Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura in Pediatric Patients
Abstract
1. Introduction
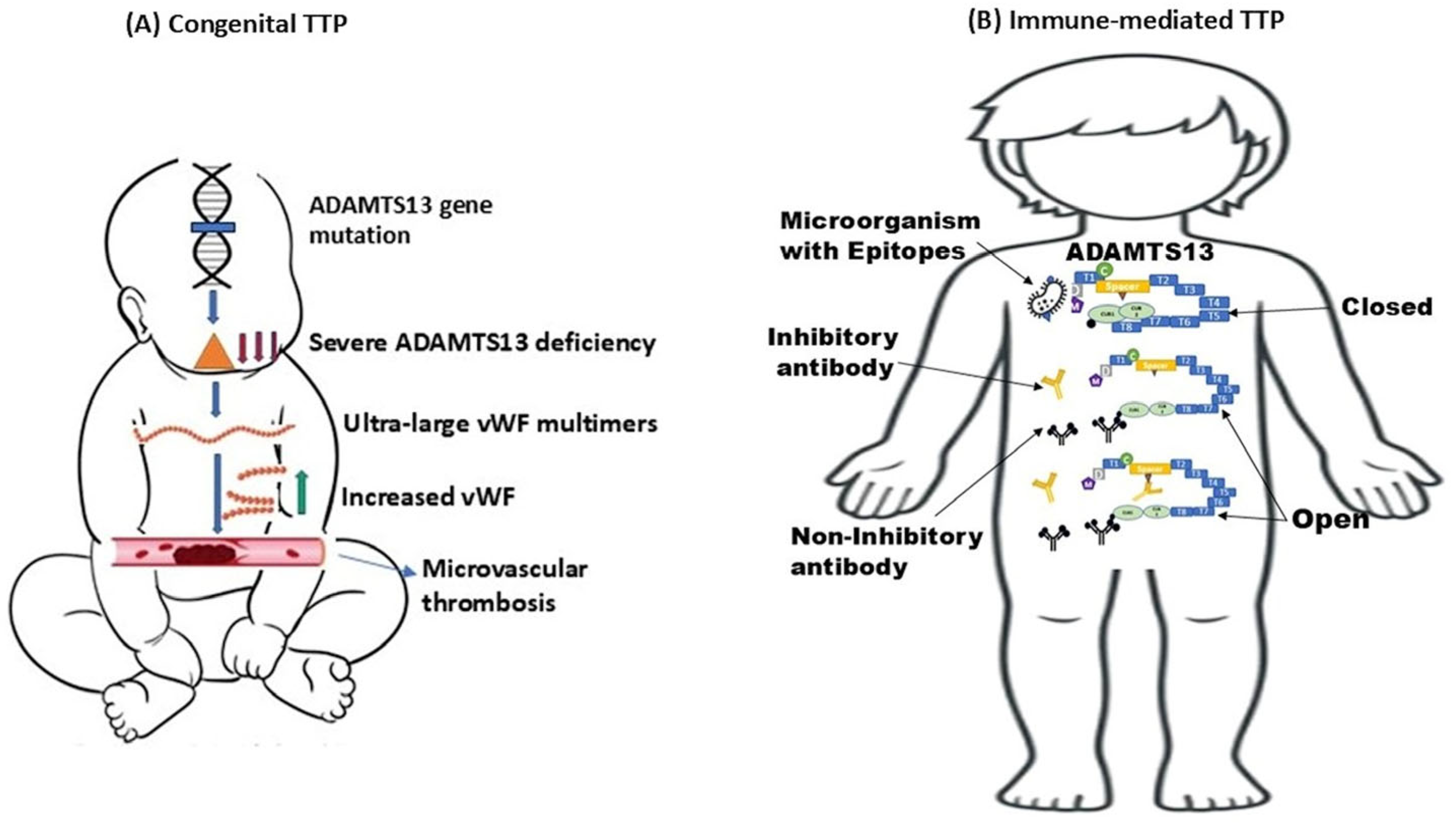
2. Congenital Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura
2.1. Pathophysiology and Genetic Alterations
2.2. Clinical Presentations, Triggers, and Diagnosis
2.3. Laboratory Workup
2.3.1. ADAMTS13 Activity Assay/Anti-ADAMTS13 Autoantibody
2.3.2. ADAMTS13 Functional Inhibitor Assay
2.3.3. Extended Platelet Profiles
2.3.4. Disease Scoring
2.4. Treatment
2.4.1. Therapeutic Plasma Exchange (TPE)
2.4.2. Immunosuppression and Emerging Therapies
2.4.3. Recombinant Human ADAMTS13 Therapy
2.4.4. Gene Therapy
3. Immune-Mediated Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura
3.1. Pathophysiology of iTTP
3.1.1. ADAMTS13 Activity
3.1.2. Anti-ADAMTS13 Autoantibodies
3.1.3. Immune Complexes
3.2. Human Leukocyte Antigens (HLAs)
3.3. Clinical Presentation and Triggers
3.4. Laboratory Diagnosis
3.5. Treatment
3.5.1. Therapeutic Plasma Exchange
3.5.2. Immunosuppression
3.5.3. Caplacizumab
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Moschcowitz, E. Hyaline thrombosis of the terminal arterioles and capillaries: A hitherto undescribed disease. Proc. N. Y. Pathol. Soc. 1924, 24, 21–24. [Google Scholar]
- Joly, B.S.; Coppo, P.; Veyradier, A. Pediatric thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Eur. J. Haematol. 2018, 101, 425–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koyfman, A.; Brem, E.; Chiang, V.W. Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Pediatr. Emerg. Care 2011, 27, 1085–1088, quiz 1089–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, M.; McDaniel, J.K.; Zheng, X.L. Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura: Pathogenesis, diagnosis and potential novel therapeutics. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2017, 15, 1889–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nusrat, S.; Beg, K.; Khan, O.; Sinha, A.; George, J. Hereditary Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura. Genes 2023, 14, 1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masias, C.; Vasu, S.; Cataland, S.R. None of the above: Thrombotic microangiopathy beyond TTP and HUS. Blood 2017, 129, 2857–2863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.L.; Tang, X.; Chen, H.B.; Peng, Q.Y.; Guo, X.; Gao, J. Hereditary Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura in a Chinese Boy With a Novel Compound Heterozygous Mutation of the ADAMTS13 Gene. Front. Pediatr. 2020, 8, 554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verbij, F.C.; Fijnheer, R.; Voorberg, J.; Sorvillo, N. Acquired TTP: ADAMTS13 meets the immune system. Blood Rev. 2014, 28, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loirat, C.; Coppo, P.; Veyradier, A. Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura in children. Curr. Opin. Pediatr. 2013, 25, 216–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokame, K.; Miyata, T. Genetic defects leading to hereditary thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Semin. Hematol. 2004, 41, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kremer Hovinga, J.A.; George, J.N. Hereditary Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 1653–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lancellotti, S.; Peyvandi, F.; Pagliari, M.T.; Cairo, A.; Abdel-Azeim, S.; Chermak, E.; Lazzareschi, I.; Mastrangelo, S.; Cavallo, L.; Oliva, R.; et al. The D173G mutation in ADAMTS-13 causes a severe form of congenital thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. A clinical, biochemical and in silico study. Thromb. Haemost. 2016, 115, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abou-Ismail, M.Y.; Kapoor, S.; Citla Sridhar, D.; Nayak, L.; Ahuja, S. Thrombotic microangiopathies: An illustrated review. Res. Pract. Thromb. Haemost. 2022, 6, e12708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snyder, M.R.; Maitta, R.W. Anti-ADAMTS13 Autoantibodies in Immune-Mediated Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura. Antibodies 2025, 14, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujimura, Y.; Matsumoto, M.; Isonishi, A.; Yagi, H.; Kokame, K.; Soejima, K.; Murata, M.; Miyata, T. Natural history of Upshaw-Schulman syndrome based on ADAMTS13 gene analysis in Japan. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2011, 9 (Suppl. S1), 283–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veyradier, A.; Lavergne, J.M.; Ribba, A.S.; Obert, B.; Loirat, C.; Meyer, D.; Girma, J.P. Ten candidate ADAMTS13 mutations in six French families with congenital thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (Upshaw-Schulman syndrome). J. Thromb. Haemost. 2004, 2, 424–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miodownik, S.; Pikovsky, O.; Erez, O.; Kezerle, Y.; Lavon, O.; Rabinovich, A. Unfolding the pathophysiology of congenital thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura in pregnancy: Lessons from a cluster of familial cases. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2021, 225, 177.e1–177.e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Rodriguez, A.; Loures, E.; Rodriguez-Trillo, A.; Costa-Pinto, J.; Garcia-Rivero, A.; Batlle-Lopez, A.; Batlle, J.; Lopez-Fernandez, M.F. Inherited ADAMTS13 deficiency (Upshaw-Schulman syndrome): A short review. Thromb. Res. 2014, 134, 1171–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Nishio, K.; Majerus, E.M.; Sadler, J.E. Cleavage of von Willebrand factor requires the spacer domain of the metalloprotease ADAMTS13. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 30136–30141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, G.G.; Nichols, W.C.; Lian, E.C.; Foroud, T.; McClintick, J.N.; McGee, B.M.; Yang, A.Y.; Siemieniak, D.R.; Stark, K.R.; Gruppo, R.; et al. Mutations in a member of the ADAMTS gene family cause thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Nature 2001, 413, 488–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- South, K.; Lane, D.A. ADAMTS-13 and von Willebrand factor: A dynamic duo. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2018, 16, 6–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lenting, P.J.; Christophe, O.D.; Denis, C.V. von Willebrand factor biosynthesis, secretion, and clearance: Connecting the far ends. Blood 2015, 125, 2019–2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossio, R.; Ferrari, B.; Cairo, A.; Mancini, I.; Pisapia, G.; Palazzo, G.; Peyvandi, F. Two novel heterozygote missense mutations of the ADAMTS13 gene in a child with recurrent thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Blood Transfus. 2013, 11, 241–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kremer Hovinga, J.A.; Heeb, S.R.; Skowronska, M.; Schaller, M. Pathophysiology of thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura and hemolytic uremic syndrome. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2018, 16, 618–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyata, T. GWA study for ADAMTS13 activity. Blood 2015, 125, 3833–3834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokame, K.; Kokubo, Y.; Miyata, T. Polymorphisms and mutations of ADAMTS13 in the Japanese population and estimation of the number of patients with Upshaw-Schulman syndrome. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2011, 9, 1654–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Dorland, H.A.; Taleghani, M.M.; Sakai, K.; Friedman, K.D.; George, J.N.; Hrachovinova, I.; Knobl, P.N.; von Krogh, A.S.; Schneppenheim, R.; Aebi-Huber, I.; et al. The International Hereditary Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura Registry: Key findings at enrollment until 2017. Haematologica 2019, 104, 2107–2115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Krogh, A.S.; Quist-Paulsen, P.; Waage, A.; Langseth, O.O.; Thorstensen, K.; Brudevold, R.; Tjonnfjord, G.E.; Largiader, C.R.; Lammle, B.; Kremer Hovinga, J.A. High prevalence of hereditary thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura in central Norway: From clinical observation to evidence. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2016, 14, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moatti-Cohen, M.; Garrec, C.; Wolf, M.; Boisseau, P.; Galicier, L.; Azoulay, E.; Stepanian, A.; Delmas, Y.; Rondeau, E.; Bezieau, S.; et al. Unexpected frequency of Upshaw-Schulman syndrome in pregnancy-onset thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Blood 2012, 119, 5888–5897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alwan, F.; Vendramin, C.; Liesner, R.; Clark, A.; Lester, W.; Dutt, T.; Thomas, W.; Gooding, R.; Biss, T.; Watson, H.G.; et al. Characterization and treatment of congenital thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Blood 2019, 133, 1644–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotta, L.A.; Garagiola, I.; Palla, R.; Cairo, A.; Peyvandi, F. ADAMTS13 mutations and polymorphisms in congenital thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Hum. Mutat. 2010, 31, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rank, C.U.; Kremer Hovinga, J.; Taleghani, M.M.; Lammle, B.; Gotze, J.P.; Nielsen, O.J. Congenital thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura caused by new compound heterozygous mutations of the ADAMTS13 gene. Eur. J. Haematol. 2014, 92, 168–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, H.M. Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura: A thrombotic disorder caused by ADAMTS13 deficiency. Hematol. Oncol. Clin. N. Am. 2007, 21, 609–632, v. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krogh, A.S.; Waage, A.; Quist-Paulsen, P. Congenital thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Tidsskr. Nor. Laegeforen 2016, 136, 1452–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peyvandi, F.; Palla, R.; Lotta, L.A.; Mackie, I.; Scully, M.A.; Machin, S.J. ADAMTS-13 assays in thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2010, 8, 631–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujimura, Y.; Lammle, B.; Tanabe, S.; Sakai, K.; Kimura, T.; Kokame, K.; Miyata, T.; Takahashi, Y.; Taniguchi, S.; Matsumoto, M. Patent ductus arteriosus generates neonatal hemolytic jaundice with thrombocytopenia in Upshaw-Schulman syndrome. Blood Adv. 2019, 3, 3191–3195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujimura, Y.; Matsumoto, M.; Kokame, K.; Isonishi, A.; Soejima, K.; Akiyama, N.; Tomiyama, J.; Natori, K.; Kuranishi, Y.; Imamura, Y.; et al. Pregnancy-induced thrombocytopenia and TTP, and the risk of fetal death, in Upshaw-Schulman syndrome: A series of 15 pregnancies in 9 genotyped patients. Br. J. Haematol. 2009, 144, 742–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.; Li, Z.; Zhang, L.; Jian, S.; Wang, C.; Song, Y.; Lv, Z.; Tang, X.; et al. Early indicators of neonatal-onset hereditary thrombotic thrombocytopenia purpura. Res. Pract. Thromb. Haemost. 2022, 6, e12820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borogovac, A.; Reese, J.A.; Gupta, S.; George, J.N. Morbidities and mortality in patients with hereditary thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Blood Adv. 2022, 6, 750–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borogovac, A.; Tarasco, E.; Kremer Hovinga, J.A.; Friedman, K.D.; Asch, A.S.; Vesely, S.K.; Prodan, C.I.; Terrell, D.R.; George, J.N. Prevalence of neuropsychiatric symptoms and stroke in patients with hereditary thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Blood 2022, 140, 785–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, B.; Cairo, A.; Pagliari, M.T.; Mancini, I.; Arcudi, S.; Peyvandi, F. Risk of diagnostic delay in congenital thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2019, 17, 666–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lozano Jaramillo, D.A.; Jimenez Ochoa, M.A. Infection as Trigger for Congenital Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura in an Adult Patient. J. Med. Cases 2021, 12, 339–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skeith, L.; Hurd, K.; Chaturvedi, S.; Chow, L.; Nicholas, J.; Lee, A.; Young, D.; Goodyear, D.; Soucie, J.; Girard, L.; et al. Hypercoagulability and Inflammatory Markers in a Case of Congenital Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura Complicated by Fetal Demise. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 7115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kokame, K.; Nobe, Y.; Kokubo, Y.; Okayama, A.; Miyata, T. FRETS-VWF73, a first fluorogenic substrate for ADAMTS13 assay. Br. J. Haematol. 2005, 129, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiasakul, T.; Cuker, A. Clinical and laboratory diagnosis of TTP: An integrated approach. Hematology Am. Soc. Hematol. Educ. Program 2018, 2018, 530–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakashima, M.O.; Zhang, X.; Rogers, H.J.; Vengal, L.; Gibson, B., Jr.; Daly, T.M.; Kottke-Marchant, K. Validation of a panel of ADAMTS13 assays for diagnosis of thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura: Activity, functional inhibitor, and autoantibody test. Int. J. Lab. Hematol. 2016, 38, 550–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukumar, S.; Lammle, B.; Cataland, S.R. Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura: Pathophysiology, Diagnosis, and Management. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeves, H.M.; Maitta, R.W. Immature Platelet Dynamics in Immune-Mediated Thrombocytopenic States. Front. Med. 2020, 7, 597734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeves, H.M.; Zhu, M.L.; Maitta, R.W. Immature platelet count responses of pediatric patients with immune-mediated thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Thromb. Res. 2024, 241, 109085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.L.; Reeves, H.M.; Maitta, R.W. Immature platelet dynamics correlate with ADAMTS13 deficiency and predict therapy response in immune-mediated thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Thromb. Res. 2021, 198, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeves, H.M.; Maitta, R.W. Comparison of absolute immature platelet count to the PLASMIC score at presentation in predicting ADAMTS13 deficiency in suspected thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Thromb. Res. 2022, 215, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coppo, P.; Schwarzinger, M.; Buffet, M.; Wynckel, A.; Clabault, K.; Presne, C.; Poullin, P.; Malot, S.; Vanhille, P.; Azoulay, E.; et al. Predictive features of severe acquired ADAMTS13 deficiency in idiopathic thrombotic microangiopathies: The French TMA reference center experience. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e10208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bendapudi, P.K.; Hurwitz, S.; Fry, A.; Marques, M.B.; Waldo, S.W.; Li, A.; Sun, L.; Upadhyay, V.; Hamdan, A.; Brunner, A.M.; et al. Derivation and external validation of the PLASMIC score for rapid assessment of adults with thrombotic microangiopathies: A cohort study. Lancet Haematol. 2017, 4, e157–e164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, M.; Miyakawa, Y.; Kokame, K.; Ueda, Y.; Wada, H.; Higasa, S.; Yagi, H.; Ogawa, Y.; Sakai, K.; Miyata, T.; et al. Diagnostic and treatment guidelines for thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (TTP) in Japan 2023. Int. J. Hematol. 2023, 118, 529–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rairikar, M.; Sartain, S.E.; Solomon, C.; Hui, S.-K.R.; Srivaths, P. Plasmic (PLASMICkid) Score for Pediatric Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura. Blood 2022, 140, 11346–11347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, N.; Rutherford, C.; Matevosyan, K.; Shen, Y.M.; Sarode, R. Role of ADAMTS13 in the management of thrombotic microangiopathies including thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (TTP). Br. J. Haematol. 2013, 163, 514–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.L.; Vesely, S.K.; Cataland, S.R.; Coppo, P.; Geldziler, B.; Iorio, A.; Matsumoto, M.; Mustafa, R.A.; Pai, M.; Rock, G.; et al. ISTH guidelines for treatment of thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2020, 18, 2496–2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rock, G.; Shumak, K.H.; Sutton, D.M.; Buskard, N.A.; Nair, R.C. Cryosupernatant as replacement fluid for plasma exchange in thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Members of the Canadian Apheresis Group. Br. J. Haematol. 1996, 94, 383–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toussaint-Hacquard, M.; Coppo, P.; Soudant, M.; Chevreux, L.; Mathieu-Nafissi, S.; Lecompte, T.; Gross, S.; Guillemin, F.; Schneider, T. Type of plasma preparation used for plasma exchange and clinical outcome of adult patients with acquired idiopathic thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura: A French retrospective multicenter cohort study. Transfusion 2015, 55, 2445–2451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeigler, Z.R.; Shadduck, R.K.; Gryn, J.F.; Rintels, P.B.; George, J.N.; Besa, E.C.; Bodensteiner, D.; Silver, B.; Kramer, R.E.; North American TTP Group. Cryoprecipitate poor plasma does not improve early response in primary adult thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (TTP). J. Clin. Apher. 2001, 16, 19–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubo, M.; Matsumoto, M. Frontiers in pathophysiology and management of thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Int. J. Hematol. 2023, 117, 331–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doyle, A.J.; Stubbs, M.J.; Lester, W.; Thomas, W.; Westwood, J.P.; Thomas, M.; Percy, C.; Prasannan, N.; Scully, M. The use of obinutuzumab and ofatumumab in the treatment of immune thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Br. J. Haematol. 2022, 198, 391–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maitta, R.W. Anti-CD20 therapeutic options in immune-mediated thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Br. J. Haematol. 2022, 198, 225–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peyvandi, F.; Scully, M.; Kremer Hovinga, J.A.; Cataland, S.; Knobl, P.; Wu, H.; Artoni, A.; Westwood, J.P.; Mansouri Taleghani, M.; Jilma, B.; et al. Caplacizumab for Acquired Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 374, 511–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scully, M.; Cataland, S.R.; Peyvandi, F.; Coppo, P.; Knobl, P.; Kremer Hovinga, J.A.; Metjian, A.; de la Rubia, J.; Pavenski, K.; Callewaert, F.; et al. Caplacizumab Treatment for Acquired Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 335–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roose, E.; Joly, B.S. Current and Future Perspectives on ADAMTS13 and Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura. Hamostaseologie 2020, 40, 322–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maitta, R.W.; Reeves, H.M.; Downes, K.A.; He, X.; Hackney, L.R.; Ahuja, S.P. Immature platelet dynamics in management of protracted response to therapy of a young pediatric patient with immune-mediated thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Thromb. Res. 2023, 228, 145–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavaz, L.; Cimasoni, L.; Kremer Hovinga, J.A.; Coppo, P.; Ansari, M. Caplacizumab as an add-on therapy in a 7-year-old girl with exacerbated immune-mediated thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura, a case report and literature review. Front. Pediatr. 2024, 12, 1448801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plaimauer, B.; Kremer Hovinga, J.A.; Juno, C.; Wolfsegger, M.J.; Skalicky, S.; Schmidt, M.; Grillberger, L.; Hasslacher, M.; Knobl, P.; Ehrlich, H.; et al. Recombinant ADAMTS13 normalizes von Willebrand factor-cleaving activity in plasma of acquired TTP patients by overriding inhibitory antibodies. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2011, 9, 936–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, Y.A. Apadamtase Alfa: First Approval. Drugs 2024, 84, 467–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scully, M.; Knobl, P.; Kentouche, K.; Rice, L.; Windyga, J.; Schneppenheim, R.; Kremer Hovinga, J.A.; Kajiwara, M.; Fujimura, Y.; Maggiore, C.; et al. Recombinant ADAMTS-13: First-in-human pharmacokinetics and safety in congenital thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Blood 2017, 130, 2055–2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scully, M.; Antun, A.; Cataland, S.R.; Coppo, P.; Dossier, C.; Biebuyck, N.; Hassenpflug, W.A.; Kentouche, K.; Knobl, P.; Kremer Hovinga, J.A.; et al. Recombinant ADAMTS13 in Congenital Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura. N. Engl. J. Med. 2024, 390, 1584–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu-Chen, S.; Connolly, B.; Cheng, L.; Subramanian, R.R.; Han, Z. mRNA treatment produces sustained expression of enzymatically active human ADAMTS13 in mice. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 7859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tersteeg, C.; Schiviz, A.; De Meyer, S.F.; Plaimauer, B.; Scheiflinger, F.; Rottensteiner, H.; Vanhoorelbeke, K. Potential for Recombinant ADAMTS13 as an Effective Therapy for Acquired Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2015, 35, 2336–2342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.L.; Kaufman, R.M.; Goodnough, L.T.; Sadler, J.E. Effect of plasma exchange on plasma ADAMTS13 metalloprotease activity, inhibitor level, and clinical outcome in patients with idiopathic and nonidiopathic thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Blood 2004, 103, 4043–4049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosler, G.A.; Cusumano, A.M.; Hutchins, G.M. Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura and hemolytic uremic syndrome are distinct pathologic entities. A review of 56 autopsy cases. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2003, 127, 834–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reese, J.A.; Muthurajah, D.S.; Kremer Hovinga, J.A.; Vesely, S.K.; Terrell, D.R.; George, J.N. Children and adults with thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura associated with severe, acquired Adamts13 deficiency: Comparison of incidence, demographic and clinical features. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2013, 60, 1676–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joly, B.S.; Stepanian, A.; Leblanc, T.; Hajage, D.; Chambost, H.; Harambat, J.; Fouyssac, F.; Guigonis, V.; Leverger, G.; Ulinski, T.; et al. Child-onset and adolescent-onset acquired thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura with severe ADAMTS13 deficiency: A cohort study of the French national registry for thrombotic microangiopathy. Lancet Haematol. 2016, 3, e537–e546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moake, J.L.; Rudy, C.K.; Troll, J.H.; Weinstein, M.J.; Colannino, N.M.; Azocar, J.; Seder, R.H.; Hong, S.L.; Deykin, D. Unusually large plasma factor VIII: Von Willebrand factor multimers in chronic relapsing thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. N. Engl. J. Med. 1982, 307, 1432–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furlan, M.; Robles, R.; Solenthaler, M.; Wassmer, M.; Sandoz, P.; Lammle, B. Deficient activity of von Willebrand factor-cleaving protease in chronic relapsing thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Blood 1997, 89, 3097–3103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, H.M.; Lian, E.C. Antibodies to von Willebrand factor-cleaving protease in acute thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. N. Engl. J. Med. 1998, 339, 1585–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scully, M.; Cataland, S.; Coppo, P.; de la Rubia, J.; Friedman, K.D.; Kremer Hovinga, J.; Lammle, B.; Matsumoto, M.; Pavenski, K.; Sadler, E.; et al. Consensus on the standardization of terminology in thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura and related thrombotic microangiopathies. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2017, 15, 312–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palma, L.M.P.; Vaisbich-Guimaraes, M.H.; Sridharan, M.; Tran, C.L.; Sethi, S. Thrombotic microangiopathy in children. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2022, 37, 1967–1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.L. ADAMTS13 and von Willebrand factor in thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Annu. Rev. Med. 2015, 66, 211–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Groot, R.; Lane, D.A.; Crawley, J.T. The ADAMTS13 metalloprotease domain: Roles of subsites in enzyme activity and specificity. Blood 2010, 116, 3064–3072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- South, K.; Luken, B.M.; Crawley, J.T.; Phillips, R.; Thomas, M.; Collins, R.F.; Deforche, L.; Vanhoorelbeke, K.; Lane, D.A. Conformational activation of ADAMTS13. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 18578–18583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roose, E.; Schelpe, A.S.; Tellier, E.; Sinkovits, G.; Joly, B.S.; Dekimpe, C.; Kaplanski, G.; Le Besnerais, M.; Mancini, I.; Falter, T.; et al. Open ADAMTS13, induced by antibodies, is a biomarker for subclinical immune-mediated thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Blood 2020, 136, 353–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zander, C.B.; Cao, W.; Zheng, X.L. ADAMTS13 and von Willebrand factor interactions. Curr. Opin. Hematol. 2015, 22, 452–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ercig, B.; Arfman, T.; Hrdinova, J.; Wichapong, K.; Reutelingsperger, C.P.M.; Vanhoorelbeke, K.; Nicolaes, G.A.F.; Voorberg, J. Conformational plasticity of ADAMTS13 in hemostasis and autoimmunity. J. Biol. Chem. 2021, 297, 101132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peyvandi, F.; Lavoretano, S.; Palla, R.; Feys, H.B.; Vanhoorelbeke, K.; Battaglioli, T.; Valsecchi, C.; Canciani, M.T.; Fabris, F.; Zver, S.; et al. ADAMTS13 and anti-ADAMTS13 antibodies as markers for recurrence of acquired thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura during remission. Haematologica 2008, 93, 232–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dainese, C.; Valeri, F.; Bruno, B.; Borchiellini, A. Anti-ADAMTS13 Autoantibodies: From Pathophysiology to Prognostic Impact-A Review for Clinicians. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 5630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonnez, Q.; Sakai, K.; Vanhoorelbeke, K. ADAMTS13 and Non-ADAMTS13 Biomarkers in Immune-Mediated Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 6169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Jin, M.; Lin, S.; Cataland, S.; Wu, H. ADAMTS13 activity and antigen during therapy and follow-up of patients with idiopathic thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura: Correlation with clinical outcome. Haematologica 2011, 96, 1521–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrari, S.; Palavra, K.; Gruber, B.; Kremer Hovinga, J.A.; Knobl, P.; Caron, C.; Cromwell, C.; Aledort, L.; Plaimauer, B.; Turecek, P.L.; et al. Persistence of circulating ADAMTS13-specific immune complexes in patients with acquired thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Haematologica 2014, 99, 779–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotta, L.A.; Valsecchi, C.; Pontiggia, S.; Mancini, I.; Cannavo, A.; Artoni, A.; Mikovic, D.; Meloni, G.; Peyvandi, F. Measurement and prevalence of circulating ADAMTS13-specific immune complexes in autoimmune thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2014, 12, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westwood, J.P.; Langley, K.; Heelas, E.; Machin, S.J.; Scully, M. Complement and cytokine response in acute Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura. Br. J. Haematol. 2014, 164, 858–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.C.; Yang, S.; Haven, S.; Holers, V.M.; Lundberg, A.S.; Wu, H.; Cataland, S.R. Complement activation and mortality during an acute episode of thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2013, 11, 1925–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karsten, C.M.; Kohl, J. The immunoglobulin, IgG Fc receptor and complement triangle in autoimmune diseases. Immunobiology 2012, 217, 1067–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reti, M.; Farkas, P.; Csuka, D.; Razso, K.; Schlammadinger, A.; Udvardy, M.L.; Madach, K.; Domjan, G.; Bereczki, C.; Reusz, G.S.; et al. Complement activation in thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2012, 10, 791–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Jay, L.; Lin, S.; Han, C.; Yang, S.; Cataland, S.R.; Masias, C. Interrelationship between ADAMTS13 activity, von Willebrand factor, and complement activation in remission from immune-mediated trhrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Br. J. Haematol. 2020, 189, e18–e20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorvillo, N.; van Haren, S.D.; Kaijen, P.H.; ten Brinke, A.; Fijnheer, R.; Meijer, A.B.; Voorberg, J. Preferential HLA-DRB1*11-dependent presentation of CUB2-derived peptides by ADAMTS13-pulsed dendritic cells. Blood 2013, 121, 3502–3510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ueda, S.; Oryoji, D.; Yamamoto, K.; Noh, J.Y.; Okamura, K.; Noda, M.; Kashiwase, K.; Kosuga, Y.; Sekiya, K.; Inoue, K.; et al. Identification of independent susceptible and protective HLA alleles in Japanese autoimmune thyroid disease and their epistasis. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 99, E379–E383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, E.; Lendas, K.A.; Chow, S.; Pirani, Y.; Gordon, D.; Dionisio, R.; Nguyen, D.; Spizuoco, A.; Fotino, M.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Disease relevant HLA class II alleles isolated by genotypic, haplotypic, and sequence analysis in North American Caucasians with pemphigus vulgaris. Hum. Immunol. 2006, 67, 125–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hrdinova, J.; D’Angelo, S.; Graca, N.A.G.; Ercig, B.; Vanhoorelbeke, K.; Veyradier, A.; Voorberg, J.; Coppo, P. Dissecting the pathophysiology of immune thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura: Interplay between genes and environmental triggers. Haematologica 2018, 103, 1099–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancini, I.; Ricano-Ponce, I.; Pappalardo, E.; Cairo, A.; Gorski, M.M.; Casoli, G.; Ferrari, B.; Alberti, M.; Mikovic, D.; Noris, M.; et al. Immunochip analysis identifies novel susceptibility loci in the human leukocyte antigen region for acquired thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2016, 14, 2356–2367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancini, I.; Giacomini, E.; Pontiggia, S.; Artoni, A.; Ferrari, B.; Pappalardo, E.; Gualtierotti, R.; Trisolini, S.M.; Capria, S.; Facchini, L.; et al. The HLA Variant rs6903608 Is Associated with Disease Onset and Relapse of Immune-Mediated Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura in Caucasians. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 3379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coppo, P.; Busson, M.; Veyradier, A.; Wynckel, A.; Poullin, P.; Azoulay, E.; Galicier, L.; Loiseau, P.; French Reference Centre For Thrombotic Microangiopathies. HLA-DRB1*11: A strong risk factor for acquired severe ADAMTS13 deficiency-related idiopathic thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura in Caucasians. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2010, 8, 856–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, G.; Smith, K.J.; Hadley, T.J.; Djulbegovic, B.; Troup, G.M.; Oldfather, J.; Barker, R.L. HLA-DR53 protects against thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura/adult hemolytic uremic syndrome. Am. J. Hematol. 1994, 47, 189–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martino, S.; Jamme, M.; Deligny, C.; Busson, M.; Loiseau, P.; Azoulay, E.; Galicier, L.; Pene, F.; Provot, F.; Dossier, A.; et al. Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura in Black People: Impact of Ethnicity on Survival and Genetic Risk Factors. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0156679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, C.T.; Zobeck, M.; Kim, T.O.; Sartain, S.E.; Raffini, L.; Srivaths, L. Adolescent acquired thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura: An analysis of the Pediatric Health Information System database. Thromb. Res. 2023, 222, 63–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waqar, S.H.B.; Khan, A.A.; Memon, S. Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura: A new menace after COVID bnt162b2 vaccine. Int. J. Hematol. 2021, 114, 626–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Althaus, K.; Marini, I.; Zlamal, J.; Pelzl, L.; Singh, A.; Haberle, H.; Mehrlander, M.; Hammer, S.; Schulze, H.; Bitzer, M.; et al. Antibody-induced procoagulant platelets in severe COVID-19 infection. Blood 2021, 137, 1061–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Picod, A.; Rebibou, J.M.; Dossier, A.; Cador, B.; Ribes, D.; Vasco-Moynet, C.; Stephan, C.; Bellal, M.; Wynckel, A.; Poullin, P.; et al. Immune-mediated thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura following COVID-19 vaccination. Blood 2022, 139, 2565–2569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saluja, P.; Gautam, N.; Yadala, S.; Venkata, A.N. Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (TTP) after COVID-19 vaccination: A systematic review of reported cases. Thromb. Res. 2022, 214, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papakonstantinou, A.; Kalmoukos, P.; Mpalaska, A.; Koravou, E.E.; Gavriilaki, E. ADAMTS13 in the New Era of TTP. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 8137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connelly-Smith, L.; Alquist, C.R.; Aqui, N.A.; Hofmann, J.C.; Klingel, R.; Onwuemene, O.A.; Patriquin, C.J.; Pham, H.P.; Sanchez, A.P.; Schneiderman, J.; et al. Guidelines on the Use of Therapeutic Apheresis in Clinical Practice—Evidence-Based Approach from the Writing Committee of the American Society for Apheresis: The Ninth Special Issue. J. Clin. Apher. 2023, 38, 77–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cataland, S.R.; Kourlas, P.J.; Yang, S.; Geyer, S.; Witkoff, L.; Wu, H.; Masias, C.; George, J.N.; Wu, H.M. Cyclosporine or steroids as an adjunct to plasma exchange in the treatment of immune-mediated thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Blood Adv. 2017, 1, 2075–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaturvedi, S.; Antun, A.G.; Farland, A.M.; Woods, R.; Metjian, A.; Park, Y.A.; de Ridder, G.; Gibson, B.; Kasthuri, R.S.; Liles, D.K.; et al. Race, rituximab, and relapse in TTP. Blood 2022, 140, 1335–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubo, M.; Sakai, K.; Yoshii, Y.; Hayakawa, M.; Matsumoto, M. Rituximab prolongs the time to relapse in patients with immune thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura: Analysis of off-label use in Japan. Int. J. Hematol. 2020, 112, 764–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sargentini-Maier, M.L.; De Decker, P.; Tersteeg, C.; Canvin, J.; Callewaert, F.; De Winter, H. Clinical pharmacology of caplacizumab for the treatment of patients with acquired thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Expert. Rev. Clin. Pharmacol. 2019, 12, 537–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsivalis, K.V.; Thomas, J. Caplacizumab for Acute Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura. J. Adv. Pract. Oncol. 2021, 12, 211–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergstrand, M.; Hansson, E.; Delaey, B.; Callewaert, F.; De Passos Sousa, R.; Sargentini-Maier, M.L. Caplacizumab Model-Based Dosing Recommendations in Pediatric Patients With Acquired Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2022, 62, 409–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalinina, I.I.; Antonova, K.S.; Avdonin, P.V.; Klebanova, E.E.; Kotskaya, N.N.; Kurnikova, E.E.; Shutova, A.D.; Matveev, V.E.; Maschan, A.A. Successful Treatment of Acquired Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura With Caplacizumab Combined With Plasma Exchanges and Immune Suppression in 3 Children. J. Pediatr. Hematol. Oncol. 2024, 46, e220–e222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, A.; Keogh, L.; Dickens, E.; Dutt, T.; Grainger, J.; Gregory, R.; Mapplebeck, C.; Richards, M.; Stokley, S.; Salta, S.; et al. Caplacizumab in pediatric immune thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura: The UK TTP Registry experience. Blood Adv. 2024, 8, 4563–4567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Diagnosis | cTTP | iTTP | ITP | HUS | DIC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pathophysiology | Congenital deficiency of ADAMTS-13 | Auto-antibodies against ADAMTS-13 | Autoantibodies against platelet antigens | Shiga toxin-producing E.coli | Clotting factor consumption |
| ADAMTS-13 activity | Deficient/absent (<10%) | Deficient (<10%) | Normal | Minimally decreased | Decreased |
| Laboratory findings | ↓ HGB, ↓ haptoglobin, ↑ LDH, ↑ indirect bilirubin, and severe thrombocytopenia (<20 × 109/L) with schistocytes Normal PT, PTT, and fibrinogen and a slight increase in D-dimer | ↓ HGB, ↓ haptoglobin, ↑ LDH,↑ indirect bilirubin, and severe thrombocytopenia (<20 × 109/L) with schistocytes Normal PT, PTT, and fibrinogen and a slight increase in D-dimer | Isolated thrombocytopenia with normal HGB and WBC ↑LDH Normal PT, PTT, fibrinogen, and D-dimer | ↓ HGB, ↓ haptoglobin, ↑ LDH,↑ indirect bilirubin, and thrombocytopenia with schistocytes Normal PT, PTT, and fibrinogen and a slight increase in D-dimer | ↑ PT, ↑ PTT, ↑ D-dimer, ↓ fibrinogen, and thrombocytopenia with schistocytes |
| Treatment | Plasma infusion; recombinant human ADAMTS13; gene therapy | TPE (first line); immune suppression (steroids, rituximab); caplacizumab | Methylprednisolone; intravenous immunoglobin; thrombopoietin receptor agonists; rituximab; splenectomy | Supportive treatment; avoid antibiotics and antimotility agents; eculizumab | Treat the underlying cause; anticoagulation; cryoprecipitate; platelet transfusion; fibrinolytic therapy |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shrestha, N.; Okpako, E.; Maitta, R.W. Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura in Pediatric Patients. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 1038. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13051038
Shrestha N, Okpako E, Maitta RW. Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura in Pediatric Patients. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(5):1038. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13051038
Chicago/Turabian StyleShrestha, Niki, Ebruphiyo Okpako, and Robert W. Maitta. 2025. "Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura in Pediatric Patients" Biomedicines 13, no. 5: 1038. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13051038
APA StyleShrestha, N., Okpako, E., & Maitta, R. W. (2025). Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura in Pediatric Patients. Biomedicines, 13(5), 1038. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13051038






