Pleiotropic Action of TGF-Beta in Physiological and Pathological Liver Conditions
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Activin stimulates the secretion of FSH by the pituitary gland; inhibin inhibits the secretion of FSH;
- Activin stimulates immune response processes (increased gamma interferon and activation of monocyte migration); inhibin inhibits immune processes (decreased gamma interferon);
- Activin stimulates erythropoiesis, inhibin inhibits it;
- In addition, activin mediates the stimulation of the dorsal mesoderm in embryonic development [6].
2. Structure, Synthesis, Receptors and Signaling Pathways
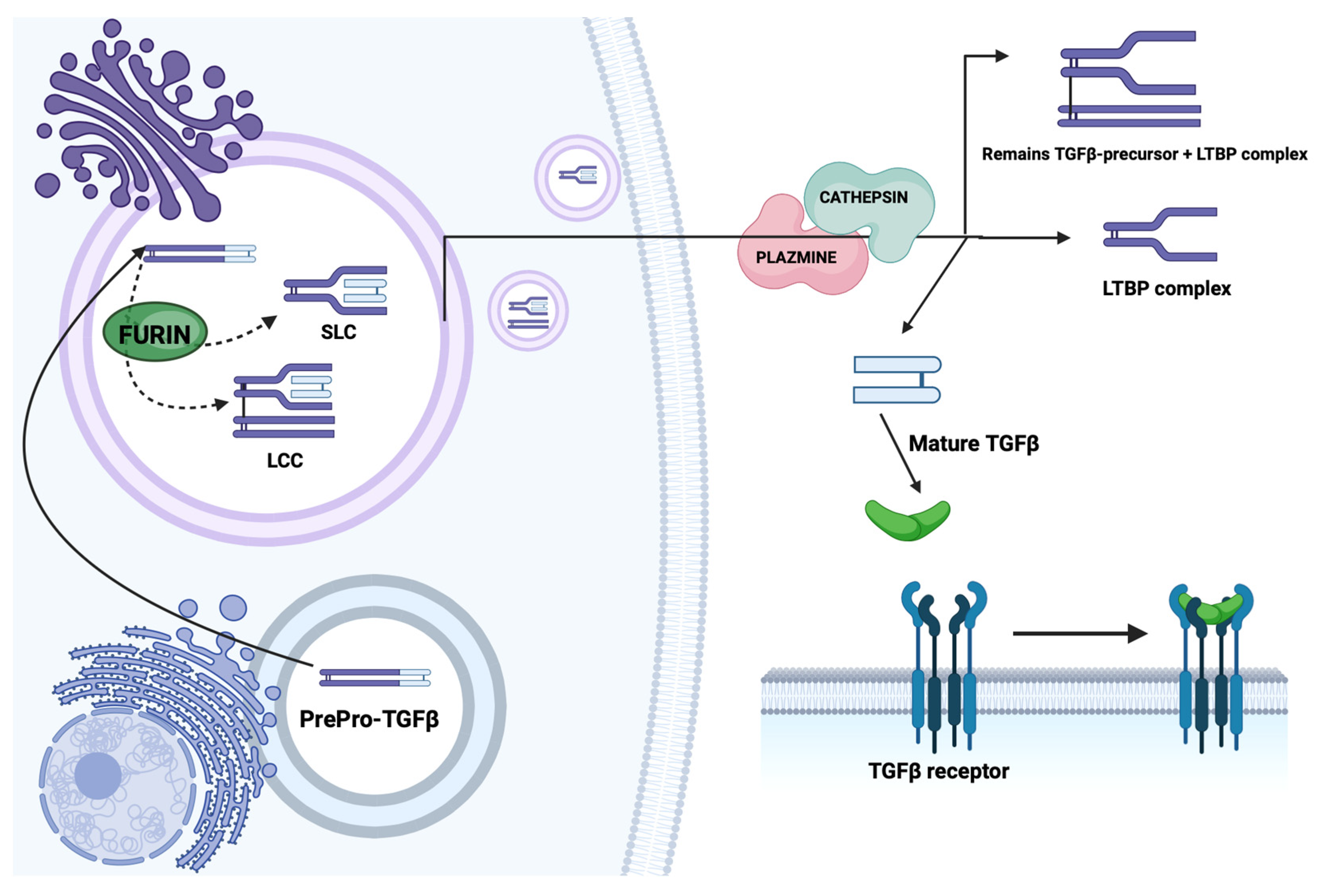
2.1. Structure and Synthesis of TGF-β
2.2. Receptors and Signaling Pathways
2.3. Alternate Pathways of Action
3. Biological Significance of TGF-β
3.1. Biological Activity
3.2. Pathogenic Effects of TGF-β
3.3. TGF-β and Apoptosis
4. The Importance of TGF-β in the Liver
4.1. Production of TGF-β by the Liver
4.2. TGF-β Involvement in Intercellular Signaling in the Liver
4.3. TGF-β Inhibition of Hepatocyte Growth
4.4. TGF-β Effect on Stellate Cells
5. Liver Fibrosis
6. Autoimmune Hepatitis
6.1. The Liver as an Immunologically Privileged Organ
6.2. Autoimmune Hepatitis
6.3. Genetic Background of AIH
6.4. The Importance of Regulatory T Cells
7. Chronic Hepatitis C
7.1. Hepatitis C Virus
7.2. The TGF-β/SMAD Signaling Pathway in HCV Infection
7.3. The Effect of HCV Infection on TGF-β Isoform Levels
8. Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
8.1. Essence of the Disease
8.2. Plasma and Serum TGF-β Levels
8.3. Molecular Background of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
9. Summary
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AAH | Adult autoimmune hepatitis |
| AG | Golgi apparatus |
| AIH | Autoimmune hepatitis |
| BMP | Bone morphogenetic protein |
| BMP-1, -2, and -3 | Isoforms of bone morphogenetic protein |
| co-Smad | Common partner Smad |
| DPP | Decapentaplegic gene |
| ECM | Extracellular matrix |
| EGF | Epidermal growth factor |
| FGF | Fibroblast growth factor |
| FSH | Follicle-stimulating hormone |
| HBV | Hepatitis B |
| HCC | Hepatocellular carcinoma |
| HGF | Hepatic growth factor |
| HLA | Human leukocyte antigen |
| I-Smads | Inhibitors of Smad |
| IFN-γ | Interferon gamma |
| IL-1 | Interleukin 1 |
| LAP | Latency-associated peptide |
| LLC | Large latent complex |
| LTBP | Latent TGF-binding protein |
| LTBP-1D | Variety of latent transforming growth factor-binding protein |
| MMP-1 | Matrix metalloproteinases 1 |
| NAFLD | Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease |
| NGF | Nerve growth factor |
| PAF | Platelet-activating factor |
| PAH | Pediatric autoimmune hepatitis |
| PDGF | Platelet derived growing factor |
| PIIINP | N-terminal propeptide of procollagen type III |
| R-Smad | Receptor-activated Smads |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| SARA | Smad anchor for receptor activation |
| Shh | Sonic Hedgehog protein |
| SLC | Small latent complex |
| SNP | Single nucleotide polymorphism |
| sTGF-R | Soluble receptor |
| TGF-1, -2, and -3 | Isoforms of transforming growth factor β |
| TGF-β | Transforming growth factor β |
| TIMP-1 | Metallopeptidase inhibitor 1 |
| TNF-α | Transforming growth factor α |
| TβRI, II, III | Receptors for transforming growth factor β |
| WZW | Hepatitis |
| α-SMA | Spinal muscular atrophy |
References
- Blokzijl, A.; Dahlqvist, C.; Reissmann, E.; Falk, A.; Moliner, A.; Lendahl, U.; Ibáñez, C.F. Cross-talk between the Notch and TGF-beta signaling pathways mediated by interaction of the Notch intracellular domain with Smad3. J. Cell Biol. 2003, 163, 723–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wells, R.G.; Yankelev, H.; Lin, H.Y.; Lodish, H.F. Biosynthesis of the type I and type II TGF-beta receptors. Implications for complex formation. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 11444–11451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brodin, G. Smad7 in TGF-β Signalling. Ph.D. Thesis, Acta Universitatis Upsaliensis, Uppsala, Sweden, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Bissell, D.M.; Roulot, D.; George, J. Transforming growth factor beta and the liver. Hepatology 2001, 34, 859–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flisiak, R.; Pytel-Krolczuk, B.; Prokopowicz, D. Circulating transforming growth factor beta(1) as an indicator of hepatic function impairment in liver cirrhosis. Cytokine 2000, 12, 677–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piek, E.; Westermark, U.; Kastemar, M.; Heldin, C.H.; van Zoelen, E.J.; Nistér, M.; Ten Dijke, P. Expression of transforming-growth-factor (TGF)-beta receptors and Smad proteins in glioblastoma cell lines with distinct responses to TGF-beta1. Int. J. Cancer 1999, 80, 756–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyazono, K.; Kusanagi, K.; Inoue, H. Divergence and convergence of TGF-beta/BMP signaling. J. Cell Physiol. 2001, 187, 265–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szczesny, G.; Deszczyński, J. The bone union process: Pathophysiology and clinical issues. Factors conditioning the occurrence of bone union on the molecular level. Ortop. Traumatol. Rehabil. 2000, 2, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Piotrowska, E.; Piotrowski, J.; Grzeszczak, W. Transforming growth factors and their role in chronic liver diseases. Wiad. Lek. 1993, 46, 378–381. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Monsivais, D.; Matzuk, M.M.; Pangas, S.A. The TGF-β Family in the Reproductive Tract. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2017, 9, a022251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gressner, A.M.; Weiskirchen, R.; Breitkopf, K.; Dooley, S. Roles of TGF-beta in hepatic fibrosis. Front. Biosci. 2002, 7, d793–d807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fajardo, L.F.; Prionas, S.D.; Kwan, H.H.; Kowalski, J.; Allison, A.C. Transforming growth factor beta1 induces angiogenesis in vivo with a threshold pattern. Lab. Investig. 1996, 74, 600–608. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sanderson, N.; Factor, V.; Nagy, P.; Kopp, J.; Kondaiah, P.; Wakefield, L.; Roberts, A.B.; Sporn, M.B.; Thorgeirsson, S.S. Hepatic expression of mature transforming growth factor beta 1 in transgenic mice results in multiple tissue lesions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 2572–2576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wrana, J.L. Transforming growth factor-beta signaling and cirrhosis. Hepatology 1999, 29, 1909–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sankar, S.; Mahooti-Brooks, N.; Centrella, M.; McCarthy, T.L.; Madri, J.A. Expression of transforming growth factor type III receptor in vascular endothelial cells increases their responsiveness to transforming growth factor beta 2. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 13567–13572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Centrella, M.; Ji, C.; McCarthy, T.L. Control of TGF-beta receptor expression in bone. Front. Biosci. 1998, 3, d113–d124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Fonsatti, E.; Del Vecchio, L.; Altomonte, M.; Sigalotti, L.; Nicotra, M.R.; Coral, S.; Natali, P.G.; Maio, M. Endoglin: An accessory component of the TGF-beta-binding receptor-complex with diagnostic, prognostic, and bioimmunotherapeutic potential in human malignancies. J. Cell Physiol. 2001, 188, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wells, R.G.; Fibrogenesis, V. TGF-beta signaling pathways. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2000, 279, G845–G850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morikawa, M.; Derynck, R.; Miyazono, K. TGF-β and the TGF-β Family: Context-Dependent Roles in Cell and Tissue Physiology. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2016, 8, a021873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Yang, J.; Deng, S.; Xu, H.; Wu, D.; Zeng, Q.; Wang, S.; Hu, T.; Wu, F.; Zhou, H. TGF-β signaling in the tumor metabolic microenvironment and targeted therapies. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2022, 15, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, J.; Roulot, D.; Koteliansky, V.E.; Bissell, D.M. In vivo inhibition of rat stellate cell activation by soluble transforming growth factor beta type II receptor: A potential new therapy for hepatic fibrosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 12719–12724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Liu, C.; Zhou, D.; Zhang, L. TGF-β/SMAD Pathway and Its Regulation in Hepatic Fibrosis. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2016, 64, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimura, M.; Moteki, H.; Ogihara, M. Role of Hepatocyte Growth Regulators in Liver Regeneration. Cells 2023, 12, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michalopoulos, G.K. Liver regeneration. J. Cell Physiol. 2007, 213, 286–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kmieć, Z. The role of hepatic stellate cells in the regulation of liver functions. II. Cooperation with other cell types in the development of liver fibrosis. Postęp. Biol. Komórki 2003, 29, 61–74. [Google Scholar]
- Kanzler, S.; Lohse, A.W.; Keil, A.; Henninger, J.; Dienes, H.P.; Schirmacher, P.; Rose-John, S.; Büschenfelde, K.H.M.Z.; Blessing, M. TGF-β1 in liver fibrosis: An inducible transgenic mouse model to study liver fibrogenesis. Am. J. Physiol.-Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 1999, 276, G1059–G1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiegs, G.; Lohse, A.W. Immune tolerance: What is unique about the liver. J. Autoimmun. 2010, 34, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prytz, H.; Holst-Christensen, J.; Korner, B.; Liehr, H. Portal venous and systemic endotoxaemia in patients without liver disease and systemic endotoxaemia in patients with cirrhosis. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 1976, 11, 857–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergani, D.; Mieli-Vergani, G. Aetiopathogenesis of autoimmune hepatitis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2008, 14, 3306–3312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorham, J.D. Transforming growth factor-beta1, Th1 responses, and autoimmune liver disease. Transfusion 2005, 45, 51s–59s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hahn, J.W.; Yang, H.R.; Moon, J.S.; Chang, J.Y.; Lee, K.; Kim, G.A.; Rahmati, M.; Koyanagi, A.; Smith, L.; Kim, M.S.; et al. Global incidence and prevalence of autoimmune hepatitis, 1970–2022: A systematic review and meta-analysis. eClinicalMedicine 2023, 65, 102280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schramm, C.; Protschka, M.; Köhler, H.H.; Podlech, J.; Reddehase, M.J.; Schirmacher, P.; Galle, P.R.; Lohse, A.W.; Blessing, M. Impairment of TGF-beta signaling in T cells increases susceptibility to experimental autoimmune hepatitis in mice. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2003, 284, G525–G535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paladino, N.; Flores, A.C.; Fainboim, H.; Schroder, T.; Cuarterolo, M.; Lezama, C.; Ballerga, E.G.; Levi, D.; Tanno, H.; Costanzo, G.; et al. The most severe forms of type I autoimmune hepatitis are associated with genetically determined levels of TGF-beta1. Clin. Immunol. 2010, 134, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yousefi, A.; Zare Bidoki, A.; Shafioyoun, A.; Sadr, M.; Varzaneh, F.N.; Shabani, M.; Motamed, F.; Farahmand, F.; Khodadad, A.; Fallahi, G.; et al. Association of IL-10 and TGF-beta cytokine gene polymorphisms with autoimmune hepatitis. Clin. Res. Hepatol. Gastroenterol. 2019, 43, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Longhi, M.S.; Mieli-Vergani, G.; Vergani, D. Regulatory T cells in autoimmune hepatitis: An updated overview. J. Autoimmun. 2021, 119, 102619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maria, A.; English, K.A.; Gorham, J.D. Appropriate development of the liver Treg compartment is modulated by the microbiota and requires TGF-β and MyD88. J. Immunol. Res. 2014, 2014, 279736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basit, H.; Tyagi, I.; Koirala, J. Hepatitis C. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing LLC.: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Hartling, H.J.; Ballegaard, V.C.; Nielsen, N.S.; Gaardbo, J.C.; Nielsen, S.D. Immune regulation in chronic hepatitis C virus infection. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 51, 1387–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schon, H.T.; Weiskirchen, R. Immunomodulatory effects of transforming growth factor-β in the liver. Hepatobiliary Surg. Nutr. 2014, 3, 386–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, L.Y.S.; Gracie, N.P.; Gowripalan, A.; Howell, L.M.; Newsome, T.P. SMAD proteins: Mediators of diverse outcomes during infection. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 2022, 101, 151204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, L.L.; Li, J.R.; Li, H.; Tan, J.L.; Wang, M.X.; Liu, N.N.; Gao, R.M.; Yan, H.Y.; Wang, X.K.; Dong, B.; et al. TGF-β isoforms inhibit hepatitis C virus propagation in transforming growth factor beta/SMAD protein signalling pathway dependent and independent manners. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2021, 25, 3498–3510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotsiri, I.; Hadziyannis, E.; Georgiou, A.; Papageorgiou, M.V.; Vlachogiannakos, I.; Papatheodoridis, G. Changes in serum transforming growth factor-β1 levels in chronic hepatitis C patients under antiviral therapy. Ann. Gastroenterol. 2016, 29, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Elbanan, W.K.; Fathy, S.A.; Ibrahim, R.A.; Hegazy, M.G.A. Assessment of interleukin 17 and transforming growth factor-beta 1 in hepatitis C patients with disease progression. Trop. Biomed. 2020, 37, 1093–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powell, E.E.; Wong, V.W.; Rinella, M. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Lancet 2021, 397, 2212–2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satapathy, S.K.; Sanyal, A.J. Epidemiology and Natural History of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Semin. Liver Dis. 2015, 35, 221–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarantino, G.; Conca, P.; Riccio, A.; Tarantino, M.; Di Minno, M.N.; Chianese, D.; Pasanisi, F.; Contaldo, F.; Scopacasa, F.; Capone, D. Enhanced serum concentrations of transforming growth factor-beta1 in simple fatty liver: Is it really benign? J. Transl. Med. 2008, 6, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, Y.; Pan, X.; Luo, J.; Xiao, X.; Li, J.; Bestman, P.L.; Luo, M. Association of Inflammatory Cytokines with Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 880298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felicidade, I.; Bocchi, M.; Ramos, M.R.Z.; Carlos, L.O.; Wagner, N.R.F.; Campos, A.C.L.; Ribeiro, L.R.; Mantovani, M.S.; Watanabe, M.A.E.; Vitiello, G.A.F. Transforming growth factor beta 1 (TGFβ1) plasmatic levels and haplotype structures in obesity: A role for TGFβ1 in steatosis development. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2021, 48, 6401–6411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Y.; Tian, Q.; Zhao, X.; Wang, X. Serum transforming growth factor beta 3 predicts future development of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2015, 8, 4545–4550. [Google Scholar]
- Barretto, J.R.; Boa-Sorte, N.; Vinhaes, C.L.; Malta-Santos, H.; Rebouças-Silva, J.; Ramos, C.F.; Torres-Nascimento, M.A.S.; Borges, V.M.; Andrade, B.B. Heightened Plasma Levels of Transforming Growth Factor Beta (TGF-β) and Increased Degree of Systemic Biochemical Perturbation Characterizes Hepatic Steatosis in Overweight Pediatric Patients: A Cross-Sectional Study. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, T.; Yoshida, K.; Murata, M.; Suwa, K.; Tsuneyama, K.; Matsuzaki, K.; Naganuma, M. Smad3 Phospho-Isoform Signaling in Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 6270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gressner, O.A.; Weiskirchen, R.; Gressner, A.M. Evolving concepts of liver fibrogenesis provide new diagnostic and therapeutic options. Comp. Hepatol. 2007, 6, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heldin, C.H.; Miyazono, K.; Dijke, P.T. TGF-beta signalling from cell membrane to nucleus through SMAD proteins. Nature 1997, 390, 465–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, Q.; Chen, J.; Beezhold, K.J.; Castranova, V.; Shi, X.; Chen, F. JNK1 activation predicts the prognostic outcome of the human hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol. Cancer 2009, 8, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pahk, K.; Lee, S.G.; Joung, C.; Kim, E.O.; Kwon, H.W.; Kim, D.H.; Hwang, J.I.; Kim, S.; Kim, W.K. SP-1154, a novel synthetic TGF-β inhibitor, alleviates obesity and hepatic steatosis in high-fat diet-induced mice. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 145, 112441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Braczkowski, M.J.; Kufel, K.M.; Kulińska, J.; Czyż, D.Ł.; Dittmann, A.; Wiertelak, M.; Młodzik, M.S.; Braczkowski, R.; Soszyński, D. Pleiotropic Action of TGF-Beta in Physiological and Pathological Liver Conditions. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 925. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12040925
Braczkowski MJ, Kufel KM, Kulińska J, Czyż DŁ, Dittmann A, Wiertelak M, Młodzik MS, Braczkowski R, Soszyński D. Pleiotropic Action of TGF-Beta in Physiological and Pathological Liver Conditions. Biomedicines. 2024; 12(4):925. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12040925
Chicago/Turabian StyleBraczkowski, Michał Jakub, Klaudia Maria Kufel, Julia Kulińska, Daniel Łukasz Czyż, Aleksander Dittmann, Michał Wiertelak, Marcin Sławomir Młodzik, Ryszard Braczkowski, and Dariusz Soszyński. 2024. "Pleiotropic Action of TGF-Beta in Physiological and Pathological Liver Conditions" Biomedicines 12, no. 4: 925. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12040925
APA StyleBraczkowski, M. J., Kufel, K. M., Kulińska, J., Czyż, D. Ł., Dittmann, A., Wiertelak, M., Młodzik, M. S., Braczkowski, R., & Soszyński, D. (2024). Pleiotropic Action of TGF-Beta in Physiological and Pathological Liver Conditions. Biomedicines, 12(4), 925. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12040925







