Rapid Decrease in Dextrose Concentration After Intra-Articular Knee Injection: Implications for Mechanism of Action of Dextrose Prolotherapy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Injection Procedure and Injectate
2.2. Aspiration Procedure
2.3. Determination of Dextrose Concentration
2.4. Analysis of Dextrose Concentration Curves
3. Results
3.1. Demographics
3.2. Injection Trial Time Points
3.3. Dextrose Concentration Results from Trials 1–3
4. Discussion
4.1. Clinical Applications and Research Implications
4.2. Strengths and Limitations
4.3. Non-Osmotic Theories for Mechanisms of Action of DPT
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cohen, S.P.; Vase, L.; Hooten, W.M. Chronic pain: An update on burden, best practices, and new advances. Lancet 2021, 397, 2082–2097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waluyo, Y.; Artika, S.R.; Insani Nanda, W.; Gunawan, A.; Zainal, A.T.F. Efficacy of Prolotherapy for Osteoarthritis: A Systematic Review. J. Rehabil. Med. 2023, 55, jrm00372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hackett, G.S. Ligament and Tendon Relaxation Treated by Prolotherapy, 1st ed.; Charles C. Thomas: Springfield, IL, USA, 1956. [Google Scholar]
- Hsu, C.; Vu, K.; Borg-Stein, J. Prolotherapy: A Narrative Review of Mechanisms, Techniques, and Protocols, and Evidence for Common Musculoskeletal Conditions. Phys. Med. Rehabil. Clin. N. Am. 2023, 34, 165–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahgat, M.M.; Abdel-Hamid, A.M. Is dextrose prolotherapy beneficial in the management of temporomandibular joint internal derangement? A systematic review. Cranio 2023, 41, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arias-Vazquez, P.I.; Tovilla-Zarate, C.A.; Gonzalez-Graniel, K.; Burad-Fonz, W.; Gonzalez-Castro, T.B.; Lopez-Narvaez, M.L.; Castillo-Avila, R.G.; Arcila-Novelo, R. Efficacy of hypertonic dextrose infiltrations for pain control in rotator cuff tendinopathy: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Acta Reumatol. Port. 2021, 46, 156–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Rabago, D.; Chung, V.C.; Reeves, K.D.; Wong, S.Y.; Sit, R.W. Effects of Hypertonic Dextrose Injection (Prolotherapy) in Lateral Elbow Tendinosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2022, 103, 2209–2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, C.Y.; Hsiao, M.Y.; Chang, K.V.; Han, D.S.; Wang, T.G. Comparative effectiveness of dextrose prolotherapy versus control injections and exercise in the management of osteoarthritis pain: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Pain Res. 2016, 9, 847–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanderson, L.M.; Bryant, A. Effectiveness and safety of prolotherapy injections for management of lower limb tendinopathy and fasciopathy: A systematic review. J. Foot Ankle Res. 2015, 8, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liang, J.; Yao, J.; Song, H.X.; Yang, X.T.; Wu, F.C.; Ye, Y.; Li, J.H.; Wu, T. Meta-analysis of clinical trials focusing on hypertonic dextrose prolotherapy (HDP) for knee osteoarthritis. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 2022, 34, 715–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morath, O.; Beck, M.; Taeymans, J.; Hirschmuller, A. Sclerotherapy and prolotherapy for chronic patellar tendinopathies—A promising therapy with limited available evidence, a systematic review. J. Exp. Orthop. 2020, 7, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chutumstid, T.; Susantitaphong, P.; Koonalinthip, N. Effectiveness of dextrose prolotherapy for the treatment of chronic plantar fasciitis: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. PMR 2023, 15, 380–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banks, A. A rationale for prolotherapy. J. Orthop. Med. 1991, 13, 54–59. [Google Scholar]
- Ekwueme, E.C.; Mohiuddin, M.; Yarborough, J.A.; Brolinson, P.G.; Docheva, D.; Fernandes, H.A.M.; Freeman, J.W. Prolotherapy Induces an Inflammatory Response in Human Tenocytes In Vitro. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2017, 475, 2117–2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guran, S.; Coban, S.D.; Yener-Karasimav, O.; Demirhan, S.; Karagac, N.; Orscelik, A.; Altayli, E.; Yiltiz, Y. Dextrose solution used for prolotherapy decreases cell viability and increases gene expressions of angiogenic and apoptotic factors. Gulhane Med. J. 2017, 60, 42–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, M.S.; Park, J.; Ok, S.H.; Park, M.; Sohn, J.T.; Cho, M.S.; Shin, I.W.; Kim, Y.A. The proper concentrations of dextrose and lidocaine in regenerative injection therapy: In vitro study. Korean J. Pain 2021, 34, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildiz, K.M.; Guler, H.; Ogut, H.; Yildizgoren, M.T.; Turhanoglu, A.D. A comparison between hypertonic dextrose prolotherapy and conventional physiotherapy in patients with knee osteoarthritis. Med. Int. 2023, 3, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.; Ettema, A.M.; Zhao, C.; Zobitz, M.E.; Wold, L.E.; An, K.N.; Amadio, P.C. Dextrose-induced subsynovial connective tissue fibrosis in the rabbit carpal tunnel: A potential model to study carpal tunnel syndrome? Hand 2008, 3, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, K.T.; Rabago, D.P.; Best, T.M.; Patterson, J.J.; Vanderby, R.J. Early inflammatory response of knee ligaments to prolotherapy in a rat model. J. Orthop. Res. 2008, 26, 816–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.T.; Wu, C.H.; Lin, J.A.; Su, D.C.; Hung, C.Y.; Lam, S.K.H. Efficacy of 5% Dextrose Water Injection for Peripheral Entrapment Neuropathy: A Narrative Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maniquis-Smigel, L.; Reeves, K.D.; Rosen, H.J.; Lyftogt, J.; Graham-Coleman, C.; Cheng, A.L.; Rabago, D. Analgesic Effect and Potential Cumulative Benefit from Caudal Epidural D5W in Consecutive Participants with Chronic Low-Back and Buttock/Leg Pain. J. Altern. Complement Med. 2018, 24, 1189–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maniquis-Smigel, L.; Celis, P.; Reeves, D. Dextrose-Based Perineural Injection Treatment, and Ultrasound Hydrodissection. In Musculoskeletal Ultrasound-Guided Regenerative Medicine; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 375–395. [Google Scholar]
- Lam, K.H.S.; Wu, Y.T.; Reeves, K.D.; Galluccio, F.; Allam, A.E.; Peng, P.W.H. Ultrasound-Guided Interventions for Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analyses. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.T.; Ho, T.Y.; Chou, Y.C.; Ke, M.J.; Li, T.Y.; Tsai, C.K.; Chen, L.C. Six-month efficacy of perineural dextrose for carpal tunnel syndrome: A prospective, randomized, double-blind, controlled trial. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2017, 92, 1179–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansiz-Kaplan, B.; Nacir, B.; Pervane-Vural, S.; Tosun-Meric, O.; Duyur-Cakit, B.; Genc, H. Effect of Perineural Dextrose Injection on Ulnar Neuropathy at the Elbow: A Randomized, Controlled, Double-Blind Study. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2022, 103, 2085–2091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murakami, Y.; Ochi, M.; Ikuta, Y.; Higashi, Y. Permeation from the synovial fluid as nutritional pathway for the anterior cruciate ligament in rabbits. Acta Physiol. Scand. 1996, 158, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carney, J.; Heckmann, N.; Mayer, E.N.; Alluri, R.K.; Vangsness, C.T., Jr.; Hatch Iii, G.F.; Weber, A.E. Should antibiotics be administered before arthroscopic knee surgery? A systematic review of the literature. World J. Orthop. 2018, 9, 262–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, T. Serial Dilution Method & Purpose. 2022. Available online: https://study.com/academy/lesson/serial-dilution-in-microbiology-calculation-method-technique.html (accessed on 17 September 2024).
- Kunst, A.; Draeger, B.; Ziegenhorn, J. Carbohydrates. In Methods of Enzymatic Analysis, 3rd ed.; Burgmeyer, H.U., Ed.; Verlag Chemie: Weinheim, Germany, 1984; Volume VI, pp. 163–172. [Google Scholar]
- Tietz, N.W. Clinical Guide to Laboratory Tests, 4th ed.; W.B. Saunders Co: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2006; pp. 444–451. [Google Scholar]
- Spurr, W.A.; Arnold, D.R. A short-cut method of fitting a logistic curve. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 2012, 43, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.W.S. Seasonal time series models. In Time Series Analysis: Univariate and Multivariate Methods; Pearson Addison Wesley: Reading, MA, USA, 2006; pp. 160–185. [Google Scholar]
- Heilmann, H.H.; Lindenhayn, K.; Walther, H.U. Synovial volume of healthy and arthritic human knee joints. Z. Orthop. Ihre Grenzgeb. 1996, 134, 144–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faryna, A.; Goldenberg, K. Chapter 166: Joint fluid. In Clinical Methods: The History, Physical, and Laboratory Examinations, 3rd ed.; Walker, H.K., Hall, W.D., Hurst, J.W., Eds.; Butterworths: Boston, MA, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Gottesman, I.; Mandarino, L.; Verdonk, C.; Rizza, R.; Gerich, J. Insulin increases the maximum velocity for glucose uptake without altering the Michaelis constant in man. Evidence that insulin increases glucose uptake merely by providing additional transport sites. J. Clin. Investig. 1982, 70, 1310–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, H.; Pallardo, F.V.; Seidner, G.A.; Vannucci, S.; Simpson, I.A.; Birnbaum, M.J. Kinetics of GLUT1 and GLUT4 glucose transporters expressed in Xenopus oocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 8514–8520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guang, Y.; McGrath, T.M.; Klug, N.R.; Nims, R.J.; Shih, C.C.; Bayguinov, P.O.; Guilak, F.; Pham, C.T.N.; Fitzpatrick, J.A.J.; Setton, L.A. Combined Experimental Approach and Finite Element Modeling of Small Molecule Transport Through Joint Synovium to Measure Effective Diffusivity. J. Biomech. Eng. 2020, 142, 0410101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenmund, C.; Stevens, C.F. Definition of the readily releasable pool of vesicles at hippocampal synapses. Neuron 1996, 16, 1197–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foers, A.D.; Cheng, L.; Hill, A.F.; Wicks, I.P.; Pang, K.C. Review: Extracellular Vesicles in Joint Inflammation. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017, 69, 1350–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cherng, J.H.; Chang, S.J.; Tsai, H.D.; Chun, C.F.; Fan, G.Y.; Reeves, K.D.; Lam, K.H.S.; Wu, Y.T. The Potential of Glucose Treatment to Reduce Reactive Oxygen Species Production and Apoptosis of Inflamed Neural Cells In Vitro. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.T.; Chen, Y.P.; Lam, K.H.S.; Reeves, K.D.; Lin, J.A.; Kuo, C.Y. Mechanism of Glucose Water as a Neural Injection: A Perspective on Neuroinflammation. Life 2022, 12, 832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sit, R.W.; Reeves, K.D.; Zhong, C.C.; Wong, C.H.L.; Wang, B.; Chung, V.C.; Wong, S.Y.; Rabago, D. Efficacy of hypertonic dextrose injection (prolotherapy) in temporomandibular joint dysfunction: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 14638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sit, R.W.; Chung, V.; Reeves, K.D.; Rabago, D.; Chan, K.K.; Chan, D.C.; Wu, X.; Ho, R.S.; Wong, S.Y. Hypertonic dextrose injections (prolotherapy) in the treatment of symptomatic knee osteoarthritis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 25247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, C.H.; Chiang, Y.C.; Chen, H.T.; Huang, P.H.; Hsu, H.C.; Tang, C.H. High glucose induces vascular endothelial growth factor production in human synovial fibroblasts through reactive oxygen species generation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1830, 2649–2658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, E.; Kou, Y.; Junge, J.; Chen, L.; Kochan, A.; Johnston, M.; Rabago, D. Hypertonic Dextrose Stimulates Chondrogenic Cells to Deposit Collagen and Proliferate. Cartilage 2021, 13 (Suppl. S2), 213S–224S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karasimav, Ö.; Çoban, Z.D. Dextrose concentration for prolotherapy: A study on human neuroblastoma cells. Gulhane Med. J. 2023, 65, 160–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.J.; Lin, C.Y.; Tsai, C.H.; Huang, Y.L.; Tang, C.H. Glucose suppresses IL-1β-induced MMP-1 expression through the FAK, MEK, ERK, and AP-1 signaling pathways. Environ. Toxicol. 2018, 33, 1061–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.J.; Fong, Y.C.; Lin, C.Y.; Huang, Y.L.; Tang, C.H. Glucose enhances aggrecan expression in chondrocytes via the PKCα/p38-miR141-3p signaling pathway. J. Cell. Physiol. 2018, 233, 6878–6887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vujovic, P.; Chirillo, M.; Silverthorn, D.U. Learning (by) osmosis: An approach to teaching osmolarity and tonicity. Adv. Physiol. Educ. 2018, 42, 626–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silverthorn, D.U. Isosmotic is not always isotonic: The five-minute version. Adv. Physiol. Educ. 2016, 40, 499–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manderville, J.R.; More, K.M.; Tennankore, K. Misunderstandings about Tonicity and Osmolality Can Lead to Patient Harm. Can. J. Hosp. Pharm. 2023, 76, 324–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byers, M.S.; Howard, C.; Wang, X. Avian and Mammalian Facilitative Glucose Transporters. Microarrays 2017, 6, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyle, R.A.; Steensma, D.P.; Shampo, M.A. Barry James Marshall-Discovery of Helicobacter pylori as a Cause of Peptic Ulcer. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2016, 91, e67–e68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellstrom, P.M. This year’s Nobel Prize to gastroenterology: Robin Warren and Barry Marshall awarded for their discovery of Helicobacter pylori as pathogen in the gastrointestinal tract. World J. Gastroenterol. 2006, 12, 3126–3127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacIver, M.B.; Tanelian, D.L. Activation of C fibers by metabolic perturbations associated with tourniquet ischemia. Anesthesiology 1992, 76, 617–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, S.K.H.; Reeves, K.D.; Cheng, A.L. Transition from Deep Regional Blocks toward Deep Nerve Hydrodissection in the Upper Body and Torso: Method Description and Results from a Retrospective Chart Review of the Analgesic Effect of 5% Dextrose Water as the Primary Hydrodissection Injectate to Enhance Safety. Biomed. Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 7920438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maniquis-Smigel, L.; Reeves, K.D.; Rosen, J.H.; Coleman, C.; Lyftogt, J.; Cheng, A.L.; Rabago, D. Short term analgesic effects of 5% dextrose epidural injection for chronic low back pain. A randomized controlled trial. Anesth. Pain Med. 2017, 7, e42550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holden, J.E.; Pizzi, J.A.; Jeong, Y. An NK1 receptor antagonist microinjected into the periaqueductal gray blocks lateral hypothalamic-induced antinociception in rats. Neurosci. Lett. 2009, 453, 115–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parenti, C.; Arico, G.; Ronsisvalle, G.; Scoto, G.M. Supraspinal injection of Substance P attenuates allodynia and hyperalgesia in a rat model of inflammatory pain. Peptides 2012, 34, 412–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, D.S.; Lee, C.H.; Shieh, Y.D.; Chang, C.T.; Li, M.H.; Chu, Y.C.; Wang, J.L.; Chang, K.V.; Lin, S.H.; Chen, C.C. A role for substance P and acid-sensing ion channel 1a in prolotherapy with dextrose-mediated analgesia in a mouse model of chronic muscle pain. Pain 2022, 163, e622–e633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Topol, G.A.; Pestalardo, I.G.; Reeves, K.D.; Elias, F.; Steinmetz, N.J.; Cheng, A.L.; Rabago, D. Dextrose Prolotherapy for Symptomatic Grade IV Knee Osteoarthritis: A Pilot Study of Early and Longer-Term Analgesia and Pain-Specific Cytokine Concentrations. Clin. Pract. 2022, 12, 926–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshii, Y.; Zhao, C.; Schmelzer, J.D.; Low, P.A.; An, K.N.; Amadio, P.C. Effects of hypertonic dextrose injections in the rabbit carpal tunnel. J. Orthop. Res. 2011, 29, 1022–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshii, Y.; Zhao, C.; Schmelzer, J.D.; Low, P.A.; An, K.N.; Amadio, P.C. Effects of multiple injections of hypertonic dextrose in the rabbit carpal tunnel: A potential model of carpal tunnel syndrome development. Hand 2014, 9, 52–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topol, G.A.; Podesta, L.A.; Reeves, K.D.; Giraldo, M.M.; Johnson, L.J.; Grasso, R.; Jamín, A.; Clark, T.; Rabago, D. The chondrogenic effect of intra-articular hypertonic-dextrose (prolotherapy) in severe knee osteoarthritis. PMR 2016, 8, 1072–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Fattah, Y.H.; Mohasseb, D.F.; Kotb, H.T.; Mostafa, S.I.; Abdelnaby, H.M.A. Effect of classical prolotherapy technique in knee osteoarthritis for a sample of Egyptian population: Clinical and imaging study. Egypt. Rheumatol. Rehabil. 2024, 51, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
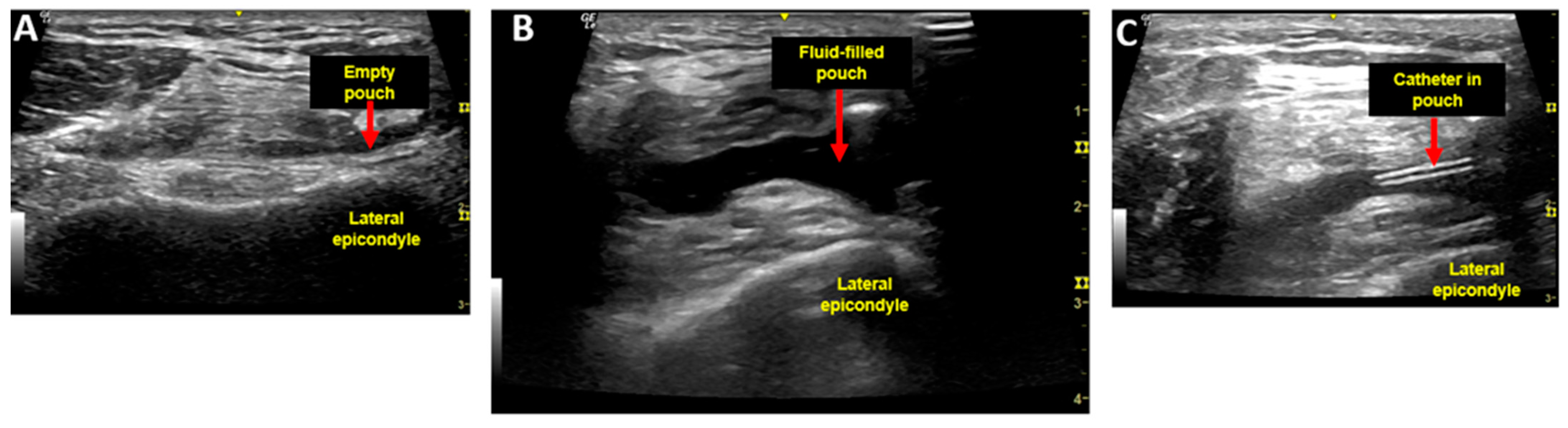
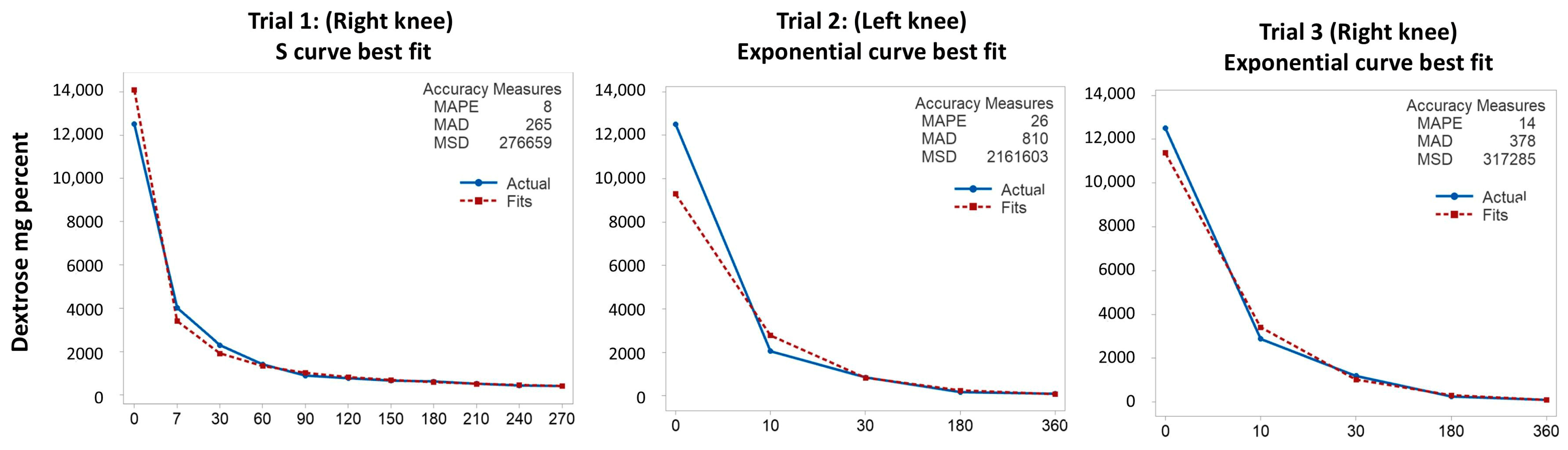
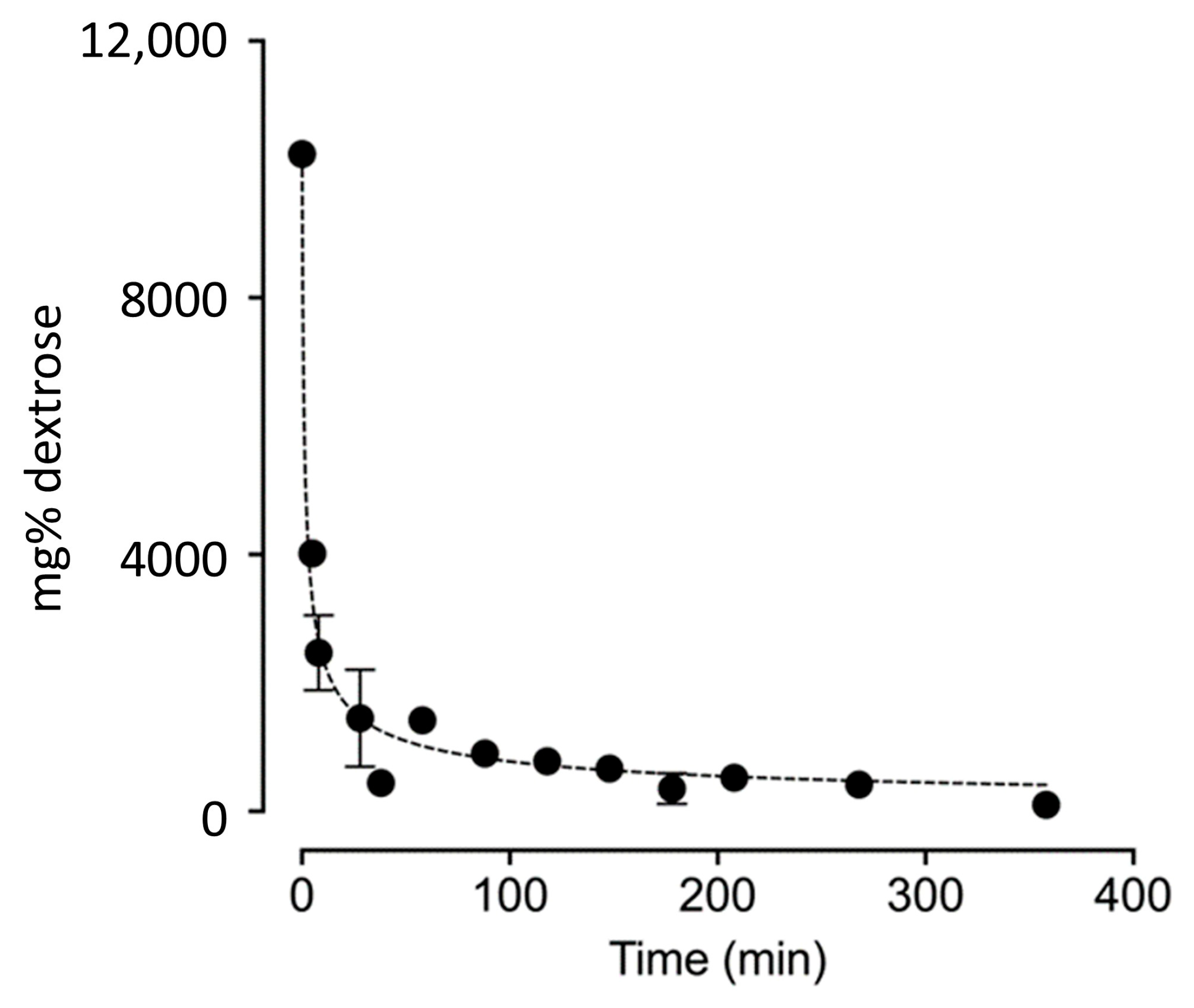
| Minutes After Beginning Injection | Trial 1 R Knee mg% (mM) | Trial 2 R Knee mg% (mM) | Trial 3 L Knee mg% (mM) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 Baseline synovial fluid dextrose (Estimated) | 100 (6) | 100 (6) | 100 (6) |
| 0 Injectate dextrose concentration | 12,500 (695) | 12,500 (695) | 12,500 (695) |
| 2 Estimated dilution effect 1 | 10,237 (641) | 10,237 (641) | 10,237 (641) |
| 7 | 4016 (223) | ||
| 10 | 2883 (160) | 2057 (114) | |
| 30 | 2303 (128) | 1195 (66) | 856 (48) |
| 60 | 1417 (79) | ||
| 90 | 899 (50) | ||
| 120 | 778 (43) | ||
| 150 | 667 (37) | ||
| 180 | 630 (35) | 258 (14) | 178 (9) |
| 210 | 523 (29) | ||
| 240 | 442 (25) | ||
| 270 | 416(23) | ||
| 300 | |||
| 330 | |||
| 360 | 102 (6) | 102 (6) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Reeves, K.D.; Atkins, J.R.; Solso, C.R.; Cheng, C.-I.; Thornell, I.M.; Lam, K.H.S.; Wu, Y.-T.; Motyka, T.; Rabago, D. Rapid Decrease in Dextrose Concentration After Intra-Articular Knee Injection: Implications for Mechanism of Action of Dextrose Prolotherapy. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 350. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13020350
Reeves KD, Atkins JR, Solso CR, Cheng C-I, Thornell IM, Lam KHS, Wu Y-T, Motyka T, Rabago D. Rapid Decrease in Dextrose Concentration After Intra-Articular Knee Injection: Implications for Mechanism of Action of Dextrose Prolotherapy. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(2):350. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13020350
Chicago/Turabian StyleReeves, Kenneth Dean, Jordan R. Atkins, Clare R. Solso, Chin-I Cheng, Ian M. Thornell, King Hei Stanley Lam, Yung-Tsan Wu, Thomas Motyka, and David Rabago. 2025. "Rapid Decrease in Dextrose Concentration After Intra-Articular Knee Injection: Implications for Mechanism of Action of Dextrose Prolotherapy" Biomedicines 13, no. 2: 350. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13020350
APA StyleReeves, K. D., Atkins, J. R., Solso, C. R., Cheng, C.-I., Thornell, I. M., Lam, K. H. S., Wu, Y.-T., Motyka, T., & Rabago, D. (2025). Rapid Decrease in Dextrose Concentration After Intra-Articular Knee Injection: Implications for Mechanism of Action of Dextrose Prolotherapy. Biomedicines, 13(2), 350. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13020350






