Perinatal Resveratrol Therapy Prevents Hypertension Programmed by Maternal Chronic Kidney Disease in Adult Male Offspring: Implications of the Gut Microbiome and Their Metabolites
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Animals and Study Design
2.2. Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry Analysis
2.3. Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry
2.4. High-Performance Liquid Chromatography
2.5. Immunohistochemistry Staining of 8-Hydroxydeoxyguanosine
2.6. Western Blot
2.7. Metagenomics Analysis of the Gut Microbiota
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
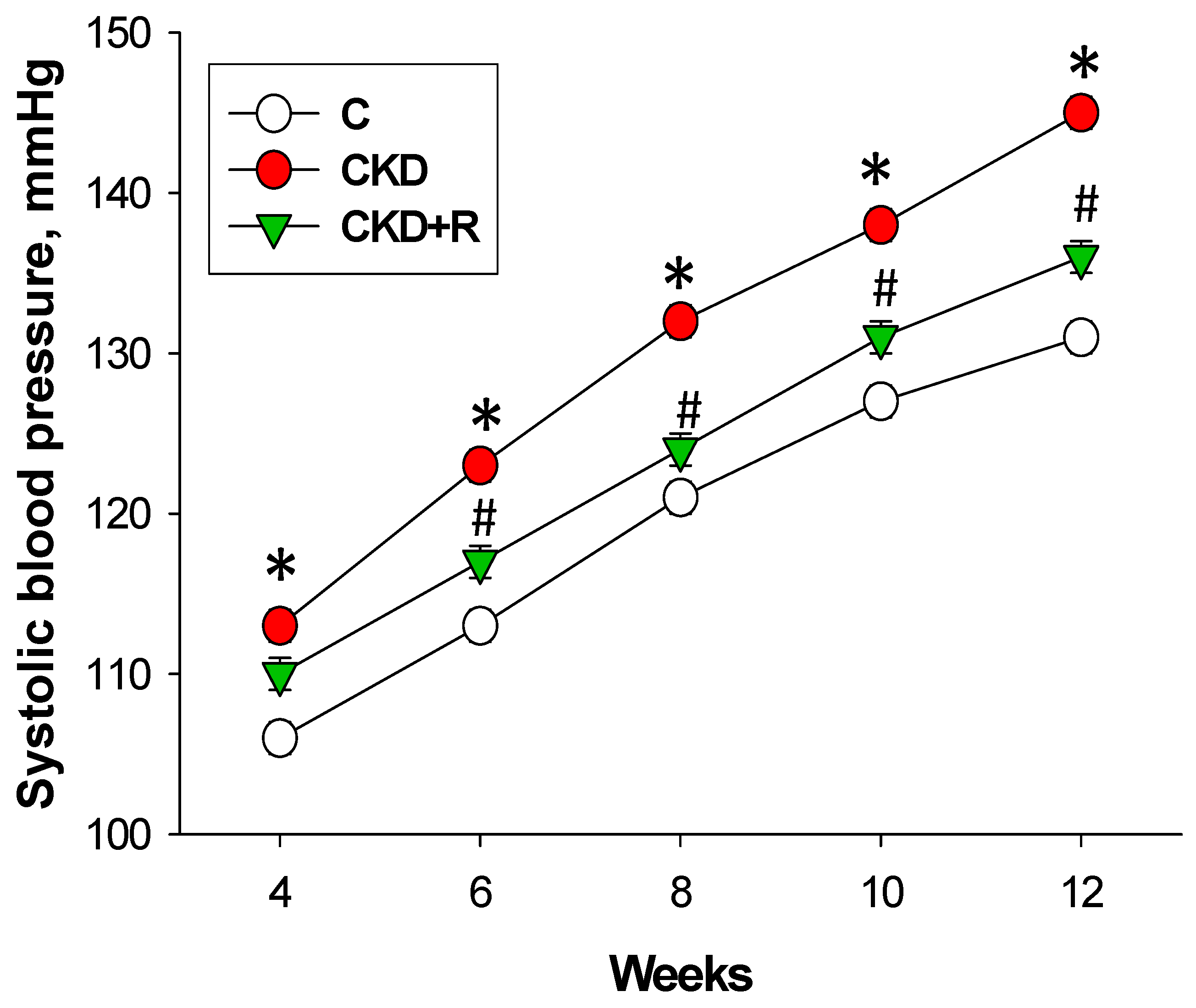
3.1. Blood Pressure and Renal Function
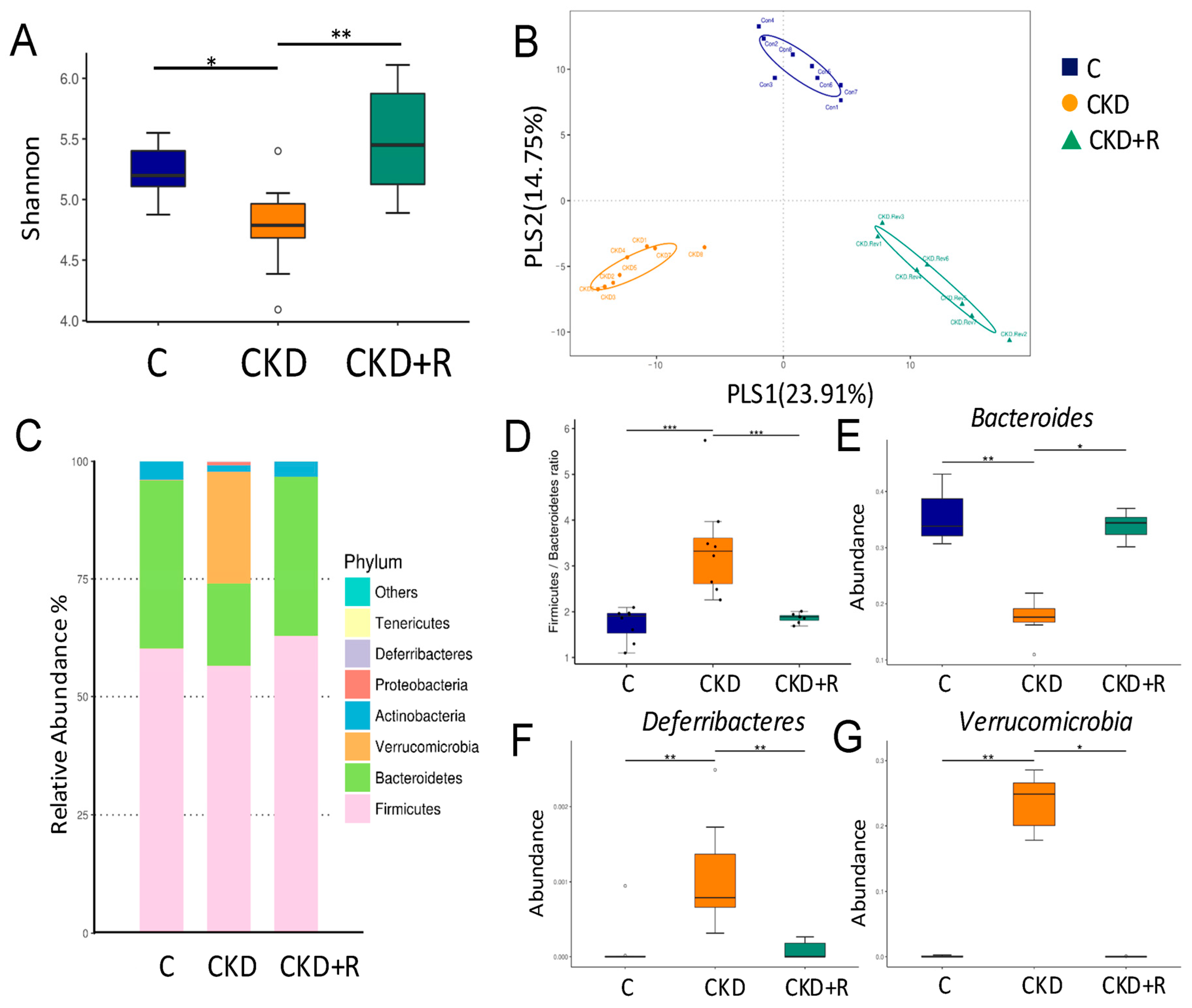
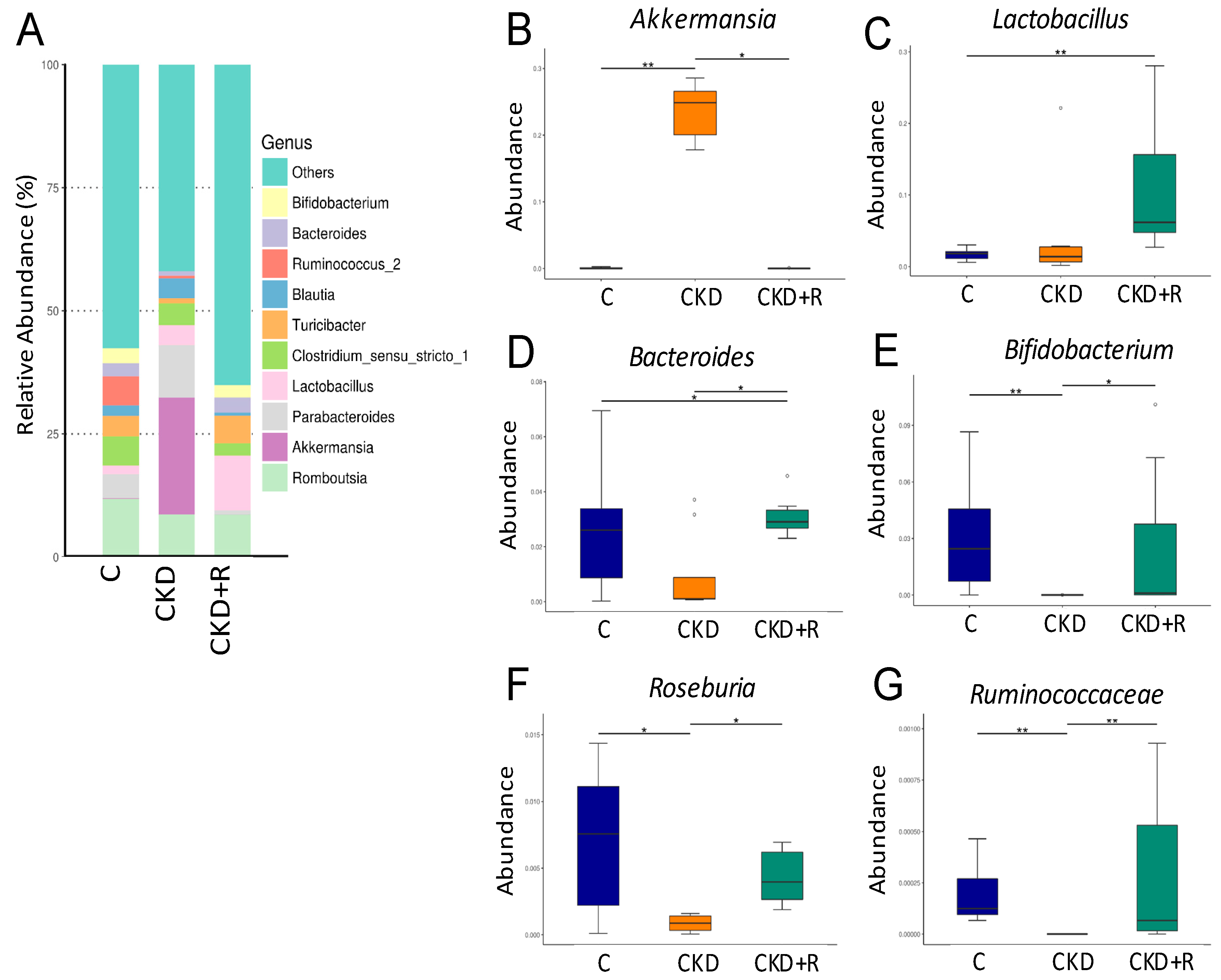
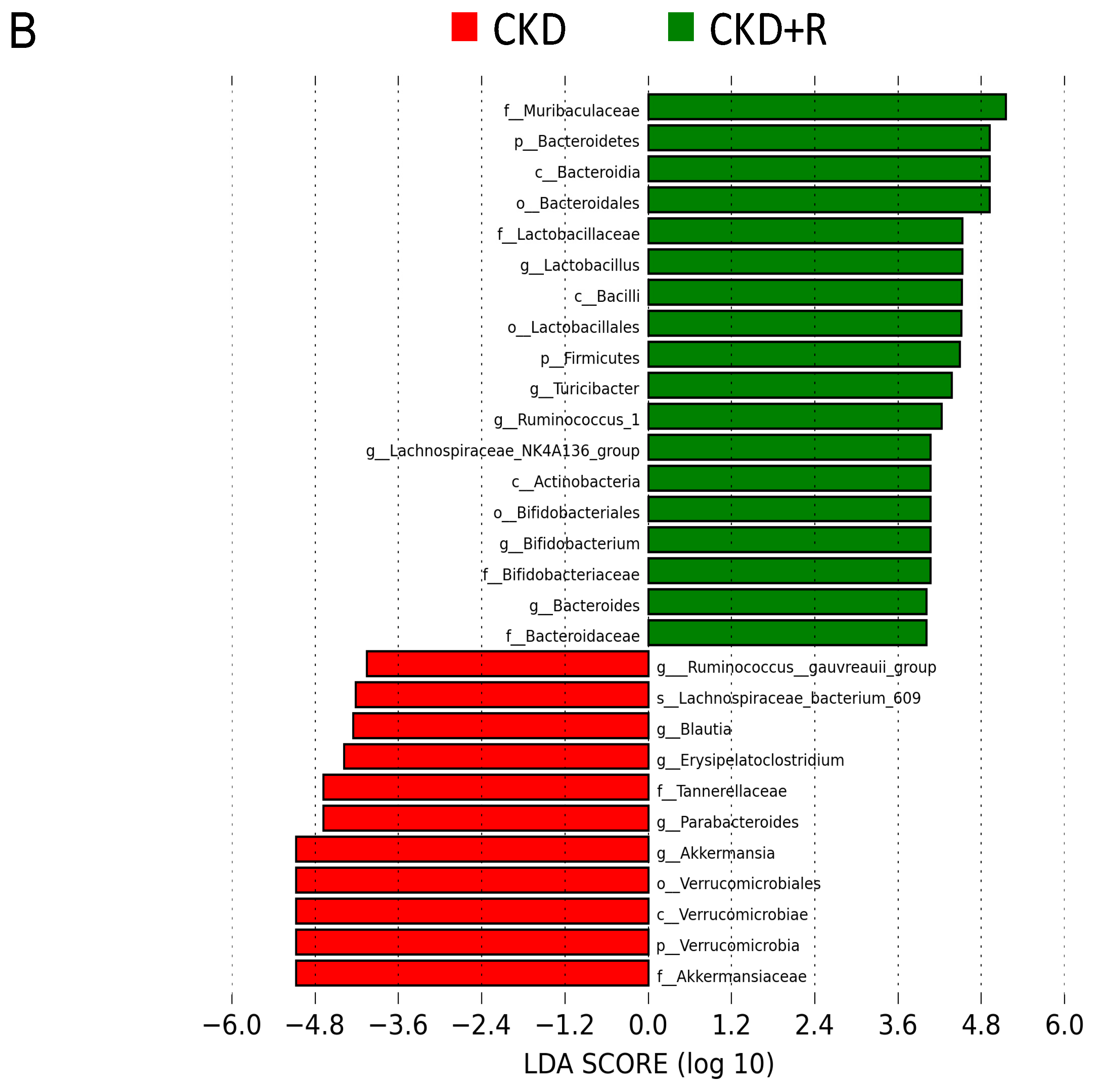
3.2. Gut Microbiota Composition
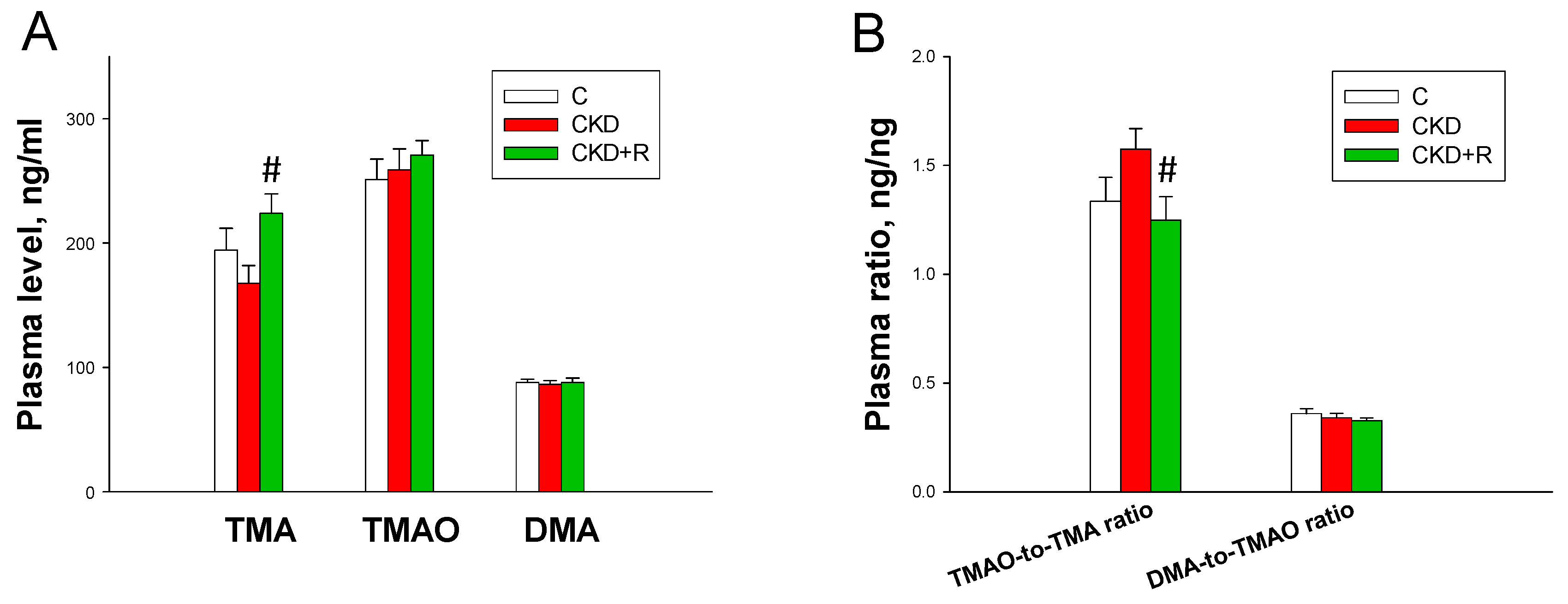
3.3. TMA, TMAO, and DMA Levels in the Plasma
3.4. SCFAs and Receptors
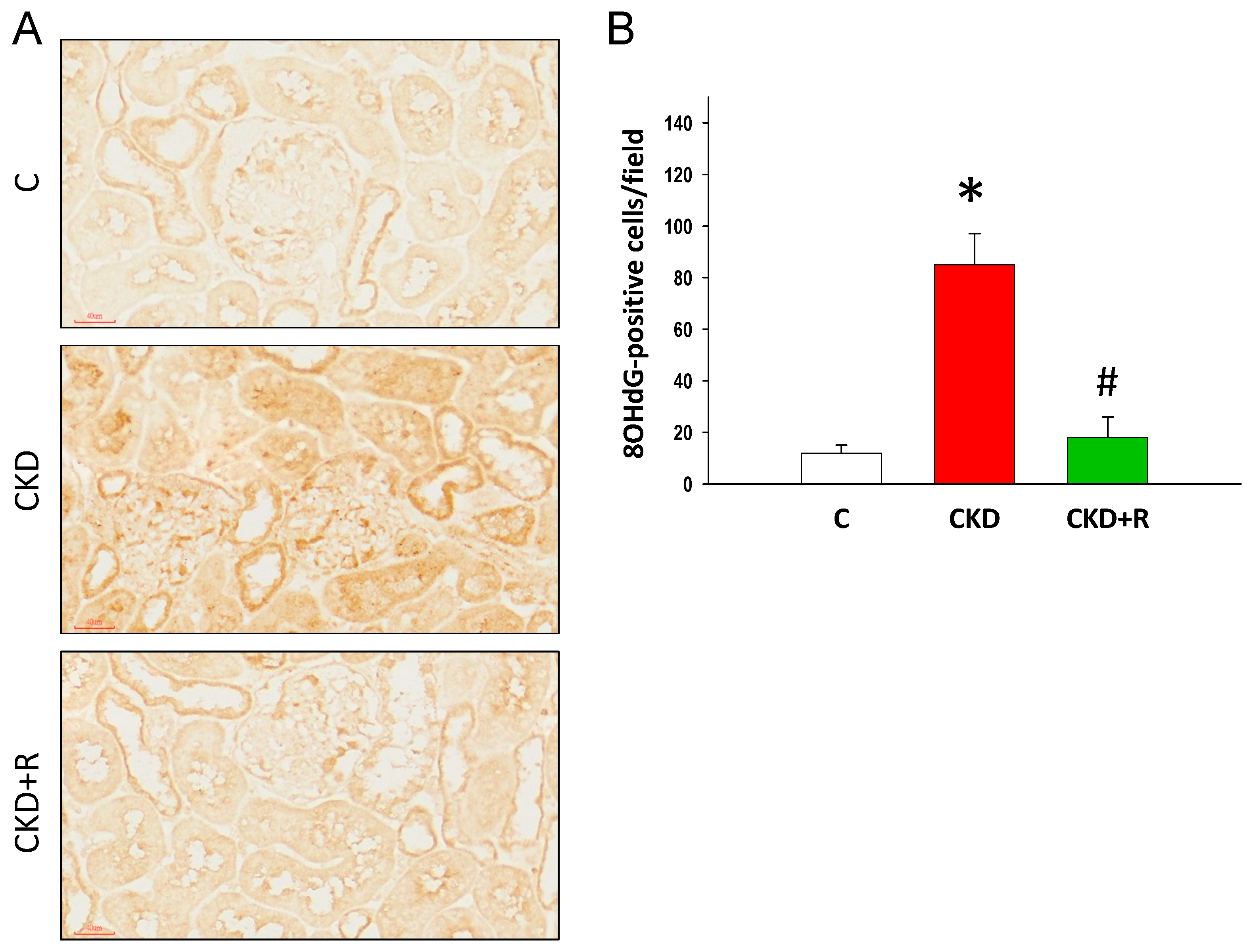
3.5. NO Pathway and Oxidative Stress
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lozano, R.; Naghavi, M.; Foreman, K.; Lim, S.; Shibuya, K.; Aboyans, V.; Abraham, J.; Adair, T.; Aggarwal, R.; Ahn, S.Y.; et al. Global and regional mortality from 235 causes of death for 20 age groups in 1990 and 2010: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet 2012, 380, 2095–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piccoli, G.B.; Alrukhaimi, M.; Liu, Z.H.; Zakharova, E.; Levin, A.; World Kidney Day Steering Committee. What we do and do not know about women and kidney diseases; Questions unanswered and answers unquestioned: Reflection on World Kidney Day and International Woman’s Day. Physiol. Int. 2018, 105, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hladunewich, M.A. Chronic Kidney Disease and Pregnancy. Semin. Nephrol. 2017, 37, 337–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, C.N.; Yang, H.W.; Hou, C.Y.; Chang-Chien, G.P.; Lin, S.; Tain, Y.L. Maternal Adenine-Induced Chronic Kidney Disease Programs Hypertension in Adult Male Rat Offspring: Implications of Nitric Oxide and Gut Microbiome Derived Metabolites. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luyckx, V.A.; Bertram, J.F.; Brenner, B.M.; Fall, C.; Hoy, W.E.; Ozanne, S.E.; Vikse, B.E. Effect of fetal and child health on kidney development and long-term risk of hypertension and kidney disease. Lancet 2013, 382, 273–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chong, E.; Yosypiv, I.V. Developmental Programming of Hypertension and Kidney Disease. Int. J. Nephrol. 2012, 2012, 760580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tain, Y.L.; Hsu, C.N. Developmental Origins of Chronic Kidney Disease: Should We Focus on Early Life? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hanson, M.; Gluckman, P. Developmental origins of noncommunicable disease: Population and public health implications. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2011, 94, 1754S–1758S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stiemsma, L.T.; Michels, K.B. The role of the microbiome in the developmental origins of health and disease. Pediatrics 2018, 141, e20172437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Al Khodor, S.; Reichert, B.; Shatat, I.F. The Microbiome and Blood Pressure: Can Microbes Regulate Our Blood Pressure? Front. Pediatr. 2017, 5, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Richards, E.M.; Pepine, C.J.; Raizada, M.K. The gut microbiota and the brain-gut-kidney axis in hypertension and chronic kidney disease. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2018, 14, 442–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tain, Y.L.; Hsu, C.N. Toxic Dimethylarginines: Asymmetric Dimethylarginine (ADMA) and Symmetric Dimethylarginine (SDMA). Toxins 2017, 9, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Velasquez, M.T.; Ramezanim, A.; Manal, A.; Raj, D.S. Trimethylamine N-Oxide: The Good, the Bad and the Unknown. Toxins 2016, 8, 326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schiattarella, G.G.; Sannino, A.; Toscano, E.; Giugliano, G.; Gargiulo, G.; Franzone, A.; Trimarco, B.; Esposito, G.; Perrino, C. Gut microbe-generated metabolite trimethylamine-N-oxide as cardiovascular risk biomarker: A systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis. Eur. Heart J. 2017, 38, 2948–2956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jaworska, K.; Hering, D.; Mosieniak, G.; Bielak-Zmijewska, A.; Pilz, M.; Konwerski, M.; Gasecka, A.; Kapłon-Cieślicka, A.; Filipiak, K.; Sikora, E.; et al. TMA, A Forgotten Uremic Toxin, but Not TMAO, Is Involved in Cardiovascular Pathology. Toxins 2019, 11, 490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pluznick, J.L. Microbial short chain fatty acids and blood pressure regulation. Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2017, 19, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hsu, C.N.; Chang-Chien, G.P.; Lin, S.; Hou, C.Y.; Tain, Y.L. Targeting on Gut Microbial Metabolite Trimethylamine-N-Oxide and Short-Chain Fatty Acid to Prevent Maternal High-Fructose-Diet-Induced Developmental Programming of Hypertension in Adult Male Offspring. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2019, 63, e1900073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.N.; Hou, C.Y.; Chan, J.Y.H.; Lee, C.T.; Tain, Y.L. Hypertension Programmed by Perinatal High-Fat Diet: Effect of Maternal Gut Microbiota-Targeted Therapy. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hsu, C.N.; Tain, Y.L. Regulation of Nitric Oxide Production in the Developmental Programming of Hypertension and Kidney Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paz Ocaranza, M.; Riquelme, J.A.; García, L.; Jalil, J.E.; Chiong, M.; Santos, R.A.S.; Lavandero, S. Counter-regulatory renin-angiotensin system in cardiovascular disease. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2020, 17, 116–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tain, Y.L.; Joles, J.A. Reprogramming: A Preventive Strategy in Hypertension Focusing on the Kidney. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Diaz-Gerevini, G.T.; Repossi, G.; Dain, A.; Tarres, M.C.; Das, U.N.; Eynard, A.R. Beneficial action of resveratrol: How and why? Nutrition 2016, 32, 174–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonnefont-Rousselot, D. Resveratrol and Cardiovascular Diseases. Nutrients 2016, 8, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tain, Y.L.; Hsu, C.N. Developmental Programming of the Metabolic Syndrome: Can We Reprogram with Resveratrol? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hsu, C.N.; Lin, Y.J.; Lu, P.C.; Tain, Y.L. Maternal Resveratrol Therapy Protects Male Rat Offspring against Programmed Hypertension Induced by TCDD and Dexamethasone Exposures: Is It Relevant to Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tain, Y.L.; Lee, W.C.; Wu, K.L.H.; Leu, S.; Chan, J.Y.H. Resveratrol Prevents the Development of Hypertension Programmed by Maternal Plus Post-Weaning High-Fructose Consumption through Modulation of Oxidative Stress, Nutrient-Sensing Signals, and Gut Microbiota. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2018, 62, e1800066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tain, Y.L.; Lin, Y.J.; Sheen, J.M.; Lin, I.C.; Yu, H.R.; Huang, L.T.; Hsu, C.N. Resveratrol prevents the combined maternal plus postweaning high-fat-diets-induced hypertension in male offspring. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2017, 48, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaplin, A.; Carpéné, C.; Mercader, J. Resveratrol, Metabolic Syndrome, and Gut Microbiota. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reckelhoff, J.F. Gender differences in the regulation of blood pressure. Hypertension 2001, 37, 1199–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hsu, C.N.; Lin, I.C.; Yu, H.R.; Huang, L.T.; Tiao, M.M.; Tain, Y.L. Maternal tryptophan supplementation protects adult rat offspring against hypertension programmed by maternal chronic kidney disease: Implication of tryptophan-metabolizing microbiome and aryl hydrocarbon receptor. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, B.D.; Grunwald, G.K.; Zerbe, G.O.; Mikulich-Gilbertson, S.K.; Robertson, C.E.; Zemanick, E.T.; Harris, J.K. On the use of diversity measures in longitudinal sequencing studies of microbial communities. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, M.L.; Yi, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, X.; Ran, L.; Yang, J.; Zhu, J.-D.; Zhang, Q.Y.; Mi, M.T. Resveratrol Attenuates Trimethylamine-N-Oxide (TMAO)-Induced Atherosclerosis by Regulating TMAO Synthesis and Bile Acid Metabolism via Remodeling of the Gut Microbiota. mBio 2016, 7, e02210–e02215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Espín, J.C.; González-Sarrías, A.; Tomás-Barberán, F.A. The gut microbiota: A key factor in the therapeutic effects of (poly) phenols. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2017, 139, 82–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Liu, S.; Shu, H.; Crawford, J.; Xing, Y.; Tao, F. Resveratrol alleviates temporomandibular joint inflammatory pain by recovering disturbed gut microbiota. Brain Behav. Immun. 2020, 87, 455–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Santisteban, M.M.; Rodriguez, V.; Li, E.; Ahmari, N.; Carvajal, J.M.; Zadeh, M.; Gong, M.; Qi, Y.; Zubcevic, J.; et al. Gut dysbiosis is linked to hypertension. Hypertension 2015, 65, 1331–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shi, L.H.; Balakrishnan, K.; Thiagarajah, K.; Mohd Ismail, N.I.; Yin, O.S. Beneficial Properties of Probiotics. Trop. Life Sci. Res. 2016, 27, 73–90. [Google Scholar]
- Hsu, C.N.; Lin, Y.J.; Hou, C.Y.; Tain, Y.L. Maternal Administration of Probiotic or Prebiotic Prevents Male Adult Rat Offspring against Developmental Programming of Hypertension Induced by High Fructose Consumption in Pregnancy and Lactation. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Silveira-Nunes, G.; Durso, D.F.; Cunha, E.H.; Maioli, T.U.; Vieira, A.T.; Speziali, E.; Corrêa-Oliveira, R.; Martins-Filho, O.A.; Teixeira-Carvalho, A.; Franceschi, C.; et al. Hypertension Is Associated with Intestinal Microbiota Dysbiosis and Inflammation in a Brazilian Population. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Natarajan, N.; Hori, D.; Flavahan, S.; Steppan, J.; Flavahan, N.A.; Berkowitz, D.E.; Pluznick, J.L. Microbial short chain fatty acid metabolites lower blood pressure via endothelial G protein-coupled receptor 41. Physiol. Genomics 2016, 48, 826–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholas, S.B.; Yuan, J.; Aminzadeh, A.; Norris, K.C.; Crum, A.; Vaziri, N.D. Salutary effects of a novel oxidative stress modulator on adenine-induced chronic progressive tubulointerstitial nephropathy. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2012, 4, 257–268. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, B.H.; Al-Husseni, I.; Beegam, S.; Al-Shukaili, A.; Nemmar, A.; Schierling, S.; Queisser, N.; Schupp, N. Effect of gum arabic on oxidative stress and inflammation in adenine-induced chronic renal failure in rats. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e55242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hsu, C.N.; Lin, Y.J.; Tain, Y.L. Maternal Exposure to Bisphenol A Combined with High-Fat Diet-Induced Programmed Hypertension in Adult Male Rat Offspring: Effects of Resveratrol. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cottart, C.H.; Nivet-Antoine, V.; Laguillier-Morizot, C.; Beaudeux, J.L. Resveratrol bioavailability and toxicity in humans. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2010, 54, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Springer, M.; Moco, S. Resveratrol and Its Human Metabolites-Effects on Metabolic Health and Obesity. Nutrients 2019, 11, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]



| Groups | C | CKD | CKD+R |
|---|---|---|---|
| Body weight (BW) (g) | 357 ± 11 | 384 ± 12 | 441 ± 17 *# |
| Left kidney weight (g) | 1.54 ± 0.07 | 1.8 ± 0.01 * | 2.14 ± 0.08 *# |
| Left kidney weight/100 g BW | 0.43 ± 0.01 | 0.47 ± 0.02 * | 0.49 ± 0.02 * |
| Systolic blood pressure (mmHg) | 131 ± 1 | 145 ± 1 * | 136 ± 1 # |
| Diastolic blood pressure (mmHg) | 83 ± 2 | 91 ± 2 * | 88 ± 1 |
| Mean arterial pressure (mmHg) | 99 ± 2 | 109 ± 2 * | 104 ± 1 |
| Creatinine (μM) | 19.2 ± 0.7 | 22.6 ± 1.5 | 17.6 ± 0.8 |
| Groups | C | CKD | CKD+R |
|---|---|---|---|
| L-Citrulline (μM) | 41.3 ± 4 | 44.6 ± 4.1 | 55.5 ± 3.1 * |
| L-Arginine (μM) | 173 ± 8.2 | 148.6 ± 7.5 * | 178.84 ± 7.8 # |
| ADMA (μM) | 1.69 ± 0.2 | 1.54 ± 0.2 | 1.13 ± 0.26 |
| SDMA (μM) | 1.32 ± 0.2 | 1.16 ± 0.23 | 0.89 ± 0.2 |
| L-Arginine-to-ADMA ratio (μM/μM) | 114 ± 17 | 108 ± 17 | 222 ± 56 # |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hsu, C.-N.; Hou, C.-Y.; Chang-Chien, G.-P.; Lin, S.; Yang, H.-W.; Tain, Y.-L. Perinatal Resveratrol Therapy Prevents Hypertension Programmed by Maternal Chronic Kidney Disease in Adult Male Offspring: Implications of the Gut Microbiome and Their Metabolites. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 567. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines8120567
Hsu C-N, Hou C-Y, Chang-Chien G-P, Lin S, Yang H-W, Tain Y-L. Perinatal Resveratrol Therapy Prevents Hypertension Programmed by Maternal Chronic Kidney Disease in Adult Male Offspring: Implications of the Gut Microbiome and Their Metabolites. Biomedicines. 2020; 8(12):567. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines8120567
Chicago/Turabian StyleHsu, Chien-Ning, Chih-Yao Hou, Guo-Ping Chang-Chien, Sufan Lin, Hung-Wei Yang, and You-Lin Tain. 2020. "Perinatal Resveratrol Therapy Prevents Hypertension Programmed by Maternal Chronic Kidney Disease in Adult Male Offspring: Implications of the Gut Microbiome and Their Metabolites" Biomedicines 8, no. 12: 567. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines8120567
APA StyleHsu, C.-N., Hou, C.-Y., Chang-Chien, G.-P., Lin, S., Yang, H.-W., & Tain, Y.-L. (2020). Perinatal Resveratrol Therapy Prevents Hypertension Programmed by Maternal Chronic Kidney Disease in Adult Male Offspring: Implications of the Gut Microbiome and Their Metabolites. Biomedicines, 8(12), 567. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines8120567








