Electroacupuncture Attenuates Intestinal Barrier Disruption via the α7nAChR-Mediated HO-1/p38 MAPK/NF-κB Pathway in a Mouse Model of Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease: A Randomized, Single-Blind, Controlled Trial
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
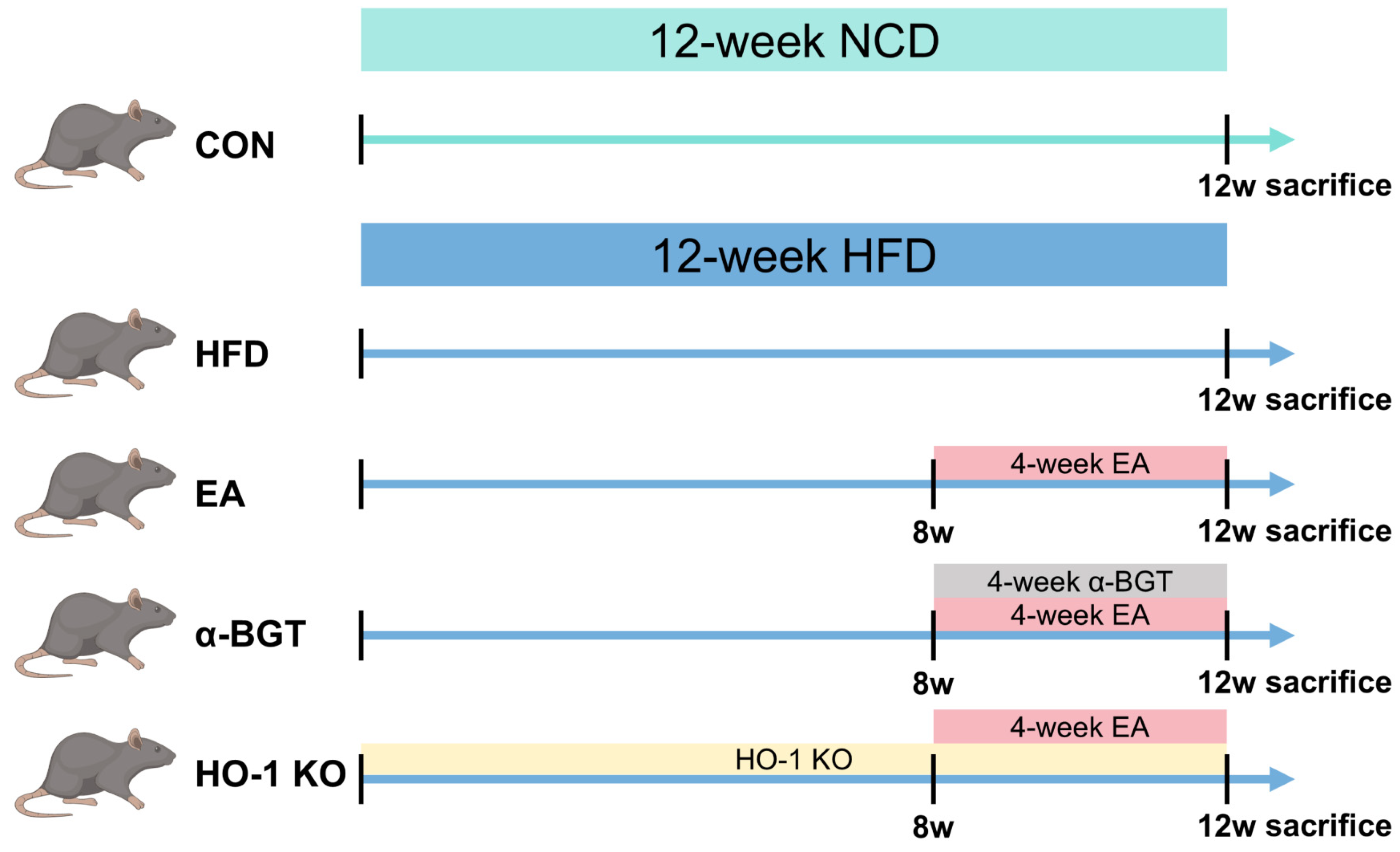
2.2. Animal Grouping and Interventions
2.3. Histological Analysis
2.4. Biochemical Measurement
2.5. Analysis of Real-Time Quantitative PCR
2.6. Assessment of Western Blot
2.7. Immunohistochemistry and Immunofluorescence Assay
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. EA Alleviated Hepatic Steatosis in MAFLD
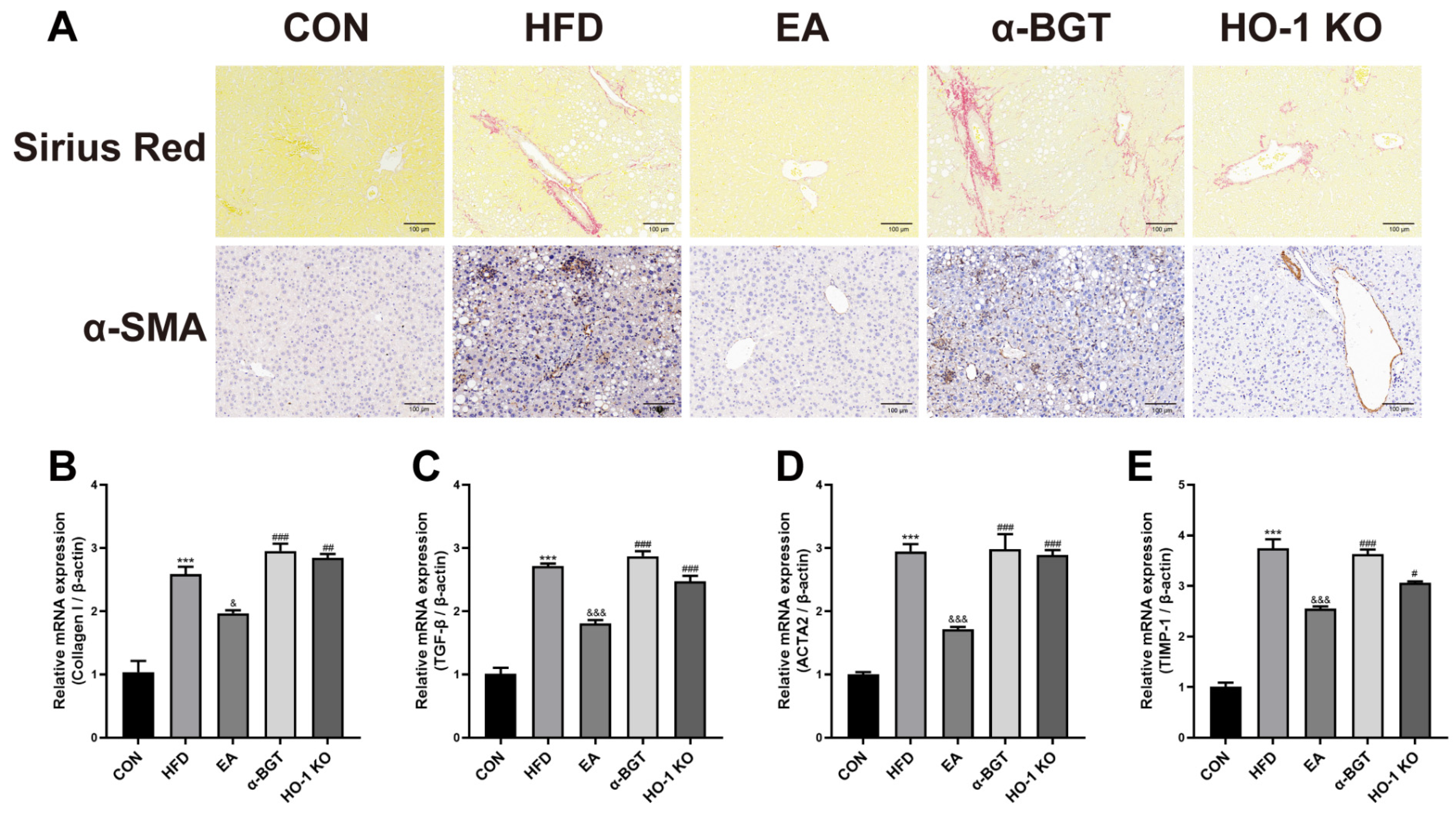
3.2. EA Ameliorated Liver Fibrosis in MAFLD
3.3. EA Restored the Homeostasis of Inflammatory Responses of MAFLD
3.4. EA Attenuated Impaired Gut Barrier in MAFLD
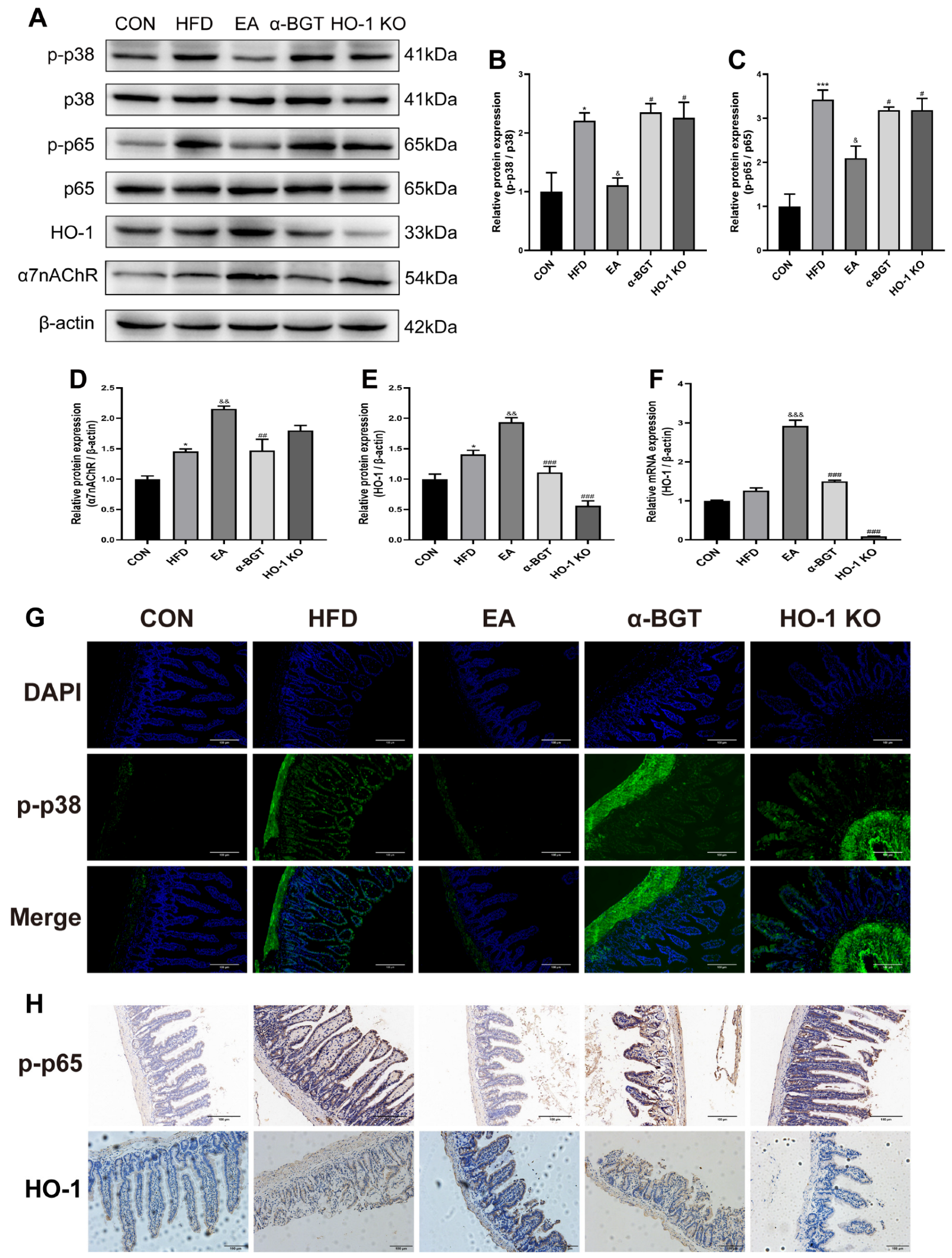
3.5. The Potential Mechanism of EA Stimulation in the Mitigation of MAFLD Might Be Attributed to the Involvement of the HO-1/p38 MAPK/NF-κB Pathway Mediated by α7nAChR
4. Discussion
5. Limitations
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rinella, M.E.; Lazarus, J.V.; Ratziu, V.; Francque, S.M.; Sanyal, A.J.; Kanwal, F.; Romero, D.; Abdelmalek, M.F.; Anstee, Q.M.; Arab, J.P.; et al. A Multisociety Delphi Consensus Statement on New Fatty Liver Disease Nomenclature. J. Hepatol. 2023, 79, 1542–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagström, H.; Shang, Y.; Hegmar, H.; Nasr, P. Natural History and Progression of Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2024, 9, 944–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benedé-Ubieto, R.; Cubero, F.J.; Nevzorova, Y.A. Breaking the Barriers: The Role of Gut Homeostasis in Metabolic-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD). Gut Microbes 2024, 16, 2331460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tilg, H.; Adolph, T.E.; Trauner, M. Gut-Liver Axis: Pathophysiological Concepts and Clinical Implications. Cell Metab. 2022, 34, 1700–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pabst, O.; Hornef, M.W.; Schaap, F.G.; Cerovic, V.; Clavel, T.; Bruns, T. Gut-Liver Axis: Barriers and Functional Circuits. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 20, 447–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Shi, H.; Cao, S.; Xie, L.; Ren, P.; Wang, J.; Shi, B. Revealing the Magic of Acupuncture Based on Biological Mechanisms: A Literature Review. Biosci. Trends 2022, 16, 73–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, G.; Sclocco, R.; Sharma, A.; Guerrero-López, I.; Kuo, B. Electroceuticals and Magnetoceuticals in Gastroenterology. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Wen, Q.; Hu, H.; Yang, S.; Lu, L.; Hu, X.; Li, H.; Huang, X.; Li, N. Electroacupuncture at ST36 Modulates the Intestinal Microecology and May Help Repair the Intestinal Barrier in the Rat Model of Severe Acute Pancreatitis. Microb. Biotechnol. 2024, 17, e14401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Fu, W.; Fu, J.; Chen, G.; He, Y.; Zheng, T.; Ma, T. Electroacupuncture Alleviates Intestinal Inflammation via a Distinct Neuro-Immune Signal Pathway in the Treatment of Postoperative Ileus. Biomed. Pharmacother. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2024, 173, 116387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Dong, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, Y.; Shi, J.; Li, X.; Liu, S.; Chen, Y.; Yu, J. Electroacupuncture Promotes Resolution of Inflammation by Modulating SPMs via Vagus Nerve Activation in LPS-Induced ALI. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2025, 147, 113941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, Y.; Lv, H.; Liu, Y.; Guo, D.; Zheng, J.; Li, Y.; Jiang, H.; Chen, D. Electroacupuncture at Zusanli (ST36) Alleviate Intestinal Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury by Regulating the Cholinergic-miRNA 124 Pathway. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2024, e14971, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, W.; Zhao, C.; Sun, J.; Jin, Y.; Duan, Z. Electroacupuncture Ameliorates Intestinal Barrier Destruction in Mice With Bile Duct Ligation–Induced Liver Injury by Activating the Cholinergic Anti-Inflammatory Pathway. Neurogastroenterol. Technol. Neural Interface 2022, 25, 1122–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.; Chen, K.; Sang, X.; Feng, Z.; Zhou, F.; Zhao, H.; Wu, S.; Deng, X.; Lin, C.; Lin, X.; et al. Huperzine a Ameliorates Sepsis-Induced Acute Lung Injury by Suppressing Inflammation and Oxidative Stress via A7 Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2024, 141, 112907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, N.K.; Fitzgerald, H.K.; Dunne, A. Regulation of Inflammation by the Antioxidant Haem Oxygenase 1. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2021, 21, 411–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancuso, C. The Heme Oxygenase/Biliverdin Reductase System and Its Genetic Variants in Physiology and Diseases. Antioxidants 2025, 14, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, W.; Zhao, C.; Sun, J.; Jin, Y.; Duan, Z. Activation of α7nAChR Preserves Intestinal Barrier Integrity by Enhancing the HO-1/STAT3 Signaling to Inhibit NF-κB Activation in Mice. Biomed. Pharmacother. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 149, 112733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.-Y.; Xu, H.; Qin, Y.; He, T.-Q.; Shi, R.-R.; Xing, Y.-R.; Xu, J.; Cong, R.-C.; Wang, M.-R.; Yang, J.-S.; et al. Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide Phosphate Alleviates Intestinal Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury via Nrf2/HO-1 Pathway. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2024, 143, 113478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Q.; Geng, Z.; Wang, L.; Zuo, L.; Deng, M.; Zhang, H.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Wen, H.; et al. Peiminine Ameliorates Crohn’s Disease-like Colitis by Enhancing the Function of the Intestinal Epithelial Barrier through Nrf2/HO1 Signal. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2024, 136, 112380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Hua, H.; Zhu, H.; Cheng, Y.; Guo, Y.; Yao, W.; Qian, H. Aloe Polysaccharides Ameliorate Acute Colitis in Mice via Nrf2/HO-1 Signaling Pathway and Short-Chain Fatty Acids Metabolism. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 185, 804–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.-C.; Jin, Y.-J.; Ning, R.; Mao, Q.-Y.; Zhang, P.-Y.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, C.-C.; Peng, Y.-C.; Chen, N. Electroacupuncture Attenuates Ferroptosis by Promoting Nrf2 Nuclear Translocation and Activating Nrf2/SLC7A11/GPX4 Pathway in Ischemic Stroke. Chin. Med. 2025, 20, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, L.; Wang, G.; Yang, S.; Zhou, S.; Xu, T.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, W.; Lu, K.; Hu, L.; Wang, Y.; et al. Electroacupuncture Reduces Duration of Postoperative Ileus After Laparoscopic Gastrectomy for Gastric Cancer: A Multicenter Randomized Trial. Gastroenterology, 2025; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, M.; Chen, T.; Tian, J.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, Z.; Liu, X.; Zhang, S.; Chen, Y. Electroacupuncture at ST36 Relieves Visceral Hypersensitivity Based on the Vagus-Adrenal Axis in the Remission Stage of Ulcerative Colitis. Neuromodul. J. Int. Neuromodul. Soc. 2025; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, X.; Liu, L.; Zhou, Y.; Zhong, K.; Gu, J.; Hu, T.; Yao, Y.; Zhou, C.; Chen, W. High-Fat Diet Promotes Colitis-Associated Tumorigenesis by Altering Gut Microbial Butyrate Metabolism. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2023, 19, 5004–5019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruppert, Z.; Neuperger, P.; Rákóczi, B.; Gémes, N.; Dukay, B.; Hajdu, P.; Péter, M.; Balogh, G.; Tiszlavicz, L.; Vígh, L.; et al. Characterization of Obesity-Related Diseases and Inflammation Using Single Cell Immunophenotyping in Two Different Diet-Induced Obesity Models. Int. J. Obes. 2005 2024, 48, 1568–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.-E.; Park, H.-Y.; Kim, Y.-S.; Park, M. The Role of Diet, Additives, and Antibiotics in Metabolic Endotoxemia and Chronic Diseases. Metabolites 2024, 14, 704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, L.; Au, R.; Dai, L.; Li, Y.; Xu, F.; Cui, Y.; Hu, J.; Shen, H. Electroacupuncture Modulates Microbial Phenylalanine Metabolism and Enhances the Intestinal Barrier Function to Alleviate Colitis in Mice. J. Inflamm. Res. 2024, 17, 7311–7324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.-B.; Dong, L.-C.; Shen, Y.; Li, H.-Y.; Huang, Q.; Yu, S.-G.; Wu, Q.-F. Electroacupuncture Alleviates Ulcerative Colitis by Targeting CXCL1: Evidence from the Transcriptome and Validation. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1187574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nan, S.; Wan, J.; Lei, Q.; Wang, X.; Ma, N.; Yin, R.; Zhu, J.; Ding, M.; Ding, Y. The Involvement of the Primo Vascular System in Local Enteritis and Its Modification by Electroacupuncture. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1072996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Lv, J.; Chen, X.; Shi, Y.; Chao, G.; Zhang, S. From Gut to Liver: Exploring the Crosstalk between Gut-Liver Axis and Oxidative Stress in Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease. Ann. Hepatol. 2025, 30, 101777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Wang, L.; Mei, M.; Guo, J.; Yang, X.; Liu, S. Electroacupuncture Repairs Intestinal Barrier by Upregulating CB1 through Gut Microbiota in DSS-Induced Acute Colitis. Chin. Med. 2023, 18, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeed, H.; Díaz, L.A.; Gil-Gómez, A.; Burton, J.; Bajaj, J.; Romero-Gomez, M.; Arrese, M.; Arab, J.P.; Khan, M.Q. Microbiome-Centered Therapies for the Management of Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2024, 31, S94–S111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remund, B.; Yilmaz, B.; Sokollik, C. D-Lactate: Implications for Gastrointestinal Diseases. Children 2023, 10, 945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keever, K.R.; Yakubenko, V.P.; Hoover, D.B. Neuroimmune Nexus in the Pathophysiology and Therapy of Inflammatory Disorders: Role of A7 Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors. Pharmacol. Res. 2023, 191, 106758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Wang, Z.; Su, Y.; Qi, L.; Yang, W.; Fu, M.; Jing, X.; Wang, Y.; Ma, Q. A Neuroanatomical Basis for Electroacupuncture to Drive the Vagal-Adrenal Axis. Nature 2021, 598, 641–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Z.; Shen, Z.; Yan, S.; Chen, G.; Yin, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, X. Electroacupuncture Ameliorates Gastrointestinal Dysfunction by Modulating DMV Cholinergic Efferent Signals to Drive the Vagus Nerve in P-MCAO Rats. Heliyon 2024, 10, e29426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Tang, N.; Zhao, X.; Jiang, J.; Ma, J.; Zhang, H. A7 Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor Agonist GTS-21 Attenuates DSS-Induced Intestinal Colitis by Improving Intestinal Mucosal Barrier Function. Mol. Med. Camb. Mass 2022, 28, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pu, W.; Su, Z.; Wazir, J.; Zhao, C.; Wei, L.; Wang, R.; Chen, Q.; Zheng, S.; Zhang, S.; Wang, H. Protective Effect of A7 Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor Activation on Experimental Colitis and Its Mechanism. Mol. Med. 2022, 28, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Li, F.; Xin, Y.; Duan, Z. Contributions of HO-1-Dependent MAPK to Regulating Intestinal Barrier Disruption. Biomol. Ther. 2021, 29, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chudy, P.; Kochan, J.; Wawro, M.; Nguyen, P.; Gorczyca, M.; Varanko, A.; Retka, A.; Ghadei, S.S.; Napieralska, E.; Grochot-Przęczek, A.; et al. Heme Oxygenase-1 Protects Cells from Replication Stress. Redox Biol. 2024, 75, 103247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Guo, Y.; Liu, C.; Yang, Y.; Fan, X.; Yang, H.; Liu, Y.; Ma, T. Function and Inhibition of P38 MAP Kinase Signaling: Targeting Multiple Inflammation Diseases. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2024, 220, 115973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Han, J.; Gao, J.; Ge, Q.; Zhang, H.; Shi, J.; Wang, H. Polysaccharide from Pyrus Pashia Buch Ameliorates DSS-Induced Colitis in Mice via MAPKP38/NF-κB P65 and SCFAs/ERK/MSK Signaling Pathways. Phytomed. Int. J. Phytother. Phytopharm. 2025, 140, 156561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, M.; Liu, S.; Zhang, N.; Liu, X.; Li, B.; Li, J.; Geng, Z.; Zuo, L.; et al. The JNK/P38 Signalling Pathway Activated by Testin Protects the Intestinal Epithelial Barrier against Crohn’s Disease-like Colitis. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2024, 403, 111222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Jin, Y.; Chen, X.; Ye, X.; Shen, X.; Lin, M.; Zeng, C.; Zhou, T.; Zhang, J. NF-κB in Biology and Targeted Therapy: New Insights and Translational Implications. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2024, 9, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; He, Y.; Zhu, X.; Zhu, J.; Deng, Z.; Zhang, H.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, G.; Shi, T.; Chen, W. Elevated SPARC Disrupts the Intestinal Barrier Integrity in Crohn’s Disease by Interacting with OTUD4 and Activating the MYD88/NF-κB Pathway. Adv. Sci. 2025, 12, e2409419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smiriglia, A.; Lorito, N.; Bacci, M.; Subbiani, A.; Bonechi, F.; Comito, G.; Kowalik, M.A.; Perra, A.; Morandi, A. Estrogen-Dependent Activation of TRX2 Reverses Oxidative Stress and Metabolic Dysfunction Associated with Steatotic Disease. Cell Death Dis. 2025, 16, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Model, J.F.A.; Normann, R.S.; Vogt, É.L.; Dentz, M.V.; de Amaral, M.; Xu, R.; Bachvaroff, T.; Spritzer, P.M.; Chung, J.S.; Vinagre, A.S. Interactions between Glucagon like Peptide 1 (GLP-1) and Estrogens Regulates Lipid Metabolism. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2024, 230, 116623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Genes | Specific Primer Sequences |
|---|---|
| Collagen I | Forward: ACAGGCGAACAAGGTGACAGAG Reverse: AGGAGAACCAGGAGAACCAGGAG |
| TGF-β | Forward: CAACAATTCCTGGCGTTACCTTGG Reverse: TGTATTCCGTCTCCTTGGTTCAGC |
| ACTA2 | Forward: ATCAGGGAGTAATGGTGGAATGGG Reverse: CAGTTGGTGATGATGCCGTGTTC |
| TIMP-1 | Forward: GGATTCAAGGCTGTGGGAAATGC Reverse: TTCACTGCGGTTCTGGGACTTG |
| ZO-1 | Forward: TATGGCTTGTGGGGTGTT Reverse: GGCTAGGTGTTTGGGGAT |
| Occludin | Forward: CTGCCTGCACGATGTCT Reverse: GAGTGTTCAGCCCAGTCAA |
| Claudin-1 | Forward: GCCTGCAAGAGGGATGT Reverse: GGGATGATAGTGCCCAGTC |
| HO-1 | Forward: ACAGCCCCACCAAGTTC Reverse: GGCGGTCTTAGCCTCTTC |
| β-actin | Forward: GATGGTGGGAATGGGTCAGAAGG Reverse: TTGTAGAAGGTGTGGTGCCAGATC |
| Measurement | Age (Week) | CON | HFD | EA | α-BGT | HO-1 KO |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline body weight (g) | 8 | 19.72 ± 0.24 | 19.85 ± 0.14 | 19.94 ± 0.15 | 20.00 ± 0.21 | 19.96 ± 0.20 |
| Ultimate body weight (g) | 20 | 28.50 ± 0.43 | 35.73 ± 0.46 *** | 29.84 ± 0.36 &&& | 35.01 ± 0.58 ### | 32.58 ± 0.25 ## |
| Visceral fat index (%) | 20 | 2.46 ± 0.19 | 5.55 ± 0.15 *** | 3.70 ± 0.17 &&& | 5.10 ± 0.20 ### | 4.93 ± 0.18 ### |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, X.; Sun, J.; Wang, P.; Zhang, Y.; Chang, J.; Duan, Z. Electroacupuncture Attenuates Intestinal Barrier Disruption via the α7nAChR-Mediated HO-1/p38 MAPK/NF-κB Pathway in a Mouse Model of Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease: A Randomized, Single-Blind, Controlled Trial. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 802. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13040802
Wang X, Sun J, Wang P, Zhang Y, Chang J, Duan Z. Electroacupuncture Attenuates Intestinal Barrier Disruption via the α7nAChR-Mediated HO-1/p38 MAPK/NF-κB Pathway in a Mouse Model of Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease: A Randomized, Single-Blind, Controlled Trial. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(4):802. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13040802
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Xiao, Jiasen Sun, Peng Wang, Yimin Zhang, Jiuyang Chang, and Zhijun Duan. 2025. "Electroacupuncture Attenuates Intestinal Barrier Disruption via the α7nAChR-Mediated HO-1/p38 MAPK/NF-κB Pathway in a Mouse Model of Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease: A Randomized, Single-Blind, Controlled Trial" Biomedicines 13, no. 4: 802. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13040802
APA StyleWang, X., Sun, J., Wang, P., Zhang, Y., Chang, J., & Duan, Z. (2025). Electroacupuncture Attenuates Intestinal Barrier Disruption via the α7nAChR-Mediated HO-1/p38 MAPK/NF-κB Pathway in a Mouse Model of Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease: A Randomized, Single-Blind, Controlled Trial. Biomedicines, 13(4), 802. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13040802







