Zinc Iodide Dimethyl Sulfoxide Reduces Collagen Deposition by Increased Matrix Metalloproteinase-2 Expression and Activity in Lung Fibroblasts
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cells
2.2. Cell Treatment
2.3. MMP-ELISA
2.4. Zymography
2.5. Collagen Type I and Fibronectin Deposition by Cell-Based ELISA
2.6. Soluble Collagen
2.7. Western Blotting
2.8. Statistics
3. Results
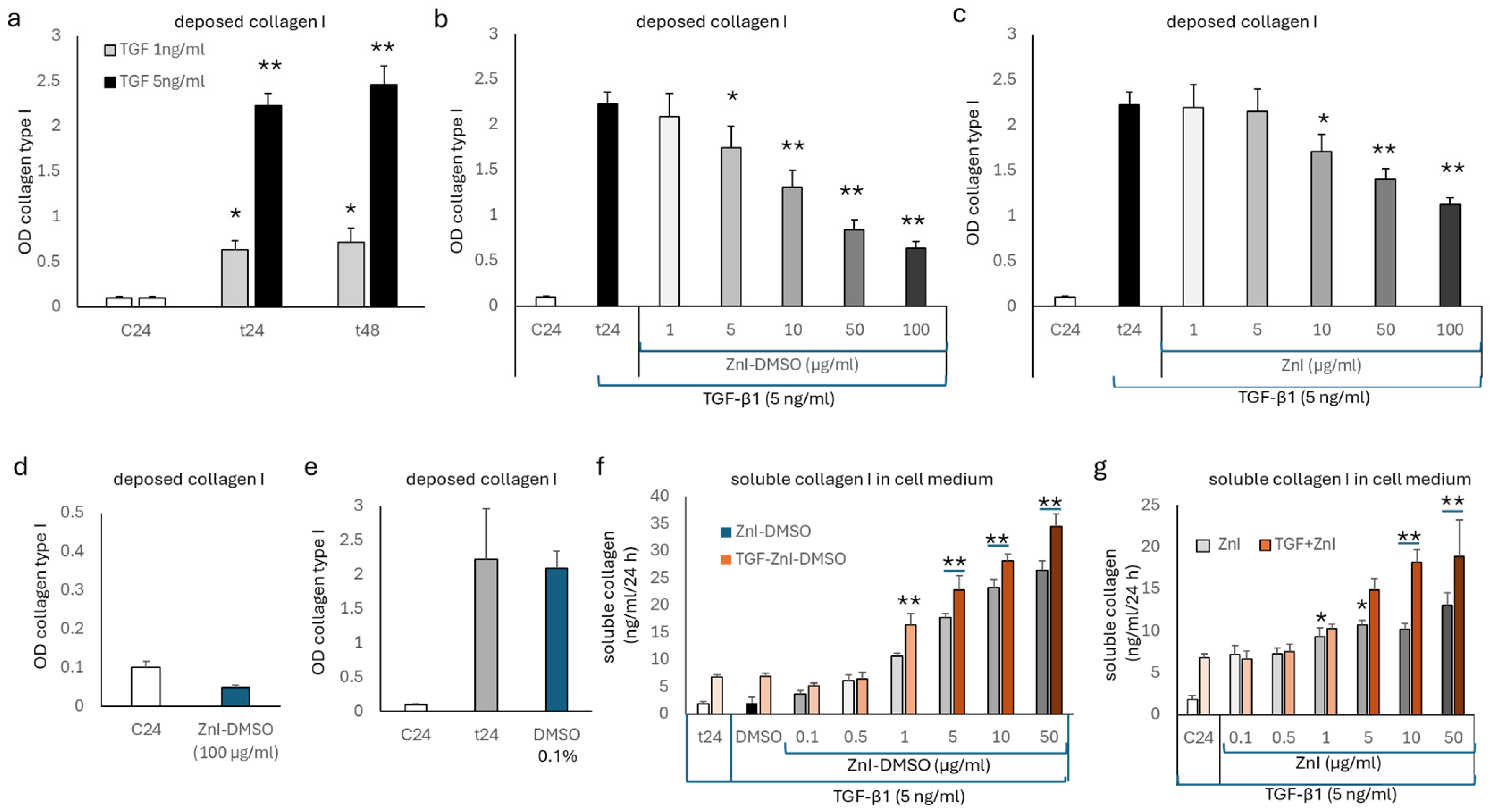
3.1. TGF-β1 Deposition of Collagen Type I, but Not Fibronectin, Is Reduced by Zinc Supplementation
3.2. Gelatinase Activity Is Up-Regulated by Zinc Supplementation and Regulates the Formation of Soluble Collagen
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DMSO | dimethyl sulfoxide |
| ECM | extracellular matrix |
| ELISA | enzyme-linked immuno-sorbent assay |
| GAPDH | glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase |
| MMP | matrix metalloproteinase |
| TGF-β1 | transforming growth factor β1/tumor growth factor β1 |
| ZnI | zinc iodide |
References
- Cheng, P.P.; Yu, F.; Chen, S.J.; Feng, X.; Jia, Z.H.; Hu, S.H.; Cui, X.L.; Zhou, Y.Y.; Niu, Q.; Liang, L.M.; et al. PM2.5 exposure-induced senescence-associated secretory phenotype in airway smooth muscle cells contributes to airway remodeling. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 347, 123674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mostaço-Guidolin, L.B.; Osei, E.T.; Ullah, J.; Hajimohammadi, S.; Fouadi, M.; Li, X.; Li, V.; Shaheen, F.; Yang, C.X.; Chu, F.; et al. Defective Fibrillar Collagen Organization by Fibroblasts Contributes to Airway Remodeling in Asthma. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2019, 200, 431–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, Y.Y.; Hu, W.P.; Zuo, Y.H.; Wang, X.R.; Zhang, J. Altered serum levels of type I collagen turnover indicators accompanied by IL-6 and IL-8 release in stable COPD. Int. J. Chronic Obstr. Pulm. Dis. 2019, 14, 163–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Y.; Dong, W.; Jackson, J.; Ho, T.C.; Le Saux, C.J.; Brumwell, A.; Li, X.; Klesney-Tait, J.; Cohen, M.L.; Wolters, P.J.; et al. Blocking LOXL2 and TGFβ1 signalling induces collagen I turnover in precision-cut lung slices derived from patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Thorax 2021, 76, 729–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, N.; Liu, K.; Wang, K.; Zhou, C.; Wang, H.; Che, S.; Liu, Z.; Yang, H. Dust induces lung fibrosis through dysregulated DNA methylation. Environ. Toxicol. 2019, 34, 728–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, J.T.; Lourenço, J.D.; Righetti, R.F.; Tibério, I.F.L.C.; Prado, C.M.; Lopes, F.D.T.Q.S. Extracellular Matrix Component Remodeling in Respiratory Diseases: What Has Been Found in Clinical and Experimental Studies? Cells 2019, 8, 342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costanzo, L.; Soto, B.; Meier, R.; Geraghty, P. The Biology and Function of Tissue Inhibitor of Metalloproteinase 2 in the Lungs. Pulm. Med. 2022, 2022, 3632764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Recillas-Román, S.; Montaño, M.; Ruiz, V.; Pérez-Ramos, J.; Becerril, C.; Herrera, I.; Amador-Muñoz, O.; Martínez-Domínguez, Y.M.; Ramos, C. Wood Smoke Extract Promotes Extracellular Matrix Remodeling in Normal Human Lung Fibroblasts. Int. J. Toxicol. 2021, 40, 506–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, R.; Yasuma, T.; Fridman D’Alessandro, V.; Toda, M.; Ito, T.; Tomaru, A.; D’Alessandro-Gabazza, C.N.; Tsuruga, T.; Okano, T.; Takeshita, A.; et al. Amelioration of Pulmonary Fibrosis by Matrix Metalloproteinase-2 Overexpression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 6695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espindola, M.S.; Habiel, D.M.; Coelho, A.L.; Stripp, B.; Parks, W.C.; Oldham, J.; Martinez, F.J.; Noth, I.; Lopez, D.; Mikels-Vigdal, A.; et al. Differential Responses to Targeting Matrix Metalloproteinase 9 in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2021, 203, 458–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ra, H.J.; Parks, W.C. Control of matrix metalloproteinase catalytic activity. Matrix Biol. 2007, 26, 587–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molière, S.; Jaulin, A.; Tomasetto, C.L.; Dali-Youcef, N. Roles of Matrix Metalloproteinases and Their Natural Inhibitors in Metabolism: Insights into Health and Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 10649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujimoto, Y.; Kaji, K.; Nishimura, N.; Enomoto, M.; Murata, K.; Takeda, S.; Takaya, H.; Kawaratani, H.; Moriya, K.; Namisaki, T.; et al. Dual therapy with zinc acetate and rifaximin prevents from ethanol-induced liver fibrosis by maintaining intestinal barrier integrity. World J. Gastroenterol. 2021, 27, 8323–8342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narula, S.; Tandon, C.; Tandon, S. Role of Matrix Metalloproteinases in Degenerative Kidney Disorders. Curr. Med. Chem. 2018, 25, 1805–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Ali, M.K.; Dua, K.; Xu, R. The Role of Zinc in the Pathogenesis of Lung Disease. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauer, S.E.; Lai, H.J.; McDonald, C.M.; Asfour, F.; Slaven, J.E.; Ren, C.L. Zinc status and growth in infants and young children with cystic fibrosis. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2021, 56, 3768–3776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davies, C.B.; Harrison, M.D.; Huygens, F. Pseudomonas aeruginosa Trent and zinc homeostasis. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2017, 364, fnx151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Xue, Y.; Fu, Y.; Bao, B.; Guo, M.Y. Zinc Deficiency Aggravates Oxidative Stress Leading to Inflammation and Fibrosis in Lung of Mice. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2022, 200, 4045–4057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, L.; Roth, M.; S’ng, C.T.; Tamm, M.; Han, B.; Hoang, B.X. Zinc salicylate reduces airway smooth muscle cells remodelling by blocking mTOR and activating p21(Waf1/Cip1). J. Nutr. Biochem. 2021, 89, 108563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambers, C.; Boehm, P.M.; Karabacak, Y.; Samaha, E.; Benazzo, A.; Jaksch, P.; Roth, M. Combined Activation of Guanylate Cyclase and Cyclic AMP in Lung Fibroblasts as a Novel Therapeutic Concept for Lung Fibrosis. BioMed Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 1345402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkesman, J.; Kurz, L. Zymography Principles. Methods Mol. Biol. 2017, 1626, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lambers, C.; Roth, M.; Jaksch, P.; Muraközy, G.; Tamm, M.; Klepetko, W.; Ghanim, B.; Zhao, F. Treprostinil inhibits proliferation and extracellular matrix deposition by fibroblasts through cAMP activation. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.; Chen, H. Aberrance of Zinc Metalloenzymes-Induced Human Diseases and Its Potential Mechanisms. Nutrients 2021, 13, 4456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knoell, D.L.; Smith, D.; Bao, S.; Sapkota, M.; Wyatt, T.A.; Zweier, J.L.; Flury, J.; Borchers, M.T.; Knutson, M. Imbalance in zinc homeostasis enhances lung Tissue Loss following cigarette smoke exposure. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2020, 60, 126483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andino, D.; Moy, J.; Gaynes, B.I. Serum vitamin A, zinc and visual function in children with moderate to severe persistent asthma. J. Asthma 2019, 56, 1198–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamed, N.A.M.; Rushdy, M.; Abdel-Rehim, A.S.M. The immunomodulatory role of zinc in asthmatic patients. Cytokine 2018, 110, 301–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stiles, L.I.; Ferrao, K.; Mehta, K.J. Role of zinc in health and disease. Clin. Exp. Med. 2024, 24, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowe, N.M.; Hall, A.G.; Broadley, M.R.; Foley, J.; Boy, E.; Bhutta, Z.A. Preventing and Controlling Zinc Deficiency Across the Life Course: A Call to Action. Adv. Nutr. 2024, 15, 100181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, R.; Chen, M.Y.; Liang, W.; Chen, Y.; Guo, M.Y. Zinc Deficiency Aggravation of ROS and Inflammatory Injury Leading to Renal Fibrosis in Mice. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2021, 199, 622–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, J.W.; Duan, S.Y.; Zhang, H.X.; Chen, Y.; Guo, M. Zinc Deficiency Promoted Fibrosis via ROS and TIMP/MMPs in the Myocardium of Mice. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2020, 196, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wang, B.; Wang, Y.; Tong, Q.; Liu, Q.; Sun, J.; Zheng, Y.; Cai, L. Zinc Prevents the Development of Diabetic Cardiomyopathy in db/db Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, F.; Sheng, Q.; Xu, X.; Huang, W.; Kang, Y.J. Zinc supplementation suppresses the progression of bile duct ligation-induced liver fibrosis in mice. Exp. Biol. Med. 2015, 240, 1197–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriya, K.; Nishimura, N.; Namisaki, T.; Takaya, H.; Sawada, Y.; Kawaratani, H.; Kaji, K.; Shimozato, N.; Sato, S.; Furukawa, M.; et al. Zinc Administration and Improved Serum Markers of Hepatic Fibrosis in Patients with Autoimmune Hepatitis. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 2465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garat, C.; Kheradmand, F.; Albertine, K.H.; Folkesson, H.G.; Matthay, M.A. Soluble and insoluble fibronectin increases alveolar epithelial wound healing in vitro. Am. J. Physiol. 1996, 271, L844–L853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patten, J.; Wang, K. Fibronectin in development and wound healing. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2021, 170, 353–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lenselink, E.A. Role of fibronectin in normal wound healing. Int. Wound J. 2015, 12, 313–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.C.; Chuang, T.Y.; Liu, C.W.; Liu, C.W.; Lee, T.L.; Lai, T.C.; Chen, Y.L. Particulate matters increase epithelial-mesenchymal transition and lung fibrosis through the ETS-1/NF-κB-dependent pathway in lung epithelial cells. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2020, 17, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, P.H.; Sermersheim, M.; Li, H.; Lee, P.H.U.; Steinberg, S.M.; Ma, J. Zinc in Wound Healing Modulation. Nutrients 2017, 10, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoang, B.X.; Hoang, H.Q.; Han, B. Zinc Iodide in combination with Dimethyl Sulfoxide for treatment of SARS-CoV-2 and other viral infections. Med. Hypotheses 2020, 143, 109866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, D.T.; Pham, T.N.; Nguyen, N.H.T.; Tran, H.D.; Hoang, H.Q.; Nguyen, A.K.; Han, B.O.; Hoang, B.X. Therapeutic Efficacy of AFree Oral Spray on the Symptoms and Course of Moderate and Severe COVID-19 in the Field Hospital. In Vivo 2023, 37, 1743–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lansdown, A.B.; Mirastschijski, U.; Stubbs, N.; Scanlon, E.; Agren, M.S. Zinc in wound healing: Theoretical, experimental, and clinical aspects. Wound Repair. Regen. 2007, 15, 2–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fröhlich, E. Animals in Respiratory Research. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 2903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petpiroon, N.; Netkueakul, W.; Sukrak, K.; Wang, C.; Liang, Y.; Wang, M.; Liu, Y.; Li, Q.; Kamran, R.; Naruse, K.; et al. Development of lung tissue models and their applications. Life Sci. 2023, 334, 122208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Upadhyay, P.; Wu, C.W.; Pham, A.; Zeki, A.A.; Royer, C.M.; Kodavanti, U.P.; Takeuchi, M.; Bayram, H.; Pinkerton, K.E. Animal models and mechanisms of tobacco smoke-induced chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). J. Toxicol. Environ. Health B Crit. Rev. 2023, 26, 275–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, D.T.; Pham, T.N.; Nguyen, N.H.; Tran, H.D.; Hoang, H.Q.; Han, B.O.; Hoang, B.X. A Prospective Study of AFree Oral Spray as an Adjuvant Therapy for Mild and Moderate COVID-19 in Community Health Stations: Clinical Progression and Viral Clearance Outcomes. In Vivo 2023, 37, 2155–2160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hara, T.; Takeda, T.A.; Takagishi, T.; Fukue, K.; Kambe, T.; Fukada, T. Physiological roles of zinc transporters: Molecular and genetic importance in zinc homeostasis. J. Physiol. Sci. 2017, 67, 283–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maret, W. Metals on the move: Zinc ions in cellular regulation and in the coordination dynamics of zinc proteins. Biometals 2011, 24, 411–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassandri, M.; Smirnov, A.; Novelli, F.; Pitolli, C.; Agostini, M.; Malewicz, M.; Melino, G.; Raschellà, G. Zinc-finger proteins in health and disease. Cell Death Discov. 2017, 3, 17071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Roth, M.; Han, B.; S’ng, C.T.; Hoang, B.X.; Lambers, C. Zinc Iodide Dimethyl Sulfoxide Reduces Collagen Deposition by Increased Matrix Metalloproteinase-2 Expression and Activity in Lung Fibroblasts. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 1257. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12061257
Roth M, Han B, S’ng CT, Hoang BX, Lambers C. Zinc Iodide Dimethyl Sulfoxide Reduces Collagen Deposition by Increased Matrix Metalloproteinase-2 Expression and Activity in Lung Fibroblasts. Biomedicines. 2024; 12(6):1257. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12061257
Chicago/Turabian StyleRoth, Michael, Bo Han, Chong Teck S’ng, Ba Xuan Hoang, and Christopher Lambers. 2024. "Zinc Iodide Dimethyl Sulfoxide Reduces Collagen Deposition by Increased Matrix Metalloproteinase-2 Expression and Activity in Lung Fibroblasts" Biomedicines 12, no. 6: 1257. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12061257
APA StyleRoth, M., Han, B., S’ng, C. T., Hoang, B. X., & Lambers, C. (2024). Zinc Iodide Dimethyl Sulfoxide Reduces Collagen Deposition by Increased Matrix Metalloproteinase-2 Expression and Activity in Lung Fibroblasts. Biomedicines, 12(6), 1257. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12061257







