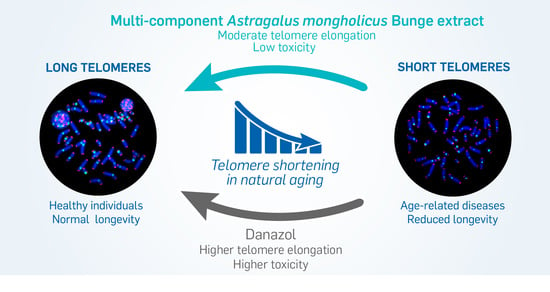
The Use of Natural Agents to Counteract Telomere Shortening: Effects of a Multi-Component Extract of Astragalus mongholicus Bunge and Danazol
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of the Hydroethanolic Root Extract of Astragalus mongholicus Bunge
2.2. High-Performance Thin-Layer Chromatography (HPTLC) Analysis of A. mongholicus Bunge HRE
2.3. Liquid Chromatography/Mass Spectrometry (LC/MS) Analysis of A. mongholicus Bunge HRE
2.4. In Vitro Exposure of Cell Lines And Cytotoxicity Approach
2.5. Peripheral Blood Lymphocyte In Vitro Exposure and Culture Conditions
2.6. Telomere Quantification
2.7. Telomerase Expression Using Immunofluorescence
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of A. mongholicus Bunge HRE
3.2. HRE Cytotoxicity
3.3. In Vitro Exposure of Peripheral Blood Lymphocytes to HRE Induced Telomere Elongation and Decreased the Proportion of Cells with Short Telomeres
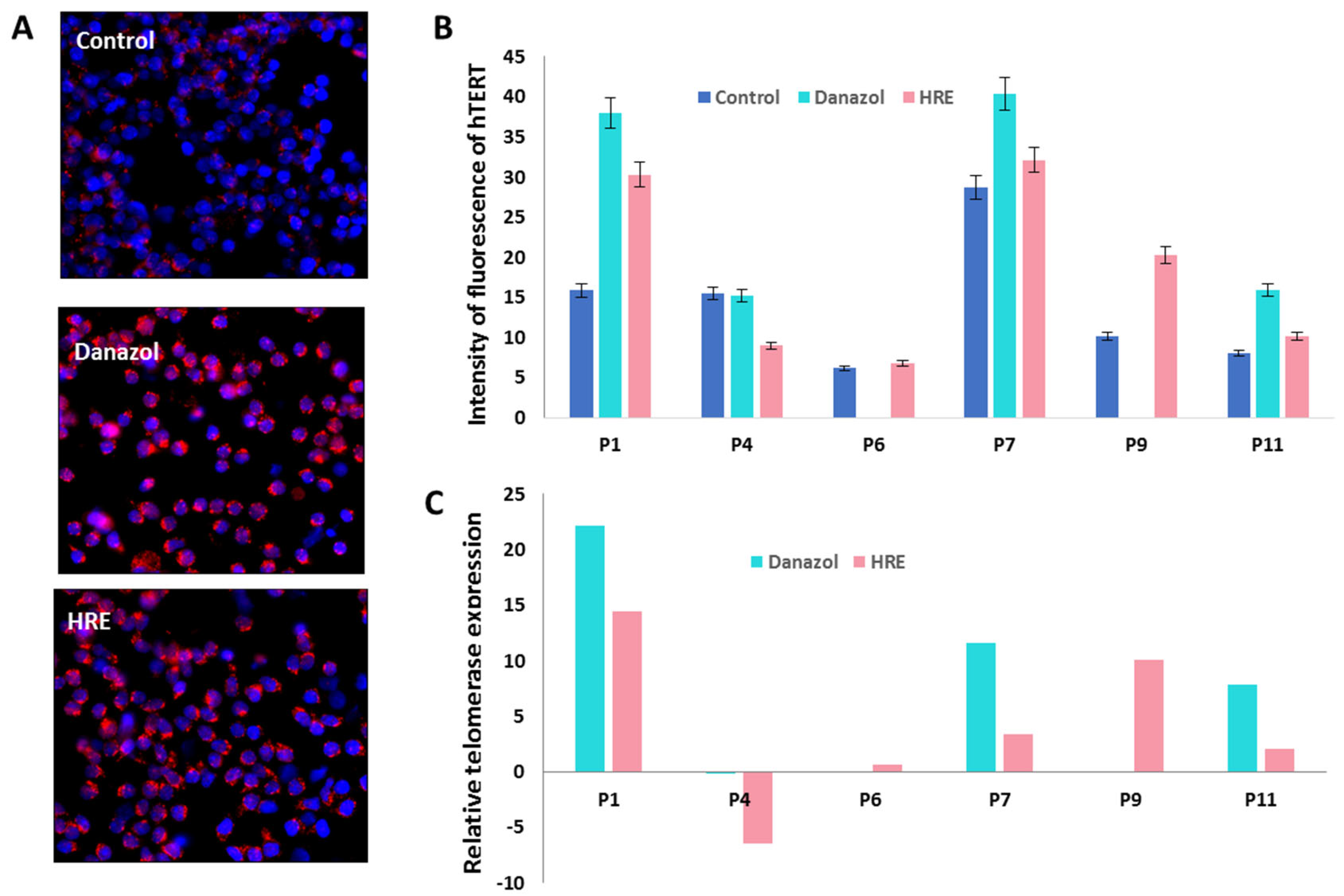
3.4. The HRE Induced Telomerase Expression and Led to Telomerase-Dependent Elongation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Patents
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shetty, A.K.; Kodali, M.; Upadhya, R.; Madhu, L.N. Emerging anti-aging strategies-scientific basis and efficacy. Aging Dis. 2018, 9, 1165–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xu, Z.; Feng, W.; Shen, Q.; Yu, N.; Yu, K.; Wang, S.; Chen, Z.; Shioda, S.; Guo, Y. Rhizoma coptidis and berberine as a natural drug to combat aging and aging-related diseases via anti-oxidation and ampk activation. Aging Dis. 2017, 8, 760–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Aunan, J.R.; Cho, W.C.; Søreide, K. The biology of aging and cancer: A brief overview of shared and divergent molecular hallmarks. Aging Dis. 2017, 8, 628–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stambler, I. Recognizing degenerative aging as a treatable medical condition: Methodology and policy. Aging Dis. 2017, 8, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chakrabarti, S.; Mohanakumar, K.P. Aging and neurodegeneration: A tangle of models and mechanisms. Aging Dis. 2016, 7, 111–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Konar, A.; Singh, P.; Thakur, M.K. Age-associated cognitive decline: Insights into molecular switches and recovery avenues. Aging Dis. 2016, 7, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martínez, P.; Blasco, M.A. Telomere-driven diseases and telomere-targeting therapies. J. Cell Biol. 2017, 216, 875–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blasco, M.A. Telomeres and human disease: Ageing, cancer and beyond. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2005, 6, 611–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasko, T.; Hoffmann, J.; Gostek, S.; Schettgen, T.; Quinete, N.; Preisinger, C.; Kraus, T.; Ziegler, P. Telomerase gene expression bioassays indicate metabolic activation of genotoxic lower chlorinated polychlorinated biphenyls. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 16903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaifie, A.; Schikowsky, C.; Vasko, T.; Kraus, T.; Brümmendorf, T.H.; Ziegler, P. Additional benefits of telomere length (TL) measurements in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Leuk Lymphoma 2019, 60, 541–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- M’kacher, R.; Bennaceur-Griscelli, A.; Girinsky, T.; Koscielny, S.; Delhommeau, F.; Dossou, J.; Violot, D.; Leclercq, E.; Courtier, M.H.; Béron-Gaillard, N.; et al. Telomere shortening and associated chromosomal instability in peripheral blood lymphocytes of patients with Hodgkin’s lymphoma prior to any treatment are predictive of second cancers. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2007, 68, 465–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- M’kacher, R.; Girinsky, T.; Colicchio, B.; Ricoul, M.; Dieterlen, A.; Jeandidier, E.; Heidingsfelder, L.; Cuceu, C.; Shim, G.; Frenze, M.; et al. Telomere shortening: A new prognostic factor for cardiovascular disease post-radiation exposure. Radiat. Prot. Dosim. 2015, 164, 134–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muraki, K.; Han, L.; Miller, D.; Murnane, J.P. Processing by MRE11 is involved in the sensitivity of subtelomeric regions to DNA double-strand breaks. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, 7911–7930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hewitt, G.; Jurk, D.; Marques, F.D.; Correia-Melo, C.; Hardy, T.; Gackowska, A.; Anderson, R.; Taschuk, M.; Mann, J.; Passos, J.F. Telomeres are favoured targets of a persistent DNA damage response in ageing and stress-induced senescence. Nat. Commun. 2012, 3, 708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murnane, J.P. Telomere loss as a mechanism for chromosome instability in human cancer. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 4255–4259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Epel, E.S.; Blackburn, E.H.; Lin, J.; Dhabhar, F.S.; Adler, N.E.; Morrow, J.D.; Cawthon, R.M. Accelerated telomere shortening in response to life stress. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 17312–17315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martínez, P.; Blasco, M.A. Telomeric and extra-telomeric roles for telomerase and the telomere-binding proteins. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2011, 11, 161–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Jesus, B.B.; Blasco, M.A. Potential of telomerase activation in extending health span and longevity. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2012, 24, 739–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kannengiesser, C.; Borie, R.; Renzoni, E.A. Pulmonary fibrosis: Genetic analysis of telomere-related genes, telomere length measurement-or both? Respirology 2019, 24, 97–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, K.N.; Wu, M.; Bondy, S.C. Telomere shortening during aging: Attenuation by antioxidants and anti-inflammatory agents. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2017, 164, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Townsley, D.M.; Dumitriu, B.; Liu, D.; Biancotto, A.; Weinstein, B.; Chen, C.; Hardy, N.; Mihalek, A.D.; Lingala, S.; Kim, Y.J.; et al. Danazol treatment for telomere diseases. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 374, 1922–1931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jäger, K.; Walter, M. Therapeutic targeting of telomerase. Genes 2016, 7, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, P.; Zhao, H.; Luo, Y. Anti-aging implications of Astragalus membranaceus (huangqi): A well-known chinese tonic. Aging Dis. 2017, 8, 868–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, Y.; Zhou, L.; Yang, Y.; Liu, Y. Cycloastragenol: An exciting novel candidate for age-associated diseases. Exp. Ther. Med. 2018, 16, 2175–2182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ait-Ghezala, G.; Hassan, S.; Tweed, M.; Paris, D.; Crynen, G.; Zakirova, Z.; Crynen, S.; Crawford, F. Identification of telomerase-activating blends from naturally occurring compounds. Altern. Ther. Health Med. 2016, 22, 6–14. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Plant, J. Effects of essential oils on telomere length in human cells. Med Aromat Plants 2016, 5, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, F.; Zhao, P.-W.; Sun, P.; Ma, L.J.; Zhao, P.W. Effect of Cynomorium songaricum polysaccharide on telomere of lung cancer A549 cells. Zhongguo Zhong Zazhi 2016, 41, 917–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Yan, G.; Li, Y.; Han, Z.; Zhang, L.; Chen, S.; Feng, C.; Huang, Q.; Ding, F.; Yu, Y.; et al. Astragalus polysaccharide attenuated iron overload-induced dysfunction of mesenchymal stem cells via suppressing mitochondrial ros. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2016, 39, 1369–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Wang, Z.; Huang, L.; Zheng, S.; Wang, D.; Chen, S.; Zhang, H.; Yang, S. Review of the botanical characteristics, phytochemistry, and pharmacology of Astragalus membranaceus (Huangqi). Phytother. Res. 2014, 28, 1275–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Qu, L.; Dong, Y.; Han, L.; Liu, E.; Fang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, T. A review of recent research progress on the Astragalus genus. Molecules 2014, 19, 18850–18880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molgora, B.; Bateman, R.; Sweeney, G.; Finger, D.; Dimler, T.; Effors, R.B.; Valenzuela, H.F. Functional assessment of pharmacological telomerase activators in human T cells. Cells 2013, 2, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salvador, L.; Singaravelu, G.; Harley, C.B.; Flom, P.; Suram, A.; Raffaele, J.M. A natural product telomerase activator lengthens telomeres in humans: A randomized, double blind, and placebo controlled study. Rejuvenation Res. 2016, 19, 478–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- M’kacher, R.; Cuceu, C.; Al Jawhari, M.; Morat, L.; Frenzel, M.; Shim, G.; Lenain, A.; Hempel, W.M.; Junker, S.; Girinsky, T.; et al. The transition between telomerase and alt mechanisms in Hodgkin lymphoma and its predictive value in clinical outcomes. Cancers 2018, 10, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cuceu, C.; Colicchio, B.; Jeandidier, E.; Junker, S.; Plassa, F.; Shim, G.; Mika, J.; Frenzel, M.; Al Jawhari, M.; Hempel, W.M.; et al. Independent mechanisms lead to genomic instability in hodgkin lymphoma: Microsatellite or chromosomal instability. Cancers 2018, 10, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Quintela-Fandino, M.; Soberon, N.; Lluch, A.; Manso, L.; Calvo, I.; Cortes, J.; Moreno-Antón, F.; Gil-Gil, M.; Martinez-Jánez, N.; Gonzalez-Martin, A.; et al. Critically short telomeres and toxicity of chemotherapy in early breast cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 21472–21482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savage, S.A. Beginning at the ends: Telomeres and human disease. F1000Research 2018, 7, F1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Girinsky, T.; M’kacher, R.; Lessard, N.; Koscielny, S.; Elfassy, E.; Raoux, F.; Carde, P.; Santos, M.D.; Margainaud, J.P.; Sabatier, L.; et al. Prospective coronary heart disease screening in asymptomatic Hodgkin lymphoma patients using coronary computed tomography angiography: Results and risk factor analysis. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2014, 89, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calado, R.T.; Yewdell, W.T.; Wilkerson, K.L.; Regal, J.A.; Kajigaya, S.; Stratakis, C.A.; Young, N.S. Sex hormones, acting on the TERT gene, increase telomerase activity in human primary hematopoietic cells. Blood 2009, 114, 2236–2243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bär, C.; Huber, N.; Beier, F.; Blasco, M.A. Therapeutic effect of androgen therapy in a mouse model of aplastic anemia produced by short telomeres. Haematologica 2015, 100, 1267–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khincha, P.P.; Bertuch, A.A.; Gadalla, S.M.; GIRI, N.; Alter, B.P.; Savage, S.A. Similar telomere attrition rates in androgen-treated and untreated patients with dyskeratosis congenita. Blood Adv. 2018, 2, 1243–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harley, C.B.; Liu, W.; Blasco, M.; Vera, E.; Andrews, W.H.; Briggs, L.A.; Raffaele, J.M. A natural product telomerase activator as part of a health maintenance program. Rejuvenation Res. 2011, 14, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- de Jesus, B.B.; Schneeberger, K.; Vera, E.; Tejera, A.; Harley, C.B.; Blasco, M.A. The telomerase activator TA-65 elongates short telomeres and increases health span of adult/old mice without increasing cancer incidence. Aging Cell 2011, 10, 604–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vera, E.; Bernardes de Jesus, B.; Foronda, M.; Flores, J.M.; Blasco, M.A. The rate of increase of short telomeres predicts longevity in mammals. Cell Rep. 2012, 2, 732–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ehrlenbach, S.; Willeit, P.; Kiechl, S.; Willeit, J.; Reindl, M.; Schanda, K.; Kronenberg, F.; Brandstätter, A. Influences on the reduction of relative telomere length over 10 years in the population-based Bruneck Study: Introduction of a well-controlled high-throughput assay. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2009, 38, 1725–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Whittemore, K.; Vera, E.; Martínez-Nevado, E.; Sanpera, C.; Blasco, M.A. Telomere shortening rate predicts species life span. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 15122–15127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lajoie, V.; Lemieux, B.; Sawan, B.; Lichtensztejn, D.; Lichtensztejn, Z.; Wellinger, R.; Mai, S.; Knecht, H. LMP1 mediates multinuclearity through downregulation of shelterin proteins and formation of telomeric aggregates. Blood 2015, 125, 2101–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Camitta, B.M.; Thomas, E.D.; Nathan, D.G.; Gale, R.P.; Kopecky, K.J.; Rappeport, J.M.; Santos, G.; Gordon-Smith, E.C.; Storb, R. A prospective study of androgens and bone marrow transplantation for treatment of severe aplastic anemia. Blood 1979, 53, 504–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, P.; Zhang, Z.; Sun, Y.; Liu, X.; Tong, T. The two isomers of HDTIC compounds from Astragali Radix slow down telomere shortening rate via attenuating oxidative stress and increasing DNA repair ability in human fetal lung diploid fibroblast cells. DNA Cell Biol. 2010, 29, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Le, A.; Ng, A.; Kwan, T.; Cusmano-Ozog, K.; Cowan, T.M. A rapid, sensitive method for quantitative analysis of underivatized amino acids by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS). J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2014, 944, 166–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MassBank of North America Spectrum KO002593 for Canavanine. 2019. Available online: http://mona.fiehnlab.ucdavis.edu/spectra/browse?query=&text=KO002593&size=10 (accessed on 25 July 2019).
- MassBank of North America Spectrum PB000459 for Asparagine. 2019. Available online: http://mona.fiehnlab.ucdavis.edu/spectra/display/PB000459 (accessed on 25 July 2019).
- MassBank of North America Spectrum CCMSLIB00003740029 for Glutamic Acid. 2019. Available online: http://mona.fiehnlab.ucdavis.edu/spectra/display/CCMSLIB00003740029 (accessed on 25 July 2019).
- MassBank of North America Spectrum PR100500 for Sucrose. 2019. Available online: http://mona.fiehnlab.ucdavis.edu/spectra/display/PR100500 (accessed on 25 July 2019).
- Jiao, J.; Gai, Q.-Y.; Luo, M.; Peng, X.; Zhao, C.J.; Fu, Y.J.; Ma, W. Direct determination of astragalosides and isoflavonoids from fresh Astragalus membranaceus hairy root cultures by high speed homogenization coupled with cavitation-accelerated extraction followed by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 34672–34681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guinobert, I.; Blondeau, C.; Colicchio, B.; Oudrhiri, N.; Dieterlen, A.; Jeandidier, E.; Deschenes, G.; Bardot, V.; Cotte, C.; Ripoche, I.; et al. The Use of Natural Agents to Counteract Telomere Shortening: Effects of a Multi-Component Extract of Astragalus mongholicus Bunge and Danazol. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 31. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines8020031
Guinobert I, Blondeau C, Colicchio B, Oudrhiri N, Dieterlen A, Jeandidier E, Deschenes G, Bardot V, Cotte C, Ripoche I, et al. The Use of Natural Agents to Counteract Telomere Shortening: Effects of a Multi-Component Extract of Astragalus mongholicus Bunge and Danazol. Biomedicines. 2020; 8(2):31. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines8020031
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuinobert, Isabelle, Claude Blondeau, Bruno Colicchio, Noufissa Oudrhiri, Alain Dieterlen, Eric Jeandidier, Georges Deschenes, Valérie Bardot, César Cotte, Isabelle Ripoche, and et al. 2020. "The Use of Natural Agents to Counteract Telomere Shortening: Effects of a Multi-Component Extract of Astragalus mongholicus Bunge and Danazol" Biomedicines 8, no. 2: 31. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines8020031
APA StyleGuinobert, I., Blondeau, C., Colicchio, B., Oudrhiri, N., Dieterlen, A., Jeandidier, E., Deschenes, G., Bardot, V., Cotte, C., Ripoche, I., Carde, P., Berthomier, L., & M’Kacher, R. (2020). The Use of Natural Agents to Counteract Telomere Shortening: Effects of a Multi-Component Extract of Astragalus mongholicus Bunge and Danazol. Biomedicines, 8(2), 31. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines8020031