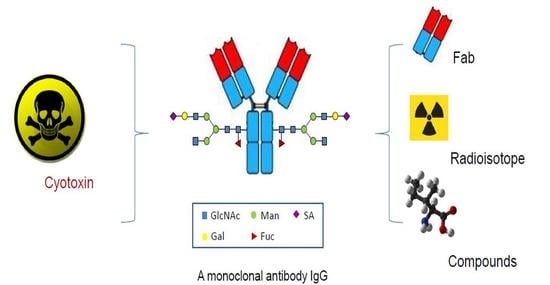
Site-Specific Antibody Conjugation for ADC and Beyond
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Site-Specific ADC through Specific Amino Acids
3. Site-Specific ADC through Unnatural Amino Acids
4. Site-Specific ADC through Glycans
5. Site-Specific ADC through Short Peptide Tags
6. Site-Specific Antibody Conjugation for Diagnosis
7. Site-Specific Antibody Conjugation for Other Therapeutic Applications
8. Conclusions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ADC | Antibody-drug conjugates |
| AML | Acute myelogenous leukemia |
| ALL | Acute lymphoblastic leukemia |
| MMAE | Monomethyl auristatin E |
| PBD | Pyrrolobenzodiazepine |
| LC | Light chain |
| mTG | Microbial transglutaminase |
| SPAAC | Strain-promoted azide-alkyne cycloaddition |
| aaRS | Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase |
| EGFR | Epidermal growth factor receptor |
| pylRS | Pyrrolysyl-tRNA synthetase |
| pAMF | p-azidomethyl-l-phenylalanine |
| DBCO-PEG-MMAF | DBCO-PEG-monomethyl auristatin F |
| Sec | Selenocysteine |
| GlaNAc | N-acetylgalactosamine |
| BCN | Bicyclononyne |
| FGE | Formylglycine generating enzyme |
| OI | Optical imaging |
| NIRF | Near-infrared fluorescent |
| PBMCs | Peripheral blood mononuclear cells |
| DUPA | 2-[3-dicarboxy propyl]-ureido] pentanedioic acid |
| APC | Antibody-polymer conjugation |
| LPS | Lipopolysaccharide |
| IgG | Immunoglobulin G |
| HER2 | Human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 |
| DAR | Drug-to-antibody ratio |
| DM1 | Mertansine |
| HC | Heavy chain |
| DBM | Dibromomaleimide |
| DBCO | Dibenzocyclooctynes |
| pAcF | p-acetylphenylalanine |
| CHO | Chinese hamster ovary |
| MMAD | Monomethyl auristatin D |
| tRNA pyl | Pyrrolysyl-tRNA |
| TyrRS | Tyrosyl tRNA synthetase |
| MMAF | Monomethyl auristatin F |
| SECIS | Sec incorporation sequence |
| GlcNAc | N-acetylglucosamine |
| SA | Sialic acid |
| PET | Position emission tomography |
| PSMA | Prostate specific membrane antigen |
| PCR | Polymerase chain reaction |
| CLL1 | C-type lectin-like molecule-1 |
| AAC | Antibody-antibiotic conjugate |
| PDE4 | phosphodiesterase 4 |
| LXR | Liver X receptor |
References
- Reichert, J.M. Antibodies to watch in 2017. Money Adv. Budg. Serv. 2017, 9, 167–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ecker, D.M.; Jones, S.D.; Levine, H.L. The therapeutic monoclonal antibody market. Money Adv. Budg. Serv. 2015, 7, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alley, S.C.; Okeley, N.M.; Senter, P.D. Antibody-drug conjugates: Targeted drug delivery for cancer. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2010, 14, 529–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beck, A. Review of Antibody-Drug Conjugates, Methods in Molecular Biology series: A book edited by Laurent Ducry. Money Adv. Budg. Serv. 2014, 6, 30–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, P.J.; Senter, P.D. Antibody-drug conjugates for cancer therapy. Cancer J. 2008, 14, 154–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teicher, B.A. Antibody-drug conjugate targets. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 2009, 9, 982–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okeley, N.M.; Alley, S.C.; Senter, P.D. Advancing antibody drug conjugation: From the laboratory to a clinically approved anticancer drug. Hematol. Oncol. Clin. N. Am. 2014, 28, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambert, J.M. Drug-conjugated antibodies for the treatment of cancer. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2012, 76, 248–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senter, P.D.; Sievers, E.L. The discovery and development of brentuximab vedotin for use in relapsed Hodgkin lymphoma and systemic anaplastic large cell lymphoma. Nat. Biotechnol. 2012, 30, 631–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sievers, E.L.; Senter, P.D. Antibody-drug conjugates in cancer therapy. Annu. Rev. Med. 2013, 64, 15–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brinkmann, U.; Kontermann, R.E. The making of bispecific antibodies. Money Adv. Budg. Serv. 2017, 9, 182–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strebhardt, K.; Ullrich, A. Paul Ehrlich’s magic bullet concept: 100 years of progress. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2008, 8, 473–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Godwin, C.D.; Gale, R.P.; Walter, R.B. Gemtuzumab ozogamicin in acute myeloid leukemia. Leukemia 2017, 31, 1855–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhillon, S. Trastuzumab Emtansine: A Review of Its Use in Patients with HER2-Positive Advanced Breast Cancer Previously Treated with Trastuzumab-Based Therapy. Drugs 2014, 74, 675–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doronina, S.O.; Toki, B.E.; Torgov, M.Y.; Mendelsohn, B.A.; Cerveny, C.G.; Chace, D.F.; DeBlanc, R.L.; Gearing, R.P.; Bovee, T.D.; Siegall, C.B.; et al. Development of potent monoclonal antibody auristatin conjugates for cancer therapy. Nat. Biotechnol. 2003, 21, 778–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gualberto, A. Brentuximab Vedotin (SGN-35), an antibody-drug conjugate for the treatment of CD30-positive malignancies. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2012, 21, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kantarjian, H.M.; DeAngelo, D.J.; Stelljes, M.; Martinelli, G.; Liedtke, M.; Stock, W.; Gökbuget, N.; O’Brien, S.; Wang, K.; Wang, T.; et al. Inotuzumab Ozogamicin versus Standard Therapy for Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 740–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambert, J.M.; Chari, R.V. Ado-trastuzumab Emtansine (T-DM1): An antibody-drug conjugate (ADC) for HER2-positive breast cancer. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 6949–6964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haddley, K. Brentuximab vedotin: Its role in the treatment of anaplastic large cell and Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Drugs Today (Barc.) 2012, 48, 259–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horwitz, S.M.; Advani, R.H.; Bartlett, N.L.; Jacobsen, E.D.; Sharman, J.P.; O’Connor, O.A.; Siddiqi, T.; Kennedy, D.A.; Oki, Y. Objective responses in relapsed T-cell lymphomas with single agent brentuximab vedotin. Blood 2014, 123, 3095–3100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krop, I.; Winer, E.P. Trastuzumab emtansine: A novel antibody-drug conjugate for HER2-positive breast cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krop, I.E.; Kim, S.B.; Gonzalez-Martin, A.; Lorusso, P.M.; Ferrero, J.M.; Smitt, M.; Badovinac-Crnjevic, T.; Hoersch, S.; Wildiers, H. Trastuzumab emtansine versus treatment of physician’s choice for pretreated HER2-positive advanced breast cancer (TH3RESA): A randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2014, 15, 689–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephan, J.P.; Kozak, K.R.; Wong, W.L. Challenges in developing bioanalytical assays for characterization of antibody-drug conjugates. Bioanalysis 2011, 3, 677–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wakankar, A.A.; Feeney, M.B.; Rivera, J.; Chen, Y.; Kim, M.; Sharma, V.K.; Wang, Y.J. Physicochemical stability of the antibody-drug conjugate Trastuzumab-DM1: Changes due to modification and conjugation processes. Bioconjug. Chem. 2010, 21, 1588–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Amphlett, G.; Blattler, W.A.; Lambert, J.M.; Zhang, W. Structural characterization of the maytansinoid-monoclonal antibody immunoconjugate, huN901-DM1, by mass spectrometry. Protein Sci. 2005, 14, 2436–2446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panowski, S.; Bhakta, S.; Raab, H.; Polakis, P.; Junutula, J.R. Site-specific antibody drug conjugates for cancer therapy. Money Adv. Budg. Serv. 2014, 6, 34–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Junutula, J.R.; Raab, H.; Clark, S.; Bhakta, S.; Leipold, D.D.; Weir, S.; Chen, Y.; Simpson, M.; Tsai, S.P.; Dennis, M.S.; et al. Site-specific conjugation of a cytotoxic drug to an antibody improves the therapeutic index. Nat. Biotechnol. 2008, 26, 925–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Junutula, J.R.; Flagella, K.M.; Graham, R.A.; Parsons, K.L.; Ha, E.; Raab, H.; Bhakta, S.; Nguyen, T.; Dugger, D.L.; Li, G.; et al. Engineered thio-trastuzumab-DM1 conjugate with an improved therapeutic index to target human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-positive breast cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2010, 16, 4769–4778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeffrey, S.C.; Burke, P.J.; Lyon, R.P.; Meyer, D.W.; Sussman, D.; Anderson, M.; Hunter, J.H.; Leiske, C.I.; Miyamoto, J.B.; Nicholas, N.D.; et al. A potent anti-CD70 antibody-drug conjugate combining a dimeric pyrrolobenzodiazepine drug with site-specific conjugation technology. Bioconjug. Chem. 2013, 24, 1256–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimasi, N.; Fleming, R.; Zhong, H.; Bezabeh, B.; Kinneer, K.; Christie, R.J.; Fazenbaker, C.; Wu, H.; Gao, C. Efficient Preparation of Site-Specific Antibody-Drug Conjugates Using Cysteine Insertion. Mol. Pharm. 2017, 14, 1501–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bryant, P.; Pabst, M.; Badescu, G.; Bird, M.; McDowell, W.; Jamieson, E.; Swierkosz, J.; Jurlewicz, K.; Tommasi, R.; Henseleit, K.; et al. In Vitro and In Vivo Evaluation of Cysteine Rebridged Trastuzumab-MMAE Antibody Drug Conjugates with Defined Drug-to-Antibody Ratios. Mol. Pharm. 2015, 12, 1872–1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behrens, C.R.; Ha, E.H.; Chinn, L.L.; Bowers, S.; Probst, G.; Fitch-Bruhns, M.; Monteon, J.; Valdiosera, A.; Bermudez, A.; Liao-Chan, S.; et al. Antibody-Drug Conjugates (ADCs) Derived from Interchain Cysteine Cross-Linking Demonstrate Improved Homogeneity and Other Pharmacological Properties over Conventional Heterogeneous ADCs. Mol. Pharm. 2015, 12, 3986–3998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dennler, P.; Schibli, R.; Fischer, E. Enzymatic antibody modification by bacterial transglutaminase. Methods Mol. Biol. 2013, 1045, 205–215. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dennler, P.; Chiotellis, A.; Fischer, E.; Bregeon, D.; Belmant, C.; Gauthier, L.; Lhospice, F.; Romagne, F.; Schibli, R. Transglutaminase-based chemo-enzymatic conjugation approach yields homogeneous antibody-drug conjugates. Bioconjug. Chem. 2014, 25, 569–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, B.Q.; Xu, K.; Liu, L.; Raab, H.; Bhakta, S.; Kenrick, M.; Parsons-Reponte, K.L.; Tien, J.; Yu, S.F.; Mai, E.; et al. Conjugation site modulates the in vivo stability and therapeutic activity of antibody-drug conjugates. Nat. Biotechnol. 2012, 30, 184–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Axup, J.Y.; Bajjuri, K.M.; Ritland, M.; Hutchins, B.M.; Kim, C.H.; Kazane, S.A.; Halder, R.; Forsyth, J.S.; Santidrian, A.F.; Stafin, K.; et al. Synthesis of site-specific antibody-drug conjugates using unnatural amino acids. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 16101–16106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, F.; Lu, Y.; Manibusan, A.; Sellers, A.; Tran, H.; Sun, Y.; Phuong, T.; Barnett, T.; Hehli, B.; Song, F.; et al. A general approach to site-specific antibody drug conjugates. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 1766–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, D.; Atkinson, J.; Guevara, C.I.; Zhang, C.; Kery, V.; Moon, S.J.; Virata, C.; Yang, P.; Lowe, C.; Pinkstaff, J.; et al. In vitro and in vivo evaluation of cysteine and site specific conjugated herceptin antibody-drug conjugates. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e83865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- VanBrunt, M.P.; Shanebeck, K.; Caldwell, Z.; Johnson, J.; Thompson, P.; Martin, T.; Dong, H.; Li, G.; Xu, H.; D’Hooge, F.; et al. Genetically Encoded Azide Containing Amino Acid in Mammalian Cells Enables Site-Specific Antibody-Drug Conjugates Using Click Cycloaddition Chemistry. Bioconjug. Chem. 2015, 26, 2249–2260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmerman, E.S.; Heibeck, T.H.; Gill, A.; Li, X.; Murray, C.J.; Madlansacay, M.R.; Tran, C.; Uter, N.T.; Yin, G.; Rivers, P.J.; et al. Production of site-specific antibody-drug conjugates using optimized non-natural amino acids in a cell-free expression system. Bioconjug. Chem. 2014, 25, 351–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Nelson, C.G.; Nair, R.R.; Hazlehurst, L.; Moroni, T.; Martinez-Acedo, P.; Nanna, A.R.; Hymel, D.; Burke, T.R., Jr.; Rader, C. Stable and Potent Selenomab-Drug Conjugates. Cell Chem. Biol. 2017, 24, 433–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okeley, N.M.; Toki, B.E.; Zhang, X.; Jeffrey, S.C.; Burke, P.J.; Alley, S.C.; Senter, P.D. Metabolic Engineering of Monoclonal Antibody Carbohydrates for Antibody-Drug Conjugation. Bioconjug. Chem. 2013, 24, 1650–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramakrishnan, B.; Qasba, P.K. Structure-based design of beta 1,4-galactosyltransferase I (beta 4Gal-T1) with equally efficient N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase activity: Point mutation broadens beta 4Gal-T1 donor specificity. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 20833–20839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramakrishnan, B.; Boeggeman, E.; Pasek, M.; Qasba, P.K. Bioconjugation using mutant glycosyltransferases for the site-specific labeling of biomolecules with sugars carrying chemical handles. Methods Mol. Biol. 2011, 751, 281–296. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Z.; Ramakrishnan, B.; Li, J.; Wang, Y.; Feng, Y.; Prabakaran, P.; Colantonio, S.; Dyba, M.A.; Qasba, P.K.; Dimitrov, D.S. Site-specific antibody-drug conjugation through an engineered glycotransferase and a chemically reactive sugar. Money Adv. Budg. Serv. 2014, 6, 1190–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Geel, R.; Wijdeven, M.A.; Heesbeen, R.; Verkade, J.M.; Wasiel, A.A.; van Berkel, S.S.; van Delft, F.L. Chemoenzymatic Conjugation of Toxic Payloads to the Globally Conserved N-Glycan of Native mAbs Provides Homogeneous and Highly Efficacious Antibody-Drug Conjugates. Bioconjug. Chem. 2015, 26, 2233–2242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Q.; Stefano, J.E.; Manning, C.; Kyazike, J.; Chen, B.; Gianolio, D.A.; Park, A.; Busch, M.; Bird, J.; Zheng, X.; et al. Site-specific antibody-drug conjugation through glycoengineering. Bioconjug. Chem. 2014, 25, 510–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Fang, T.; Boons, G.J. Preparation of Well-Defined Antibody-Drug Conjugates through Glycan Remodeling and Strain-Promoted Azide-Alkyne Cycloadditions. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2014, 53, 7179–7182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, F.; Wang, L.X.; Huang, W. Chemoenzymatic synthesis of glycoengineered IgG antibodies and glycosite-specific antibody-drug conjugates. Nat. Protoc. 2017, 12, 1702–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strop, P.; Liu, S.H.; Dorywalska, M.; Delaria, K.; Dushin, R.G.; Tran, T.T.; Ho, W.H.; Farias, S.; Casas, M.G.; Abdiche, Y.; et al. Location matters: Site of conjugation modulates stability and pharmacokinetics of antibody drug conjugates. Chem. Biol. 2013, 20, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beerli, R.R.; Hell, T.; Merkel, A.S.; Grawunder, U. Sortase Enzyme-Mediated Generation of Site-Specifically Conjugated Antibody Drug Conjugates with High In Vitro and In Vivo Potency. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0131177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, P.; Shui, W.; Carlson, B.L.; Hu, N.; Rabuka, D.; Lee, J.; Bertozzi, C.R. Site-specific chemical modification of recombinant proteins produced in mammalian cells by using the genetically encoded aldehyde tag. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 3000–3005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabuka, D.; Rush, J.S.; deHart, G.W.; Wu, P.; Bertozzi, C.R. Site-specific chemical protein conjugation using genetically encoded aldehyde tags. Nat. Protoc. 2012, 7, 1052–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moek, K.L.; Giesen, D.; Kok, I.C.; de Groot, D.J.A.; Jalving, M.; Fehrmann, R.S.N.; Lub-de Hooge, M.N.; Brouwers, A.H.; de Vries, E.G.E. Theranostics Using Antibodies and Antibody-Related Therapeutics. J. Nucl. Med. Off. Publ. Soc. Nucl. Med. 2017, 58, 83s–90s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeglis, B.M.; Davis, C.B.; Aggeler, R.; Kang, H.C.; Chen, A.; Agnew, B.J.; Lewis, J.S. Enzyme-mediated methodology for the site-specific radiolabeling of antibodies based on catalyst-free click chemistry. Bioconjug. Chem. 2013, 24, 1057–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeglis, B.M.; Davis, C.B.; Abdel-Atti, D.; Carlin, S.D.; Chen, A.; Aggeler, R.; Agnew, B.J.; Lewis, J.S. Chemoenzymatic strategy for the synthesis of site-specifically labeled immunoconjugates for multimodal PET and optical imaging. Bioconjug. Chem. 2014, 25, 2123–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houghton, J.L.; Zeglis, B.M.; Abdel-Atti, D.; Aggeler, R.; Sawada, R.; Agnew, B.J.; Scholz, W.W.; Lewis, J.S. Site-specifically labeled CA19.9-targeted immunoconjugates for the PET, NIRF, and multimodal PET/NIRF imaging of pancreatic cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 15850–15855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cook, B.E.; Adumeau, P.; Membreno, R.; Carnazza, K.E.; Brand, C.; Reiner, T.; Agnew, B.J.; Lewis, J.S.; Zeglis, B.S. Pretargeted PET Imaging Using a Site-Specifically Labeled Immunoconjugate. Bioconjug. Chem. 2016, 27, 1789–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazane, S.A.; Sok, D.; Cho, E.H.; Uson, M.L.; Kuhn, P.; Schultz, P.G.; Smider, V.V. Site-specific DNA-antibody conjugates for specific and sensitive immuno-PCR. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 3731–3736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rader, C. Chemically programmed antibodies. Trends Biotechnol. 2014, 32, 186–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, C.H.; Axup, J.Y.; Dubrovska, A.; Kazane, S.A.; Hutchins, B.A.; Wold, E.D.; Smider, V.V.; Schultz, P.G. Synthesis of bispecific antibodies using genetically encoded unnatural amino acids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 9918–9921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, H.; Zhou, Q.; Deshmukh, V.; Phull, H.; Ma, J.; Tardif, V.; Naik, R.R.; Bouvard, C.; Zhang, Y.; Choi, S.; et al. Targeting human C-type lectin-like molecule-1 (CLL1) with a bispecific antibody for immunotherapy of acute myeloid leukemia. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2014, 53, 9841–9845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazane, S.A.; Axup, J.Y.; Kim, C.H.; Ciobanu, M.; Wold, E.D.; Barluenga, S.; Hutchins, B.A.; Schultz, P.G.; Winssinger, N.; Smider, V.V. Self-assembled antibody multimers through peptide nucleic acid conjugation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 340–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, C.H.; Axup, J.Y.; Lawson, B.R.; Yun, H.; Tardif, V.; Choi, S.H.; Zhou, Q.; Dubrovska, A.; Biroc, S.L.; Marsden, R.; et al. Bispecific small molecule-antibody conjugate targeting prostate cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 17796–17801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, H.; Thomas, J.D.; Burke, T.R., Jr.; Rader, C. Chemically programmed bispecific antibodies that recruit and activate T cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 28206–28214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walseng, E.; Nelson, C.G.; Qi, J.; Nanna, A.R.; Roush, W.R.; Goswami, R.K.; Sinha, S.C.; Burke, T.R., Jr.; Rader, C. Chemically Programmed Bispecific Antibodies in Diabody Format. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 19661–19673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehar, S.M.; Pillow, T.; Xu, M.; Staben, L.; Kajihara, K.K.; Vandlen, R.; DePalatis, L.; Raab, H.; Hazenbos, W.L.; Morisaki, J.H.; et al. Novel antibody-antibiotic conjugate eliminates intracellular S. aureus. Nature 2015, 527, 323–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, H.; Wang, D.; Kazane, S.; Javahishvili, T.; Tian, F.; Song, F.; Sellers, A.; Barnett, B.; Schultz, P.G. Site-specific antibody-polymer conjugates for siRNA delivery. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 13885–13891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, S.; Pearson, A.D.; Lim, R.K.; Rodgers, D.T.; Li, S.; Parker, H.B.; Weglarz, M.; Hampton, E.N.; Bollong, M.J.; Shen, J.; et al. Targeted Delivery of an Anti-inflammatory PDE4 Inhibitor to Immune Cells via an Antibody-drug Conjugate. Mol. Ther. J. Am. Soc. Gene Ther. 2016, 24, 2078–2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, R.K.; Yu, S.; Cheng, B.; Li, S.; Kim, N.J.; Cao, Y.; Chi, V.; Kim, J.Y.; Chatterjee, A.K.; Schultz, P.G.; et al. Targeted Delivery of LXR Agonist Using a Site-Specific Antibody-Drug Conjugate. Bioconjug. Chem. 2015, 26, 2216–2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Technologiees | Specific Amino Acids | Unnatural Amino Acids | Glycans | Short Peptide Tags |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Conjugation sites | C, Q | pAcF, pAMF, Sec etc. | SA, Gal, Fuc etc. | LLQG, LCxPxR etc. |
| Cell line engineering | − | + | − | ± |
| Metabolic labeling | − | + | ± | − |
| In vivo protein engineering | + | + | − | + |
| In vitro enzymatic modification | ± | ± | + | + |
| Chemical modification | + | − | ± | − |
| Selected references | [27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35] | [36,37,38,39,40,41] | [42,43,44,45,46,47,48,49] | [50,51,52,53] |
© 2017 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, Q. Site-Specific Antibody Conjugation for ADC and Beyond. Biomedicines 2017, 5, 64. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines5040064
Zhou Q. Site-Specific Antibody Conjugation for ADC and Beyond. Biomedicines. 2017; 5(4):64. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines5040064
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Qun. 2017. "Site-Specific Antibody Conjugation for ADC and Beyond" Biomedicines 5, no. 4: 64. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines5040064
APA StyleZhou, Q. (2017). Site-Specific Antibody Conjugation for ADC and Beyond. Biomedicines, 5(4), 64. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines5040064