Neuroimaging Changes in the Sensorimotor Network and Visual Network in Bipolar Disorder and Their Relationship with Genetic Characteristics
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Procedure
2.3. Imaging Data Acquisition and Preprocessing
2.4. FC Analysis
2.5. Gene Expression Data
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Demographic and Clinical Characteristics
3.2. The Treatment Outcome
3.3. FC Analysis in Pre-Treatment Patients with BD and HCs
3.4. FC Analysis in Pre-Treatment and Post-Treatment Patients with BD
3.5. Correlation Analysis Results
3.6. Enrichment Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- McIntyre, R.S.; Berk, M.; Brietzke, E.; Goldstein, B.I.; López-Jaramillo, C.; Kessing, L.V.; Malhi, G.S.; Nierenberg, A.A.; Rosenblat, J.D.; Majeed, A.; et al. Bipolar disorders. Lancet 2020, 396, 1841–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, M.; Lu, L.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Q.; Ungvari, G.S.; Ng, C.H.; Yuan, Z.; Xiang, Y.; Wang, G.; Xiang, Y.T. Prevalence of suicide attempts in bipolar disorder: A systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. Epidemiol. Psychiatr. Sci. 2019, 29, e63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tietbohl-Santos, B.; Chiamenti, P.; Librenza-Garcia, D.; Cassidy, R.; Zimerman, A.; Manfro, G.G.; Kapczinski, F.; Passos, I.C. Risk factors for suicidality in patients with panic disorder: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2019, 105, 34–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grande, I.; Berk, M.; Birmaher, B.; Vieta, E. Bipolar disorder. Lancet 2016, 387, 1561–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dean, B.B.; Gerner, D.; Gerner, R.H. A systematic review evaluating health-related quality of life, work impairment, and healthcare costs and utilization in bipolar disorder. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 2004, 20, 139–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonda, X.; Pompili, M.; Serafini, G.; Montebovi, F.; Campi, S.; Dome, P.; Duleba, T.; Girardi, P.; Rihmer, Z. Suicidal behavior in bipolar disorder: Epidemiology, characteristics and major risk factors. J. Affect. Disord. 2012, 143, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas, C.; López-Jaramillo, C.; Vieta, E. A systematic literature review of resting state network--functional MRI in bipolar disorder. J. Affect. Disord. 2013, 150, 727–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syan, S.K.; Smith, M.; Frey, B.N.; Remtulla, R.; Kapczinski, F.; Hall, G.B.C.; Minuzzi, L. Resting-state functional connectivity in individuals with bipolar disorder during clinical remission: A systematic review. J. Psychiatry Neurosci. 2018, 43, 298–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voineskos, A.N.; Hawco, C.; Neufeld, N.H.; Turner, J.A.; Ameis, S.H.; Anticevic, A.; Buchanan, R.W.; Cadenhead, K.; Dazzan, P.; Dickie, E.W.; et al. Functional magnetic resonance imaging in schizophrenia: Current evidence, methodological advances, limitations and future directions. World Psychiatry Off. J. World Psychiatr. Assoc. (WPA) 2024, 23, 26–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Bo, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Li, F.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, C. Disrupted default mode network connectivity in bipolar disorder: A resting-state fMRI study. BMC Psychiatry 2024, 24, 428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magioncalda, P.; Martino, M.; Conio, B.; Escelsior, A.; Piaggio, N.; Presta, A.; Marozzi, V.; Rocchi, G.; Anastasio, L.; Vassallo, L.; et al. Functional connectivity and neuronal variability of resting state activity in bipolar disorder—Reduction and decoupling in anterior cortical midline structures. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2015, 36, 666–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Todeva-Radneva, A.; Kandilarova, S.; Paunova, R.; Stoyanov, D.; Zdravkova, T.; Sladky, R. Functional Connectivity of the Anterior Cingulate Cortex and the Right Anterior Insula Differentiates between Major Depressive Disorder, Bipolar Disorder and Healthy Controls. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Huang, H.; Jia, Y.; Zheng, S.; Zhong, S.; Chen, G.; Huang, L.; Huang, R. Abnormal dynamic functional network connectivity in unmedicated bipolar and major depressive disorders based on the triple-network model. Psychol. Med. 2020, 50, 465–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandel, E.R.; Schwartz, J.H.; Jessell, T.M.; Siegelbaum, S.; Hudspeth, A.J.; Mack, S. Principles of Neural Science; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2000; Volume 4. [Google Scholar]
- Fox, M.D.; Raichle, M.E. Spontaneous fluctuations in brain activity observed with functional magnetic resonance imaging. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2007, 8, 700–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Stein, E.A. Resting state functional connectivity: Its physiological basis and application in neuropharmacology. Neuropharmacology 2014, 84, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeo, B.T.; Krienen, F.M.; Chee, M.W.; Buckner, R.L. Estimates of segregation and overlap of functional connectivity networks in the human cerebral cortex. Neuroimage 2014, 88, 212–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Li, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, B.; Liu, X.; Mo, L.; Chen, Q. Multisensory Competition Is Modulated by Sensory Pathway Interactions with Fronto-Sensorimotor and Default-Mode Network Regions. J. Neurosci. 2015, 35, 9064–9077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, R.; Di, X.; Taylor, P.A.; Gohel, S.; Tsai, Y.H.; Biswal, B.B. Functional topography of the thalamocortical system in human. Brain Struct. Funct. 2016, 221, 1971–1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Davis, H.I.; Wolff, A.; Northoff, G. Thalamo-Sensorimotor Functional Connectivity Correlates with World Ranking of Olympic, Elite, and High Performance Athletes. Neural Plast. 2017, 2017, 1473783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishida, T.; Donishi, T.; Iwatani, J.; Yamada, S.; Takahashi, S.; Ukai, S.; Shinosaki, K.; Terada, M.; Kaneoke, Y. Interhemispheric disconnectivity in the sensorimotor network in bipolar disorder revealed by functional connectivity and diffusion tensor imaging analysis. Heliyon 2017, 3, e00335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walton, E.; Turner, J.; Gollub, R.L.; Manoach, D.S.; Yendiki, A.; Ho, B.C.; Sponheim, S.R.; Calhoun, V.D.; Ehrlich, S. Cumulative genetic risk and prefrontal activity in patients with schizophrenia. Schizophr. Bull. 2013, 39, 703–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flint, J. The genetic basis of major depressive disorder. Mol. Psychiatry 2023, 28, 2254–2265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connell, K.S.; Coombes, B.J. Genetic contributions to bipolar disorder: Current status and future directions. Psychol. Med. 2021, 51, 2156–2167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chao-Gan, Y.; Yu-Feng, Z. DPARSF: A MATLAB Toolbox for “Pipeline” Data Analysis of Resting-State fMRI. Front. Syst. Neurosci. 2010, 4, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.W.; Dong, Z.Y.; Long, X.Y.; Li, S.F.; Zuo, X.N.; Zhu, C.Z.; He, Y.; Yan, C.G.; Zang, Y.F. REST: A toolkit for resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging data processing. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e25031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitfield-Gabrieli, S.; Nieto-Castanon, A. Conn: A functional connectivity toolbox for correlated and anticorrelated brain networks. Brain Connect. 2012, 2, 125–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hawrylycz, M.J.; Lein, E.S.; Guillozet-Bongaarts, A.L.; Shen, E.H.; Ng, L.; Miller, J.A.; van de Lagemaat, L.N.; Smith, K.A.; Ebbert, A.; Riley, Z.L.; et al. An anatomically comprehensive atlas of the adult human brain transcriptome. Nature 2012, 489, 391–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aragona, M. Unitary psychosis (Einheitspsychose): A conceptual history. J. Affect. Disord. 2024, 359, 86–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoyanov, D. State and trait markers to define the continuum of affective disorders. J. Affect. Disord. 2025, 372, 37–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mai, J.K.; Majtanik, M. Toward a Common Terminology for the Thalamus. Front. Neuroanat. 2018, 12, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anticevic, A.; Cole, M.W.; Repovs, G.; Murray, J.D.; Brumbaugh, M.S.; Winkler, A.M.; Savic, A.; Krystal, J.H.; Pearlson, G.D.; Glahn, D.C. Characterizing thalamo-cortical disturbances in schizophrenia and bipolar illness. Cerebral Cortex 2014, 24, 3116–3130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lui, S.; Yao, L.; Xiao, Y.; Keedy, S.K.; Reilly, J.L.; Keefe, R.S.; Tamminga, C.A.; Keshavan, M.S.; Pearlson, G.D.; Gong, Q.; et al. Resting-state brain function in schizophrenia and psychotic bipolar probands and their first-degree relatives. Psychol. Med. 2015, 45, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skåtun, K.C.; Kaufmann, T.; Brandt, C.L.; Doan, N.T.; Alnæs, D.; Tønnesen, S.; Biele, G.; Vaskinn, A.; Melle, I.; Agartz, I.; et al. Thalamo-cortical functional connectivity in schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. Brain Imaging Behav. 2018, 12, 640–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buzsáki, G.; Draguhn, A. Neuronal oscillations in cortical networks. Science 2004, 304, 1926–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engel, A.K.; Fries, P.; Singer, W. Dynamic predictions: Oscillations and synchrony in top-down processing. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2001, 2, 704–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dougherty, K.; Schmid, M.C.; Maier, A. Binocular response modulation in the lateral geniculate nucleus. J. Comp. Neurol. 2019, 527, 522–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briggs, F.; Usrey, W.M. Corticogeniculate feedback and visual processing in the primate. J. Physiol. 2011, 589 Pt 1, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adusei, M.; Hasse, J.M.; Briggs, F. Morphological evidence for multiple distinct channels of corticogeniculate feedback originating in mid-level extrastriate visual areas of the ferret. Brain Struct. Funct. 2021, 226, 2777–2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fridberg, D.J.; Hetrick, W.P.; Brenner, C.A.; Shekhar, A.; Steffen, A.N.; Malloy, F.W.; O’Donnell, B.F. Relationships between auditory event-related potentials and mood state, medication, and comorbid psychiatric illness in patients with bipolar disorder. Bipolar Disord. 2009, 11, 857–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degabriele, R.; Lagopoulos, J.; Malhi, G. Neural correlates of emotional face processing in bipolar disorder: An event-related potential study. J. Affect. Disord. 2011, 133, 212–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abé, C.; Ekman, C.J.; Sellgren, C.; Petrovic, P.; Ingvar, M.; Landén, M. Cortical thickness, volume and surface area in patients with bipolar disorder types I and II. J. Psychiatry Neurosci. 2016, 41, 240–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Du, J.L.; Fang, X.Y.; Ni, L.Y.; Zhu, Y.Y.; Yan, W.; Lu, S.P.; Zhang, R.R.; Xie, S.P. Shared and distinct structural brain alterations and cognitive features in drug-naïve schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. Asian J. Psychiatr. 2023, 82, 103513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kropf, E.; Syan, S.K.; Minuzzi, L.; Frey, B.N. From anatomy to function: The role of the somatosensory cortex in emotional regulation. Rev. Bras. Psiquiatr. 2019, 41, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, K.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, H.; Li, X.; Zou, F.; Wang, Y.; Wu, X.; Zhang, H. The spontaneous activity and functional network of the occipital cortex is correlated with state anxiety in healthy adults. Neurosci. Lett. 2020, 715, 134596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, P.; Li, Q.; Zhang, A.; Liu, Z.; Sun, N.; Yang, C.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, K. Similar and Different Regional Homogeneity Changes Between Bipolar Disorder and Unipolar Depression: A Resting-State fMRI Study. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2020, 16, 1087–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Rees, G.; Yin, X.; Song, C.; Han, Y.; Ge, H.; Pang, Z.; Xu, W.; Tang, Y.; Friston, K.; et al. Spontaneous neuronal activity predicts intersubject variations in executive control of attention. Neuroscience 2014, 263, 181–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.S.; Zhou, S.Z.; Zhang, Y.J.; Cai, X.L.; Wang, Y.; Cheung, E.F.C.; Lui, S.S.Y.; Yu, X.; Madsen, K.H.; Ma, Y.T.; et al. Altered empathy-related resting-state functional connectivity in patients with bipolar disorder. Eur. Arch. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2022, 272, 839–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, C.L.; Caselli, R.J. The nature of tactile agnosia: A case study. Neuropsychologia 1994, 32, 527–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caspers, S.; Schleicher, A.; Bacha-Trams, M.; Palomero-Gallagher, N.; Amunts, K.; Zilles, K. Organization of the human inferior parietal lobule based on receptor architectonics. Cerebral Cortex 2013, 23, 615–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Sweeney, J.A.; Yao, L.; Li, S.; Zeng, J.; Xu, M.; Tallman, M.J.; Gong, Q.; DelBello, M.P.; Lui, S.; et al. Brain structural correlates of familial risk for mental illness: A meta-analysis of voxel-based morphometry studies in relatives of patients with psychotic or mood disorders. Neuropsychopharmacol. Off. Publ. Am. Coll. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2020, 45, 1369–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Qi, S.; Yu, W.; Gao, Y.; Ma, J. Regional Homogeneity of the Left Posterior Cingulate Gyrus May Be a Potential Imaging Biomarker of Manic Episodes in First-Episode, Drug-Naive Bipolar Disorder. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2023, 19, 2775–2785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malhi, G.S.; Lagopoulos, J.; Sachdev, P.S.; Ivanovski, B.; Shnier, R.; Ketter, T. Is a lack of disgust something to fear? A functional magnetic resonance imaging facial emotion recognition study in euthymic bipolar disorder patients. Bipolar Disord. 2007, 9, 345–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellison-Wright, I.; Bullmore, E. Anatomy of bipolar disorder and schizophrenia: A meta-analysis. Schizophr. Res. 2010, 117, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silani, G.; Lamm, C.; Ruff, C.C.; Singer, T. Right supramarginal gyrus is crucial to overcome emotional egocentricity bias in social judgments. J. Neurosci. 2013, 33, 15466–15476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gernsbacher, M.A.; Kaschak, M.P. Neuroimaging studies of language production and comprehension. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 2003, 54, 91–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chenji, S.; Jha, S.; Lee, D.; Brown, M.; Seres, P.; Mah, D.; Kalra, S. Investigating Default Mode and Sensorimotor Network Connectivity in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0157443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Hofsten, C.; Rosander, K. The Development of Sensorimotor Intelligence in Infants. Adv. Child Dev. Behav. 2018, 55, 73–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Supekar, K.; Cai, W.; Krishnadas, R.; Palaniyappan, L.; Menon, V. Dysregulated Brain Dynamics in a Triple-Network Saliency Model of Schizophrenia and Its Relation to Psychosis. Biol. Psychiatry 2019, 85, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishida, T.; Nakamura, Y.; Tanaka, S.C.; Mitsuyama, Y.; Yokoyama, S.; Shinzato, H.; Itai, E.; Okada, G.; Kobayashi, Y.; Kawashima, T.; et al. Aberrant Large-Scale Network Interactions Across Psychiatric Disorders Revealed by Large-Sample Multi-Site Resting-State Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging Datasets. Schizophr. Bull. 2023, 49, 933–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullins, N.; Forstner, A.J.; O’Connell, K.S.; Coombes, B.; Coleman, J.R.I.; Qiao, Z.; Als, T.D.; Bigdeli, T.B.; Børte, S.; Bryois, J.; et al. Genome-wide association study of more than 40,000 bipolar disorder cases provides new insights into the underlying biology. Nat. Genet. 2021, 53, 817–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurung, R.; Prata, D.P. What is the impact of genome-wide supported risk variants for schizophrenia and bipolar disorder on brain structure and function? A systematic review. Psychol. Med. 2015, 45, 2461–2480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lippard, E.T.C.; Jensen, K.P.; Wang, F.; Johnston, J.A.Y.; Spencer, L.; Pittman, B.; Gelernter, J.; Blumberg, H.P. Effects of ANK3 variation on gray and white matter in bipolar disorder. Mol. Psychiatry 2017, 22, 1345–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.T.; Jiang, X.; Akula, N.; Shugart, Y.Y.; Wendland, J.R.; Steele, C.J.; Kassem, L.; Park, J.H.; Chatterjee, N.; Jamain, S.; et al. Genome-wide association study meta-analysis of European and Asian-ancestry samples identifies three novel loci associated with bipolar disorder. Mol. Psychiatry 2013, 18, 195–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stahl, E.A.; Breen, G.; Forstner, A.J.; McQuillin, A.; Ripke, S.; Trubetskoy, V.; Mattheisen, M.; Wang, Y.; Coleman, J.R.I.; Gaspar, H.A.; et al. Genome-wide association study identifies 30 loci associated with bipolar disorder. Nat. Genet. 2019, 51, 793–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, G.S. Pleiotropy, Natural Selection, and the Evolution of Senescence: Evolution 11, 398–411 (1957). Sci. Aging Knowl. Environ. 2001, 2001, cp13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ching, C.R.K.; Hibar, D.P.; Gurholt, T.P.; Nunes, A.; Thomopoulos, S.I.; Abé, C.; Agartz, I.; Brouwer, R.M.; Cannon, D.M.; de Zwarte, S.M.C.; et al. What we learn about bipolar disorder from large-scale neuroimaging: Findings and future directions from the ENIGMA Bipolar Disorder Working Group. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2022, 43, 56–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radonjić, N.V.; Hess, J.L.; Rovira, P.; Andreassen, O.; Buitelaar, J.K.; Ching, C.R.K.; Franke, B.; Hoogman, M.; Jahanshad, N.; McDonald, C.; et al. Structural brain imaging studies offer clues about the effects of the shared genetic etiology among neuropsychiatric disorders. Mol. Psychiatry 2021, 26, 2101–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, Y.; Parker, N.; Shin, J.; Howard, D.; French, L.; Thomopoulos, S.I.; Pozzi, E.; Abe, Y.; Abé, C.; Anticevic, A.; et al. Virtual Histology of Cortical Thickness and Shared Neurobiology in 6 Psychiatric Disorders. JAMA Psychiatry 2021, 78, 47–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannon, T.D.; Thompson, P.M.; van Erp, T.G.; Toga, A.W.; Poutanen, V.P.; Huttunen, M.; Lonnqvist, J.; Standerskjold-Nordenstam, C.G.; Narr, K.L.; Khaledy, M.; et al. Cortex mapping reveals regionally specific patterns of genetic and disease-specific gray-matter deficits in twins discordant for schizophrenia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 3228–3233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

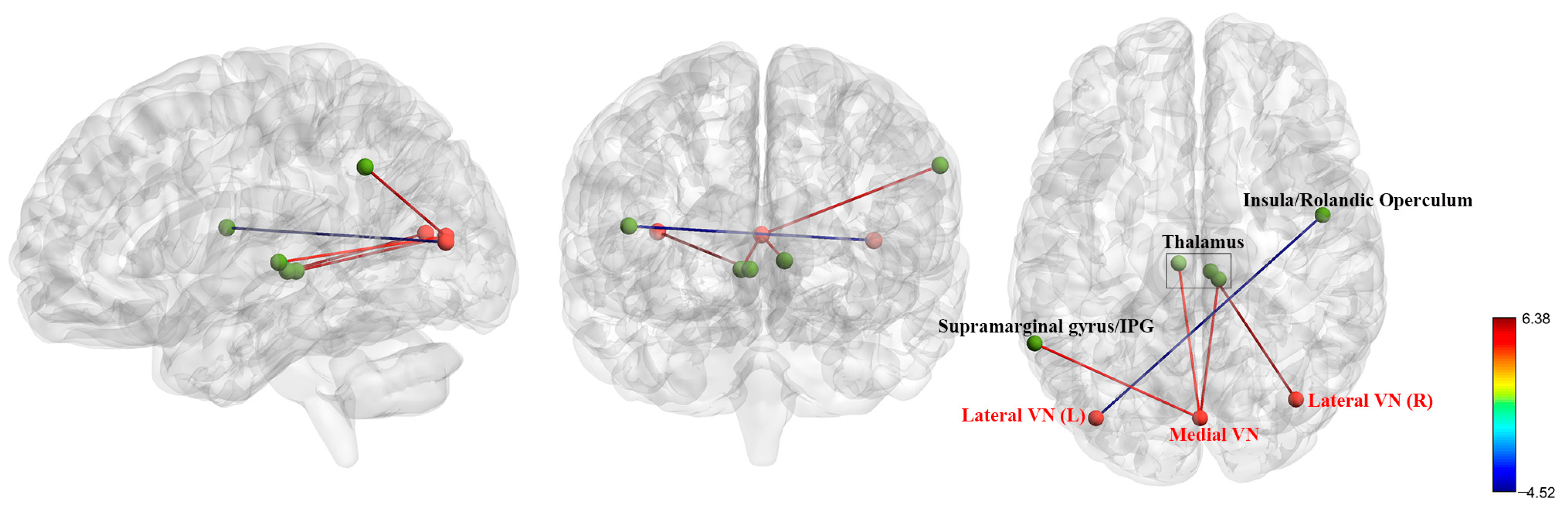
| ROIs | Brain Regions | MNI (x, y, z) | T Values | Cluster Size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sensorimotor Network (SMN) | ||||
| Lateral SMN (L) | L Thalamus | −12, −21, 9 | 5.73 | 184 |
| R Thalamus | 6, −21, 0 | 5.73 | 127 | |
| R Postcentral Gyrus | 66, −6, 33 | −5.41 | 65 | |
| Lateral SMN (R) | Bilateral Thalamus | 6, −24, 0 | 5.15 | 271 |
| R SOG/MOG | 21, −84, 18 | −3.95 | 167 | |
| L Lingual/Fusiform Gyrus | −18, −72, −6 | −3.94 | 116 | |
| R Fusiform/Lingual Gyrus | 33, −66, −12 | −3.40 | 92 | |
| L Postcentral Gyrus | −63, −9, 18 | −4.09 | 80 | |
| Superior SMN | Bilateral Thalamus | 6, −27, 3 | 4.82 | 135 |
| Visual Network (VN) | ||||
| Medial VN | L Thalamus | −6, −21, 3 | 4.84 | 112 |
| L Supramarginal Gyrus/IPG | −60, −51, 36 | 5.19 | 102 | |
| R Thalamus | 9, −27, 0 | 5.65 | 100 | |
| Occipital VN | / | / | / | / |
| Lateral VN (L) | R Insula/Rolandic Operculum | 48, −3, 15 | −4.52 | 164 |
| Lateral VN (R) | Bilateral Thalamus | 6, −24, 0 | 6.38 | 423 |
| ROIs | The Names of Common Genes That Showed Positive Correlations with FC Alterations | The Name of Common Genes that Showed Negative Correlations with FC Alterations | The Proportion of Common Genes in FC Alteration-Related Genes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sensorimotor Network | |||
| ROI 1&2 | RFLNB | CMBL; EPHA5-AS1 | 1/1 in ROI 1; 1/10 in ROI 2 |
| 2/3 in ROI 1; 2/24 in ROI 2 | |||
| ROI 1&3 | RFLNB | CMBL; EPHA5-AS1 | 1/1 in ROI 1; 1/12 in ROI 3 |
| 2/3 in ROI 1; 2/22 in ROI 3 | |||
| ROI 2&3 | RFLNB | CCDC181; CMBL; EPHA5-AS1; HIST1H1A; LAMA3; MBP; PXDN; ZMYM2 | 1/10 in ROI 2; 1/12 in ROI 3 |
| 8/24 in ROI 2 8/22 in ROI 3 | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, C.; Han, Y.; Yan, H.; Ou, Y.; Liang, J.; Huang, W.; Li, X.; Tang, C.; Xu, J.; Xie, G.; et al. Neuroimaging Changes in the Sensorimotor Network and Visual Network in Bipolar Disorder and Their Relationship with Genetic Characteristics. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 898. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13040898
Zhang C, Han Y, Yan H, Ou Y, Liang J, Huang W, Li X, Tang C, Xu J, Xie G, et al. Neuroimaging Changes in the Sensorimotor Network and Visual Network in Bipolar Disorder and Their Relationship with Genetic Characteristics. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(4):898. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13040898
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Chunguo, Yiding Han, Haohao Yan, Yangpan Ou, Jiaquan Liang, Wei Huang, Xiaoling Li, Chaohua Tang, Jinbing Xu, Guojun Xie, and et al. 2025. "Neuroimaging Changes in the Sensorimotor Network and Visual Network in Bipolar Disorder and Their Relationship with Genetic Characteristics" Biomedicines 13, no. 4: 898. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13040898
APA StyleZhang, C., Han, Y., Yan, H., Ou, Y., Liang, J., Huang, W., Li, X., Tang, C., Xu, J., Xie, G., & Guo, W. (2025). Neuroimaging Changes in the Sensorimotor Network and Visual Network in Bipolar Disorder and Their Relationship with Genetic Characteristics. Biomedicines, 13(4), 898. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13040898







