Causal Relationships Between Iron Deficiency Anemia, Gut Microbiota, and Metabolites: Insights from Mendelian Randomization and In Vivo Data
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
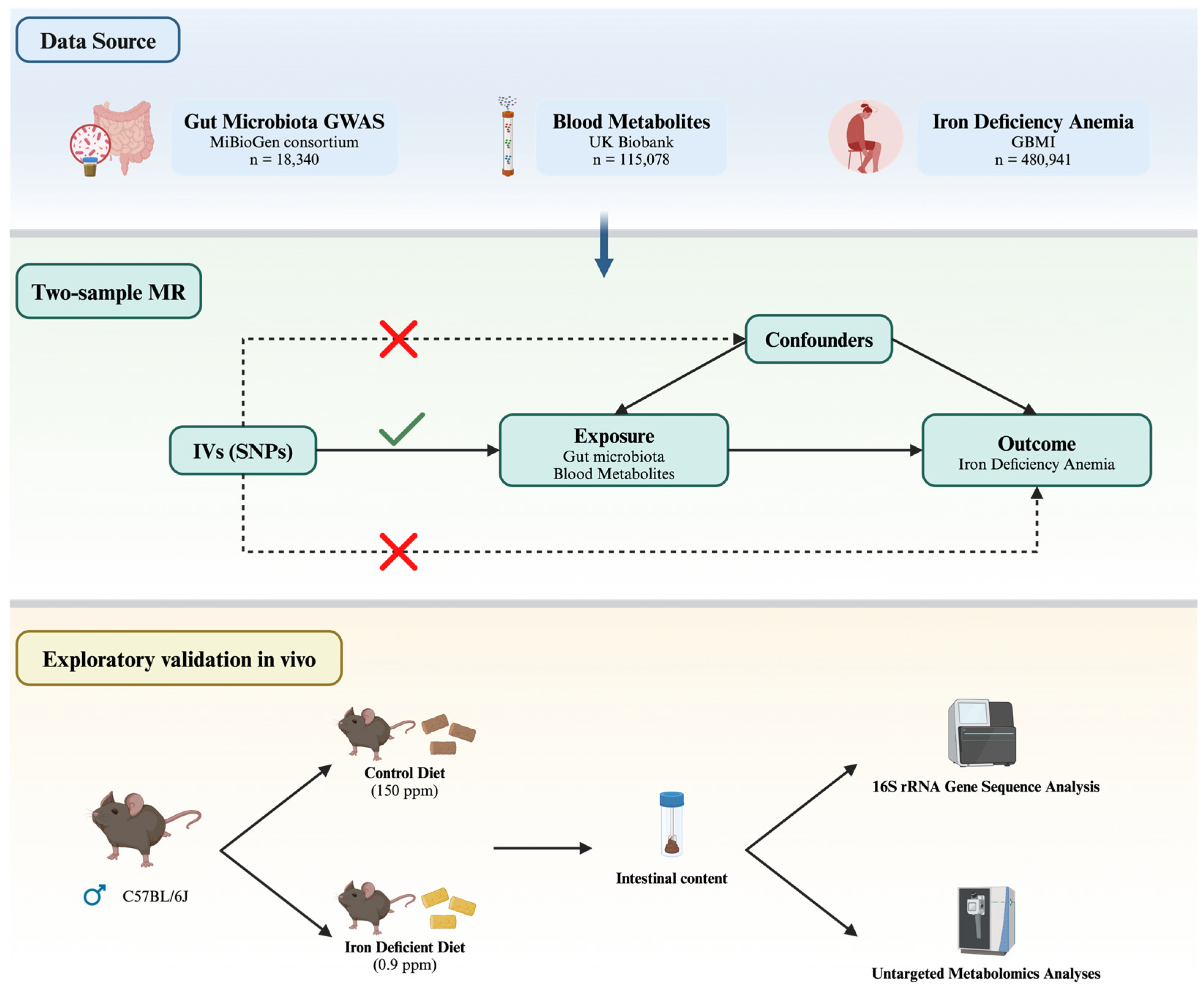
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Data Source and Instruments
2.3. Selection and Verification of Instrumental Variables
2.4. MR Analysis
2.5. Animals
2.6. DNA Extraction and 16S rRNA Gene Sequence Analysis
2.7. Untargeted Metabolomics Analyses
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Instrument Variables Included
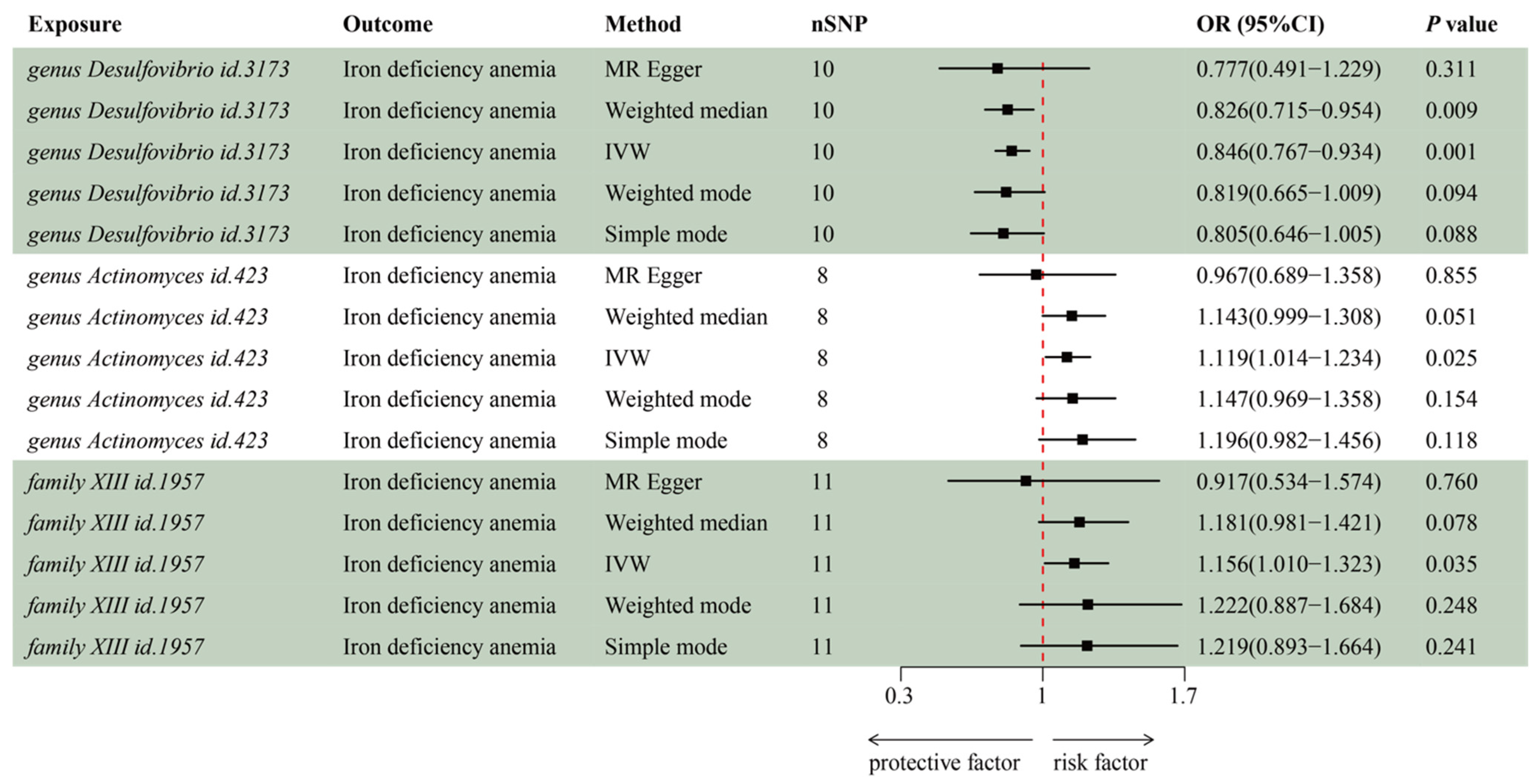
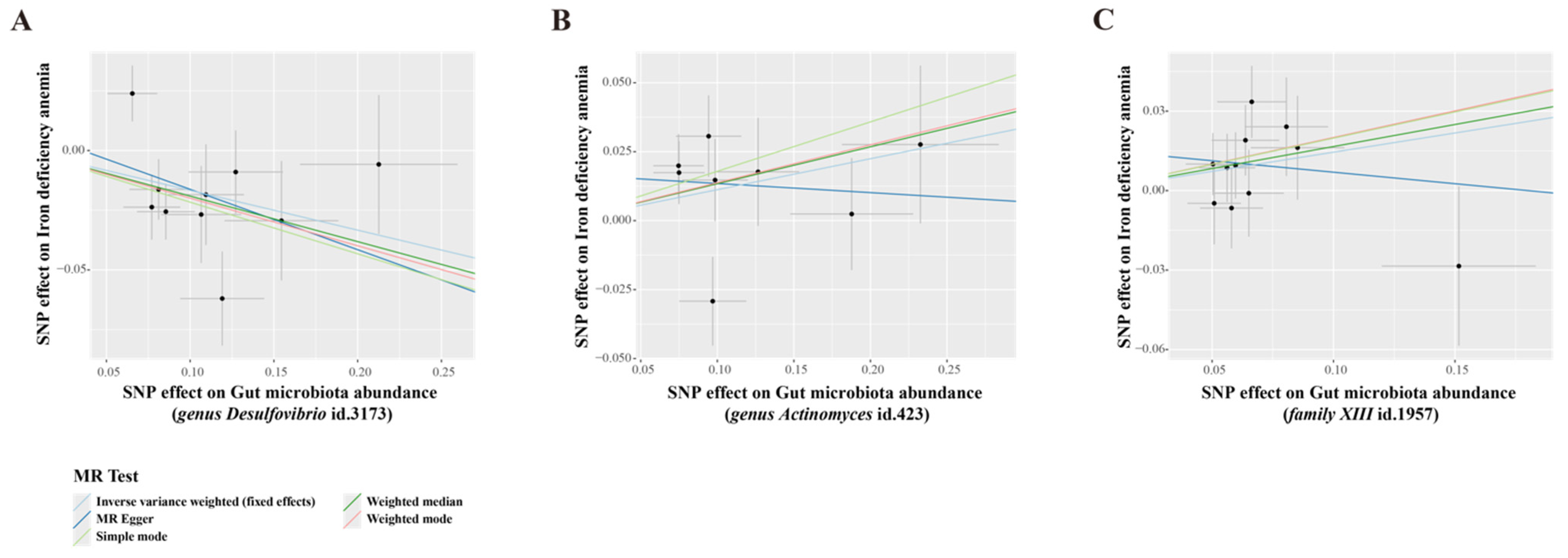
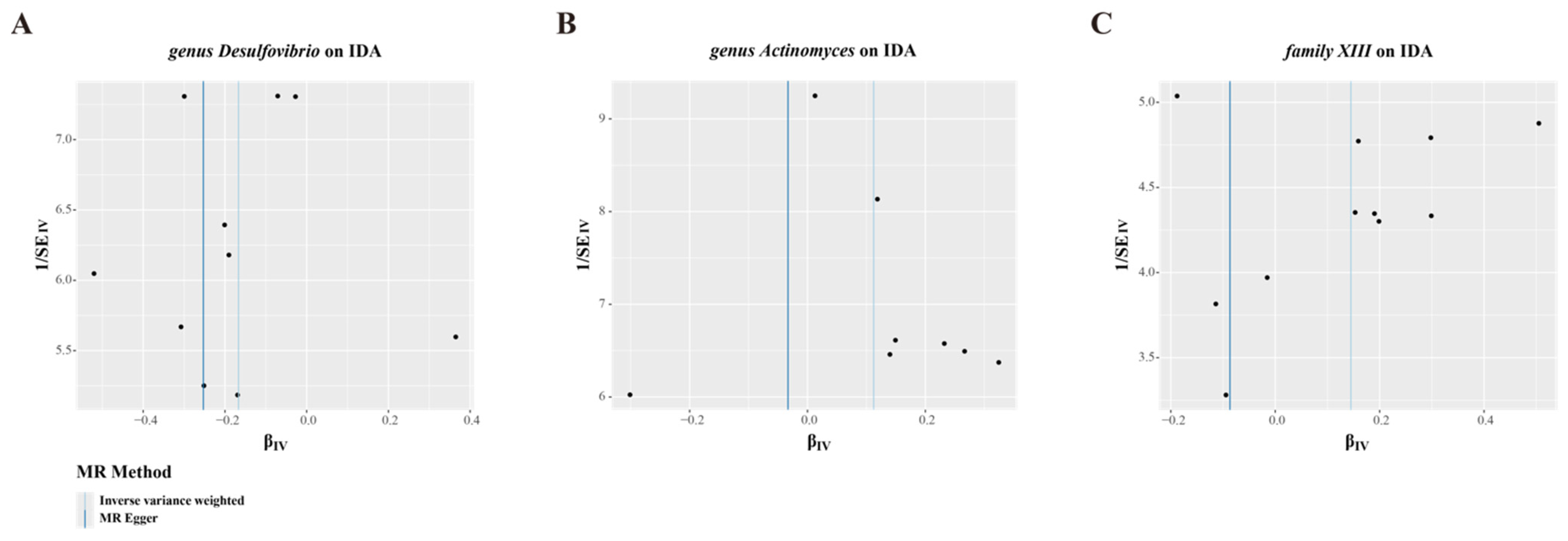
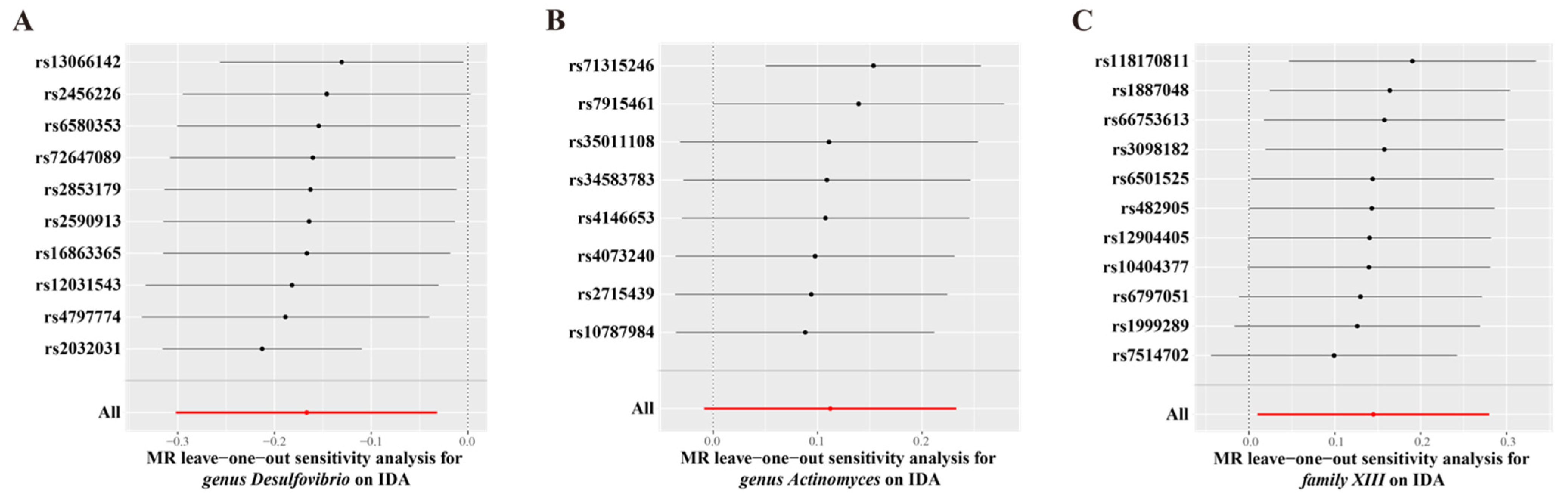
3.2. MR Analysis of Gut Microbiota’s Effect on IDA
3.3. MR Analysis of Blood Metabolites’ Effect on IDA and Gut Microbiota
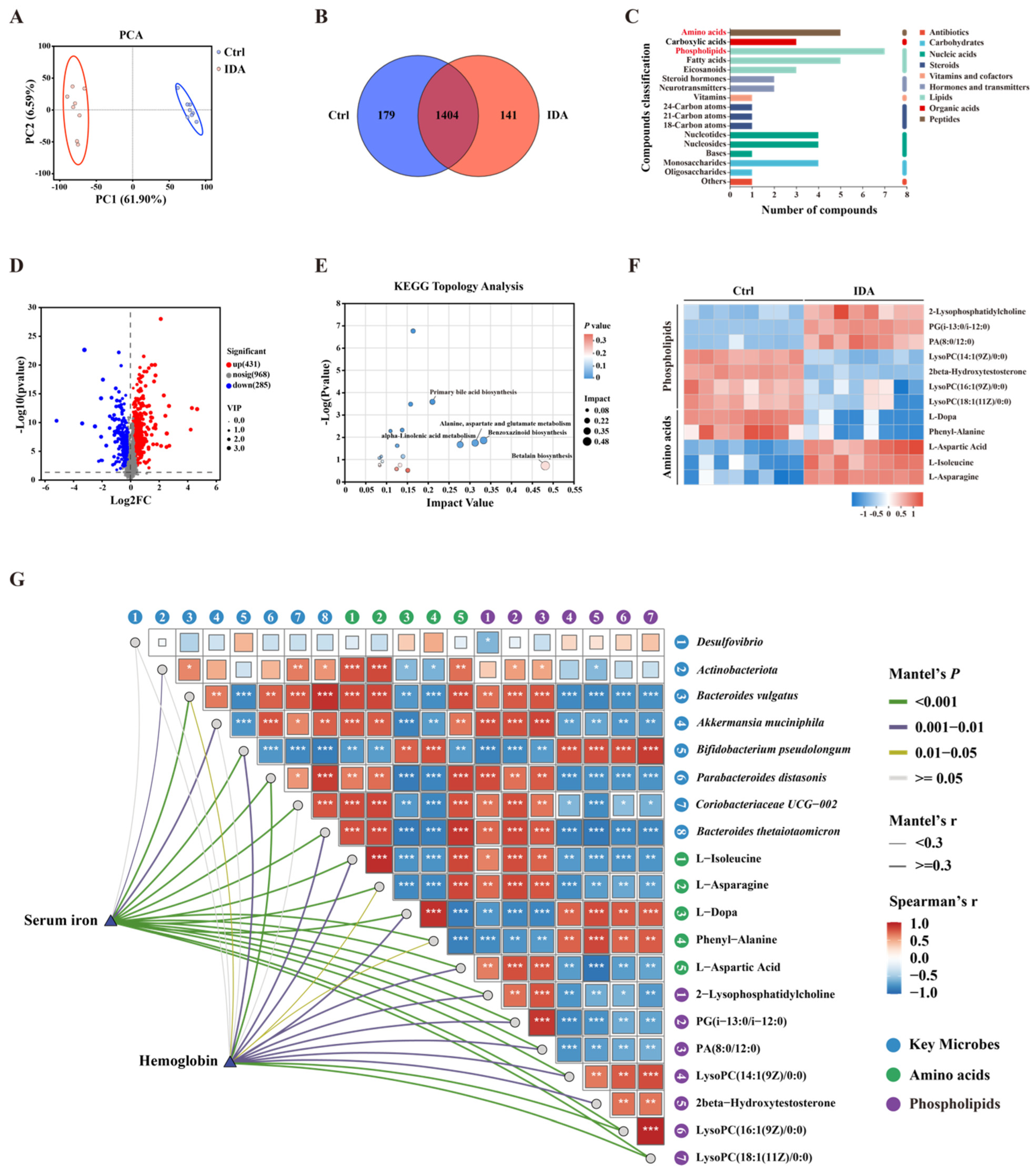
3.4. Iron Deficiency Anemia Affects Gut Microbiota Composition and Diversity
3.5. Iron Deficiency Anemia Impacts Gut Microbial Metabolites
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lopez, A.; Cacoub, P.; Macdougall, I.C.; Peyrin-Biroulet, L. Iron deficiency anaemia. Lancet 2016, 387, 907–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasricha, S.R.; Tye-Din, J.; Muckenthaler, M.U.; Swinkels, D.W. Iron deficiency. Lancet 2021, 397, 233–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cantor, A.G.; Holmes, R.; Bougatsos, C.; Atchison, C.; DeLoughery, T.; Chou, R. Screening and Supplementation for Iron Deficiency and Iron Deficiency Anemia During Pregnancy: Updated Evidence Report and Systematic Review for the US Preventive Services Task Force. JAMA 2024, 332, 914–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeLoughery, T.G.; Jackson, C.S.; Ko, C.W.; Rockey, D.C. AGA Clinical Practice Update on Management of Iron Deficiency Anemia: Expert Review. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2024, 22, 1575–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Lancet, H. Iron deficiency anaemia-an ongoing challenge. Lancet Haematol. 2022, 9, e797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayneris-Perxachs, J.; Moreno-Navarrete, J.M.; Fernandez-Real, J.M. The role of iron in host-microbiota crosstalk and its effects on systemic glucose metabolism. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2022, 18, 683–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phipps, O.; Al-Hassi, H.O.; Quraishi, M.N.; Kumar, A.; Brookes, M.J. Influence of Iron on the Gut Microbiota in Colorectal Cancer. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Tan, B.; Zhang, P.; Zhu, L.; Wei, H.; Huang, T.; Li, C.; Yang, W. Iron deficiency anemia: A critical review on iron absorption, supplementation and its influence on gut microbiota. Food Funct. 2024, 15, 1144–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muleviciene, A.; D’Amico, F.; Turroni, S.; Candela, M.; Jankauskiene, A. Iron deficiency anemia-related gut microbiota dysbiosis in infants and young children: A pilot study. Acta Microbiol. Immunol. Hung. 2018, 65, 551–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Wu, W.; Tang, S.; Fu, R.; Gong, X.; Hou, H.; Xu, J. Altered fecal microbial and metabolic profile reveals potential mechanisms underlying iron deficiency anemia in pregnant women in China. Bosn. J. Basic Med. Sci. 2022, 22, 923–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, T.; Li, L. The influence of microbiota on ferroptosis in intestinal diseases. Gut Microbes 2023, 15, 2263210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sekula, P.; Del Greco, M.F.; Pattaro, C.; Kottgen, A. Mendelian Randomization as an Approach to Assess Causality Using Observational Data. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2016, 27, 3253–3265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skrivankova, V.W.; Richmond, R.C.; Woolf, B.A.R.; Yarmolinsky, J.; Davies, N.M.; Swanson, S.A.; VanderWeele, T.J.; Higgins, J.P.T.; Timpson, N.J.; Dimou, N.; et al. Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology Using Mendelian Randomization: The STROBE-MR Statement. JAMA 2021, 326, 1614–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurilshikov, A.; Medina-Gomez, C.; Bacigalupe, R.; Radjabzadeh, D.; Wang, J.; Demirkan, A.; Le Roy, C.I.; Raygoza Garay, J.A.; Finnicum, C.T.; Liu, X.; et al. Large-scale association analyses identify host factors influencing human gut microbiome composition. Nat. Genet. 2021, 53, 156–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.; Wang, H.; Guo, L.; Gou, X.; Chen, G.; Lin, D.; Fan, D.; Guo, X.; Liu, Z. Association between gut microbiota and preeclampsia-eclampsia: A two-sample Mendelian randomization study. BMC Med. 2022, 20, 443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burgess, S.; Thompson, S.G. Bias in causal estimates from Mendelian randomization studies with weak instruments. Stat. Med. 2011, 30, 1312–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verbanck, M.; Chen, C.Y.; Neale, B.; Do, R. Detection of widespread horizontal pleiotropy in causal relationships inferred from Mendelian randomization between complex traits and diseases. Nat. Genet. 2018, 50, 693–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowden, J.; Davey Smith, G.; Burgess, S. Mendelian randomization with invalid instruments: Effect estimation and bias detection through Egger regression. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2015, 44, 512–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Report of the American Institute of Nurtition ad hoc Committee on Standards for Nutritional Studies. J. Nutr. 1977, 107, 1340–1348. [CrossRef]
- Rusu, I.G.; Suharoschi, R.; Vodnar, D.C.; Pop, C.R.; Socaci, S.A.; Vulturar, R.; Istrati, M.; Morosan, I.; Farcas, A.C.; Kerezsi, A.D.; et al. Iron Supplementation Influence on the Gut Microbiota and Probiotic Intake Effect in Iron Deficiency-A Literature-Based Review. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malesza, I.J.; Bartkowiak-Wieczorek, J.; Winkler-Galicki, J.; Nowicka, A.; Dzieciolowska, D.; Blaszczyk, M.; Gajniak, P.; Slowinska, K.; Niepolski, L.; Walkowiak, J.; et al. The Dark Side of Iron: The Relationship between Iron, Inflammation and Gut Microbiota in Selected Diseases Associated with Iron Deficiency Anaemia-A Narrative Review. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Vos, W.M.; Nguyen Trung, M.; Davids, M.; Liu, G.; Rios-Morales, M.; Jessen, H.; Fiedler, D.; Nieuwdorp, M.; Bui, T.P.N. Phytate metabolism is mediated by microbial cross-feeding in the gut microbiota. Nat. Microbiol. 2024, 9, 1812–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, E.J.; Han, K.; Lim, T.J.; Lim, S.; Chung, M.J.; Nam, M.H.; Kim, H.; Nam, Y.D. Effect of probiotics on obesity-related markers per enterotype: A double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized clinical trial. EPMA J. 2020, 11, 31–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Druart, C.; Dewulf, E.M.; Cani, P.D.; Neyrinck, A.M.; Thissen, J.P.; Delzenne, N.M. Gut microbial metabolites of polyunsaturated fatty acids correlate with specific fecal bacteria and serum markers of metabolic syndrome in obese women. Lipids 2014, 49, 397–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coffman, C.N.; Varga, M.G.; Alcock, J.; Carrol-Portillo, A.; Singh, S.B.; Xue, X.; Lin, H.C. Norepinephrine induces growth of Desulfovibrio vulgaris in an iron dependent manner. Anaerobe 2022, 75, 102582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leigh, J.; Saha, M.N.; Mok, A.; Champsi, O.; Wang, R.; Lobb, I.; Sener, A. Hydrogen Sulfide Induced Erythropoietin Synthesis is Regulated by HIF Proteins. J. Urol. 2016, 196, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodard, T.L.; Ueki, T.; Lovley, D.R. H2 is a Major Intermediate in Desulfovibrio vulgaris Corrosion of Iron. mBio 2023, 14, e0007623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taglialegna, A. Fat, Desulfovibrio and cancer. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2024, 22, 388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ternes, D.; Tsenkova, M.; Pozdeev, V.I.; Meyers, M.; Koncina, E.; Atatri, S.; Schmitz, M.; Karta, J.; Schmoetten, M.; Heinken, A.; et al. The gut microbial metabolite formate exacerbates colorectal cancer progression. Nat. Metab. 2022, 4, 458–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguayo-Ceron, K.A.; Sanchez-Munoz, F.; Gutierrez-Rojas, R.A.; Acevedo-Villavicencio, L.N.; Flores-Zarate, A.V.; Huang, F.; Giacoman-Martinez, A.; Villafana, S.; Romero-Nava, R. Glycine: The Smallest Anti-Inflammatory Micronutrient. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 11236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razak, M.A.; Begum, P.S.; Viswanath, B.; Rajagopal, S. Multifarious Beneficial Effect of Nonessential Amino Acid, Glycine: A Review. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2017, 2017, 1716701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Que, X.; Hung, M.Y.; Yeang, C.; Gonen, A.; Prohaska, T.A.; Sun, X.; Diehl, C.; Maatta, A.; Gaddis, D.E.; Bowden, K.; et al. Oxidized phospholipids are proinflammatory and proatherogenic in hypercholesterolaemic mice. Nature 2018, 558, 301–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, T.L.; Vieira-Silva, S.; Liston, A.; Raes, J. How informative is the mouse for human gut microbiota research? Dis. Model. Mech. 2015, 8, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbay, B.; Omarova, Z.; Trofimov, A.; Sailike, B.; Karapina, O.; Molnar, F.; Tokay, T. Double-Edge Effects of Leucine on Cancer Cells. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulusma, C.C.; Lamers, W.H.; Broer, S.; van de Graaf, S.F.J. Amino acid metabolism, transport and signalling in the liver revisited. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2022, 201, 115074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knuplez, E.; Marsche, G. An Updated Review of Pro- and Anti-Inflammatory Properties of Plasma Lysophosphatidylcholines in the Vascular System. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hishikawa, D.; Hashidate, T.; Shimizu, T.; Shindou, H. Diversity and function of membrane glycerophospholipids generated by the remodeling pathway in mammalian cells. J. Lipid Res. 2014, 55, 799–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, Q.; Chen, L.; Gao, X.; Shen, S.; Sheng, W.; Min, J.; Wang, F. The role of iron homeostasis in remodeling immune function and regulating inflammatory disease. Sci. Bull. 2021, 66, 1806–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Casal, M.N.; Pasricha, S.R.; Martinez, R.X.; Lopez-Perez, L.; Pena-Rosas, J.P. Serum or plasma ferritin concentration as an index of iron deficiency and overload. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2021, 5, CD011817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soliman, A.T.; De Sanctis, V.; Yassin, M.; Wagdy, M.; Soliman, N. Chronic anemia and thyroid function. Acta Biomed. 2017, 88, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Mao, M.; Guo, T.; Wu, Y.; Xu, Q.; Dai, J.; Huang, Y. Iron Status, Thyroid Dysfunction, and Iron Deficiency Anemia: A Two-Sample Mendelian Randomization Study. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2024, 80, 295–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Exposure | Odd Ratio | 95% CI | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Glycine | |||
| MR Egger | 0.96 | 0.91–1.01 | 0.161 |
| Weighted median | 0.95 | 0.91–1.00 | 0.038 |
| IVW | 0.95 | 0.91–0.99 | 0.011 |
| Weighted mode | 0.96 | 0.92–1.00 | 0.048 |
| Simple mode | 0.90 | 0.75–1.09 | 0.301 |
| Phospholipids in medium LDL | |||
| MR Egger | 1.12 | 0.99–1.26 | 0.087 |
| Weighted median | 1.11 | 0.99–1.23 | 0.063 |
| IVW | 1.07 | 1.00–1.15 | 0.040 |
| Weighted mode | 1.14 | 1.02–1.26 | 0.024 |
| Simple mode | 0.97 | 0.81–1.16 | 0.730 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, H.; Fan, Z.; Da, Y.; Liu, X.; Wang, C.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, J.; Wu, T.; Liang, J. Causal Relationships Between Iron Deficiency Anemia, Gut Microbiota, and Metabolites: Insights from Mendelian Randomization and In Vivo Data. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 677. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13030677
Zhou H, Fan Z, Da Y, Liu X, Wang C, Zhang T, Zhang J, Wu T, Liang J. Causal Relationships Between Iron Deficiency Anemia, Gut Microbiota, and Metabolites: Insights from Mendelian Randomization and In Vivo Data. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(3):677. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13030677
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, He, Zhenzhen Fan, Yu Da, Xiaoning Liu, Chen Wang, Tiantian Zhang, Jiaqi Zhang, Tong Wu, and Jie Liang. 2025. "Causal Relationships Between Iron Deficiency Anemia, Gut Microbiota, and Metabolites: Insights from Mendelian Randomization and In Vivo Data" Biomedicines 13, no. 3: 677. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13030677
APA StyleZhou, H., Fan, Z., Da, Y., Liu, X., Wang, C., Zhang, T., Zhang, J., Wu, T., & Liang, J. (2025). Causal Relationships Between Iron Deficiency Anemia, Gut Microbiota, and Metabolites: Insights from Mendelian Randomization and In Vivo Data. Biomedicines, 13(3), 677. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13030677







