The Role of STEAP1 in Prostate Cancer: Implications for Diagnosis and Therapeutic Strategies
Abstract
:1. Introduction
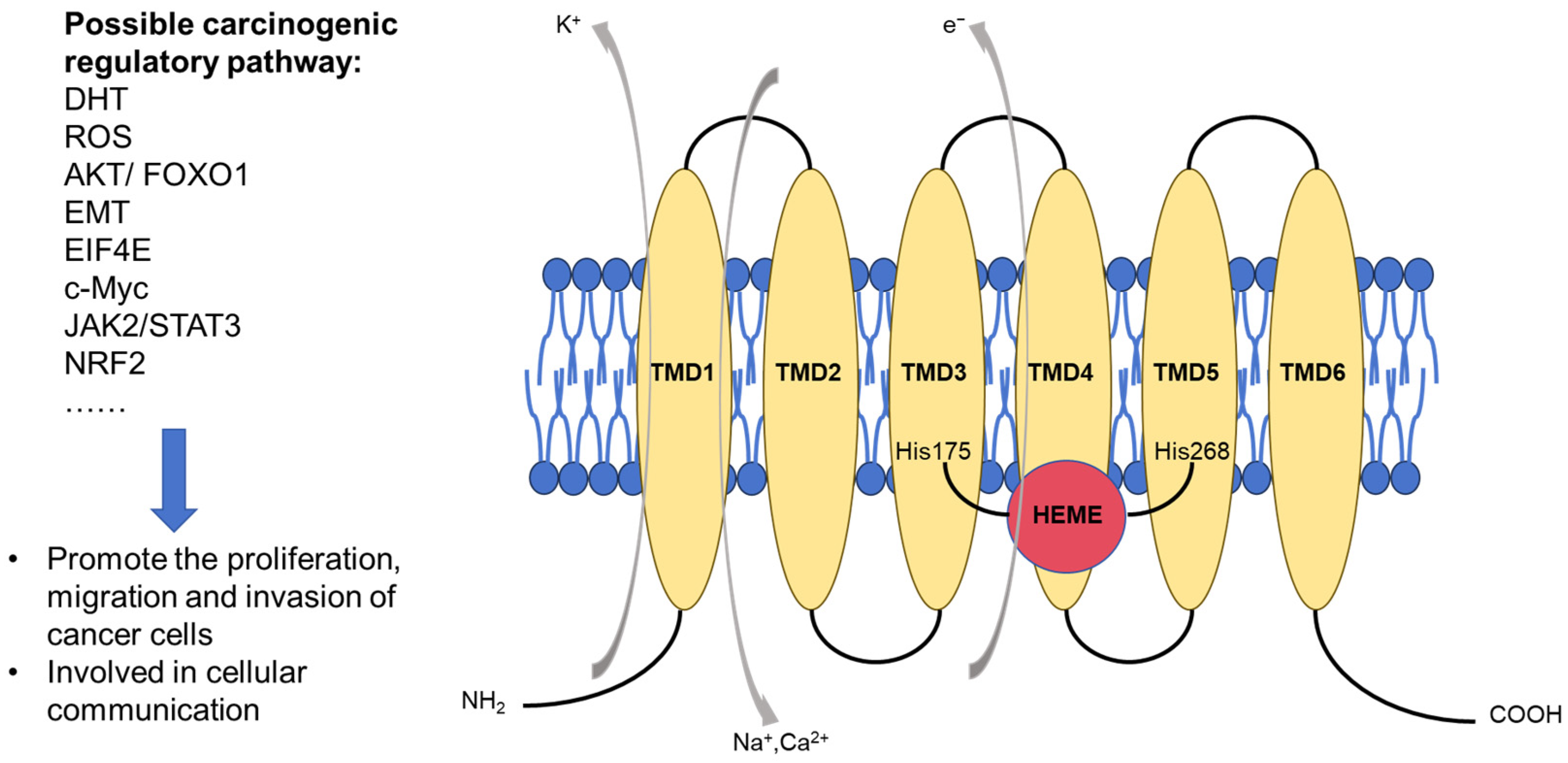
2. Structure and Oncogenic Properties of STEAP1
3. STEAP1 as a Promising Biomarker for PCa Diagnosis
4. STEAP1 as a Potential Therapeutic Target
4.1. ADC
4.2. CAR-T
4.3. TCE
4.4. Vaccine
4.5. Limitations of Targeted Therapy
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bray, F.; Laversanne, M.; Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A. Global Cancer Statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2024, 74, 229–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergengren, O.; Pekala, K.R.; Matsoukas, K.; Fainberg, J.; Mungovan, S.F.; Bratt, O.; Bray, F.; Brawley, O.; Luckenbaugh, A.N.; Mucci, L.; et al. 2022 Update on Prostate Cancer Epidemiology and Risk Factors—A Systematic Review. Eur. Urol. 2023, 84, 191–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lillard, J.W.; Moses, K.A.; Mahal, B.A.; George, D.J. Racial Disparities in Black Men with Prostate Cancer: A Literature Review. Cancer 2022, 128, 3787–3795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, P.N.D.; Tannock, I.; N’Dow, J.; Feng, F.; Gillessen, P.S.; Ali, S.A.; Trujillo, B.; Al-Lazikani, B.; Attard, G.; Bray, F.; et al. The Lancet Commission on Prostate Cancer: Planning for the Surge in Cases. Lancet 2024, 403, 1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merriel, S.W.D.; Pocock, L.; Gilbert, E.; Creavin, S.; Walter, F.M.; Spencer, A.; Hamilton, W. Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of the Diagnostic Accuracy of Prostate-Specific Antigen (PSA) for the Detection of Prostate Cancer in Symptomatic Patients. BMC Med. 2022, 20, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatia, V.; Kamat, N.V.; Pariva, T.E.; Wu, L.-T.; Tsao, A.; Sasaki, K.; Sun, H.; Javier, G.; Nutt, S.; Coleman, I.; et al. Targeting Advanced Prostate Cancer with STEAP1 Chimeric Antigen Receptor T Cell and Tumor-Localized IL-12 Immunotherapy. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 2041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Evans, L.; Bizzaro, C.L.; Quaglia, F.; Verrillo, C.E.; Li, L.; Stieglmaier, J.; Schiewer, M.J.; Languino, L.R.; Kelly, W.K. STEAP1–4 (Six-Transmembrane Epithelial Antigen of the Prostate 1–4) and Their Clinical Implications for Prostate Cancer. Cancers 2022, 14, 4034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekhoacha, M.; Riet, K.; Motloung, P.; Gumenku, L.; Adegoke, A.; Mashele, S. Prostate Cancer Review: Genetics, Diagnosis, Treatment Options, and Alternative Approaches. Molecules 2022, 27, 5730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cornford, P.; van den Bergh, R.C.N.; Briers, E.; Van den Broeck, T.; Brunckhorst, O.; Darraugh, J.; Eberli, D.; De Meerleer, G.; De Santis, M.; Farolfi, A.; et al. EAU-EANM-ESTRO-ESUR-ISUP-SIOG Guidelines on Prostate Cancer—2024 Update. Part I: Screening, Diagnosis, and Local Treatment with Curative Intent. Eur. Urol. 2024, 86, 148–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilki, D.; van den Bergh, R.C.N.; Briers, E.; Van den Broeck, T.; Brunckhorst, O.; Darraugh, J.; Eberli, D.; De Meerleer, G.; De Santis, M.; Farolfi, A.; et al. EAU-EANM-ESTRO-ESUR-ISUP-SIOG Guidelines on Prostate Cancer. Part II-2024 Update: Treatment of Relapsing and Metastatic Prostate Cancer. Eur. Urol. 2024, 86, 164–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hennrich, U.; Eder, M. [177Lu]Lu-PSMA-617 (PluvictoTM): The First FDA-Approved Radiotherapeutical for Treatment of Prostate Cancer. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barroca-Ferreira, J.; Pais, J.P.; Santos, M.M.; Goncalves, A.M.; Gomes, I.M.; Sousa, I.; Rocha, S.M.; Passarinha, L.A.; Maia, C.J. Targeting STEAP1 Protein in Human Cancer: Current Trends and Future Challenges. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 2018, 18, 222–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubert, R.S.; Vivanco, I.; Chen, E.; Rastegar, S.; Leong, K.; Mitchell, S.C.; Madraswala, R.; Zhou, Y.; Kuo, J.; Raitano, A.B.; et al. STEAP: A Prostate-Specific Cell-Surface Antigen Highly Expressed in Human Prostate Tumors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 14523–14528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohgami, R.S.; Campagna, D.R.; McDonald, A.; Fleming, M.D. The Steap Proteins Are Metalloreductases. Blood 2006, 108, 1388–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oosterheert, W.; Gros, P. Cryo-Electron Microscopy Structure and Potential Enzymatic Function of Human Six-Transmembrane Epithelial Antigen of the Prostate 1 (STEAP1). J. Biol. Chem. 2020, 295, 9502–9512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oosterheert, W.; Reis, J.; Gros, P.; Mattevi, A. An Elegant Four-Helical Fold in NOX and STEAP Enzymes Facilitates Electron Transport across Biomembranes-Similar Vehicle, Different Destination. Accounts Chem. Res. 2020, 53, 1969–1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oosterheert, W.; van Bezouwen, L.S.; Rodenburg, R.N.P.; Granneman, J.; Förster, F.; Mattevi, A.; Gros, P. Cryo-EM Structures of Human STEAP4 Reveal Mechanism of Iron(III) Reduction. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 4337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Mitra, S.; Wu, G.; Berka, V.; Song, J.; Yu, Y.; Poget, S.; Wang, D.-N.; Tsai, A.-L.; Zhou, M. Six-Transmembrane Epithelial Antigen of Prostate 1 (STEAP1) Has a Single b Heme and Is Capable of Reducing Metal Ion Complexes and Oxygen. Biochemistry 2016, 55, 6673–6684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nolan-Stevaux, O.; Li, C.; Liang, L.; Zhan, J.; Estrada, J.; Osgood, T.; Li, F.; Zhang, H.; Case, R.; Murawsky, C.M.; et al. AMG 509 (Xaluritamig), an Anti-STEAP1 XmAb 2+1 T-Cell Redirecting Immune Therapy with Avidity-Dependent Activity Against Prostate Cancer. Cancer Discov. 2023, 14, 90–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doran, M.G.; Watson, P.A.; Cheal, S.M.; Spratt, D.E.; Wongvipat, J.; Steckler, J.M.; Carrasquillo, J.A.; Evans, M.J.; Lewis, J.S. Annotating STEAP1 Regulation in Prostate Cancer with 89Zr Immuno-PET. J. Nucl. Med. 2014, 55, 2045–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, I.M.; Rocha, S.M.; Gaspar, C.; Alvelos, M.I.; Santos, C.R.; Socorro, S.; Maia, C.J. Knockdown of STEAP1 Inhibits Cell Growth and Induces Apoptosis in LNCaP Prostate Cancer Cells Counteracting the Effect of Androgens. Med. Oncol. 2018, 35, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huo, S.-F.; Shang, W.-L.; Yu, M.; Ren, X.-P.; Wen, H.-X.; Chai, C.-Y.; Sun, L.; Hui, K.; Liu, L.-H.; Wei, S.-H.; et al. STEAP1 Facilitates Metastasis and Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition of Lung Adenocarcinoma via the JAK2/STAT3 Signaling Pathway. Biosci. Rep. 2020, 40, BSR20193169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iijima, K.; Nakamura, H.; Takada, K.; Hayasaka, N.; Kubo, T.; Umeyama, Y.; Iyama, S.; Miyanishi, K.; Kobune, M.; Kato, J. Six-Transmembrane Epithelial Antigen of the Prostate 1 Accelerates Cell Proliferation by Targeting c-Myc in Liver Cancer Cells. Oncol. Lett. 2021, 22, 546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Hou, W.-B.; Zhang, C.; Tan, Y.-E.; Zhang, D.-D.; An, W.; Pan, S.-W.; Wu, W.; Chen, Q.-C.; Xu, H.-M. A Research of STEAP1 Regulated Gastric Cancer Cell Proliferation, Migration and Invasion in Vitro and in Vivos. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 14217–14230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.-N.; Wu, Y.-Y.; Fang, X.-D.; Ji, F.-J. EIF4E Regulates STEAP1 Expression in Peritoneal Metastasis. J. Cancer 2020, 11, 990–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, H.; Takada, K.; Arihara, Y.; Hayasaka, N.; Murase, K.; Iyama, S.; Kobune, M.; Miyanishi, K.; Kato, J. Six-Transmembrane Epithelial Antigen of the Prostate 1 Protects against Increased Oxidative Stress via a Nuclear Erythroid 2-Related Factor Pathway in Colorectal Cancer. Cancer Gene Ther. 2019, 26, 313–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Challita-Eid, P.M.; Morrison, K.; Etessami, S.; An, Z.; Morrison, K.J.; Perez-Villar, J.J.; Raitano, A.B.; Jia, X.-C.; Gudas, J.M.; Kanner, S.B.; et al. Monoclonal Antibodies to Six-Transmembrane Epithelial Antigen of the Prostate-1 Inhibit Intercellular Communication in Vitro and Growth of Human Tumor Xenografts in Vivo. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 5798–5805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, T.; Tamura, Y.; Kobayashi, J.-I.; Kamiguchi, K.; Hirohashi, Y.; Miyazaki, A.; Torigoe, T.; Asanuma, H.; Hiratsuka, H.; Sato, N. Six-Transmembrane Epithelial Antigen of the Prostate-1 Plays a Role for in Vivo Tumor Growth via Intercellular Communication. Exp. Cell Res. 2013, 319, 2617–2626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, I.M.; Arinto, P.; Lopes, C.; Santos, C.R.; Maia, C.J. STEAP1 Is Overexpressed in Prostate Cancer and Prostatic Intraepithelial Neoplasia Lesions, and It Is Positively Associated with Gleason Score. Urol. Oncol. 2014, 32, 53.e23–53.e29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ihlaseh-Catalano, S.M.; Drigo, S.A.; de Jesus, C.M.N.; Domingues, M.A.C.; Trindade Filho, J.C.S.; de Camargo, J.L.V.; Rogatto, S.R. STEAP1 Protein Overexpression Is an Independent Marker for Biochemical Recurrence in Prostate Carcinoma. Histopathology 2013, 63, 678–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreaux, J.; Kassambara, A.; Hose, D.; Klein, B. STEAP1 Is Overexpressed in Cancers: A Promising Therapeutic Target. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2012. epub ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rocha, S.M.; Barroca-Ferreira, J.; Passarinha, L.A.; Socorro, S.; Maia, C.J. The Usefulness of STEAP Proteins in Prostate Cancer Clinical Practice. In Prostate Cancer [Internet]; Exon Publications: Brisbane, Australia, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Minciacchi, V.R.; Zijlstra, A.; Rubin, M.A.; Di Vizio, D. Extracellular Vesicles for Liquid Biopsy in Prostate Cancer: Where Are We and Where Are We Headed? Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2017, 20, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariscal, J.; Vagner, T.; Kim, M.; Zhou, B.; Chin, A.; Zandian, M.; Freeman, M.R.; You, S.; Zijlstra, A.; Yang, W.; et al. Comprehensive Palmitoyl-Proteomic Analysis Identifies Distinct Protein Signatures for Large and Small Cancer-Derived Extracellular Vesicles. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2020, 9, 1764192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, M.; Gomes, R.M.; Moreira Rocha, S.; Barroca-Ferreira, J.; Maia, C.J.; Guillade, L.; Correa-Duarte, M.A.; Passarinha, L.A.; Moreira, F.T.C. Development of a Novel Electrochemical Biosensor Based on Plastic Antibodies for Detection of STEAP1 Biomarker in Cancer. Bioelectrochemistry 2023, 152, 108461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houshmand, S.; Lawhn-Heath, C.; Behr, S. PSMA PET Imaging in the Diagnosis and Management of Prostate Cancer. Abdom. Radiol. 2023, 48, 3610–3623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farolfi, A.; Calderoni, L.; Mattana, F.; Mei, R.; Telo, S.; Fanti, S.; Castellucci, P. Current and Emerging Clinical Applications of PSMA PET Diagnostic Imaging for Prostate Cancer. J. Nucl. Med. 2021, 62, 596–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandit-Taskar, N.; O’Donoghue, J.A.; Ruan, S.; Lyashchenko, S.K.; Carrasquillo, J.A.; Heller, G.; Martinez, D.F.; Cheal, S.M.; Lewis, J.S.; Fleisher, M.; et al. First-in-Human Imaging with 89Zr-Df-IAB2M Anti-PSMA Minibody in Patients with Metastatic Prostate Cancer: Pharmacokinetics, Biodistribution, Dosimetry, and Lesion Uptake. J. Nucl. Med. 2016, 57, 1858–1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrasquillo, J.A.; Fine, B.M.; Pandit-Taskar, N.; Larson, S.M.; Fleming, S.E.; Fox, J.J.; Cheal, S.M.; O’Donoghue, J.A.; Ruan, S.; Ragupathi, G.; et al. Imaging Patients with Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer Using 89Zr-DFO-MSTP2109A Anti-STEAP1 Antibody. J. Nucl. Med. 2019, 60, 1517–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Donoghue, J.A.; Danila, D.C.; Pandit-Taskar, N.; Beylergil, V.; Cheal, S.M.; Fleming, S.E.; Fox, J.J.; Ruan, S.; Zanzonico, P.B.; Ragupathi, G.; et al. Pharmacokinetics and Biodistribution of a [89Zr]Zr-DFO-MSTP2109A Anti-STEAP1 Antibody in Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer Patients. Mol. Pharm. 2019, 16, 3083–3090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, X.-M.; Hu, J.; Zhao, C.-Y.; Jiang, F. Six-Transmembrane Epithelial Antigen of the Prostate-1 (STEAP-1)-Targeted Ultrasound Imaging Microbubble Improves Detection of Prostate Cancer In Vivo. J. Ultrasound Med. 2019, 38, 299–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.-X.; Xia, Q.-D.; Xu, J.-Z.; An, Y.; Ma, S.-Y.; Xu, J.-Y.; Xiang, J.-C.; Liu, C.-Q.; Xu, M.-Y.; Zhang, S.-H.; et al. A Novel Prostate Cancer-Specific Fluorescent Probe Based on Extracellular Vesicles Targeting STEAP1 Applied in Fluorescence Guided Surgery. J. Control. Release 2025, 380, 199–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Harten, M.J.; Roobol, M.J.; van Leeuwen, P.J.; Willemse, P.-P.M.; van den Bergh, R.C.N. Evolution of European Prostate Cancer Screening Protocols and Summary of Ongoing Trials. BJU Int. 2024, 134, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mari, A.; Cadenar, A.; Giudici, S.; Cianchi, G.; Albisinni, S.; Autorino, R.; Di Maida, F.; Gandaglia, G.; Mir, M.C.; Valerio, M.; et al. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis to Evaluate the Diagnostic Accuracy of PSMA PET/CT in the Initial Staging of Prostate Cancer. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2025, 28, 56–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Ketteler, S.; Bagheri, S.; Ebrahimifard, A.; Luster, M.; Librizzi, D.; Yousefi, B.H. Diagnostic Efficacy of [99mTc]Tc-PSMA SPECT/CT for Prostate Cancer: A Meta-Analysis. BMC Cancer 2024, 24, 982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Kadeerhan, G.; Zhang, J.; Guo, W.; Guo, H.; Wang, D. Advances in Prostate-Specific Membrane Antigen-Targeted Theranostics: From Radionuclides to near-Infrared Fluorescence Technology. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1533532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perera, R.H.; de Leon, A.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Ramamurthy, G.; Peiris, P.; Abenojar, E.; Basilion, J.P.; Exner, A.A. Real Time Ultrasound Molecular Imaging of Prostate Cancer with PSMA-Targeted Nanobubbles. Nanomedicine 2020, 28, 102213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Han, W.; Chang, J.H.; Lee, H.J. PMP(Porphyrin-Micelle-PSMA) Nanoparticles for Photoacoustic and Ultrasound Signal Amplification in Mouse Prostate Cancer Xenografts. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesniak, W.G.; Wu, Y.; Kang, J.; Boinapally, S.; Ray Banerjee, S.; Lisok, A.; Jablonska, A.; Boctor, E.M.; Pomper, M.G. Dual Contrast Agents for Fluorescence and Photoacoustic Imaging: Evaluation in a Murine Model of Prostate Cancer. Nanoscale 2021, 13, 9217–9228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.; Lou, K.; He, H.; Wang, Y.; Mi, Y.; Li, W.; Chen, L.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, C. A Novel PSMA Targeted Dual-Function near-Infrared Fluorescence and PET Probe for the Image-Guided Surgery and Detection of Prostate Cancer. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2024, 51, 2998–3008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, J.; Zhang, J.; Wen, W.; Qin, W.; Chen, X. Prostate-Specific Membrane Antigen-Targeted Surgery in Prostate Cancer: Accurate Identification, Real-Time Diagnosis, and Precise Resection. Theranostics 2024, 14, 2736–2756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muniz, M.; Loprinzi, C.L.; Orme, J.J.; Koch, R.M.; Mahmoud, A.M.; Kase, A.M.; Riaz, I.B.; Andrews, J.R.; Thorpe, M.P.; Johnson, G.B.; et al. Salivary Toxicity from PSMA-Targeted Radiopharmaceuticals: What We Have Learned and Where We Are Going. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2024, 127, 102748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danila, D.C.; Szmulewitz, R.Z.; Vaishampayan, U.; Higano, C.S.; Baron, A.D.; Gilbert, H.N.; Brunstein, F.; Milojic-Blair, M.; Wang, B.; Kabbarah, O.; et al. Phase I Study of DSTP3086S, an Antibody-Drug Conjugate Targeting Six-Transmembrane Epithelial Antigen of Prostate 1, in Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 3518–3527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adcentrx Therapeutics A Phase 1a/b Study of ADRX-0405 in Subjects with Select Advanced Solid Tumors. 2024. Available online: www.clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT06710379?cond=NCT06710379&rank=1 (accessed on 23 March 2025).
- Yang, Q.; Huang, Y.; Jia, J.; Guo, H.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, Y.; Ye, Z.; Ye, H.; Xu, Y.; Li, W.; et al. Abstract 5821: DXC008, a Novel STEAP1 Antibody-Tubulysin Analog Conjugate with a Function Linker, Demonstrates a Potential to Broaden Therapeutic Opportunities for Prostate Tumors. Cancer Res. 2024, 84, 5821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Lorvik, K.B.; Jin, Y.; Beck, C.; Sike, A.; Persiconi, I.; Kvaløy, E.; Saatcioglu, F.; Dunn, C.; Kyte, J.A. Development of STEAP1 Targeting Chimeric Antigen Receptor for Adoptive Cell Therapy against Cancer. Mol. Ther. Oncolytics 2022, 26, 189–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amgen A Phase 1 Study Evaluating the Safety, Tolerability, Pharmacokinetics, and Efficacy of AMG 509 in Subjects with Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer. 2025. Available online: www.clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT04221542?cond=NCT04221542&rank=1 (accessed on 23 March 2025).
- Amgen A Phase 1b, Open-Label, Multicenter Study Evaluating the Safety, Tolerability, and Efficacy of Xaluritamig in Subjects with High-Risk Biochemical Recurrence of Nonmetastatic Castration-Sensitive Prostate Cancer After Definitive Therapy. 2025. Available online: www.clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT06555796?cond=NCT06555796%20&rank=1 (accessed on 23 March 2025).
- Amgen A Phase 1b, Open-Label, Multicenter Study Evaluating the Safety, Tolerability, and Feasibility of Neoadjuvant Xaluritamig Therapy Prior to Radical Prostatectomy in Subjects with Newly Diagnosed Localized Intermediate or High-Risk Prostate Cancer. 2025. Available online: www.clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT06613100?cond=NCT06613100&rank=1 (accessed on 23 March 2025).
- Lin, T.-Y.; Park, J.A.; Long, A.; Guo, H.-F.; Cheung, N.-K.V. Novel Potent Anti-STEAP1 Bispecific Antibody to Redirect T Cells for Cancer Immunotherapy. J. Immunother. Cancer 2021, 9, e003114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kübler, H.; Scheel, B.; Gnad-Vogt, U.; Miller, K.; Schultze-Seemann, W.; Vom Dorp, F.; Parmiani, G.; Hampel, C.; Wedel, S.; Trojan, L.; et al. Self-Adjuvanted mRNA Vaccination in Advanced Prostate Cancer Patients: A First-in-Man Phase I/IIa Study. J. Immunother. Cancer 2015, 3, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Xie, H.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Peng, S.; Niu, Y.; Shang, Z. Fusion Protein Vaccine Based on Ag85B and STEAP1 Induces a Protective Immune Response against Prostate Cancer. Vaccines 2021, 9, 786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Wang, R.; Chen, A.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Cao, R. Inhibition of Mouse RM-1 Prostate Cancer and B16F10 Melanoma by the Fusion Protein of HSP65 & STEAP1 186–193. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 111, 1124–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bordoloi, D.; Xiao, P.; Choi, H.; Ho, M.; Perales-Puchalt, A.; Khoshnejad, M.; Kim, J.J.; Humeau, L.; Srinivasan, A.; Weiner, D.B.; et al. Immunotherapy of Prostate Cancer Using Novel Synthetic DNA Vaccines Targeting Multiple Tumor Antigens. Genes Cancer 2021, 12, 51–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marofi, F.; Motavalli, R.; Safonov, V.A.; Thangavelu, L.; Yumashev, A.V.; Alexander, M.; Shomali, N.; Chartrand, M.S.; Pathak, Y.; Jarahian, M.; et al. CAR T Cells in Solid Tumors: Challenges and Opportunities. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2021, 12, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, C.; Gong, J.; Li, J.; Liu, D.; Qin, Y.; Ge, S.; Zhang, M.; Peng, Z.; Zhou, J.; Cao, Y.; et al. Claudin18.2-Specific CAR T Cells in Gastrointestinal Cancers: Phase 1 Trial Interim Results. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 1189–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, S.; Liu, M.; Ren, F.; Meng, X.; Yu, J. The Landscape of Bispecific T Cell Engager in Cancer Treatment. Biomark. Res. 2021, 9, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arvedson, T.; Bailis, J.M.; Britten, C.D.; Klinger, M.; Nagorsen, D.; Coxon, A.; Egen, J.G.; Martin, F. Targeting Solid Tumors with Bispecific T Cell Engager Immune Therapy. Annu. Rev. Cancer Biol. 2022, 6, 17–34. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Fort, M.; Liang, L.; Moore, G.; Bernett, M.; Muchhal, U.; Osgood, T.; Yabut, R.; Kaliyaperumal, S.; Harrold, J.; et al. 718 AMG 509, a STEAP1 × CD3 Bispecific XmAb® 2+1 Immune Therapy, Exhibits Avidity-Driven Binding and Preferential Killing of High STEAP1-Expressing Prostate and Ewing Sarcoma Cancer Cells. J. Immunother. Cancer 2020, 8, A430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, W.K.; Danila, D.C.; Lin, C.-C.; Lee, J.-L.; Matsubara, N.; Ward, P.J.; Armstrong, A.J.; Pook, D.; Kim, M.; Dorff, T.B.; et al. Xaluritamig, a STEAP1 × CD3 XmAb 2+1 Immune Therapy for Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer: Results from Dose Exploration in a First-in-Human Study. Cancer Discov. 2024, 14, 76–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machlenkin, A.; Paz, A.; Bar Haim, E.; Goldberger, O.; Finkel, E.; Tirosh, B.; Volovitz, I.; Vadai, E.; Lugassy, G.; Cytron, S.; et al. Human CTL Epitopes Prostatic Acid Phosphatase-3 and Six-Transmembrane Epithelial Antigen of Prostate-3 as Candidates for Prostate Cancer Immunotherapy. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 6435–6442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, H.; Nagato, T.; Sato, K.; Aoki, N.; Kimura, S.; Murakami, M.; Iizuka, H.; Azumi, M.; Kakizaki, H.; Tateno, M.; et al. Recognition of Prostate and Melanoma Tumor Cells by Six-Transmembrane Epithelial Antigen of Prostate-Specific Helper T Lymphocytes in a Human Leukocyte Antigen Class II-Restricted Manner. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 5498–5504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodeberg, D.A.; Nuss, R.A.; Elsawa, S.F.; Celis, E. Recognition of Six-Transmembrane Epithelial Antigen of the Prostate-Expressing Tumor Cells by Peptide Antigen-Induced Cytotoxic T Lymphocytes. Clin. Cancer Res. 2005, 11, 4545–4552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, P.M.S.; Faure, O.; Graff-Dubois, S.; Cornet, S.; Bolonakis, I.; Gross, D.-A.; Miconnet, I.; Chouaib, S.; Fizazi, K.; Soria, J.C.; et al. STEAP, a Prostate Tumor Antigen, Is a Target of Human CD8+ T Cells. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2006, 55, 1515–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vardeu, A.; Davis, C.; McDonald, I.; Stahlberg, G.; Thapa, B.; Piotrowska, K.; Marshall, M.A.; Evans, T.; Wheeler, V.; Sebastian, S.; et al. Intravenous Administration of Viral Vectors Expressing Prostate Cancer Antigens Enhances the Magnitude and Functionality of CD8+ T Cell Responses. J. Immunother. Cancer 2022, 10, e005398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de la Luz Garcia-Hernandez, M.; Gray, A.; Hubby, B.; Kast, W.M. In Vivo Effects of Vaccination with Six-Transmembrane Epithelial Antigen of the Prostate: A Candidate Antigen for Treating Prostate Cancer. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 1344–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krupa, M.; Canamero, M.; Gomez, C.E.; Najera, J.L.; Gil, J.; Esteban, M. Immunization with Recombinant DNA and Modified Vaccinia Virus Ankara (MVA) Vectors Delivering PSCA and STEAP1 Antigens Inhibits Prostate Cancer Progression. Vaccine 2011, 29, 1504–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorne, A.H.; Malo, K.N.; Wong, A.J.; Nguyen, T.T.; Cooch, N.; Reed, C.; Yan, J.; Broderick, K.E.; Smith, T.R.F.; Masteller, E.L.; et al. Adjuvant Screen Identifies Synthetic DNA-Encoding Flt3L and CD80 Immunotherapeutics as Candidates for Enhancing Anti-Tumor T Cell Responses. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rausch, S.; Schwentner, C.; Stenzl, A.; Bedke, J. mRNA Vaccine CV9103 and CV9104 for the Treatment of Prostate Cancer. Hum. Vaccin. Immunother. 2014, 10, 3146–3152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cappuccini, F.; Stribbling, S.; Pollock, E.; Hill, A.V.S.; Redchenko, I. Immunogenicity and Efficacy of the Novel Cancer Vaccine Based on Simian Adenovirus and MVA Vectors Alone and in Combination with PD-1 mAb in a Mouse Model of Prostate Cancer. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2016, 65, 701–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plosker, G.L. Sipuleucel-T: In Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer. Drugs 2011, 71, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheever, M.A.; Higano, C.S. PROVENGE (Sipuleucel-T) in Prostate Cancer: The First FDA-Approved Therapeutic Cancer Vaccine. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 3520–3526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flugel, C.L.; Majzner, R.G.; Krenciute, G.; Dotti, G.; Riddell, S.R.; Wagner, D.L.; Abou-El-Enein, M. Overcoming On-Target, off-Tumour Toxicity of CAR T Cell Therapy for Solid Tumours. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 20, 49–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bitounis, D.; Jacquinet, E.; Rogers, M.A.; Amiji, M.M. Strategies to Reduce the Risks of mRNA Drug and Vaccine Toxicity. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2024, 23, 281–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumontet, C.; Reichert, J.M.; Senter, P.D.; Lambert, J.M.; Beck, A. Antibody-Drug Conjugates Come of Age in Oncology. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2023, 22, 641–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goebeler, M.-E.; Bargou, R.C. T Cell-Engaging Therapies—BiTEs and Beyond. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 17, 418–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Zhu, J. Progresses of T-Cell-Engaging Bispecific Antibodies in Treatment of Solid Tumors. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2024, 138, 112609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Xu, Y.-X.; Wang, Y.-S.; Ren, Y.-Y.; Dong, X.-M.; Wu, P.; Xie, T.; Zhang, Q.; Zhou, J.-L. Prostate Cancer Microenvironment: Multidimensional Regulation of Immune Cells, Vascular System, Stromal Cells, and Microbiota. Mol. Cancer 2024, 23, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulvey, A.; Trueb, L.; Coukos, G.; Arber, C. Novel Strategies to Manage CAR-T Cell Toxicity. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2025, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordas Dos Santos, D.M.; Tix, T.; Shouval, R.; Gafter-Gvili, A.; Alberge, J.-B.; Cliff, E.R.S.; Theurich, S.; von Bergwelt-Baildon, M.; Ghobrial, I.M.; Subklewe, M.; et al. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Nonrelapse Mortality after CAR T Cell Therapy. Nat. Med. 2024, 30, 2667–2678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Géraud, A.; Hueso, T.; Laparra, A.; Bige, N.; Ouali, K.; Cauquil, C.; Stoclin, A.; Danlos, F.-X.; Hollebecque, A.; Ribrag, V.; et al. Reactions and Adverse Events Induced by T-Cell Engagers as Anti-Cancer Immunotherapies, a Comprehensive Review. Eur. J. Cancer 2024, 205, 114075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, G.; Elkashif, A.; Saha, C.; Coulter, J.A.; Dunne, N.J.; McCarthy, H.O. Key Considerations for a Prostate Cancer mRNA Vaccine. Crit. Rev. Oncol./Hematol. 2025, 208, 104643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, M.; Peng, X.; Yang, Y.; Chen, Q.; Liu, J.; She, Q.; Tan, J.; Lou, C.; Liao, Z.; et al. mRNA Vaccine in Cancer Therapy: Current Advance and Future Outlook. Clin. Transl. Med. 2023, 13, e1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, W.; Zhou, K.; Lei, Y.; Li, Q.; Zhu, H. Cancer Vaccines: Platforms and Current Progress. Mol. Biomed. 2025, 6, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Biomarker | Key Characteristics | Diagnostic Utility | Therapeutic Utility | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PSA |
|
|
|
|
| PSMA |
|
| ||
| STEAP1 |
|
|
|
|
| Drug Class | Drug Name | Company or Author | Report Date/Launch Date | Status | Cancer | Study/Citation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ADC | DSTP3086S | Danila DC | 2019 | Phase I Completed | mCRPC | NCT01283373 [53] |
| ADC | ADRX-0405 | Adcentrx Therapeutics | 2024 | Phase Ia/b Recruiting | Advanced Solid Tumors | NCT06710379 [54] |
| ADC | DXC008 | DAC Biotechnology | 2024 | Phase I Recruiting | PCa | CXSL2400868 [55] |
| CAR-T | CAR-T with Oslo1 scFv and 4-1BB co-stimulatory domain | Jin Y | 2022 | Preclinical | Mouse PCa | [56] |
| CAR-T | anti-STEAP1-BBζ CAR-T +Enzalutamide | Bhatia V | 2023 | Phase I/II Recruiting | mCRPC | NCT06236139 [6] |
| TCE | AMG 509 (Xaluritamig) | Amgen | 2020 | Phase I Recruiting | mCRPC | NCT04221542 [57] |
| TCE | AMG 509 (Xaluritamig) | Amgen | 2024 | Phase I Recruiting | nmCSPC | NCT06555796 [58] |
| TCE | AMG 509 (Xaluritamig) | Amgen | 2024 | Phase I Recruiting | Localized Pca | NCT06613100 [59] |
| TCE | BC261 | Lin TY | 2021 | Preclinical | Mouse EFT and Pca | [60] |
| mRNA vaccine | CV9104 | Kübler H | 2015 | Phase I/IIB Completed | mCRPC | NCT01817738 [61] |
| Fusion protein vaccine | Ag85B-3 × STEAP1186–193 | Guo L | 2021 | Preclinical | PCa | [62] |
| Fusion protein vaccine | HSP65 and STEAP1186–193 | Chen X | 2019 | Preclinical | Mouse PCa and Melanoma | [63] |
| DNA vaccine | PCaA-SEV | Bordoloi D | 2021 | Preclinical | Mouse PCa | [64] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, L.; Ren, X.; An, R.; Song, H.; Tian, Y.; Wei, X.; Shi, M.; Wang, Z. The Role of STEAP1 in Prostate Cancer: Implications for Diagnosis and Therapeutic Strategies. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 794. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13040794
Zhang L, Ren X, An R, Song H, Tian Y, Wei X, Shi M, Wang Z. The Role of STEAP1 in Prostate Cancer: Implications for Diagnosis and Therapeutic Strategies. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(4):794. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13040794
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Lingling, Xinyi Ren, Ran An, Hongchen Song, Yaqi Tian, Xuan Wei, Mingjun Shi, and Zhenchang Wang. 2025. "The Role of STEAP1 in Prostate Cancer: Implications for Diagnosis and Therapeutic Strategies" Biomedicines 13, no. 4: 794. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13040794
APA StyleZhang, L., Ren, X., An, R., Song, H., Tian, Y., Wei, X., Shi, M., & Wang, Z. (2025). The Role of STEAP1 in Prostate Cancer: Implications for Diagnosis and Therapeutic Strategies. Biomedicines, 13(4), 794. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13040794







