The Repertoire of Adenovirus in Human Disease: The Innocuous to the Deadly
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Structure
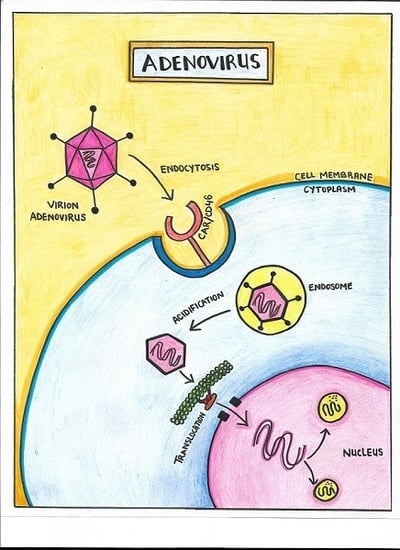
3. Biology of Infection
4. Transmission
5. Epidemiology and Global Trends
6. Disease Spectrum
7. Workup
8. Management
9. Infection Control
10. Vaccination
11. Immunocompetent Patients with Mild Disease
12. Immunocompromised Patients and Antiviral Drugs
13. Antiviral Agents
14. Summary
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Smith, J.G.; Wiethoff, C.M.; Stewart, P.L.; Nemerow, G.R. Adenovirus. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2010, 343, 195–224. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Han, G.; Niu, H.; Zhao, S.; Zhu, B.; Wang, C.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, M.; Yang, S.; Liu, F.; Wan, C.; et al. Identification and typing of respiratory adenoviruses in Guangzhou, Southern China using a rapid and simple method. Virol. Sin. 2013, 28, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergelson, J.M.; Krithivas, A.; Celi, L.; Droguett, G.; Horwitz, M.S.; Wickham, T.; Crowell, R.L.; Finberg, R.W. The murine CAR homolog is a receptor for coxsackie B viruses and adenoviruses. J. Virol. 1998, 72, 415–419. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gaggar, A.; Shayakhmetov, D.M.; Lieber, A. CD46 is a cellular receptor for group B adeno-viruses. Nat. Med. 2003, 9, 1408–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varga, M.J.; Weibull, C.; Everitt, E. Infectious entry pathway of adenovirus type 2. J. Virol. 1991, 65, 6061–6070. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Greber, U.F.; Willetts, M.; Webster, P.; Helenius, A. Stepwise dismantling of adenovirus 2 during entry into cells. Cell 1993, 75, 477–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chardonnet, Y.; Dales, S. Early events in the interaction of adenoviruses with HeLa cells. I. Penetration of type 5 and intracellular release of the DNA genome. Virology 1970, 40, 462–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.G.; Nemerow, G.R. Mechanism of adenovirus neutralization by human alpha-defen-sins. Cell Host Microbe 2008, 3, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montone, K.T.; Furth, E.E.; Pietra, G.G.; Gupta, P.K. Neonatal adenovirus infection: A case report with in situ hybridization confirmation of ascending intrauterine infection. Diagn. Cytopathol. 1995, 12, 341–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koneru, B.; Atchison, R.; Jaffe, R.; Cassavilla, A.; Van Thiel, D.H.; Starzl, T.E. Serological studies of adenoviral hepatitis following pediatric liver transplantation. Transplant. Proc. 1990, 22, 1547–1548. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rowe, W.P.; Huebner, R.J.; Gilmore, L.K.; Parrot, R.H.; Ward, T.G. Isolation of a cytopathogenic agent from human adenoids undergoing spontaneous degeneration in tissue culture. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 1953, 84, 570–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hendrix, R.M.; Lindner, J.L.; Benton, F.R.; Monteith, S.C.; Tuchscherer, M.A.; Gray, G.C.; Gaydos, J.C. Large, persistent epidemic of adenovirus type 4-associated acute respiratory disease in U. S. army trainees. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 1999, 5, 798–801. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Binder, A.M.; Biggs, H.M.; Haynes, A.K.; Chommanard, C.; Lu, X.; Erdman, D.D.; Watson, J.T.; Gerber, S.I. Human Adenovirus Surveillance—United States, 2003–2016. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2017, 66, 1039–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization (WHO). Viruses. In Water Recreation and Disease. Plausibility of Associated Infections: Acute Effects, Sequelae and Mortality; Pond, K., Ed.; IWA Publishing: London, UK; Available online: http://www.who.int/water_sanitation_health/bathing/recreadischap6.pdf (accessed on 14 December 2017).
- Cheng, J.; Qi, X.; Chen, D.; Xu, X.; Wang, G.; Dai, Y.; Cui, D.; Chen, Q.; Fan, P.; Ni, L.; et al. Epidemiology and transmission characteristics of human adenovirus type 7 caused acute respiratory disease outbreak in military trainees in East China. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2016, 8, 2331. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yusof, M.A.; Rashid, T.R.; Thayan, R.; Othman, K.A.; Hasan, N.A.; Adnan, N.; Saat, Z. Human adenovirus type 7 outbreak in Police Training Center, Malaysia, 2011. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2012, 18, 852–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeon, K.; Kang, C.I.; Yoon, C.H.; Lee, D.J.; Kim, C.H.; Chung, Y.S.; Kang, C.; Choi, C.M. High isolation rate of adenovirus serotype 7 from South Korean military recruits with mild acute respiratory disease. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2007, 26, 481–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, P.; Ma, C.; Nawaz, M.; Han, L.; Zhang, J.; Du, Q.; Zhang, L.; Feng, Q.; Wang, J.; Xu, J. Outbreak of acute respiratory disease caused by human adenovirus type 7 in a military training camp in Shaanxi, China. Microbiol. Immunol. 2013, 57, 553–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munoz, F.M.; Piedra, P.A.; Demmler, G. Disseminated adenovirus disease in immunocompromised and immunocompetent children. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1998, 27, 1194–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abd-Jamil, J.; Teoh, B.T.; Hassan, E.H.; Nuruliza, R.; Sazaly, A.B. Molecular identification of adenovirus causing respiratory tract infection in paediatric patients at the University of Malaya Medical Center. BMC Pediatr. 2010, 10, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trei, J.S.; Johns, N.M.; Garner, J.L.; Noel, L.B.; Ortman, B.V.; Ensz, K.L.; Johns, M.C.; Bunning, M.L.; Gaydos, J.C. Spread of adenovirus to geographically dispersed military installations, May–October 2007. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2010, 16, 769–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sivan, A.V.; Lee, T.; Binn, L.N.; Gaydos, J.C. Adenovirus associated acute respiratory disease in healthy adolescent and adults: A literature review. Mil. Med. 2007, 172, 1198–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radin, J.M.; Hawksworth, A.W.; Blair, P.J.; Faix, D.J.; Raman, R.; Russell, K.L.; Gray, G.C. Dramatic decline of respiratory illness among US military recruits after the renewed use of adenovirus vaccines. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2014, 59, 962–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyons, A.; Longfield, J.; Kuschner, R.; Straight, T.; Binn, L.; Seriwatana, J.; Reitstetter, R.; Froh, I.B.; Craft, D.; McNabb, K.; et al. A double-blind, placebo-controlled study of the safety and immunogenicity of live, oral type 4 and type 7 adenovirus vaccines in adults. Vaccine 2008, 26, 2890–2898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Acute respiratory disease associated with adenovirus serotype 14—Four states, 2006–2007. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2007, 56, 1181. [Google Scholar]
- Ariga, T.; Shimada, Y.; Shiratori, K.; Ohgami, K.; Yamazaki, S.; Tagawa, Y.; Kikuchi, M.; Miyakita, Y.; Fujita, K.; Ishiko, H.; et al. Five new genome types of adenovirus type 37 caused epidemic keratoconjunctivitis in Sapporo, Japan, for more than 10 years. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2005, 43, 726–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-López, J.J.; Morcillo-Laiz, R.; Muñoz-Negrete, F.J. Adenoviral keratoconjunctivitis: An update. Arch. Soc. Esp. Oftalmol. 2013, 88, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, S.C.; Shen, S.C.; Chang, S.W.; Huang, S.C.; Hsiao, C.H. Corneal superinfection in acute viral conjunctivitis in young children. J. Pediatr. Ophthalmol. Strabismus 2008, 45, 374–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aronson, B.; Aronson, S.; Sobel, G.; Walker, D. Pharyngoconjunctival fever; report of an epidemic outbreak. AMA J. Dis. Child. 1956, 92, 596–612. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.Y.; Luo, Y.P.; Huang, D.D.; Fan, H.; Lu, Q.B.; Wo, Y.; Chen, G.; Zhang, X.A.; Li, Y.; Tong, Y.G.; et al. Fatal pneumonia cases caused by human adenovirus 55 in immunocompetent adults. Infect. Dis. 2016, 48, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, S.; Williams, D.J.; Arnold, S.R.; Ampofo, K.; Bramley, A.M.; Reed, C.; Stockmann, C.; Anderson, E.J.; Grijalva, C.G.; Self, W.H.; et al. Community-acquired pneumonia requiring hospitalization among U.S. children. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 835–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Similä, S.; Jouppila, R.; Salmi, A.; Pohjonen, R. Encephaloningitis in children associated with an adenovirus type 7 epidemic. Acta Paediatr. Scand. 1970, 59, 310–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wadell, G.; Varsányi, T.M.; Lord, A.; Sutton, R.N. Epidemic outbreaks of adenovirus 7 with special reference to the pathogenicity of adenovirus genome type 7b. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1980, 112, 619–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoşnut, F.Ö.; Özçay, F.; Malbora, B.; Hızlı, Ş.; Özbek, N. Severe Adenovirus Infection Associated with Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis. Turk. J. Hematol. 2014, 31, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hakim, F.A.; Tleyjeh, I.M. Severe adenovirus pneumonia in immunocompetent adults: A case report and review of the literature. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2008, 27, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, C.K.; Kwon, H.; Park, J.Y. Thin-section computed tomography findings in 104 immunocompetent patients with adenovirus pneumonia. Acta Radiol. 2017, 58, 937–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, D.; Fu, Y.; Xu, J.; Wang, Z.; Cao, J.; Walline, J.; Zhu, H.; Yu, X. Severe adenovirus community-acquired pneumonia in immunocompetent adults: Chest radiographic and CT findings. J. Thorac. Dis. 2016, 8, 848–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cha, M.J.; Chung, M.J.; Lee, K.S.; Kim, T.J.; Kim, T.S.; Chong, S.; Han, J. Clinical Features and Radiological Findings of Adenovirus Pneumonia Associated with Progression to Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome: A Single Center Study in 19 Adult Patients. Korean J. Radiol. 2016, 17, 940–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becroft, D.M.O. Histopathology of fatal adenovirus infection of the respiratory tract in young children. J. Clin. Pathol. 1967, 20, 561–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schonland, M.; Strong, M.L.; Wesley, A. Fatal adenovirus pneumonia: Clinical and pathological features. S. Afr. Med. J. 1976, 50, 1748–1751. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Low, S.Y.; Tan, T.T.; Lee, C.H.; Loo, C.M.; Chew, H.C. Severe adenovirus pneumonia requiring extracorporeal membrane oxygenation support—Serotype 7 revisited. Respir. Med. 2013, 107, 1810–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, B.; He, H.; Wang, Z.; Qu, J.; Li, X.; Ban, C.; Wan, J.; Cao, B.; Tong, Z.; Wang, C. Emergent severe acute respiratory distress syndrome caused by adenovirus type 55 in immunocompetent adults in 2013: A prospective observational study. Crit. Care. 2014, 18, 456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.Y.; Qian, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Jia, L.P.; Dong, H.J.; Deng, J. Investigation of adenovirus infection in hospitalized children with diarrhea during 2010 in Beijing, China. Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi 2012, 50, 450–454. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hart, C.A.; Cunliffe, N.A.; Nakagomi, O. Diarrhoea caused by viruses. In Manson’s Tropical Diseases, 22nd ed.; Cook, G.C., Zumla, A.I., Eds.; Saunders Elsevier: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2009; pp. 815–824. [Google Scholar]
- Cunliffe, N.A.; Booth, J.A.; Elliot, C.; Lowe, S.J.; Sopwith, W.; Kitchin, N.; Nakagomi, O.; Nakagomi, T.; Hart, C.A.; Regan, M. Healthcare-associated Viral Gastroenteritis among Children in a Large Pediatric Hospital, United Kingdom. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2010, 16, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, T.K.; Bresee, J.S.; Glass, R.I. Rotavirus vaccines and the prevention of hospital-acquired diarrhea in children. Vaccine 2004, 22, S49–S54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osborne, C.M.; Montano, A.C.; Robinson, C.C.; Schultz-Cherry, S.; Dominguez, S.R. Viral gastroenteritis in children in Colorado 2006–2009. J. Med. Virol. 2015, 87, 931–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosulin, K.; Geiger, E.; Vécsei, A.; Huber, W.D.; Rauch, M.; Brenner, E.; Wrba, F.; Hammer, K.; Innerhofer, A.; Pötschger, U.; et al. Persistence and reactivation of human adenoviruses in the gastrointestinal tract. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2016, 22, 381e1–381e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mufson, M.A.; Belshe, R.B. A review of adenoviruses in the etiology of acute hemorrhagic cystitis. J. Urol. 1976, 115, 191–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Numazaki, Y.; Kumasaka, T.; Yano, N.; Yamanaka, M.; Miyazawa, T.; Takai, S.; Ishida, N. Further Study on Acute Hemorrhagic Cystitis Due to Adenovirus Type 11. N. Engl. J. Med. 1973, 289, 344–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, M.; Hirabayashi, N.; Uno, Y.; Nakayama, A.; Asai, J. Necrotizing tubulointerstitial nephritis associated with adenovirus infection. Hum Pathol. 1991, 22, 1225–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soeur, M.; Wouters, A.; de Saint-Georges, A.; Content, J.; Depierreux, M. Meningoencephalitis and meningitis due to an adenovirus type 5 in two immunocompetent adults. Acta Neurol. Belg. 1991, 91, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Landry, M.L.; Hsiung, G.D. Adenovirus-associated meningoencephalitis in a healthy adult. Ann Neurol. 1988, 23, 627–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, A.B.; Webber, S.; Fricker, F.J.; Jaffe, R.; Demmler, G.; Kearney, D.; Zhang, Y.H.; Bodurtha, J.; Gelb, B.; Ni, J. Acute myocarditis. Rapid diagnosis by PCR in children. Circulation 1994, 90, 330–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowles, N.E.; Ni, J.; Kearney, D.L.; Pauschinger, M.; Schultheiss, H.P.; McCarthy, R.; Hare, J.; Bricker, J.T.; Bowles, K.R.; Towbin, J.A. Detection of viruses in myocardial tissues by polymerase chain reaction. evidence of adenovirus as a common cause of myocarditis in children and adults. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2003, 42, 466–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Herz, W.; Moussa, M.A. Survival and predictors of death among primary immunodeficient patients: A registry-based study. J. Clin. Immunol. 2012, 32, 467–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kampmann, B.; Cubitt, D.; Walls, T.; Naik, P.; Depala, M.; Samarasinghe, S.; Robson, D.; Hassan, A.; Rao, K.; Gaspar, H.; et al. Improved outcome for children with disseminated adenoviral infection following allogeneic stem cell transplantation. Br. J. Haematol. 2005, 130, 595–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiwarkar, P.; Gaspar, H.B.; Gilmour, K.; Jagani, M.; Chiesa, R.; Bennett-Rees, N.; Breuer, J.; Rao, K.; Cale, C.; Goulden, N.; et al. Impact of viral reactivations in the era of pre-emptive antiviral drug therapy following allogeneic haematopoietic SCT in paediatric recipients. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2013, 48, 803–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Echavarria, M. Adenoviruses in immunocompromised hosts. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2008, 21, 704–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nebbia, G.; Chawla, A.; Schutten, M.; Atkinson, C.; Raza, M.; Johnson, M.; Geretti, A. Adenovirus viraemia and dissemination unresponsive to antiviral therapy in advanced HIV-1 infection. AIDS 2005, 19, 1339–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adeyemi, O.A.; Yeldandi, A.V.; Ison, M.G. Fatal adenovirus pneumonia in a person with AIDS and Burkitt lymphoma: A case report and review of the literature. AIDS Read. 2008, 18, 196–198. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Steiner, I.; Aebi, C.; RidolfiLuthy, A.; Wagner, B.; Leibundgut, K. Fatal adenovirus hepatitis during maintenance therapy for childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2008, 50, 647–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffman, J.A. Adenovirus infections in solid organ transplant recipients. Curr. Opin. Organ Transplant. 2009, 14, 625–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Humar, A.; Kumar, D.; Mazzulli, T.; Razonable, R.R.; Moussa, G.; Paya, C.V.; Covington, E.; Alecock, E.; Pescovitz, M.D. A surveillance study of adenovirus infection in adult solid organ transplant recipients. Am. J. Transplant. 2005, 5, 2555–2559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Florescu, M.C.; Miles, C.D.; Florescu, D.F. What do we know about adenovirus in renal transplantation? Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2013, 28, 2003–2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abinun, M.; Flood, T.J.; Cant, A.J.; Veys, P.; Gennery, A.R.; Foster, H.E.; Friswell, M.; Baildam, E.; Davidson, J.; Southwood, T.R.; et al. Autologous T cell depleted haematopoietic stem cell transplantation in children with severe juvenile idiopathic arthritis in the UK (2000–2007). Mol. Immunol. 2009, 47, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rocholl, C.; Gerber, K.; Daly, J.; Pavia, A.T.; Byington, C.L. Adenoviral infections in children: The impact of rapid diagnosis. Pediatrics 2004, 113 Pt 1, e51–e56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shetty, A.K.; Treynor, E.; Hill, D.W.; Gutierrez, K.M.; Warford, A.; Baron, E.J. Comparison of conventional viral cultures with direct fluorescent antibody stains for diagnosis of community-acquired respiratory virus infections in hospitalized children. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2003, 22, 789–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lion, T.; Baumgartinger, R.; Watzinger, F.; Matthes-Martin, S.; Suda, M.; Preuner, S.; Futterknecht, B.; Lawitschka, A.; Peters, C.; Potschger, U.; et al. Molecular monitoring of adenovirus in peripheral blood after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation permits early diagnosis of disseminated disease. Blood 2003, 102, 1114–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ison, M.G. Adenovirus infections in transplant recipients. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2006, 43, 331–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lankester, A.C.; van Tol, M.J.; Claas, E.C.; Vossen, J.M.; Kroes, A.C. Quantification of adenovirus DNA in plasma for management of infection in stem cell graft recipients. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2002, 34, 864–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganzenmueller, T.; Buchholz, S.; Harste, G.; Dammann, E.; Trenschel, R.; Heim, A. High lethality of human adenovirus disease in adult allogeneic stem cell transplant recipients with high adenoviral blood load. J. Clin. Virol. 2011, 52, 55–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Claas, E.C.; Schilham, M.W.; de Brouwer, C.S.; Hubacek, P.; Echavarria, M.; Lankester, A.C.; van Tol, M.J.; Kroes, A.C. Internally controlled real-time PCR monitoring of adenovirus DNA load in serum or plasma of transplant recipients. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2005, 43, 1738–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teramura, T.; Naya, M.; Yoshihara, T.; Kanoh, G.; Morimoto, A.; Imashuku, S. Adenoviral infection in hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: Early diagnosis with quantitative detection of the viral genome in serum and urine. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2004, 33, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Jong, J.C.; Wermenbol, A.G.; Verweij-Uijterwaal, M.W.; Slaterus, K.W.; Wertheim-Van Dillen, P.; Van Doornum, G.J.; Khoo, S.H.; Hierholzer, J.C. Adenoviruses from human immunodeficiency virus-infected individuals, including two strains that represent new candidate serotypes Ad50 and Ad51 of species B1 and D, respectively. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1999, 37, 3940–3945. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Matthes-Martin, S.; Feuchtinger, T.; Shaw, P.J.; Engelhard, D.; Hirsch, H.H.; Cordonnier, C.; Ljungman, P. European guidelines for diagnosis and treatment of adenovirus infection in leukemia and stem cell transplantation: Summary of ECIL-4 (2011). Transpl. Infect. Dis. 2012, 14, 555–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinkerton, H.; Carroll, S. Fatal adenovirus pneumonia in infants. Correlation of histologic and electron microscopic observations. Am. J. Pathol. 1971, 65, 543. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Florescu, D.F.; Hoffman, J.A. Adenovirus in solid organ transplantation. Am. J. Transplant. 2013, 13 (Suppl. S4), 206–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prevention & Treatment. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/adenovirus/about/prevention-treatment.html (accessed on 14 December 2017).
- Rutala, W.A.; Peacock, J.E.; Gergen, M.F.; Sobsey, M.D.; Weber, D.J. Efficacy of Hospital Germicides against Adenovirus 8, a Common Cause of Epidemic Keratoconjunctivitis in Health Care Facilities. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2006, 50, 1419–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lynch, J.P., 3rd; Fishbein, M.; Echavarria, M. Adenovirus. Semin. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2011, 32, 494–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomblyn, M.; Chiller, T.; Einsele, H.; Gress, R.; Sepkowitz, K.; Storek, J.; Wingard, J.R.; Young, J.A.; Boeckh, M.J. Guidelines for preventing infectious complications among hematopoietic cell transplant recipients: A global perspective. Preface. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2009, 44, 453–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watson, T.; MacDonald, D.; Song, X.; Bromwich, K.; Campos, J.; Sande, J.; DeBiasi, R.L. Risk factors for molecular detection of adenovirus in pediatric hematopoietic stem cell transplantation recipients. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2012, 18, 1227–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kodama, E.; Shigeta, S.; Suzuki, T.; De Clercq, E. Application of a gastric cancer cell line (MKN-28) for anti-adenovirus screening using the MTT method. Antivir. Res. 1996, 31, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, E.J.; Guzman-Cottrill, J.A.; Kletzel, M.; Thormann, K.; Sullivan, C.; Zheng, X.; Katz, B.Z. High-risk adenovirus-infected pediatric allogeneic hematopoietic progenitor cell transplant recipients and preemptive cidofovir therapy. Pediatr. Transplant. 2008, 12, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ljungman, P.; Ribaud, P.; Eyrich, M.; Matthes-Martin, S.; Einsele, H.; Bleakley, M.; Machaczka, M.; Bierings, M.; Bosi, A.; Gratecos, N.; et al. Cidofovir for adenovirus infections after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: A survey by the Infectious Diseases Working Party of the European Group for Blood and Marrow Transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2003, 31, 481–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lenaerts, L.; Naesens, L. Antiviral therapy for adenovirus infections. Antivir. Res. 2006, 71, 172–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- La Rosa, A.M.; Champlin, R.E.; Mirza, N.; Gajewski, J.; Giralt, S.; Rolston, K.V.; Raad, I.; Jacobson, K.; Kontoyiannis, D.; Elting, L.; et al. Adenovirus infections in adult recipients of blood and marrow transplants. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2001, 32, 871–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neofytos, D.; Ojha, A.; Mookerjee, B.; Wagner, J.; Filicko, J.; Ferber, A.; Dessain, S.; Grosso, D.; Brunner, J.; Flomenberg, N.; et al. Treatment of adenovirus disease in stem cell transplant recipients with cidofovir. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2007, 13, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doan, M.L.; Mallory, G.B.; Kaplan, S.L.; Dishop, M.K.; Schecter, M.G.; McKenzie, E.D.; Heinle, J.S.; Elidemir, O. Treatment of adenovirus pneumonia with cidofovir in pediatric lung transplant recipients. J. Heart Lung Transplant. 2007, 26, 883–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciesla, S.L.; Trahan, J.; Wan, W.B.; Beadle, J.R.; Aldern, K.A.; Painter, G.R.; Hostetler, K.Y. Esterification of cidofovir with alkoxyalkanols increases oral bioavailability and diminishes drug accumulation in kidney. Antivir. Res. 2003, 59, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naesens, L.; Lenaerts, L.; Andrei, G.; Snoeck, R.; Van Beers, D.; Holy, A.; Balzarini, J.; De Clercq, E. Antiadenovirus activities of several classes of nucleoside and nucleotide analogues. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2005, 49, 1010–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feuchtinger, T.; Matthes-Martin, S.; Richard, C.; Lion, T.; Fuhrer, M.; Hamprecht, K.; Handgretinger, R.; Peters, C.; Schuster, F.R.; Beck, R.; et al. Safe adoptive transfer of virus-specific T-cell immunity for the treatment of systemic adenovirus infection after allogeneic stem cell transplantation. Br. J. Haematol. 2006, 134, 64–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dagan, R.; Schwartz, R.H.; Insel, R.A.; Menegus, M.A. Severe diffuse adenovirus pneumonia in a child with combined immunodeficiency: Possible therapeutic effect of human immune serum globulin containing specific neutralizing antibody. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. 1984, 3, 246–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khanal, S.; Ghimire, P.; Dhamoon, A.S. The Repertoire of Adenovirus in Human Disease: The Innocuous to the Deadly. Biomedicines 2018, 6, 30. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines6010030
Khanal S, Ghimire P, Dhamoon AS. The Repertoire of Adenovirus in Human Disease: The Innocuous to the Deadly. Biomedicines. 2018; 6(1):30. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines6010030
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhanal, Subrat, Pranita Ghimire, and Amit S. Dhamoon. 2018. "The Repertoire of Adenovirus in Human Disease: The Innocuous to the Deadly" Biomedicines 6, no. 1: 30. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines6010030