Novel Small-Molecule Treatment and Emerging Biological Therapy for Psoriasis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Small Molecules
2.1. Corticosteroids
2.1.1. Micro/Nanocarrier-Loaded Hydrogels
2.1.2. Microneedles
2.1.3. Nanoparticles
2.1.4. Cubosomes
2.2. Immunosuppressants
2.2.1. Hydrogel
2.2.2. Microneedles
2.2.3. Niosomes and Nanoparticles
2.2.4. Micelles
2.2.5. Nanoemulsion
2.2.6. Ionic Liquids
2.3. Retinoids
2.3.1. Liposome and Transethosome (Vesicles)
2.3.2. Nanoparticles
2.3.3. Solid Lipid Nanoparticles
2.4. Vitamin D Analogs
2.4.1. Hydrogel
2.4.2. Microneedles
2.4.3. Micelles
2.4.4. Nanoemulsion
3. Biomacromolecules
3.1. Protein and Peptide
3.1.1. Protein and Peptide Delivery
3.1.2. Gene Editing
3.2. Nucleic Acid
3.2.1. RNAi Therapy
3.2.2. miRNA Delivery
3.2.3. Oligonucleotide Delivery
3.2.4. DNA Aptamers
3.3. Monoclonal Antibody
3.3.1. Anti-TNF Agents
3.3.2. Anti-IL-17 Agents
3.3.3. Anti-IL12/IL23 Agents
3.3.4. Anti-IL-36 Agents
4. Cell-Based Therapy
4.1. Mesenchymal Stem Cell
4.2. Extracellular Vesicles
4.3. Adoptive Cell Therapy
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nestle, F.O.; Kaplan, D.H.; Barker, J. Psoriasis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 361, 496–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parisi, R.; Iskandar, I.Y.K.; Kontopantelis, E.; Augustin, M.; Griffiths, C.E.M.; Ashcroft, D.M. National, regional, and worldwide epidemiology of psoriasis: Systematic analysis and modelling study. BMJ 2020, 369, m1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, A.W.; Read, C. Pathophysiology, Clinical Presentation, and Treatment of Psoriasis: A Review. JAMA 2020, 323, 1945–1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Zhao, Y.; Cao, X. Global burden and future trends in psoriasis epidemiology: Insights from the global burden of disease study 2019 and predictions to 2030. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2024, 316, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Psoriasis Treatment Market Size|Share and Trends 2024 to 2034. Available online: https://www.precedenceresearch.com/psoriasis-treatment-market (accessed on 22 February 2025).
- Guo, J.; Zhang, H.; Lin, W.; Lu, L.; Su, J.; Chen, X. Signaling pathways and targeted therapies for psoriasis. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mabuchi, T.; Hirayama, N. Binding Affinity and Interaction of LL-37 with HLA-C*06:02 in Psoriasis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2016, 136, 1901–1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prinz, J.C. Melanocytes: Target Cells of an HLA-C*06:02-Restricted Autoimmune Response in Psoriasis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2017, 137, 2053–2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, P.; Yang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Luo, Z.; Tu, W.; Han, J.; Deng, Y.; Yin, L. Characterization of Autoantigen Presentation by HLA-C*06:02 in Psoriasis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2017, 137, 2238–2241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greb, J.E.; Goldminz, A.M.; Elder, J.T.; Lebwohl, M.G.; Gladman, D.D.; Wu, J.J.; Mehta, N.N.; Finlay, A.Y.; Gottlieb, A.B. Psoriasis. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2016, 2, 16082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramic, L.; Sator, P. Topical treatment of psoriasis vulgaris. J. Dtsch. Dermatol. Ges. 2023, 21, 631–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswasroy, P.; Pradhan, D.; Kar, B.; Ghosh, G.; Rath, G. Recent Advancement in Topical Nanocarriers for the Treatment of Psoriasis. AAPS PharmSciTech 2021, 22, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, A.; Luo, Y.; Xu, J.; Guan, X.; He, H.; Xuan, X.; Wu, J. Latest on biomaterial-based therapies for topical treatment of psoriasis. J. Mater. Chem. B 2022, 10, 7397–7417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawarkar, S.P.; Yadav, V. Novel drug delivery strategies and gene therapy regimen as a promising perspective for management of psoriasis. Indian J. Dermatol. Venereol. Leprol. 2021, 87, 333–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wollina, U.; Tirant, M.; Vojvodic, A.; Lotti, T. Treatment of Psoriasis: Novel Approaches to Topical Delivery. Open Access Maced. J. Med. Sci. 2019, 7, 3018–3025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valenzuela, F.; Flores, R. Immunogenicity to biological drugs in psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis. Clinics 2021, 76, e3015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brownstone, N.D.; Hong, J.; Mosca, M.; Hadeler, E.; Liao, W.; Bhutani, T.; Koo, J. Biologic Treatments of Psoriasis: An Update for the Clinician. Biologics 2021, 15, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Zhao, J.; Wei, K.; Jiang, P.; Shi, Y.; Chang, C.; Zheng, Y.; Shan, Y.; Li, Y.; He, B.; et al. Targeted siRNA Therapy for Psoriasis: Translating Preclinical Potential into Clinical Treatments. Immunotargets Ther. 2024, 13, 259–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purewal, J.S.; Doshi, G.M. RNAi in psoriasis: A melodic exploration of miRNA, shRNA, and amiRNA with a spotlight on siRNA. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2024, 985, 177083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lwin, S.M.; Snowden, J.A.; Griffiths, C.E.M. The promise and challenges of cell therapy for psoriasis. Br. J. Dermatol. 2021, 185, 887–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Fleming, C.; Yan, J. New insights of T cells in the pathogenesis of psoriasis. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2012, 9, 302–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dairov, A.; Sekenova, A.; Alimbek, S.; Nurkina, A.; Shakhatbayev, M.; Kumasheva, V.; Kuanysh, S.; Adish, Z.; Issabekova, A.; Ogay, V. Psoriasis: The Versatility of Mesenchymal Stem Cell and Exosome Therapies. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nussbaum, L.; Chen, Y.L.; Ogg, G.S. Role of regulatory T cells in psoriasis pathogenesis and treatment. Br. J. Dermatol. 2021, 184, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uva, L.; Miguel, D.; Pinheiro, C.; Antunes, J.; Cruz, D.; Ferreira, J.; Filipe, P. Mechanisms of action of topical corticosteroids in psoriasis. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2012, 2012, 561018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardy, R.S.; Raza, K.; Cooper, M.S. Therapeutic glucocorticoids: Mechanisms of actions in rheumatic diseases. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2020, 16, 133–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shetty, K.; Sherje, A.P. Nano intervention in topical delivery of corticosteroid for psoriasis and atopic dermatitis-a systematic review. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2021, 32, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stacey, S.K.; McEleney, M. Topical Corticosteroids: Choice and Application. Am. Fam. Physician 2021, 103, 337–343. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vasowala, T.; Gharat, S.; Mhase, M.; Momin, M. Advances in hydrogels based cutaneous drug delivery system for management of psoriasis. Eur. Polym. J. 2024, 202, 112630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Fu, X.; Zhao, G.; Du, X.; Georgesen, C.; Thiele, G.M.; Goldring, S.R.; Wang, D. Intradermal Injection of a Thermoresponsive Polymeric Dexamethasone Prodrug (ProGel-Dex) Ameliorate Dermatitis in an Imiquimod (IMQ)-Induced Psoriasis-like Mouse Model. Mol. Pharm. 2024, 21, 4995–5004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondiah, P.P.D.; Rants’o, T.A.; Mdanda, S.; Mohlomi, L.M.; Choonara, Y.E. A Poly (Caprolactone)-Cellulose Nanocomposite Hydrogel for Transdermal Delivery of Hydrocortisone in Treating Psoriasis Vulgaris. Polymers 2022, 14, 2633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, K.; Pani, T.; Jha, S.K.; Mehta, D.; Yadav, P.; Jain, D.; Pradhan, M.K.; Mishra, S.; Kar, R.; Srivastava, A.; et al. Hydrogel-mediated topical delivery of steroids can effectively alleviate psoriasis via attenuating the autoimmune responses. Nanoscale 2022, 14, 3834–3848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, N.; Kumar, S.; Prasad, M.; Rao, R. Eudragit RS100 based microsponges for dermal delivery of clobetasol propionate in psoriasis management. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2020, 55, 101347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradhan, M.; Yadav, K.; Singh, D.; Singh, M.R. Topical delivery of fluocinolone acetonide integrated NLCs and salicylic acid enriched gel: A potential and synergistic approach in the management of psoriasis. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2021, 61, 102282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, F.; Sun, Y.; Bi, D.; Peng, S.; Li, M.; Liu, H.; Zhang, L.; Tao, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, J. Regulating Size and Charge of Liposomes in Microneedles to Enhance Intracellular Drug Delivery Efficiency in Skin for Psoriasis Therapy. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2023, 12, e2302314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, N.; Jeong, Y.G.; Lee, S.; Kang, J.; Kim, Y.; Choi, Y.A.; Khang, D.; Kim, S.H. Ameliorated Skin Inflammation through the Synergistic Effect of Gold Nanorod-Dexamethasone and Photothermal Therapy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2024, 16, 12217–12231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrade, J.F.M.; Cunha-Filho, M.; Gelfuso, G.M.; Gratieri, T. Iontophoresis for the cutaneous delivery of nanoentraped drugs. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2023, 20, 785–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Gong, S.; Mu, Y.; Jia, X.; Zhou, Y.; Tian, Y.; Chao, D. Wearable dual-drug controlled release patch for psoriasis treatment. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2024, 669, 835–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, P.; Goodyear, B.; Dholaria, N.; Puri, V.; Michniak-Kohn, B. Nanostructured Non-Ionic Surfactant Carrier-Based Gel for Topical Delivery of Desoximetasone. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Prasad, M.; Rao, R. Topical delivery of clobetasol propionate loaded nanosponge hydrogel for effective treatment of psoriasis: Formulation, physicochemical characterization, antipsoriatic potential and biochemical estimation. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2021, 119, 111605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, M.; Sheng, T.; Yu, J.; Gu, Z.; Xu, C. Microneedle biomedical devices. Nat. Rev. Bioeng. 2024, 2, 324–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Fu, Y.; Liu, P.; Qu, F.; Du, S.; Li, Y.; Du, H.; Zhang, L.; Tao, J.; Zhu, J. Supramolecular Dissolving Microneedle Patch Loading Hydrophobic Glucocorticoid for Effective Psoriasis Treatment. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 15162–15171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Chen, G.; Lu, M.; Zhao, Y. Multifunctional structural color triboelectric microneedle patches for psoriasis treatment. Matter 2023, 6, 1555–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolz-Pérez, I.; Sallam, M.A.; Masiá, E.; Morelló-Bolumar, D.; Pérez Del Caz, M.D.; Graff, P.; Abdelmonsif, D.; Hedtrich, S.; Nebot, V.J.; Vicent, M.J. Polypeptide-corticosteroid conjugates as a topical treatment approach to psoriasis. J. Control. Release 2020, 318, 210–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mai, Y.; Ouyang, Y.; Yu, M.; Qin, Y.; Girardi, M.; Saltzman, W.M.; Cocco, E.; Zhao, C.; Yu, L.; Jia, Y.; et al. Topical formulation based on disease-specific nanoparticles for single-dose cure of psoriasis. J. Control. Release 2022, 349, 354–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalaby, R.A.; El-Gazayerly, O.; Abdallah, M. Cubosomal Betamethasone-Salicylic Acid Nano Drug Delivery System for Enhanced Management of Scalp Psoriasis. Int. J. Nanomed. 2022, 17, 1659–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Todke, P.; Shah, V.H. Psoriasis: Implication to disease and therapeutic strategies, with an emphasis on drug delivery approaches. Int. J. Dermatol. 2018, 57, 1387–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kochkina, N.; Nikitina, M.; Agafonov, M.; Delyagina, E.; Terekhova, I. iota-Carrageenan hydrogels for methotrexate delivery. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 368, 120790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Fu, S.; Lu, Y.; Lai, R.; Liu, Z.; Luo, W.; Xu, Y. Chitosan/hyaluronan nanogels co-delivering methotrexate and 5-aminolevulinic acid: A combined chemo-photodynamic therapy for psoriasis. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 277, 118819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Liu, H.; Wang, W.; Qian, H.; Cheng, S.; Wang, Y.; Zha, Z.; Zhong, Y.; Hu, Y. Scalable fabrication of ZnxCd1-xS double-shell hollow nanospheres for highly efficient hydrogen production. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2018, 239, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Chen, H.; Chu, Z.; Li, Z.; Chen, B.; Sun, J.; Lai, W.; Ma, Y.; He, Y.; Qian, H.; et al. A multifunctional composite hydrogel as an intrinsic and extrinsic coregulator for enhanced therapeutic efficacy for psoriasis. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2022, 20, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.; Permana, A.D.; Li, M.; Habibie Nur Amir, M.; Peng, K.; Zhang, C.; Dai, H.; Paredes, A.J.; Vora, L.K.; Donnelly, R.F. Calcipotriol Nanosuspension-Loaded Trilayer Dissolving Microneedle Patches for the Treatment of Psoriasis: In Vitro Delivery and In Vivo Antipsoriatic Activity Studies. Mol. Pharm. 2024, 21, 2813–2827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, Y.; Xue, R.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, W.; Wang, J. A thermo-responsive hydrogel loaded with an ionic liquid microemulsion for transdermal delivery of methotrexate. J. Mater. Chem. B 2023, 11, 5494–5502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asad, M.I.; Khan, D.; Rehman, A.U.; Elaissari, A.; Ahmed, N. Development and In Vitro/In Vivo Evaluation of pH-Sensitive Polymeric Nanoparticles Loaded Hydrogel for the Management of Psoriasis. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 3433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandey, S.S.; Shah, K.M.; Maulvi, F.A.; Desai, D.T.; Gupta, A.R.; Joshi, S.V.; Shah, D.O. Topical delivery of cyclosporine loaded tailored niosomal nanocarriers for improved skin penetration and deposition in psoriasis: Optimization, ex vivo and animal studies. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2021, 63, 102441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, S.S.; Maulvi, F.A.; Patel, P.S.; Shukla, M.R.; Shah, K.M.; Gupta, A.R.; Joshi, S.V.; Shah, D.O. Cyclosporine laden tailored microemulsion-gel depot for effective treatment of psoriasis: In vitro and in vivo studies. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2020, 186, 110681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sartawi, Z.; Blackshields, C.; Faisal, W. Dissolving microneedles: Applications and growing therapeutic potential. J. Control. Release 2022, 348, 186–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rawas-Qalaji, M.; Thu, H.E.; Hussain, Z. Oromucosal delivery of macromolecules: Challenges and recent developments to improve bioavailability. J. Control. Release 2022, 352, 726–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tekko, I.A.; Permana, A.D.; Vora, L.; Hatahet, T.; McCarthy, H.O.; Donnelly, R.F. Localised and sustained intradermal delivery of methotrexate using nanocrystal-loaded microneedle arrays: Potential for enhanced treatment of psoriasis. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 152, 105469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, H.; Yang, J.; Li, M.; Xia, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, L.; Tao, J. Microneedle-assisted percutaneous delivery of methotrexate-loaded nanoparticles enabling sustained anti-inflammatory effects in psoriasis therapy. J. Mater. Chem. B 2024, 12, 2618–2627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Yang, L.; Lyu, Y.; Wu, D.; Zhu, Y.; Li, J.; Jiang, D.; Xin, X.; Yin, L. Topical Delivery of ROS-Responsive Methotrexate Prodrug Nanoassemblies by a Dissolvable Microneedle Patch for Psoriasis Therapy. Int. J. Nanomed. 2023, 18, 899–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Li, Z.; Ling, Z.; Zheng, Y.; Chang, H. Efficient Loading and Sustained Delivery of Methotrexate Using a Tip-Swellable Microneedle Array Patch for Psoriasis Treatment. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2024, 10, 921–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halder, J.; Rath, G.; Rai, V.K. Cyclosporine coated microneedle for transcutaneous delivery: Characterization, in vitro evaluation, and in vivo anti-psoriatic efficacy against IMQ-induced psoriasis. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2022, 73, 103450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Tang, Y.; Wang, M.; Wang, Y.; Wang, W.; Pang, M.; Xu, Y. Co-delivery of methotrexate and nicotinamide by cerosomes for topical psoriasis treatment with enhanced efficacy. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 605, 120826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bessar, H.; Venditti, I.; Benassi, L.; Vaschieri, C.; Azzoni, P.; Pellacani, G.; Magnoni, C.; Botti, E.; Casagrande, V.; Federici, M.; et al. Functionalized gold nanoparticles for topical delivery of methotrexate for the possible treatment of psoriasis. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2016, 141, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhardwaj, P.; Tripathi, P.; Pandey, S.; Gupta, R.; Ramchandra Patil, P. Cyclosporine and Pentoxifylline laden tailored niosomes for the effective management of psoriasis: In-vitro optimization, Ex-vivo and animal study. Int. J. Pharm. 2022, 626, 122143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Zhang, E.; Yang, J.; Cao, Z. Strategies to improve micelle stability for drug delivery. Nano Res. 2018, 11, 4985–4998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.C.; Zheng, H.L.; Wang, X.R.; Zheng, X.L.; Chen, Y.; Fei, W.D.; Zheng, Y.Q.; Wang, W.X.; Zheng, C.H. Enhanced Percutaneous Delivery of Methotrexate Using Micelles Prepared with Novel Cationic Amphipathic Material. Int. J. Nanomed. 2020, 15, 3539–3550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, D.; Shi, C.; Wang, L.; Ji, X.; Zhang, S.; Luo, J. A Rationally Designed Micellar Nanocarrier for the Delivery of Hydrophilic Methotrexate in Psoriasis Treatment. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2020, 3, 4832–4846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musa, S.H.; Razali, F.N.; Shamsudin, N.; Salim, N.; Basri, M. Novel topical nano-colloidal carrier loaded with cyclosporine: Biological evaluation potentially for psoriasis treatment. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2021, 63, 102440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.K.; Savoy, A.W. Ionic liquids synthesis and applications: An overview. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 297, 112038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yu, Q.; Lu, Y.; Ma, Y.; Qi, J.; Chen, Z.; Zhu, Q.; Wu, W. Choline-based ionic liquids enhance the dermal delivery of cyclosporine a for potential treatment of psoriasis. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datta, D.; Bandi, S.P.; Venuganti, V.V.K. Ionic Liquid-Mediated Transdermal Delivery of Organogel Containing Cyclosporine A for the Effective Treatment of Psoriasis. ACS Omega 2024, 9, 41565–41582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, R.; Napoli, J.; Enver, T.; Bernardino, L.; Ferreira, L. Advances and challenges in retinoid delivery systems in regenerative and therapeutic medicine. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Xu, X.; Song, Y.; Lan, L.; Wang, J.; Xu, X.; Du, Y. Nano transdermal system combining mitochondria-targeting cerium oxide nanoparticles with all-trans retinoic acid for psoriasis. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 2023, 18, 100846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, C.; Zou, B.; Fu, L.; Ren, S.; Zhang, X. Design and Evaluation of Tretinoin Fatty Acid Vesicles for the Topical Treatment of Psoriasis. Molecules 2023, 28, 7868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saka, R.; Jain, H.; Kommineni, N.; Chella, N.; Khan, W. Enhanced penetration and improved therapeutic efficacy of bexarotene via topical liposomal gel in imiquimod induced psoriatic plaque model in BALB/c mice. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2020, 58, 101691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, N.; Kaur, M.; Mahajan, M.; Jain, S.K. Development, characterization and evaluation of nanocarrier based formulations of antipsoriatic drug “acitretin” for skin targeting. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2020, 60, 102010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bevinakoppamath, S.S.; Dandagi, P.M.; Hulyalkar, S.; Biradar, P. Formulation, Evaluation and Optimization of Acitretin Loaded Transethosomes for the Management of Psoriasis. J. Pharm. Innov. 2024, 19, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kshirsagar, S.M.; Shrestha, N.; Kipping, T.; Banga, A.K. Formulation development of tazarotene-loaded PLGA nanoparticles for follicular delivery in the treatment of inflammatory skin diseases. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2024, 200, 114346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, M.C.; Carbone, C.; Souto, E.B. Beyond liposomes: Recent advances on lipid based nanostructures for poorly soluble/poorly permeable drug delivery. Prog. Lipid Res. 2017, 68, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schäfer-Korting, M.; Mehnert, W.; Korting, H.C. Lipid nanoparticles for improved topical application of drugs for skin diseases. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2007, 59, 427–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aland, R.; Ganesan, M.; Rajeswararao, P. Development and Optimization of Tazarotene Loaded Solid Lipid NANOPARTICLES for Topical Delivery. Asian J. Pharm. Clin. Res. 2019, 12, 63–77. [Google Scholar]
- Trémezaygues, L.; Reichrath, J. Vitamin D analogs in the treatment of psoriasis: Where are we standing and where will we be going? Derm.-Endocrinol. 2011, 3, 180–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggeletopoulou, I.; Kalafateli, M.; Geramoutsos, G.; Triantos, C. Recent Advances in the Use of Vitamin D Organic Nanocarriers for Drug Delivery. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradhan, M.; Alexander, A.; Singh, M.R.; Singh, D.; Saraf, S.; Saraf, S.; Yadav, K. Statistically optimized calcipotriol fused nanostructured lipid carriers for effectual topical treatment of psoriasis. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2021, 61, 102168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, S.; Anjum, M.M.; Jaiswal, S.; Kumar, A.; Deepak, P.; Anand, S.; Singh, S.; Rajinikanth, P.S. Novel Synergistic Approach: Tazarotene-Calcipotriol-Loaded-PVA/PVP-Nanofibers Incorporated in Hydrogel Film for Management and Treatment of Psoriasis. Mol. Pharm. 2023, 20, 997–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Bian, Q.; Ma, X.; Xu, Y.; Gao, J. A double-edged sword: ROS related therapies in the treatment of psoriasis. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 2022, 17, 798–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hua, Y.; Chang, T.; Jiang, K.; Wang, J.; Cui, X.; Cheng, M.; Yan, F.; Song, B.; Wang, Y. ROS-sensitive calcipotriol nano-micelles prepared by methoxypolyethylene glycol (mPEG)—Modified polymer for the treatment of psoriasis. Drug Deliv. 2022, 29, 1903–1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Li, H.; Dong, F.; Yan, F.; Cheng, M.; Li, W.; Chang, Q.; Song, T.; Liu, A.; Song, B. Therapeutic Effect of Calcipotriol Pickering Nanoemulsions Prepared by Exopolysaccharides Produced by Bacillus halotolerans FYS Strain on Psoriasis. Int. J. Nanomed. 2020, 15, 10371–10384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Tan, Y.; Peng, S.; Chen, L.; He, Y. C19, a C-terminal peptide of CKLF1, decreases inflammation and proliferation of dermal capillaries in psoriasis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 13890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Li, M.; Liu, H. Selenium-Rich Yeast Peptide Fraction Ameliorates Imiquimod-Induced Psoriasis-like Dermatitis in Mice by Inhibiting Inflammation via MAPK and NF-κB Signaling Pathways. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asai, C.; Takamura, N.; Watanabe, T.; Asami, M.; Ikeda, N.; Reese, C.F.; Hoffman, S.; Yamaguchi, Y. A water-soluble caveolin-1 peptide inhibits psoriasis-like skin inflammation by suppressing cytokine production and angiogenesis. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 20553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Wang, P.; Chen, X.Y.; Yan, B.X.; Landeck, L.; Wang, Z.Y.; Xu, F.; Zheng, M.; Man, X.Y. Sprouty1 exerts a preventive effect on the initiation of psoriasis by inhibiting innate immune antimicrobial peptide cathelicidin and immunocytes. Cell Prolif. 2022, 55, e13290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.Y.; Ahn, J.; Kim, J.; Choi, M.; Jeon, H.; Choe, K.; Lee, D.Y.; Kim, P.; Jon, S. Nanoparticle-Assisted Transcutaneous Delivery of a Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3-Inhibiting Peptide Ameliorates Psoriasis-like Skin Inflammation. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 6904–6916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javia, A.; Misra, A.; Thakkar, H. Liposomes encapsulating novel antimicrobial peptide Omiganan: Characterization and its pharmacodynamic evaluation in atopic dermatitis and psoriasis mice model. Int. J. Pharm. 2022, 624, 122045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.Q.; Chen, B.Z.; Gan, J.L.; Feng, Y.H.; Liang, L.; Yu, L.; Wang, Z.Y.; Abbaszadeh, S.; Shahbazi, M.-A.; Yu, R.; et al. Dual-functional microneedle with programmatic regulation of macrophage for autoimmune psoriasis treatment. Nano Res. 2024, 17, 7436–7448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Severi, A.A.; Akbari, B. CRISPR-Cas9 delivery strategies and applications: Review and update. Genesis 2024, 62, e23598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, T.; Pan, Q.; Ping, Y. Microneedle-assisted genome editing: A transdermal strategy of targeting NLRP3 by CRISPR-Cas9 for synergistic therapy of inflammatory skin disorders. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabe2888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, E.; Wan, T.; Pan, Q.; Duan, J.; Zhang, S.; Wang, R.; Gao, P.; Lv, J.; Wang, H.; Li, D.; et al. Dual-responsive nanocarriers for efficient cytosolic protein delivery and CRISPR-Cas9 gene therapy of inflammatory skin disorders. Sci. Adv. 2024, 10, eadl4336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moazzam, M.; Zhang, M.; Hussain, A.; Yu, X.; Huang, J.; Huang, Y. The landscape of nanoparticle-based siRNA delivery and therapeutic development. Mol. Ther. 2024, 32, 284–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, W.; Zhang, X.Q.; Xu, X. Biomaterials in siRNA Delivery: A Comprehensive Review. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2016, 5, 2715–2731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Qin, X.; Gao, Y.; Liang, J.; Xiao, D.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, M.; Lin, Y. Transcutaneous Immunotherapy for RNAi: A Cascade-Responsive Decomposable Nanocomplex Based on Polyphenol-Mediated Framework Nucleic Acid in Psoriasis. Adv. Sci. 2023, 10, e2303706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, X.; Zhou, Y.; Lyu, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Wu, D.; Li, J.; Qin, C.; Yin, L. Disease-specific corona mediated co-delivery of MTX and siRNA-TNFα by a polypeptide nanoplatform with antigen-scavenging functions in psoriasis. J. Control. Release 2023, 364, 326–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.R.; Chou, W.L.; Lin, Z.C.; Sung, C.T.; Lin, C.Y.; Fang, J.Y. Laser-assisted nanocarrier delivery to achieve cutaneous siRNA targeting for attenuating psoriasiform dermatitis. J. Control. Release 2022, 347, 590–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silvestrini, A.V.P.; Garcia Praça, F.; Leite, M.N.; de Abreu Fantini, M.C.; Frade, M.A.C.; Badra Bentley, M.V.L. Liquid crystalline nanoparticles enable a multifunctional approach for topical psoriasis therapy by co-delivering triptolide and siRNAs. Int. J. Pharm. 2023, 640, 123019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viegas, J.S.R.; Praça, F.G.; Caron, A.L.; Suzuki, I.; Silvestrini, A.V.P.; Medina, W.S.G.; Del Ciampo, J.O.; Kravicz, M.; Bentley, M. Nanostructured lipid carrier co-delivering tacrolimus and TNF-α siRNA as an innovate approach to psoriasis. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2020, 10, 646–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Wu, X.; Wu, J.; Zhang, X.; Miao, F.; Wang, J.; Lu, J.; Liu, J.; Chen, Z.; Tai, Z.; et al. Transdermal delivery of Fn14 siRNA using a novel composite ionic liquid for treatment of psoriasis-like skin lesions. J. Control. Release 2024, 365, 818–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shobeiri, S.S.; Rezaee, M.; Pordel, S.; Haghnnavaz, N.; Dashti, M.; Moghadam, M.; Sankian, M. Anti-IL-17A ssDNA aptamer ameliorated psoriasis skin lesions in the imiquimod-induced psoriasis mouse model. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2022, 110, 108963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, I.L.; de Araujo, M.M.; Bagnato, V.S.; Bentley, M. TNFα siRNA delivery by nanoparticles and photochemical internalization for psoriasis topical therapy. J. Control. Release 2021, 338, 316–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, A.; Kumbhojkar, N.; Reilly, C.; Dharamdasani, V.; Ukidve, A.; Ingber, D.E.; Mitragotri, S. Treatment of psoriasis with NFKBIZ siRNA using topical ionic liquid formulations. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eabb6049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkes, J.E.; Nguyen, G.H.; Fujita, M.; Florell, S.R.; Callis Duffin, K.; Krueger, G.G.; O’Connell, R.M. microRNAs in Psoriasis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2016, 136, 365–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Huang, Y.; Shao, K.; Yan, J.; Sun, Q. High Expression of miR-6785-5p in the Serum Exosomes of Psoriasis Patients Alleviates Psoriasis-Like Skin Damage by Interfering with the MNK2/p-eIF4E Axis in Keratinocytes. Inflammation 2024, 47, 1585–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Y.; Xi, L.; Leng, F.; Xu, C.; Zheng, Y. Topical Delivery of microRNA-125b by Framework Nucleic Acids for Psoriasis Treatment. Int. J. Nanomed. 2024, 19, 2625–2638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, T.C.; Langer, R.; Wood, M.J.A. Advances in oligonucleotide drug delivery. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2020, 19, 673–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukuta, T.; Tanaka, D.; Inoue, S.; Michiue, K.; Kogure, K. Overcoming thickened pathological skin in psoriasis via iontophoresis combined with tight junction-opening peptide AT1002 for intradermal delivery of NF-κB decoy oligodeoxynucleotide. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 602, 120601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Cai, J.; Fei, F.; Zhong, T.; Ren, M.; Wang, D.; Li, Y.; Zhang, K. Targeting the Skin: The Study of a Bottlebrush Polymer-Antisense Oligonucleotide Conjugate in a Psoriasis Mouse Model. Small 2024, 20, e2403949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Rossi, J. Aptamers as targeted therapeutics: Current potential and challenges. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2017, 16, 181–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonardi, C.L.; Powers, J.L.; Matheson, R.T.; Goffe, B.S.; Zitnik, R.; Wang, A.; Gottlieb, A.B. Etanercept as monotherapy in patients with psoriasis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 349, 2014–2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottlieb, A.B. Infliximab for psoriasis. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2003, 49, S112–S117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, A.; Scott, L.J. Certolizumab Pegol: A Review in Moderate to Severe Plaque Psoriasis. BioDrugs 2020, 34, 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Love, T.J.; Kavanaugh, A. Golimumab in the treatment of psoriatic arthritis. Expert Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2018, 14, 893–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuta, T.; Oshima, Y.; Michiue, K.; Tanaka, D.; Kogure, K. Non-invasive delivery of biological macromolecular drugs into the skin by iontophoresis and its application to psoriasis treatment. J. Control. Release 2020, 323, 323–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blair, H.A. Secukinumab: A Review in Psoriatic Arthritis. Drugs 2021, 81, 483–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markham, A. Ixekizumab: First Global Approval. Drugs 2016, 76, 901–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blair, H.A. Brodalumab: A Review in Moderate to Severe Plaque Psoriasis. Drugs 2018, 78, 495–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitas, E.; Blauvelt, A.; Torres, T. Bimekizumab for the Treatment of Psoriasis. Drugs 2021, 81, 1751–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, D.; Shou, X.; Yu, Y.; Wang, X.; Chen, G.; Zhao, Y.; Sun, L. Biologics-Loaded Photothermally Dissolvable Hyaluronic Acid Microneedle Patch for Psoriasis Treatment. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2205847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, C.E.; Strober, B.E.; van de Kerkhof, P.; Ho, V.; Fidelus-Gort, R.; Yeilding, N.; Guzzo, C.; Xia, Y.; Zhou, B.; Li, S.; et al. Comparison of ustekinumab and etanercept for moderate-to-severe psoriasis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 362, 118–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blair, H.A. Risankizumab: A Review in Moderate to Severe Plaque Psoriasis. Drugs 2020, 80, 1235–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morita, A.; Okubo, Y.; Imafuku, S.; Terui, T. Spesolimab, the first-in-class anti-IL-36R antibody: From bench to clinic. J. Dermatol. 2024, 51, 1379–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corradetti, B.; Ferrari, M. Nanotechnology for mesenchymal stem cell therapies. J. Control. Release 2016, 240, 242–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Zhong, W.; Li, W.; Tang, M.; Zhang, K.; Zhou, F.; Shi, X.; Wu, J.; Yu, B.; Huang, C.; et al. Human Umbilical Cord-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Alleviate Psoriasis Through TNF-α/NF-κB/MMP13 Pathway. Inflammation 2023, 46, 987–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuesta-Gomez, N.; Medina-Ruiz, L.; Graham, G.J.; Campbell, J.D.M. IL-6 and TGF-β-Secreting Adoptively-Transferred Murine Mesenchymal Stromal Cells Accelerate Healing of Psoriasis-like Skin Inflammation and Upregulate IL-17A and TGF-β. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 10132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Gong, P.; Jiang, J.; Feng, C.; Li, Y.; Su, X.; Bai, X.; Xu, C.; Liu, C.; Yang, J.; et al. Mesenchymal stem/stromal cells primed by inflammatory cytokines alleviate psoriasis-like inflammation via the TSG-6-neutrophil axis. Cell Death Dis. 2022, 13, 996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, X.; Cai, L.; Nie, M.; Wu, X.; Liang, G.; Shang, L.; Zhao, Y. Light-activated extracellular matrix microcarriers with engineered MSCs loading for autoimmune psoriasis treatment. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 470, 144118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrillo, D.; Edwards, N.; Arancibia-Altamirano, D.; Otárola, F.; Villarroel, C.; Prieto, C.P.; Villamizar-Sarmiento, M.G.; Sauma, D.; Valenzuela, F.; Lattus, J.; et al. Efficacy of stem cell secretome loaded in hyaluronate sponge for topical treatment of psoriasis. Bioeng. Transl. Med. 2023, 8, e10443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Fei, Z.; Dai, H.; Xu, J.; Fan, Q.; Shen, S.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, Q.; Chu, J.; Peng, F.; et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles with High PD-L1 Expression for Autoimmune Diseases Treatment. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, e2106265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, S.C.; Cardoso, R.M.S.; Freire, P.C.; Gomes, C.F.; Duarte, F.V.; Neves, R.P.D.; Simões-Correia, J. Immunomodulatory Properties of Umbilical Cord Blood-Derived Small Extracellular Vesicles and Their Therapeutic Potential for Inflammatory Skin Disorders. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Jiang, Z.; Huang, S.; Mao, P.; Zhang, L.; Wang, M.; Ye, J.; Sun, L.; Sun, M.; Lu, R.; et al. Ultraviolet B radiation-induced JPH203-loaded keratinocyte extracellular vesicles exert etiological interventions for psoriasis therapy. J. Control. Release 2023, 362, 468–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Gan, Y.; Qi, F.; Lu, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, J.; Wang, H.; Li, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, X.; et al. Innate lymphoid cell-based immunomodulatory hydrogel microspheres containing Cutibacterium acnes extracellular vesicles for the treatment of psoriasis. Acta Biomater. 2024, 184, 296–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Chávez, F.; Cedillo-Peláez, C.; Zapi-Colín, L.A.; Gutiérrez-González, G.; Martínez-Torres, I.; Peralta, H.; Chavez-Galan, L.; Avila-Calderón, E.D.; Contreras-Rodríguez, A.; Bartolo-Aguilar, Y.; et al. The Extracellular Vesicles from the Commensal Staphylococcus Epidermidis ATCC12228 Strain Regulate Skin Inflammation in the Imiquimod-Induced Psoriasis Murine Model. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 13029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizenko, R.R.; Feaver, M.; Bozkurt, B.T.; Lowe, N.; Nguyen, B.; Huang, K.W.; Wang, A.; Carney, R.P. A critical systematic review of extracellular vesicle clinical trials. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2024, 13, e12510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
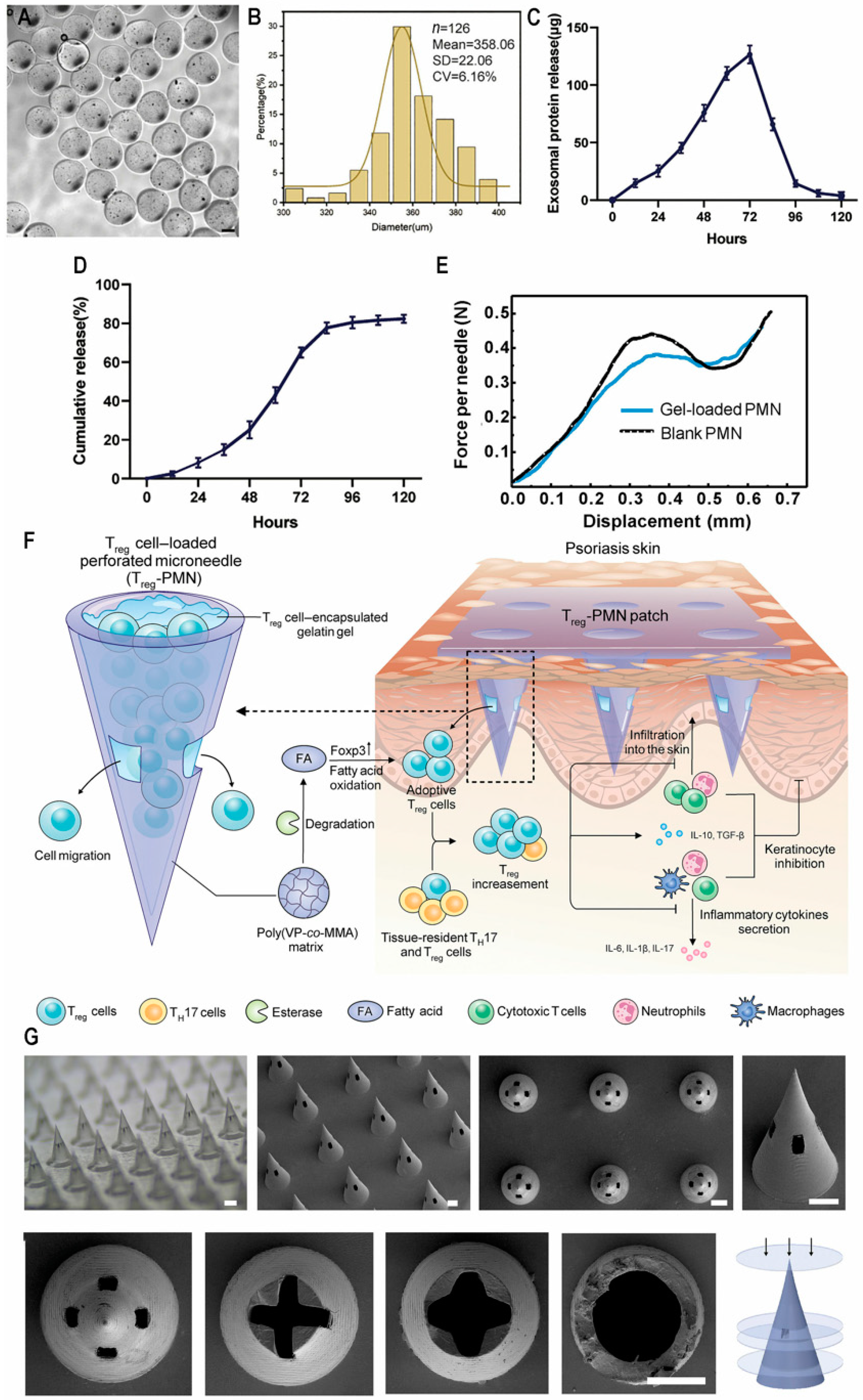
- Zhang, W.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Zheng, H.; Wang, S.; Liao, Z.; Sheng, T.; Zhao, S.; Hou, W.; Yu, X.; et al. Adoptive T(reg) therapy with metabolic intervention via perforated microneedles ameliorates psoriasis syndrome. Sci. Adv. 2023, 9, eadg6007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leite Dantas, R.; Masemann, D.; Schied, T.; Bergmeier, V.; Vogl, T.; Loser, K.; Brachvogel, B.; Varga, G.; Ludwig, S.; Wixler, V. Macrophage-mediated psoriasis can be suppressed by regulatory T lymphocytes. J. Pathol. 2016, 240, 366–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Drug | Delivery System | Administration Route | Characterization | Improvement | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dexamethasone | Hydrogel | Topical | Temperature-responsive property and modified prodrug | Immune microenvironment-responsive and lower dosage | [29] |
| Microneedles | Topical | Liposome-loaded | High permeation efficiency | [34] | |
| Gold nanorods | Topical | Near-infrared laser-assisted | High skin permeation, epidermis retention, and lower risk of systemic side effects | [35] | |
| Methotrexate | Hydrogel | Topical | Photodynamic assisted therapy | Noninvasive manner and high permeation efficiency | [48] |
| Microneedles | Topical | Modified prodrug and ROS responsiveness | High targeting efficiency | [60] | |
| Niosomes (non-ionic surfactant vesicles) | Topical | Co-delivery of MTX and niacinamide | Improved skin permeation and retention | [63] | |
| Tazarotene | PLGA nanoparticles | Topical | Follicular delivery | Controlled and extended-release | [79] |
| Solid lipid nanoparticles | Topical | Solubilization of poorly soluble drugs | Improved viscoelastic properties | [82] | |
| Calcipotriol | Microneedles | Topical | Soluble microneedles | Good biocompatibility | [85] |
| Micelles | Topical | Modified prodrug and ROS responsiveness | Reduced off-target efficiency | [88] | |
| Nanoemulsion | Topical | Natural components | Enhanced skin permeation | [89] | |
| siRNA | Framework nucleic acid | Topical | siRNA targeting NF-κB | Excellent transdermal efficiency | [102] |
| Polypeptide platforms | Intravenous injection (i.v.) | siRNA targeting TNF-α | High macrophage targeting mediated by the protein corona | [103] | |
| Ionic liquids | Topical | siRNA targeting Fn14 | High knockdown efficiency | [107] | |
| Cas9 ribonucleoprotein | Microneedles | Topical | NLRP3 inflammasome elimination | Promoted indel efficiency | [98] |
| Polymer nanoparticles | Subcutaneous injection (s.c.) | Co-delivery of lipoic acid and RNPs | High cellular internalization | [99] | |
| MSCs | / | i.v. | Derived from bone marrow and adipose tissue | Healing response acceleration and severity alleviation | [134] |
| / | i.v. | Derived from umbilical cord | Proinflammatory cytokine reduction and blocking of keratinocyte proliferation | [132] |
| Drug | Type | Formulation | Physiological Target | Phase | No. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VTP-43742 | Small molecule | Oral tablet | Retinoic acid receptor-related orphan receptor gamma t (RORγt) | Phase II | NCT05153148 |
| Roflumilast Cream (ZORYVE®) | PDE4 inhibitor | Topical cream | Phosphodiesterase-4 (PDE4) in skin cells | Phase III | NCT05028582 |
| Upadacitinib (RINVOQ®) | JAK1 inhibitor | Oral tablet | Janus kinase 1 (JAK1) | Phase III | NCT03569293 |
| Deucravacitinib (BMS-986165) | TYK2 inhibitor | Oral tablet | Tyrosine kinase 2 (TYK2) in JAK-STAT pathway | Phase III | NCT05650827 |
| Sonelokimab (M1095) | Nanobody (anti-IL-23) | Subcutaneous injection | IL-23/IL-17 pathway | Phase II/III | NCT05643590 |
| Spesolimab (BI 655130) | Monoclonal antibody | Intravenous infusion | IL-36 receptor (for pustular psoriasis) | Phase III | NCT05799801 |
| Bimekizumab | Dual IL-17A/IL-17F inhibitor | s.c. | IL-17A and IL-17F cytokines | Phase IV | NCT06026900 |
| Tapinarof (VTAMA®) | Aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) modulator | Topical cream | AhR pathway to reduce inflammation | Phase IV | NCT05604960 |
| Exagamglogene autotemcel (exa-cel) | CRISPR-Cas9 gene-edited therapy | Intravenous infusion | Gene correction in hematopoietic stem cells (early-phase exploration for autoimmune diseases) | Preclinical/Phase I | / |
| Tofacitinib-loaded nanoparticles | JAK inhibitor + nanotechnology | Topical gel | Localized JAK/STAT pathway inhibition | Phase I/II | NCT05462071 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Cai, Y.; Duan, Z.; Xu, H.; Huang, Y.; Ma, X.; Xin, X.; Yin, L. Novel Small-Molecule Treatment and Emerging Biological Therapy for Psoriasis. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 781. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13040781
Li Y, Cheng Y, Cai Y, Duan Z, Xu H, Huang Y, Ma X, Xin X, Yin L. Novel Small-Molecule Treatment and Emerging Biological Therapy for Psoriasis. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(4):781. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13040781
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Yuanyuan, Yiheng Cheng, Yuchen Cai, Zhenduo Duan, Hong Xu, Yunan Huang, Xiaonan Ma, Xiaofei Xin, and Lifang Yin. 2025. "Novel Small-Molecule Treatment and Emerging Biological Therapy for Psoriasis" Biomedicines 13, no. 4: 781. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13040781
APA StyleLi, Y., Cheng, Y., Cai, Y., Duan, Z., Xu, H., Huang, Y., Ma, X., Xin, X., & Yin, L. (2025). Novel Small-Molecule Treatment and Emerging Biological Therapy for Psoriasis. Biomedicines, 13(4), 781. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13040781







