Clinical Features, Video Head Impulse Test, and Subjective Visual Vertical of Acute and Symptom-Free Phases in Patients with Definite Vestibular Migraine
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
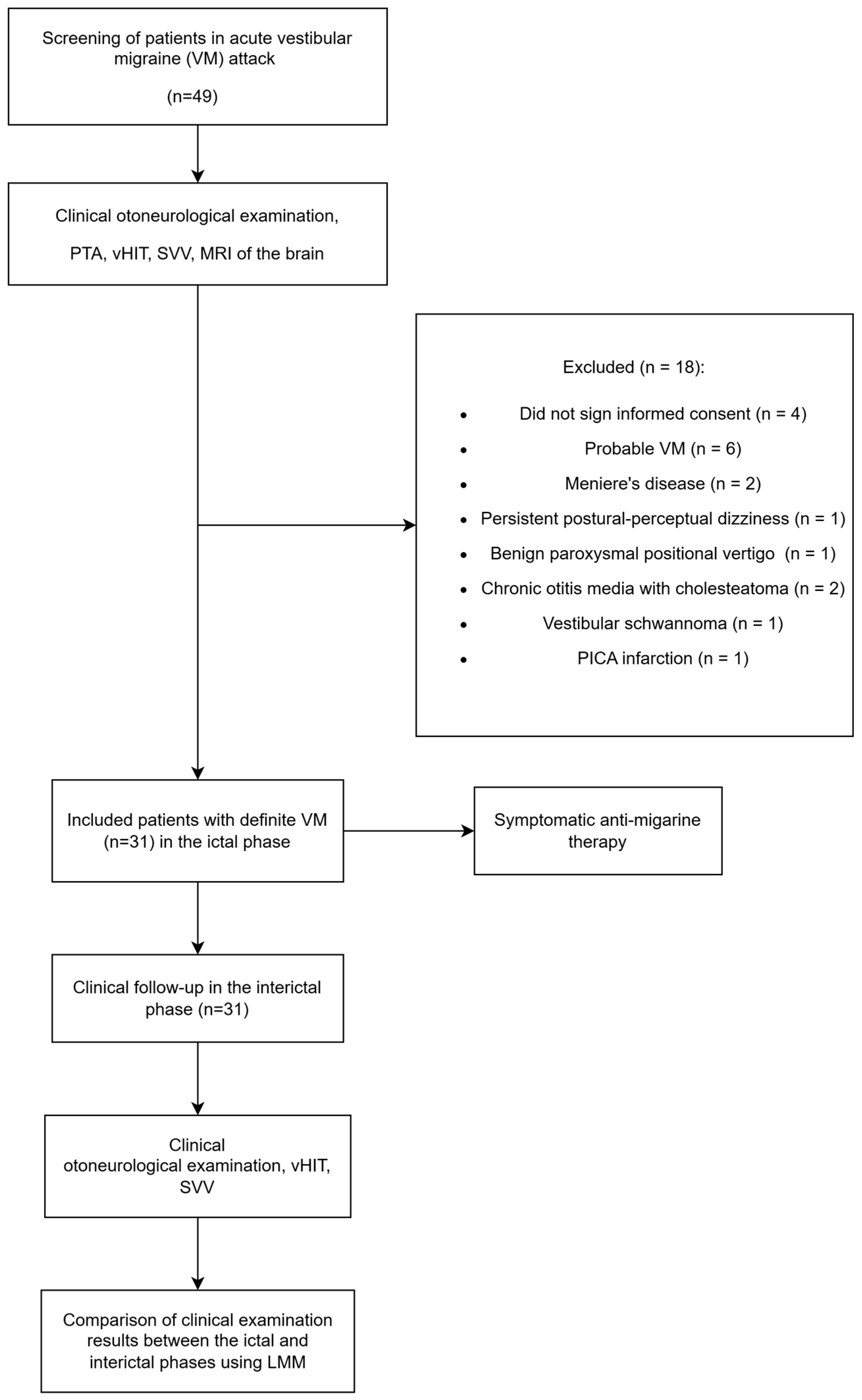
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Participants
2.3. Otoneurological Examination
2.4. Specific Diagnostic Tools
2.4.1. Video Head Impulse Test (vHIT)
2.4.2. Subjective Visual Vertical (SVV)
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dieterich, M.; Obermann, M.; Celebisoy, N. Vestibular migraine: The most frequent entity of episodic vertigo. J. Neurol. 2016, 263 (Suppl. S1), S82–S89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, P.S.; Carey, J.P. Vestibular Migraine: Clinical Aspects and Pathophysiology. Otolaryngol. Clin. N. Am. 2022, 55, 531–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Formeister, E.J.; Rizk, H.G.; Kohn, M.A.; Sharon, J.D. The Epidemiology of Vestibular Migraine: A Population-based Survey Study. Otol. Neurotol. 2018, 39, 1037–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Carpena, P.; Lopez-Escamez, J.A. Do we need to reconsider the classification of vestibular migraine? Expert Rev. Neurother. 2021, 21, 503–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vukovic, V.; Plavec, D.; Pavelin, S.; Janculjak, D.; Ivankovic, M.; Demarin, V. Prevalence of migraine, probable migraine and tension-type headache in the Croatian population. Neuroepidemiology 2010, 35, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beh, S.C.; Masrour, S.; Smith, S.V.; Friedman, D.I. The Spectrum of Vestibular Migraine: Clinical Features, Triggers, and Examination Findings. Headache 2019, 59, 727–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furman, J.M.; Marcus, D.A.; Balaban, C.D. Vestibular migraine: Clinical aspects and pathophysiology. Lancet Neurol. 2013, 12, 706–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winnick, A.; Sadeghpour, S.; Otero-Millan, J.; Chang, T.-P.; Kheradmand, A. Errors of Upright Perception in Patients with Vestibular Migraine. Front. Neurol. 2018, 9, 892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kheradmand, A.; Winnick, A. Perception of Upright: Multisensory Convergence and the Role of Temporo-Parietal Cortex. Front. Neurol. 2017, 8, 552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Gu, H.; Xu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Li, F.; Feng, M.; Tian, Q.; Shang, C.; Zhuang, J. Purkinje cells of vestibulocerebellum play an important role in acute vestibular migraine. J. Integr. Neurosci. 2019, 18, 409–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.C.; Wang, S.J.; Kheradmand, A. Vestibular migraine: An update on current understanding and future directions. Cephalalgia 2020, 40, 107–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lempert, T.; Olesen, J.; Furman, J.; Waterston, J.; Seemungal, B.; Carey, J.; Bisdorff, A.; Versino, M.; Evers, S.; Newman-Toker, D. Vestibular migraine: Diagnostic criteria. J. Vestib. Res. 2012, 22, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olesen, J. Headache Classification Committee of the International Headache Society (IHS) The International Classification of Headache Disorders, 3rd edition. Cephalalgia 2018, 38, 1–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morganti, L.O.G.; Salmito, M.C.; Duarte, J.A.; Sumi, K.C.; Simões, J.C.; Ganança, F.F. Vestibular migraine: Clinical and epidemiological aspects. Braz. J. Otorhinolaryngol. 2016, 82, 397–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polensek, S.H.; Tusa, R.J. Nystagmus during Attacks of Vestibular Migraine: An Aid in Diagnosis. Audiol. Neurotol. 2010, 15, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radtke, A.; von Brevern, M.; Neuhauser, H.; Hottenrott, T.; Lempert, T. Vestibular migraine: Long-term follow-up of clinical symptoms and vestibulo-cochlear findings. Neurology 2012, 79, 1607–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, W.S.; Lee, S.H.; Yang, C.J.; Ahn, J.H.; Chung, J.W.; Park, H.J. Vestibular Function Tests for Vestibular Migraine: Clinical Implication of Video Head Impulse and Caloric Tests. Front. Neurol. 2016, 7, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denia-Lafuente, A.; Lombardero, B. Vestibular Function Measured Using the Video Head Impulse Test in Congenital Nystagmus and Vertigo: A Case Report. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 690402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, T.-P.; Winnick, A.A.; Hsu, Y.-C.; Sung, P.-Y.; Schubert, M.C. The bucket test differentiates patients with MRI confirmed brainstem/cerebellar lesions from patients having migraine and dizziness alone. BMC Neurol. 2019, 19, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Xu, J.; Li, G.-R.; Gao, R.; Shang, C.-Y.; Tian, E.; Kong, W.-J.; Zhuang, J.-H.; Zhang, S.-L. The Value of Subjective Visual Vertical in Diagnosis of Vestibular Migraine. Curr. Med. Sci. 2021, 41, 654–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhabib, S.F.; Saliba, I. Video head impulse test: A review of the literature. Eur. Arch. Oto-Rhino-Laryngol. 2017, 274, 1215–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwergal, A.; Rettinger, N.; Frenzel, C.; Dieterich, M.; Brandt, T.; Strupp, M. A bucket of static vestibular function. Neurology 2009, 72, 1689–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kattah, J.C.; Talkad, A.V.; Wang, D.Z.; Hsieh, Y.-H.; Newman-Toker, D.E. HINTS to Diagnose Stroke in the Acute Vestibular Syndrome. Stroke 2009, 40, 3504–3510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.-Y.; Lee, S.-H.; Kim, J.-S. Central vertigo. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2018, 31, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machner, B.; Erber, K.; Choi, J.H.; Sprenger, A.; Helmchen, C.; Trillenberg, P. A Simple Gain-Based Evaluation of the Video Head Impulse Test Reliably Detects Normal Vestibulo-Ocular Reflex Indicative of Stroke in Patients with Acute Vestibular Syndrome. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 741859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nham, B.; Wang, C.; Reid, N.; Calic, Z.; Kwok, B.Y.C.; Black, D.A.; Bradshaw, A.; Halmagyi, G.; Welgampola, M.S. Modern vestibular tests can accurately separate stroke and vestibular neuritis. J. Neurol. 2022, 270, 2031–2041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koç, A.; Akkılıç, E.C. Evaluation of video head impulse test during vertiginous attack in vestibular migraine. Acta Otorhinolaryngol. Ital. 2022, 42, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, M.S.; Egilmez, O.K.; Kara, A.; Guven, M.; Demir, D.; Genc Elden, S. Comparison of the results of caloric and video head impulse tests in patients with Meniere’s disease and vestibular migraine. Eur. Arch. Oto-Rhino-Laryngol. 2020, 278, 1829–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yollu, U.; Uluduz, D.U.; Yilmaz, M.; Yener, H.M.; Akil, F.; Kuzu, B.; Kara, E.; Hayir, D.; Ceylan, D.; Korkut, N. Vestibular migraine screening in a migraine-diagnosed patient population, and assessment of vestibulocochlear function. Clin. Otolaryngol. 2016, 42, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Kang, B.C.; Yoo, M.H.; Park, H.J. Differential Involvement of Lateral Semicircular Canal and Otolith Organs in Common Vestibular Disorders. Front. Neurol. 2022, 13, 819385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ElSherif, M.; Reda, M.I.; Saadallah, H.; Mourad, M. Eye movements and imaging in vestibular migraine. Acta Otorrinolaringol. Esp. 2020, 71, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, T.; Kurien, G.; Lin, V.Y.W. Mobile phone app Vs bucket test as a subjective visual vertical test: A validation study. J. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2020, 49, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. Available online: www.r-project.org (accessed on 12 October 2023).
- Neuhauser, H.K.; Radtke, A.; von Brevern, M.; Feldmann, M.; Lezius, F.; Ziese, T.; Lempert, T. Migrainous vertigo. Neurology 2006, 67, 1028–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salmito, M.C.; Ganança, F.F. Video head impulse test in vestibular migraine. Braz. J. Otorhinolaryngol. 2021, 87, 671–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Dong, H.; Yang, L.; Zhao, H.; Dong, W.; Yang, Y. Severity and Its Contributing Factors in Patients With Vestibular Migraine: A Cohort Study. Front. Neurol. 2020, 11, 595328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Brevern, M.; Zeise, D.; Neuhauser, H.; Clarke, A.H.; Lempert, T. Acute migrainous vertigo: Clinical and oculographic findings. Brain A J. Neurol. 2004, 128, 365–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cutrer, F.M.; Baloh, R.W. Migraine-associated Dizziness. Headache J. Head Face Pain 1992, 32, 300–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayan, A.; Hood, J.D. Neuro-Otological Manifestations of Migraine. Brain 1984, 107, 1123–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, M.; Guo, X.; Liu, W.; Lu, J.; Wang, J.; Hu, L.; Xia, K.; Ni, J.; Lu, H.; Zhao, H. Temporal Patterns of Vertigo and Migraine in Vestibular Migraine. Front. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reploeg, M.D.; Goebel, J.A. Migraine-associated Dizziness: Patient Characteristics and Management Options. Otol. Neurotol. 2002, 23, 364–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérennou, D.; Piscicelli, C.; Barbieri, G.; Jaeger, M.; Marquer, A.; Barra, J. Measuring verticality perception after stroke: Why and how? Neurophysiol. Clin. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2014, 44, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obrero-Gaitán, E.; Manrique-Navarro, M.; Lérida-Ortega, M.Á.; Rodríguez-Almagro, D.; Osuna-Pérez, M.C.; Lomas-Vega, R. Misperception of Visual Verticality in Patients with Primary Headache Disorders: A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis. Brain Sci. 2020, 10, 664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, M.A.; Crane, B.T. Static and dynamic visual vertical perception in subjects with migraine and vestibular migraine. World J. Otorhinolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2016, 2, 175–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blödow, A.; Heinze, M.; Bloching, M.B.; von Brevern, M.; Radtke, A.; Lempert, T. Caloric stimulation and video-head impulse testing in Ménière’s disease and vestibular migraine. Acta Oto-Laryngol. 2014, 134, 1239–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, A.S.; Nham, B.; Bradshaw, A.P.; Calic, Z.; Pogson, J.M.; D’Souza, M.; Halmagyi, G.M.; Welgampola, M.S. Clinical, oculographic, and vestibular test characteristics of vestibular migraine. Cephalalgia 2021, 41, 1039–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwedt, T.J. Multisensory integration in migraine. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2013, 26, 248–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| IC and II Phase (n = 31) | |
|---|---|
| Age (years) | 46.6 (15.9) |
| Female | 28 (90.32%) |
| Duration of the last VM attack | 10 (6–12) |
| Nr. of VM attacks until now | 10 (10–15) |
| Marital status | |
| Single | 7 (22.58%) |
| Married | 18 (58.06%) |
| Divorced | 4 (12.90%) |
| Widowed | 2 (6.45%) |
| Separated | 0 (0%) |
| Coffee use | |
| Yes | 10 (32.26%) |
| No | 21 (67.74%) |
| Alcohol use | |
| Yes | 0 (0%) |
| No | 31 (100%) |
| Smoking | |
| Yes | 11 (35.48%) |
| No | 20 (64.52%) |
| IC Phase (n = 31) | |
|---|---|
| Type of vertigo | |
| Spontaneous | 26 (83.87%) |
| Positional | 3 (9.68%) |
| Both spontaneous and positional | 2 (6.45%) |
| Vomiting | |
| Yes | 10 (32.26%) |
| No | 21 (67.74%) |
| Trigger | |
| Poor sleep | 20 (64.52%) |
| Weather change | 18 (58.06%) |
| Stress | 15 (48.39%) |
| Spontaneous start | 10 (32.26%) |
| Sharp movement of the head | 7 (22.58%) |
| Excessive computer use | 4 (12.90%) |
| Excessive cell phone use | 3 (9.68%) |
| Strong light and sound | 3 (9.68%) |
| Nr. of current vestibular symptoms | |
| 2 | 1 (3.23%) |
| 3 | 9 (29.03%) |
| 4 | 21 (67.74%) |
| Migraine headache | |
| No | 0 (0%) |
| Before the VM attack | 29 (93.55%) |
| During the VM attack | 2 (6.45%) |
| After the VM attack | 1 (3.23%) |
| Aura | |
| No | 18 (58.06%) |
| Before the VM attack | 13 (41.94%) |
| During the VM attack | 0 (0%) |
| After the VM attack | 0 (0%) |
| Hearing | |
| Inconspicuous | 18 (58.06%) |
| Tonal tinnitus unilaterally | 4 (12.90%) |
| Tonal tinnitus bilaterally | 5 (16.13%) |
| Sense of fulness | 2 (6.45%) |
| Hearing loss unilaterally | 0 (0%) |
| Hearing loss bilaterally | 0 (0%) |
| Phobic symptoms | |
| Yes | 10 (32.26%) |
| No | 21 (67.74%) |
| Diplopia, dysphagia, dysphonia | |
| Yes | 0 (0%) |
| No | 31 (100%) |
| Migraine in family | |
| Yes | 28 (90.32%) |
| No | 3 (9.68%) |
| Otoneurological examination | |
| OTS | |
| Inconspicuous/negative | 31 (100%) |
| Pathologic/positive | 0 (0%) |
| ABCD2 | |
| 1 | 25 (80.65%) |
| 2 | 6 (19.35%) |
| Truncal ataxy | |
| 1 | 31 (100%) |
| House–Brackmann score | |
| 1/6 | 31 (100%) |
| PTA right (dB) | 16 (10–22.50) |
| PTA left (dB) | 15 (11–22.50) |
| NRS for vertigo | 8 (7–9) |
| NRS for headache | 2 (1–3) |
| MRI (UBO lesion) | 15 (48.39%) |
| IC Phase (n = 31) | II Phase (n = 31) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nausea | 6.591 × 10−8 a | ||
| Yes | 31 (100%) | 12 (38.71%) | |
| No | 0 (0%) | 19 (61.29%) | |
| Photophobia | 1.839 × 10−8 a | ||
| Yes | 31 (100%) | 11 (35.48%) | |
| No | 0 (0%) | 20 (64.52%) | |
| Phonophobia | 9.336 × 10−12 a | ||
| Yes | 28 (90.32%) | 2 (6.45%) | |
| No | 3 (9.68%) | 28 (90.32%) | |
| Osmophobia | 0.612 a | ||
| Yes | 3 (9.68%) | 1 (3.22%) | |
| No | 28 (90.32%) | 30 (96.77%) | |
| bHIT | N/A | ||
| Inconspicuous/negative | 31 (100%) | 31 (100%) | |
| Pathologic/positive | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | |
| Skew test | N/A | ||
| Inconspicuous/negative | 31 (100%) | 31 (100%) | |
| Pathologic/positive | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | |
| Smooth pursuit | 0.473 a | ||
| Inconspicuous/negative | 6 (19.35%) | 3 (9.68%) | |
| Pathologic/positive | 25 (80.65%) | 28 (90.32%) | |
| Saccade | N/A | ||
| Inconspicuous/negative | 31 (100%) | 31 (100%) | |
| Pathologic/positive | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | |
| Head shaking test | N/A | ||
| Inconspicuous/negative | 31 (100%) | 31 (100%) | |
| Pathologic/positive | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | |
| Romberg test | 0.492 a | ||
| Inconspicuous/negative | 29 (93.55%) | 31 (100%) | |
| Pathologic | 2 (6.45%) | 0 (0%) | |
| Spontaneous nystagmus | 0.011 a | ||
| Inconspicuous/negative | 24 (77.42%) | 31 (100%) | |
| Pathologic/positive | 7 (22.58%) | 0 (0%) | |
| Nystagmus in Dix–Hallpike test | 0.043 a | ||
| Inconspicuous/negative | 22 (70.97%) | 29 (93.55%) | |
| Pathologic/positive | 9 (29.03%) | 2 (6.45%) | |
| Nystagmus in Lateral roll test | |||
| Inconspicuous/negative | 31 (100%) | 31 (100%) | N/A |
| Pathologic/positive | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | |
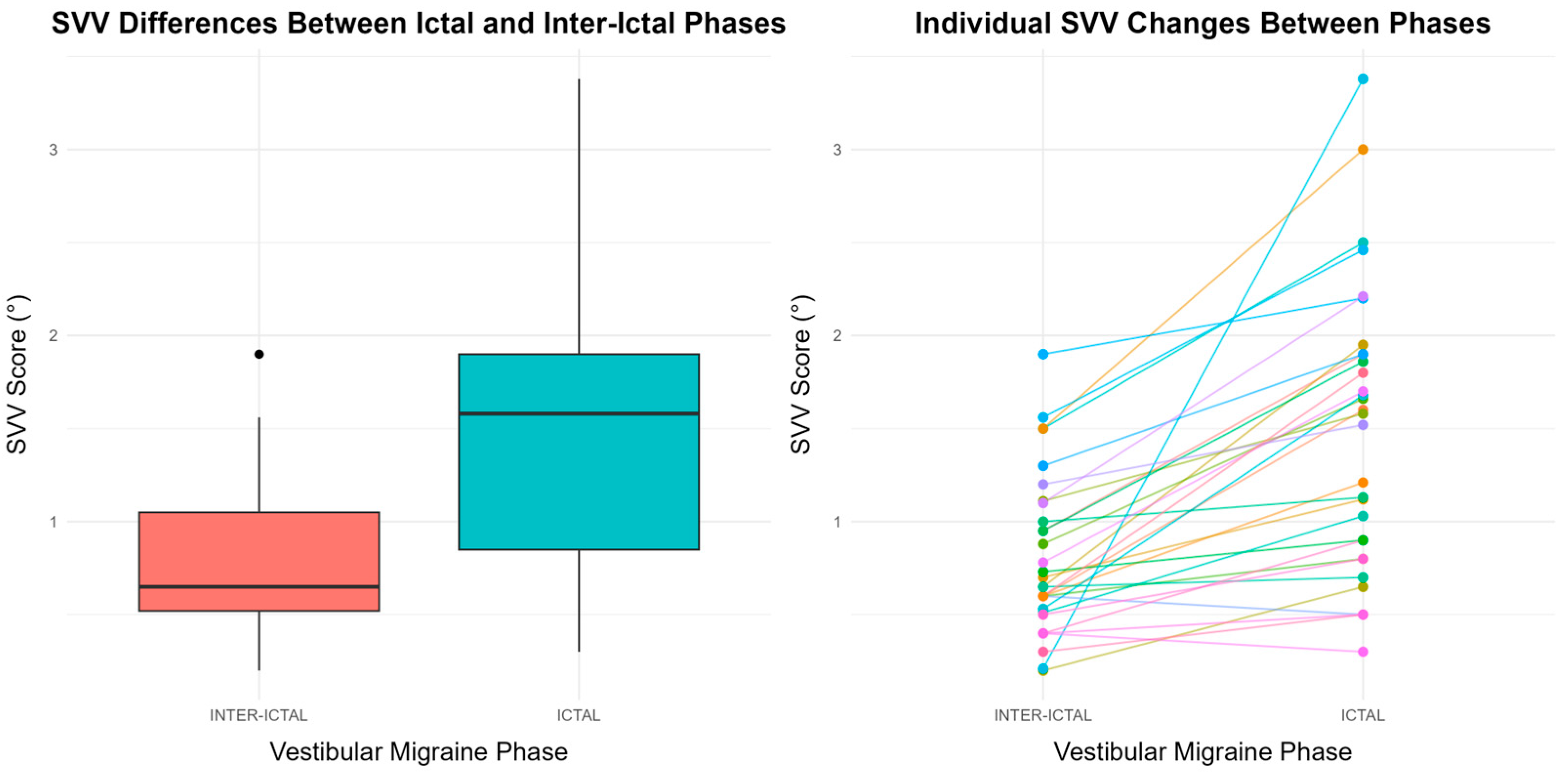
| SVV | 1.58 (0.85–1.9) | 0.65 (0.52–1.5) | 1.51 × 10−6 b |
| Existence of refixation saccades and VOR in vHIT | |||
| Overt saccades | 28 (15.05%) | 22 (11.83%) | 0.396 c |
| Covert saccades | 22 (11.83%) | 17 (9.14%) | 0.423 c |
| Right ear | |||
| Lateral SC | 1.09 (0.175) | 1.06 (0.127) | 0.083 b |
| Anterior SC | 0.912 (0.231) | 0.896 (0.120) | 0.723 b |
| Posterior SC | 0.846 (0.174) | 0.87 (0.116) | 0.416 b |
| Left ear | |||
| Lateral SC | 1.01 (0.205) | 1.01 (0.162) | 0.915 b |
| Anterior SC | 0.836 (0.197) | 0.846 (0.166) | 0.770 b |
| Posterior SC | 0.909 (0.186) | 0.892 (0.159) | 0.729 b |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Batinović, F.; Sunara, D.; Pleić, N.; Košta, V.; Gulišija, J.; Paladin, I.; Hrgović, Z.; Maglica, M.; Đogaš, Z. Clinical Features, Video Head Impulse Test, and Subjective Visual Vertical of Acute and Symptom-Free Phases in Patients with Definite Vestibular Migraine. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 825. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13040825
Batinović F, Sunara D, Pleić N, Košta V, Gulišija J, Paladin I, Hrgović Z, Maglica M, Đogaš Z. Clinical Features, Video Head Impulse Test, and Subjective Visual Vertical of Acute and Symptom-Free Phases in Patients with Definite Vestibular Migraine. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(4):825. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13040825
Chicago/Turabian StyleBatinović, Franko, Davor Sunara, Nikolina Pleić, Vana Košta, Jelena Gulišija, Ivan Paladin, Zrinka Hrgović, Mirko Maglica, and Zoran Đogaš. 2025. "Clinical Features, Video Head Impulse Test, and Subjective Visual Vertical of Acute and Symptom-Free Phases in Patients with Definite Vestibular Migraine" Biomedicines 13, no. 4: 825. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13040825
APA StyleBatinović, F., Sunara, D., Pleić, N., Košta, V., Gulišija, J., Paladin, I., Hrgović, Z., Maglica, M., & Đogaš, Z. (2025). Clinical Features, Video Head Impulse Test, and Subjective Visual Vertical of Acute and Symptom-Free Phases in Patients with Definite Vestibular Migraine. Biomedicines, 13(4), 825. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13040825








