peyron, D.; Vezzio, N.; Copois, V.; Bibeau, F.; Orsetti, B.; Scheffer, G.L.; Ychou, M.; Khan, Q.A.; et al. ABCG2 overexpression in colon cancer cells resistant to SN38 and in irinotecan-treated metastases. Int. J. Cancer 2004, 109, 848–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grigoreva, T.; Sagaidak, A.; Novikova, D.; Tribulovich, V. Implication of ABC transporters in non-proliferative diseases. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2022, 935, 175327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuy, H.D.; Shiomi, H.; Mukaisho, K.I.; Naka, S.; Shimizu, T.; Sonoda, H.; Mekata, E.; Endo, Y.; Kurumi, Y.; Sugihara, H.; et al. ABCG2 expression in colorectal adenocarcinomas may predict resistance to irinotecan. Oncol. Lett. 2016, 12, 27522760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, D.; Qin, S.; Mu, Y.; Zhong, M. The role of MRP1 in the multidrug resistance of colorectal cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 13, 2471–2476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grigoreva, T.; Vorona, S.; Novikova, D.; Tribulovich, V. Analysis of P-glycoprotein transport cycle reveals a new way to identify efflux inhibitors. ACS Omega 2022, 47, 42835–42844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natarajan, K.; Xie, Y.; Baer, M.R.; Ross, D.D. Role of breast cancer resistance protein (BCRP/ABCG2) in cancer drug resistance. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2012, 83, 1084–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, W.; Xiang, D.; Wang, T.; Zhang, Y.; Pham, C.V.; Zhou, S.; Jiang, G.; Hou, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Han, Y.; et al. The inhibition of ABCB1/MDR1 or ABCG2/BCRP enables doxorubicin to eliminate liver cancer stem cells. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 10791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duz, M.B.; Karatas, O.F. Differential expression of ABCB1, ABCG2, and KLF4 as putative indicators for paclitaxel resistance in human epithelial type 2 cells. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2021, 48, 1393–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCorkle, J.R.; Gorski, J.W.; Liu, J.; Riggs, M.B.; McDowell, A.B.; Lin, N.; Wang, C.; Ueland, F.R.; Kolesar, J.M. Lapatinib and poziotinib overcome ABCB1-mediated paclitaxel resistance in ovarian cancer. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0254205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francois, L.N.; Gorczyca, L.; Du, J.; Bircsak, K.M.; Yen, E.; Wen, X.; Tu, M.J.; Yu, A.M.; Illsley, N.P.; Zamudio, S.; et al. Down-regulation of the placental BCRP/ABCG2 transporter in response to hypoxia signaling. Placenta 2017, 51, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Z.; Shi, X.; Qiu, Y.; Jia, T.; Yuan, X.; Zou, Y.; Liu, C.; Yu, H.; Yuan, Y.; He, X.; et al. Reversal of P-gp-mediated multidrug resistance in colon cancer by cinobufagin. Oncol. Rep. 2017, 37, 1815–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambudkar, S.V.; Dey, S.; Hrycyna, C.A.; Ramachandra, M.; Pastan, I.; Gottesman, M.M. Biochemical, cellular, and pharmacological aspects of the multidrug transporter. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 1999, 39, 361–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, M.; Bakos, E.; Welker, E.; Varadi, A.; Germann, U.A.; Gottesman, M.M.; Morse, B.S.; Roninson, I.B.; Sarkadi, B. Altered drug-stimulated ATPase activity in mutants of the human multidrug resistance protein. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 1877–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loo, T.W.; Clarke, D.M. Tariquidar inhibits P-glycoprotein drug efflux but activates ATPase activity by blocking transition to an open conformation. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2014, 92, 558–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harper, J.W.; Adami, G.R.; Wei, N.; Keyomarsi, K.; Elledge, S.J. The P21 Cdk-interacting protein Cip1 is a potent inhibitor of G1 cyclin-dependent kinases. Cell 1993, 75, 805–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.Y.; Jee, H.J.; Um, J.H.; Kim, Y.M.; Bae, S.S.; Yun, J. Cooperation between p21 and Akt is required for p53-dependent cellular senescence. Aging Cell 2017, 16, 1094–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M. The role of P53 up-regulated modulator of apoptosis (PUMA) in ovarian development, cardiovascular and neurodegenerative diseases. Apoptosis 2021, 26, 235–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bloch, N.B.; Wales, T.E.; Prew, M.S.; Levy, H.R.; Engen, J.R.; Walensky, L.D. The conformational stability of pro-apoptotic BAX is dictated by discrete residues of the protein core. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, J.M.A.; Ohlsson, G.; Rank, F.E.; Celis, J.E. Down-regulation of the tumor suppressor protein 14-3-3 sigma is a sporadic event in cancer of the breast. Mol. Cell Proteom. 2005, 4, 555–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Gene | Protein | Forward | Reverse |
|---|---|---|---|
| ABCB1 | MDR1 | GGGAGCTTAACACCCGACTTA | GCCAAAATCACAAGGGTTAGCTT |
| ABCC1 | MRP1 | TCAGGAGCACACGAAAGTCC | AAGAAGCTCATGGGTGACCG |
| ABCG2 | BCRP | AAGCCACAGAGATCATAGAGCC | TCTTCTTCTCACCCCCGGAA |
| P21 | P21 | ACTGTCTTGTACCCTTGTGCC | AAATCTGTCATGCTGGTCTGC |
| Puma | Puma | GCGAGACTGTGGCCTTGTGT | CGTTCCAGGGTCCACAAAGT |
| Noxa | Noxa | GCTGGAAGTCGAGTGTGCTA | TTCCTGAGCAGAAGAGTTTGG |
| Bax | Bax | CCGAGAGGTCTTTTTCCGAG | CCAGCCCATGATGGTTCTGAT |
| 14-3-3σ | Stratifin | CATCATTGACTCAGCCCGGT | AGTGTCAGGTTGTCTCGCAG |
| GAPDH | GAPDH | GGGAAGGTGAAGGTCGGAGT | TTGAGGTCAATGAAGGGGTCA |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Grigoreva, T.; Sagaidak, A.; Novikova, D.; Tribulovich, V. New Insights into Chemoresistance Mediated by Mdm2 Inhibitors: The Benefits of Targeted Therapy over Common Cytostatics. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 547. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12030547
Grigoreva T, Sagaidak A, Novikova D, Tribulovich V. New Insights into Chemoresistance Mediated by Mdm2 Inhibitors: The Benefits of Targeted Therapy over Common Cytostatics. Biomedicines. 2024; 12(3):547. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12030547
Chicago/Turabian StyleGrigoreva, Tatyana, Aleksandra Sagaidak, Daria Novikova, and Vyacheslav Tribulovich. 2024. "New Insights into Chemoresistance Mediated by Mdm2 Inhibitors: The Benefits of Targeted Therapy over Common Cytostatics" Biomedicines 12, no. 3: 547. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12030547
APA StyleGrigoreva, T., Sagaidak, A., Novikova, D., & Tribulovich, V. (2024). New Insights into Chemoresistance Mediated by Mdm2 Inhibitors: The Benefits of Targeted Therapy over Common Cytostatics. Biomedicines, 12(3), 547. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12030547





