Associations between Serum Iron Indices and Self-Assessed Multiple Intelligence Scores among Adolescents in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia
Abstract
1. Introduction
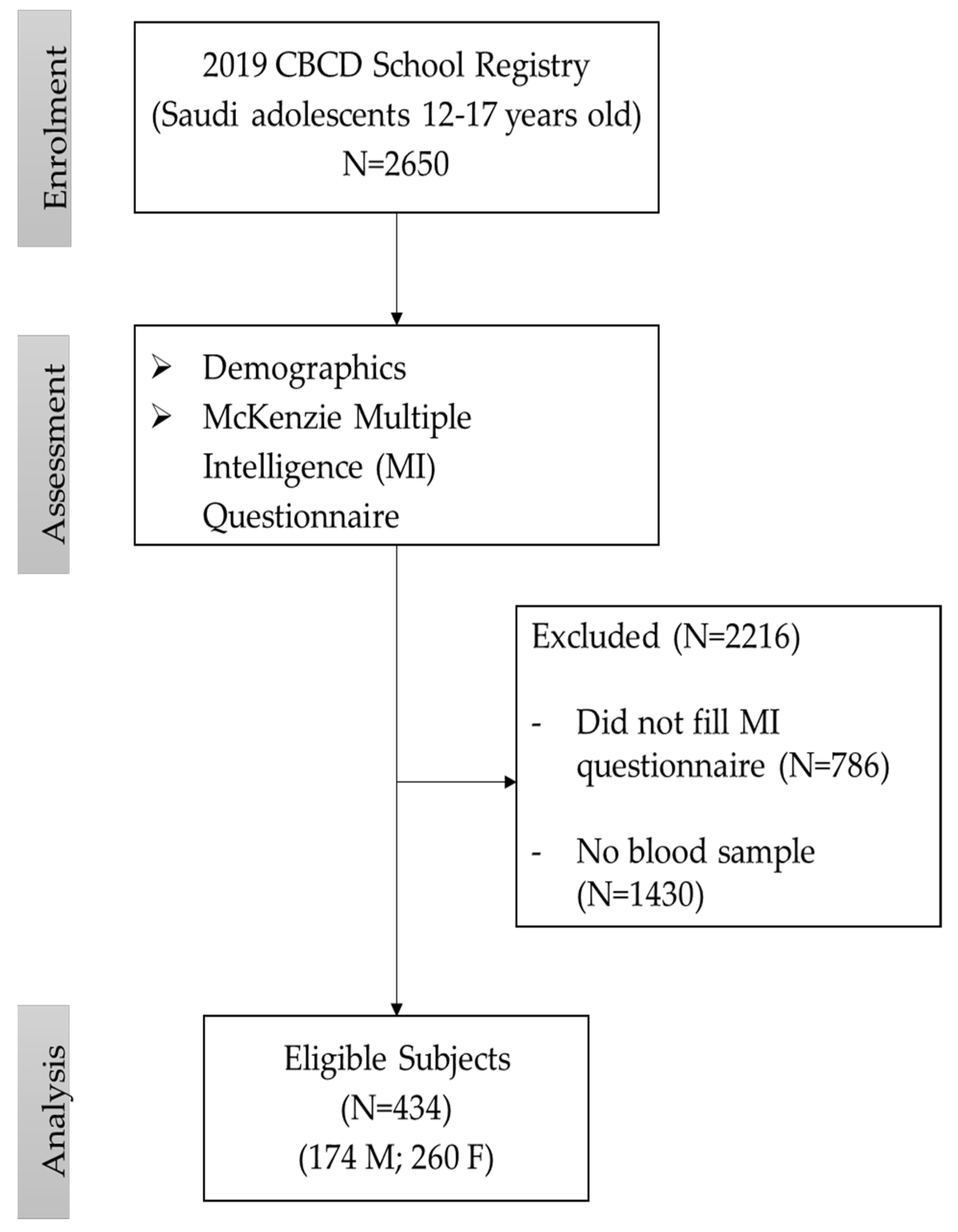
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Participants
2.2. Questionnaire Data
2.3. Biochemical Parameters
2.4. Power Calculation and Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Clinical Characteristics and MI Scores in Study Participants
3.2. Comparison of MI Scores between Genders
3.3. Correlation Analysis of Serum Iron and Transferrin Saturation Levels with Other Parameters
3.4. Association of Serum Iron Levels with MI Scores for All Participants
3.5. Association of Serum Iron Levels with MI Scores According to TSAT Levels
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jáuregui-Lobera, I. Iron deficiency and cognitive functions. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2014, 10, 2087–2095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiley, J.; Jee, B. Cognition: Overview and recent trends. Learn. Cogn. Educ. 2011, 3–8. Available online: https://books.google.com.sa/books?hl=en&lr=&id=j-loT41ln34C&oi=fnd&pg=PA3&dq=2.%09Wiley,+J.%3B+Jee,+B.+Cognition:+Overview+and+recent+trends.+Learn.+Cogn.+Educ.+2011,+3%E2%80%938&ots=UTNh4SHziL&sig=APjvCJRy3ZW81s-0o7oSv79Nojc&redir_esc=y#v=onepage&q&f=false (accessed on 8 December 2021).
- Beard, J. One person’s view of iron deficiency, development, and cognitive function. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1995, 62, 709–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kretchmer, N.; Beard, J.L.; Carlson, S. The role of nutrition in the development of normal cognition. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1996, 63, S997–S1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lozoff, B. Early iron deficiency has brain and behavior effects consistent with dopaminergic dysfunction. J. Nutr. 2011, 141, 740S–746S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamura, T.; Goldenberg, R.L.; Hou, J.; Johnston, K.E.; Cliver, S.P.; Ramey, S.L.; Nelson, K.G. Cord serum ferritin concentrations and mental and psychomotor development of children at five years of age. J. Pediatr. 2002, 140, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benton, D.; ILSI Europe a.i.s.b.l. Micronutrient status, cognition and behavioral problems in childhood. Eur. J. Nutr. 2008, 47, 38–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCann, S.; Perapoch Amadó, M.; Moore, S.E. The role of iron in brain development: A systematic review. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Möller, H.E.; Bossoni, L.; Connor, J.R.; Crichton, R.R.; Does, M.D.; Ward, R.J.; Zecca, L.; Zucca, F.A.; Ronen, I. Iron, myelin, and the brain: Neuroimaging meets neurobiology. Trends Neurosci. 2019, 42, 384–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izquierdo-Álvarez, S.; Urrechaga-Igartua, E.; Llorente-Ballesteros, M.T.; Escanero, J.F. The Role of Iron and Other Trace Elements on Mental Development and Cognitive Function. Psychiatry Neurosci. Update Bridg. Divid. 2015, 157–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarthy, R.C.; Kosman, D.J. Iron transport across the blood–brain barrier: Development, neurovascular regulation and cerebral amyloid angiopathy. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2015, 72, 709–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, D.C.; Angulo-Barroso, R.M.; Li, M.; Bian, Y.; Sturza, J.; Richards, B.; Lozoff, B. Timing, duration, and severity of iron deficiency in early development and motor outcomes at 9 months. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 72, 332–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faa, G.; Marcialis, M.; Ravarino, A.; Piras, M.; Pintus, M.; Fanos, V. Fetal programming of the human brain: Is there a link with insurgence of neurodegenerative disorders in adulthood? Curr. Med. Chem. 2014, 21, 3854–3876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Hussaini, A.A.; Alshehry, Z.; AlDehaimi, A.; Bashir, M.S. Vitamin D and iron deficiencies among Saudi children and adolescents: A persistent problem in the 21: St: Century. Saudi J. Gastroenterol. 2022, 28, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abalkhail, B.; Shawky, S. Prevalence of daily breakfast intake, iron deficiency anaemia and awareness of being anaemic among Saudi school students. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2002, 53, 519–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owaidah, T.; Al-Numair, N.; Al-Suliman, A.; Zolaly, M.; Hasanato, R.; Al Zahrani, F.; Albalawi, M.; Bashawri, L.; Siddiqui, K.; Alalaf, F. Iron deficiency and iron deficiency anemia are common epidemiological conditions in Saudi Arabia: Report of the national epidemiological survey. Anemia 2020, 2020, 6642568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ackerman, P.L.; Beier, M.E.; Boyle, M.O. Working memory and intelligence: The same or different constructs? Psychol. Bull. 2005, 131, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gardner, H. Developmental psychology after Piaget. An approach in terms of symbolization. Hum. Dev. 1979, 22, 73–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Daghri, N.M.; Wani, K.; Khattak, M.N.; Alnaami, A.M.; Amer, O.E.; Aljohani, N.J.; Hameidi, A.; Alfawaz, H.; Alharbi, M.; Sabico, S. Cardiometabolic Effects of a 12-Month, COVID-19 Lockdown-Interrupted Lifestyle Education Program for Arab Adolescents. Front. Pediatr. 2022, 10, 887138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Daghri, N.M.; Amer, O.E.; Hameidi, A.; Alfawaz, H.; Alharbi, M.; Khattak, M.N.; Alnaami, A.M.; Aljohani, N.J.; Alkhaldi, G.; Wani, K. Effects of a 12-Month Hybrid (In-Person+ Virtual) Education Program in the Glycemic Status of Arab Youth. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Daghri, N.; Aljohani, N.; Al-Attas, O.; Al-Saleh, Y.; Alnaami, A.; Sabico, S.; Amer, O.; Alharbi, M.; Kumar, S.; Alokail, M. Comparisons in childhood obesity and cardiometabolic risk factors among urban Saudi Arab adolescents in 2008 and 2013. Child Care Health Dev. 2016, 42, 652–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKenzie, W. Multiple Intelligences Survey. Available online: http://surfaquarium.com/MI/MIinvent.htm (accessed on 8 December 2021).
- Metwally, A.S.M.; Yakout, S.M.; Khattak, M.N.; Alkhaldi, G.; Al-Daghri, N.M. Vitamin D Status and Its Association with Multiple Intelligence among Arab Adolescents. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 13036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karpagavalli, K. An Open Clinical Study on Paandu Noi (Iron Deficiency Anemia); Government Siddha Medical College: Chennai, India, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- El-Hawy, M.A.; Abd Al-Salam, S.A.; Bahbah, W.A. Comparing oral iron bisglycinate chelate, lactoferrin, lactoferrin with iron and iron polymaltose complex in the treatment of children with iron deficiency anemia. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2021, 46, 367–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rohr, M.; Brandenburg, V.; Brunner-La Rocca, H.-P. How to diagnose iron deficiency in chronic disease: A review of current methods and potential marker for the outcome. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2023, 28, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buczyłowska, D.; Ronniger, P.; Melzer, J.; Petermann, F. Sex similarities and differences in intelligence in children aged two to eight: Analysis of SON-R 2–8 scores. J. Intell. 2019, 7, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahzada, G.; Khan, U.A.; Ghazi, S.R.; Hayat, Y. Gender Differences in Self-estimated Multiple Intelligences Among Secondary School Students. Pak. J. Psychol. Res. 2015, 30, 81–94. [Google Scholar]
- Aydemir, H.; Karalı, Y. Study of secondary school students’ multiple intelligence areas (Malatya case). Procedia-Soc. Behav. Sci. 2014, 152, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhillon, S.K. Emotional intelligence: A comparative study on age and gender differences. Int. J. Basic Appl. Res. 2018, 8, 670–681. [Google Scholar]
- Lando-King, E.; McRee, A.-L.; Gower, A.L.; Shlafer, R.J.; McMorris, B.J.; Pettingell, S.; Sieving, R.E. Relationships between social-emotional intelligence and sexual risk behaviors in adolescent girls. J. Sex Res. 2015, 52, 835–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobs, J.E.; Lanza, S.; Osgood, D.W.; Eccles, J.S.; Wigfield, A. Changes in children’s self-competence and values: Gender and domain differences across grades one through twelve. Child Dev. 2002, 73, 509–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamson, D.K.; Roes, M.M.; Galea, L.A. Sex hormones and cognition: Neuroendocrine influences on memory and learning. Compr. Physiol. 2016, 6, 1295–1337. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Janowsky, J.S.; Chavez, B.; Zamboni, B.D.; Orwoll, E. The cognitive neuropsychology of sex hormones in men and women. In Gonadal Hormones and Sex Differences in Behavior; Psychology Press: London, UK, 2014; pp. 421–440. [Google Scholar]
- Reilly, D.; Neumann, D.L.; Andrews, G. Gender differences in self-estimated intelligence: Exploring the male hubris, female humility problem. Front. Psychol. 2022, 13, 812483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, L.; Kong, F.; Luo, Y.; Zeng, S.; Lan, J.; You, X. Gender differences in large-scale and small-scale spatial ability: A systematic review based on behavioral and neuroimaging research. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hooshyar, F.; Afghari, A.; Hadian, B. Vulnerability of Multiple Intelligences Assessment Instrumentation to Gender Variance in EFL Context. Iran. J. Engl. Acad. Purp. 2019, 8, 77–92. [Google Scholar]
- GréGoire, J. Intellectual differences between boys and girls, 35 years of evolution between WISC-R and WISC-V. ANAE 2020, 169, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Moschonis, G.; Papandreou, D.; Mavrogianni, C.; Giannopoulou, A.; Damianidi, L.; Malindretos, P.; Lionis, C.; Chrousos, G.P.; Manios, Y. Association of iron depletion with menstruation and dietary intake indices in pubertal girls: The healthy growth study. BioMed Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 423263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akramipour, R.; Rezaei, M.; Rahimi, Z. Prevalence of iron deficiency anemia among adolescent schoolgirls from Kermanshah, Western Iran. Hematology 2008, 13, 352–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mesías, M.; Seiquer, I.; Navarro, M.P. Iron nutrition in adolescence. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2013, 53, 1226–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munro, M.G.; Mast, A.E.; Powers, J.M.; Kouides, P.A.; O’Brien, S.H.; Richards, T.; Lavin, M.; Levy, B.S. The relationship between heavy menstrual bleeding, iron deficiency, and iron deficiency anemia. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2023, 229, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, L.A.; Rodriguez, G.; Fleta, J.; Bueno-Lozano, M.; Lazaro, A.; Bueno, G. Trends of dietary habits in adolescents. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2010, 50, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cepeda-Lopez, A.C.; Aeberli, I.; Zimmermann, M.B. Does obesity increase risk for iron deficiency? A review of the literature and the potential mechanisms. Int. J. Vitam. Nutr. Res. 2010, 80, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hutchinson, C. A review of iron studies in overweight and obese children and adolescents: A double burden in the young? Eur. J. Nutr. 2016, 55, 2179–2197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tussing-Humphreys, L.; Pustacioglu, C.; Nemeth, E.; Braunschweig, C. Rethinking iron regulation and assessment in iron deficiency, anemia of chronic disease, and obesity: Introducing hepcidin. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2012, 112, 391–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alshwaiyat, N.M.; Ahmad, A.; Wan Hassan, W.M.R.; Al-Jamal, H.A.N. Association between obesity and iron deficiency. Exp. Ther. Med. 2021, 22, 1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tucker-Drob, E.M.; Briley, D.A. Continuity of genetic and environmental influences on cognition across the life span: A meta-analysis of longitudinal twin and adoption studies. Psychol. Bull. 2014, 140, 949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richmond, S.; Johnson, K.A.; Seal, M.L.; Allen, N.B.; Whittle, S. Development of brain networks and relevance of environmental and genetic factors: A systematic review. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2016, 71, 215–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Yang, H.; Wang, D.; Sudfeld, C.R.; Zhao, A.; Xin, Y.; Chen, J.C.; Fawzi, W.W.; Xing, Y.; Li, Z. Effect of Oral Iron Supplementation on Cognitive Function among Children and Adolescents in Low-and Middle-Income Countries: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2022, 14, 5332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutema, B.T.; Sorrie, M.B.; Megersa, N.D.; Yesera, G.E.; Yeshitila, Y.G.; Pauwels, N.S.; De Henauw, S.; Abbeddou, S. Effects of iron supplementation on cognitive development in school-age children: Systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0287703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samson, K.L.; Fischer, J.A.; Roche, M.L. Iron status, anemia, and iron interventions and their associations with cognitive and academic performance in adolescents: A systematic review. Nutrients 2022, 14, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlson, E.S.; Stead, J.D.; Neal, C.R.; Petryk, A.; Georgieff, M.K. Perinatal iron deficiency results in altered developmental expression of genes mediating energy metabolism and neuronal morphogenesis in hippocampus. Hippocampus 2007, 17, 679–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todorich, B.; Pasquini, J.M.; Garcia, C.I.; Paez, P.M.; Connor, J.R. Oligodendrocytes and myelination: The role of iron. Glia 2009, 57, 467–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grubić Kezele, T.; Ćurko-Cofek, B. Age-related changes and sex-related differences in brain iron metabolism. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Parameters | All | Boys | Girls | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | 434 (100.0) | 174 (40.1) | 260 (59.9) | |
| Age (years) | 14.7 ± 1.5 | 14.9 ± 1.5 | 14.5 ± 1.5 | 0.02 |
| Weight (kg) | 56.3 ± 17.1 | 61.1 ± 19.7 | 53.1 ± 14.3 | <0.001 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 23.3 ± 7.3 | 23.6 ± 6.4 | 23.1 ± 7.8 | 0.49 |
| Waist (cm) | 71.1 ± 17.3 | 69.2 ± 22.7 | 72.4 ± 12.5 | 0.06 |
| Hips (cm) | 86.6 ± 19.8 | 79.3 ± 26.5 | 91.4 ± 11.6 | <0.001 |
| WHR | 0.82 ± 0.11 | 0.86 ± 0.11 | 0.79 ± 0.11 | <0.001 |
| Systolic BP (mmHg) | 117.9 ± 14.9 | 118.4 ± 14.5 | 117.5 ± 15.4 | 0.52 |
| Diastolic BP (mmHg) | 71.4 ± 11.8 | 66.4 ± 9.7 | 74.6 ± 11.9 | <0.001 |
| Glucose (mmol/L) | 5.22 ± 0.6 | 5.32 ± 0.6 | 5.16 ± 0.6 | 0.008 |
| T-Cholesterol (mmol/L) | 4.39 ± 0.7 | 4.33 ± 0.7 | 4.44 ± 0.7 | 0.14 |
| HDL-Cholesterol (mmol/L) | 1.02 ± 0.2 | 1.02 ± 0.2 | 1.01 ± 0.2 | 0.61 |
| Triglycerides (mmol/L) | 0.95 (0.8–1.3) | 1.04 (0.8–1.4) | 0.91 (0.7–1.2) | 0.02 |
| Iron (μmol/L) | 16.76 (12.4–21.8) | 17.86 (15.4–23.3) | 15.39 (11.2–20.8) | <0.001 |
| Transferrin (mg/dL) | 301.76 (166.8–377.2) | 310.00 (217.3–378.1) | 239.30 (66.8–368.4) | 0.002 |
| TIBC (µg/dL) | 430.96 (262.4–525.3) | 441.34 (325.4–526.4) | 352.83 (137.3–514.2) | 0.002 |
| TSAT (%) | 25.17 (16.4–40.9) | 25.17 (17.4–38.9) | 25.28 (14.9–53.9) | 0.646 |
| TSAT (≤20%) | 37.7 | 36.8 | 38.7 | 0.771 |
| MI scores (9 categories) | ||||
| Logical | 2.49 ± 0.9 | 2.28 ± 0.9 | 2.63 ± 0.9 | <0.001 |
| Musical | 2.77 ± 0.9 | 2.80 ± 1.1 | 2.75 ± 0.9 | 0.56 |
| Naturalist | 2.63 ± 0.9 | 2.55 ± 0.9 | 2.68 ± 0.8 | 0.13 |
| Linguistic | 2.58 ± 0.9 | 2.50 ± 0.9 | 2.64 ± 0.8 | 0.09 |
| Social | 2.49 ± 0.9 | 2.33 ± 0.9 | 2.60 ± 0.8 | 0.001 |
| Kinesthetic | 2.46 ± 0.9 | 2.33 ± 0.9 | 2.54 ± 0.9 | 0.02 |
| Spatial | 2.53 ± 0.9 | 2.43 ± 0.9 | 2.60 ± 0.9 | 0.06 |
| Interpersonal | 2.25 ± 0.8 | 2.11 ± 0.9 | 2.34 ± 0.8 | 0.006 |
| Existential | 2.45 ± 0.9 | 2.37 ± 1.0 | 2.51 ± 0.9 | 0.133 |
| MI scores (3 domains) | ||||
| Analytical | 2.63 ± 0.8 | 2.54 ± 0.9 | 2.69 ± 0.8 | 0.08 |
| Interactive | 2.51 ± 0.8 | 2.38 ± 0.9 | 2.59 ± 0.8 | 0.01 |
| Introspective | 2.41 ± 0.8 | 2.30 ± 0.9 | 2.48 ± 0.8 | 0.03 |
| Total MI | 2.52 ± 0.8 | 2.41 ± 0.9 | 2.59 ± 0.7 | 0.02 |
| MI Categories | Boys | Girls | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unadjusted | Adjusted with Age and BMI | ||||
| OR (95% CI) | p | OR (95% CI) | p | ||
| Logical | Ref | 1.56 (1.25–1.96) | <0.001 | 1.57 (1.25–1.97) | <0.001 |
| Musical | Ref | 0.94 (0.78–1.45) | 0.56 | 0.90 (0.74–1.10) | 0.32 |
| Naturalist | Ref | 1.18 (0.95–1.47) | 0.12 | 1.17 (0.94–1.46) | 0.16 |
| Linguistic | Ref | 1.21 (0.96–1.51) | 0.09 | 1.22 (0.97–1.54) | 0.09 |
| Social | Ref | 1.45 (1.15–1.82) | 0.001 | 1.44 (1.14–1.82) | 0.002 |
| Kinesthetic | Ref | 1.27 (1.03–1.57) | 0.022 | 1.27 (1.03–1.58) | 0.03 |
| Spatial | Ref | 1.22 (0.99–1.50) | 0.06 | 1.19 (0.96–1.48) | 0.11 |
| Interpersonal | Ref | 1.42 (1.11–1.82) | 0.005 | 1.37 (1.10–1.76) | 0.01 |
| Existential | Ref | 1.17 (0.95–1.43) | 0.13 | 1.14 (0.93–1.40) | 0.2 |
| MI domains | |||||
| Analytical | Ref | 1.23 (0.98–1.56) | 0.08 | 1.21 (0.94–1.53) | 0.12 |
| Interactive | Ref | 1.35 (1.07–1.71) | 0.01 | 1.36 (1.07–1.73) | 0.01 |
| Introspective | Ref | 1.29 (1.03–1.63) | 0.03 | 1.26 (0.99–1.59) | 0.06 |
| Total MI | Ref | 1.33 (1.04–1.69) | 0.02 | 1.31 (1.02–1.67) | 0.035 |
| Parameters | Iron | TSAT | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| All | Boys | Females | All | Boys | Females | |
| Age | −0.1 | 0.03 | −0.22 ** | −0.01 | 0.09 | −0.08 |
| BMI | −0.11 * | −0.1 | −0.14 * | 0.02 | 0.08 | −0.01 |
| Waist | −0.13 ** | −0.05 | −0.19 ** | 0.07 | 0.19 * | −0.13 |
| Hips | −0.18 ** | −0.04 | −0.23 ** | 0.13 * | 0.20 * | 0.01 |
| WHR | 0.07 | 0.06 | −0.03 | |||
| Systolic BP | −0.05 | −0.02 | −0.07 | 0.09 | 0.19 * | 0.01 |
| Diastolic BP | −0.05 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.08 | 0.19 * | −0.02 |
| Glucose | 0.01 | −0.1 | 0.02 | 0.14 * | 0.16 | 0.23 * |
| T-Cholesterol | 0.16 ** | 0.13 | 0.21 ** | 0.09 | 0.07 | 0.11 |
| HDL-Cholesterol (mmol/L) | −0.05 | −0.06 | −0.06 | 0.07 | −0.06 | 0.16 |
| Triglycerides | 0.28 ** | 0.26 ** | 0.27 ** | 0.12 | 0.18 * | 0.09 |
| MI categories | ||||||
| Logical | −0.03 | 0.07 | −0.02 | 0.04 | 0.16 | −0.09 |
| Musical | 0.04 | −0.01 | 0.07 | 0.06 | 0.12 | −0.01 |
| Naturalist | −0.01 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.05 | 0.14 | −0.05 |
| Linguistic | −0.04 | 0.02 | −0.03 | 0.04 | 0.18 * | −0.11 |
| Social | −0.03 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.05 | 0.16 | −0.06 |
| Kinesthetic | −0.05 | 0.02 | −0.1 | 0.06 | 0.21 * | −0.1 |
| Spatial | −0.02 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.05 | 0.17 | −0.07 |
| Interpersonal | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.1 | 0.03 | 0.12 | −0.09 |
| Existential | 0.01 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 0.06 | 0.22 * | −0.09 |
| MI Domains | ||||||
| Analytical | 0.01 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.05 | 0.15 | −0.05 |
| Interactive | −0.04 | 0.02 | −0.03 | 0.05 | 0.19 * | −0.1 |
| Introspective | −0.01 | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.05 | 0.18 * | −0.09 |
| Total MI | −0.02 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.05 | 0.18 * | −0.08 |
| Unadjusted | Adjusted for Age and BMI | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MI Categories | β (95%CI) | p | β (95%CI) | p |
| Logical | −0.15 (−0.9, 0.6) | 0.70 | −0.08 (−0.9, 0.7) | 0.84 |
| Musical | 0.26 (−0.5, 1.0) | 0.47 | 0.38 (−0.3, 1.1) | 0.30 |
| Naturalist | −0.03 (−0.8, 0.8) | 0.94 | 0.05 (−0.8, 0.9) | 0.88 |
| Linguistic | −0.18 (−1, 0.7) | 0.66 | −0.04 (−0.9, 0.8) | 0.92 |
| Social | −0.12 (−1, 0.7) | 0.78 | −0.004 (−0.8, 0.8) | 0.99 |
| Kinesthetic | −0.27 (−1, 0.5) | 0.49 | −0.15 (−0.9, 0.6) | 0.70 |
| Spatial | −0.09 (−0.9, 0.7) | 0.83 | 0.05 (−0.7, 0.8) | 0.89 |
| Interpersonal | 0.21 (−0.7, 1.1) | 0.64 | 0.22 (−0.7, 1.1) | 0.62 |
| Existential | 0.05 (−0.7, 0.8) | 0.89 | 0.12 (−0.6, 0.9) | 0.75 |
| MI domains | ||||
| Analytical | 0.06 (−0.8, 0.9) | 0.89 | 0.17 (−0.7, 1) | 0.69 |
| Interactive | −0.22 (−1.1, 0.6) | 0.61 | −0.08 (−1, 0.8) | 0.86 |
| Introspective | 0.05 (−0.8, 0.9) | 0.91 | 0.14 (−0.7, 1.0) | 0.74 |
| Total MI | −0.06 (−0.9, 0.8) | 0.89 | 0.06 (−0.8, 1.0) | 0.89 |
| MI Categories | TSAT ≤ 20% | TSAT > 20% | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| All Subjects (434) | Boys (174) | Girls (260) | |||||||||||
| Unadjusted | Adjusted for Age and BMI | Unadjusted | Adjusted for Age and BMI | Unadjusted | Adjusted for Age and BMI | ||||||||
| OR (95% CI) | p | OR (95% CI) | p | OR (95% CI) | p | OR (95% CI) | p | OR (95% CI) | p | OR (95% CI) | p | ||
| Logical | Ref | 1.01 (0.8, 1.3) | 0.92 | 1.03 (0.8, 1.3) | 0.82 | 1.39 (0.9, 2.1) | 0.081 | 1.44 (0.9, 2.1) | 0.06 | 0.71 (0.5, 1.1) | 0.10 | 0.72 (0.5, 1.1) | 0.72 |
| Musical | Ref | 1.25 (0.7, 1.6) | 0.07 | 1.27 (0.9, 1.6) | 0.05 | 1.52 (1.1, 2.1) | 0.011 | 1.59 (1.1, 2.2) | 0.006 | 0.93 (0.6, 1.4) | 0.73 | 0.94 (0.6, 1.4) | 0.77 |
| Naturalist | Ref | 1.07 (0.8, 1.4) | 0.60 | 1.09 (0.8, 1.4) | 0.52 | 1.32 (0.9, 1.8) | 0.115 | 1.36 (0.9, 1.9) | 0.08 | 0.81 (0.5, 1.2) | 0.80 | 0.82 (0.5, 1.3) | 0.38 |
| Linguistic | Ref | 1.08 (0.8, 1.4) | 0.57 | 1.11 (0.8, 1.4) | 0.50 | 1.51 (1.1, 2.2) | 0.024 | 1.57 (1.1, 2.3) | 0.02 | 0.66 (0.4, 1.1) | 0.66 | 0.68 (0.4, 1.1) | 0.10 |
| Social | Ref | 1.11 (0.9, 1.4) | 0.42 | 1.14 (0.9, 1.5) | 0.35 | 1.39 (0.9, 2.1) | 0.076 | 1.44 (0.9, 2.1) | 0.06 | 0.86 (0.6, 1.3) | 0.86 | 0.89 (0.6, 1.4) | 0.60 |
| Kinesthetic | Ref | 1.14 (0.9, 1.5) | 0.30 | 1.16 (0.9, 1.5) | 0.25 | 1.45 (1.1, 2.1) | 0.033 | 1.48 (1.1, 2.1) | 0.02 | 0.84 (0.6, 1.2) | 0.39 | 0.87 (0.6, 1.3) | 0.51 |
| Spatial | Ref | 1.11 (0.9, 1.4) | 0.45 | 1.12 (0.9, 1.4) | 0.37 | 1.38 (0.9, 1.9) | 0.056 | 1.45 (1.1, 2.1) | 0.03 | 0.81 (0.5, 1.2) | 0.30 | 0.84 (0.6, 1.3) | 0.39 |
| Interpersonal | Ref | 1.03 (0.8, 1.4) | 0.84 | 1.04 (0.8, 1.4) | 0.77 | 1.35 (0.9, 1.9) | 0.123 | 1.39 (0.9, 2.1) | 0.09 | 0.71 (0.4, 1.1) | 0.15 | 0.73 (0.5, 1.2) | 0.72 |
| Existential | Ref | 1.12 (0.9, 1.4) | 0.37 | 1.13 (0.9, 1.4) | 0.32 | 1.49 (1.1, 2.1) | 0.021 | 1.56 (1.1, 2.2) | 0.01 | 0.77 (0.5, 1.1) | 0.20 | 0.79 (0.5, 1.2) | 0.26 |
| MI domains | |||||||||||||
| Analytical | Ref | 1.13 (0.9, 1.5) | 0.36 | 1.16 (0.9, 1.5) | 0.30 | 1.49 (1.1, 2.2) | 0.032 | 1.56 (1.1, 2.3) | 0.02 | 0.77 (0.5, 1.2) | 0.27 | 0.81 (0.5, 1.3) | 0.34 |
| Interactive | Ref | 1.12 (0.9, 1.5) | 0.40 | 1.14 (0.9, 1.5) | 0.34 | 1.51 (1.1, 2.2) | 0.032 | 1.55 (1.1, 2.3) | 0.02 | 0.77 (0.5, 1.2) | 0.24 | 0.79 (0.5, 1.3) | 0.33 |
| Introspective | Ref | 1.09 (0.8, 1.4) | 0.50 | 1.11 (0.9, 1.5) | 0.43 | 1.46 (1.1, 2.1) | 0.043 | 1.52 (1.1, 2.2) | 0.03 | 0.74 (0.5, 1.2) | 0.18 | 0.76 (0.5, 1.2) | 0.24 |
| Total MI | Ref | 1.12 (0.9, 1.5) | 0.41 | 1.14 (0.9, 1.5) | 0.34 | 1.51 (1.1, 2.2) | 0.032 | 1.57 (1.1, 2.3) | 0.02 | 0.75 (0.5, 1.2) | 0.22 | 0.78 (0.5, 1.2) | 0.29 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Farhan, H.A.; Al-Ghannam, F.A.A.; Wani, K.; Khattak, M.N.K.; Alnaami, A.M.; Alharbi, M.G.; Alamro, A.A.; Sabico, S.; Al-Daghri, N.M. Associations between Serum Iron Indices and Self-Assessed Multiple Intelligence Scores among Adolescents in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 1578. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12071578
Farhan HA, Al-Ghannam FAA, Wani K, Khattak MNK, Alnaami AM, Alharbi MG, Alamro AA, Sabico S, Al-Daghri NM. Associations between Serum Iron Indices and Self-Assessed Multiple Intelligence Scores among Adolescents in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia. Biomedicines. 2024; 12(7):1578. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12071578
Chicago/Turabian StyleFarhan, Hibah A., Fatimah A. A. Al-Ghannam, Kaiser Wani, Malak N. K. Khattak, Abdullah M. Alnaami, Mona G. Alharbi, Abir A. Alamro, Shaun Sabico, and Nasser M. Al-Daghri. 2024. "Associations between Serum Iron Indices and Self-Assessed Multiple Intelligence Scores among Adolescents in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia" Biomedicines 12, no. 7: 1578. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12071578
APA StyleFarhan, H. A., Al-Ghannam, F. A. A., Wani, K., Khattak, M. N. K., Alnaami, A. M., Alharbi, M. G., Alamro, A. A., Sabico, S., & Al-Daghri, N. M. (2024). Associations between Serum Iron Indices and Self-Assessed Multiple Intelligence Scores among Adolescents in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia. Biomedicines, 12(7), 1578. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12071578






