Blood Plasma Markers in Depressed Mice under Chronic Social Defeat Stress
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. The Chronic Social Conflict Model
2.3. The Partition Test
2.4. Proteomic Data Processing and Analysis
2.5. Functional Annotation of the Proteins
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Animal Weight
3.2. The Partition Test
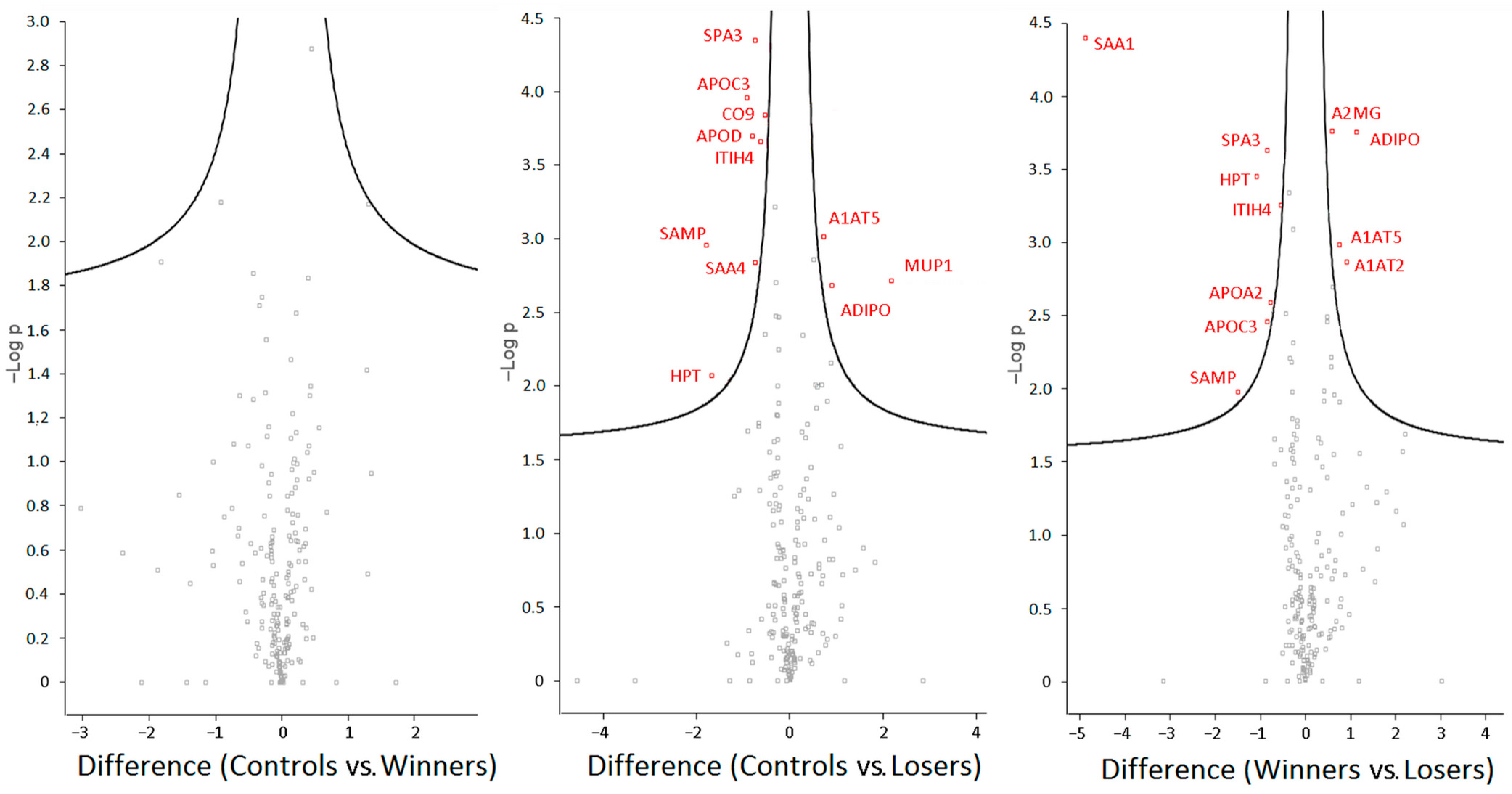
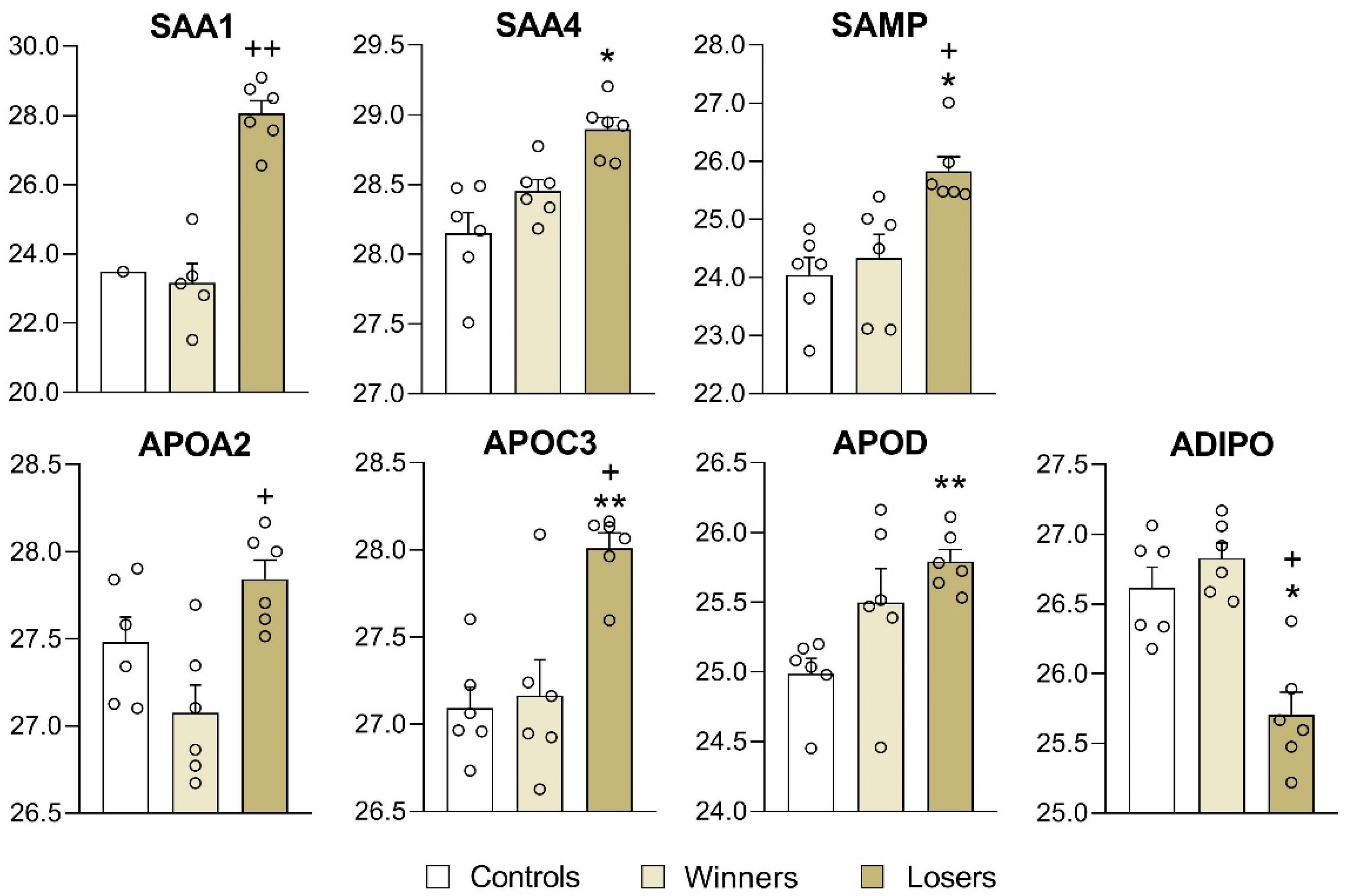
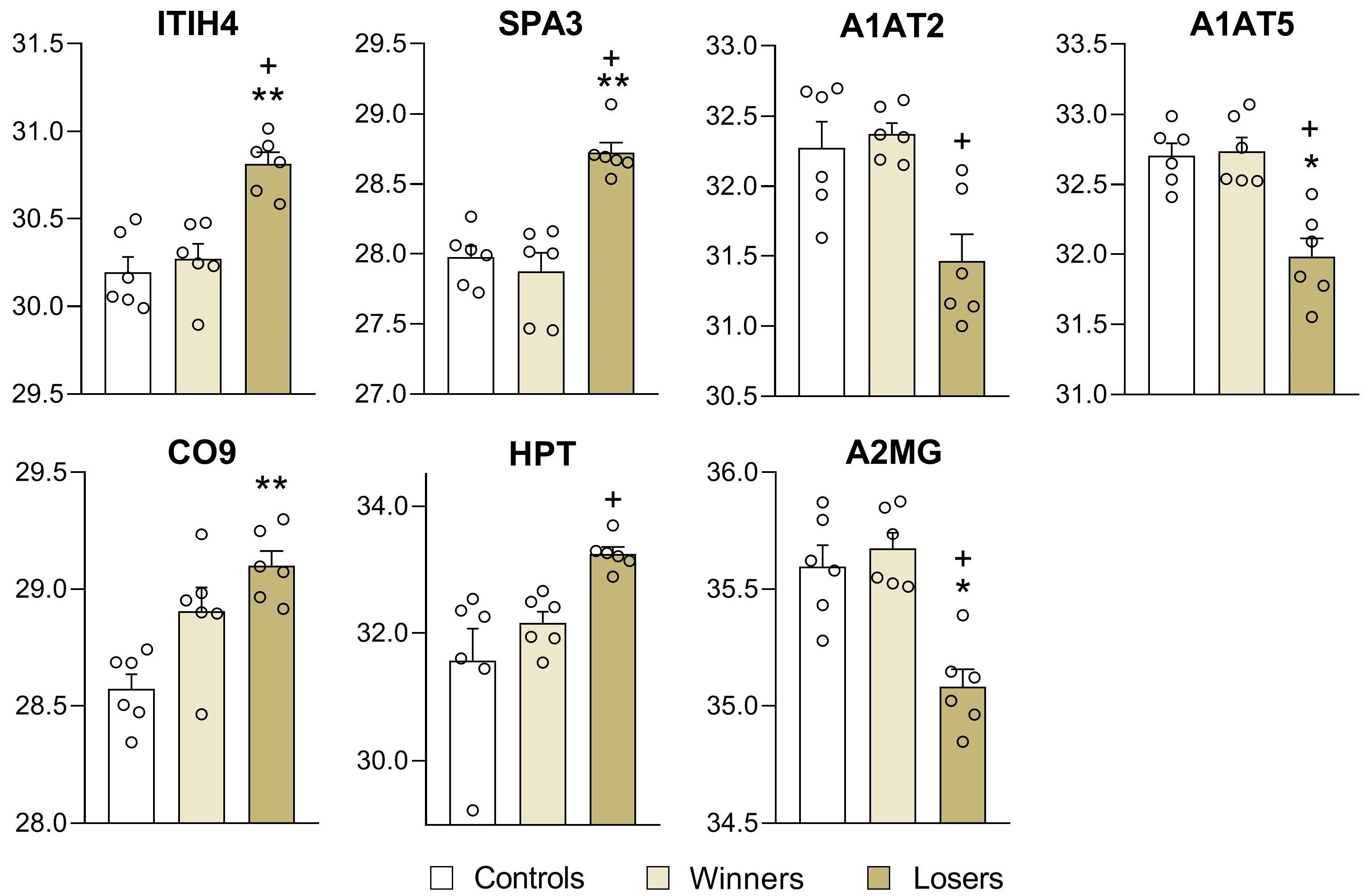
3.3. Analysis of Differentially Expressed Proteins in Blood Plasma of Male Mice
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Duan, J.; Xie, P. The potential for metabolomics in the study and treatment of major depressive disorder and related conditions. Expert Rev. Proteom. 2020, 17, 309–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woods, A.G.; Iosifescu, D.V.; Darie, C.C. Biomarkers in major depressive disorder: The role of mass spectrometry. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2014, 806, 545–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, D.; Peng, Y.; Zhou, J.; Yang, Y.T.; Rao, C.L.; Bai, S.J.; Zhou, X.Y.; Chen, J.; Liao, L.; Liang, Z.H.; et al. Identification and validation of argininosuccinate synthase as a candidate urinary biomarker for major depressive disorder. Clin. Chim. Acta 2015, 451 Pt B, 142–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Zhao, G.; Sun, X.; Liu, H.; Jiang, P.; Chen, J.; Wu, Z.; Peng, D.; Fang, Y.; Zhang, C. Identification of plasma biomarkers for distinguishing bipolar depression from major depressive disorder by iTRAQ-coupled LC-MS/MS and bioinformatics analysis. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2017, 86, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Preece, R.L.; Han, S.Y.S.; Bahn, S. Proteomic approaches to identify blood-based biomarkers for depression and bipolar disorders. Expert Rev. Proteom. 2018, 15, 325–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gui, S.W.; Liu, Y.Y.; Zhong, X.G.; Liu, X.; Zheng, P.; Pu, J.C.; Zhou, J.; Chen, J.J.; Zhao, L.B.; Liu, L.X.; et al. Plasma disturbance of phospholipid metabolism in major depressive disorder by integration of proteomics and metabolomics. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2018, 14, 1451–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wells, D.A.; Lennon, S.R. Major depression and amyloidosis. Case Rep. Gen. Hosp. Psychiatry 1989, 11, 425–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.M.; Gao, X.; Cooke, C.E.; Berg, D.; Labotka, R.; Faller, D.V.; Seal, B.; Hari, P. Disease burden of systemic light-chain amyloidosis: A systematic literature review. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 2017, 33, 1017–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Planton, M.; Raposo, N.; Albucher, J.-F.; Pariente, J. Cerebral amyloid angiopathy-related cognitive impairment: The search for a specific neuropsychological pattern. Rev. Neurol. 2017, 173, 562–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsworthy, R.J.; Aldred, S. Depression in Alzheimer’s disease: An alternative role for selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors? Rev. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2019, 69, 651–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudryavtseva, N.N.; Bakshtanovskaya, I.V.; Koryakina, L.A. Social model of depression in mice of C57BL/6J strain. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 1991, 38, 315–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudryavtseva, N.N. Agonistic behavior: A model, experimental studies, and perspectives. Neurosci. Behav. Physiol. 2000, 30, 293–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galyamina, A.G.; Kovalenko, I.L.; Smagin, D.A.; Kudryavtseva, N.N. Interaction of depression and anxiety in the development of mixed anxiety/depression disorder: Experimental studies of the mechanisms of comorbidity (review). Neurosci. Behav. Physiol. 2017, 47, 699–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudryavtseva, N.N. Development of mixed anxiety/depression-like state as a consequences of chronic anxiety: Review of experimental data. In Current Topics in Behavioral Neurosciences; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keeney, A.J.; Hogg, S. Behavioural consequences of repeated social defeat in the mouse: Preliminary evaluation of a potential animal model of depression. Behav. Pharmacol. 1999, 10, 753–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartolomucci, A.; Leopardi, R. Stress and depression: Preclinical research and clinical implications. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e4265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berton, O.; McClung, C.A.; Dileone, R.J.; Krishnan, V.; Renthal, W.; Russo, S.J.; Graham, D.; Tsankova, N.M.; Bolanos, C.A.; Rios, M.; et al. Essential role of BDNF in the mesolimbic dopamine pathway in social defeat stress. Science 2006, 311, 864–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golden, S.A.; Covington, H.E., 3rd; Berton, O.; Russo, S.J. A standardized protocol for repeated social defeat stress in mice. Nat. Protoc. 2011, 6, 1183–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKinney, W.T.; Bunney, W.E. Animal model of depression. I. Review of evidence: Implications for research. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 1969, 21, 240–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudryavtseva, N.N.; Shurlygina, A.V.; Galyamina, A.G.; Smagin, D.A.; Kovalenko, I.L.; Popova, N.A.; Nikolin, V.P.; Ilnitskaya, S.I.; Melnikova, E.V.; Trufakin, V.A. Immunopathology of mixed anxiety/depression disorders: An experimental approach to studies of immunodeficiency states. Neurosci. Behav. Physiol. 2019, 49, 384–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudryavtseva, N.N. The sensory contact model for the study of aggressive and submissive behavior in male mice. Agress. Behav. 1991, 17, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudryavtseva, N.N.; Smagin, D.A.; Kovalenko, I.L.; Vishnivetskaya, G.B. Repeated positive fighting experience in male inbred mice. Nat. Protoc. 2014, 9, 2705–2717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudryavtseva, N.N. Use of the partition test in behavioral and pharmacological experiments. Neurosci. Behav. Physiol. 2003, 33, 461–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zavialova, M.; Kamaeva, D.; Kazieva, L.; Skvortsov, V.S.; Smirnova, L. Some structural features of the peptide profile of myelin basic protein-hydrolyzing antibodies in schizophrenic patients. PeerJ 2023, 11, e15584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carr, S.; Aebersold, R.; Baldwin, M.; Burlingame, A.; Clauser, K.; Nesvizhskii, A. Working group on publication guidelines for peptide and protein identification data. The need for guidelines in publication of peptide and protein identification data: Working group on publication guidelines for peptide and protein Identification Data. Mol. Cell Proteom. 2004, 6, 531–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravasi, T.; Suzuki, H.; Cannistraci, C.V.; Katayama, S.; Bajic, V.B.; Tan, K.; Akalin, A.; Schmeier, S.; Kanamori-Katayama, M.; Bertin, N.; et al. An atlas of combinatorial transcriptional regulation in mouse and man. Cell 2010, 140, 744–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Hong, F.; Yang, S. Amyloidosis in Alzheimer’s disease: Pathogeny, etiology, and related therapeutic directions. Molecules 2022, 27, 1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Zhang, G.; Vong, C.T.; Ye, R.D. Serum amyloid A and immunomodulation. In Amyloid Diseases; Kurouski, D., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, M.J.; Sorci-Thomas, M.G. SAA: A link between cholesterol efflux capacity and inflammation? J. Lipid Res. 2015, 56, 1383–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramasamy, I. Recent advances in physiological lipoprotein metabolism. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2014, 52, 1695–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sack, G.H., Jr. Sack Serum amyloid A—A review. Mol. Med. 2018, 24, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, W.Y.; Lee, B.R.; Jeong, J.; Sung, Y.; Choi, M.; Song, P.; Kim, H.; Jang, S.; Kim, H.; Joo, K.I.; et al. Overexpression of serum amyloid a 1 induces depressive-like behavior in mice. Brain Res. 2017, 1654 Pt A, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dib, I.; Khalil, A.; Chouaib, R.; El-Makhour, Y.; Noureddine, H. Apolipoprotein C-III and cardiovascular diseases: When genetics meet molecular pathologies. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2021, 48, 875–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Navarro, A.; González-Soria, I.; Caldiño-Bohn, R.; Bobadilla, N.A. An integrative view of serpins in health and disease: The contribution of SerpinA3. Am. J. Physiol. Cell. Physiol. 2021, 320, 106–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, R.H.; Zhang, Q.; McGowan, S.; Buckle, A.M.; Silverman, G.A.; Wong, W.; Rosado, C.J.; Langendorf, C.G.; Pike, R.N.; Bird, P.I.; et al. An overview of the serpin superfamily. Genome Biol. 2006, 7, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Davis, R.L.; Shrimpton, A.E.; Holohan, P.D.; Bradshaw, C.; Feiglin, D.; Collins, G.H.; Sonderegger, P.; Kinter, J.; Becker, L.M.; Lacbawan, F.; et al. Familial dementia caused by polymerization of mutant neuroserpin. Nature 1999, 401, 376–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, G.; Liu, Y.E.; Gentz, R.; Sang, Q.A.; Ni, J.; Goldberg, I.D.; Shi, Y.E. Suppression of breast cancer growth and metastasis by a serpin myoepithelium-derived serine proteinase inhibitor expressed in the mammary myoepithelial cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 3700–3705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silverman, G.A.; Bird, P.I.; Carrell, R.W.; Church, F.C.; Coughlin, P.B.; Gettins, P.G.; Irving, J.A.; Lomas, D.A.; Luke, C.J.; Moyer, R.W.; et al. The serpins are an expanding superfamily of structurally similar but functionally diverse proteins. Evolution, mechanism of inhibition, novel functions, and a revised nomenclature. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 33293–33296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomas, D.A.; Carrell, R.W. Serpinopathies and the conformational dementias. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2002, 3, 759–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomas, D.A. Molecular mousetraps, alpha1-antitrypsin deficiency and the serpinopathies. Clin. Med. 2005, 5, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbor, M.M.; Kurosawa, N.; Nakayama, H.; Nakatani, A.; Tomobe, K.; Chiba, Y.; Ueno, M.; Tanaka, M.; Nomura, Y.; Isobe, M. Polymorphic SERPINA3 prolongs oligomeric state of amyloid beta. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0248027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouton, M.C.; Geiger, M.; Sheffield, W.P.; Irving, J.A.; Lomas, D.A.; Song, S.; Satyanarayanan, R.S.; Zhang, L.; McFadden, G.; Lucas, A.R. The under-appreciated world of the serpin family of serine proteinase inhibitors. EMBO. Mol. Med. 2023, 15, e17144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fra, A.; D’Acunto, E.; Laffranchi, M.; Miranda, E. Cellular models for the serpinopathies. Methods Mol. Biol. 2018, 1826, 109–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, A.; Yaron, J.R.; Zhang, L.; Macaulay, C.; McFadden, G. Serpins: Development for therapeutic applications. Methods Mol. Biol. 2018, 1826, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Acunto, E.; Fra, A.; Visentin, C.; Manno, M.; Ricagno, S.; Galliciotti, G.; Miranda, E. Neuroserpin: Structure, function, physiology and pathology. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2021, 78, 6409–6430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Mezer, M.; Rogaliński, J.; Przewoźny, S.; Chojnicki, M.; Niepolski, L.; Sobieska, M.; Przystańska, A. SERPINA3: Stimulator or inhibitor of pathological changes. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Yu, C.; Shi, S.; Su, X.; Zhang, J.; Ding, Y.; Sun, Y.; Liu, M.; Li, C.; Zhao, X.; et al. An analysis of plasma reveals proteins in the acute phase response pathway to be candidate diagnostic biomarkers for depression. Psychiatry Res. 2019, 272, 404–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joyce, P.R.; Hawes, C.R.; Mulder, R.T.; Sellman, J.D.; Wilson, D.A.; Boswell, D.R. Elevated levels of acute phase plasma proteins in major depression. Biol. Psychiatry 1992, 32, 1035–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maes, M.; Scharpe, S.; Bosmans, E.; Vandewoude, M.; Suy, E.; Uyttenbroeck, W.; Cooreman, W.; Vandervorst, C.; Raus, J. Disturbances in acute phase plasma proteins during melancholia: Additional evidence for the presence of an inflammatory process during that illness. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 1992, 16, 501–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maes, M.; Delange, J.; Ranjan, R.; Meltzer, H.Y.; Desnyder, R.; Cooremans, W.; Scharpé, S. Acute phase proteins in schizophrenia, mania and major depression: Modulation by psychotropic drugs. Psychiatry Res. 1997, 66, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maes, M.; Scharpé, S.; Van Grootel, L.; Uyttenbroeck, W.; Cooreman, W.; Cosyns, P.; Suy, E. Higher alpha 1-antitrypsin, haptoglobin, ceruloplasmin and lower retinol binding protein plasma levels during depression: Further evidence for the existence of an inflammatory response during that illness. J. Affect. Disord. 1992, 24, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Song, R.; Wang, L.; Qi, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, X.; Tang, X.; Zhan, Q.; Zhao, Y.; et al. Identifying plasma biomarkers with high specificity for major depressive disorder: A multi-level proteomics study. J. Affect. Disord. 2020, 277, 620–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lint, T.F.; Zeitz, H.J.; Gewurz, H. Inherited deficiency of the ninth component of complement in man. J. Immunol. 1980, 125, 2252–2257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goetzl, E.J.; Schwartz, J.B.; Abner, E.L.; Jicha, G.A.; Kapogiannis, D. High complement levels in astrocyte-derived exosomes of Alzheimer disease. Ann. Neurol. 2018, 83, 544–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winston, C.N.; Goetzl, E.J.; Schwartz, J.B.; Elahi, F.M.; Rissman, R.A. Complement protein levels in plasma astrocyte-derived exosomes are abnormal in conversion from mild cognitive impairment to Alzheimer’s disease dementia. Alzheimers Dement. 2019, 11, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, H.; Pang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Qin, W.; Wei, C.; Li, Y.; Li, T.; Li, F.; Wang, Q.; Li, Y.; et al. Proteomic profiling of circulating plasma exosomes reveals novel biomarkers of Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Res. Ther. 2022, 14, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovacs, D.M. Alpha2-macroglobulin in late-onset Alzheimer’s disease. Exp. Gerontol. 2000, 35, 473–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovacs, D.M.; Blacker, D.; Wilcox, M.A.; Laird, N.M.; Rodes, L.; Horvath, S.M.; Go, R.C.; Perry, R.; Watson, B.; Bassett, S.S.; et al. Alpha-2 macroglobulin is genetically associated with Alzheimer disease. Nat. Genet. 1998, 19, 357–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandooren, J.; Itoh, Y. Alpha-2-Macroglobulin in inflammation, immunity and infections. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 803244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Jiang, L.; Rui, L. Identification of MUP1 as a regulator for glucose and lipid metabolism in mice. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 11152–11159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, M.; Vécsei, L. From Lab to Life: Exploring Cutting-Edge Models for Neurological and Psychiatric Disorders. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, M.; Chen, C. Towards a mechanistic understanding of depression, anxiety, and their comorbidity: Perspectives from cognitive neuroscience. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2023, 17, 1268156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czéh, B.; Fuchs, E.; Wiborg, O.; Simon, M. Animal models of major depression and their clinical implications. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2016, 64, 293–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Ge, H.; Sun, M.; Gao, Y. Selecting an appropriate animal model of depression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Losers | Winners | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Before | 27.4 ± 0.42 | 27.8 ± 0.33 | ns |
| After | 28.9 ± 0.32 | 30.2 ± 0.39 | p < 0.05 |
| p < 0.001 | p < 0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Smagin, D.A.; Bezryadnov, D.V.; Zavialova, M.G.; Abramova, A.Y.; Pertsov, S.S.; Kudryavtseva, N.N. Blood Plasma Markers in Depressed Mice under Chronic Social Defeat Stress. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 1485. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12071485
Smagin DA, Bezryadnov DV, Zavialova MG, Abramova AY, Pertsov SS, Kudryavtseva NN. Blood Plasma Markers in Depressed Mice under Chronic Social Defeat Stress. Biomedicines. 2024; 12(7):1485. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12071485
Chicago/Turabian StyleSmagin, Dmitry A., Dmitry V. Bezryadnov, Maria G. Zavialova, Anastasia Yu. Abramova, Sergey S. Pertsov, and Natalia N. Kudryavtseva. 2024. "Blood Plasma Markers in Depressed Mice under Chronic Social Defeat Stress" Biomedicines 12, no. 7: 1485. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12071485
APA StyleSmagin, D. A., Bezryadnov, D. V., Zavialova, M. G., Abramova, A. Y., Pertsov, S. S., & Kudryavtseva, N. N. (2024). Blood Plasma Markers in Depressed Mice under Chronic Social Defeat Stress. Biomedicines, 12(7), 1485. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12071485







