Suspected Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Complex Pathophysiology in Fatal Hypermobile Ehlers–Danlos Syndrome: Insights from a Case Report and Post-Mortem Findings
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Case Report: Clinical Course of Advanced Hypermobile Ehlers–Danlos Syndrome (hEDS)
2.1. Patient Background
2.2. Primary Diagnoses, Treatments, and Surgical Interventions
2.2.1. Hypermobile Ehlers–Danlos Syndrome
2.2.2. Progressive Spinal and Vascular Complications
2.2.3. Psychological and Psychosocial
2.2.4. Dysphagia and Vocal Cord Paralysis
2.2.5. Gastroparesis and Dysautonomia
2.2.6. Postural Orthostatic Tachycardia Syndrome (POTS)
2.2.7. Immune System Dysfunction and Recurrent Infections
2.2.8. Endocrine System
2.2.9. Post-Operative and Compounding Complications
2.2.10. Terminal Course
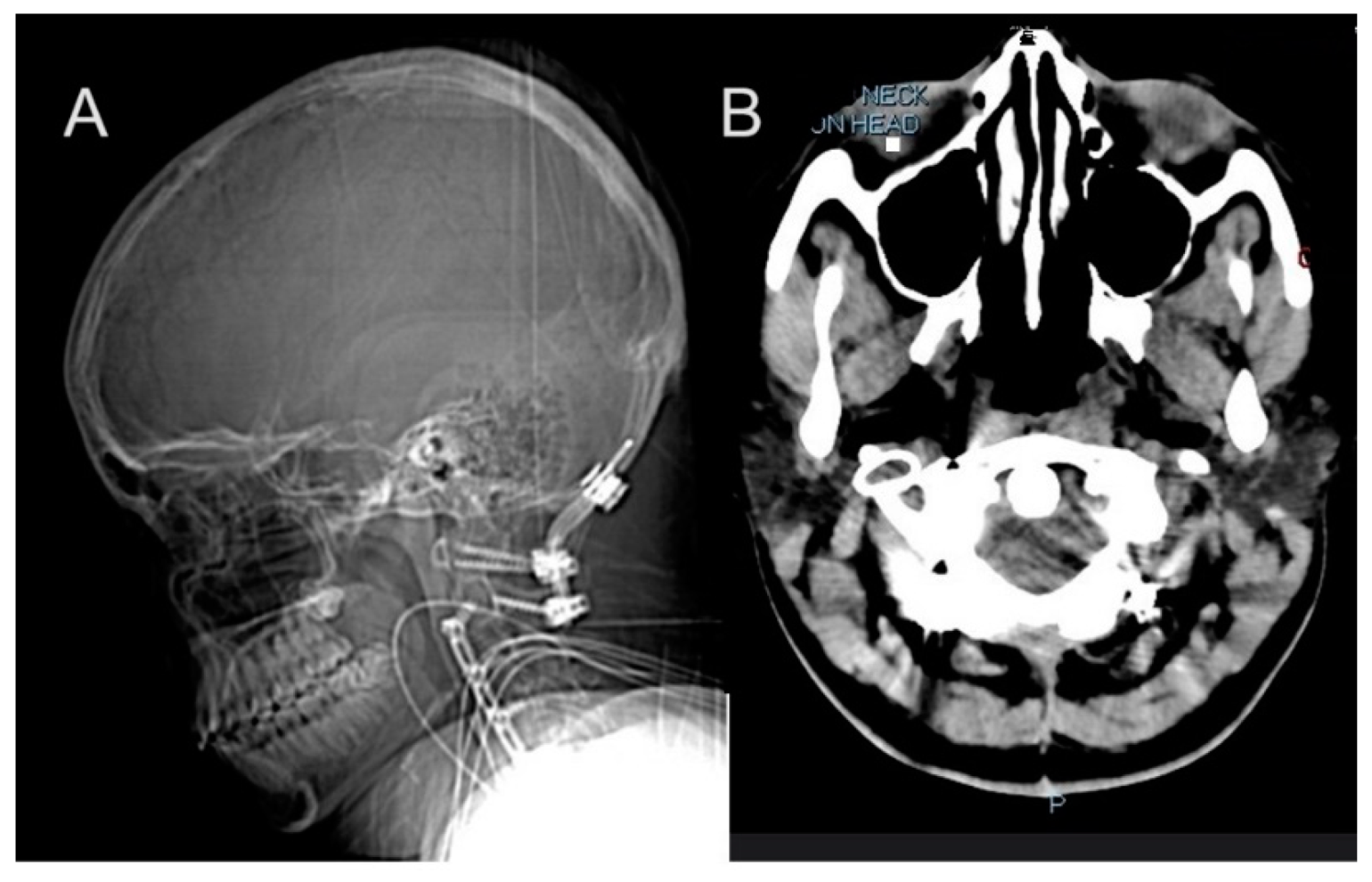
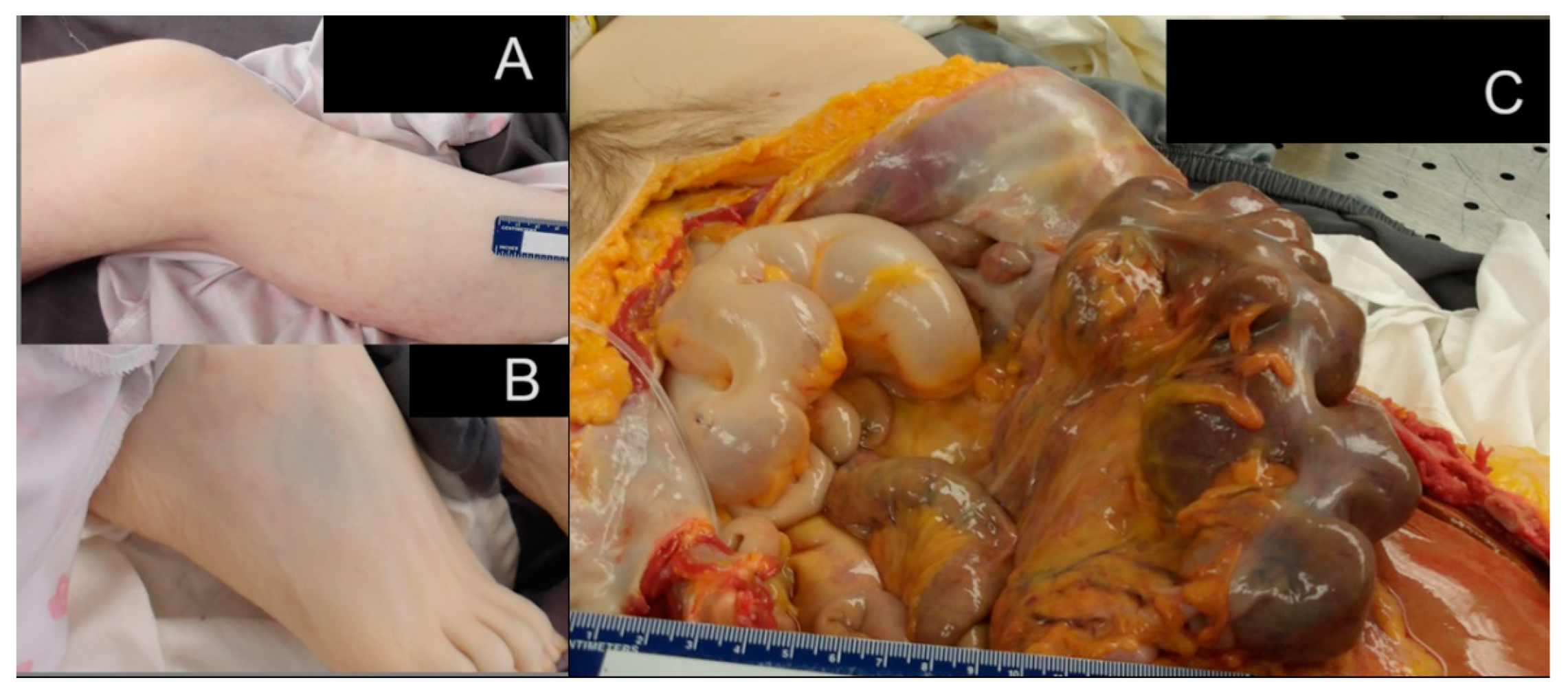
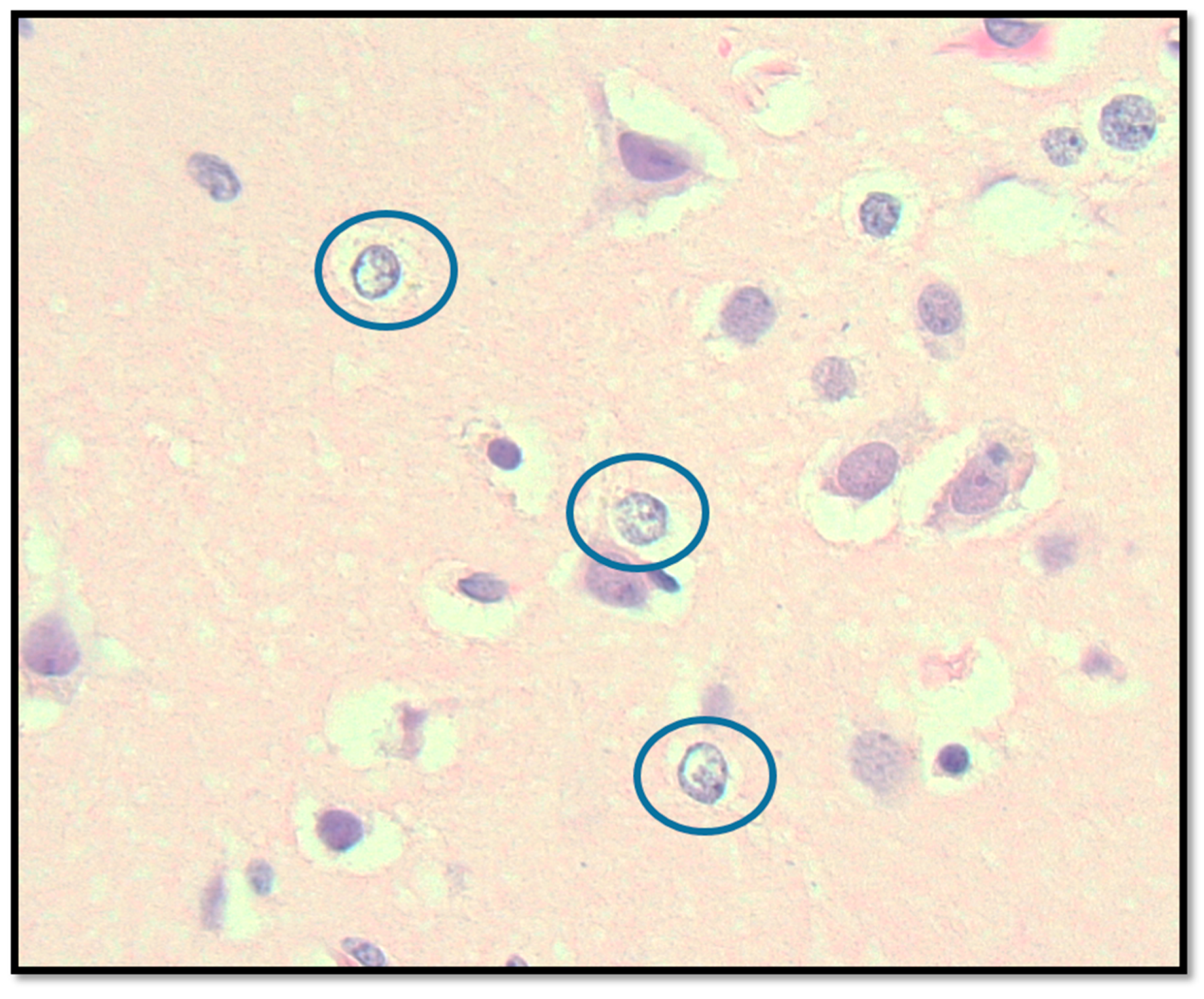
2.3. Post-Mortem Findings
2.3.1. Gastrointestinal System Findings
2.3.2. Central Nervous System Findings
2.3.3. Cardiovascular System Findings
2.3.4. Additional Significant Findings
2.3.5. Multifactorial Causes of Death
3. Molecular Mechanisms Underlying Multi-System Dysfunction in Advanced hEDS
3.1. Neurological Complications and Blood–Brain Barrier (BBB) Dysfunction
3.2. Mast Cell Activation Syndrome in hEDS
Gastrointestinal and Respiratory Complications
3.3. Metabolic Dysfunction and Chronic Fatigue
3.4. Genetic Variations and Biochemical Findings in the Patient
3.5. Suspicion of Mitochondrial Involvement in This Patient with Advanced hEDS
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Malfait, F.; Francomano, C.; Byers, P.; Belmont, J.; Berglund, B.; Black, J.; Bloom, L.; Bowen, J.M.; Brady, A.F.; Burrows, N.P.; et al. The Ehlers-Danlos Syndromes: An Updated Nosology Based on the 2017 International Classification. Am. J. Med. Genet. C Semin. Med. Genet. 2017, 175, 8–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinmann, B.; Royce, P.M.; Superti-Furga, A. The Ehlers-Danlos syndrome In Connective Tissue and Its Heritable Disorders: Molecular, Genetic, and Medical Aspects; Royce, P.M., Steinmann, B., Eds.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2002; pp. 431–523. [Google Scholar]
- Demmler, J.C.; Atkinson, M.D.; Reinhold, E.J.; Choy, E.; Lyons, R.A.; Brophy, S.T. Diagnosed prevalence of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome and hypermobility spectrum disorder in Wales, UK: A national electronic cohort study and case-control comparison. BMJ Open 2019, 9, e031365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gensemer, C.; Burks, R.; Kautz, S.; Judge, D.P.; Lavallee, M.; Norris, R.A. Hypermobile Ehlers-Danlos syndromes: Complex phenotypes, challenging diagnoses, and poorly understood causes. Dev. Dyn. 2021, 250, 318–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levy, H.P. Hypermobile Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome: Clinical Description and Natural History. Genet. Med. 2017, 19, 552–557. [Google Scholar]
- Wrennall, L. Misdiagnosis of child abuse related to delay in diagnosing a paediatric brain tumour. Clin. Med. Insights Pediatr. 2008, 1, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holick, M.F.; Hossein-Nezhad, A.; Tabatabaei, F. Multiple fractures in infants who have Ehlers-Danlos/hypermobility syndrome and or vitamin D deficiency: A case series of 72 infants whose parents were accused of child abuse and neglect. Dermato-Endocrinology 2017, 16, e1279768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fikree, A.; Chelimsky, G.; Collins, H.; Kovacic, K.; Aziz, Q. Gastrointestinal Involvement in the Ehlers-Danlos Syndromes: A Review on Pathophysiology and Management Strategies. Am. J. Med. Genet. C Semin. Med. Genet. 2017, 175, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakim, A.; O’Callaghan, C.; De Wandele, I.; Pocinki, A.; Rowe, P. Cardiovascular autonomic dysfunction in Ehlers-Danlos syndrome-Hypermobile type. Am. J. Med. Genet. Part C Semin. Med. Genet. 2017, 175, 168–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tinkle, B.T.; Castori, M.; Berglund, B.; Cohen, H.; Grahame, R.; Kazkaz, H.; Levy, H.P. Hypermobile Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome (hEDS): Complexities of Diagnosis and Management. Lancet Rheumatol. 2020, 2, e153–e161. [Google Scholar]
- Bowen, J.M.; Sobey, G.J.; Burrows, N.P.; Colombi, M.; Lavallee, M.E.L.; Malfait, F.; Francomano, C.A. Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome: A Review of the Clinical Phenotype and Molecular Pathogenesis of the Classic and Vascular Subtypes and Management of the Adult Patient with Vascular EDS (vEDS). J. Mol. Med. 2019, 97, 473–481. [Google Scholar]
- Chiarelli, N.; Zoppi, N.; Venturini, M.; Capitanio, D.; Gelfi, C.; Ritelli, M.; Colombi, M. Matrix Metalloproteinases Inhibition by Doxycycline Rescues Extracellular Matrix Organization and Partly Reverts Myofibroblast Differentiation in Hypermobile Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome Dermal Fibroblasts: A Potential Therapeutic Target? Cells 2021, 19, 3236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colombo, R.; Zoppi, N.; Ritelli, M.; Colombi, M. Molecular Insights into the Pathogenesis of Classical and Vascular Ehlers-Danlos Syndromes: New Mutations and Pathogenic Mechanisms Identified by Next Generation Sequencing Technologies. Genes 2020, 11, 611. [Google Scholar]
- Wrennall, L. Munchausen Syndrome by Proxy/Fabricated and Induced Illness: Does the diagnosis serve economic vested interests, rather than the interests of children? Med. Hypotheses 2007, 68, 960–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiarelli, N.; Ritelli, M.; Zoppi, N.; Colombi, M. Cellular and Molecular Mechanisms in the Pathogenesis of Classical, Vascular, and Hypermobile Ehlers—Danlos Syndromes. Genes 2019, 12, 609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malek, S.; Köster, D.V. The Role of Cell Adhesion and Cytoskeleton Dynamics in the Pathogenesis of the Ehlers-Danlos Syndromes and Hypermobility Spectrum Disorders. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 21, 649082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ritelli, M.; Chiarelli, N.; Cinquina, V.; Zoppi, N.; Bertini, V.; Venturini, M.; Colombi, M. RNA-Seq of Dermal Fibroblasts from Patients with Hypermobile Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome and Hypermobility Spectrum Disorders Supports Their Categorization as a Single Entity with Involvement of Extracellular Matrix Degrading and Proinflammatory Pathomechanisms. Cells 2022, 14, 4040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoppi, N.; Chiarelli, N.; Binetti, S.; Ritelli, M.; Colombi, M. Dermal fibroblast-to-myofibroblast transition sustained by αvβ3 integrin-ILK-Snail1/Slug signaling is a common feature for hypermobile Ehlers-Danlos syndrome and hypermobility spectrum disorders. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Mol. Basis Dis. 2018, 1864, 1010–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Royer, S.P.; Han, S.J. Mechanobiology in the Comorbidities of Ehlers Danlos Syndrome. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 25, 874840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Severance, S.; Daylor, V.; Petrucci, T.; Gensemer, C.; Patel, S.; Norris, R.A. Hypermobile Ehlers-Danlos syndrome and spontaneous CSF leaks: The connective tissue conundrum. Front. Neurol. 2024, 15, 1452409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baeten, K.M.; Akassoglou, K. Extracellular matrix and matrix receptors in blood-brain barrier formation and stroke. Dev. Neurobiol. 2011, 71, 1018–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Nirwane, A.; Yao, Y. Basement membrane and blood-brain barrier. Stroke Vasc. Neurol. 2019, 4, 78–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pöschl, E.; Schlötzer-Schrehardt, U.; Brachvogel, B.; Saito, K.; Ninomiya, Y.; Mayer, U. Collagen IV is essential for basement membrane stability but dispensable for initiation of its assembly during early development. Development 2004, 131, 1619–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derk, J.; Jones, H.E.; Como, C.; Pawlikowski, B.; Siegenthaler, J.A. Living on the edge of the CNS: Meninges cell diversity in health and disease. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 703944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirvani, P.; Shirvani, A.; Holick, M.F. Decoding the Genetic Basis of Mast Cell Hypersensitivity and Infection Risk in Hypermobile Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2024, 46, 11613–11629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engelhardt, B. β1-integrin/matrix interactions support blood-brain barrier integrity. J. Cereb. Blood Flow. Metab. 2011, 31, 1969–1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cole, M.A.; Quan, T.; Voorhees, J.J.; Fisher, G.J. Extracellular matrix regulation of fibroblast function: Redefining our perspective on skin aging. J. Cell Commun. Signal. 2018, 12, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monaco, A.; Choi, D.; Uzun, S.; Maitland, A.; Riley, B. Association of mast-cell-related conditions with hypermobile syndromes: A review of the literature. Immunol. Res. 2022, 70, 419–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiménez, M.; Cervantes-García, D.; Córdova-Dávalos, L.E.; Pérez-Rodríguez, M.J.; Gonzalez-Espinosa, C.; Salinas, E. Responses of Mast Cells to Pathogens: Beneficial and Detrimental Roles. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 685865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasler, W.L.; Grabauskas, G.; Singh, P.; Owyang, C. Mast cell mediation of visceral sensation and permeability in irritable bowel syndrome. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2022, 34, e14339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chohan, K.; Mittal, N.; McGillis, L.; Lopez-Hernandez, L.; Camacho, E.; Rachinsky, M.; Mina, D.S.; Reid, W.D.; Ryan, C.M.; Champagne, K.A.; et al. A review of respiratory manifestations and their management in Ehlers-Danlos syndromes and hypermobility spectrum disorders. Chron. Respir. Dis. 2021, 18, 14799731211025313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jahanbani, F.; Sing, J.C.; Maynard, R.D.; Jahanbani, S.; Dafoe, J.; Dafoe, W.; Jones, N.; Wallace, K.J.; Rastan, A.; Maecker, H.T.; et al. Longitudinal cytokine and multi-modal health data of an extremely severe ME/CFS patient with HSD reveals insights into immunopathology, and disease severity. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1369295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jansen, K.A.; Licup, A.J.; Sharma, A.; Rens, R.; MacKintosh, F.C.; Koenderink, G.H. The Role of Network Architecture in Collagen Mechanics. Biophys. J. 2018, 114, 2665–2678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiarelli, N.; Zoppi, N.; Ritelli, M.; Venturini, M.; Capitanio, D.; Gelfi, C.; Colombi, M. Biological insights in the pathogenesis of hypermobile Ehlers-Danlos syndrome from proteome profiling of patients′ dermal myofibroblasts. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Mol. Basis Dis. 2021, 1867, 166051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blalock, D.; Miller, A.; Tilley, M.; Wang, J. Joint instability and osteoarthritis. Clin. Med. Insights Arthritis Musculoskelet. Disord. 2015, 8, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolan, E.; Koehler, K.; Areta, J.; Longman, D.P.; Pontzer, H. Energy constraint and compensation: Insights from endurance athletes. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2023, 285, 111500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sood, V.; Kaul, A.; El-Chammas, K.I.; Mukkada, V.A.; Sun, Q.; Fei, L.; Santucci, N.R. High prevalence of gastrointestinal disorders in a large cohort of patients with joint hypermobility. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2024, 79, 42–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacourt, T.E.; Vichaya, E.G.; Chiu, G.S.; Dantzer, R.; Heijnen, C.J. The High Costs of Low-Grade Inflammation: Persistent Fatigue as a Consequence of Reduced Cellular-Energy Availability and Non-adaptive Energy Expenditure. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AlphaFold Protein Structure Database. Entry P00846 [Internet]. European Bioinformatics Institute. 2025. Available online: https://alphafold.ebi.ac.uk/entry/P00846 (accessed on 29 January 2025).
- Shayota, B.J. Biomarkers of mitochondrial disorders. Neurotherapeutics 2024, 21, e00325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Alomari, M.; Hitawala, A.; Chadalavada, P.; Covut, F.; Al Momani, L.; Khazaaleh, S.; Gosai, F.; Al Ashi, S.; Abushahin, A.; Schneider, A. Prevalence and Predictors of Gastrointestinal Dysmotility in Patients with Hypermobile Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome: A Tertiary Care Center Experience. Cureus 2020, 29, e7881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarate, N.; Farmer, A.D.; Grahame, R.; Mohammed, S.D.; Knowles, C.H.; Scott, S.M.; Aziz, Q. Unexplained gastrointestinal symptoms and joint hypermobility: Is connective tissue the missing link? Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2010, 22, 252-e78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thwaites, P.A.; Gibson, P.R.; Burgell, R.E. Hypermobile Ehlers-Danlos syndrome and disorders of the gastrointestinal tract: What the gastroenterologist needs to know. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 37, 1693–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watson-Fargie, T.; Raeside, D.; Davidson, S.; McCartney, R.; Clarke, A.; Farrugia, M.E. Morbidity and mortality associated with gastrointestinal dysfunction in neuromuscular disease: A single-centre case series. Neuromuscul. Disord. 2022, 32, 578–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaefer, P.M.; Scherer Alves, L.; Lvova, M.; Huang, J.; Rathi, K.; Janssen, K.; Butic, A.; Yardeni, T.; Morrow, R.; Lott, M.; et al. Combination of common mtDNA variants results in mitochondrial dysfunction and a connective tissue dysregulation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 8, e2212417119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thorburn, D.R.; Rahman, J.; Rahman, S. Mitochondrial DNA-Associated Leigh Syndrome and NARP; GeneReviews®: Seattle, WA, USA, 2017; pp. 1993–2023. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sala, D.; Marchet, S.; Nanetti, L.; Legati, A.; Mariotti, C.; Lamantea, E.; Ghezzi, D.; Catania, A.; Lamperti, C. A novel MT-ATP6 variant associated with complicated ataxia in two unrelated Italian patients: Case report and functional studies. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2024, 19, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turton, N.; Cufflin, N.; Dewsbury, M.; Fitzpatrick, O.; Islam, R.; Watler, L.L.; McPartland, C.; Whitelaw, S.; Connor, C.; Morris, C.; et al. The Biochemical Assessment of Mitochondrial Respiratory Chain Disorders. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 7487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stendel, C.; Neuhofer, C.; Floride, E.; Yuqing, S.; Ganetzky, R.D.; Park, J.; Freisinger, P.; Kornblum, C.; Kleinle, S.; Schöls, L.; et al. Delineating MT-ATP6-associated disease: From isolated neuropathy to early onset neurodegeneration. Neurol. Genet. 2020, 6, e393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, G.N.; Tonk, V.S. Clinical-Genomic Analysis of 1261 Patients with Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome Outlines an Articulo-Autonomic Gene Network (Entome). Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2024, 19, 2620–2643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Gonçalves, F.G.; Alves, C.A.P.F.; Heuer, B.; Peterson, J.; Viaene, A.N.; Reis Teixeira, S.; Martín-Saavedra, J.S.; Andronikou, S.; Goldstein, A.; Vossough, A. Primary Mitochondrial Disorders of the Pediatric Central Nervous System: Neuroimaging Findings. Radiographics 2020, 40, 2042–2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ball, M.; Thorburn, D.R.; Rahman, S. Mitochondrial DNA-Associated Leigh Syndrome Spectrum. In GeneReviews® [Internet]; Adam, M.P., Feldman, J., Mirzaa, G.M., Pagon, R.A., Wallace, S.E., Amemiya, A., Eds.; University of Washington: Seattle, WA, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chelombitko, M.A.; Chernyak, B.V.; Fedorov, A.V.; Zinovkin, R.A.; Razin, E.; Paruchuru, L.B. The Role Played by Mitochondria in FcεRI-Dependent Mast Cell Activation. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 584210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, D.; Sheeja Prabhakaran, H.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Luo, G.; He, W.; Liou, Y.C. Mitochondrial dysfunction in sepsis: Mechanisms and therapeutic perspectives. Crit. Care 2024, 28, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, N.K.; Singh, P.; Varshney, P.; Singh, A.; Bhushan, B. Multimodal action of phosphodiesterase 5 inhibitors against neurodegenerative disorders: An update review. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2024, 38, e70021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, N.; Yang, M.; Gaur, U.; Xu, H.; Yao, Y.; Li, D. Alpha-Ketoglutarate: Physiological Functions and Applications. Biomol. Ther. 2016, 24, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engelbert, R.H.; Juul-Kristensen, B.; Pacey, V.; de Wandele, I.; Smeenk, S.; Woinarosky, N.; Sabo, S.; Scheper, M.C.; Russek, L.; Simmonds, J.V. The evidence-based rationale for physical therapy treatment of children, adolescents, and adults diagnosed with joint hypermobility syndrome/hypermobile Ehlers Danlos syndrome. Am. J. Med. Genet. C Semin. Med. Genet. 2017, 175, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bulbena, A.; Baeza-Velasco, C.; Bulbena-Cabré, A.; Pailhez, G.; Critchley, H.; Chopra, P.; Mallorquí-Bagué, N.; Frank, C.; Porges, S. Psychiatric and psychological aspects in the Ehlers-Danlos syndromes. Am. J. Med. Genet. C Semin. Med. Genet. 2017, 175, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, M.; Stolfi, A.; Ayoub, D. Findings of metabolic bone disease in infants with unexplained fractures in contested child abuse investigations: A case series of 75 infants. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 2019, 25, 1103–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Gemert, M.J.C.; Zwinderman, A.H.; Koppen, P.J.V.; Neumann, H.A.M.; Vlaming, M. Child Abuse, Misdiagnosed by an Expertise Center-Part II-Misuse of Bayes’ Theorem. Children 2023, 6, 843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Vlaming, M.; Sauer, P.J.J.; Janssen, E.P.F.; van Koppen, P.J.; Bruijninckx, C.M.A.; Akkerman-Zaalberg van Zelst, M.W.M.; Neumann, H.A.M.; van Gemert, M.J.C. Child Abuse, Misdiagnosed by an Expertise Center: Part I-Medico-Social Aspects. Children 2023, 29, 963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Holick, M.F.; Shirvani, A.; Charoenngam, N. Fetal Fractures in an Infant with Maternal Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome, CCDC134 Pathogenic Mutation and a Negative Genetic Test for Osteogenesis Imperfecta. Children 2021, 17, 512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]



| Nucleotide Change | Amino Acid Changes | Coding Context | Gene Name | ALFA Allele Frequency | Manifestation | dbSNP ID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| m.3480A>G | p.Lys58Lys | c.174G>A | MT-ND1 | G = 0.09 | Homoplasmy | rs28358584 |
| m.4561T>C | p.Val31Ala | c.92C>T | MT-ND2 | C = 0.02 | Homoplasmy | rs41376350 |
| m.9055G>A | p.Ala177Thr | c.529A>G | MT-ATP6 | A = 0.15 | Homoplasmy | rs193303045 |
| m.9698T>C | p.Leu164Leu | c.174G>A | MT-CO3 | C = 0.15 | Homoplasmy | rs9743 |
| m.9716T>C | p.Gly170Gly | c.510C>T | MT-CO3 | C = 0.018 | Homoplasmy | rs41502750 |
| m.10550A>G | p.Met27Met | c.81G>A | MT-ND4L | G = 0.09 | Homoplasmy | rs28358280 |
| m.11299T>C | p.Thr180Thr | c.540C>T | MT-ND4 | C = 0.14 | Homoplasmy | rs28358285 |
| m.11467A>G | p.Leu236Leu | c.708G>A | MT-ND4 | G = 0.25 | Homoplasmy | rs2853493 |
| m.11719G>A | p.Gly320Gly | c.960A>G | MT-ND4 | A = 0.59 | Homoplasmy | rs2853495 |
| m.12308A>G | n/a * | n/a | MT-TRNL2 | G = 0.21 | Homoplasmy | rs2853498 |
| m.12372G>A | p.Leu12Leu | c.36A>G | MT-ND5 | A = 0.25 | Homoplasmy | rs2853499 |
| m.14167C>T | p.Glu169Glu | c.507A>G | MT-ND6 | T = 0.15 | Homoplasmy | rs193302977 |
| m.14766C>T | p.Thr7Ile | c.20T>C | MT-CYB | T = 0.65 | Homoplasmy | rs193302980 |
| m.14798T>C | p.Phe18Leu | c.52C>T | CYTB | C = 0.16 | Homoplasmy | rs28357681 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shirvani, A.; Shirvani, P.; Jonah, U.; Moore, B.E.; Holick, M.F. Suspected Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Complex Pathophysiology in Fatal Hypermobile Ehlers–Danlos Syndrome: Insights from a Case Report and Post-Mortem Findings. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 469. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13020469
Shirvani A, Shirvani P, Jonah U, Moore BE, Holick MF. Suspected Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Complex Pathophysiology in Fatal Hypermobile Ehlers–Danlos Syndrome: Insights from a Case Report and Post-Mortem Findings. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(2):469. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13020469
Chicago/Turabian StyleShirvani, Arash, Purusha Shirvani, Ugochukwu Jonah, Brian E. Moore, and Michael F. Holick. 2025. "Suspected Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Complex Pathophysiology in Fatal Hypermobile Ehlers–Danlos Syndrome: Insights from a Case Report and Post-Mortem Findings" Biomedicines 13, no. 2: 469. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13020469
APA StyleShirvani, A., Shirvani, P., Jonah, U., Moore, B. E., & Holick, M. F. (2025). Suspected Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Complex Pathophysiology in Fatal Hypermobile Ehlers–Danlos Syndrome: Insights from a Case Report and Post-Mortem Findings. Biomedicines, 13(2), 469. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13020469







