Diminishing Hepcidin via Reducing IL-6/STAT3 Pathway by Utilizing Ferulic Acid: An In Vitro Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemical Reagents and Ferulic Acid (FA) Preparation
2.2. Cell Line and Culture Conditions
2.3. Cell Viability Assessment
2.4. Cell Treatment
2.5. RNA Extraction, cDNA Synthesis, and qRT-PCR
2.6. Quantification of IL-6, STAT3 and Hepcidin Levels
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
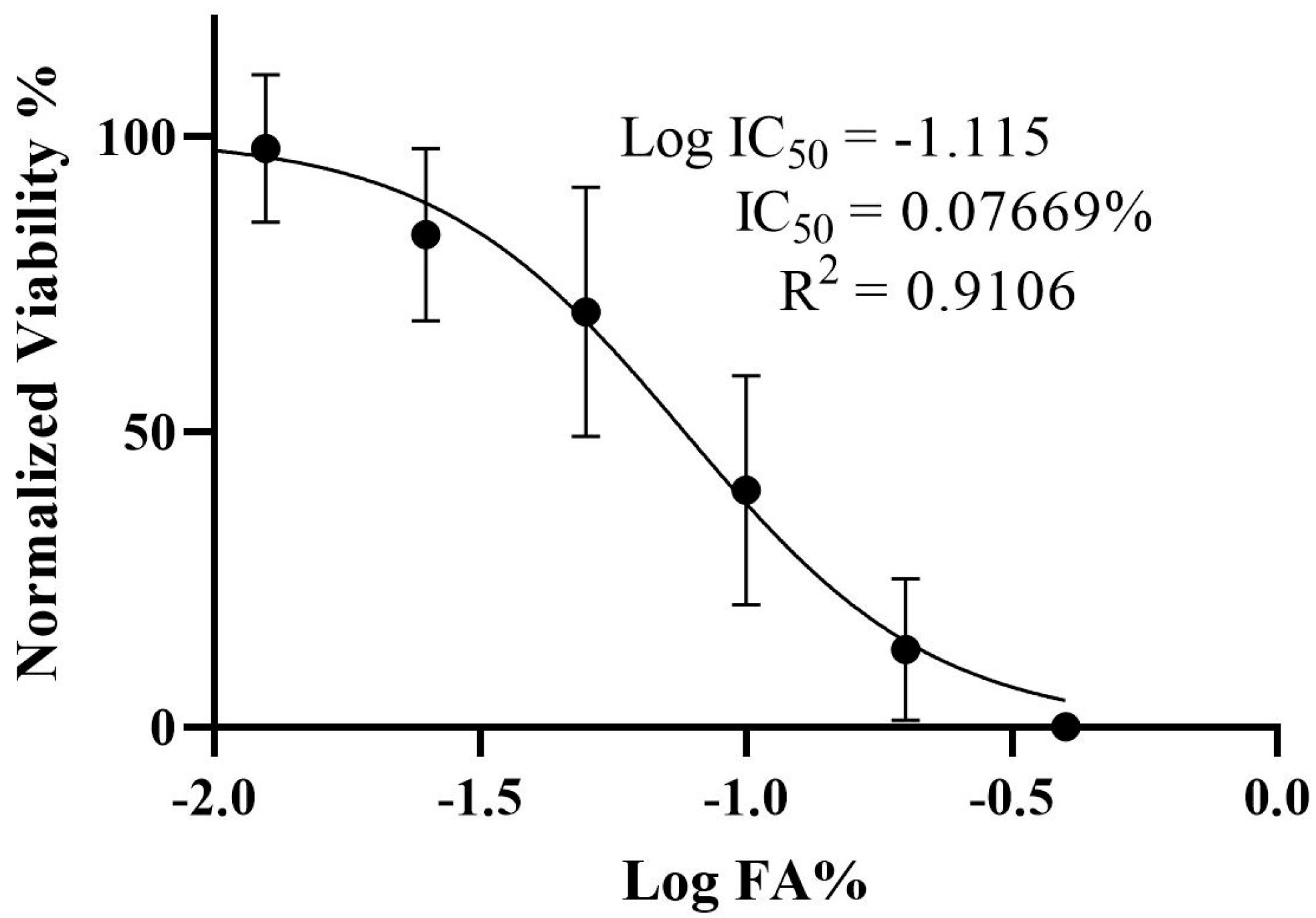
3.1. Determination of the IC50 and Viability of HepG2 Cells Treated with Ferulic Acid
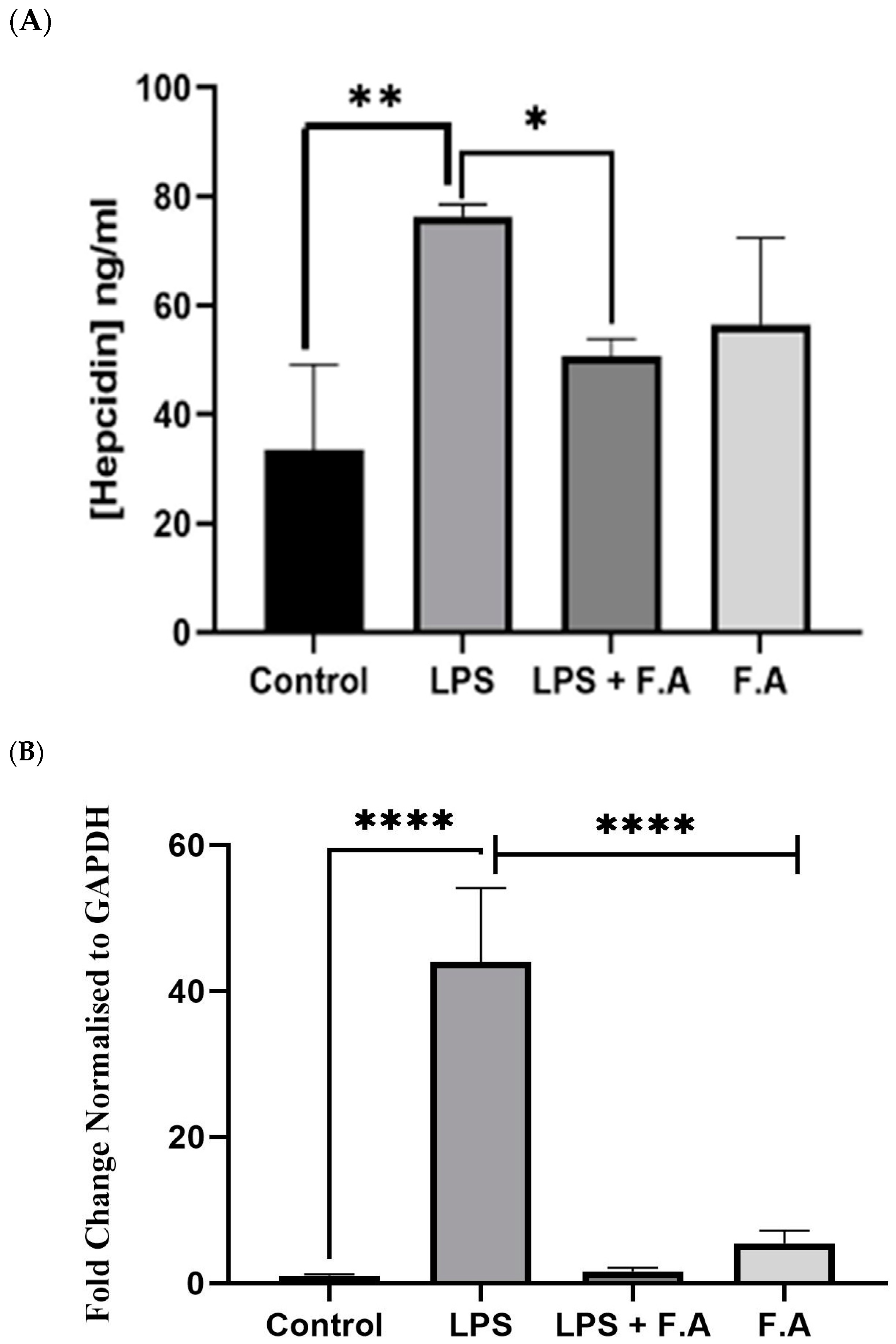
3.2. Effect of Ferulic Acid on Hepcidin Secretion and Expression
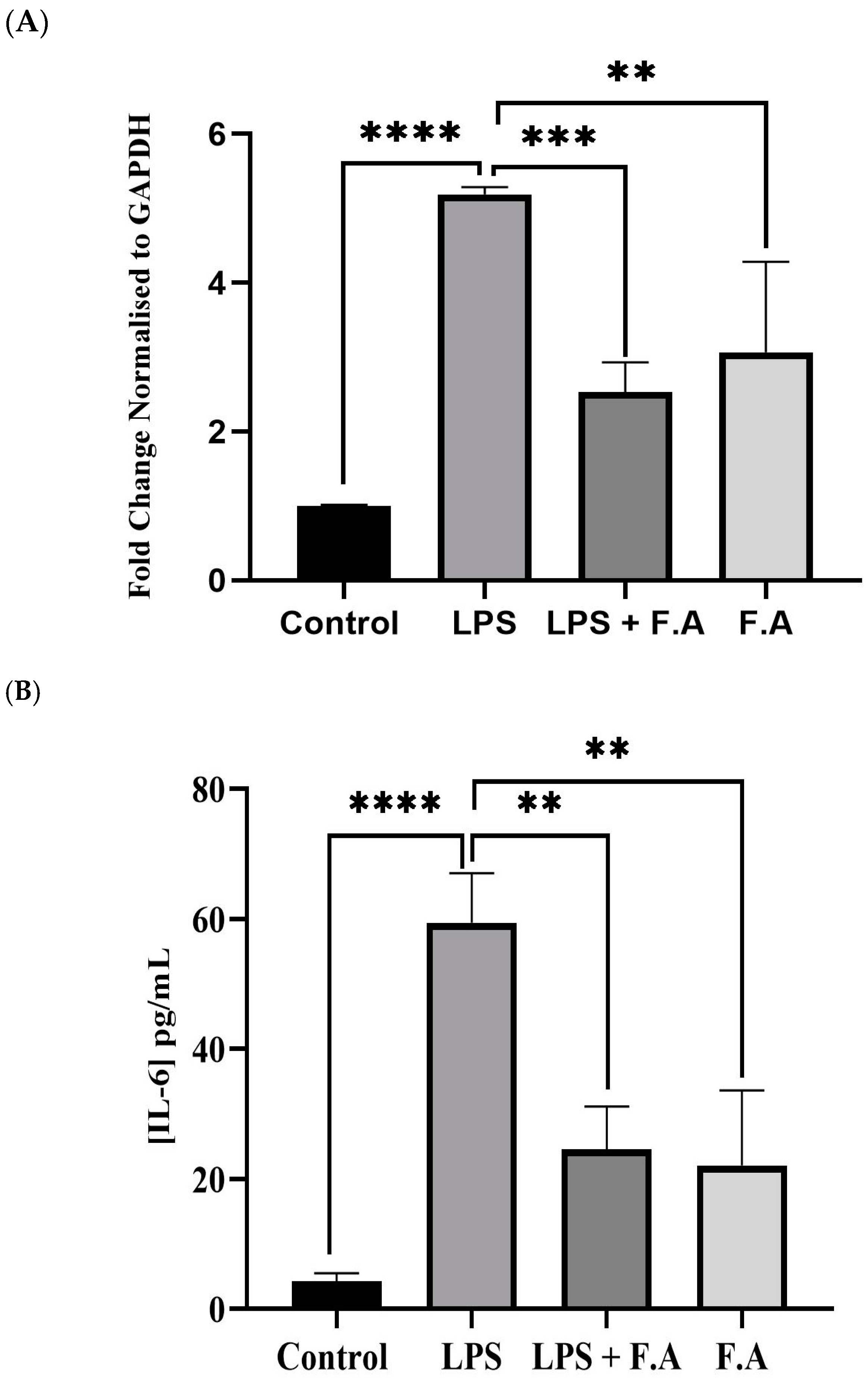
3.3. Effect of Ferulic Acid on IL-6 Expression and Secretion
3.4. Effect of Ferulic Acid on Phospho-STAT3 Secretion
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| FA | Ferulic acid |
| HCC | Hepatocellular carcinoma |
| DMSO | Dimethyl sulfoxide |
| ACHN | Apoptosis in renal carcinoma |
References
- Crosby, W.H.; Likhite, V.V.; O’Brien, J.E.; Forman, D. Serum iron levels in ostensibly normal people. JAMA 1974, 227, 310–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.Y.; Li, J.H.; Jiang, Y.; Peng, B.S.; Li, J.; Zhu, S.L.; Su, Z.W.; Chang, J.P. Serum prohepcidin positively correlates with erythropoietin in normal adults. Int. J. Lab. Hematol. 2011, 33, 110–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camaschella, C.; Nai, A.; Silvestri, L. Iron metabolism and iron disorders revisited in the hepcidin era. Haematologica 2020, 105, 260–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, C.L.R.; Wilairatana, P.; Silva, L.R.; Moreira, P.S.; Vilar Barbosa, N.M.M.; da Silva, P.R.; Coutinho, H.D.M.; de Menezes, I.R.A.; Felipe, C.F.B. Biochemical aspects of the inflammatory process: A narrative review. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 168, 115764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wrighting, D.M.; Andrews, N.C. Interleukin-6 induces hepcidin expression through STAT3. Blood 2006, 108, 3204–3209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowdley, K.V.; Gochanour, E.M.; Sundaram, V.; Shah, R.A.; Handa, P. Hepcidin Signaling in Health and Disease: Ironing out the Details. Hepatol. Commun. 2021, 5, 723–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gyamfi, J.; Kim, J.; Choi, J. Cancer as a Metabolic Disorder. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.Y.; Han, Y.; Li, W.N.; Xu, R.H.; Ju, H.Q. Tumor iron homeostasis and immune regulation. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2024, 45, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakamoto, S.; Kawabata, H.; Kanda, J.; Uchiyama, T.; Mizumoto, C.; Kitano, T.; Kondo, T.; Hishizawa, M.; Tomosugi, N.; Takaori-Kondo, A. High pretransplant hepcidin levels are associated with poor overall survival and delayed platelet engraftment after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Cancer Med. 2017, 6, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, A.J.; Goyert, J.W.; Solanki, S.; Kerk, S.A.; Chen, B.; Castillo, C.; Hsu, P.P.; Do, B.T.; Singhal, R.; Dame, M.K.; et al. Hepcidin sequesters iron to sustain nucleotide metabolism and mitochondrial function in colorectal cancer epithelial cells. Nat. Metab. 2021, 3, 969–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutlu, T.; Ozoran, E.; Trabulus, D.C.; Talu, C.K.; Erhan, D.; Mete, M.; Guven, M. Expression of genes related to iron homeostasis in breast cancer. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2023, 50, 5157–5163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, R.; Zhao, F.; Dong, Z.; Li, Z.; Li, S. A stratification system of ferroptosis and iron-metabolism related LncRNAs guides the prediction of the survival of patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 1010074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traeger, L.; Ellermann, I.; Wiethoff, H.; Ihbe, J.; Gallitz, I.; Eveslage, M.; Moritz, R.; Herrmann, E.; Schrader, A.J.; Steinbicker, A.U. Serum Hepcidin and GDF-15 levels as prognostic markers in urothelial carcinoma of the upper urinary tract and renal cell carcinoma. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joachim, J.H.; Mehta, K.J. Hepcidin in hepatocellular carcinoma. Br. J. Cancer 2022, 127, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdulal, Z.A.; Altahhan, M.Y.; Qindil, A.F.; Al-Juhani, A.M.; Alatawi, M.A.; Hassan, H.M.; Al-Gayyar, M.M. Ferulic acid inhibits tumor proliferation and attenuates inflammation of hepatic tissues in experimentally induced HCC in rats. J. Investig. Med. 2024, 72, 900–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishayee, A. The role of inflammation and liver cancer. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2014, 816, 401–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.C.; Wang, C.C.; Huang, H.M.; Lin, C.L.; Leu, S.J.; Lee, Y.L. Ferulic Acid Induces Th1 Responses by Modulating the Function of Dendritic Cells and Ameliorates Th2-Mediated Allergic Airway Inflammation in Mice. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2015, 2015, 678487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, S.; Ochiai, H.; Nakajima, K.; Terasawa, K. Inhibitory effect of ferulic acid on macrophage inflammatory protein-2 production in a murine macrophage cell line, RAW264.7. Cytokine 1997, 9, 242–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iriarte-Gahete, M.; Tarancon-Diez, L.; Garrido-Rodriguez, V.; Leal, M.; Pacheco, Y.M. Absolute and functional iron deficiency: Biomarkers, impact on immune system, and therapy. Blood Rev. 2024, 68, 101227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotze, M.J.; van Velden, D.P.; van Rensburg, S.J.; Erasmus, R. Pathogenic Mechanisms Underlying Iron Deficiency and Iron Overload: New Insights for Clinical Application. EJIFCC 2009, 20, 108–123. [Google Scholar]
- Rosenblum, S.L. Inflammation, dysregulated iron metabolism, and cardiovascular disease. Front. Aging 2023, 4, 1124178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.D.; Geng, M.Y.; Dou, S.R.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Z.H.; Chang, Y.Z. Caffeine Decreases Hepcidin Expression to Alleviate Aberrant Iron Metabolism under Inflammation by Regulating the IL-6/STAT3 Pathway. Life 2022, 12, 1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, D.Y.; Sp, N.; Jo, E.S.; Lee, J.M.; Jang, K.J. New Insights into the Pivotal Role of Iron/Heme Metabolism in TLR4/NF-kappaB Signaling-Mediated Inflammatory Responses in Human Monocytes. Cells 2021, 10, 2549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werneck Cerqueira, A.F.L.; de Mello Brandao, H.; Tavares, G.D.; Rodarte, M.P. Ferulic Acid: A Review of Mechanisms of Action, Absorption, Toxicology, Application on Wound Healing. Antiinflamm. Antiallergy Agents Med. Chem. 2024, 23, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatun, M.M.; Bhuia, M.S.; Chowdhury, R.; Sheikh, S.; Ajmee, A.; Mollah, F.; Al Hasan, M.S.; Coutinho, H.D.M.; Islam, M.T. Potential utilization of ferulic acid and its derivatives in the management of metabolic diseases and disorders: An insight into mechanisms. Cell. Signal. 2024, 121, 111291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, M.; Ye, A.; Zhang, H.; Chen, J.; Yang, T.; Wei, X.; Gao, Y.; Ma, Z. Ferulic Acid Alleviates Radiation-Induced Immune Damage by Acting on JAK/STAT Signaling Pathway. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatih, N.; Camberlein, E.; Island, M.L.; Corlu, A.; Abgueguen, E.; Detivaud, L.; Leroyer, P.; Brissot, P.; Loreal, O. Natural and synthetic STAT3 inhibitors reduce hepcidin expression in differentiated mouse hepatocytes expressing the active phosphorylated STAT3 form. J. Mol. Med. 2010, 88, 477–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, H.; Wang, M.; Tang, W.; Shen, Z.; Miao, L.; Wu, W.; Li, C.; Wang, X.; Xin, X.; Zhu, Y.Z. Hydrogen Sulfide Attenuates Inflammatory Hepcidin by Reducing IL-6 Secretion and Promoting SIRT1-Mediated STAT3 Deacetylation. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2016, 24, 70–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Zhu, S.; Tong, Y.; Peng, S. Ferulic Acid Induces Apoptosis of HeLa and Caski Cervical Carcinoma Cells by Down-Regulating the Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase (PI3K)/Akt Signaling Pathway. Med. Sci. Monit. 2020, 26, e920095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janus, E.; Pinheiro, L.R.; Nowak, A.; Kucharska, E.; Swiatek, E.; Podolak, N.; Peruzynska, M.; Piotrowska, K.; Duchnik, W.; Kucharski, L.; et al. New Ferulic Acid and Amino Acid Derivatives with Increased Cosmeceutical and Pharmaceutical Potential. Pharmaceutics 2022, 15, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd-Allah, H.; Abdel Jaleel, G.A.; Hassan, A.; El Madani, M.; Nasr, M. Ferulic acid nanoemulsion as a promising anti-ulcer tool: In vitro and in vivo assessment. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2024, 50, 460–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, S.; Cheng, D.; Yao, H.; Wen, Y.; Yu, Y.; Li, H.; Wang, J.; Sun, B. Cascade Microbial Metabolism of Ferulic Acid In Vitro Fermented by the Human Fecal Inoculum. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2024, 72, 9807–9817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Target Gene | Forward (3′ to 5′) | Reverse (3′ to 5′) |
|---|---|---|
| HAMP | TTCCTTCCTGGGCATGGA GT | GCAATGATCTTGATCTTCATT |
| IL-6 | CACAACAGACGGGACAACTT | CGCAGCAGAAAATGCAGATG |
| GAPDH | GCCAAAAGGGTCATCATCTC | GGTGCTAAGCAGTTGGTGGT |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Al-Sanabra, O.M.; Abu-Qatouseh, L.F.; Ahmad, M.I.A.; Al-Khreisat, M.J.; Alsaleh, M.M. Diminishing Hepcidin via Reducing IL-6/STAT3 Pathway by Utilizing Ferulic Acid: An In Vitro Study. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 923. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13040923
Al-Sanabra OM, Abu-Qatouseh LF, Ahmad MIA, Al-Khreisat MJ, Alsaleh MM. Diminishing Hepcidin via Reducing IL-6/STAT3 Pathway by Utilizing Ferulic Acid: An In Vitro Study. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(4):923. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13040923
Chicago/Turabian StyleAl-Sanabra, Ola M., Luay F. Abu-Qatouseh, Mohammad I. A. Ahmad, Mutaz Jamal Al-Khreisat, and Majd M. Alsaleh. 2025. "Diminishing Hepcidin via Reducing IL-6/STAT3 Pathway by Utilizing Ferulic Acid: An In Vitro Study" Biomedicines 13, no. 4: 923. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13040923
APA StyleAl-Sanabra, O. M., Abu-Qatouseh, L. F., Ahmad, M. I. A., Al-Khreisat, M. J., & Alsaleh, M. M. (2025). Diminishing Hepcidin via Reducing IL-6/STAT3 Pathway by Utilizing Ferulic Acid: An In Vitro Study. Biomedicines, 13(4), 923. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13040923








