Integrated Management of Persistent Atrial Fibrillation
Abstract
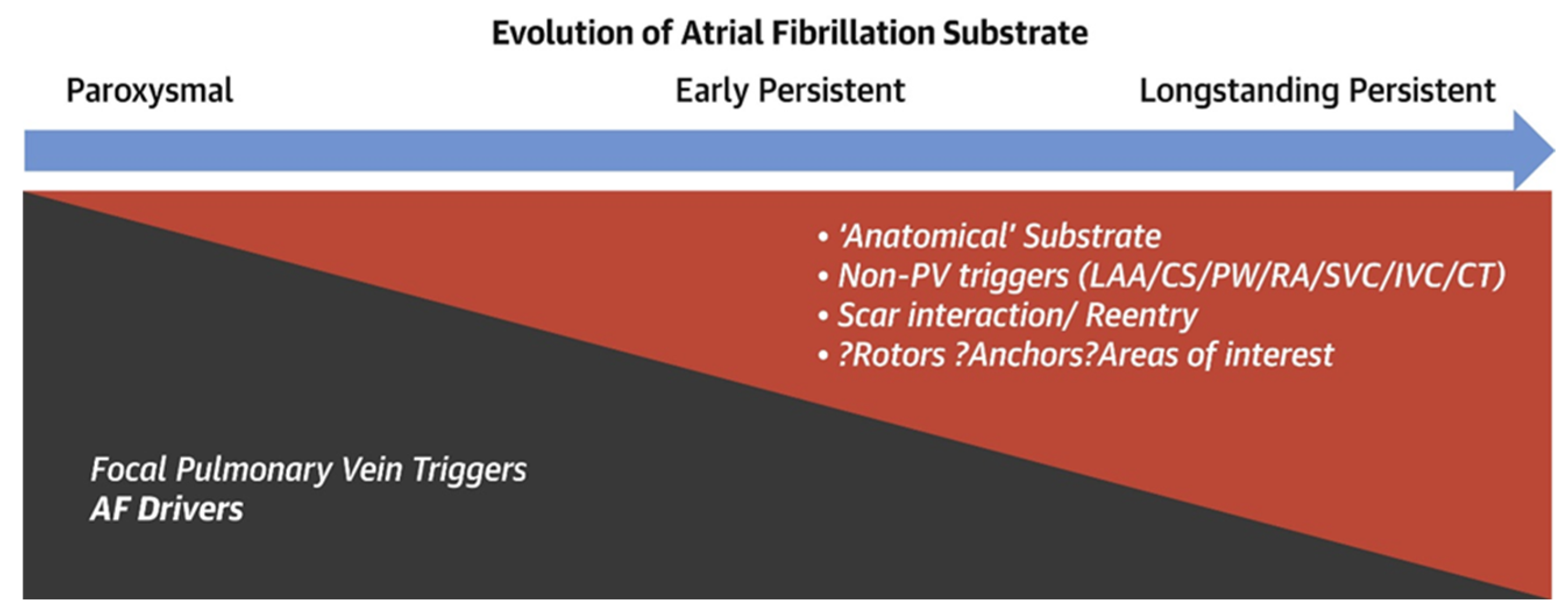
1. Introduction
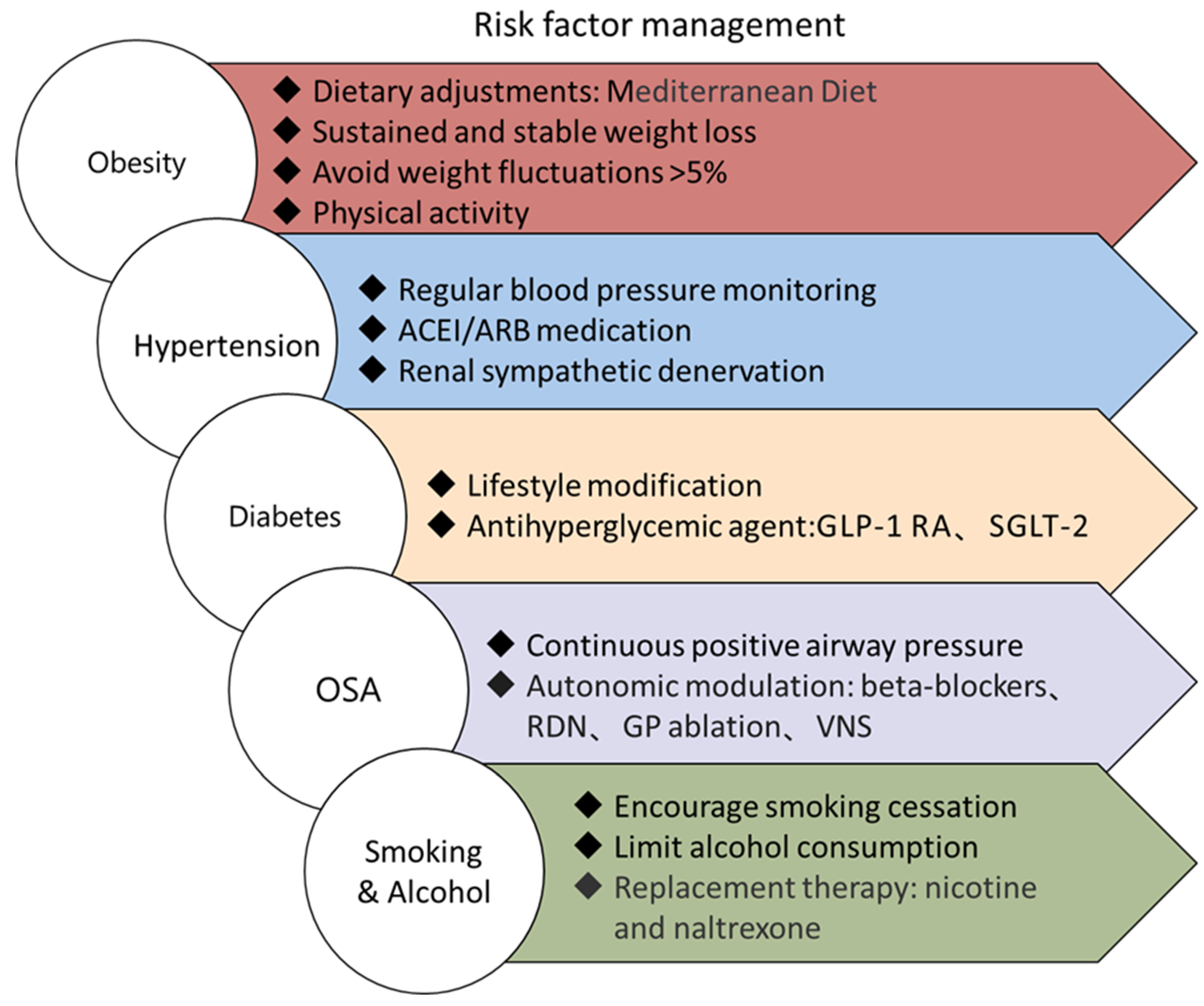
2. Risk Factor Management in Persistent Atrial Fibrillation
3. Rate Control
4. Rhythm Control
4.1. Drug Rhythm Control
4.2. Empiric Approaches
- (1).
- Posterior wall isolation (PWI)
- (2).
- Vein of Marshall ablation
- (3).
- The abundant innervation, myocardial connections, and arrhythmic foci in the vein of Marshall (VOM) make it an ideal target for AF ablation. Retrograde balloon cannulation from the coronary sinus to the VOM and infusion of ethanol enables rapid ablation of adjacent myocardium and innervation. Research indicates that combining pulmonary vein isolation with VOM ethanol infusion enhances ablation success in persistent atrial fibrillation. In the VENUS trial, persistent AF patients were randomly assigned to PVI alone or PVI plus vein of Marshall ethanol infusion. There are higher success rates of sinus rhythm maintenance in the PVI plus Marshall ethanol infusion group [108]. The subsequent MARSHALL-Plan trial further explored the effectiveness of a combined ablation strategy (Marshall ablation, PVI, and linear ablation) in patients with persistent atrial fibrillation and patients in the combined-strategy ablation group had up to 79% AF/AT recurrence-free rate at 12 months [109]. Of note, the location of the Marshall vein in the mitral isthmus makes it strongly associated with perimitral atrial tachycardia. Achieving a bi-directional blockade of the mitral isthmus is currently the main challenge in catheter ablation of persistent atrial fibrillation. Based on data from long-term follow-up outcomes in atrial fibrillation, researchers found that VOM ethanol infusion facilitates mitral isthmus ablation [110]. Furthermore, a recent study confirmed that VOM ethanol infusion can reduce the risk of acute reconnection after mitral isthmus block [111]. Therefore, VOM ethanol infusion can be regarded as a valuable complement to mitral isthmus ablation.Ganglionated plexi ablation:
4.3. Map-Guided Approach
- (1).
- Low-voltage area (LVA) ablation
- (2).
- Rotor mapping and ablation
- (3).
- Non-pulmonary vein triggers
4.4. Surgical Epicardial Ablation and Hybrid Ablation
- (1).
- Cox maze procedure
- (2).
- Hybrid Approaches
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hindricks, G.; Potpara, T.; Dagres, N.; Arbelo, E.; Bax, J.J.; Blomström-Lundqvist, C.; Boriani, G.; Castella, M.; Dan, J.-A.; Dilaveris, P.E.; et al. 2020 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of atrial fibrillation developed in collaboration with the European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery (EACTS). Eur. Heart J. 2021, 42, 373–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyasaka, Y.; Barnes, M.E.; Gersh, B.J.; Cha, S.S.; Bailey, K.R.; Abhayaratna, W.P.; Seward, J.B.; Tsang, T.S. Secular Trends in Incidence of Atrial Fibrillation in Olmsted County, Minnesota, 1980 to 2000, and Implications on the Projections for Future Prevalence. Circulation 2006, 114, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schotten, U.; Verheule, S.; Kirchhof, P.; Goette, A. Pathophysiological Mechanisms of Atrial Fibrillation: A Translational Appraisal. Physiol. Rev. 2011, 91, 265–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, M.K.; Refaat, M.; Shen, W.-K.; Kutyifa, V.; Cha, Y.-M.; Di Biase, L.; Baranchuk, A.; Lampert, R.; Natale, A.; Fisher, J.; et al. Atrial Fibrillation. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2020, 75, 1689–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.J.; Parise, H.; Levy, D.; D’Agostino, R.B., Sr.; Wolf, P.A.; Vasan, R.S.; Benjamin, E.J. Obesity and the risk of new-onset atrial fibrillation. JAMA 2004, 292, 2471–2477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- E Middeldorp, M.; Pathak, R.K.; Meredith, M.; Mehta, A.B.; Elliott, A.D.; Mahajan, R.; Twomey, D.; Gallagher, C.; Hendriks, J.M.L.; Linz, D.; et al. PREVEntion and regReSsive Effect of weight-loss and risk factor modification on Atrial Fibrillation: The REVERSE-AF study. EP Eur. 2018, 20, 1929–1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahajan, R.; Lau, D.H.; Brooks, A.G.; Shipp, N.J.; Wood, J.P.; Manavis, J.; Samuel, C.S.; Patel, K.P.; Finnie, J.W.; Alasady, M.; et al. Atrial Fibrillation and Obesity. JACC Clin. Electrophysiol. 2021, 7, 630–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathak, R.K.; Middeldorp, M.E.; Meredith, M.; Mehta, A.B.; Mahajan, R.; Wong, C.X.; Twomey, D.; Elliott, A.D.; Kalman, J.M.; Abhayaratna, W.P.; et al. Long-Term Effect of Goal-Directed Weight Management in an Atrial Fibrillation Cohort: A Long-Term Follow-Up Study (LEGACY). J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2015, 65, 2159–2169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Field, A.E.; Byers, T.; Hunter, D.J.; Laird, N.M.; Manson, J.E.; Williamson, D.R.; Willett, W.C.; Colditz, G.A. Weight Cycling, Weight Gain, and Risk of Hypertension in Women. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1999, 150, 573–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lissner, L.; Odell, P.M.; D’Agostino, R.B.; Stokes, J.I.; Kreger, B.E.; Belanger, A.J.; Brownell, K.D. Variability of Body Weight and Health Outcomes in the Framingham Population. New Engl. J. Med. 1991, 324, 1839–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waring, M.E.; Eaton, C.B.; Lasater, T.M.; Lapane, K.L. Incident Diabetes in Relation to Weight Patterns During Middle Age. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2010, 171, 550–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-González, M.; Toledo, E.; Arós, F.; Fiol, M.; Corella, D.; Salas-Salvadó, J.; Ros, E.; Covas, M.I.; Fernández-Crehuet, J.; Lapetra, J.; et al. Extravirgin Olive Oil Consumption Reduces Risk of Atrial Fibrillation. Circulation 2014, 130, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrio-Lopez, M.T.; Ruiz-Canela, M.; Goni, L.; Valiente, A.M.; Garcia, S.R.; de la O, V.; Anton, B.D.; Fernandez-Friera, L.; Castellanos, E.; Martínez-González, M.A.; et al. Mediterranean diet and epicardial adipose tissue in patients with atrial fibrillation treated with ablation: A substudy of the ‘PREDIMAR’ trial. Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2023, 31, 348–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandyam, M.C.; Vedantham, V.; Scheinman, M.M.; Tseng, Z.H.; Badhwar, N.; Lee, B.K.; Lee, R.J.; Gerstenfeld, E.P.; Olgin, J.E.; Marcus, G.M. Alcohol and Vagal Tone as Triggers for Paroxysmal Atrial Fibrillation. Am. J. Cardiol. 2012, 110, 364–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piano, M.R. Alcoholic Cardiomyopathy. Chest 2002, 121, 1638–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kodama, S.; Saito, K.; Tanaka, S.; Horikawa, C.; Saito, A.; Heianza, Y.; Anasako, Y.; Nishigaki, Y.; Yachi, Y.; Iida, K.T.; et al. Alcohol Consumption and Risk of Atrial Fibrillation. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2011, 57, 427–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruigómez, A.; Johansson, S.; Wallander, M.-A.; Rodríguez, L.A.G. Predictors and prognosis of paroxysmal atrial fibrillation in general practice in the UK. BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 2005, 5, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gémes, K.; Malmo, V.; Laugsand, L.E.; Loennechen, J.P.; Ellekjaer, H.; László, K.D.; Ahnve, S.; Vatten, L.J.; Mukamal, K.J.; Janszky, I. Does Moderate Drinking Increase the Risk of Atrial Fibrillation? The Norwegian HUNT (Nord-Trøndelag Health) Study. J. Am. Hear. Assoc. 2017, 6, e007094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-R.; Choi, E.-K.; Jung, J.-H.; Han, K.-D.; Oh, S.; Lip, G.Y.H. Lower risk of stroke after alcohol abstinence in patients with incident atrial fibrillation: A nationwide population-based cohort study. Eur. Hear. J. 2021, 42, 4759–4768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voskoboinik, A.; Kalman, J.M.; De Silva, A.; Nicholls, T.; Costello, B.; Nanayakkara, S.; Prabhu, S.; Stub, D.; Azzopardi, S.; Vizi, D.; et al. Alcohol Abstinence in Drinkers with Atrial Fibrillation. New Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heeringa, J.; Kors, J.A.; Hofman, A.; van Rooij, F.J.; Witteman, J.C. Cigarette smoking and risk of atrial fibrillation: The Rotterdam Study. Am. Hear. J. 2008, 156, 1163–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aune, D.; Schlesinger, S.; Norat, T.; Riboli, E. Tobacco smoking and the risk of atrial fibrillation: A systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective studies. Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2018, 25, 1437–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giomi, A.; Bernardini, A.; Perini, A.P.; Ciliberti, D.; Zaccaria, C.S.; Signorini, U.; Milli, M. Clinical impact of smoking on atrial fibrillation recurrence after pulmonary vein isolation. Int. J. Cardiol. 2024, 413, 132342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rom, O.; Avezov, K.; Aizenbud, D.; Reznick, A.Z. Cigarette smoking and inflammation revisited. Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 2013, 187, 5–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tappia, P.S.; Troughton, K.L.; Langley-Evans, S.C.; Grimble, R.F. Cigarette Smoking Influences Cytokine Production and Antioxidant Defences. Clin. Sci. 1995, 88, 485–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goette, A.; Lendeckel, U.; Kuchenbecker, A.; Bukowska, A.; Peters, B.; Klein, H.U.; Huth, C.; Röcken, C. Cigarette smoking induces atrial fibrosis in humans via nicotine. Heart 2007, 93, 1056–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lip, G.Y.; Frison, L.; Halperin, J.L.; Lane, D.A. Identifying Patients at High Risk for Stroke Despite Anticoagulation. Stroke 2010, 41, 2731–2738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneko, H.; Yano, Y.; Itoh, H.; Morita, K.; Kiriyama, H.; Kamon, T.; Fujiu, K.; Michihata, N.; Jo, T.; Takeda, N.; et al. Association of Blood Pressure Classification Using the 2017 American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Blood Pressure Guideline With Risk of Heart Failure and Atrial Fibrillation. Circulation 2021, 143, 2244–2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Georgiopoulos, G.; Ntritsos, G.; Stamatelopoulos, K.; Tsioufis, C.; Aimo, A.; Masi, S.; Evangelou, E. The relationship between blood pressure and risk of atrial fibrillation: A Mendelian randomization study. Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2021, 29, 1494–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, F.; Yin, X.; Larson, M.G.; Ellinor, P.T.; Lubitz, S.A.; Vasan, R.S.; McManus, D.D.; Magnani, J.W.; Benjamin, E.J. Trajectories of Risk Factors and Risk of New-Onset Atrial Fibrillation in the Framingham Heart Study. Hypertension 2016, 68, 597–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soliman, E.Z.; Rahman, A.F.; Zhang, Z.-M.; Rodriguez, C.J.; Chang, T.I.; Bates, J.T.; Ghazi, L.; Blackshear, J.L.; Chonchol, M.; Fine, L.J.; et al. Effect of Intensive Blood Pressure Lowering on the Risk of Atrial Fibrillation. Hypertension 2020, 75, 1491–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larstorp, A.C.K.; Stokke, I.M.; Kjeldsen, S.E.; Olsen, M.H.; Okin, P.M.; Devereux, R.B.; Wachtell, K. Antihypertensive therapy prevents new-onset atrial fibrillation in patients with isolated systolic hypertension: The LIFE study. Blood Press. 2019, 28, 317–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santoro, F.; Di Biase, L.; Trivedi, C.; Burkhardt, J.D.; Perini, A.P.; Sanchez, J.; Horton, R.; Mohanty, P.; Mohanty, S.; Bai, R.; et al. Impact of Uncontrolled Hypertension on Atrial Fibrillation Ablation Outcome. JACC Clin. Electrophysiol. 2015, 1, 164–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parkash, R.; Wells, G.A.; Sapp, J.L.; Healey, J.S.; Tardif, J.-C.; Greiss, I.; Rivard, L.; Roux, J.-F.; Gula, L.; Nault, I.; et al. Effect of Aggressive Blood Pressure Control on the Recurrence of Atrial Fibrillation After Catheter Ablation. Circulation 2017, 135, 1788–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Huang, C.; Zhao, Q.; Huang, H.; Tang, Y.; Dai, Z.; Guo, Z.; Xiao, J. Effect of renal sympathetic denervation on the progression of paroxysmal atrial fibrillation in canines with long-term intermittent atrial pacing. EP Eur. 2014, 17, 647–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Zhao, Q.; Huang, H.; Tang, Y.; Xiao, J.; Dai, Z.; Yu, S.; Huang, C. Effect of Renal Sympathetic Denervation on Atrial Substrate Remodeling in Ambulatory Canines with Prolonged Atrial Pacing. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e64611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Q.; Yu, S.; Huang, H.; Tang, Y.; Xiao, J.; Dai, Z.; Wang, X.; Huang, C. Effects of renal sympathetic denervation on the development of atrial fibrillation substrates in dogs with pacing-induced heart failure. Int. J. Cardiol. 2013, 168, 1672–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Yu, S.; Zou, M.; Dai, Z.; Wang, X.; Xiao, J.; Huang, C. Effect of renal sympathetic denervation on the inducibility of atrial fibrillation during rapid atrial pacing. J. Interv. Card. Electrophysiol. 2012, 35, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinberg, J.S.; Shabanov, V.; Ponomarev, D.; Losik, D.; Ivanickiy, E.; Kropotkin, E.; Polyakov, K.; Ptaszynski, P.; Keweloh, B.; Yao, C.J.; et al. Effect of Renal Denervation and Catheter Ablation vs Catheter Ablation Alone on Atrial Fibrillation Recurrence Among Patients With Paroxysmal Atrial Fibrillation and Hypertension. JAMA 2020, 323, 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevenson, I.H.; Teichtahl, H.; Cunnington, D.; Ciavarella, S.; Gordon, I.; Kalman, J.M. Prevalence of sleep disordered breathing in paroxysmal and persistent atrial fibrillation patients with normal left ventricular function. Eur. Hear. J. 2008, 29, 1662–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Xu, W.; Yun, F.; Zhao, H.; Li, W.; Gong, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Yan, S.; Zhang, S.; Ding, X.; et al. Chronic obstructive sleep apnea causes atrial remodeling in canines: Mechanisms and implications. Basic Res. Cardiol. 2014, 109, 427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linz, B.; Hohl, M.; Lang, L.; Wong, D.W.; Nickel, A.G.; De La Torre, C.; Sticht, C.; Wirth, K.; Boor, P.; Maack, C.; et al. Repeated exposure to transient obstructive sleep apnea–related conditions causes an atrial fibrillation substrate in a chronic rat model. Hear. Rhythm. 2020, 18, 455–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linz, D.; McEvoy, R.D.; Cowie, M.R.; Somers, V.K.; Nattel, S.; Lévy, P.; Kalman, J.M.; Sanders, P. Associations of Obstructive Sleep Apnea With Atrial Fibrillation and Continuous Positive Airway Pressure Treatment. JAMA Cardiol. 2018, 3, 532–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nalliah, C.J.; Wong, G.R.; Lee, G.; Voskoboinik, A.; Kee, K.; Goldin, J.; Watts, T.; Linz, D.; Parameswaran, R.; Sugumar, H.; et al. Impact of CPAP on the Atrial Fibrillation Substrate in Obstructive Sleep Apnea. JACC Clin. Electrophysiol. 2022, 8, 869–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fein, A.S.; Shvilkin, A.; Shah, D.; Haffajee, C.I.; Das, S.; Kumar, K.; Kramer, D.B.; Zimetbaum, P.J.; Buxton, A.E.; Josephson, M.E.; et al. Treatment of Obstructive Sleep Apnea Reduces the Risk of Atrial Fibrillation Recurrence After Catheter Ablation. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2013, 62, 300–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naruse, Y.; Tada, H.; Satoh, M.; Yanagihara, M.; Tsuneoka, H.; Hirata, Y.; Ito, Y.; Kuroki, K.; Machino, T.; Yamasaki, H.; et al. Concomitant obstructive sleep apnea increases the recurrence of atrial fibrillation following radiofrequency catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation: Clinical impact of continuous positive airway pressure therapy. Heart Rhythm 2012, 10, 331–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neilan, T.G.; Farhad, H.; Dodson, J.A.; Shah, R.V.; Abbasi, S.A.; Bakker, J.P.; Michaud, G.F.; van der Geest, R.; Blankstein, R.; Steigner, M.; et al. Effect of Sleep Apnea and Continuous Positive Airway Pressure on Cardiac Structure and Recurrence of Atrial Fibrillation. J. Am. Hear. Assoc. 2013, 2, e000421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Traaen, G.M.; Aakerøy, L.; Hunt, T.-E.; Øverland, B.; Bendz, C.; Sande, L..; Aakhus, S.; Fagerland, M.W.; Steinshamn, S.; Anfinsen, O.-G.; et al. Effect of Continuous Positive Airway Pressure on Arrhythmia in Atrial Fibrillation and Sleep Apnea: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2021, 204, 573–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunt, T.-E.; Hunt, T.-E.; Traaen, G.M.; Traaen, G.M.; Aakerøy, L.; Aakerøy, L.; Bendz, C.; Bendz, C.; Øverland, B.; Øverland, B.; et al. Effect of continuous positive airway pressure therapy on recurrence of atrial fibrillation after pulmonary vein isolation in patients with obstructive sleep apnea: A randomized controlled trial. Hear. Rhythm. 2022, 19, 1433–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghias, M.; Scherlag, B.J.; Lu, Z.; Niu, G.; Moers, A.; Jackman, W.M.; Lazzara, R.; Po, S.S. The Role of Ganglionated Plexi in Apnea-Related Atrial Fibrillation. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2009, 54, 2075–2083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Yan, S.; Wang, X.; Zhao, S.; Li, H.; Wang, Y.; Lu, S.; Dong, X.; Zhao, J.; Yu, S.; et al. Metoprolol prevents chronic obstructive sleep apnea-induced atrial fibrillation by inhibiting structural, sympathetic nervous and metabolic remodeling of the atria. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 14941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, H.; Yuan, Y.; Yin, S.; Zhang, Y.; Han, Y.; Sun, L.; Li, T.; Xu, J.; Sheng, L.; Gong, Y.; et al. Metoprolol Inhibits Profibrotic Remodeling of Epicardial Adipose Tissue in a Canine Model of Chronic Obstructive Sleep Apnea. J. Am. Hear. Assoc. 2019, 8, e011155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linz, D.; Hohl, M.; Nickel, A.; Mahfoud, F.; Wagner, M.; Ewen, S.; Schotten, U.; Maack, C.; Wirth, K.; Böhm, M. Effect of Renal Denervation on Neurohumoral Activation Triggering Atrial Fibrillation in Obstructive Sleep Apnea. Hypertension 2013, 62, 767–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linz, D.; Mahfoud, F.; Schotten, U.; Ukena, C.; Neuberger, H.-R.; Wirth, K.; Böhm, M. Renal Sympathetic Denervation Suppresses Postapneic Blood Pressure Rises and Atrial Fibrillation in a Model for Sleep Apnea. Hypertension 2012, 60, 172–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, M.; Zhang, L.; Scherlag, B.J.; Huang, B.; Stavrakis, S.; Hou, Y.-M.; Hou, Y.; Po, S.S. Low-level vagosympathetic trunk stimulation inhibits atrial fibrillation in a rabbit model of obstructive sleep apnea. Hear. Rhythm. 2015, 12, 818–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tavares, L.; Rodríguez-Mañero, M.; Kreidieh, B.; Ibarra-Cortez, S.H.; Chen, J.; Wang, S.; Markovits, J.; Barrios, R.; Valderrábano, M. Cardiac Afferent Denervation Abolishes Ganglionated Plexi and Sympathetic Responses to Apnea. Circ. Arrhythmia Electrophysiol. 2019, 12, e006942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.; Lu, Z.; He, W.; He, B.; Ma, R.; Xie, J.; Jiang, H. Cardiac autonomic ganglia ablation suppresses atrial fibrillation in a canine model of acute intermittent hypoxia. Auton. Neurosci. 2017, 205, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Movahed, M.-R.; Hashemzadeh, M.; Jamal, M.M. Diabetes mellitus is a strong, independent risk for atrial fibrillation and flutter in addition to other cardiovascular disease. Int. J. Cardiol. 2005, 105, 315–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huxley, R.R.; Filion, K.B.; Konety, S.; Alonso, A. Meta-Analysis of Cohort and Case–Control Studies of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Risk of Atrial Fibrillation. Am. J. Cardiol. 2011, 108, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, J.; Chen, H.; Liu, Q.; Zhou, S.; Liu, Z.; Xiao, Y. GLP-1 receptor agonists and myocardial metabolism in atrial fibrillation. J. Pharm. Anal. 2023, 14, 100917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bohne, L.J.; Jansen, H.J.; Dorey, T.W.; Daniel, I.M.; Jamieson, K.L.; Belke, D.D.; McRae, M.D.; Rose, R.A. Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Protects Against Atrial Fibrillation and Atrial Remodeling in Type 2 Diabetic Mice. JACC Basic Transl. Sci. 2023, 8, 922–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, W.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, D.; Ren, G.; Wang, P.; Gao, L.; Chen, H.; Ding, C. Comparison of the effect of glucose-lowering agents on the risk of atrial fibrillation: A network meta-analysis. Hear. Rhythm. 2021, 18, 1090–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamedi, Z.; Mishriky, B.M.; Okunrintemi, V.; Powell, J.R.; Cummings, D.M. GLP-1 RA and atrial fibrillation in the cardiovascular outcome trials. Diabetes/Metabolism Res. Rev. 2021, 37, e3436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monami, M.; Nreu, B.; Scatena, A.; Giannini, S.; Andreozzi, F.; Sesti, G.; Mannucci, E. Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists and atrial fibrillation: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2017, 40, 1251–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karakasis, P.; Patoulias, D.; Tzeis, S.; Fragakis, N. Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists and Atrial Fibrillation Recurrence After Ablation: A Fire Without the Smoke? Clin. Electrophysiol. 2024, 10, 1940–1941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abu-Qaoud, M.R.; Kumar, A.; Tarun, T.; Abraham, S.; Ahmad, J.; Khadke, S.; Husami, R.; Kulbak, G.; Sahoo, S.; Januzzi, J.L.; et al. Impact of SGLT2 Inhibitors on AF Recurrence After Catheter Ablation in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes. JACC Clin. Electrophysiol. 2023, 9, 2109–2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mozaffarian, D.; Furberg, C.D.; Psaty, B.M.; Siscovick, D. Physical Activity and Incidence of Atrial Fibrillation in Older Adults. Circulation 2008, 118, 800–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegbom, F.; Stavem, K.; Sire, S.; Heldal, M.; Orning, O.M.; Gjesdal, K. Effects of short-term exercise training on symptoms and quality of life in patients with chronic atrial fibrillation. Int. J. Cardiol. 2007, 116, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, M.; Ogano, M.; Mori, Y.; Kochi, K.; Morimoto, D.; Kito, K.; Green, F.N.; Tsukamoto, T.; Kubo, A.; Takagi, H.; et al. Exercise-based cardiac rehabilitation for patients with catheter ablation for persistent atrial fibrillation: A randomized controlled clinical trial. Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2019, 26, 1931–1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michaud, G.F.; Stevenson, W.G. Atrial Fibrillation. New Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 353–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, D.; Rienstra, M.; van Gelder, I.C.; Fauchier, L. Atrial fibrillation: Better symptom control with rate and rhythm management. Lancet Reg. Heal. Eur. 2024, 37, 100801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Gelder, I.C.; Groenveld, H.F.; Crijns, H.J.; Tuininga, Y.S.; Tijssen, J.G.; Alings, A.M.; Hillege, H.L.; Bergsma-Kadijk, J.A.; Cornel, J.H.; Kamp, O.; et al. Lenient versus Strict Rate Control in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation. New Engl. J. Med. 2010, 362, 1363–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khurshid, S.; Epstein, A.E.; Verdino, R.J.; Lin, D.; Goldberg, L.R.; Marchlinski, F.E.; Frankel, D.S. Incidence and predictors of right ventricular pacing-induced cardiomyopathy. Hear. Rhythm. 2014, 11, 1619–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brignole, M.; Pokushalov, E.; Pentimalli, F.; Palmisano, P.; Chieffo, E.; Occhetta, E.; Quartieri, F.; Calò, L.; Ungar, A.; Mont, L. A randomized controlled trial of atrioventricular junction ablation and cardiac resynchronization therapy in patients with permanent atrial fibrillation and narrow QRS. Eur. Hear. J. 2018, 39, 3999–4008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brignole, M.; Pentimalli, F.; Palmisano, P.; Landolina, M.; Quartieri, F.; Occhetta, E.; Calò, L.; Mascia, G.; Mont, L.; Vernooy, K.; et al. AV junction ablation and cardiac resynchronization for patients with permanent atrial fibrillation and narrow QRS: The APAF-CRT mortality trial. Eur. Hear. J. 2021, 42, 4731–4739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ploux, S.; Eschalier, R.; Whinnett, Z.I.; Lumens, J.; Derval, N.; Sacher, F.; Hocini, M.; Jaïs, P.; Dubois, R.; Ritter, P.; et al. Electrical dyssynchrony induced by biventricular pacing: Implications for patient selection and therapy improvement. Hear. Rhythm. 2015, 12, 782–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, P.; Su, L.; Chen, X.; Xu, L.; Ni, X.; Huang, W. Direct His-Bundle Pacing Improved Left Ventricular Function and Remodelling in a Biventricular Pacing Nonresponder. Can. J. Cardiol. 2016, 32, 1577.e1–1577.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Su, L.; Wu, S.; Xu, L.; Xiao, F.; Zhou, X.; Mao, G.; Vijayaraman, P.; A Ellenbogen, K. Long-term outcomes of His bundle pacing in patients with heart failure with left bundle branch block. Heart 2018, 105, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayaraman, P.; A Subzposh, F.; Naperkowski, A. Atrioventricular node ablation and His bundle pacing. EP Eur. 2017, 19, iv10–iv16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wu, S.; Xu, L.; Xiao, F.; Whinnett, Z.I.; Vijayaraman, P.; Su, L.; Huang, W. Feasibility and Efficacy of His Bundle Pacing or Left Bundle Pacing Combined With Atrioventricular Node Ablation in Patients With Persistent Atrial Fibrillation and Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillator Therapy. J. Am. Hear. Assoc. 2019, 8, e014253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, L.; Cai, M.; Wu, S.; Wang, S.; Xu, T.; Vijayaraman, P.; Huang, W. Long-term performance and risk factors analysis after permanent His-bundle pacing and atrioventricular node ablation in patients with atrial fibrillation and heart failure. EP Eur. 2020, 22, ii19–ii26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Wang, S.; Su, L.; Fu, G.; Su, Y.; Chen, K.; Zou, J.; Han, H.; Wu, S.; Sheng, X.; et al. His-bundle pacing vs biventricular pacing following atrioventricular nodal ablation in patients with atrial fibrillation and reduced ejection fraction: A multicenter, randomized, crossover study—The ALTERNATIVE-AF trial. Hear. Rhythm. 2022, 19, 1948–1955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirchhof, P.; Camm, A.J.; Goette, A.; Brandes, A.; Eckardt, L.; Elvan, A.; Fetsch, T.; van Gelder, I.C.; Haase, D.; Haegeli, L.M.; et al. Early Rhythm-Control Therapy in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation. New Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 1305–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olshansky, B.; Rosenfeld, L.E.; Warner, A.L.; Solomon, A.J.; O’Neill, G.; Sharma, A.; Platia, E.; Feld, G.K.; Akiyama, T.; Brodsky, M.A.; et al. The Atrial Fibrillation Follow-up Investigation of Rhythm Management (AFFIRM) study: Approaches to control rate in atrial fibrillation. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2004, 43, 1201–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valembois, L.; Audureau, E.; Takeda, A.; Jarzebowski, W.; Belmin, J.; Lafuente-Lafuente, C. Antiarrhythmics for maintaining sinus rhythm after cardioversion of atrial fibrillation. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2019, 2019, CD005049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, D.; Talajic, M.; Dorian, P.; Connolly, S.; Eisenberg, M.J.; Green, M.; Kus, T.; Lambert, J.; Dubuc, M.; Gagné, P.; et al. Amiodarone to Prevent Recurrence of Atrial Fibrillation. New Engl. J. Med. 2000, 342, 913–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lappe, J.M.; Cutler, M.J.; Day, J.D.; Bunch, T.J. Ablation for Persistent Atrial Fibrillation—Is There a Role for More Than PVI? Curr. Treat. Options Cardiovasc. Med. 2016, 18, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaïs, P.; Cauchemez, B.; Macle, L.; Daoud, E.; Khairy, P.; Subbiah, R.; Hocini, M.; Extramiana, F.; Sacher, F.; Bordachar, P.; et al. Catheter Ablation Versus Antiarrhythmic Drugs for Atrial Fibrillation. Circulation 2008, 118, 2498–2505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, Y.; Feng, W.; Huang, Q.; Yu, F.; Chen, J.; Wang, H. Meta-analysis of cryoballoon ablation versus antiarrhythmic drugs as initial therapy for symptomatic atrial fibrillation. Clin. Cardiol. 2021, 44, 1393–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciconte, G.; Ottaviano, L.; de Asmundis, C.; Baltogiannis, G.; Conte, G.; Sieira, J.; Di Giovanni, G.; Saitoh, Y.; Irfan, G.; Mugnai, G.; et al. Pulmonary vein isolation as index procedure for persistent atrial fibrillation: One-year clinical outcome after ablation using the second-generation cryoballoon. Hear. Rhythm. 2015, 12, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latchamsetty, R.; Morady, F. Long-Term Benefits Following Catheter Ablation of Atrial Fibrillation. Circ. J. 2013, 77, 1091–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romero, J.; Gianni, C.; Di Biase, L.; Natale, A. Catheter Ablation for Long-Standing Persistent Atrial Fibrillation. Methodist DeBakey Cardiovasc. J. 2015, 11, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorgente, A.; Tung, P.; Wylie, J.; Josephson, M.E. Six Year Follow-Up After Catheter Ablation of Atrial Fibrillation: A Palliation More Than a True Cure. Am. J. Cardiol. 2012, 109, 1179–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weerasooriya, R.; Khairy, P.; Litalien, J.; Macle, L.; Hocini, M.; Sacher, F.; Lellouche, N.; Knecht, S.; Wright, M.; Nault, I.; et al. Catheter Ablation for Atrial Fibrillation. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2011, 57, 160–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugumar, H.; Thomas, S.P.; Prabhu, S.; Voskoboinik, A.; Kistler, P.M. How to perform posterior wall isolation in catheter ablation for atrial fibrillation. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2017, 29, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, R.; Di Biase, L.; Mohanty, P.; Trivedi, C.; Russo, A.D.; Themistoclakis, S.; Casella, M.; Santarelli, P.; Fassini, G.; Santangeli, P.; et al. Proven isolation of the pulmonary vein antrum with or without left atrial posterior wall isolation in patients with persistent atrial fibrillation. Hear. Rhythm. 2015, 13, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLellan, A.J.; Prabhu, S.; Voskoboinik, A.; Wong, M.C.; Walters, T.E.; Pathik, B.; Morris, G.M.; Nisbet, A.; Lee, G.; Morton, J.B.; et al. Isolation of the posterior left atrium for patients with persistent atrial fibrillation: Routine adenosine challenge for dormant posterior left atrial conduction improves long-term outcome. Eur. 2017, 19, 1958–1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, S.Y.; Na, J.O.; Choi, C.U.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, J.W.; Kim, E.J.; Rha, S.-W.; Park, C.G.; Seo, H.S.; Oh, D.J.; et al. Does isolation of the left atrial posterior wall improve clinical outcomes after radiofrequency catheter ablation for persistent atrial fibrillation? Int. J. Cardiol. 2015, 181, 277–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kistler, P.M.; Chieng, D.; Sugumar, H.; Ling, L.-H.; Segan, L.; Azzopardi, S.; Al-Kaisey, A.; Parameswaran, R.; Anderson, R.D.; Hawson, J.; et al. Effect of Catheter Ablation Using Pulmonary Vein Isolation With vs Without Posterior Left Atrial Wall Isolation on Atrial Arrhythmia Recurrence in Patients With Persistent Atrial Fibrillation. JAMA 2023, 329, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.M.; Shim, J.; Park, J.; Yu, H.T.; Kim, T.-H.; Park, J.-K.; Uhm, J.-S.; Kim, J.-B.; Joung, B.; Lee, M.-H.; et al. The Electrical Isolation of the Left Atrial Posterior Wall in Catheter Ablation of Persistent Atrial Fibrillation. JACC Clin. Electrophysiol. 2019, 5, 1253–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masuda, M.; Inoue, K.; Tanaka, N.; Watanabe, T.; Makino, N.; Egami, Y.; Oka, T.; Minamiguchi, H.; Miyoshi, M.; Okada, M.; et al. Long-Term Impact of Additional Ablation After Pulmonary Vein Isolation: Results From EARNEST-PVI Trial. J. Am. Hear. Assoc. 2023, 12, e029651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, X.; Liao, J.; Ling, Z.; Meyer, C.; Sommer, P.; Futyma, P.; Martinek, M.; Schratter, A.; Acou, W.-J.; Wang, J.; et al. Adjunctive Left Atrial Posterior Wall Isolation in Treating Atrial Fibrillation. JACC Clin. Electrophysiol. 2022, 8, 605–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, V.Y.; Anic, A.; Koruth, J.; Petru, J.; Funasako, M.; Minami, K.; Breskovic, T.; Sikiric, I.; Dukkipati, S.R.; Kawamura, I.; et al. Pulsed Field Ablation in Patients With Persistent Atrial Fibrillation. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2020, 76, 1068–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, J.; Shin, D.G.; Han, S.J.; Lim, H.E. Does isolation of the left atrial posterior wall using cryoballoon ablation improve clinical outcomes in patients with persistent atrial fibrillation? A prospective randomized controlled trial. EP Eur. 2022, 24, 1093–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aryana, A.; Allen, S.L.; Pujara, D.K.; Bowers, M.R.; O’neill, P.G.; Yamauchi, Y.; Shigeta, T.; Vierra, E.C.; Okishige, K.; Natale, A. Concomitant Pulmonary Vein and Posterior Wall Isolation Using Cryoballoon With Adjunct Radiofrequency in Persistent Atrial Fibrillation. JACC Clin. Electrophysiol. 2020, 7, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, T.W.; Koay, C.H.; See, V.A.; McCall, R.; Chik, W.; Zecchin, R.; Byth, K.; Seow, S.-C.; Thomas, L.; Ross, D.L.; et al. Single-Ring Posterior Left Atrial (Box) Isolation Results in a Different Mode of Recurrence Compared With Wide Antral Pulmonary Vein Isolation on Long-Term Follow-Up. Circ. Arrhythmia Electrophysiol. 2012, 5, 968–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamborero, D.; Mont, L.; Berruezo, A.; Matiello, M.; Benito, B.; Sitges, M.; Vidal, B.; de Caralt, T.M.; Perea, R.J.; Vatasescu, R.; et al. Left Atrial Posterior Wall Isolation Does Not Improve the Outcome of Circumferential Pulmonary Vein Ablation for Atrial Fibrillation. Circ. Arrhythmia Electrophysiol. 2009, 2, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valderrábano, M.; Peterson, L.E.; Swarup, V.; Schurmann, P.A.; Makkar, A.; Doshi, R.N.; DeLurgio, D.; Athill, C.A.; Ellenbogen, K.A.; Natale, A.; et al. Effect of Catheter Ablation With Vein of Marshall Ethanol Infusion vs Catheter Ablation Alone on Persistent Atrial Fibrillation. JAMA 2020, 324, 1620–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derval, N.; Duchateau, J.; Denis, A.; Ramirez, F.D.; Mahida, S.; André, C.; Krisai, P.; Nakatani, Y.; Kitamura, T.; Takigawa, M.; et al. Marshall bundle elimination, Pulmonary vein isolation, and Line completion for ANatomical ablation of persistent atrial fibrillation (Marshall-PLAN): Prospective, single-center study. Heart Rhythm 2020, 18, 529–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lador, A.; Peterson, L.E.; Swarup, V.; Schurmann, P.A.; Makkar, A.; Doshi, R.N.; DeLurgio, D.; Athill, C.A.; Ellenbogen, K.A.; Natale, A.; et al. Determinants of outcome impact of vein of Marshall ethanol infusion when added to catheter ablation of persistent atrial fibrillation: A secondary analysis of the VENUS randomized clinical trial. Hear. Rhythm. 2021, 18, 1045–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, S.; Sang, C.; Long, D.; Bo, X.; Lai, Y.; Guo, Q.; Wang, Y.; Li, M.; He, L.; Zhao, X.; et al. Efficiency and Durability of EIVOM on Acute Reconnection After Mitral Isthmus Bidirectional Block. JACC Clin. Electrophysiol. 2024, 10, 685–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karatela, M.F.; Fudim, M.; Mathew, J.P.; Piccini, J.P. Neuromodulation therapy for atrial fibrillation. Hear. Rhythm. 2022, 20, 100–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pokushalov, E.; Romanov, A.; Katritsis, D.G.; Artyomenko, S.; Shirokova, N.; Karaskov, A.; Mittal, S.; Steinberg, J.S. Ganglionated plexus ablation vs linear ablation in patients undergoing pulmonary vein isolation for persistent/long-standing persistent atrial fibrillation: A randomized comparison. Hear. Rhythm. 2013, 10, 1280–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Driessen, A.H.; Berger, W.R.; Krul, S.P.; Berg, N.W.v.D.; Neefs, J.; Piersma, F.R.; Yin, D.R.C.P.; de Jong, J.S.; van Boven, W.P.; de Groot, J.R. Ganglion Plexus Ablation in Advanced Atrial Fibrillation. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2016, 68, 1155–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katritsis, D.G.; Pokushalov, E.; Romanov, A.; Giazitzoglou, E.; Siontis, G.C.; Po, S.S.; Camm, A.J.; Ioannidis, J.P. Autonomic Denervation Added to Pulmonary Vein Isolation for Paroxysmal Atrial Fibrillation. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2013, 62, 2318–2325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musikantow, D.R.; Neuzil, P.; Petru, J.; Koruth, J.S.; Kralovec, S.; Miller, M.A.; Funasako, M.; Chovanec, M.; Turagam, M.K.; Whang, W.; et al. Pulsed Field Ablation to Treat Atrial Fibrillation. JACC Clin. Electrophysiol. 2022, 9, 481–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kueffer, T.; Stettler, R.; Maurhofer, J.; Madaffari, A.; Stefanova, A.; Iqbal, S.U.R.; Thalmann, G.; Kozhuharov, N.A.; Galuszka, O.; Servatius, H.; et al. Pulsed-field vs cryoballoon vs radiofrequency ablation: Outcomes after pulmonary vein isolation in patients with persistent atrial fibrillation. Hear. Rhythm. 2024, 21, 1227–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rostock, T.; Salukhe, T.V.; Steven, D.; Drewitz, I.; Hoffmann, B.A.; Bock, K.; Servatius, H.; Müllerleile, K.; Sultan, A.; Gosau, N.; et al. Long-term single- and multiple-procedure outcome and predictors of success after catheter ablation for persistent atrial fibrillation. Hear. Rhythm. 2011, 8, 1391–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oakes, R.S.; Badger, T.J.; Kholmovski, E.G.; Akoum, N.; Burgon, N.S.; Fish, E.N.; Blauer, J.J.; Rao, S.N.; DiBella, E.V.; Segerson, N.M.; et al. Detection and Quantification of Left Atrial Structural Remodeling With Delayed-Enhancement Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Patients With Atrial Fibrillation. Circulation 2009, 119, 1758–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rolf, S.; Kircher, S.; Arya, A.; Eitel, C.; Sommer, P.; Richter, S.; Gaspar, T.; Bollmann, A.; Altmann, D.; Piedra, C.; et al. Tailored Atrial Substrate Modification Based on Low-Voltage Areas in Catheter Ablation of Atrial Fibrillation. Circ. Arrhythmia Electrophysiol. 2014, 7, 825–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kircher, S.; Arya, A.; Altmann, D.; Rolf, S.; Bollmann, A.; Sommer, P.; Dagres, N.; Richter, S.; Breithardt, O.-A.; Dinov, B.; et al. Individually tailored vs. standardized substrate modification during radiofrequency catheter ablation for atrial fibrillation: A randomized study. Europace 2017, 20, 1766–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marrouche, N.F.; Wazni, O.; McGann, C.; Greene, T.; Dean, J.M.; Dagher, L.; Kholmovski, E.; Mansour, M.; Marchlinski, F.; Wilber, D.; et al. Effect of MRI-Guided Fibrosis Ablation vs Conventional Catheter Ablation on Atrial Arrhythmia Recurrence in Patients With Persistent Atrial Fibrillation. JAMA 2022, 327, 2296–2305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zghaib, T.; Nazarian, S. New Insights Into the Use of Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Imaging to Guide Decision Making in Atrial Fibrillation Management. Can. J. Cardiol. 2018, 34, 1461–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Zheng, L.; Jiang, C.; Fan, J.; Liu, X.; Zhan, X.; Li, J.; Wang, L.; Yang, H.; Zhu, W.; et al. Circumferential Pulmonary Vein Isolation Plus Low-Voltage Area Modification in Persistent Atrial Fibrillation: The STABLE-SR-II Trial. JACC Clin. Electrophysiol. 2022, 8, 882–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chieng, D.; Sugumar, H.; Hunt, A.; Ling, L.-H.; Segan, L.; Al-Kaisey, A.; Hawson, J.; Prabhu, S.; Voskoboinik, A.; Wong, G.; et al. Impact of Posterior Left Atrial Voltage on Ablation Outcomes in Persistent Atrial Fibrillation. JACC Clin. Electrophysiol. 2023, 9, 2291–2299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huo, Y.; Gaspar, T.; Schönbauer, R.; Wójcik, M.; Fiedler, L.; Roithinger, F.X.; Martinek, M.; Pürerfellner, H.; Kirstein, B.; Richter, U.; et al. Low-Voltage Myocardium-Guided Ablation Trial of Persistent Atrial Fibrillation. NEJM Évid. 2022, 1, EVIDoa2200141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cutler, M.J.; Sattayaprasert, P.; Pivato, E.; Jabri, A.; AlMahameed, S.T.; Ziv, O. Low voltage-guided ablation of posterior wall improves 5-year arrhythmia-free survival in persistent atrial fibrillation. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2022, 33, 2475–2484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, B.; Jiang, C.; Lin, Y.; Yang, G.; Chu, H.; Cai, H.; Lu, F.; Zhan, X.; Xu, J.; Wang, X.; et al. STABLE-SR (Electrophysiological Substrate Ablation in the Left Atrium During Sinus Rhythm) for the Treatment of Nonparoxysmal Atrial Fibrillation. Circ. Arrhythmia Electrophysiol. 2017, 10, e005405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.-H.; Li, Z.; Mao, J.-L.; He, B. A novel individualized substrate modification approach for the treatment of long-standing persistent atrial fibrillation: Preliminary results. Int. J. Cardiol. 2014, 175, 162–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiener, N.; Rosenblueth, A. The mathematical formulation of the problem of conduction of impulses in a network of connected excitable elements, specifically in cardiac muscle. Arch. Inst. Cardiol. Mex. 1946, 16, 205–265. [Google Scholar]
- Narayan, S.M.; Krummen, D.E.; Shivkumar, K.; Clopton, P.; Rappel, W.-J.; Miller, J.M. Treatment of Atrial Fibrillation by the Ablation of Localized Sources. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2012, 60, 628–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narayan, S.M.; Baykaner, T.; Clopton, P.; Schricker, A.; Lalani, G.G.; Krummen, D.E.; Shivkumar, K.; Miller, J.M. Ablation of Rotor and Focal Sources Reduces Late Recurrence of Atrial Fibrillation Compared With Trigger Ablation Alone. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2014, 63, 1761–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gianni, C.; Mohanty, S.; Di Biase, L.; Metz, T.; Trivedi, C.; Gökoğlan, Y.; Güneş, M.F.; Bai, R.; Al-Ahmad, A.; Burkhardt, J.D.; et al. Acute and early outcomes of focal impulse and rotor modulation (FIRM)-guided rotors-only ablation in patients with nonparoxysmal atrial fibrillation. Hear. Rhythm. 2015, 13, 830–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berntsen, R.F.; Håland, T.F.; Skårdal, R.; Holm, T. Focal impulse and rotor modulation as a stand-alone procedure for the treatment of paroxysmal atrial fibrillation: A within-patient controlled study with implanted cardiac monitoring. Hear. Rhythm. 2016, 13, 1768–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tilz, R.R.; Lenz, C.; Sommer, P.; Roza, M.-S.; E Sarver, A.; Williams, C.G.; Heeger, C.; Hindricks, G.; Vogler, J.; Eitel, C. Focal Impulse and Rotor Modulation Ablation vs. Pulmonary Vein isolation for the treatment of paroxysmal Atrial Fibrillation: Results from the FIRMAP AF study. Europace 2020, 23, 722–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benharash, P.; Buch, E.; Frank, P.; Share, M.; Tung, R.; Shivkumar, K.; Mandapati, R. Quantitative Analysis of Localized Sources Identified by Focal Impulse and Rotor Modulation Mapping in Atrial Fibrillation. Circ. Arrhythmia Electrophysiol. 2015, 8, 554–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, J.M.; Kalra, V.; Das, M.K.; Jain, R.; Garlie, J.B.; Brewster, J.A.; Dandamudi, G. Clinical Benefit of Ablating Localized Sources for Human Atrial Fibrillation. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2017, 69, 1247–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knecht, S.; Sohal, M.; Deisenhofer, I.; Albenque, J.-P.; Arentz, T.; Neumann, T.; Cauchemez, B.; Duytschaever, M.; Ramoul, K.; Verbeet, T.; et al. Multicentre evaluation of non-invasive biatrial mapping for persistent atrial fibrillation ablation: The AFACART study. Eur. 2017, 19, 1302–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.-J.; Lo, M.-T.; Chang, S.-L.; Lo, L.-W.; Hu, Y.-F.; Chao, T.-F.; Chung, F.-P.; Liao, J.-N.; Lin, C.-Y.; Kuo, H.-Y.; et al. Benefits of Atrial Substrate Modification Guided by Electrogram Similarity and Phase Mapping Techniques to Eliminate Rotors and Focal Sources Versus Conventional Defragmentation in Persistent Atrial Fibrillation. JACC Clin. Electrophysiol. 2016, 2, 667–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baykaner, T.; Clopton, P.; Lalani, G.G.; Schricker, A.A.; Krummen, D.E.; Narayan, S.M. Targeted Ablation at Stable Atrial Fibrillation Sources Improves Success Over Conventional Ablation in High-Risk Patients: A Substudy of the CONFIRM Trial. Can. J. Cardiol. 2013, 29, 1218–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudry, S.; Mansour, M.; Sundaram, S.; Nguyen, D.T.; Dukkipati, S.R.; Whang, W.; Kessman, P.; Reddy, V.Y. RADAR. Circ. Arrhythmia Electrophysiol. 2020, 13, e007825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haissaguerre, M.; Hocini, M.; Denis, A.; Shah, A.J.; Komatsu, Y.; Yamashita, S.; Daly, M.; Amraoui, S.; Zellerhoff, S.; Picat, M.-Q.; et al. Driver Domains in Persistent Atrial Fibrillation. Circulation 2014, 130, 530–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Tai, C. Catheter Ablation of Atrial Fibrillation Originating from the Non-Pulmonary Vein Foci. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2005, 16, 229–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.-S.; Tai, C.-T.; Hsieh, M.-H.; Tsai, C.-F.; Lin, Y.-K.; Tsao, H.-M.; Huang, J.-L.; Yu, W.-C.; Yang, S.-P.; Ding, Y.-A.; et al. Catheter Ablation of Paroxysmal Atrial Fibrillation Initiated by Non–Pulmonary Vein Ectopy. Circulation 2003, 107, 3176–3183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-H.; Tai, C.-T.; Hsieh, M.-H.; Tsao, H.-M.; Lin, Y.-J.; Chang, S.-L.; Huang, J.-L.; Lee, K.-T.; Chen, Y.-J.; Cheng, J.-J.; et al. Predictors of Non-Pulmonary Vein Ectopic Beats Initiating Paroxysmal Atrial Fibrillation. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2005, 46, 1054–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Della Rocca, D.G.; Di Biase, L.; Mohanty, S.; Trivedi, C.; Gianni, C.; Romero, J.; Tarantino, N.; Magnocavallo, M.; Bassiouny, M.; Natale, V.N.; et al. Targeting non-pulmonary vein triggers in persistent atrial fibrillation: Results from a prospective, multicentre, observational registry. Eur. 2021, 23, 1939–1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calkins, H.; Hindricks, G.; Cappato, R.; Kim, Y.-H.; Saad, E.B.; Aguinaga, L.; Akar, J.G.; Badhwar, V.; Brugada, J.; Camm, J.; et al. 2017 HRS/EHRA/ECAS/APHRS/SOLAECE expert consensus statement on catheter and surgical ablation of atrial fibrillation. Heart Rhythm. 2017, 14, e275–e444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gianni, C.; Mohanty, S.; Trivedi, C.; Di Biase, L.; Natale, A. Novel concepts and approaches in ablation of atrial fibrillation: The role of non-pulmonary vein triggers. Eur. 2018, 20, 1566–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thind, M.; Arceluz, M.R.; Lucena-Padros, I.; Kubala, M.; Mirwais, M.; Bode, W.; Cerantola, M.; Sugrue, A.; Van Niekerk, C.; Vigdor, A.; et al. Identifying Origin of Nonpulmonary Vein Triggers Using 2 Stationary Linear Decapolar Catheters. JACC Clin. Electrophysiol. 2023, 9, 2275–2287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tonchev, I.R.; Chieng, D.; Hawson, J.; Segan, L.; Sugumar, H.; Voskoboinik, A.; Prabhu, S.; Ling, L.H.; Lee, G.; Kalman, J.M.; et al. P-Wave Morphology From Common Nonpulmonary Vein Trigger Sites Following Pulmonary Vein and Posterior Wall Isolation. JACC Clin. Electrophysiol. 2024, 10, 527–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, J.L.; Schuessler, R.B.; D’Agostino, H.J.; Stone, C.M.; Chang, B.C.; E Cain, M.; Corr, P.B.; Boineau, J.P. The surgical treatment of atrial fibrillation. III. Development of a definitive surgical procedure. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 1991, 101, 569–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cox, J.L.; Schuessler, R.B.; Lappas, D.G.; Boineau, J.P. An 8½-Year Clinical Experience with Surgery for Atrial Fibrillation. Ann. Surg. 1996, 224, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melby, S.J.; Zierer, A.; Bailey, M.S.; Cox, J.L.; Lawton, J.S.; Munfakh, N.; Crabtree, T.D.; Moazami, N.; Huddleston, C.B.; Moon, M.R.; et al. A New Era in the Surgical Treatment of Atrial Fibrillation. Ann Surg. 2006, 244, 583–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeLurgio, D.B.; Crossen, K.J.; Gill, J.; Blauth, C.; Oza, S.R.; Magnano, A.R.; Mostovych, M.A.; Halkos, M.E.; Tschopp, D.R.; Kerendi, F.; et al. Hybrid Convergent Procedure for the Treatment of Persistent and Long-Standing Persistent Atrial Fibrillation. Circ. Arrhythmia Electrophysiol. 2020, 13, e009288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Heijden, C.A.; Weberndörfer, V.; Vroomen, M.; Luermans, J.G.; Chaldoupi, S.-M.; Bidar, E.; Vernooy, K.; Maessen, J.G.; Pison, L.; van Kuijk, S.M.; et al. Hybrid Ablation Versus Repeated Catheter Ablation in Persistent Atrial Fibrillation. JACC Clin. Electrophysiol. 2023, 9, 1013–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Study (Year) | Participants | PeAF (%) | Randomization | Sinus Rhythm Outcome (%) | Follow Up Time | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intervention | Control | |||||
| 2023 (The CAPLA study) [99] | 338 | 100 | PVI + PWI vs. PVIalone | 52.4 | 53.6 | 12 m |
| 2022 [104] | 100 | 100 | PVI + PWI vs. PVIalone | 76 | 54 | 457.9 ± 61.8 d |
| 2021 [105] | 110 | 100 | PVI + PWI vs. PVIalone | 74.5 | 54.5 | 12 m |
| 2019 (POBI-AF) [100] | 217 | 100 | PVI + posterior wall Box Isolation vs. PVIalone | 73.5 | 76.2 | 16.2 ± 8.8 m |
| 2015 [98] | 120 | 100 | PVI + PWI vs. PVIalone | 83.3 | 63.3 | 12 m |
| 2012 [106] | 220 | 39 | PVI + single-ring isolation vs. wide antral pulmonary vein isolation | 67 | 64 | 2 y |
| 2009 [107] | 120 | 40 | PVI + linear lesions along the LA roof vs. PVI + Left atrial posterior wall isolation | 55 | 55 | 10 ± 4 m |
| Study (Year) | Participant | PeAF (%) | Randomization | Sinus Rhythm Outcome (%) | Follow Up Time | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intervention | Control | |||||
| 2023 (CAPLA Substudy) [125] | 210 | 100 | PVI plus PWI with posterior wall LVAs vs. PVI alone | 44.8 | 41.9 | 12 m |
| 2022 (STABLE-SR-II) [124] | 300 | 100 | CPVI plus low-voltage area modification vs. CPVI alone | 67.2 | 67.4 | 18 m |
| 2022 (DECAAF II) [122] | 815 | 100 | PVI plus MRI-guided atrial fibrosis ablation vs. PVI alone | 57 | 53.9 | 12–18 m |
| 2022 (ERASE-AF) [126] | 324 | 100 | PVI vs. PVI plus individualized substrate ablation of atrial low-voltage myocardium | 65 | 50 | 12 m |
| 2022 [127] | 152 | 100 | PVI alone or PVI + PW ablation vs. voltage-guided ablation | 64 | 34 | 60 m |
| 2018 [121] | 124 | 49 | Low-voltage guided ablation + CPVI vs. PVI with (persistent AF) or without (paroxysmal AF) additional linear ablation | 68 | 42 | 12 ± 3 m |
| STABLE-SR (2017) [128] | 229 | 100 | Low-voltage guided ablation + CPVI vs. CPVI + additional linear lesions and defragmentation | 74 | 71.5 | 18 m |
| 2014 [129] | 124 | 100 (L-PeAF *) | CPVI + individualized substrate modification vs. Stepwise ablation | 65.5 | 45 | 12 m |
| Study (Year) | Participants | PeAF (%) | Intervention | Sinus Rhythm Outcome (%) Time | Follow Up Time | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intervention | Control | |||||
| 2017 The Indiana University FIRM * Registry [137] | 170 | 31 | FIRMguided ablation | 70 | / | 1 y (179 to 570 d) |
| 2017(AFACART study) [138] | 118 | 100 | Non-invasive mapping guided ablation targeted drivers + PVI | 76.8 | / | 12 m |
| 2016 [139] | 68 | 100 | Nonlinear phase mapping- guided substrate ablation vs. extensive complex fractionated atrial electrograms ablation | 58.3 (group-1) | 77.3 (group-2) | 17.7 ± 8.17 m |
| 2015 [133] | 29 | 100 | FIRM-guided only ablation | 17 | / | 5.7 m |
| 2013 [140] | 73 | 49.3 | Conventional ablation vs. FIRM plus conventional ablation | 74 | 39 | 890 d |
| CONFIRM (2012) [131] | 92 | 70.7 | FIRM + conventional ablation vs. conventional ablation alone | 82.4 | 44.9 | 273 d (132–681) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yue, X.; Zhou, L.; Zhao, C. Integrated Management of Persistent Atrial Fibrillation. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 91. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13010091
Yue X, Zhou L, Zhao C. Integrated Management of Persistent Atrial Fibrillation. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(1):91. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13010091
Chicago/Turabian StyleYue, Xindi, Ling Zhou, and Chunxia Zhao. 2025. "Integrated Management of Persistent Atrial Fibrillation" Biomedicines 13, no. 1: 91. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13010091
APA StyleYue, X., Zhou, L., & Zhao, C. (2025). Integrated Management of Persistent Atrial Fibrillation. Biomedicines, 13(1), 91. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13010091








