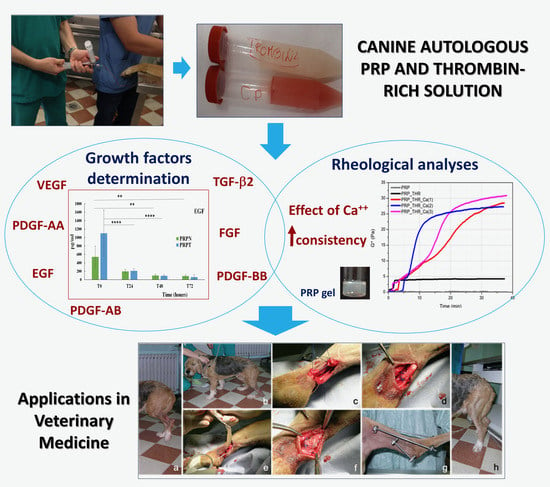
Rheological Properties and Growth Factors Content of Platelet-Rich Plasma: Relevance in Veterinary Biomedical Treatments
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Blood Collection and PRP Preparation
2.2. PRP Gels Preparation and Rheological Characterization
2.3. Determination of Growth Factors Content in PRP
2.4. Application of PRP in Veterinary Medicine
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Rheological Properties of PRP
3.2. Quantitative Determination of Growth Factors in PRP
3.3. Application of PRP Gel in Veterinary Medicine
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tambella, A.M.; Martin, S.; Cantalamessa, A.; Serri, E.; Attili, A.R. Platelet-rich Plasma and Other Hemocomponents in Veterinary Regenerative Medicine. Wounds Compend. Clin. Res. Pract. 2018, 30, 329–336. [Google Scholar]
- Farndale, R.W. Collagen-induced platelet activation. Blood Cells. Mol. Dis. 2006, 36, 162–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, E.-C.; Chou, T.-C.; Gau, C.-H.; Tu, H.-P.; Chen, Y.-T.; Fu, E. Releasing growth factors from activated human platelets after chitosan stimulation: A possible bio-material for platelet-rich plasma preparation. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2006, 17, 572–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landesberg, R.; Roy, M.; Glickman, R.S. Quantification of growth factor levels using a simplified method of platelet-rich plasma gel preparation. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2000, 58, 297–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martineau, I.; Lacoste, E.; Gagnon, G. Effects of Calcium and Thrombin on Growth Factor Release from Platelet Concentrates: Kinetics and Regulation of Endothelial Cell Proliferation. Biomaterials 2004, 25, 4489–4502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semple, E.; Speck, E.; Aslam, R.; Kim, M.; Kumar, V.; Semple, J. Evaluation of Platelet Gel Characteristics Using Thrombin Produced by the Thrombin Processing Device: A Comparative Study. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2008, 66, 632–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frelinger, A.L.; Torres, A.S.; Caiafa, A.; Morton, C.A.; Berny-Lang, M.A.; Gerrits, A.J.; Carmichael, S.L.; Neculaes, V.B.; Michelson, A.D. Platelet-rich plasma stimulated by pulse electric fields: Platelet activation, procoagulant markers, growth factor release and cell proliferation. Platelets 2016, 27, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rughetti, A.; Gallo, R.; Caloprisco, G.; Borean, A.; Necozione, S.; Dell’Orso, L.; Leocata, P.; Rivellini, C.; Di Marzio, D.; Di Natale, D.; et al. Platelet gel: Assays of three growth factors. Blood Transfus 2006, 4, 92–101. [Google Scholar]
- Carter, C.A.; Jolly, D.G.; Worden, C.E.; Hendren, D.G.; Kane, C.J.M. Platelet-rich plasma gel promotes differentiation and regeneration during equine wound healing. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2003, 74, 244–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crovetti, G.; Martinelli, G.; Issi, M.; Barone, M.; Guizzardi, M.; Campanati, B.; Moroni, M.; Carabelli, A. Platelet gel for healing cutaneous chronic wounds. Transfus. Apher. Sci. 2004, 30, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzucco, L.; Borzini, P.; Gope, R. Platelet-derived Factors Involved in Tissue Repair-From Signal to Function. Transfus. Med. Rev. 2010, 24, 218–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anitua, E.; Alkhraisat, M.H.; Orive, G. Perspectives and challenges in regenerative medicine using plasma rich in growth factors. J. Control. Release 2012, 157, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marques, L.F.; Stessuk, T.; Camargo, I.C.C.; Sabeh Junior, N.; dos Santos, L.; Ribeiro-Paes, J.T. Platelet-rich plasma (PRP): Methodological aspects and clinical applications. Platelets 2015, 26, 101–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giraldo, C.; López, C.; Álvarez, M.; Samudio, I.; Prades, M.; Carmona, J. Effects of the Breed, Sex and Age on Cellular Content and Growth Factor Release From Equine Pure-Platelet Rich Plasma and Pure-Platelet Rich Gel. BMC Vet. Res. 2013, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Karayannopoulou, M.; Papazoglou, L.; Loukopoulos, P.; Kazakos, G.; Chantes, A.; Giannakas, N.; Savvas, I.; Psalla, D.; Kritsepi-Konstantinou, M.; Dionyssiou, D. Locally Injected Autologous Platelet-Rich Plasma Enhanced Tissue Perfusion and Improved Survival of Long Subdermal Plexus Skin Flaps in Dogs. Vet. Comp. Orthop. Traumatol. 2014, 27, 379–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, S.H.; Jeong, H.-S.; Kim, J.P.; Koh, E.-H.; Lee, S.U.; Jin, S.M.; Kim, D.H.; Sohn, J.H.; Lee, S.H. Favorable Vocal Fold Wound Healing Induced by Platelet-Rich Plasma Injection. Clin. Exp. Otorhinolaryngol. 2014, 7, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anitua, E.; Nurden, P.; Prado, P.; Nurden, A.; Padilla, S. Autologous Fibrin Scaffolds: When Platelet- And Plasma-Derived Biomolecules Meet Fibrin. Biomaterials 2019, 192, 440–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brossi, P.M.; Moreira, J.J.; Machado, T.S.L.; Baccarin, R.Y.A. Platelet-rich plasma in orthopedic therapy: A comparative systematic review of clinical and experimental data in equine and human musculoskeletal lesions. BMC Vet. Res. 2015, 11, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, J.; Park, C.; Park, H. Curative Effect of Autologous Platelet-Rich Plasma on a Large Cutaneous Lesion in a Dog. Vet. Dermatol. 2009, 20, 123–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgos-Alonso, N.; Lobato, I.; Hernández, I.; Sebastian, K.S.; Rodríguez, B.; March, A.G.; Perez-Salvador, A.; Arce, V.; Garcia-Alvarez, A.; Gomez-Fernandez, M.C.; et al. Autologous platelet-rich plasma in the treatment of venous leg ulcers in primary care: A randomised controlled, pilot study. J. Wound Care 2018, 27, S20–S24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tambella, A.; Attili, A.; Dupré, G.; Cantalamessa, A.; Martin, S.; Cuteri, V.; Marcazzan, S.; Del Fabbro, M. Platelet-rich Plasma to Treat Experimentally-Induced Skin Wounds in Animals: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2018, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moneib, H.; Youssef, S.; Aly, D.; Rizk, M.; Abdelhakeem, Y. Autologous Platelet-Rich Plasma Versus Conventional Therapy for the Treatment of Chronic Venous Leg Ulcers: A Comparative Study. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2018, 17, 495–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Zapata, M.J.; Martí-Carvajal, A.J.; Solà, I.; Expósito, J.A.; Bolíbar, I.; Rodríguez, L.; Garcia, J.; Zaror, C. Autologous platelet-rich plasma for treating chronic wounds. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tambella, A.; Attili, A.; Dini, F.; Palumbo Piccionello, A.; Vullo, C.; Serri, E.; Scrollavezza, P.; Dupré, G. Autologous Platelet Gel to Treat Chronic Decubital Ulcers: A Randomized, Blind Controlled Clinical Trial in Dogs. Vet. Surg. 2014, 43, 726–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Picard, F.; Hersant, B.; Bosc, R.; Meningaud, J.-P. Should we use platelet-rich plasma as an adjunct therapy to treat “acute wounds”, “burns”, and “laser therapies”: A review and a proposal of a quality criteria checklist for further studies. Wound Repair Regen. 2015, 23, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samy, A.M. The role of platelet rich plasma in management of fracture neck femur: New insights. Int. Orthop. 2016, 40, 1019–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faillace, V.; Tambella, A.M.; Fratini, M.; Paggi, E.; Dini, F.; Laus, F. Use of autologous platelet-rich plasma for a delayed consolidation of a tibial fracture in a young donkey. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2017, 79, 618–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Marcazzan, S.; Taschieri, S.; Weinstein, R.; Del Fabbro, M. Efficacy of Platelet Concentrates in Bone Healing: A Systematic Review on Animal Studies—Part B: Large-size Animal Models. Platelets 2018, 29, 338–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Liu, X.; Xu, X.; Liu, J. Intra-articular injections of platelet-rich plasma, hyaluronic acid or corticosteroids for knee osteoarthritis: A prospective randomized controlled study. Orthopade 2019, 48, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weibrich, G.; Kleis, W.; Hafner, G.; Hitzler, W. Growth Factor Levels in Platelet-Rich Plasma and Correlations with Donor Age, Sex, and Platelet Count. J. Craniomaxillofac. Surg. 2002, 30, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leitner, G.C.; Gruber, R.; Neumüller, J.; Wagner, A.; Kloimstein, P.; Höcker, P.; Körmöczi, G.F.; Buchta, C. Platelet content and growth factor release in platelet-rich plasma: A comparison of four different systems. Vox Sang. 2006, 91, 135–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarrel, T.; Fortier, L. Temporal growth factor release from platelet-rich plasma, trehalose lyophilized platelets, and bone marrow aspirate and their effect on tendon and ligament gene expression. J. Orthop. Res. 2009, 27, 1033–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pallotta, I.; Kluge, J.; Moreau, J.; Calabrese, R.; Kaplan, D.; Balduini, A. Characteristics of Platelet Gels Combined with Silk. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 3678–3687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Russo, F.; D’Este, M.; Vadalà, G.; Cattani, C.; Papalia, R.; Alini, M.; Denaro, V. Platelet Rich Plasma and Hyaluronic Acid Blend for the Treatment of Osteoarthritis: Rheological and Biological Evaluation. PLoS ONE 2016, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ghazouane, R.; Bertrand, B.; Philandrianos, C.; Veran, J.; Abellan, M.; Francois, P.; Velier, M.; Orneto, C.; Piccerelle, P.; Magalon, J. What about the Rheological Properties of PRP/Microfat Mixtures in Fat Grafting Procedure? Aesthetic Plast. Surg. 2017, 41, 1217–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vadalà, G.; Russo, F.; Musumeci, M.; D’Este, M.; Cattani, C.; Catanzaro, G.; Tirindelli, M.; Lazzari, L.; Alini, M.; Giordano, R.; et al. Clinically Relevant Hydrogel-Based on Hyaluronic Acid and Platelet Rich Plasma as a Carrier for Mesenchymal Stem Cells: Rheological and Biological Characterization. J. Orthop. Res. 2017, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Del Fabbro, M.; Bucchi, C.; Lolato, A.; Corbella, S.; Testori, T.; Taschieri, S. Healing of Postextraction Sockets Preserved with Autologous Platelet Concentrates. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2017, 75, 1601–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stief, M.; Gottschalk, J.; Ionita, J.-C.; Einspanier, A.; Oechtering, G.; Böttcher, P. Concentration of platelets and growth factors in canine autologous conditioned plasma. Vet. Comp. Orthop. Traumatol. 2011, 24, 122–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franklin, S.; Birdwhistell, K. Assessment of Canine Autologous Conditioned Plasma TM Cellular and Transforming Growth Factor-β1 Content. Front. Vet. Sci. 2018, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, H.-S.; Woo, H.-M.; Kang, B.-J. Optimisation of a double-centrifugation method for preparation of canine platelet-rich plasma. BMC Vet. Res. 2017, 13, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jalowiec, J.M.; D’Este, M.; Bara, J.J.; Denom, J.; Menzel, U.; Alini, M.; Verrier, S.; Herrmann, M. An In Vitro Investigation of Platelet-Rich Plasma-Gel as a Cell and Growth Factor Delivery Vehicle for Tissue Engineering. Tissue Eng. Part C. Methods 2016, 22, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Toyoda, T.; Isobe, K.; Tsujino, T.; Koyata, Y.; Ohyagi, F.; Watanabe, T.; Nakamura, M.; Kitamura, Y.; Okudera, H.; Nakata, K.; et al. Direct activation of platelets by addition of CaCl2 leads coagulation of platelet-rich plasma. Int. J. Implant Dent. 2018, 4, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weibrich, G.; Hansen, T.; Kleis, W.; Buch, R.; Hitzler, W. Effect of Platelet Concentration in Platelet-Rich Plasma on Peri-Implant Bone Regeneration. Bone 2004, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, J.V.; Janmey, P.A. Strain hardening of fibrin gels and plasma clots. Rheol. Acta 1997, 36, 262–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavallo, C.; Roffi, A.; Grigolo, B.; Mariani, E.; Pratelli, L.; Merli, G.; Kon, E.; Marcacci, M.; Filardo, G. Platelet-Rich Plasma: The Choice of Activation Method Affects the Release of Bioactive Molecules. BioMed Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greppi, N.; Mazzucco, L.; Galetti, G.; Bona, F.; Petrillo, E.; Smacchia, C.; Raspollini, E.; Cossovich, P.; Caprioli, R.; Borzini, P.; et al. Treatment of recalcitrant ulcers with allogeneic platelet gel from pooled platelets in aged hypomobile patients. Biologicals 2011, 39, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huber, S.C.; Cunha Júnior, J.L.R.; Montalvão, S.; da Silva, L.Q.; Paffaro, A.U.; da Silva, F.A.R.; Rodrigues, B.L.; Lana, J.F.S.D.; Annichino-Bizzacchi, J.M. In vitro study of the role of thrombin in platelet rich plasma (PRP) preparation: Utility for gel formation and impact in growth factors release. J. Stem Cells Regen. Med. 2016, 12, 2–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brass, E.; Forman, W.; Edwards, R.; Lindan, O. Fibrin formation: Effect of calcium ions. Blood 1978, 52, 654–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weisel, J.W.; Litvinov, R.I. Mechanisms of fibrin polymerization and clinical implications. Blood 2013, 121, 1712–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Oosten, A.S.G.; Vahabi, M.; Licup, A.J.; Sharma, A.; Galie, P.A.; MacKintosh, F.C.; Janmey, P.A. Uncoupling shear and uniaxial elastic moduli of semiflexible biopolymer networks: Compression-softening and stretch-stiffening. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 19270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bale, M.; Ferry, J. Strain Enhancement of Elastic Modulus in Fine Fibrin Clots. Thromb. Res. 1988, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janmey, P.; Erdile, L.; Bale, M.; Ferry, J. Kinetics of Fibrin Oligomer Formation Observed by Electron Microscopy. Biochemistry 1983, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Storm, C.; Pastore, J.; MacKintosh, F.; Lubensky, T.; Janmey, P. Nonlinear Elasticity in Biological Gels. Nature 2005, 435, 191–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Onck, P.R.; Koeman, T.; van Dillen, T.; van der Giessen, E. Alternative explanation of stiffening in cross-linked semiflexible networks. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2005, 95, 178102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marx, R.E.; Carlson, E.R.; Eichstaedt, R.M.; Schimmele, S.R.; Strauss, J.E.; Georgeff, K.R. Platelet-rich Plasma: Growth factor enhancement for bone grafts. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endod. 1998, 85, 638–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chambers, R.; Leoni, P.; Blanc-Brude, O.; Wembridge, D.; Laurent, G. Thrombin Is a Potent Inducer of Connective Tissue Growth Factor Production via Proteolytic Activation of Protease-Activated receptor-1. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anitua, E.; Andia, I.; Ardanza, B.; Nurden, P.; Nurden, A.T. Autologous platelets as a source of proteins for healing and tissue regeneration. Thromb. Haemost. 2004, 91, 4–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barry, F.; Boynton, R.; Liu, B.; Murphy, J. Chondrogenic Differentiation of Mesenchymal Stem Cells from Bone Marrow: Differentiation-Dependent Gene Expression of Matrix Components. Exp. Cell Res. 2001, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hock, J.; Canalis, E. Platelet-derived Growth Factor Enhances Bone Cell Replication, but Not Differentiated Function of Osteoblasts. Endocrinology 1994, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.R.; Silva, E.A.; Yuen, W.W.; Mooney, D.J. Spatio-temporal VEGF and PDGF delivery patterns blood vessel formation and maturation. Pharm. Res. 2007, 24, 258–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakudo, N.; Minakata, T.; Mitsui, T.; Kushida, S.; Notodihardjo, F.; Kusumoto, K. Proliferation-promoting Effect of Platelet-Rich Plasma on Human Adipose-Derived Stem Cells and Human Dermal Fibroblasts. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2008, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raica, M.; Cimpean, A.M. Platelet-Derived Growth Factor (PDGF)/PDGF Receptors (PDGFR) Axis as Target for Antitumor and Antiangiogenic Therapy. Pharmaceuticals 2010, 3, 572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hosnuter, M.; Aslan, C.; Isik, D.; Caliskan, G.; Arslan, B.; Durgun, M. Functional assessment of autologous platelet-rich plasma (PRP) after long-term storage at -20 °C without any preservation agent. J. Plast. Surg. Hand Surg. 2017, 51, 235–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, G.; Maloney, J.; Archer, R.; Brown, K.; Mayger, K.; Bromidge, E.; Najafi, M. Platelet-rich Plasma for Tissue Regeneration Can Be Stored at Room Temperature for at Least Five Days. Br. J. Biomed. Sci. 2017, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.I.; Bae, H.C.; Park, H.J.; Lee, M.C.; Han, H.S. Effect of Storage Conditions and Activation on Growth Factor Concentration in Platelet-Rich Plasma. J. Orthop. Res. 2020, 38, 777–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, J.; Mo, X.; Shi, Z.; Li, T.; Xue, J.; Mei, G.; Li, X. A Prospective Study of Platelet-Rich Plasma as Biological Augmentation for Acute Achilles Tendon Rupture Repair. BioMed Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schulz, K.S.; Ash, K.J.; Cook, J.L. Clinical outcomes after common calcanean tendon rupture repair in dogs with a loop-suture tenorrhaphy technique and autogenous leukoreduced platelet-rich plasma. Vet. Surg. 2019, 48, 1262–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Growth Factor | PRPN-T0 (pg/mL) | PRPN-FT (pg/mL) |
|---|---|---|
| VEGF | 541.3 ± 255.4 a | 114.8 ± 44.2 b |
| TGFβ-2 | 48.8 ± 25.1 a | 254.8 ± 102.2 c |
| EGF | 4.7 ± 0.9 | N.D. |
| FGF | N.D. | N.D. |
| PDGF-AA | 146.9 ± 108.4 | 155.5 ± 68.5 |
| PDGF-BB | N.D. | 80.3 ± 33.4 |
| PDGF-AB | 218.9 ± 130.6 | 154.9 ± 84.9 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Perinelli, D.R.; Bonacucina, G.; Pucciarelli, S.; Cespi, M.; Serri, E.; Polzonetti, V.; Tambella, A.M.; Vincenzetti, S. Rheological Properties and Growth Factors Content of Platelet-Rich Plasma: Relevance in Veterinary Biomedical Treatments. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 429. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines8100429
Perinelli DR, Bonacucina G, Pucciarelli S, Cespi M, Serri E, Polzonetti V, Tambella AM, Vincenzetti S. Rheological Properties and Growth Factors Content of Platelet-Rich Plasma: Relevance in Veterinary Biomedical Treatments. Biomedicines. 2020; 8(10):429. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines8100429
Chicago/Turabian StylePerinelli, Diego Romano, Giulia Bonacucina, Stefania Pucciarelli, Marco Cespi, Evelina Serri, Valeria Polzonetti, Adolfo Maria Tambella, and Silvia Vincenzetti. 2020. "Rheological Properties and Growth Factors Content of Platelet-Rich Plasma: Relevance in Veterinary Biomedical Treatments" Biomedicines 8, no. 10: 429. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines8100429
APA StylePerinelli, D. R., Bonacucina, G., Pucciarelli, S., Cespi, M., Serri, E., Polzonetti, V., Tambella, A. M., & Vincenzetti, S. (2020). Rheological Properties and Growth Factors Content of Platelet-Rich Plasma: Relevance in Veterinary Biomedical Treatments. Biomedicines, 8(10), 429. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines8100429