Potential Utility of a 4th-Generation EGFR-TKI and Exploration of Resistance Mechanisms—An In Vitro Study
Abstract
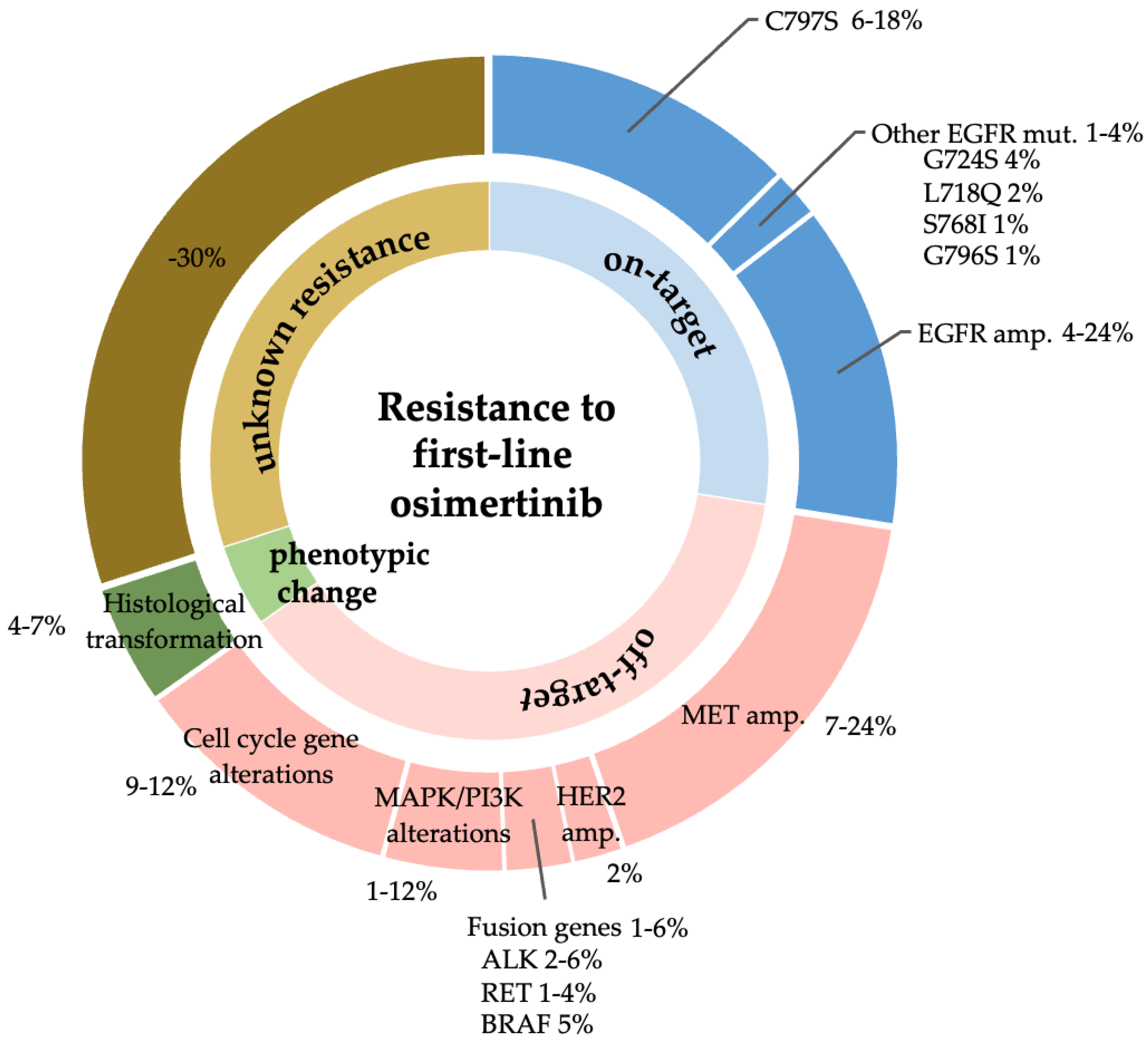
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Exploration of Acquired Resistance Mechanisms to Front-Line Osimertinib
2.2. Cell Lines and Reagents
2.3. Growth Inhibition Assay
2.4. Western Blot Analysis
2.5. Human Phospho-RTK Array
2.6. Mutation Analysis and Gene Copy Number Analysis
3. Results
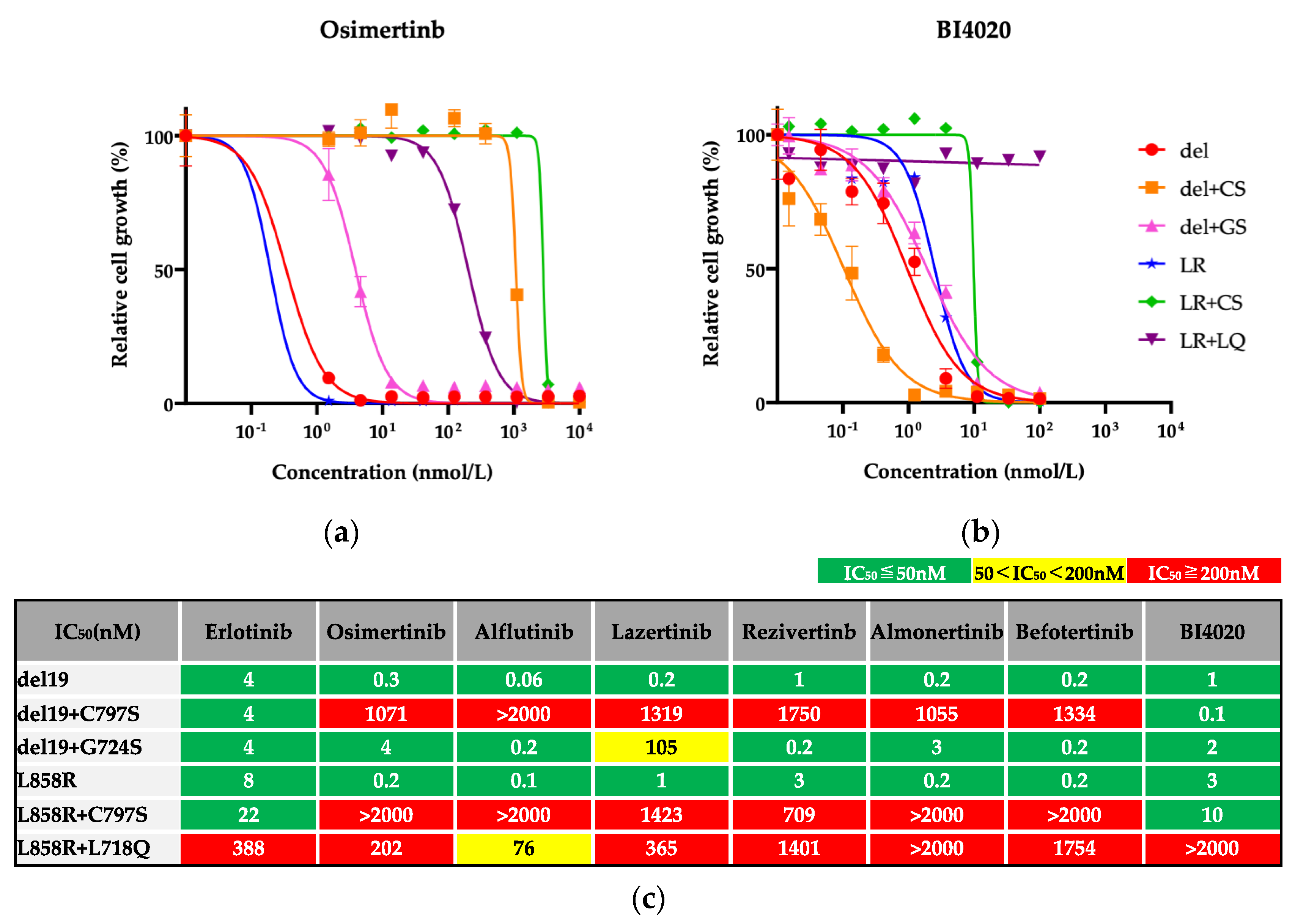
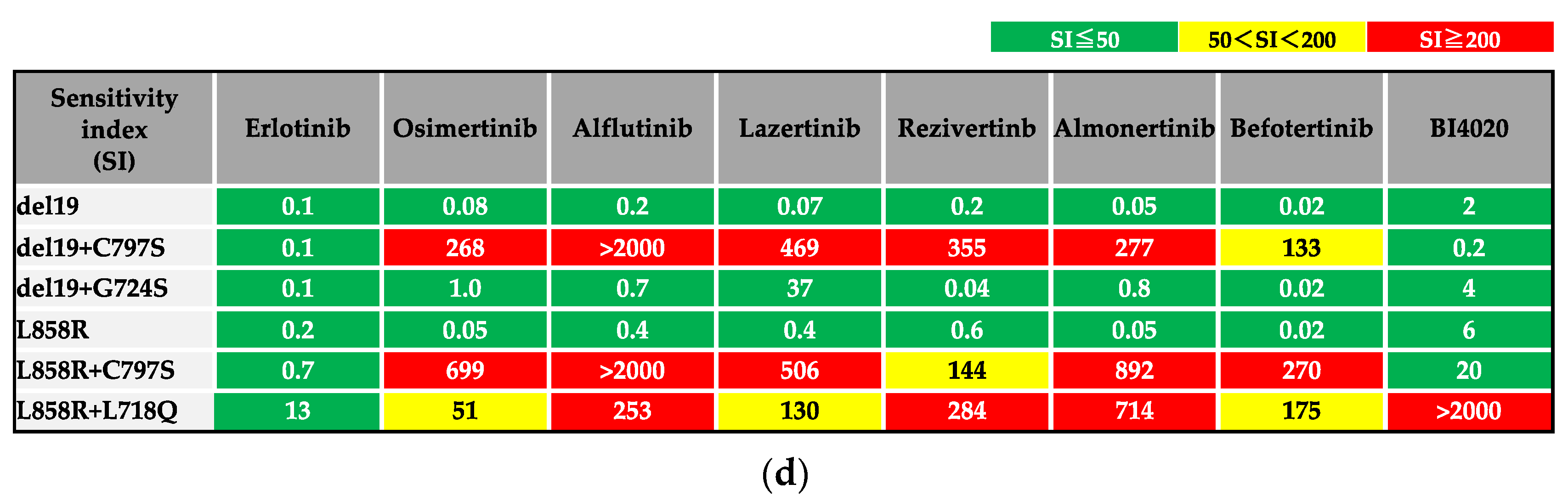
3.1. Efficacy of BI4020 and Other TKIs against Osimertinib-Resistant Secondary Mutations
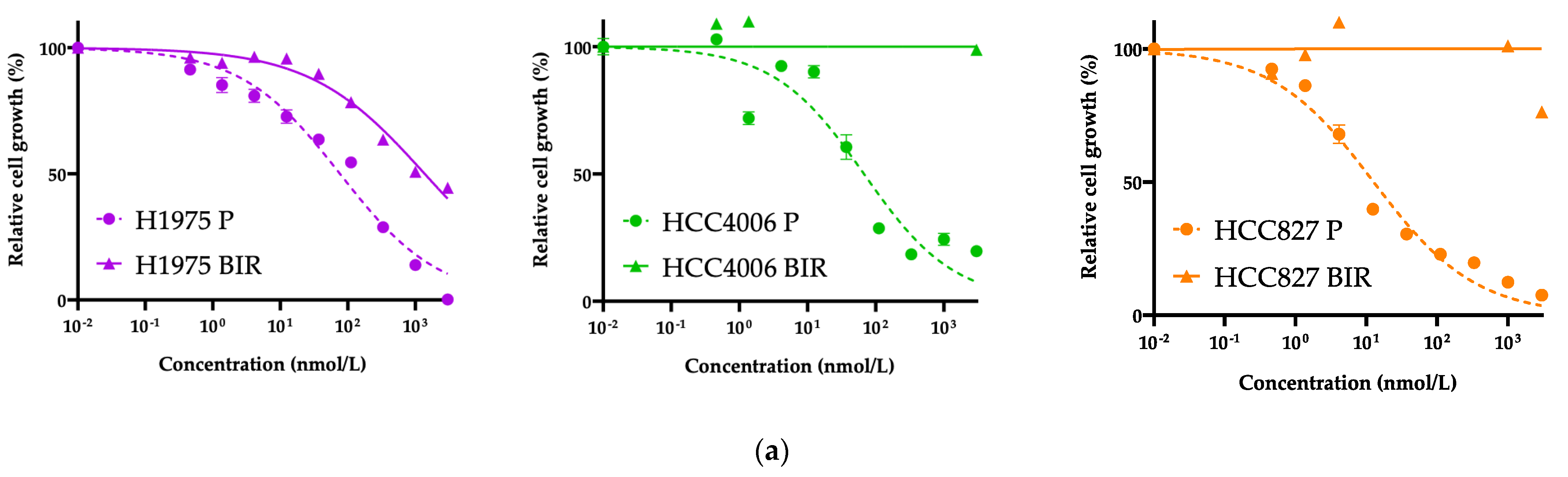
3.2. Exploration of Acquired Resistance Mechanisms to Front-Line BI4020
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hirsch, F.R.; Suda, K.; Wiens, J.; Bunn, P.A., Jr. New and emerging targeted treatments in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. Lancet 2016, 388, 1012–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramalingam, S.S.; Vansteenkiste, J.; Planchard, D.; Cho, B.C.; Gray, J.E.; Ohe, Y.; Zhou, C.; Reungwetwattana, T.; Cheng, Y.; Chewaskulyong, B.; et al. Overall Survival with Osimertinib in Untreated, EGFR-Mutated Advanced NSCLC. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakata, Y.; Sakata, S.; Oya, Y.; Tamiya, M.; Suzuki, H.; Shibaki, R.; Okada, A.; Kobe, H.; Matsumoto, H.; Yokoi, T.; et al. Osimertinib as first-line treatment for advanced epidermal growth factor receptor mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer in a real-world setting (OSI-FACT). Eur. J. Cancer 2021, 159, 144–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, B.C.; Ahn, M.J.; Kang, J.H.; Soo, R.A.; Reungwetwattana, T.; Yang, J.C.; Cicin, I.; Kim, D.W.; Wu, Y.L.; Lu, S.; et al. Lazertinib Versus Gefitinib as First-Line Treatment in Patients With EGFR-Mutated Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: Results From LASER301. J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41, 4208–4217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Passaro, A.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Lee, S.H.; Melosky, B.; Shih, J.Y.; Wang, J.; Azuma, K.; Juan-Vidal, O.; Cobo, M.; et al. Amivantamab plus chemotherapy with and without lazertinib in EGFR-mutant advanced NSCLC after disease progression on osimertinib: Primary results from the phase III MARIPOSA-2 study. Ann. Oncol. 2024, 35, 77–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y.; Chen, G.; Wang, X.; Liu, Y.; Wu, L.; Hao, Y.; Liu, C.; Zhu, S.; Zhang, X.; Li, Y.; et al. Furmonertinib (AST2818) versus gefitinib as first-line therapy for Chinese patients with locally advanced or metastatic EGFR mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (FURLONG): A multicentre, double-blind, randomised phase 3 study. Lancet Respir. Med. 2022, 10, 1019–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, S.; Boggon, T.J.; Dayaram, T.; Jänne, P.A.; Kocher, O.; Meyerson, M.; Johnson, B.E.; Eck, M.J.; Tenen, D.G.; Halmos, B. EGFR mutation and resistance of non-small-cell lung cancer to gefitinib. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 352, 786–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suda, K.; Murakami, I.; Obata, K.; Sakai, K.; Fujino, T.; Koga, T.; Ohara, S.; Hamada, A.; Soh, J.; Nishio, K.; et al. Spatial heterogeneity of acquired resistance mechanisms to 1st/2nd generation EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors in lung cancer. Lung Cancer 2020, 148, 100–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Ko, J.; Cui, Z.; Abolhoda, A.; Ahn, J.S.; Ou, S.H.; Ahn, M.J.; Park, K. The EGFR T790M mutation in acquired resistance to an irreversible second-generation EGFR inhibitor. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2012, 11, 784–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chmielecki, J.; Gray, J.E.; Cheng, Y.; Ohe, Y.; Imamura, F.; Cho, B.C.; Lin, M.C.; Majem, M.; Shah, R.; Rukazenkov, Y.; et al. Candidate mechanisms of acquired resistance to first-line osimertinib in EGFR-mutated advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.J.; Oh, S.Y.; Lee, Y.W.; Kim, J.Y.; Kim, M.J.; Kim, T.H.; Lee, J.B.; Hong, M.H.; Lim, S.M.; Baum, A.; et al. Discovery of a novel potent EGFR inhibitor against EGFR activating mutations and on-target resistance in NSCLC. Clin. Cancer Res. 2024, 30, 1582–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, S.M.; Fujino, T.; Kim, C.; Lee, G.; Lee, Y.H.; Kim, D.W.; Ahn, J.S.; Mitsudomi, T.; Jin, T.; Lee, S.Y. BBT-176, a Novel Fourth-Generation Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor for Osimertinib-Resistant EGFR Mutations in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2023, 29, 3004–3016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soria, J.C.; Ohe, Y.; Vansteenkiste, J.; Reungwetwattana, T.; Chewaskulyong, B.; Lee, K.H.; Dechaphunkul, A.; Imamura, F.; Nogami, N.; Kurata, T.; et al. Osimertinib in Untreated EGFR-Mutated Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uozu, S.; Imaizumi, K.; Yamaguchi, T.; Goto, Y.; Kawada, K.; Minezawa, T.; Okamura, T.; Akao, K.; Hayashi, M.; Isogai, S.; et al. Feasibility of tissue re-biopsy in non-small cell lung cancers resistant to previous epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor therapies. BMC Pulm. Med. 2017, 17, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Facchinetti, F.; Braye, F.; Yurchenko, A.A.; Bigot, L.; Ponce, S.; Planchard, D.; Gazzah, A.; Nikolaev, S.; Michiels, S.; et al. Single-cell DNA-seq depicts clonal evolution of multiple driver alterations in osimertinib-resistant patients. Ann. Oncol. 2022, 33, 434–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roper, N.; Brown, A.L.; Wei, J.S.; Pack, S.; Trindade, C.; Kim, C.; Restifo, O.; Gao, S.; Sindiri, S.; Mehrabadi, F.; et al. Clonal Evolution and Heterogeneity of Osimertinib Acquired Resistance Mechanisms in EGFR Mutant Lung Cancer. Cell Rep. Med. 2020, 1, 100007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suda, K.; Mizuuchi, H.; Maehara, Y.; Mitsudomi, T. Acquired resistance mechanisms to tyrosine kinase inhibitors in lung cancer with activating epidermal growth factor receptor mutation--diversity, ductility, and destiny. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2012, 31, 807–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thress, K.S.; Paweletz, C.P.; Felip, E.; Cho, B.C.; Stetson, D.; Dougherty, B.; Lai, Z.; Markovets, A.; Vivancos, A.; Kuang, Y.; et al. Acquired EGFR C797S mutation mediates resistance to AZD9291 in non-small cell lung cancer harboring EGFR T790M. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 560–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bersanelli, M.; Minari, R.; Bordi, P.; Gnetti, L.; Bozzetti, C.; Squadrilli, A.; Lagrasta, C.A.; Bottarelli, L.; Osipova, G.; Capelletto, E.; et al. L718Q Mutation as New Mechanism of Acquired Resistance to AZD9291 in EGFR-Mutated NSCLC. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2016, 11, e121–e123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fassunke, J.; Müller, F.; Keul, M.; Michels, S.; Dammert, M.A.; Schmitt, A.; Plenker, D.; Lategahn, J.; Heydt, C.; Brägelmann, J.; et al. Overcoming EGFR(G724S)-mediated osimertinib resistance through unique binding characteristics of second-generation EGFR inhibitors. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 4655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramalingam, S.S.; Cheng, Y.; Zhou, C.; Ohe, Y.; Imamura, F.; Cho, B.C.; Lin, M.C.; Majem, M.; Shah, R.; Rukazenkov, Y.; et al. Mechanisms of acquired resistance to first-line osimertinib: Preliminary data from the phase III FLAURA study. Ann. Oncol. 2018, 29, viii740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonetti, A.; Sharma, S.; Minari, R.; Perego, P.; Giovannetti, E.; Tiseo, M. Resistance mechanisms to osimertinib in EGFR-mutated non-small cell lung cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2019, 121, 725–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmid, S.; Li, J.J.N.; Leighl, N.B. Mechanisms of osimertinib resistance and emerging treatment options. Lung Cancer 2020, 147, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoenfeld, A.J.; Chan, J.M.; Kubota, D.; Sato, H.; Rizvi, H.; Daneshbod, Y.; Chang, J.C.; Paik, P.K.; Offin, M.; Arcila, M.E.; et al. Tumor Analyses Reveal Squamous Transformation and Off-Target Alterations As Early Resistance Mechanisms to First-line Osimertinib in EGFR-Mutant Lung Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 26, 2654–2663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartmaier, R.J.; Markovets, A.; Cho, B.C.; de Langen, A.J.; Goldberg, S.B.; Goldman, J.; Le, X.; Okamoto, I.; Riess, J.W.; Cosaert, J.; et al. Abstract LB078: Tumor genomics in patients (pts) with advanced epidermal growth factor receptor mutant (EGFRm) non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) whose disease has progressed on first-line (1L) osimertinib therapy in the Phase II ORCHARD study. Cancer Res. 2022, 82 (Suppl. S12), LB078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piotrowska, Z.; Ahn, M.J.; Pang, Y.K.; How, S.H.; Kim, S.W.; Voon, P.J.; Cortinovis, D.L.; De Castro Carpeno, J.; Tiseo, M.; Abreu, D.R.; et al. LBA53 ELIOS: A multicentre, molecular profiling study of patients (pts) with epidermal growth factor receptor-mutated (EGFRm) advanced NSCLC treated with first-line (1L) osimertinib. Ann. Oncol. 2022, 33, S1420–S1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonetti, A.; Verzè, M.; Minari, R.; Perrone, F.; Gnetti, L.; Bordi, P.; Pluchino, M.; Nizzoli, R.; Azzoni, C.; Bottarelli, L.; et al. Resistance to osimertinib in advanced EGFR-mutated NSCLC: A prospective study of molecular genotyping on tissue and liquid biopsies. Br. J. Cancer 2024, 130, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishino, M.; Suda, K.; Kobayashi, Y.; Ohara, S.; Fujino, T.; Koga, T.; Chiba, M.; Shimoji, M.; Tomizawa, K.; Takemoto, T.; et al. Effects of secondary EGFR mutations on resistance against upfront osimertinib in cells with EGFR-activating mutations in vitro. Lung Cancer 2018, 126, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koga, T.; Suda, K.; Nishino, M.; Fujino, T.; Ohara, S.; Hamada, A.; Soh, J.; Tirunagaru, V.; Vellanki, A.; Doebele, R.C.; et al. Activity and mechanism of acquired resistance to tarloxotinib in HER2 mutant lung cancer: An in vitro study. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2021, 10, 3659–3670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suda, K.; Murakami, I.; Katayama, T.; Tomizawa, K.; Osada, H.; Sekido, Y.; Maehara, Y.; Yatabe, Y.; Mitsudomi, T. Reciprocal and complementary role of MET amplification and EGFR T790M mutation in acquired resistance to kinase inhibitors in lung cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2010, 16, 5489–5498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suda, K.; Tomizawa, K.; Fujii, M.; Murakami, H.; Osada, H.; Maehara, Y.; Yatabe, Y.; Sekido, Y.; Mitsudomi, T. Epithelial to mesenchymal transition in an epidermal growth factor receptor-mutant lung cancer cell line with acquired resistance to erlotinib. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2011, 6, 1152–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suda, K.; Murakami, I.; Yu, H.; Kim, J.; Tan, A.C.; Mizuuchi, H.; Rozeboom, L.; Ellison, K.; Rivard, C.J.; Mitsudomi, T.; et al. CD44 Facilitates Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition Phenotypic Change at Acquisition of Resistance to EGFR Kinase Inhibitors in Lung Cancer. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2018, 17, 2257–2265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishino, M.; Suda, K.; Koga, T.; Ohara, S.; Fujino, T.; Soh, J.; Tirunagaru, V.; Vellanki, A.; Doebele, R.C.; Mitsudomi, T. Activity of tarloxotinib-E in cells with EGFR exon-20 insertion mutations and mechanisms of acquired resistance. Thorac. Cancer 2021, 12, 1511–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soucheray, M.; Capelletti, M.; Pulido, I.; Kuang, Y.; Paweletz, C.P.; Becker, J.H.; Kikuchi, E.; Xu, C.; Patel, T.B.; Al-Shahrour, F.; et al. Intratumoral Heterogeneity in EGFR-Mutant NSCLC Results in Divergent Resistance Mechanisms in Response to EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibition. Cancer Res. 2015, 75, 4372–4383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, T.; Song, L.; Bai, Y.; Kinose, F.; Li, J.; Ohaegbulam, K.C.; Muñoz-Antonia, T.; Qu, X.; Eschrich, S.; Uramoto, H.; et al. ZEB1 Mediates Acquired Resistance to the Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor-Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0147344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sequist, L.V.; Waltman, B.A.; Dias-Santagata, D.; Digumarthy, S.; Turke, A.B.; Fidias, P.; Bergethon, K.; Shaw, A.T.; Gettinger, S.; Cosper, A.K.; et al. Genotypic and histological evolution of lung cancers acquiring resistance to EGFR inhibitors. Sci. Transl. Med. 2011, 3, 75ra26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, C.H.; Chen, L.Y.; Lin, Y.C.; Shih, J.Y.; Lin, Y.C.; Tseng, R.Y.; Chiu, A.C.; Yeh, Y.H.; Liu, C.; Lin, Y.T.; et al. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) beyond EGFR mutations per se is a common mechanism for acquired resistance to EGFR TKI. Oncogene 2019, 38, 455–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, W.; Choi, Y.J.; Kang, M.H.; Sung, K.J.; Kim, D.H.; Jung, S.; Choi, C.M.; Lee, J.C.; Rho, J.K. Efficacy of the CDK7 Inhibitor on EMT-Associated Resistance to 3rd Generation EGFR-TKIs in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Cell Lines. Cells 2020, 9, 2596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engelman, J.A.; Zejnullahu, K.; Mitsudomi, T.; Song, Y.; Hyland, C.; Park, J.O.; Lindeman, N.; Gale, C.M.; Zhao, X.; Christensen, J.; et al. MET amplification leads to gefitinib resistance in lung cancer by activating ERBB3 signaling. Science 2007, 316, 1039–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappuzzo, F.; Jänne, P.A.; Skokan, M.; Finocchiaro, G.; Rossi, E.; Ligorio, C.; Zucali, P.A.; Terracciano, L.; Toschi, L.; Roncalli, M.; et al. MET increased gene copy number and primary resistance to gefitinib therapy in non-small-cell lung cancer patients. Ann. Oncol. 2009, 20, 298–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, T.; Okamoto, I.; Okamoto, W.; Hatashita, E.; Yamada, Y.; Kuwata, K.; Nishio, K.; Fukuoka, M.; Jänne, P.A.; Nakagawa, K. Effects of Src inhibitors on cell growth and epidermal growth factor receptor and MET signaling in gefitinib-resistant non-small cell lung cancer cells with acquired MET amplification. Cancer Sci. 2010, 101, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turke, A.B.; Zejnullahu, K.; Wu, Y.L.; Song, Y.; Dias-Santagata, D.; Lifshits, E.; Toschi, L.; Rogers, A.; Mok, T.; Sequist, L.; et al. Preexistence and clonal selection of MET amplification in EGFR mutant NSCLC. Cancer Cell 2010, 17, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goss, G.; Tsai, C.M.; Shepherd, F.A.; Bazhenova, L.; Lee, J.S.; Chang, G.C.; Crino, L.; Satouchi, M.; Chu, Q.; Hida, T.; et al. Osimertinib for pretreated EGFR Thr790Met-positive advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (AURA2): A multicentre, open-label, single-arm, phase 2 study. Lancet Oncol. 2016, 17, 1643–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mok, T.S.; Wu, Y.-L.; Ahn, M.-J.; Garassino, M.C.; Kim, H.R.; Ramalingam, S.S.; Shepherd, F.A.; He, Y.; Akamatsu, H.; Theelen, W.S.M.E.; et al. Osimertinib or Platinum–Pemetrexed in EGFR T790M–Positive Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 629–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uchibori, K.; Inase, N.; Araki, M.; Kamada, M.; Sato, S.; Okuno, Y.; Fujita, N.; Katayama, R. Brigatinib combined with anti-EGFR antibody overcomes osimertinib resistance in EGFR-mutated non-small-cell lung cancer. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.A.; Tian, S.K.; Drilon, A.E.; Borsu, L.; Riely, G.J.; Arcila, M.E.; Ladanyi, M. Acquired Resistance of EGFR-Mutant Lung Cancer to a T790M-Specific EGFR Inhibitor: Emergence of a Third Mutation (C797S) in the EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Domain. JAMA Oncol. 2015, 1, 982–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yun, M.R.; Yu, M.R.; Duggirala, K.B.; Lee, K.; Lim, S.M.; Jo, A.; Seah, E.; Kim, C.; Cho, B.C. 999P JIN-A02, a fourth-generation, highly effective tyrosine kinase inhibitor with intracranial activity, targeting EGFR C797S mutations in NSCLC. Ann. Oncol. 2022, 33, S1010–S1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elamin, Y.Y.; Nagasaka, M.; Shum, E.; Bazhenova, L.; Camidge, D.R.; Cho, B.C.; Felip, E.; Goto, K.; Lin, C.-C.; Piotrowska, Z.; et al. BLU-945 monotherapy and in combination with osimertinib (OSI) in previously treated patients with advanced EGFR-mutant (EGFRm) NSCLC in the phase 1/2 SYMPHONY study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41 (Suppl. S16), 9011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Planchard, D.; Jänne, P.A.; Cheng, Y.; Yang, J.C.; Yanagitani, N.; Kim, S.W.; Sugawara, S.; Yu, Y.; Fan, Y.; Geater, S.L.; et al. Osimertinib with or without Chemotherapy in EGFR-Mutated Advanced NSCLC. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 389, 1935–1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jänne, P.A.; Planchard, D.; Kobayashi, K.; Cheng, Y.; Lee, C.K.; Valdiviezo, N.; Laktionov, K.; Yang, T.Y.; Yu, Y.; Kato, T.; et al. CNS Efficacy of Osimertinib With or Without Chemotherapy in Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor-Mutated Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2024, 42, 808–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, B.C.; Felip, E.; Spira, A.I.; Girard, N.; Lee, J.S.; Lee, S.H.; Ostapenko, Y.V.; Danchaivijitr, P.; Liu, B.; Alip, A.; et al. LBA14 Amivantamab plus lazertinib vs osimertinib as first-line treatment in patients with EGFR-mutated, advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC): Primary results from MARIPOSA, a phase III, global, randomized, controlled trial. Ann. Oncol. 2023, 34, S1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ercan, D.; Choi, H.G.; Yun, C.H.; Capelletti, M.; Xie, T.; Eck, M.J.; Gray, N.S.; Jänne, P.A. EGFR Mutations and Resistance to Irreversible Pyrimidine-Based EGFR Inhibitors. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 3913–3923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uchibori, K.; Inase, N.; Nishio, M.; Fujita, N.; Katayama, R. Identification of Mutation Accumulation as Resistance Mechanism Emerging in First-Line Osimertinib Treatment. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2018, 13, 915–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rangachari, D.; To, C.; Shpilsky, J.E.; VanderLaan, P.A.; Kobayashi, S.S.; Mushajiang, M.; Lau, C.J.; Paweletz, C.P.; Oxnard, G.R.; Jänne, P.A.; et al. EGFR-Mutated Lung Cancers Resistant to Osimertinib through EGFR C797S Respond to First-Generation Reversible EGFR Inhibitors but Eventually Acquire EGFR T790M/C797S in Preclinical Models and Clinical Samples. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2019, 14, 1995–2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araki, T.; Kanda, S.; Obara, M.; Agatsuma, T.; Kakizaki, Y.; Hama, M.; Yamamoto, H.; Takada, M.; Yamamoto, M.; Matsuo, A.; et al. EGFR-TKI rechallenge in patients with EGFR-mutated non-small-cell lung cancer who progressed after first-line osimertinib treatment: A multicenter retrospective observational study. Respir. Investig. 2024, 62, 262–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araki, T.; Kanda, S.; Komatsu, M.; Sonehara, K.; Tateishi, K.; Takada, M.; Kato, A.; Yamamoto, M.; Nishie, K.; Hama, M.; et al. Rechallenge of afatinib for EGFR-mutated non-small cell lung cancer previously treated with osimertinib: A multicenter phase II trial protocol (REAL study). Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2023, 12, 1320–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.L.; Cheng, Y.; Zhou, J.; Lu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, J.; Kim, D.W.; Soo, R.A.; Kim, S.W.; Pan, H.; et al. Tepotinib plus gefitinib in patients with EGFR-mutant non-small-cell lung cancer with MET overexpression or MET amplification and acquired resistance to previous EGFR inhibitor (INSIGHT study): An open-label, phase 1b/2, multicentre, randomised trial. Lancet Respir. Med. 2020, 8, 1132–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.L.; Zhang, L.; Kim, D.W.; Liu, X.; Lee, D.H.; Yang, J.C.; Ahn, M.J.; Vansteenkiste, J.F.; Su, W.C.; Felip, E.; et al. Phase Ib/II Study of Capmatinib (INC280) Plus Gefitinib After Failure of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) Inhibitor Therapy in Patients With EGFR-Mutated, MET Factor-Dysregulated Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 3101–3109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fukuda, S.; Suda, K.; Hamada, A.; Oiki, H.; Ohara, S.; Ito, M.; Soh, J.; Mitsudomi, T.; Tsutani, Y. Potential Utility of a 4th-Generation EGFR-TKI and Exploration of Resistance Mechanisms—An In Vitro Study. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 1412. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12071412
Fukuda S, Suda K, Hamada A, Oiki H, Ohara S, Ito M, Soh J, Mitsudomi T, Tsutani Y. Potential Utility of a 4th-Generation EGFR-TKI and Exploration of Resistance Mechanisms—An In Vitro Study. Biomedicines. 2024; 12(7):1412. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12071412
Chicago/Turabian StyleFukuda, Shota, Kenichi Suda, Akira Hamada, Hana Oiki, Shuta Ohara, Masaoki Ito, Junichi Soh, Tetsuya Mitsudomi, and Yasuhiro Tsutani. 2024. "Potential Utility of a 4th-Generation EGFR-TKI and Exploration of Resistance Mechanisms—An In Vitro Study" Biomedicines 12, no. 7: 1412. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12071412
APA StyleFukuda, S., Suda, K., Hamada, A., Oiki, H., Ohara, S., Ito, M., Soh, J., Mitsudomi, T., & Tsutani, Y. (2024). Potential Utility of a 4th-Generation EGFR-TKI and Exploration of Resistance Mechanisms—An In Vitro Study. Biomedicines, 12(7), 1412. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12071412









