Unlocking the Therapeutic Potential of Oral Cancer Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes
Abstract
1. Background
1.1. Cancer Stem Cells: Biological Functions and Characteristics
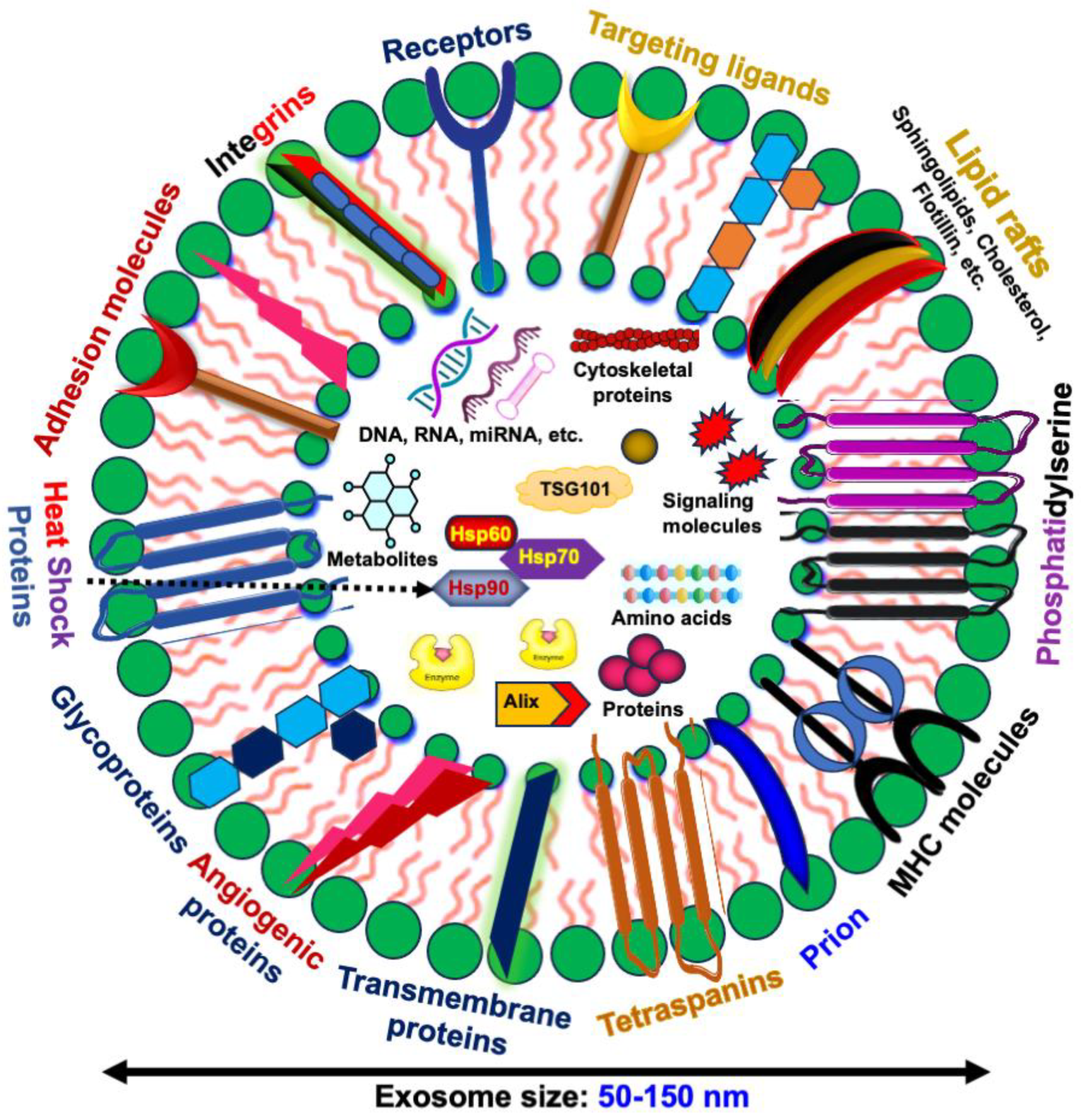
1.2. Exosomes and Their Cargo
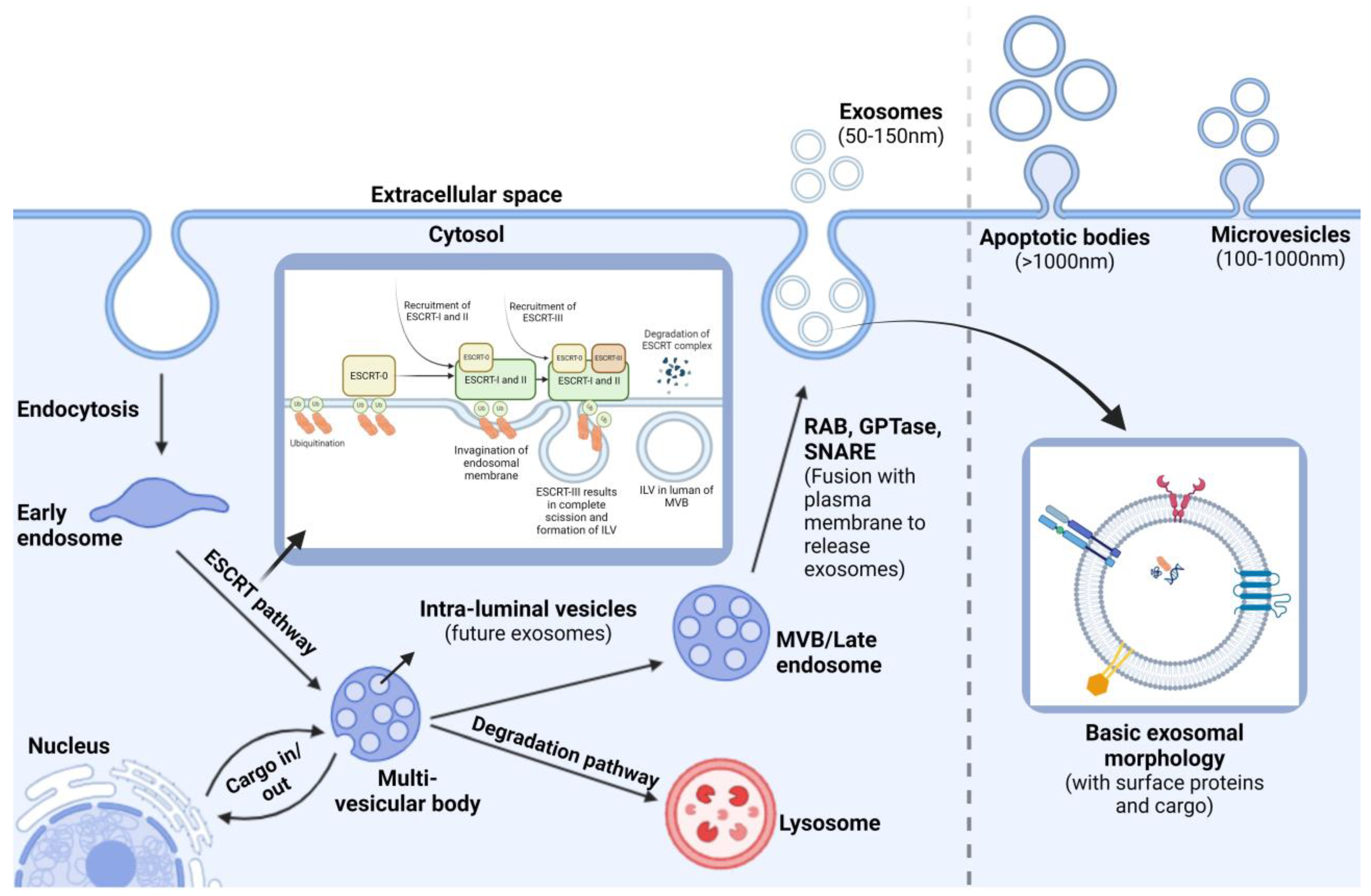
1.3. Exosome Biogenesis
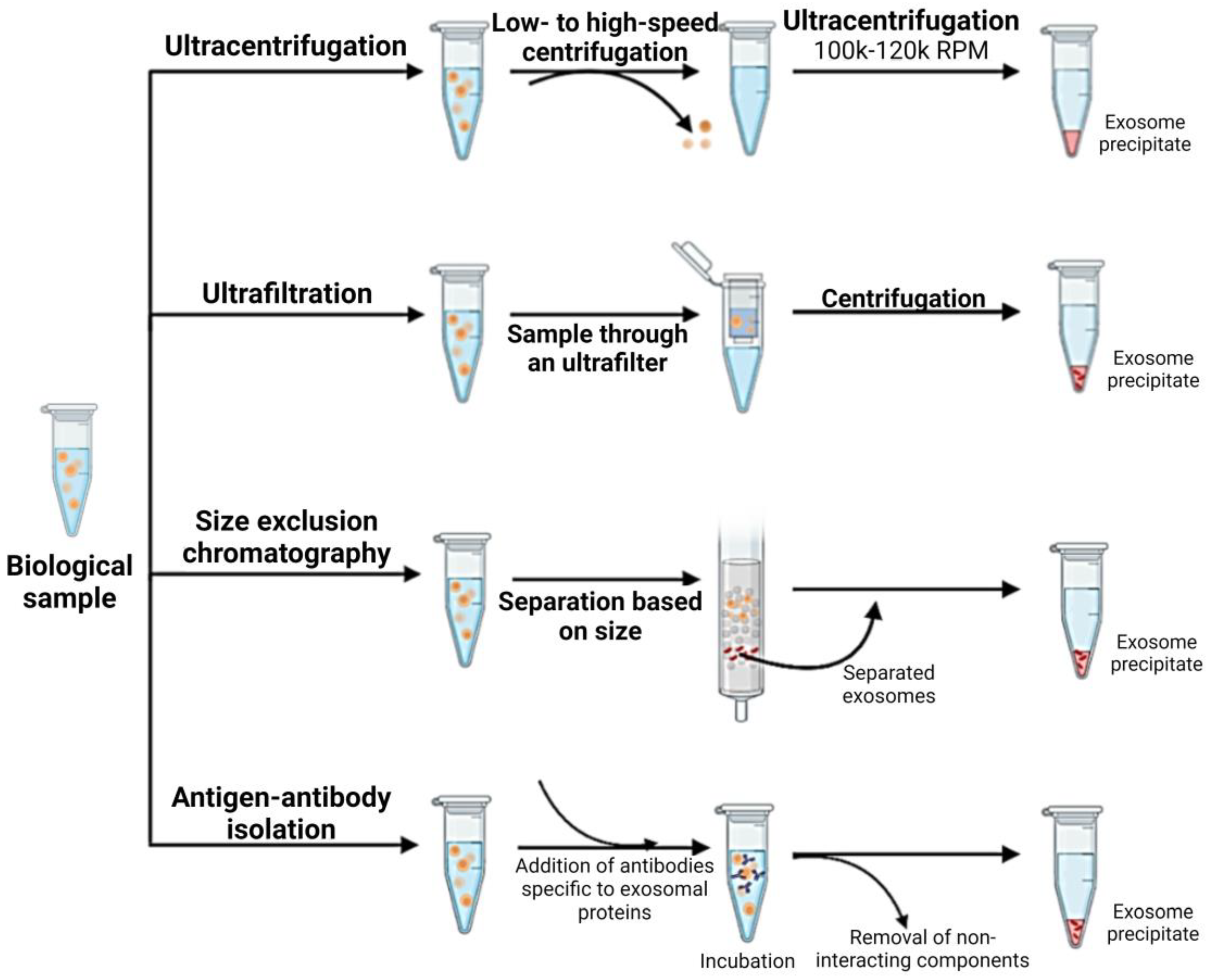
1.4. Isolation and Characterization of CSC-Derived Exosomes
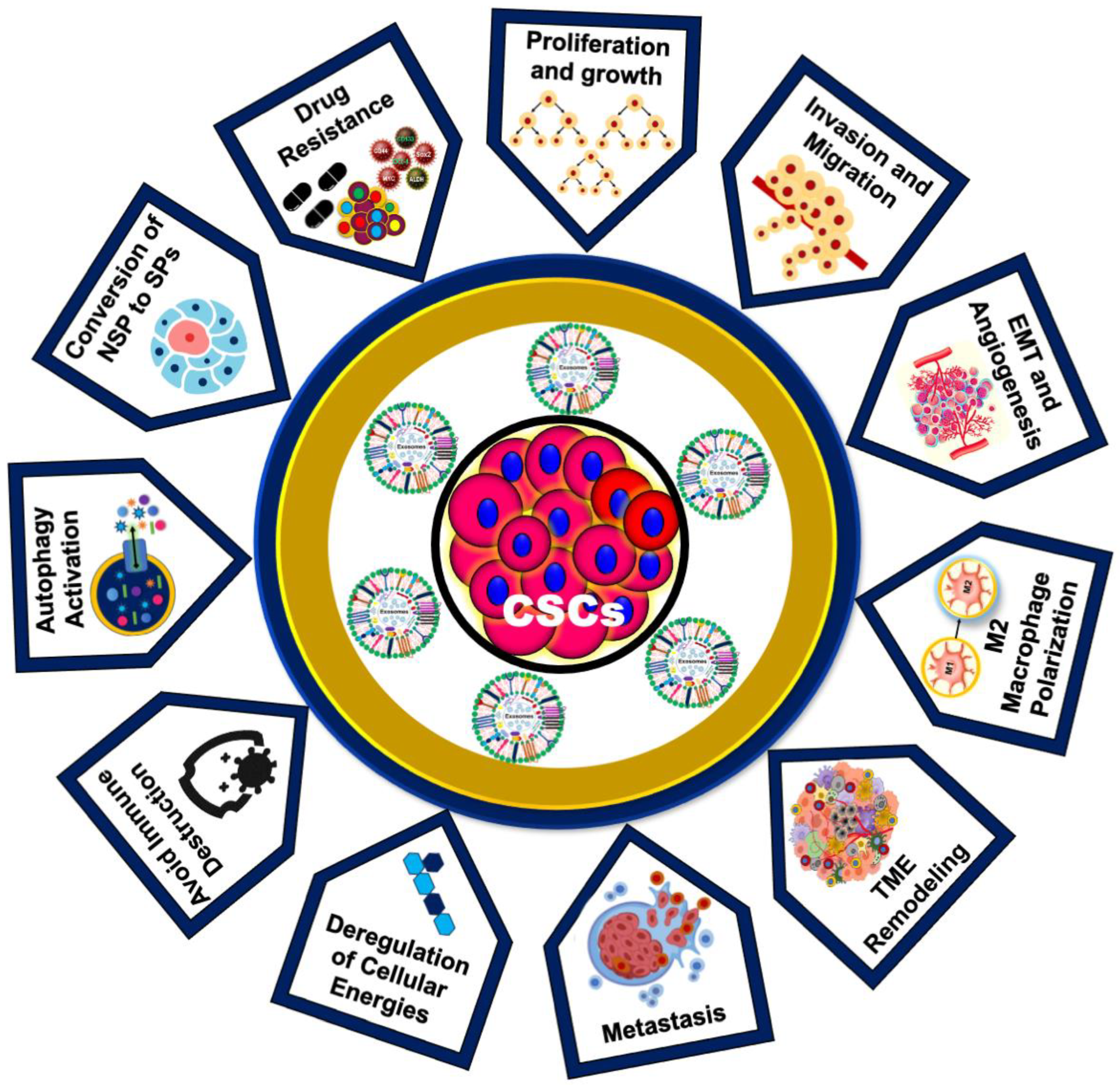
1.5. Role of CSC-Exos in Cancer Development and Drug Resistance
1.6. Emerging Roles of CSC-Exos in Oral Cancer Progression
1.7. Therapeutic Potential of CSC-Derived Exosomes
| CSC-Exo Origin | Isolation and Characterization Techniques Used | Therapeutic Potentials of CSC-Exos | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Oral cancer stem cell EVs | Exosome isolation via total exosome isolation reagent and characterization by immunofluorescence imaging | Reduction in miR-21-5p, PI3K, and STAT3, leading to tumor suppression | [132] |
| Breast cancer stem cell EVs | - | Doxorubicin delivery via CSC-derived exosomes result in a reduction in cell proliferation | [135] |
| Glioblastoma stem cell EVs | Exosome isolation was achieved by immuno-magnetic based method and characterization by TEM | The overexpression of miR-26a is associated with enhanced tumor characteristics, whereas its inhibition is associated with diminished tumorigenicity | [141] |
| Lung cancer stem cell EVs | Exosome isolation by the ultracentrifugation method | CSC-derived exosomal miR-210-3p targets FGFRL1, which may have potential as a tumor suppressor | [17] |
| Liver cancer stem cell EVs | Exosome isolation by the ultracentrifugation method | Exosomes rich in lncRNA-H19 show increased angiogenesis and may be useful as therapeutic targets | [142] |
| Pancreatic cancer stem cell EVs | Exosome isolation via ultracentrifugation and characterization by TEM and immunogold staining | Surface Glypican-1 may be useful as a biomarker for distinguishing between normal and tumor cells in pancreatic cancer | [137] |
| Pancreatic cancer stem cell EVs | - | Modified CSC-derived exosomes transfected with siRNA may potentially reduce tumor growth by targeting KRAS | [138] |
| Prostate cancer stem cell EVs | Isolation via the ExoQuick-TC isolation kit | CSC-derived exosomes containing miR-100-5p and miR-21-5p contribute to prostate cancer progression and may have potential as biomarkers | [110] |
1.8. Challenges Associated with the Clinical Translation of OCSC-Derived Exosomes
1.9. Future Perspective of OCSC-EVs as a Therapeutic Target for Cancer Treatment
2. Concluding Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- D’Cruz, A.K.; Vaish, R.; Dhar, H. Oral cancers: Current status. Oral Oncol. 2018, 87, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, X.; Wang, Z. Oral Cancer. In Pharynx-Diagnosis and Treatment; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Borse, V.; Konwar, A.N.; Buragohain, P. Oral cancer diagnosis and perspectives in India. Sens. Int. 2020, 1, 100046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gharat, S.A.; Momin, M.M.; Bhavsar, C. Oral squamous cell carcinoma: Current treatment strategies and nanotechnology-based approaches for prevention and therapy. Crit. Rev.™ Ther. Drug Carr. Syst. 2016, 33, 363–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Longley, D.B.; Harkin, D.P.; Johnston, P.G. 5-fluorouracil: Mechanisms of action and clinical strategies. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2003, 3, 330–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chi, A.C.; Day, T.A.; Neville, B.W. Oral cavity and oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma—An update. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2015, 65, 401–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Epstein, J.B.; Thariat, J.; Bensadoun, R.J.; Barasch, A.; Murphy, B.A.; Kolnick, L.; Popplewell, L.; Maghami, E. Oral complications of cancer and cancer therapy: From cancer treatment to survivorship. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2012, 62, 400–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2018. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 7–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qie, Y.; Sun, X.; Yang, Y.; Yan, T. Emerging functions and applications of exosomes in oral squamous cell carcinoma. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2023, 52, 886–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Kumar, P.; Das, B.C. HPV+ ve/−ve oral-tongue cancer stem cells: A potential target for relapse-free therapy. Transl. Oncol. 2021, 14, 100919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prince, M.; Sivanandan, R.; Kaczorowski, A.; Wolf, G.; Kaplan, M.; Dalerba, P.; Weissman, I.; Clarke, M.; Ailles, L. Identification of a subpopulation of cells with cancer stem cell properties in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 973–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, M.; Wang, J.; Pan, S.; Zheng, L.; Wang, Z.-W.; Zhu, X. Nucleic acids and proteins carried by exosomes of different origins as potential biomarkers for gynecologic cancers. Mol. Ther. Oncolyt. 2022, 24, 101–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Gao, N.; Gao, Z.; Liu, W.; Pang, B.; Dong, X.; Li, Y.; Fan, T. The emerging role of exosomes in cancer chemoresistance. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 737962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nawaz, M. Extracellular vesicle-mediated transport of non-coding RNAs between stem cells and cancer cells: Implications in tumor progression and therapeutic resistance. Stem Cell Investig. 2017, 4, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Z.-P.; Li, A.-Q.; Jia, W.-H.; Ye, S.; Van Eps, G.; Yu, J.-M.; Yang, W.-J. MicroRNA expression profiling in exosomes derived from gastric cancer stem-like cells. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 93839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; He, J.; Hu, H.; Tu, L.; Sun, Z.; Liu, Y.; Luo, F. Lung CSC-derived exosomal miR-210-3p contributes to a pro-metastatic phenotype in lung cancer by targeting FGFRL1. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 6324–6339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez-Callejo, P.; Guo, Z.; Ziglari, T.; Claudio, N.M.; Nguyen, K.H.; Oshimori, N.; Seras-Franzoso, J.; Pucci, F. Cancer stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles preferentially target MHC-II–macrophages and PD1+ T cells in the tumor microenvironment. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0279400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.; Ye, S.; Yao, Y.; Zhang, C.; Liu, W. Oral Cancer Stem Cell-Derived Small Extracellular Vesicles Promote M2 Macrophage Polarization and Suppress CD4+ T-Cell Activity by Transferring UCA1 and Targeting LAMC2. Stem Cells Int. 2022, 2022, 5817684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, W.; Zhao, M.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, J.; Xie, C.; Li, X.; Geng, S.; Zhong, C.; Fu, J.; Wu, J. Low-dose phthalates promote breast cancer stem cell properties via the oncogene ΔNp63α and the Sonic hedgehog pathway. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 252, 114605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, S.; Mitra, P.; Saha, U.; Ghosh, A.; Biswas, N.K.; Roy, S.S.; Acharya, M.; Singh, S. NOTCH-pathway inactivation reprograms oral-stem-like cancer cells to JAK-STAT dependent state and provides the opportunity of synthetic lethality. Transl. Oncol. 2022, 32, 101669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, L.; Tunger, A.; Plesca, I.; Wehner, R.; Temme, A.; Westphal, D.; Meier, F.; Bachmann, M.; Schmitz, M. Bidirectional crosstalk between cancer stem cells and immune cell subsets. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walcher, L.; Kistenmacher, A.-K.; Suo, H.; Kitte, R.; Dluczek, S.; Strauß, A.; Blaudszun, A.-R.; Yevsa, T.; Fricke, S.; Kossatz-Boehlert, U. Cancer stem cells—Origins and biomarkers: Perspectives for targeted personalized therapies. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonnet, D. Normal and leukemic CD34-negative human hematopoietic stem cells. Rev. Clin. Exp. Hematol. 2001, 5, 42–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pattabiraman, D.R.; Weinberg, R.A. Tackling the cancer stem cells—What challenges do they pose? Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2014, 13, 497–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batlle, E.; Clevers, H. Cancer stem cells revisited. Nat. Med. 2017, 23, 1124–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kakarala, M.; Wicha, M.S. Cancer stem cells: Implications for cancer treatment and prevention. Cancer J. 2007, 13, 271–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borlongan, M.C.; Saha, D.; Wang, H. Tumor microenvironment: A niche for cancer stem cell immunotherapy. Stem Cell Rev. Rep. 2024, 20, 3–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cierpikowski, P.; Lis-Nawara, A.; Bar, J. Prognostic value of WNT1, NOTCH1, PDGFRβ, and CXCR4 in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Anticancer Res. 2023, 43, 591–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komura, N.; Mabuchi, S.; Shimura, K.; Yokoi, E.; Kozasa, K.; Kuroda, H.; Takahashi, R.; Sasano, T.; Kawano, M.; Matsumoto, Y. The role of myeloid-derived suppressor cells in increasing cancer stem-like cells and promoting PD-L1 expression in epithelial ovarian cancer. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2020, 69, 2477–2499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talukdar, J.; Srivastava, T.P.; Sahoo, O.S.; Karmakar, A.; Rai, A.K.; Sarma, A.; Gogoi, G.; Alqahtani, M.S.; Abbas, M.; Dhar, R. Cancer stem cells: Signaling pathways and therapeutic targeting. MedComm–Oncol. 2023, 2, e62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Huang, L.; Lu, Y.-G.; Zheng, D.-L. Roles of the Wnt signaling pathway in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2021, 7, 590912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Shi, P.; Zhao, G.; Xu, J.; Peng, W.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, G.; Wang, X.; Dong, Z.; Chen, F. Targeting cancer stem cell pathways for cancer therapy. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2020, 5, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, S.; Stewart, K.S.; Yang, Y.; Abdusselamoglu, M.D.; Parigi, S.M.; Feinberg, T.Y.; Tumaneng, K.; Yang, H.; Levorse, J.M.; Polak, L. Ras drives malignancy through stem cell crosstalk with the microenvironment. Nature 2022, 612, 555–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scanlon, C.; Van Tubergen, E.; Inglehart, R.; D’silva, N. Biomarkers of epithelial-mesenchymal transition in squamous cell carcinoma. J. Dent. Res. 2013, 92, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, B.N.; Bhowmick, N.A. Role of EMT in metastasis and therapy resistance. J. Clin. Med. 2016, 5, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, Y.; Xiao, X.; Wang, J.; Dasari, S.; Pepin, D.; Nephew, K.P.; Zamarin, D.; Mitra, A.K. Cancer associated fibroblasts serve as an ovarian cancer stem cell niche through noncanonical Wnt5a signaling. NPJ Precis. Oncol. 2024, 8, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, M.; Hwang, J.W.; Cho, Y.; Kim, S.; Han, S.H.; Yu, J.; Ha, S.; Kim, W.-Y.; Kim, S.-N.; Kim, I.S. A novel synthetic microtubule inhibitor exerts antiproliferative effects in multidrug resistant cancer cells and cancer stem cells. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 10822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spisak, S.; Chen, D.; Likasitwatanakul, P.; Doan, P.; Li, Z.; Bala, P.; Vizkeleti, L.; Tisza, V.; De Silva, P.; Giannakis, M. Identifying regulators of aberrant stem cell and differentiation activity in colorectal cancer using a dual endogenous reporter system. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 2230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tyagi, A.; Vishnoi, K.; Mahata, S.; Verma, G.; Srivastava, Y.; Masaldan, S.; Roy, B.G.; Bharti, A.C.; Das, B.C. Cervical cancer stem cells selectively overexpress HPV oncoprotein E6 that controls stemness and self-renewal through upregulation of HES1. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 4170–4184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Visvader, J.E.; Lindeman, G.J. Cancer stem cells in solid tumours: Accumulating evidence and unresolved questions. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2008, 8, 755–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez, K.E.; Wu, F.; Keysar, S.B.; Morton, J.J.; Miller, B.; Chimed, T.-S.; Le, P.N.; Nieto, C.; Chowdhury, F.N.; Tyagi, A. Cancer cell CD44 mediates macrophage/monocyte-driven regulation of head and neck cancer stem cells. Cancer Res. 2020, 80, 4185–4198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eini, L.; Naseri, M.; Karimi-Busheri, F.; Bozorgmehr, M.; Ghods, R.; Madjd, Z. Preventive cancer stem cell-based vaccination modulates tumor development in syngeneic colon adenocarcinoma murine model. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 149, 4101–4116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Shen, L.; Shi, H.; Pan, Z.; Wu, L.; Yan, Y.; Zhang, X.; Mao, F.; Qian, H.; Xu, W. Exosomes from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells: Identification, purification, and biological characteristics. Stem Cells Int. 2016, 2016, 1929536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, S.; Wu, Q.; Sathornsumetee, S.; Hao, Y.; Li, Z.; Hjelmeland, A.B.; Shi, Q.; McLendon, R.E.; Bigner, D.D.; Rich, J.N. Stem cell–like glioma cells promote tumor angiogenesis through vascular endothelial growth factor. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 7843–7848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dean, M.; Fojo, T.; Bates, S. Tumour stem cells and drug resistance. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2005, 5, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diehn, M.; Cho, R.W.; Lobo, N.A.; Kalisky, T.; Dorie, M.J.; Kulp, A.N.; Qian, D.; Lam, J.S.; Ailles, L.E.; Wong, M. Association of reactive oxygen species levels and radioresistance in cancer stem cells. Nature 2009, 458, 780–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luzhna, L.; Lykkesfeldt, A.E.; Kovalchuk, O. Altered radiation responses of breast cancer cells resistant to hormonal therapy. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Yang, M.; Luo, J.; Zhou, H. Radiotherapy targeting cancer stem cells “awakens” them to induce tumour relapse and metastasis in oral cancer. Int. J. Oral Sci. 2020, 12, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.-C.; Chen, Y.-W.; Hsu, H.-S.; Tseng, L.-M.; Huang, P.-I.; Lu, K.-H.; Chen, D.-T.; Tai, L.-K.; Yung, M.-C.; Chang, S.-C. Aldehyde dehydrogenase 1 is a putative marker for cancer stem cells in head and neck squamous cancer. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2009, 385, 307–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clay, M.R.; Tabor, M.; Owen, J.H.; Carey, T.E.; Bradford, C.R.; Wolf, G.T.; Wicha, M.S.; Prince, M.E. Single-marker identification of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cancer stem cells with aldehyde dehydrogenase. Head Neck 2010, 32, 1195–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiou, S.-H.; Yu, C.-C.; Huang, C.-Y.; Lin, S.-C.; Liu, C.-J.; Tsai, T.-H.; Chou, S.-H.; Chien, C.-S.; Ku, H.-H.; Lo, J.-F. Positive correlations of Oct-4 and Nanog in oral cancer stem-like cells and high-grade oral squamous cell carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 4085–4095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, M.-Y.; Hu, F.-W.; Yu, C.-H.; Yu, C.-C. Sox2 expression involvement in the oncogenicity and radiochemoresistance of oral cancer stem cells. Oral Oncol. 2015, 51, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kageyama, R.; Ohtsuka, T.; Tomita, K. The bHLH gene Hes1 regulates differentiation of multiple cell types. Mol. Cells 2000, 10, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.; Wu, M.; Li, Y.; Chang, I.; Yuan, Q.; Ekimyan-Salvo, M.; Deng, P.; Yu, B.; Yu, Y.; Dong, J. Targeting BMI1+ cancer stem cells overcomes chemoresistance and inhibits metastases in squamous cell carcinoma. Cell Stem Cell 2017, 20, 621–634.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, R.H.; Kang, M.K.; Shin, K.-H.; Oo, Z.M.; Han, T.; Baluda, M.A.; Park, N.-H. Bmi-1 cooperates with human papillomavirus type 16 E6 to immortalize normal human oral keratinocytes. Exp. Cell Res. 2007, 313, 462–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Li, Z.; Wu, Y.; Huang, R.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Wang, Y.; Cheng, J. Pharmacological inhibition of Bmi1 by PTC-209 impaired tumor growth in head neck squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Cell Int. 2017, 17, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.U.; Jan, S.; Fatima, K.; Malik, F. Immune Cells: Critical Players in Drug Resistance. In Drug Resistance in Cancer: Mechanisms and Strategies; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2024; pp. 121–151. [Google Scholar]
- Mani, S.A.; Guo, W.; Liao, M.-J.; Eaton, E.N.; Ayyanan, A.; Zhou, A.Y.; Brooks, M.; Reinhard, F.; Zhang, C.C.; Shipitsin, M. The epithelial-mesenchymal transition generates cells with properties of stem cells. Cell 2008, 133, 704–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mannelli, G.; Gallo, O. Cancer stem cells hypothesis and stem cells in head and neck cancers. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2012, 38, 515–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olmedo, I.; Martínez, D.; Carrasco-Rojas, J.; Jara, J.A. Mitochondria in oral cancer stem cells: Unraveling the potential drug targets for new and old drugs. Life Sci. 2023, 331, 122065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sha, J.; Bai, Y.; Ngo, H.X.; Okui, T.; Kanno, T. Overview of evidence-based chemotherapy for oral cancer: Focus on drug resistance related to the epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Tie, Y.; Alu, A.; Ma, X.; Shi, H. Targeted therapy for head and neck cancer: Signaling pathways and clinical studies. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patni, A.P.; Harishankar, M.; Joseph, J.P.; Sreeshma, B.; Jayaraj, R.; Devi, A. Comprehending the crosstalk between Notch, Wnt and Hedgehog signaling pathways in oral squamous cell carcinoma-clinical implications. Cell. Oncol. 2021, 44, 473–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takebe, N.; Miele, L.; Harris, P.J.; Jeong, W.; Bando, H.; Kahn, M.; Yang, S.X.; Ivy, S.P. Targeting Notch, Hedgehog, and Wnt pathways in cancer stem cells: Clinical update. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 12, 445–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Li, H.; Yang, Z.; Liu, R.; Li, Y.; Hu, Y.; Zhao, S.; Gao, X.; Yang, X.; Wei, J. SALL4 promotes cancer stem-like cell phenotype and radioresistance in oral squamous cell carcinomas via methyltransferase-like 3-mediated m6A modification. Cell Death Dis. 2024, 15, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, J.; Liu, S.; Yu, L.; Liu, S.; Li, M.; Jin, F. Extracellular vesicles in oral squamous cell carcinoma: Current progress and future prospect. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2023, 11, 1149662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doyle, L.M.; Wang, M.Z. Overview of extracellular vesicles, their origin, composition, purpose, and methods for exosome isolation and analysis. Cells 2019, 8, 727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pegtel, D.M.; Gould, S.J. Exosomes. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2019, 88, 487–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Théry, C.; Zitvogel, L.; Amigorena, S. Exosomes: Composition, biogenesis and function. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2002, 2, 569–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnstone, R.M.; Adam, M.; Hammond, J.; Orr, L.; Turbide, C. Vesicle formation during reticulocyte maturation. Association of plasma membrane activities with released vesicles (exosomes). J. Biol. Chem. 1987, 262, 9412–9420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raposo, G.; Stoorvogel, W. Extracellular vesicles: Exosomes, microvesicles, and friends. J. Cell Biol. 2013, 200, 373–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bebelman, M.P.; Smit, M.J.; Pegtel, D.M.; Baglio, S.R. Biogenesis and function of extracellular vesicles in cancer. Pharmacol. Ther. 2018, 188, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brinton, L.T.; Sloane, H.S.; Kester, M.; Kelly, K.A. Formation and role of exosomes in cancer. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2015, 72, 659–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrmann, I.K.; Wood, M.J.A.; Fuhrmann, G. Extracellular vesicles as a next-generation drug delivery platform. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2021, 16, 748–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urabe, F.; Kosaka, N.; Ito, K.; Kimura, T.; Egawa, S.; Ochiya, T. Extracellular vesicles as biomarkers and therapeutic targets for cancer. Am. J. Physiol.-Cell Physiol. 2020, 318, C29–C39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurung, S.; Perocheau, D.; Touramanidou, L.; Baruteau, J. The exosome journey: From biogenesis to uptake and intracellular signalling. Cell Commun. Signal. 2021, 19, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Liu, H.; Tang, W.H. Exosomes: Biogenesis, biologic function and clinical potential. Cell Biosci. 2019, 9, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kowal, J.; Tkach, M.; Théry, C. Biogenesis and secretion of exosomes. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2014, 29, 116–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Teng, Y. Harnessing cancer stem cell-derived exosomes to improve cancer therapy. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2023, 42, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henne, W.M.; Buchkovich, N.J.; Emr, S.D. The ESCRT pathway. Dev. Cell 2011, 21, 77–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piper, R.C.; Katzmann, D.J. Biogenesis and function of multivesicular bodies. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2007, 23, 519–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, S.; Rawat, S.; Arora, V.; Kottarath, S.K.; Dinda, A.K.; Vaishnav, P.K.; Nayak, B.; Mohanty, S. An improvised one-step sucrose cushion ultracentrifugation method for exosome isolation from culture supernatants of mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2018, 9, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonbhadra, S.; Mehak; Pandey, L.M. Biogenesis, isolation, and detection of exosomes and their potential in therapeutics and Diagnostics. Biosensors 2023, 13, 802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.J.; Wang, B.; Kodali, M.C.; Chen, C.; Kim, E.; Patters, B.J.; Lan, L.; Kumar, S.; Wang, X.; Yue, J. In vivo evidence for the contribution of peripheral circulating inflammatory exosomes to neuroinflammation. J. Neuroinflamm. 2018, 15, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Yan, P.; Xu, X.; Jiang, W. A unique dual recognition hairpin probe mediated fluorescence amplification method for sensitive detection of uracil-DNA glycosylase and endonuclease IV activities. Analyst 2016, 141, 1789–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiba, M.; Uehara, H.; Kuwata, H.; Niiyama, I. Extracellular miRNAs in the serum and feces of mice exposed to high-dose radiation. Biomed. Rep. 2024, 20, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, S.; Ohi, T.; Murakami, T.; Komiyama, T.; Miyoshi, Y.; Endo, K.; Satoh, M.; Asayama, K.; Inoue, R.; Kikuya, M. Association between tooth loss and cognitive impairment in community-dwelling older Japanese adults: A 4-year prospective cohort study from the Ohasama study. BMC Oral Health 2018, 18, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fatima, F.; Nawaz, M. Stem cell-derived exosomes: Roles in stromal remodeling, tumor progression, and cancer immunotherapy. Chin. J. Cancer 2015, 34, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koch, R.; Demant, M.; Aung, T.; Diering, N.; Cicholas, A.; Chapuy, B.; Wenzel, D.; Lahmann, M.; Güntsch, A.; Kiecke, C. Populational equilibrium through exosome-mediated Wnt signaling in tumor progression of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Blood J. Am. Soc. Hematol. 2014, 123, 2189–2198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dickman, C.T.; Lawson, J.; Jabalee, J.; MacLellan, S.A.; LePard, N.E.; Bennewith, K.L.; Garnis, C. Selective extracellular vesicle exclusion of miR-142-3p by oral cancer cells promotes both internal and extracellular malignant phenotypes. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 15252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Callejo, P.; Gener, P.; Díaz-Riascos, Z.V.; Conti, S.; Cámara-Sánchez, P.; Riera, R.; Mancilla, S.; García-Gabilondo, M.; Peg, V.; Arango, D. Extracellular vesicles secreted by triple-negative breast cancer stem cells trigger premetastatic niche remodeling and metastatic growth in the lungs. Int. J. Cancer 2023, 152, 2153–2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Wang, J.; Xie, D.; Pei, Q.; Wan, X.; Xing, H.R.; Ye, T. Characteristics of the PI3K/AKT and MAPK/ERK pathways involved in the maintenance of self-renewal in lung cancer stem-like cells. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 17, 1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoff, M.; Booker, T.; Leavitt, B.; Harmon, D.; Kingsley, K.; Howard, K. Differential exosome miRNA expression in oral cancer stem cells. ExRNA 2020, 2, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Zhang, L.; Guo, B.; Deng, J.; Wu, S.; Li, F.; Wang, Y.; Lu, J.; Zhou, Y. Exosomal FMR1-AS1 facilitates maintaining cancer stem-like cell dynamic equilibrium via TLR7/NFκB/c-Myc signaling in female esophageal carcinoma. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, P.; Almeida, F. Role of exosomal miRNAs and the tumor microenvironment in drug resistance. Cells 2020, 9, 1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, M.; Dong, C.; Ruan, X.; Yan, W.; Cao, M.; Pizzo, D.; Wu, X.; Yang, L.; Liu, L.; Ren, X. Chemotherapy-induced extracellular vesicle miRNAs promote breast cancer stemness by targeting ONECUT2. Cancer Res. 2019, 79, 3608–3621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, J.; Jiang, Y.; Hu, H.; Zhang, S.; Chen, Y. Extracellular vesicles as modulators of glioblastoma progression and tumor microenvironment. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 2024, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, L.; Xiao, J.; Li, X.; Tao, Y.; Zhou, P.; Lyu, L.; Shi, Z.; Liang, X.; Jia, Z.; Jiang, S. Autophagy-related CMTM6 promotes glioblastoma progression by activating Wnt/β-catenin pathway and acts as an onco-immunological biomarker. J. Gene Med. 2024, 26, e3685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabrusiewicz, K.; Li, X.; Wei, J.; Hashimoto, Y.; Marisetty, A.L.; Ott, M.; Wang, F.; Hawke, D.; Yu, J.; Healy, L.M. Glioblastoma stem cell-derived exosomes induce M2 macrophages and PD-L1 expression on human monocytes. Oncoimmunology 2018, 7, e1412909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirzaei, R.; Sarkar, S.; Dzikowski, L.; Rawji, K.S.; Khan, L.; Faissner, A.; Bose, P.; Yong, V.W. Brain tumor-initiating cells export tenascin-C associated with exosomes to suppress T cell activity. Oncoimmunology 2018, 7, e1478647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyuno, D.; Takasawa, A.; Takasawa, K.; Ono, Y.; Aoyama, T.; Magara, K.; Nakamori, Y.; Takemasa, I.; Osanai, M. Claudin-18.2 as a therapeutic target in cancers: Cumulative findings from basic research and clinical trials. Tissue Barriers 2022, 10, 1967080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, W.C.; Liao, T.T.; Lin, C.C.; Yuan, L.T.E.; Lan, H.Y.; Lin, H.H.; Teng, H.W.; Chang, H.C.; Lin, C.H.; Yang, C.Y. RAB27B-activated secretion of stem-like tumor exosomes delivers the biomarker microRNA-146a-5p, which promotes tumorigenesis and associates with an immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment in colorectal cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2019, 145, 2209–2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Q.; Ye, A.; Ye, W.; Liao, X.; Qin, G.; Xu, Y.; Yin, Y.; Luo, H.; Yi, M.; Xian, L. Cancer-secreted exosomal miR-21-5p induces angiogenesis and vascular permeability by targeting KRIT1. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, W.-L.; Jiang, J.-K.; Yang, S.-H.; Huang, T.-S.; Lan, H.-Y.; Teng, H.-W.; Yang, C.-Y.; Tsai, Y.-P.; Lin, C.-H.; Wang, H.-W. MicroRNA-146a directs the symmetric division of Snail-dominant colorectal cancer stem cells. Nat. Cell Biol. 2014, 16, 268–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Sun, H.; Provaznik, J.; Hackert, T.; Zöller, M. Pancreatic cancer-initiating cell exosome message transfer into noncancer-initiating cells: The importance of CD44v6 in reprogramming. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Zhao, N.; Cui, J.; Wu, H.; Xiong, J.; Peng, T. Exosomes derived from cancer stem cells of gemcitabine-resistant pancreatic cancer cells enhance drug resistance by delivering miR-210. Cell. Oncol. 2020, 43, 123–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grange, C.; Tapparo, M.; Collino, F.; Vitillo, L.; Damasco, C.; Deregibus, M.C.; Tetta, C.; Bussolati, B.; Camussi, G. Microvesicles released from human renal cancer stem cells stimulate angiogenesis and formation of lung premetastatic niche. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 5346–5356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Yang, G.; Zhao, D.; Wang, J.; Bai, Y.; Peng, Q.; Wang, H.; Fang, R.; Chen, G.; Wang, Z. CD103-positive CSC exosome promotes EMT of clear cell renal cell carcinoma: Role of remote MiR-19b-3p. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez, C.A.; Andahur, E.I.; Valenzuela, R.; Castellón, E.A.; Fullá, J.A.; Ramos, C.G.; Triviño, J.C. Exosomes from bulk and stem cells from human prostate cancer have a differential microRNA content that contributes cooperatively over local and pre-metastatic niche. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 3993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bliss, S.A.; Sinha, G.; Sandiford, O.A.; Williams, L.M.; Engelberth, D.J.; Guiro, K.; Isenalumhe, L.L.; Greco, S.J.; Ayer, S.; Bryan, M. Mesenchymal stem cell–derived exosomes stimulate cycling quiescence and early breast cancer dormancy in bone marrow. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 5832–5844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.-J.; Huang, T.-H.; Yadav, V.K.; Sumitra, M.R.; Tzeng, D.T.; Wei, P.-L.; Shih, J.-W.; Wu, A.T. Preclinical investigation of ovatodiolide as a potential inhibitor of colon cancer stem cells via downregulating sphere-derived exosomal β-catenin/STAT3/miR-1246 cargoes. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2020, 10, 2337. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Xu, W.; Guo, H.; Zhang, Y.; He, Y.; Lee, S.H.; Song, X.; Li, X.; Guo, Y.; Zhao, Y. NOTCH1 signaling regulates self-renewal and platinum chemoresistance of cancer stem–like cells in human non–small cell lung cancer. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 3082–3091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Zhou, L.; Yu, F.; Zhang, Y.; Li, P.; Wang, K. The functional roles of exosomal long non-coding RNAs in cancer. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2019, 76, 2059–2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peinado, H.; Alečković, M.; Lavotshkin, S.; Matei, I.; Costa-Silva, B.; Moreno-Bueno, G.; Hergueta-Redondo, M.; Williams, C.; García-Santos, G.; Ghajar, C.M. Melanoma exosomes educate bone marrow progenitor cells toward a pro-metastatic phenotype through MET. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 883–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.; Huang, A.C.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, G.; Wu, M.; Xu, W.; Yu, Z.; Yang, J.; Wang, B.; Sun, H. Exosomal PD-L1 contributes to immunosuppression and is associated with anti-PD-1 response. Nature 2018, 560, 382–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raghavan, S.; Mehta, P.; Xie, Y.; Lei, Y.L.; Mehta, G. Ovarian cancer stem cells and macrophages reciprocally interact through the WNT pathway to promote pro-tumoral and malignant phenotypes in 3D engineered microenvironments. J. Immunother. Cancer 2019, 7, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Sun, Y. Efflux mechanism and pathway of verapamil pumping by human P-glycoprotein. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2020, 696, 108675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gholami, A. Cancer stem cell-derived exosomes in CD8+ T cell exhaustion. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2024, 137, 112509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleffel, S.; Schatton, T. Tumor dormancy and cancer stem cells: Two sides of the same coin? Syst. Biol. Tumor Dormancy 2013, 145–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardin, H.; Helein, H.; Meyer, K.; Robertson, S.; Zhang, R.; Zhong, W.; Lloyd, R.V. Thyroid cancer stem-like cell exosomes: Regulation of EMT via transfer of lncRNAs. Lab. Investig. 2018, 98, 1133–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mori, K.; Hiroi, M.; Shimada, J.; Ohmori, Y. Infiltration of m2 tumor-associated macrophages in oral squamous cell carcinoma correlates with tumor malignancy. Cancers 2011, 3, 3726–3739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, X.; Zhang, L.; Wei, W. Regulatory B cells in inflammatory diseases and tumor. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2019, 67, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirave, P.; Gondaliya, P.; Kulkarni, B.; Rawal, R.; Garg, R.; Jain, A.; Kalia, K. Exosome mediated miR-155 delivery confers cisplatin chemoresistance in oral cancer cells via epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Oncotarget 2020, 11, 1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Law, Z.-J.; Khoo, X.H.; Lim, P.T.; Goh, B.H.; Ming, L.C.; Lee, W.-L.; Goh, H.P. Extracellular vesicle-mediated chemoresistance in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2021, 8, 629888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Momen-Heravi, F.; Bala, S. Emerging role of non-coding RNA in oral cancer. Cell. Signal. 2018, 42, 134–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, G.; Li, H.; Guo, Q.; Zhou, A.; Wang, X.; Li, P.; Zhang, S. Exosomal Sonic Hedgehog derived from cancer-associated fibroblasts promotes proliferation and migration of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Med. 2020, 9, 2500–2513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cierpikowski, P.; Lis-Nawara, A.; Bar, J. SHH expression is significantly associated with cancer stem cell markers in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Anticancer Res. 2021, 41, 5405–5413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.-y.; Tao, Y.-w.; Gao, S.; Li, P.; Zheng, J.-m.; Zhang, S.-e.; Liang, J.; Zhang, Y. Cancer-associated fibroblasts contribute to oral cancer cells proliferation and metastasis via exosome-mediated paracrine miR-34a-5p. EBioMedicine 2018, 36, 209–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singha, A.; Magesh, K.; Mahalingam, R.; Aravindhan, R.; Sivachandran, A. Therapeutic signature of stem cell derivative exosomes in oral cancer: A scoping review. Cureus 2023, 15, e39957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Ouyang, P.; He, G.; Wang, X.; Song, D.; Yang, Y.; He, X. Exosomes from microRNA-126 overexpressing mesenchymal stem cells promote angiogenesis by targeting the PIK3R2-mediated PI3K/Akt signalling pathway. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2021, 25, 2148–2162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.-H.; Wu, A.T.; Bamodu, O.A.; Yadav, V.K.; Chao, T.-Y.; Tzeng, Y.-M.; Mukhopadhyay, D.; Hsiao, M.; Lee, J.-C. Ovatodiolide suppresses oral cancer malignancy by down-regulating exosomal Mir-21/STAT3/β-catenin cargo and preventing oncogenic transformation of normal gingival fibroblasts. Cancers 2019, 12, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludwig, N.; Yerneni, S.S.; Azambuja, J.H.; Pietrowska, M.; Widłak, P.; Hinck, C.S.; Głuszko, A.; Szczepański, M.J.; Kärmer, T.; Kallinger, I. TGFβ+ small extracellular vesicles from head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cells reprogram macrophages towards a pro-angiogenic phenotype. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2022, 11, 12294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, Y.; Tian, Z.; Du, Z.; Wu, K.; Xu, G.; Dai, M.; Wang, Y.a.; Xiao, M. M1-like tumor-associated macrophages cascade a mesenchymal/stem-like phenotype of oral squamous cell carcinoma via the IL6/Stat3/THBS1 feedback loop. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2022, 41, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Y.; Li, S.; Song, J.; Ji, T.; Zhu, M.; Anderson, G.J.; Wei, J.; Nie, G. A doxorubicin delivery platform using engineered natural membrane vesicle exosomes for targeted tumor therapy. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 2383–2390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trajkovic, K.; Hsu, C.; Chiantia, S.; Rajendran, L.; Wenzel, D.; Wieland, F.; Schwille, P.; Brügger, B.; Simons, M. Ceramide triggers budding of exosome vesicles into multivesicular endosomes. Science 2008, 319, 1244–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melo, S.A.; Luecke, L.B.; Kahlert, C.; Fernandez, A.F.; Gammon, S.T.; Kaye, J.; LeBleu, V.S.; Mittendorf, E.A.; Weitz, J.; Rahbari, N. Glypican-1 identifies cancer exosomes and detects early pancreatic cancer. Nature 2015, 523, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamerkar, S.; LeBleu, V.S.; Sugimoto, H.; Yang, S.; Ruivo, C.F.; Melo, S.A.; Lee, J.J.; Kalluri, R. Exosomes facilitate therapeutic targeting of oncogenic KRAS in pancreatic cancer. Nature 2017, 546, 498–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Wang, F.; Zhu, D.; Hu, S.; Cheng, K.; Li, Z. Engineering Exosomes and Exosome-like Nanovesicles for Improving Tissue Targeting and Retention. Fundam. Res. 2024; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morishita, M.; Takahashi, Y.; Matsumoto, A.; Nishikawa, M.; Takakura, Y. Exosome-based tumor antigens–adjuvant co-delivery utilizing genetically engineered tumor cell-derived exosomes with immunostimulatory CpG DNA. Biomaterials 2016, 111, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.-F.; Liao, F.; Wu, H.; Dai, J. Glioma stem cells-derived exosomal miR-26a promotes angiogenesis of microvessel endothelial cells in glioma. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conigliaro, A.; Costa, V.; Lo Dico, A.; Saieva, L.; Buccheri, S.; Dieli, F.; Manno, M.; Raccosta, S.; Mancone, C.; Tripodi, M. CD90+ liver cancer cells modulate endothelial cell phenotype through the release of exosomes containing H19 lncRNA. Mol. Cancer 2015, 14, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahoumi, L.A. Oral cancer stem cells: Therapeutic implications and challenges. Front. Oral Health 2021, 2, 685236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, C.; Zhang, J.; Yarden, Y.; Fu, L. The key roles of cancer stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| CSC Source | Cargo | Study Observations | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Oral cancer stem cells (OC-CSCs) Head and neck cancer stem cells (HNC-CSCs) Esophageal cancer stem cells (EC-CSCs) | miRNAs lncRNA UCA1 O-GlcNAc transferase (OGT) IncRNA FMR1-AS1 |
| [14,18,19,91,92,93,94,95] |
| Breast cancer stem cells (BC-CSCs) | miRNAs |
| [96,97] |
| Glioblastoma stem cells (GB-CSCs) | Tenascin C miRNAs Linc01060 NOTCH1 STAT3 |
| [98,99,100,101] |
| Lung cancer stem cells (LC-CSCs) | miRNAs |
| [17] |
| Gastric cancer stem cells (GC-CSCs) | miRNAs Claudin-7 |
| [16,102] |
| Colorectal cancer stem cells (CC-CSCs) | miRNAs miRNA-146a-5p Tri-phosphate RNAs |
| [103,104,105] |
| Pancreatic cancer (PC-CSCs) | miRNAs, CD44v6 |
| [106,107] |
| Renal carcinoma (RC-CSCs) | miRNAs, MMPs |
| [108,109] |
| Prostate cancer (PC-CSCs) | miRNAs |
| [110] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kumar, P.; Lakhera, R.; Aggarwal, S.; Gupta, S. Unlocking the Therapeutic Potential of Oral Cancer Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 1809. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12081809
Kumar P, Lakhera R, Aggarwal S, Gupta S. Unlocking the Therapeutic Potential of Oral Cancer Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes. Biomedicines. 2024; 12(8):1809. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12081809
Chicago/Turabian StyleKumar, Prabhat, Rishabh Lakhera, Sadhna Aggarwal, and Shilpi Gupta. 2024. "Unlocking the Therapeutic Potential of Oral Cancer Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes" Biomedicines 12, no. 8: 1809. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12081809
APA StyleKumar, P., Lakhera, R., Aggarwal, S., & Gupta, S. (2024). Unlocking the Therapeutic Potential of Oral Cancer Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes. Biomedicines, 12(8), 1809. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12081809







