Astilbin Alleviates Radiation-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis via circPRKCE Targeting the TGF-β/Smad7 Pathway to Inhibit Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture and Irradiation
2.2. Animals and Irradiation
2.3. AST Treatment
2.4. Western Blotting (WB)
2.5. Real-Time RT-PCR
2.6. Cell Counting Kit 8 Assays (CCK-8)
2.7. Histopathology
2.8. Immunohistochemistry
2.9. Bioinformatics Analysis
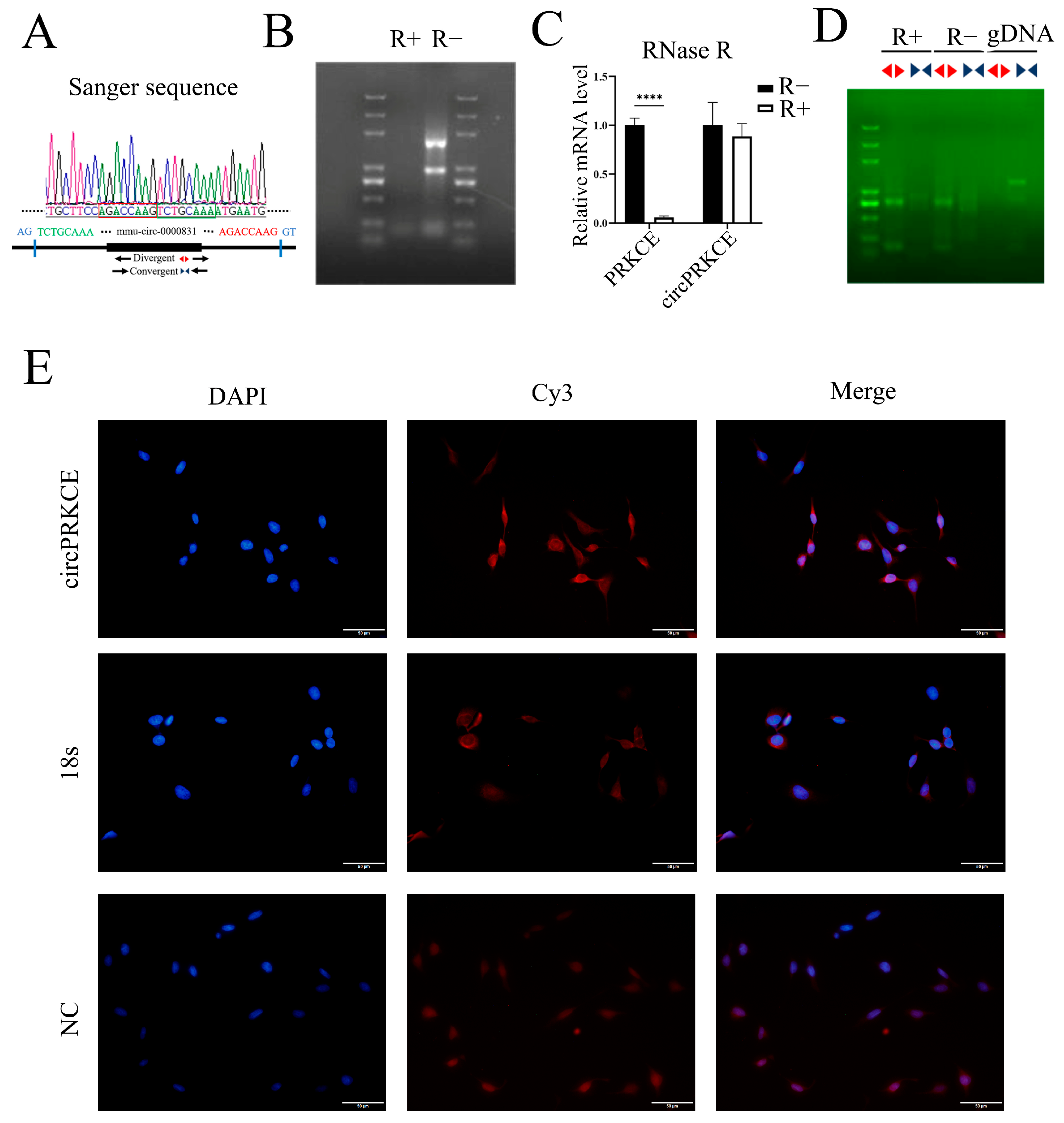
2.10. Sanger Sequencing, RNase R Digestion, and DNA Gel Electrophoresis
2.11. Fluorescent In Situ Hybridization (FISH)
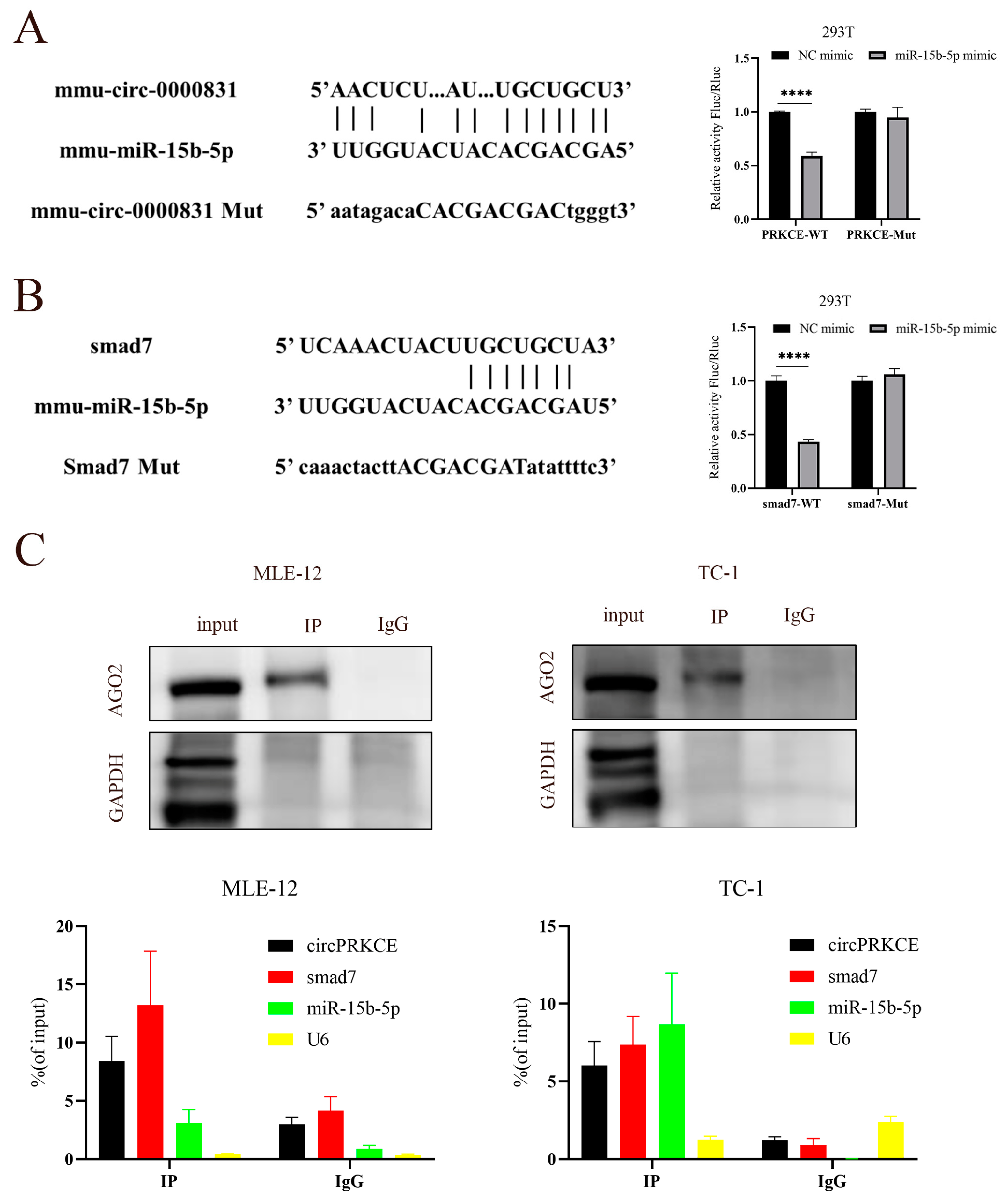
2.12. RNA Immunoprecipitation (RIP) Assay
2.13. Dual-Luciferase Reporter Assay
2.14. Construction of Stable-Infected Cell Lines
2.15. Flow Cytometry
2.16. Statistical Analysis Doses and Times
3. Results
3.1. AST Reduces Radiation-Induced Inhibition of Proliferation in Mouse-Derived Lung Epithelial Cells In Vitro
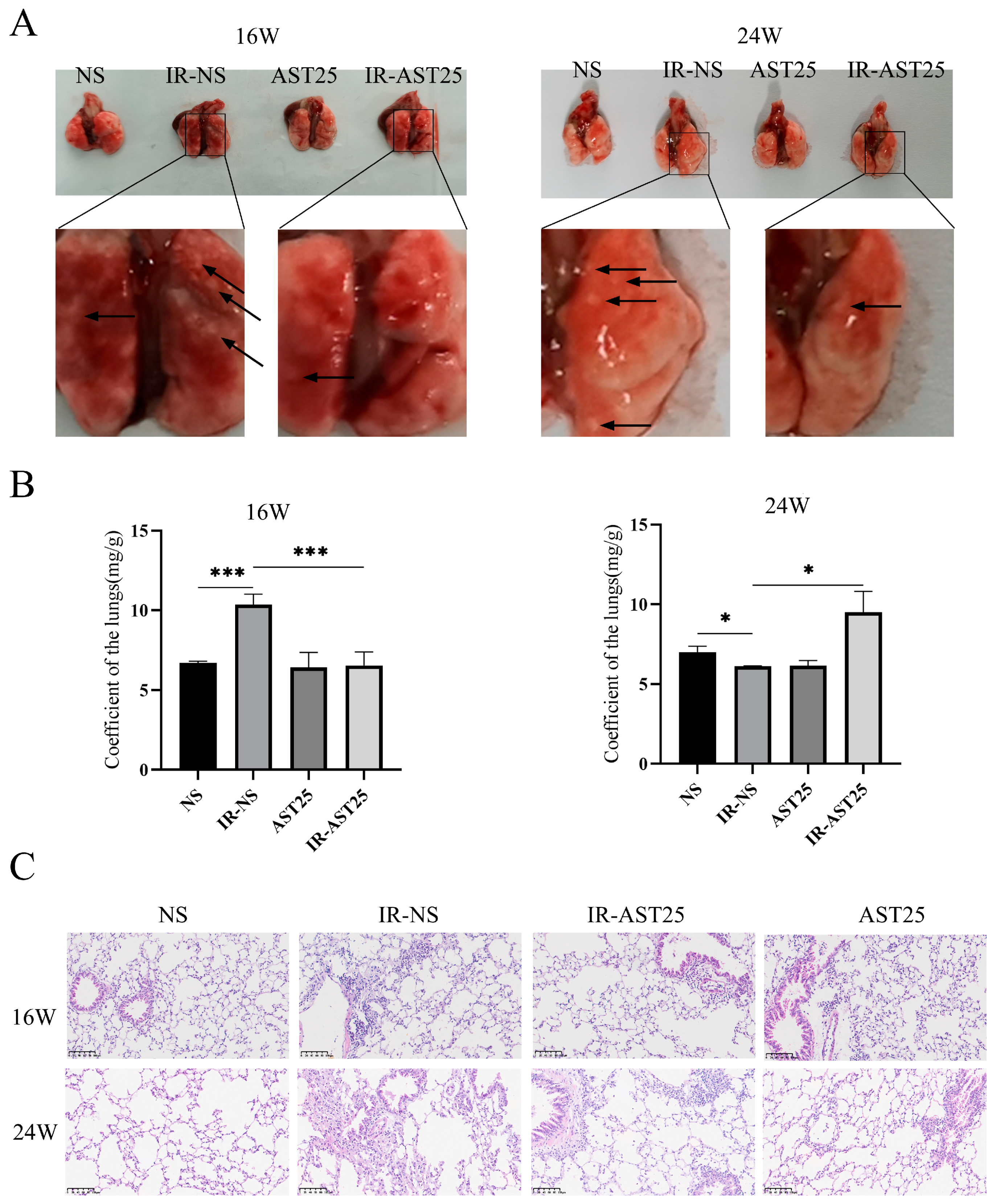
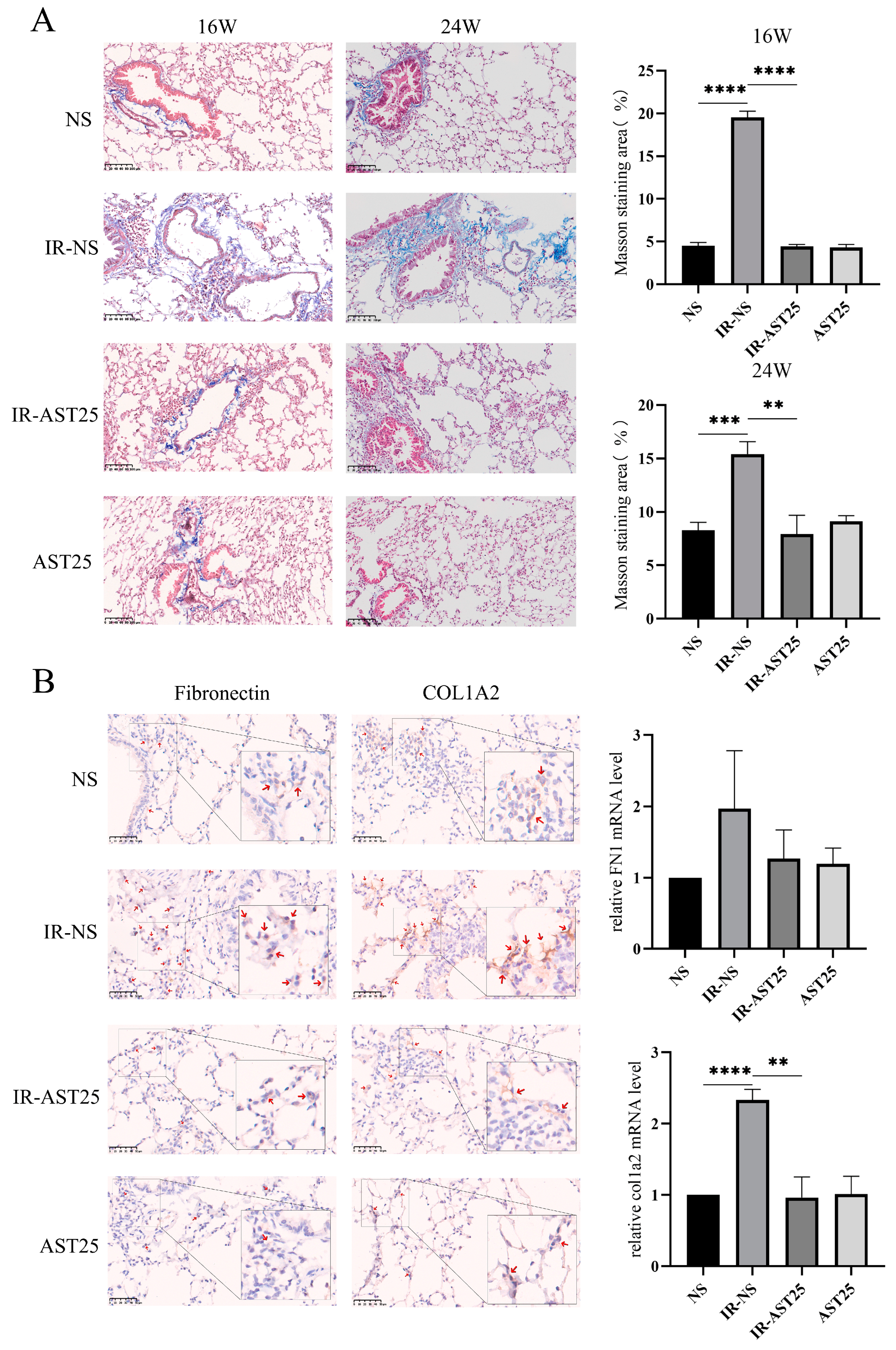
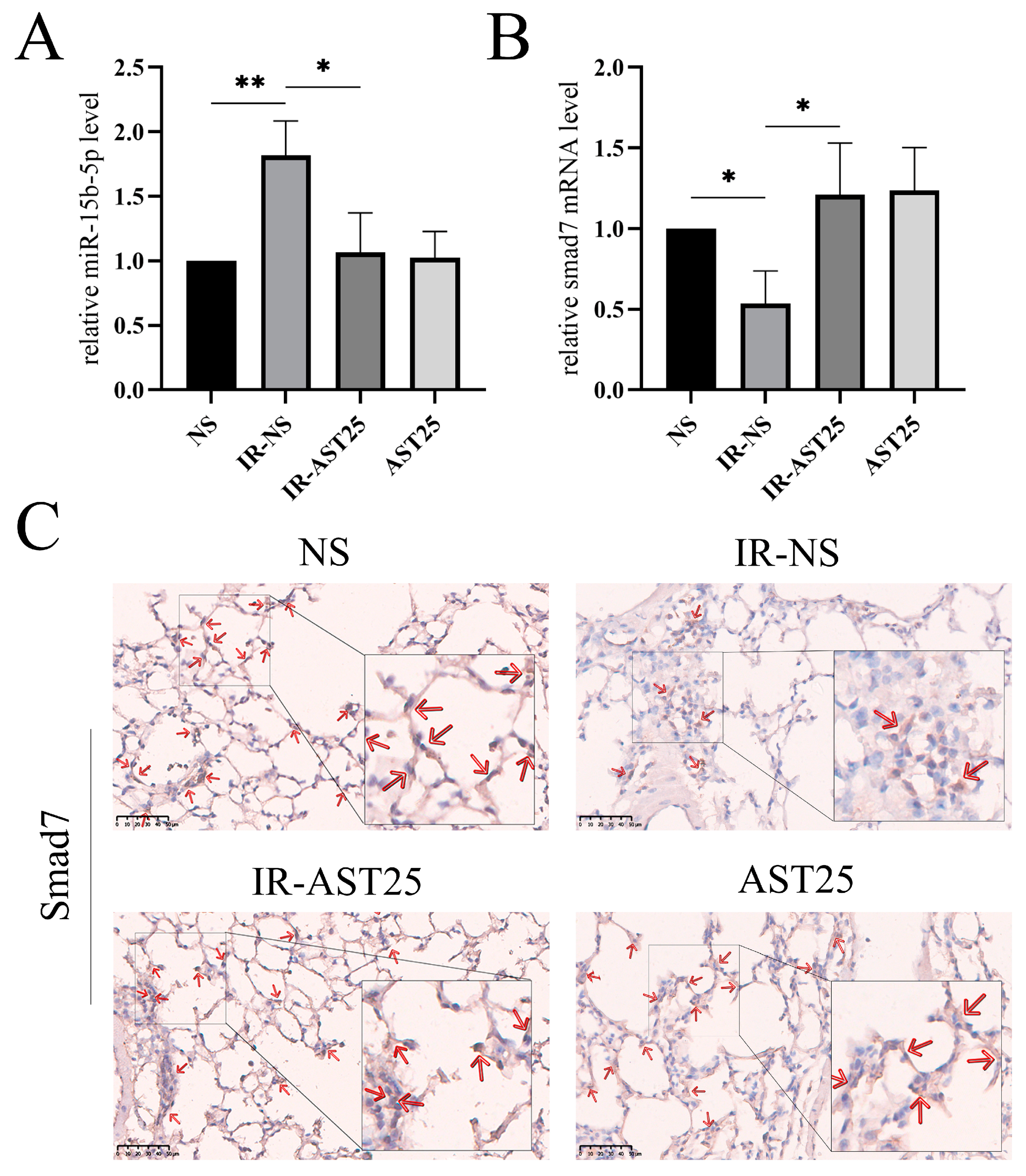
3.2. AST Alleviates Radiation-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis In Vivo
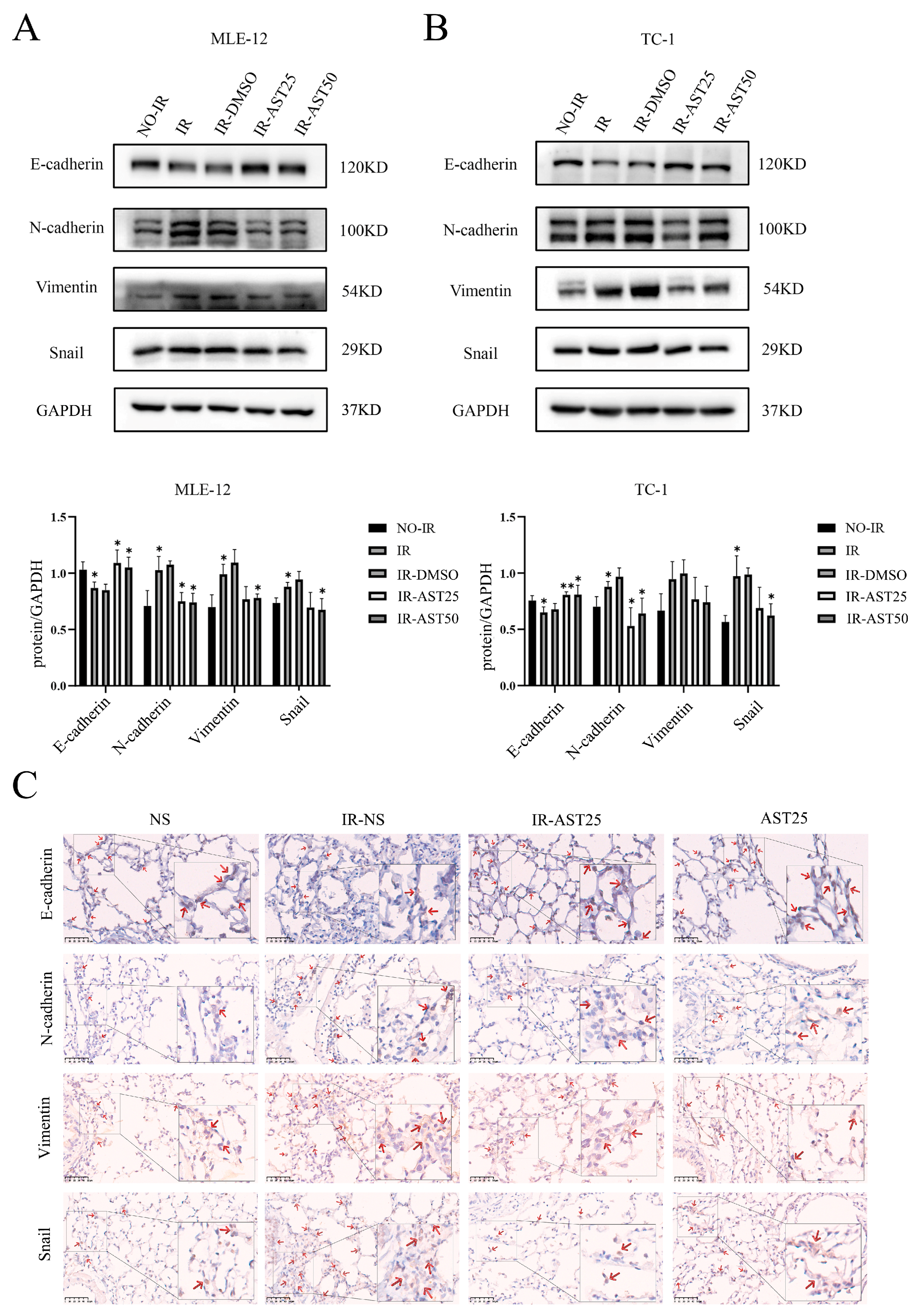
3.3. AST Inhibits Radiation-Mediated Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition Progression
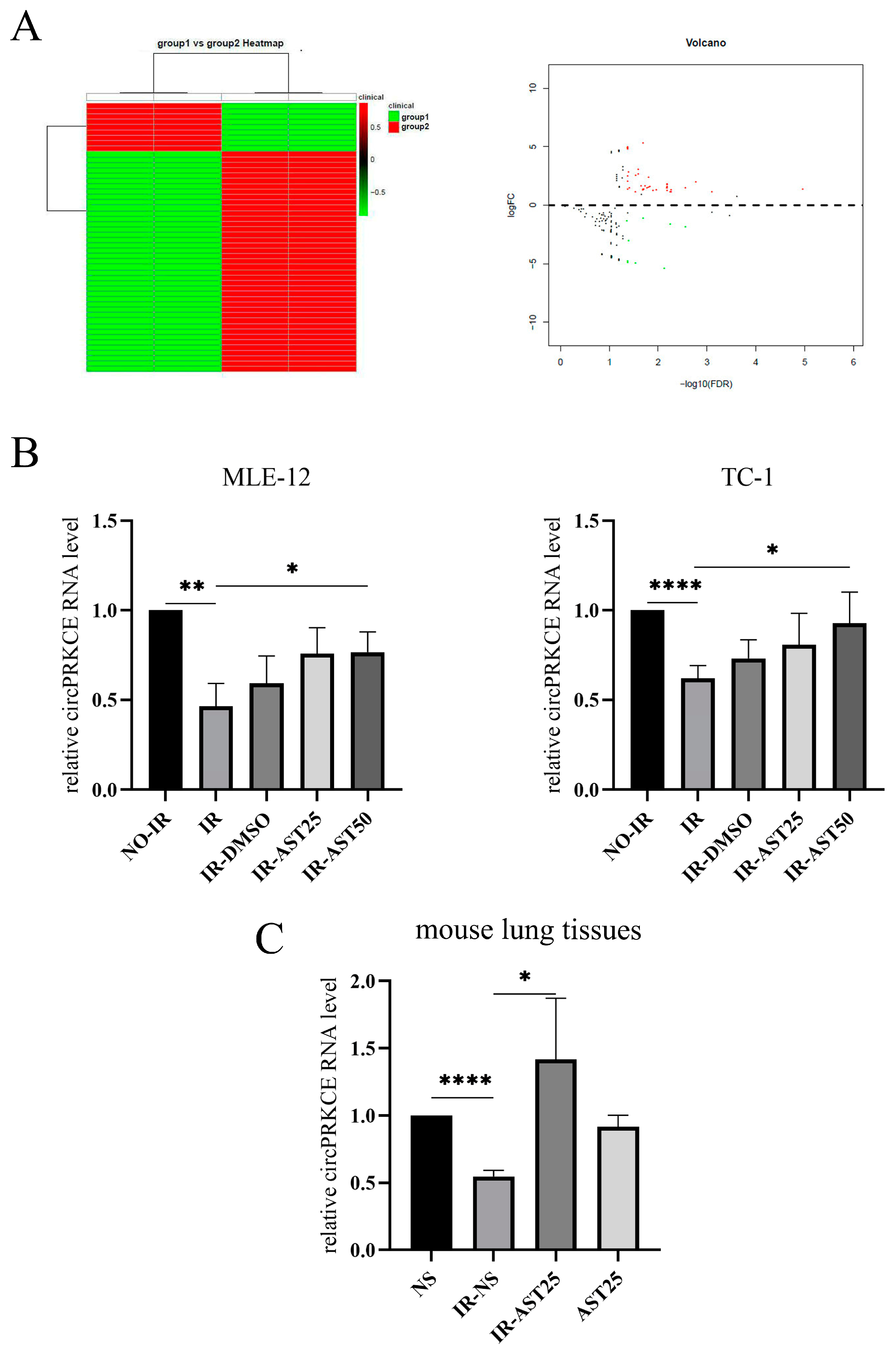
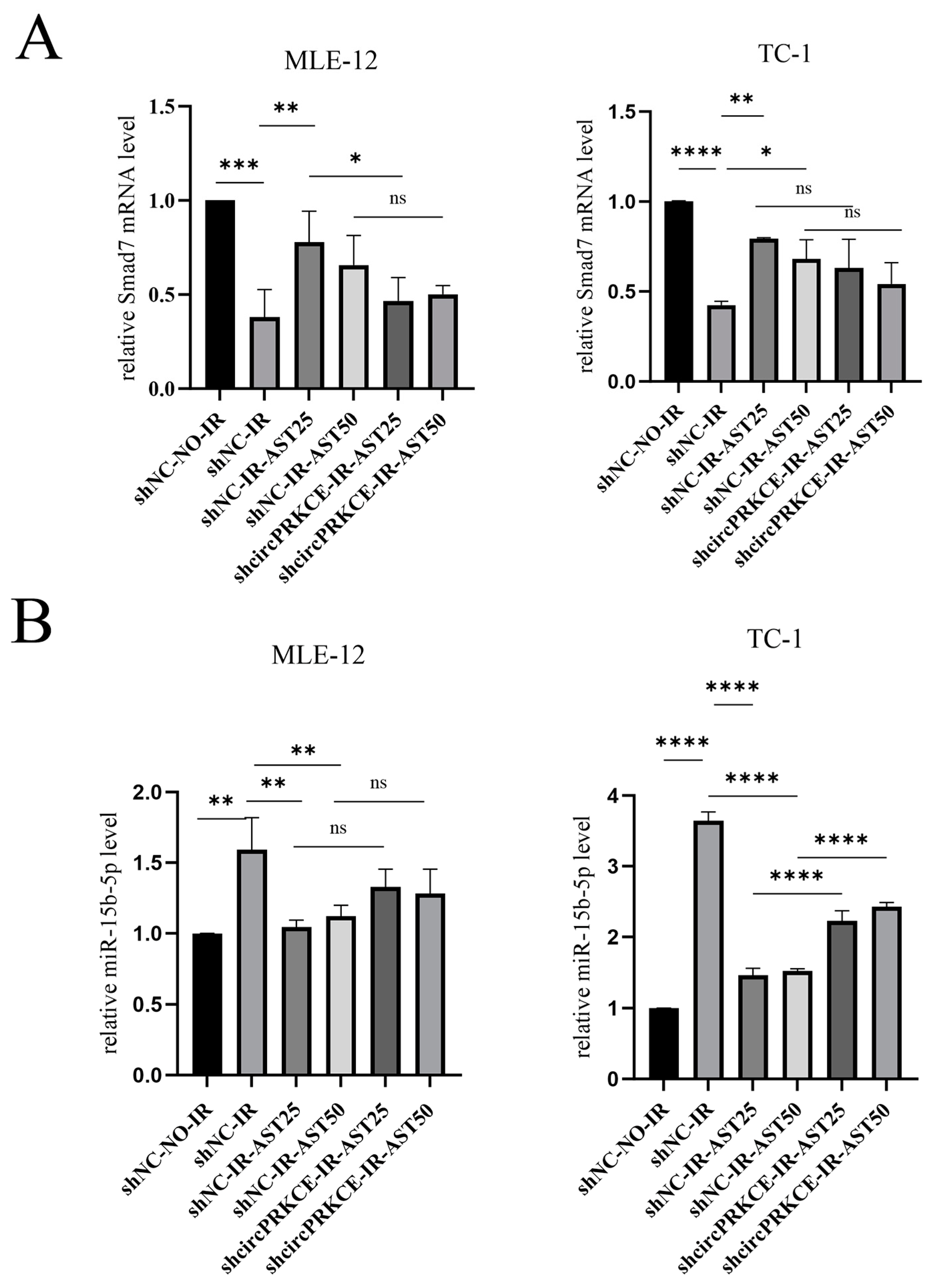
3.4. AST Inhibits Radiation-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis by Enhancing circPRKCE Expression
3.5. AST Inhibited Radiation Induced Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition by Regulating circPEKCE/miR-15b-5p/smad7 Axis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Bray, F.; Laversanne, M.; Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA A Cancer J. Clin. 2024, 74, 229–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinod, S.K.; Hau, E. Radiotherapy treatment for lung cancer: Current status and future directions. Respirology 2020, 25, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bensenane, R.; Helfre, S.; Cao, K.; Carton, M.; Champion, L.; Girard, N.; Glorion, M.; Vieira, T.; Waissi, W.; Crehange, G.; et al. Optimizing lung cancer radiation therapy: A systematic review of multifactorial risk assessment for radiation-induced lung toxicity. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2024, 124, 102684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalluri, R.; Weinberg, R.A. The basics of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J. Clin. Investig. 2009, 119, 1420–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, V.; Bhattacharya, S.; Chikkaputtaiah; Channakeshavaiah; Hazra, S.; Pal, M. The basics of epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT): A study from a structure, dynamics, and functional perspective. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 14535–14555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marconi, G.D.; Fonticoli, L.; Rajan, T.S.; Pierdomenico, S.D.; Trubiani, O.; Pizzicannella, J.; Diomede, F. Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition (EMT): The Type-2 EMT in Wound Healing, Tissue Regeneration and Organ Fibrosis. Cells 2021, 10, 1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reilkoff, R.A.; Bucala, R.; Herzog, E.L. Fibrocytes: Emerging effector cells in chronic inflammation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2011, 11, 427–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andarawewa, K.L.; Erickson, A.C.; Chou, W.S.; Costes, S.V.; Gascard, P.; Mott, J.D.; Bissell, M.J.; Barcellos-Hoff, M.H. Ionizing Radiation Predisposes Nonmalignant Human Mammary Epithelial Cells to Undergo Transforming Growth Factor β–Induced Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 8662–8670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Zhong, Y.; Chen, J.; Lin, X.; Lin, Z.; Wang, N.; Lin, S. Radiation Enhances the Epithelial– Mesenchymal Transition of A549 Cells via miR3591-5p/USP33/PPM1A. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 50, 721–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Xie, F.; Tang, X.; Wang, T.; Wang, S. Insights into the role of circular RNA in macrophage activation and fibrosis disease. Pharmacol. Res. 2020, 156, 104777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghafouri-Fard, S.; Abak, A.; Talebi, S.F.; Shoorei, H.; Branicki, W.; Taheri, M.; Akbari Dilmaghani, N. Role of miRNA and lncRNAs in organ fibrosis and aging. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 143, 112132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, W.; Li, Y.; Han, L.; Ji, X.; Pan, H.; Liu, Y.; Yuan, J.; Yan, W.; Ni, C. The CDR1as/miR-7/TGFBR2 Axis Modulates EMT in Silica-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis. Toxicol. Sci. Off. J. Soc. Toxicol. 2018, 166, 465–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.-x.; Lu, J.; Xie, H.; Wang, D.-p.; Ni, H.-e.; Zhu, Y.; Ren, L.-h.; Meng, X.-x.; Wang, R.-l. circHIPK3 regulates lung fibroblast-to-myofibroblast transition by functioning as a competing endogenous RNA. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Kwon, O.-S.; Kim, K.-T.; Lee, E.; Kim, M.; Choi, S.-H.; Li, H.; Fornace, A.J.; Cho, J.-H.; Lee, Y.-S.; et al. Induction of MiR-21 by Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy Contributes to the Pulmonary Fibrotic Response. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0154942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibáñez, B.; Melero, A.; Montoro, A.; Merino-Torres, J.F.; Soriano, J.M.; San Onofre, N. A Narrative Review of the Herbal Preparation of Ayurvedic, Traditional Chinese, and Kampō Medicines Applied as Radioprotectors. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, H.; Hu, K.; Jiang, J.; Chen, Y.; Liu, W.; Wang, R. Sarcandra glabra inhibits the epithelial-mesenchymal transition in radiation-induced lung injury in minipigs. World Sci. Technol.-Mod. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2016, 18, 846–853. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, S.; Yan, Z.; Shui, X.; Qi, W.; Chen, Y.; Xu, X.; Hu, Y.; Guo, W.; Shang, P. Astilbin prevents osteoarthritis development through the TLR4/MD-2 pathway. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 13104–13114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Lin, Z.; Wen, J.; Wu, K.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, G.; Xiao, W.; Ding, Y.; Jia, X.; et al. Astilbin promotes the induction of regulatory NK1.1− CD4+ NKG2D+ T cells through the PI3K, STAT3, and MAPK signaling pathways. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2020, 81, 106143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, S.; Lu, G.; Wang, B.; Xiang, J.; Hu, C.; Lin, Z.; Ding, Y.; Xiao, W.; Gong, W. Astilbin Activates the Reactive Oxidative Species/PPARγ Pathway to Suppress Effector CD4+ T Cell Activities via Direct Binding with Cytochrome P450 1B1. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 848957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Z.; Wang, G.; Huang, R.; Liu, C.; Yushanjiang, F.; Mao, T.; Li, J. Astilbin protects from sepsis-induced cardiac injury through the NRF2/HO-1 and TLR4/NF-κB pathway. Phytother. Res. 2023, 38, 1044–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Ye, Y.; Ji, J.; Zhang, S.; Yang, X.; Xu, J.; Wang, J.-S.; Chen, Z.; Xia, B.; Shen, H.; et al. Astilbin fromSmilax glabraRoxb. alleviates high-fat diet-induced metabolic dysfunction. Food Funct. 2022, 13, 5023–5036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, G.; Zhang, J.; Liu, X.; Liu, W.; Cao, G.; Lv, C.; Zhang, X.; Xu, P.; Li, M.; Song, X. Regulatory network of two circRNAs and an miRNA with their targeted genes under astilbin treatment in pulmonary fibrosis. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2019, 23, 6720–6729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, H.; Song, C.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Y.; Lv, C.; Song, X. Astilbin ameliorates pulmonary fibrosis via blockade of Hedgehog signaling pathway. Pulm. Pharmacol. Ther. 2018, 50, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Sun, S.; Zhao, J.; Wu, Q.; He, W.; Sun, W. Yishen-Qingli-Huoxue formula attenuates renal fibrosis by inhibiting indoxyl sulfate via AhR/snai1 signaling. Phytomedicine 2023, 108, 154546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.-H.; Zhang, H.; Fan, X.-P.; Wang, Z.-H. Astilbin Protects Against Carbon Tetrachloride-Induced Liver Fibrosis in Rats. Pharmacology 2021, 106, 323–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, L.; Huang, Y.; Chen, L.; Shi, Z.; Wang, H.; Zhang, T.; Li, Z.; Mi, J.; Fan, T.; Lu, Y.; et al. Radioprotective efficacy of Astilbin in mitigating radiation-induced lung injury through inhibition of p53 acetylation. Environ. Toxicol. 2023, 38, 2967–2980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Mi, J.; Qin, X.; Ouyang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Li, Z.; He, S.; Hu, K.; Wang, R.; Huang, W. Rosmarinic Acid Alleviates Radiation-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis by Downregulating the tRNA N7-Methylguanosine Modification-Regulated Fibroblast-to-Myofibroblast Transition Through the Exosome Pathway. J. Inflamm. Res. 2024, 17, 5567–5586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Gao, X.; Zhang, M.; Yan, S.; Sun, C.; Xiao, F.; Huang, N.; Yang, X.; Zhao, K.; Zhou, H.; et al. Novel Role of FBXW7 Circular RNA in Repressing Glioma Tumorigenesis. JNCI J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2018, 110, 304–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Shi, M.; He, X.; Cao, Y.; Liu, P.; Li, F.; Zou, S.; Wen, C.; Zhan, Q.; Xu, Z.; et al. LncRNA-PACERR induces pro-tumour macrophages via interacting with miR-671-3p and m6A-reader IGF2BP2 in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2022, 15, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Fu, J.; Kowalchuk, R.O.; Wright, C.M.; Zhang, R.; Li, X.; Xu, Y. Exploration of radiation-induced lung injury, from mechanism to treatment: A narrative review. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2022, 11, 307–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, S.; Pan, X.; Xu, L.; Yang, Z.; Guo, R.; Gu, Y.; Li, R.; Wang, Q.; Xiao, F.; Du, L.; et al. Regulatory T Cells Promote β-Catenin–Mediated Epithelium-to-Mesenchyme Transition During Radiation-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. *Biol. *Phys. 2015, 93, 425–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tofilon, P.J.; Almeida, C.; Nagarajan, D.; Tian, J.; Leal, S.W.; Wheeler, K.; Munley, M.; Blackstock, W.; Zhao, W. The Role of Alveolar Epithelium in Radiation-Induced Lung Injury. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e53628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kartha, R.V.; Subramanian, S. Competing endogenous RNAs (ceRNAs): New entrants to the intricacies of gene regulation. Front. Genet. 2014, 5, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, D.; Fu, M.; Wang, M.; Wei, Y.; Wei, X. Targeting TGF-β signal transduction for fibrosis and cancer therapy. Mol. Cancer 2022, 21, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanania, A.N.; Mainwaring, W.; Ghebre, Y.T.; Hanania, N.A.; Ludwig, M. Radiation-Induced Lung Injury. Chest 2019, 156, 150–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.-y.; Zhu, J.-y.; Ye, Y.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, L.-j.; Wang, S.-j.; Song, Y.-n.; Zhang, H. Erhuang Formula ameliorates renal damage in adenine–induced chronic renal failure rats via inhibiting inflammatory and fibrotic responses. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 95, 520–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Shen, Z.; Jiang, X.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Z.; Mao, Y.; Wu, Z.; Li, G.; Chen, H. Mouse mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomal miR-466f-3p reverses EMT process through inhibiting AKT/GSK3β pathway via c-MET in radiation-induced lung injury. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2022, 41, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Song, C.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, W.; Zheng, W.; Zhou, H.; Deng, G.; Li, H.; Xiao, W.; Yang, Z.; et al. Re-Du-Ning injection ameliorates radiation-induced pneumonitis and fibrosis by inhibiting AIM2 inflammasome and epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Phytomedicine 2022, 102, 154184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, Z.; Ao, X.; Liang, X.; Chen, Z.; Liu, Y.; Wang, P.; Wang, D.; Liu, Z.; Liu, X.; Zhu, J.; et al. Transcriptional inhibition of miR-486-3p by BCL6 upregulates Snail and induces epithelial–mesenchymal transition during radiation-induced pulmonary fibrosis. Respir. Res. 2022, 23, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.-R.; Jo, S.-K.; Jung, U. Ionizing Radiation Promotes Epithelial–to–Mesenchymal Transition in Lung Epithelial Cells by TGF-β-producing M2 Macrophages. Vivo 2019, 33, 1773–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, H.; Fang, M.; Hang, Q.; Chen, Y.; Qian, X.; Chen, M. Pirfenidone modulates macrophage polarization and ameliorates radiation-induced lung fibrosis by inhibiting the TGF-β1/Smad3 pathway. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2021, 25, 8662–8675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.-H.; Kim, J.-Y.; Kim, J.-M.; Yoo, B.R.; Han, S.Y.; Jung, Y.J.; Bae, H.; Cho, J. PM014 attenuates radiation-induced pulmonary fibrosis via regulating NF-kB and TGF-b1/NOX4 pathways. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 16112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, Y.; Jian, X.; Zhang, Z.; Ning, Q.; Kan, B.; Kong, L. Effects of tacrolimus on the TGF-β1/SMAD signaling pathway in paraquat-exposed rat alveolar type II epithelial cells. Mol. Med. Rep. 2020, 22, 3687–3694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.; Jiang, Y.-N.; Wang, W.-J.; Zhang, J.; Shang, D.-S.; Sun, C.-B.; Tian, J.-T.; Tian, J.-W.; Yu, B.; Zhang, Y. Comprehensive circRNA expression profile and construction of circRNA-related ceRNA network in cardiac fibrosis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 125, 109944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, L.; Wei, J.; Zeng, Y.; Liu, J.; Xiao, E.; Kang, Y.; Kang, Y. Mesenchymal stem cell-originated exosomal circDIDO1 suppresses hepatic stellate cell activation by miR-141-3p/PTEN/AKT pathway in human liver fibrosis. Drug Deliv. 2022, 29, 440–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, F.; Gong, W.; Li, S.; Yin, B.; Zhao, C.; Liu, W.; Chen, X.; Luo, C.; Huang, Q.; Chen, T.; et al. circRNA_010383 Acts as a Sponge for miR-135a, and Its Downregulated Expression Contributes to Renal Fibrosis in Diabetic Nephropathy. Diabetes 2021, 70, 603–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Cheng, D.; Li, G.; Liu, Y.; Li, P.; Sun, W.; Ma, D.; Ni, C. CircHIPK3 regulates pulmonary fibrosis by facilitating glycolysis in miR-30a-3p/FOXK2-dependent manner. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 17, 2294–2307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.-P.; Ai, W.-B.; Wan, L.-Y.; Zhang, Y.-Q.; Wu, J.-F. The roles of microRNA families in hepatic fibrosis. Cell Biosci. 2017, 7, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawal, S.; Munasinghe, P.E.; Nagesh, P.T.; Lew, J.K.S.; Jones, G.T.; Williams, M.J.A.; Davis, P.; Bunton, D.; Galvin, I.F.; Manning, P.; et al. Down-regulation of miR-15a/b accelerates fibrotic remodelling in the Type 2 diabetic human and mouse heart. Clin. Sci. 2017, 131, 847–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tijsen, A.J.; van der Made, I.; van den Hoogenhof, M.M.; Wijnen, W.J.; van Deel, E.D.; de Groot, N.E.; Alekseev, S.; Fluiter, K.; Schroen, B.; Goumans, M.-J.; et al. The microRNA-15 family inhibits the TGFβ-pathway in the heart. Cardiovasc. Res. 2014, 104, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasanna, P.G.S.; Aryankalayil, M.; Citrin, D.E.; Coleman, C.N. Radiation-induced pulmonary fibrosis: Roles of therapy-induced senescence and microRNAs. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2023, 99, 1027–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, D.; Zhang, Q.-F. The natural source, physicochemical properties, biological activities and metabolism of astilbin. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 63, 9506–9518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shi, Z.; Liu, J.; Qin, J.; Liang, X.; Ou, X.; Zhang, T.; Yan, X.; Hu, Q.; Huang, W.; Hu, K. Astilbin Alleviates Radiation-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis via circPRKCE Targeting the TGF-β/Smad7 Pathway to Inhibit Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 689. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13030689
Shi Z, Liu J, Qin J, Liang X, Ou X, Zhang T, Yan X, Hu Q, Huang W, Hu K. Astilbin Alleviates Radiation-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis via circPRKCE Targeting the TGF-β/Smad7 Pathway to Inhibit Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(3):689. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13030689
Chicago/Turabian StyleShi, Zhiling, Jing Liu, Jing Qin, Xian Liang, Xue Ou, Tingting Zhang, Xueting Yan, Qianxin Hu, Weimei Huang, and Kai Hu. 2025. "Astilbin Alleviates Radiation-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis via circPRKCE Targeting the TGF-β/Smad7 Pathway to Inhibit Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition" Biomedicines 13, no. 3: 689. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13030689
APA StyleShi, Z., Liu, J., Qin, J., Liang, X., Ou, X., Zhang, T., Yan, X., Hu, Q., Huang, W., & Hu, K. (2025). Astilbin Alleviates Radiation-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis via circPRKCE Targeting the TGF-β/Smad7 Pathway to Inhibit Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition. Biomedicines, 13(3), 689. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13030689







