A Senescence-Associated Gene Signature for Prognostic Prediction and Therapeutic Targeting in Adrenocortical Carcinoma
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Acquisition
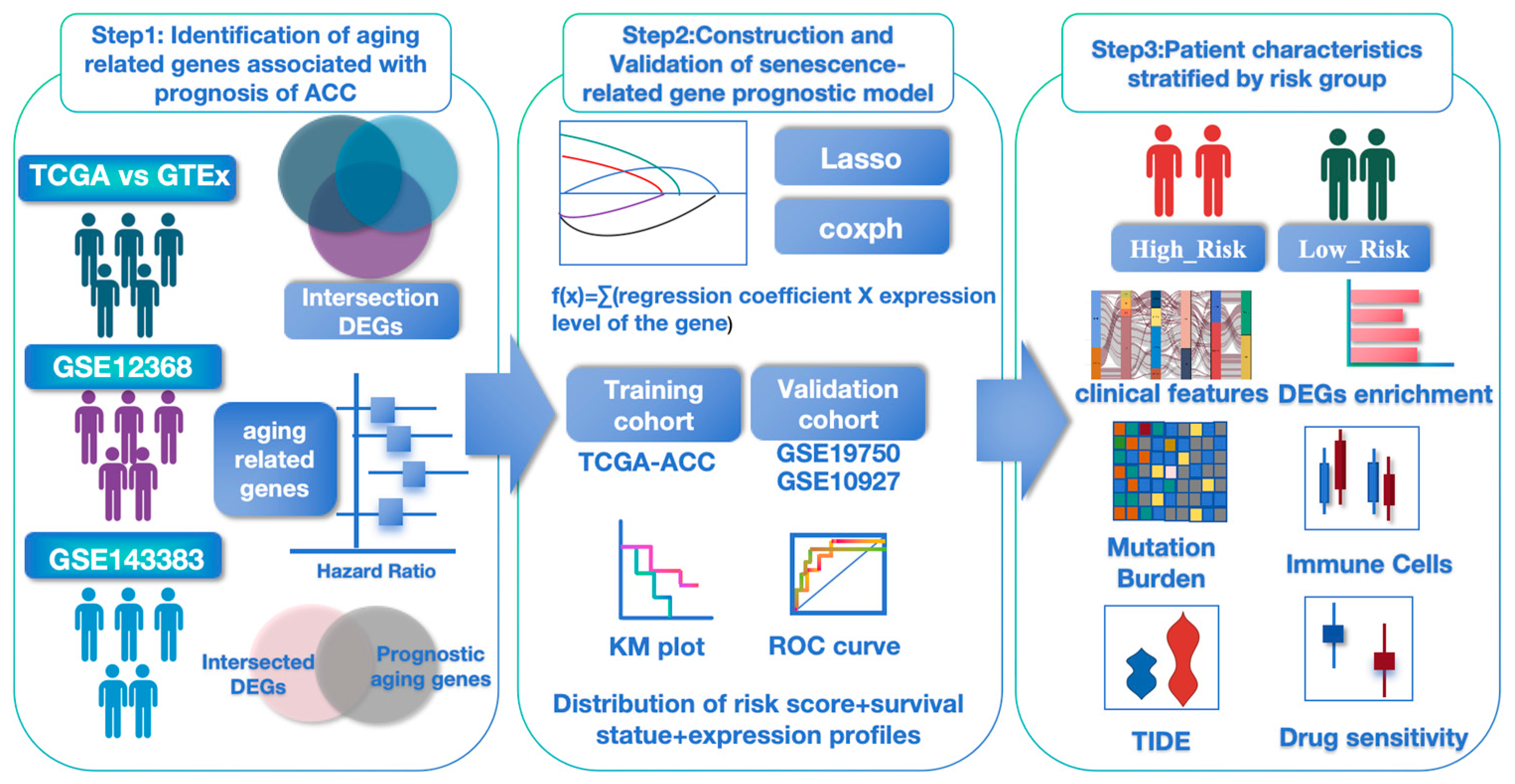
2.2. Establishment and Validation of Aging-Associated Gene Signature
2.3. Mutation Analysis
2.4. Differential Gene and Enrichment Analysis Between High-Risk and Low-Risk Groups
2.5. Immune-Related Signature Profiling
2.6. Immunotherapy Response
2.7. Drug Response Prediction
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
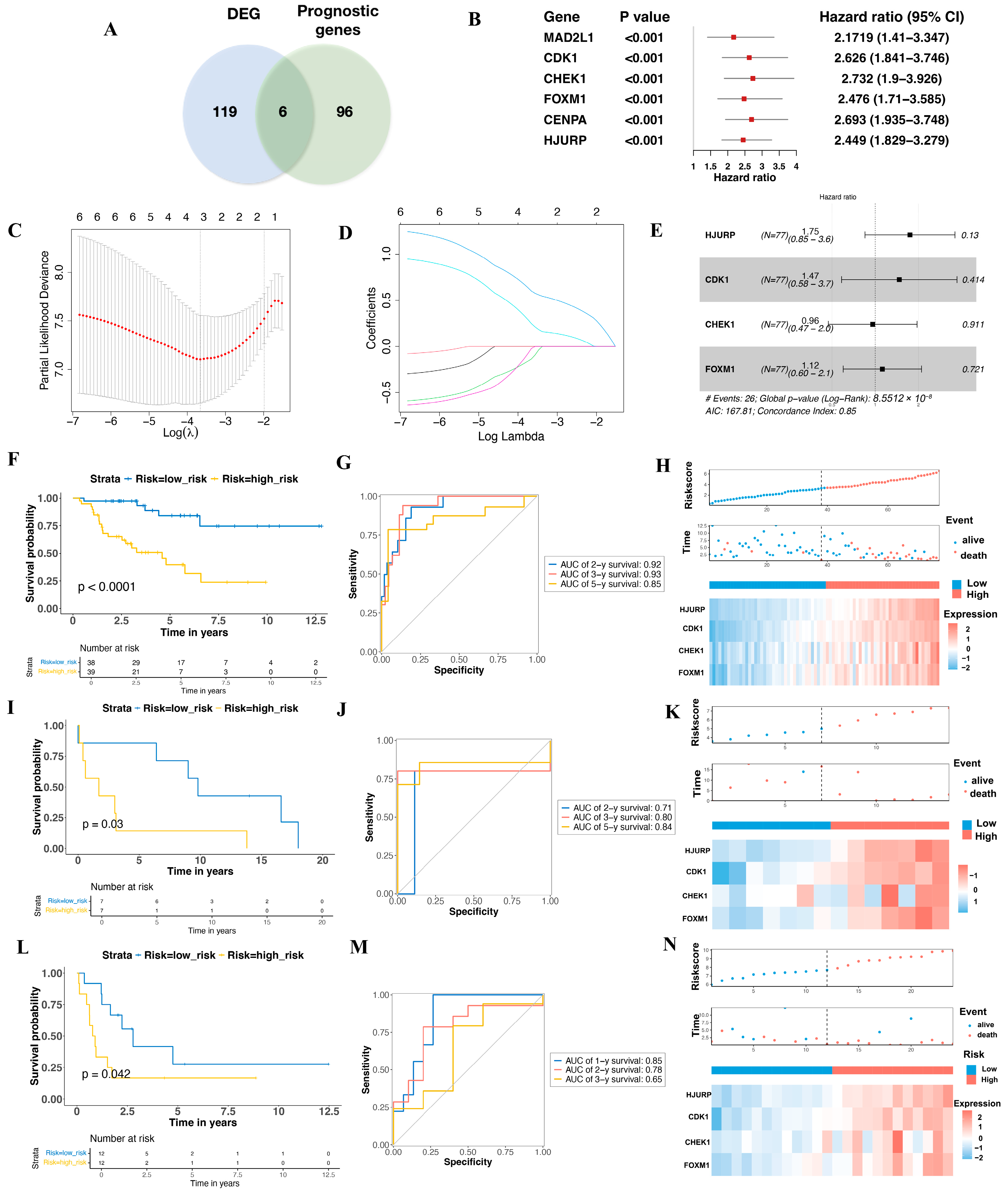
3.1. Aging-Related Prognostic Gene Screening and Senescence Model Construction in ACC
3.2. Validation the Prognostic Value of the Aging-Related Gene Signature in Two Independent GEO Cohorts
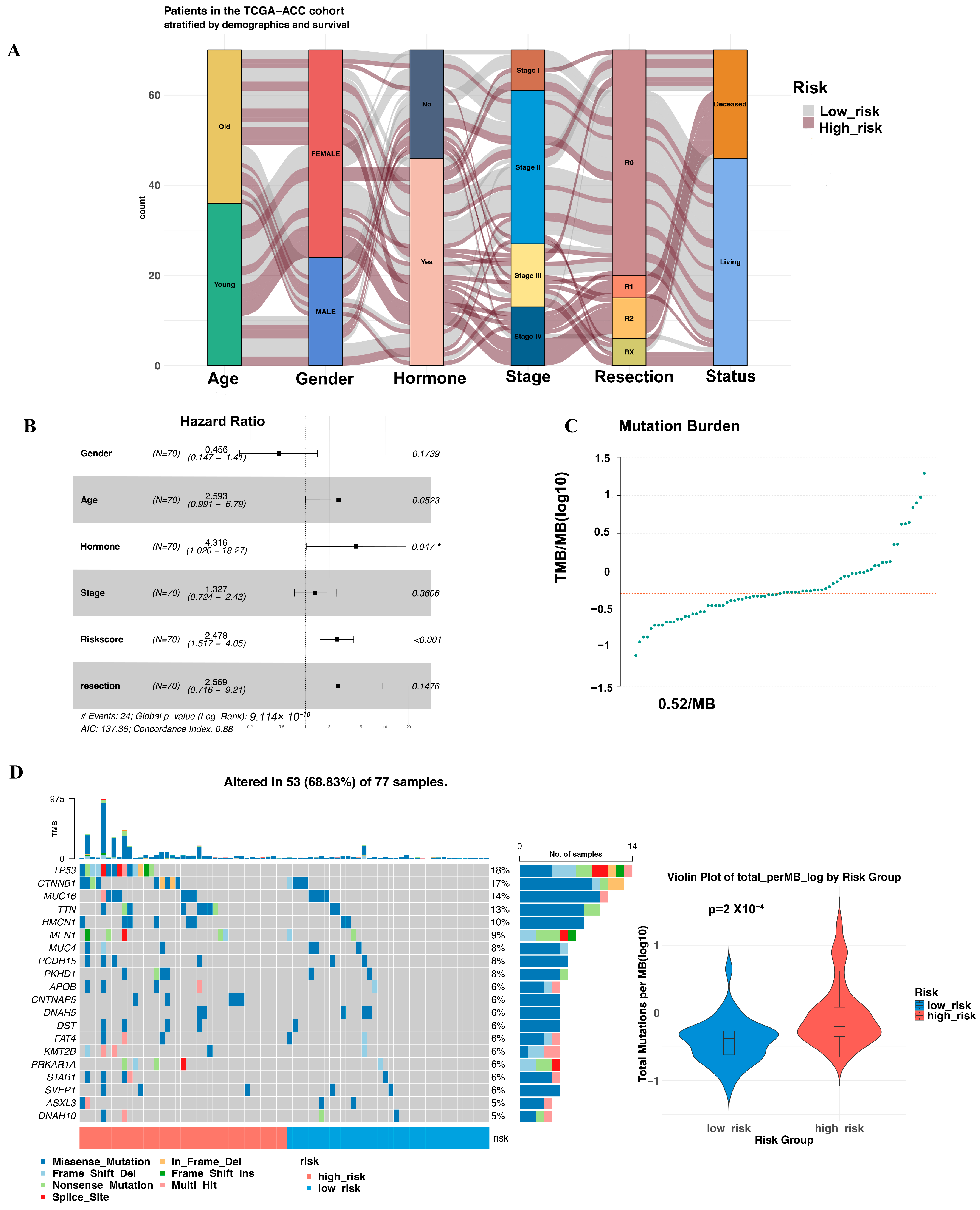
3.3. Multivariate Cox Proportional Hazards Regression Analysis of the Risk Score
3.4. Mutation Landscape Across the Two Groups
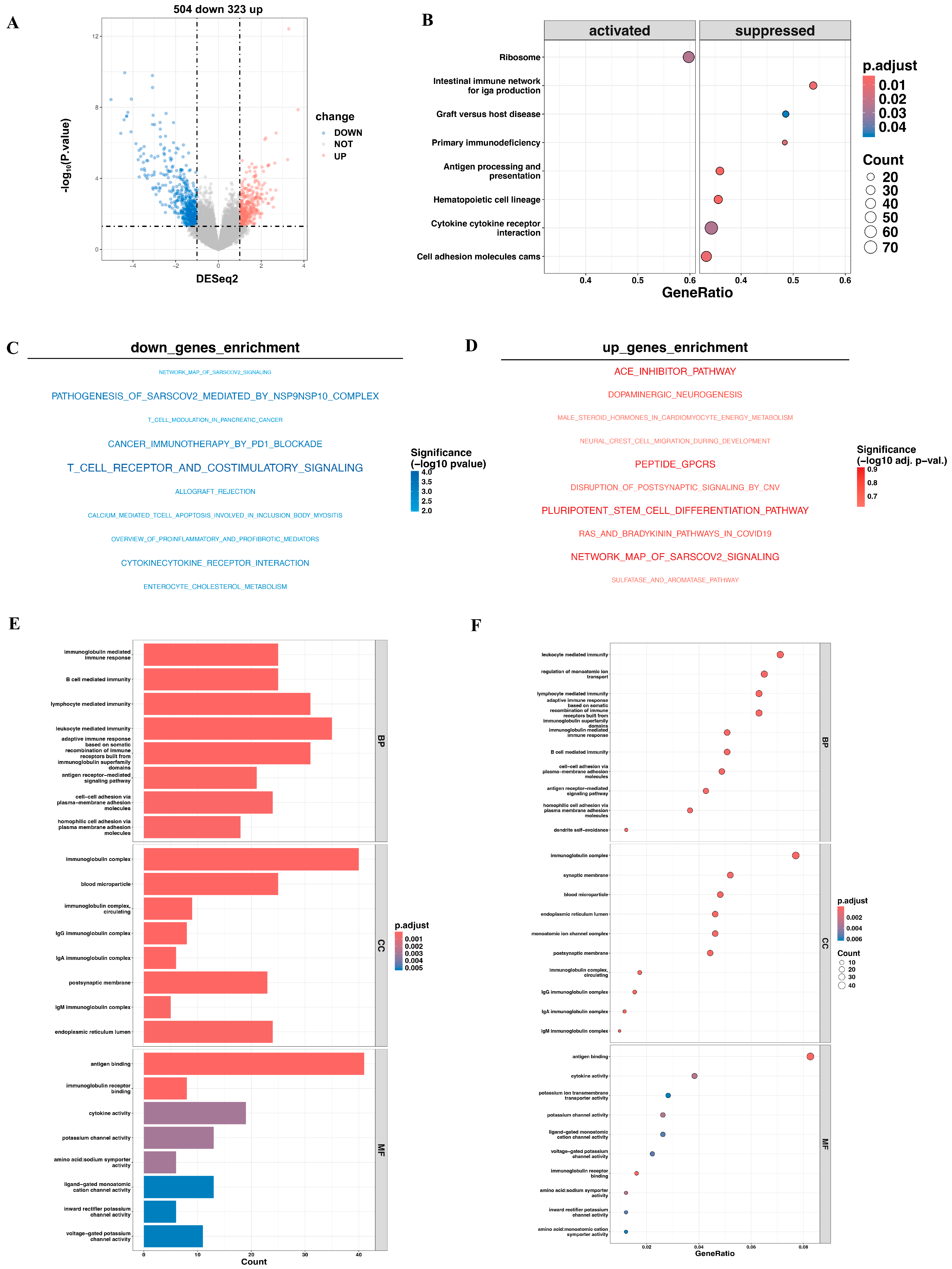
3.5. Pathway Enrichment Analysis of DEGs Expression Between High- and Low-Risk Cohorts
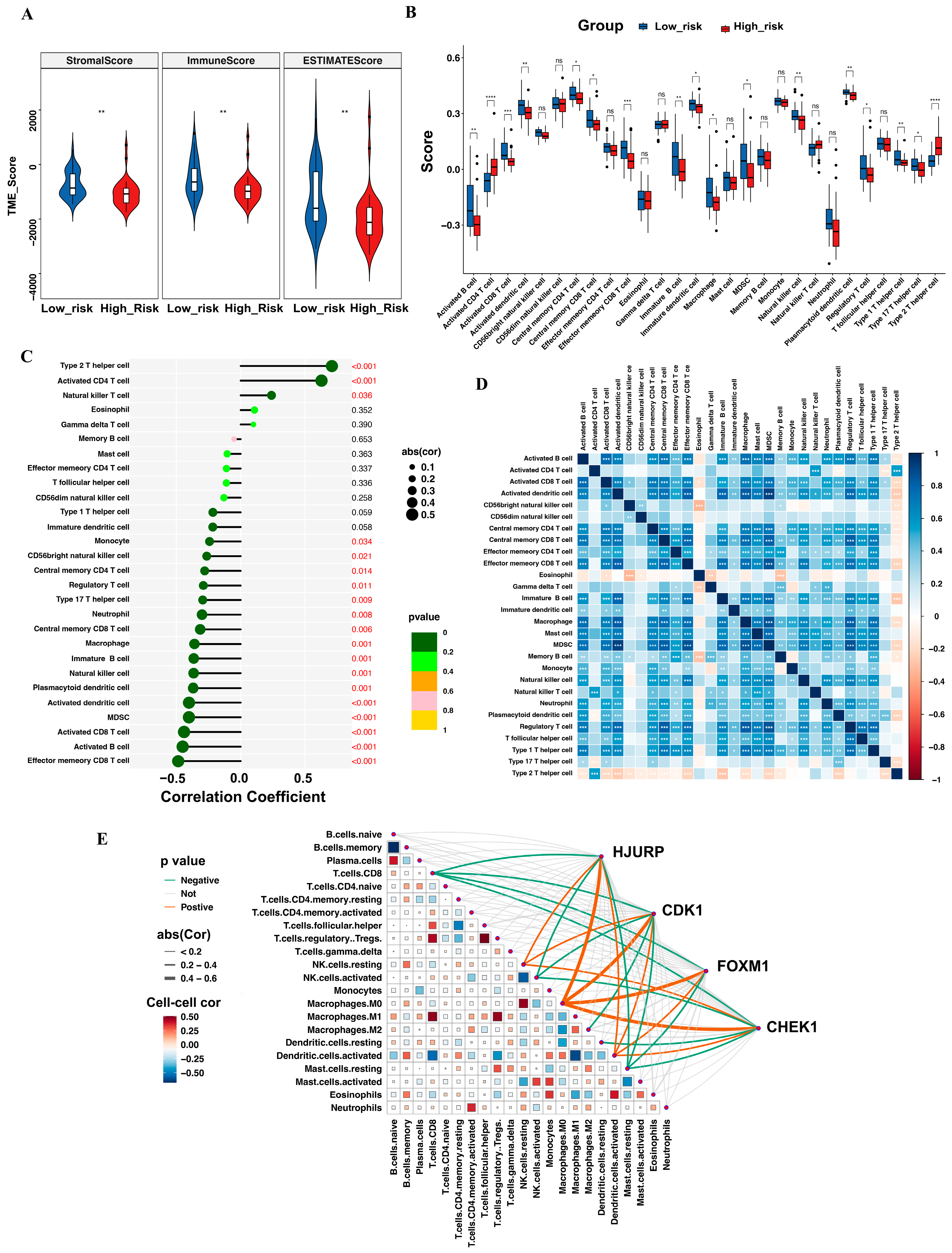
3.6. Tumor-Infiltrating Immune Cell Profile
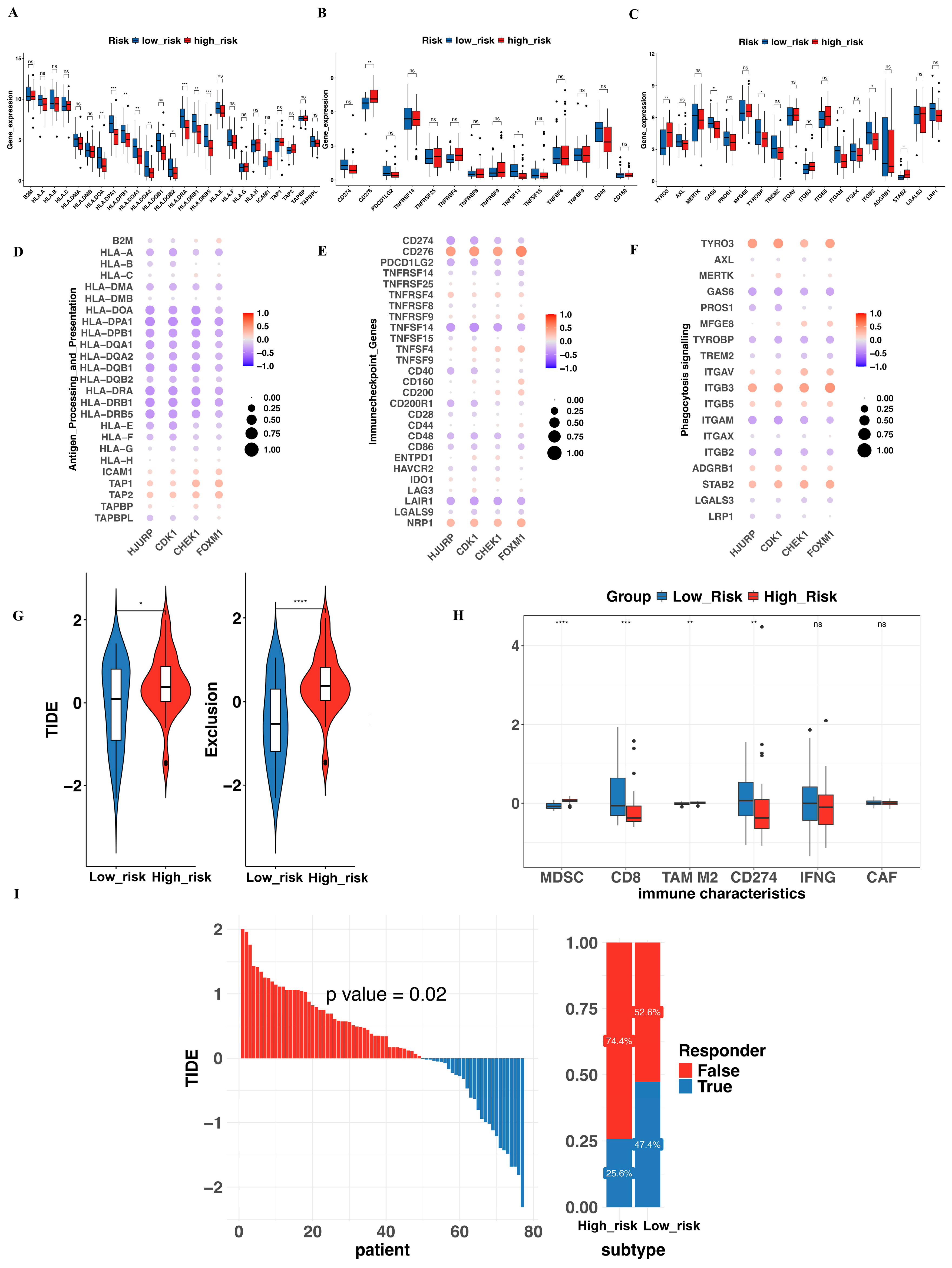
3.7. Evaluation of Immune Function and Prediction of Immunotherapy Response
3.8. Predictive Analysis for Drug Therapy
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ghosh, C.; Hu, J.; Kebebew, E. Advances in translational research of the rare cancer type adrenocortical carcinoma. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2023, 23, 805–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crona, J.; Beuschlein, F. Adrenocortical carcinoma—Towards genomics guided clinical care. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2019, 15, 548–560. [Google Scholar]
- Fassnacht, M.; Assie, G.; Baudin, E.; Eisenhofer, G.; de la Fouchardiere, C.; Haak, H.R.; de Krijger, R.; Porpiglia, F.; Terzolo, M.; Berruti, A. Adrenocortical carcinomas and malignant phaeochromocytomas: ESMO-EURACAN Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 2020, 31, 1476–1490. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Terzolo, M.; Fassnacht, M.; Perotti, P.; Libé, R.; Kastelan, D.; Lacroix, A.; Arlt, W.; Haak, H.R.; Loli, P.; Decoudier, B.; et al. Adjuvant mitotane versus surveillance in low-grade, localised adrenocortical carcinoma (ADIUVO): An international, multicentre, open label, randomised, phase 3 trial and observational study. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2023, 11, 720–730. [Google Scholar]
- Fassnacht, M.; Terzolo, M.; Allolio, B.; Baudin, E.; Haak, H.; Berruti, A.; Welin, S.; Schade-Brittinger, C.; Lacroix, A.; Jarzab, B.; et al. Combination chemotherapy in advanced adrenocortical carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 2189–2197. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Klein, O.; Senko, C.; Carlino, M.S.; Markman, B.; Jackett, L.; Gao, B.; Lum, C.; Kee, D.; Behren, A.; Palmer, J.; et al. Combination immunotherapy with ipilimumab and nivolumab in patients with advanced adrenocortical carcinoma: A subgroup analysis of CA209-538. Oncoimmunology 2021, 10, 1908771. [Google Scholar]
- Patel, S.P.; Othus, M.; Chae, Y.K.; Huynh, T.; Tan, B.; Kuzel, T.; McLeod, C.; Lopez, G.; Chen, H.X.; Sharon, E.; et al. Phase II basket trial of Dual Anti-CTLA-4 and Anti-PD-1 blockade in Rare Tumors (DART) SWOG S1609: Adrenocortical carcinoma cohort. J. Immunother Cancer. 2024, 12, e009074. [Google Scholar]
- Kroiss, M.; Quinkler, M.; Johanssen, S.; van Erp, N.P.; Lankheet, N.; Pöllinger, A.; Laubner, K.; Strasburger, C.J.; Hahner, S.; Müller, H.H.; et al. Sunitinib in refractory adrenocortical carcinoma: A phase II, single-arm, open-label trial. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 97, 3495–3503. [Google Scholar]
- Campbell, M.T.; Balderrama-Brondani, V.; Jimenez, C.; Tamsen, G.; Marcal, L.P.; Varghese, J.; Shah, A.Y.; Long, J.P.; Zhang, M.; Ochieng, J.; et al. Cabozantinib monotherapy for advanced adrenocortical carcinoma: A single-arm, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2024, 25, 649–657. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, K.; Liu, X.; Liu, Z.; Lu, Y.; Wang, X.; Li, X. Benefit of Postoperative Radiotherapy for Patients with Nonmetastatic Adrenocortical Carcinoma: A Population-Based Analysis. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2021, 19, 1425–1432. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, L.; Chen, J.; Su, T.; Jiang, L.; Han, Y.; Zhang, C.; Zhou, W.; Jiang, Y.; Zhong, X.; Wang, W. Efficacy and safety of adjuvant radiation therapy in localized adrenocortical carcinoma. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1308231. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, Z.; Luo, Y.; Yuan, Z.; Tian, Y.; Jin, T.; Xu, F. Cellular senescence and SASP in tumor progression and therapeutic opportunities. Mol. Cancer 2024, 23, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Han, J.; Elisseeff, J.H.; Demaria, M. The senescence-associated secretory phenotype and its physiological and pathological implications. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2024, 25, 958–978. [Google Scholar]
- Saleh, T.; Carpenter, V.J.; Bloukh, S.; Gewirtz, D.A. Targeting tumor cell senescence and polyploidy as potential therapeutic strategies. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2022, 81, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Birch, J.; Gil, J. Senescence and the SASP: Many. therapeutic avenues. Genes. Dev. 2020, 34, 1565–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Guo, J.; Yu, S.; Zheng, Y.; Duan, M.; Zhao, L.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Z.; Jiang, X. Cellular senescence and metabolic reprogramming: Unraveling the intricate crosstalk in the immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment. Cancer Commun. 2024, 44, 929–966. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Pitcher, L.E.; Yousefzadeh, M.J.; Niedernhofer, L.J.; Robbins, P.D.; Zhu, Y. Cellular senescence: A key therapeutic target in aging and diseases. J. Clin. Investig. 2022, 132, e158450. [Google Scholar]
- Warde, K.M.; Smith, L.J.; Liu, L.; Stubben, C.J.; Lohman, B.K.; Willett, P.W.; Ammer, J.L.; Castaneda-Hernandez, G.; Imodoye, S.O.; Zhang, C.; et al. Senescence-induced immune remodeling facilitates metastatic adrenal cancer in a sex-dimorphic manner. Nat. Aging 2023, 3, 846–865. [Google Scholar]
- Wilmouth, J.J., Jr.; Olabe, J.; Garcia-Garcia, D.; Lucas, C.; Guiton, R.; Roucher-Boulez, F.; Dufour, D.; Damon-Soubeyrand, C.; Sahut-Barnola, I.; Pointud, J.C.; et al. Sexually dimorphic activation of innate antitumor immunity prevents adrenocortical carcinoma development. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, eadd0422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, S.S.; Morais, T.; Costa, M.M.; Monteiro, M.P.; Pignatelli, D. The emerging role of the molecular marker p27 in the differential diagnosis of adrenocortical tumors. Endocr. Connect. 2013, 2, 137–145. [Google Scholar]
- Babinska, A.; Sworczak, K.; Wisniewski, P.; Nałecz, A.; Jaskiewicz, K. The role of immunohistochemistry in histopathological diagnostics of clinically “silent” incidentally detected adrenal masses. Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Diabetes 2008, 116, 246–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galassi, C.; Chan, T.A.; Vitale, I.; Galluzzi, L. The hallmarks of cancer immune evasion. Cancer Cell 2024, 42, 1825–1863. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lasser, S.A.; Ozbay Kurt, F.G.; Arkhypov, I.; Utikal, J.; Umansky, V. Myeloid-derived suppressor cells in cancer and cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2024, 21, 147–164. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Wang, J.; Chen, Z.; Luo, J.; Guo, W.; Sun, L.; Lin, L. Targeting M2-like tumor-associated macrophages is a potential therapeutic approach to overcome antitumor drug resistance. NPJ Precis. Oncol. 2024, 8, 31. [Google Scholar]
- Hayflick, L.; Moorhead, P.S. The serial cultivation of human diploid cell strains. Exp. Cell Res. 1961, 25, 585–621. [Google Scholar]
- Mannelli, M.; Gelmini, S.; Arnaldi, G.; Becherini, L.; Bemporad, D.; Crescioli, C.; Pazzagli, M.; Mantero, F.; Serio, M.; Orlando, C. Telomerase activity is significantly enhanced in malignant adrenocortical tumors in comparison to benign adrenocortical adenomas. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2000, 85, 468–470. [Google Scholar]
- Takasugi, M.; Yoshida, Y.; Hara, E.; Ohtani, N. The role of cellular senescence and SASP in tumour microenvironment. FEBS J. 2023, 290, 1348–1361. [Google Scholar]
- Kyjacova, L.; Saup, R.; Rönsch, K.; Wallbaum, S.; Dukowic-Schulze, S.; Foss, A.; Scherer, S.D.; Rothley, M.; Neeb, A.; Grau, N.; et al. IER2-induced senescence drives melanoma invasion through osteopontin. Oncogene 2021, 40, 6494–6512. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Y.H.; Choi, Y.W.; Lee, J.; Soh, E.Y.; Kim, J.H.; Park, T.J. Senescent tumor cells lead the collective invasion in thyroid cancer. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15208. [Google Scholar]
- Piskorz, W.M.; Cechowska-Pasko, M. Senescence of Tumor Cells in Anticancer Therapy-Beneficial and Detrimental Effects. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 11082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tront, J.S.; Hoffman, B.; Liebermann, D.A. Gadd45a suppresses Ras-driven mammary tumorigenesis by activation of c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase and p38 stress signaling resulting in apoptosis and senescence. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 8448–8454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Yuan, Q.; Chu, Y.M.; Jiang, H.Y.; Zhao, J.H.; Su, Q.; Huo, D.Q.; Zhang, X.F. Advances in holiday junction recognition protein (HJURP): Structure, molecular functions, and roles in cancer. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2023, 11, 1106638. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Zheng, J.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y. Pan-cancer analysis based on epigenetic modification explains the value of HJURP in the tumor microenvironment. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 20871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, M.; Jia, Y.; Chen, Y.; Yang, J.; Xu, L.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, J.; Li, Z.; Chen, C.; Ju, S.; et al. HJURP regulates cell proliferation and chemo-resistance via YAP1/NDRG1 transcriptional axis in triple-negative breast cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2022, 13, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.J.; Li, X.; Shi, P.; Ding, H.Y.; Liu, Y.P.; Li, T.; Lin, P.P.; Wang, Y.S.; Zhang, G.Q.; Cao, Y. Holliday junction recognition protein promotes pancreatic cancer growth and metastasis via modulation of the MDM2/p53 signaling. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, W.; Zhu, W.; Xiao, C.; Li, X.; Wang, Y.; Han, Y.; Zheng, J.; Li, Y.; Li, M.; Wen, X. HJURP promotes proliferation in prostate cancer cells through increasing CDKN1A degradation via the GSK3β/JNK signaling pathway. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Y.; Ouyang, G.L.; Yao, W.X.; Zhu, Y.J.; Li, X.; Huang, L.X.; Yang, X.W.; Jiang, W.J. Knockdown of HJURP inhibits non-small cell lung cancer cell proliferation, migration, and invasion by repressing Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2019, 23, 3847–3856. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, F.; Yuan, D.; Song, J.; Chen, W.; Wang, W.; Zhu, G.; Hu, B.; Chen, X.; Zhu, J. HJURP is a prognostic biomarker for clear cell renal cell carcinoma and is linked to immune infiltration. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2021, 99, 107899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Bode, A.M.; Zhang, T. Targeting CDK1 in cancer: Mechanisms and implications. NPJ Precis. Oncol. 2023, 7, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, L.; Yang, Y.; Li, W.; Zheng, X.; Liu, J.; Li, S.; Yang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Ge, B.; Zhang, S.; et al. CDK1 serves as a therapeutic target of adrenocortical carcinoma via regulating epithelial-mesenchymal transition, G2/M phase transition, and PANoptosis. J. Transl. Med. 2022, 20, 444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.A.; Khan, P.; Ahmad, A.; Fatima, M.; Nasser, M.W. FOXM1: A small fox that makes more tracks for cancer progression and metastasis. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2023, 92, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liang, S.K.; Hsu, C.C.; Song, H.L.; Huang, Y.C.; Kuo, C.W.; Yao, X.; Li, C.C.; Yang, H.C.; Hung, Y.L.; Chao, S.Y.; et al. FOXM1 is required for small cell lung cancer tumorigenesis and associated with poor clinical prognosis. Oncogene 2021, 40, 4847–4858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pilié, P.G.; Tang, C.; Mills, G.B.; Yap, T.A. State-of-the-art strategies for targeting the DNA damage response in cancer. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 16, 81–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaaks, P.; Coker, E.A.; Vis, D.J.; Edwards, O.; Carpenter, E.F.; Leto, S.M.; Dwane, L.; Sassi, F.; Lightfoot, H.; Barthorpe, S.; et al. Effective drug combinations in breast, colon and pancreatic cancer cells. Nature 2022, 603, 166–173. [Google Scholar]
- Kandhaya-Pillai, R.; Miro-Mur, F.; Alijotas-Reig, J.; Tchkonia, T.; Schwartz, S.; Kirkland, J.L.; Oshima, J. Key elements of cellular senescence involve transcriptional repression of mitotic and DNA repair genes through the p53-p16/RB-E2F-DREAM complex. Aging 2023, 15, 4012–4034. [Google Scholar]
- Galon, J.; Bruni, D. Approaches to treat immune hot, altered and cold tumours with combination immunotherapies. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2019, 18, 197–218. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Huang, D.; Saw, P.E.; Song, E. Turning cold tumors hot: From molecular mechanisms to clinical applications. Trends Immunol. 2022, 43, 523–545. [Google Scholar]
- Pegna, G.J.; Roper, N.; Kaplan, R.N.; Bergsland, E.; Kiseljak-Vassiliades, K.; Habra, M.A.; Pommier, Y.; Del Rivero, J. The Immunotherapy Landscape in Adrenocortical Cancer. Cancers 2021, 13, 2660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araujo-Castro, M.; Pascual-Corrales, E.; Molina-Cerrillo, J.; Alonso-Gordoa, T. Immunotherapy in Adrenocortical Carcinoma: Predictors of Response, Efficacy, Safety, and Mechanisms of Resistance. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remde, H.; Schmidt-Pennington, L.; Reuter, M.; Landwehr, L.S.; Jensen, M.; Lahner, H.; Kimpel, O.; Altieri, B.; Laubner, K.; Schreiner, J.; et al. Outcome of immunotherapy in adrenocortical carcinoma: A retrospective cohort study. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2023, 188, 485–493. [Google Scholar]
- Landwehr, L.S.; Altieri, B.; Schreiner, J.; Sbiera, I.; Weigand, I.; Kroiss, M.; Fassnacht, M.; Sbiera, S. Interplay between glucocorticoids and tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes on the prognosis of adrenocortical carcinoma. J. Immunother. Cancer. 2020, 8, e000469. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, S.; Cherniack, A.D.; Dewal, N.; Moffitt, R.A.; Danilova, L.; Murray, B.A.; Lerario, A.M.; Else, T.; Knijnenburg, T.A.; Ciriello, G.; et al. Comprehensive Pan-Genomic Characterization of Adrenocortical Carcinoma. Cancer Cell 2016, 30, 2976. [Google Scholar]
- Pai, S.G.; Carneiro, B.A.; Mota, J.M.; Costa, R.; Leite, C.A.; Barroso-Sousa, R.; Kaplan, J.B.; Chae, Y.K.; Giles, F.J. Wnt/beta-catenin pathway: Modulating anticancer immune response. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2017, 10, 101. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gaujoux, S.; Grabar, S.; Fassnacht, M.; Ragazzon, B.; Launay, P.; Libé, R.; Chokri, I.; Audebourg, A.; Royer, B.; Sbiera, S.; et al. β-catenin activation is associated with specific clinical and pathologic characteristics and a poor outcome in adrenocortical carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 328–336. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ruiz de Galarreta, M.; Bresnahan, E.; Molina-Sánchez, P.; Lindblad, K.E.; Maier, B.; Sia, D.; Puigvehi, M.; Miguela, V.; Casanova-Acebes, M.; Dhainaut, M.; et al. β-Catenin Activation Promotes Immune Escape and Resistance to Anti-PD-1 Therapy in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancer Discov. 2019, 9, 1124–1141. [Google Scholar]
- Behmoaras, J.; Gil, J. Similarities and interplay between senescent cells and macrophages. J. Cell. Biol. 2021, 220, e202010162. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, K.; Halima, A.; Chan, T.A. Antigen presentation in cancer—Mechanisms and clinical implications for immunotherapy. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 20, 604–623. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, M.; Chen, S.; Li, K.; Wang, G.; Xiong, G.; Ling, R.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, Z.; Han, H.; Chen, Z.; et al. CD276-dependent efferocytosis by tumor-associated macrophages promotes immune evasion in bladder cancer. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 2818. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Li, Y.; Jia, L.; Kim, J.K.; Li, J.; Deng, P.; Zhang, W.; Krebsbach, P.H.; Wang, C.Y. CD276 expression enables squamous cell carcinoma stem cells to evade immune surveillance. Cell Stem Cell 2021, 28, 1597–1613.e7. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.; Somasundaram, A.; Manne, S.; Gocher, A.M.; Szymczak-Workman, A.L.; Vignali, K.M.; Scott, E.N.; Normolle, D.P.; John Wherry, E.; Lipson, E.J.; et al. Neuropilin-1 is a T cell memory checkpoint limiting long-term antitumor immunity. Nat. Immunol. 2020, 21, 1010–1021. [Google Scholar]
- Fernández-Palanca, P.; Payo-Serafín, T.; Méndez-Blanco, C.; San-Miguel, B.; Tuñón, M.J.; González-Gallego, J.; Mauriz, J.L. Neuropilins as potential biomarkers in hepatocellular carcinoma: A systematic review of basic and clinical implications. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2023, 29, 293–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skeate, J.G.; Otsmaa, M.E.; Prins, R.; Fernandez, D.J.; Da Silva, D.M.; Kast, W.M. TNFSF14: LIGHTing the Way for Effective Cancer Immunotherapy. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeRyckere, D.; Huelse, J.M.; Earp, H.S.; Graham, D.K. TAM family kinases as therapeutic targets at the interface of cancer and immunity. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 20, 755–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Z.; Lim, S.O.; Yan, M.; Hsu, J.L.; Yao, J.; Wei, Y.; Chang, S.S.; Yamaguchi, H.; Lee, H.H.; Ke, B.; et al. TYRO3 induces anti-PD-1/PD-L1 therapy resistance by limiting innate immunity and tumoral ferroptosis. J. Clin. Investig. 2021, 131, e139434. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhu, C.; Kong, Z.; Wang, B.; Cheng, W.; Wu, A.; Meng, X. ITGB3/CD61: A hub modulator and target in the tumor microenvironment. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2019, 11, 7195–7208. [Google Scholar]
- Fuentes, P.; Sesé, M.; Guijarro, P.J.; Emperador, M.; Sánchez-Redondo, S.; Peinado, H.; Hümmer, S.; Ramón, Y.C.S. ITGB3-mediated uptake of small extracellular vesicles facilitates intercellular communication in breast cancer cells. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grover, A.; Sanseviero, E.; Timosenko, E.; Gabrilovich, D.I. Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells: A Propitious Road to Clinic. Cancer Discov. 2021, 11, 2693–2706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Shi, H.; Zhang, B.; Ou, X.; Ma, Q.; Chen, Y.; Shu, P.; Li, D.; Wang, Y. Myeloid-derived suppressor cells as immunosuppressive regulators and therapeutic targets in cancer. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, K.; Cai, N.; Zhu, J.; Yang, X.; Liang, H.; Zhang, W. Tumor-associated macrophages in liver cancer: From mechanisms to therapy. Cancer Commun. 2022, 42, 1112–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; Luo, T.; Dong, P.; Zhang, N.; Chen, J.; Zhang, S.; Dong, L.; Janssen, H.L.A.; Zhang, S. M2-polarized tumor-associated macrophages promote epithelial-mesenchymal transition via activation of the AKT3/PRAS40 signaling pathway in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. J. Cell Biochem. 2020, 121, 2828–2838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, X.; Wang, J.; Lu, D.; Xu, X. Targeting tumor-associated macrophages to synergize tumor immunotherapy. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 75. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Johnson, K.C.C.; Gatti-Mays, M.E.; Li, Z. Emerging strategies in targeting tumor-resident myeloid cells for cancer immunotherapy. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2022, 15, 118. [Google Scholar]
- Sebastian, M.; Reck, M.; Waller, C.F.; Kortsik, C.; Frickhofen, N.; Schuler, M.; Fritsch, H.; Gaschler-Markefski, B.; Hanft, G.; Munzert, G.; et al. The efficacy and safety of BI 2536, a novel Plk-1 inhibitor, in patients with stage IIIB/IV non-small cell lung cancer who had relapsed after, or failed, chemotherapy: Results from an open-label, randomized phase II clinical trial. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2010, 5, 1060–1067. [Google Scholar]
- Mateo, J.; Olmos, D.; Dumez, H.; Poondru, S.; Samberg, N.L.; Barr, S.; Van Tornout, J.M.; Jie, F.; Sandhu, S.; Tan, D.S.; et al. A first in man, dose-finding study of the mTORC1/mTORC2 inhibitor OSI-027 in patients with advanced solid malignancies. Br. J. Cancer 2016, 114, 889–896. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kelly, R.J.; Thomas, A.; Rajan, A.; Chun, G.; Lopez-Chavez, A.; Szabo, E.; Spencer, S.; Carter, C.A.; Guha, U.; Khozin, S.; et al. A phase I/II study of sepantronium bromide (YM155, survivin suppressor) with paclitaxel and carboplatin in patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2013, 24, 2601–2606. [Google Scholar]
- Falchook, G.S.; Bastida, C.C.; Kurzrock, R. Aurora Kinase Inhibitors in Oncology Clinical Trials: Current State of the Progress. Semin. Oncol. 2015, 42, 832–848. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Reiten, O.K.; Wilvang, M.A.; Mitchell, S.J.; Hu, Z.; Fang, E.F. Preclinical and clinical evidence of NAD(+) precursors in health, disease, and ageing. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2021, 199, 111567. [Google Scholar]
- von Mehren, M.; George, S.; Heinrich, M.C.; Schuetze, S.M.; Yap, J.T.; Yu, J.Q.; Abbott, A.; Litwin, S.; Crowley, J.; Belinsky, M.; et al. Linsitinib (OSI-906) for the Treatment of Adult and Pediatric Wild-Type Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors, a SARC Phase II Study. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 26, 1837–1845. [Google Scholar]
- Respondek, M.; Beberok, A.; Rzepka, Z.; Rok, J.; Wrześniok, D. MIM1 induces COLO829 melanoma cell death through mitochondrial membrane breakdown, GSH depletion, and DNA damage. Fundam. Clin. Pharmacol. 2020, 34, 20–31. [Google Scholar]
- Song, B.; Jiang, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Lin, Y.; Liu, J. ML323 suppresses the progression of ovarian cancer via regulating USP1-mediated cell cycle. Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 917481. [Google Scholar]
- Mizunuma, M.; Redon, C.E.; Saha, L.K.; Tran, A.D.; Dhall, A.; Sebastian, R.; Taniyama, D.; Kruhlak, M.J.; Reinhold, W.C.; Takebe, N.; et al. Acetalax (Oxyphenisatin Acetate, NSC 59687) and Bisacodyl Cause Oncosis in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cell Lines by Poisoning the Ion Exchange Membrane Protein TRPM4. Cancer Res. Commun. 2024, 4, 2101–2111. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Urbina-Jara, L.K.; Martinez-Ledesma, E.; Rojas-Martinez, A.; Rodriguez-Recio, F.R.; Ortiz-Lopez, R. DNA Repair Genes as Drug Candidates for Early Breast Cancer Onset in Latin America: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 13030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bussey, K.J.; Bapat, A.; Linnehan, C.; Wandoloski, M.; Dastrup, E.; Rogers, E.; Gonzales, P.; Demeure, M.J. Targeting polo-like kinase 1, a regulator of p53, in the treatment of adrenocortical carcinoma. Clin. Transl. Med. 2016, 5, 1. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Driscoll, D.L.; Chakravarty, A.; Bowman, D.; Shinde, V.; Lasky, K.; Shi, J.; Vos, T.; Stringer, B.; Amidon, B.; D’Amore, N.; et al. Plk1 inhibition causes post-mitotic DNA damage and senescence in a range of human tumor cell lines. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e111060. [Google Scholar]

| Low Risk Group (n = 36) | High Risk Group (n = 34) | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 46.94 ± 2.62 | 46.84 ± 2.69 | 0.335 |
| Gender | |||
| Female | 23 (63.89%) | 23 (67.65%) | 0.741 |
| Male | 13 (36.11%) | 11 (32.35%) | |
| Hormone Secretion | |||
| Yes | 21 (58.33%) | 25 (73.53%) | 0.181 |
| No | 15 (41.67%) | 9 (26.47%) | |
| ENSAT stage | <0.001 | ||
| I | 6 (16.67%) | 3 (8.82%) | |
| II | 24 (66.67%) | 10 (29.41%) | |
| III | 4 (11.10%) | 10 (29.41%) | |
| IV | 2 (5.56%) | 11 (32.35%) | |
| Resection Status | <0.001 | ||
| R0 | 34 (94.44%) | 16 (47.05%) | |
| R1 | 0 | 5 (14.71%) | |
| R2 | 1 (2.78%) | 8 (23.53%) | |
| Rx | 1 (2.78%) | 5 (14.71%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Peng, H.; Chen, Q.; Ye, L.; Wang, W. A Senescence-Associated Gene Signature for Prognostic Prediction and Therapeutic Targeting in Adrenocortical Carcinoma. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 894. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13040894
Peng H, Chen Q, Ye L, Wang W. A Senescence-Associated Gene Signature for Prognostic Prediction and Therapeutic Targeting in Adrenocortical Carcinoma. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(4):894. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13040894
Chicago/Turabian StylePeng, Hangya, Qiujing Chen, Lei Ye, and Weiqing Wang. 2025. "A Senescence-Associated Gene Signature for Prognostic Prediction and Therapeutic Targeting in Adrenocortical Carcinoma" Biomedicines 13, no. 4: 894. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13040894
APA StylePeng, H., Chen, Q., Ye, L., & Wang, W. (2025). A Senescence-Associated Gene Signature for Prognostic Prediction and Therapeutic Targeting in Adrenocortical Carcinoma. Biomedicines, 13(4), 894. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13040894






