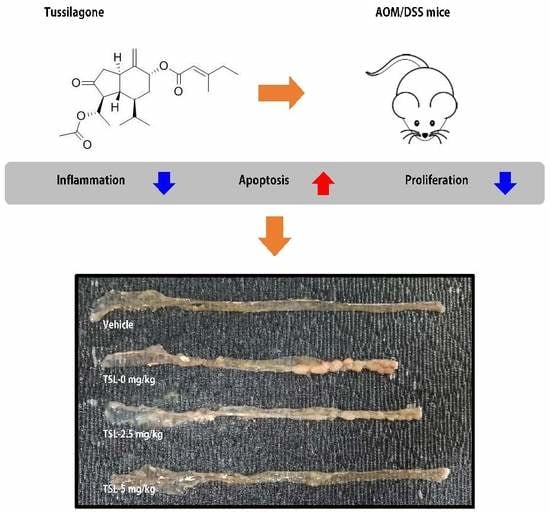
Tussilagone Reduces Tumorigenesis by Diminishing Inflammation in Experimental Colitis-Associated Colon Cancer
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Reagents and Antibodies
2.2. AOM/DSS-Induced Colitis-Associated Colon Carcinogenesis and Design of Drug Treatment
2.3. Histopathology and Immunohistochemistry (IHC)
2.4. Western Blot Analysis
2.5. RT-qPCR Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Tussilagone Treatment Diminishes AOM/DSS-Induced Tumorigenesis in Mice
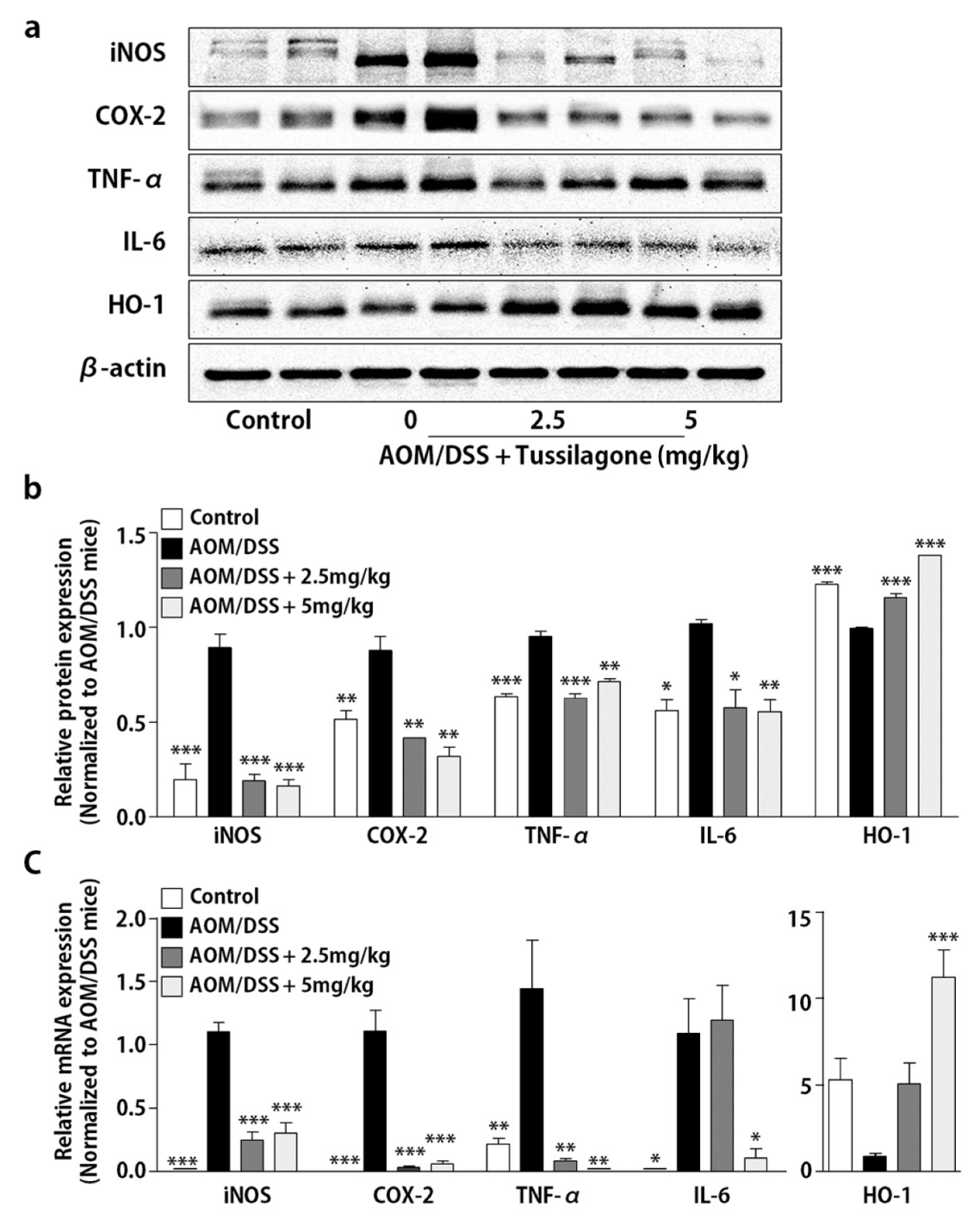
3.2. Tussilagone Treatment Inhibits Inflammatory Responses in Colon Tissues
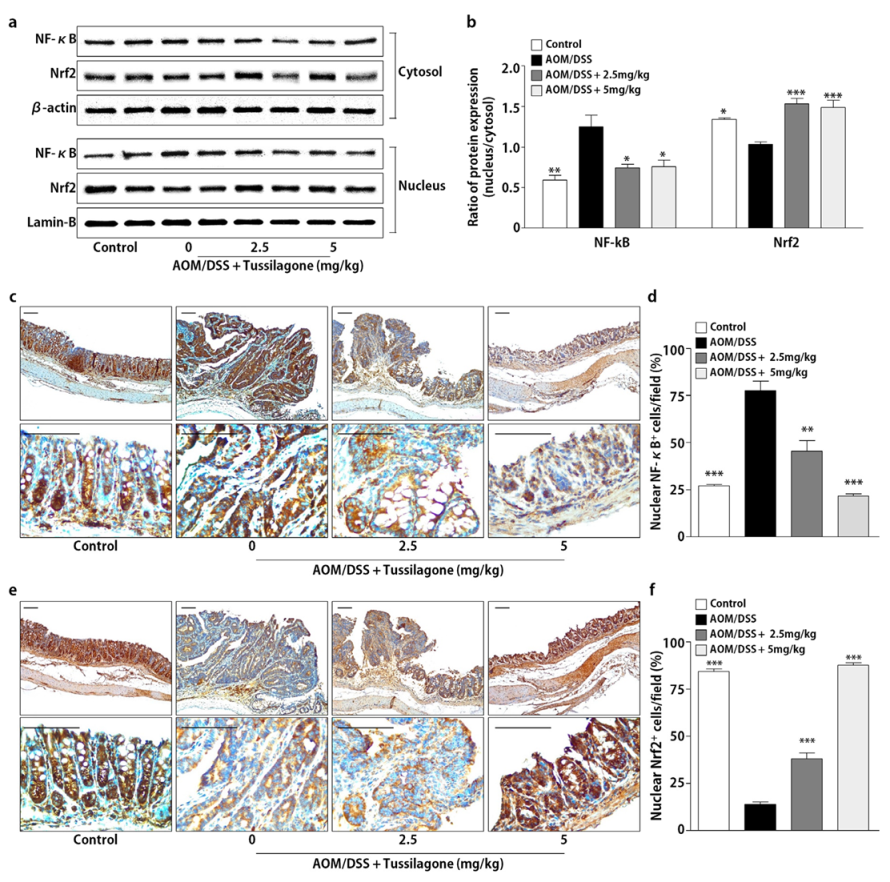
3.3. Tussilagone Treatment Inhibits NF-κB and Activates Nrf2 in Colon Tissues
3.4. Tussilagone Induces Apoptosis and Inhibits Cell Proliferation in Colon Tissues
3.5. Tussilagone Administration Inhibits β-catenin Activation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Das, V.; Kalita, J.; Pal, M. Predictive and prognostic biomarkers in colorectal cancer: A systematic review of recent advances and challenges. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2016, 87, 8–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Fedewa, S.A.; Ahnen, D.J.; Meester, R.G.S.; Barzi, A.; Jemal, A. Colorectal cancer statistics, 2017. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2017, 67, 177–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnold, M.; Sierra, M.S.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jema, A.; Bray, F. Global patterns and trends in colorectal cancer incidence and mortality. Gut 2017, 66, 683–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Grivennikov, S.I. Inflammation and colorectal cancer: Colitis-associated neoplasia. Semin. Immunopathol. 2013, 35, 229–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Pitmon, E.; Wang, K. Microbiome, inflammation and colorectal cancer. Semin. Immunol. 2017, 32, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keller, D.S.; Windsor, A.; Cohen, R.; Chand, M. Colorectal cancer in inflammatory bowel disease: Review of the evidence. Tech. Coloproctol. 2019, 23, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francescone, R.; Hou, V.; Grivennikov, S.I. Cytokines, IBD and colitis-associated cancer. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2015, 21, 409–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zubair, H.; Azim, S.; Ahmad, A.; Khan, M.A.; Patel, G.K.; Singh, S.; Singh, A.P. Cancer chemoprevention by phytochemicals: Nature’s healing touch. Molecules 2017, 22, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kaur, V.; Kumar, M.; Kumar, A.; Kaur, K.; Dhillon, V.S.; Kaur, S. Pharmacotherapeutic potential of phytochemicals: Implications in cancer chemoprevention and future perspectives. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 97, 564–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.H.; Kwon, H.S.; Kim, D.H.; Shin, E.K.; Kang, Y.H.; Park, J.H.; Shin, H.K.; Kim, J.K. 3,3’-diindolylmethane attenuates colonic inflammation and tumorigenesis in mice. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2009, 15, 1164–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.K.; Shin, E.K.; Park, J.H.; Kim, Y.H.; Park, J.H. Antitumor and antimetastatic effects of licochalcone A in mouse models. J. Mol. Med. 2010, 88, 829–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.J.; Park, J.H.; Kim, J.K. Cucurbitacin-I, a natural cell-permeable triterpenoid isolated from Cucurbitaceae, exerts potent anticancer effect in colon cancer. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2014, 219, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.H.; Kim, J.K. Pristimerin, a naturally occurring triterpenoid, attenuates tumorigenesis in experimental colitis-associated colon cancer. Phytomedicine 2018, 42, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.K.; Yeo, M.G.; Oh, B.K.; Kim, H.Y.; Yang, H.J.; Cho, S.S.; Gil, M.; Lee, K.J. Tussilagone inhibits the inflammatory response and improves survival in CLP-induced septic mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jarić, S.; Kostić, O.; Mataruga, Z.; Pavlović, D.; Pavlović, M.; Mitrović, M.; Pavlović, P. Traditional wound-healing plants used in the Balkan region (Southeast Europe). J. Ethnopharmacol. 2018, 211, 311–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Kang, U.; Seo, E.K.; Kim, Y.S. Heme oxygenase-1-mediated anti-inflammatory effects of tussilagonone on macrophages and 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate-induced skin inflammation in mice. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2016, 34, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheon, H.J.; Nam, S.H.; Kim, J.K. Tussilagone, a major active component in Tussilago farfara, ameliorates inflammatory responses in dextran sulphate sodium-induced murine colitis. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2018, 294, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Lee, H.J.; Ahn, Y.H.; Kwon, H.J.; Jang, C.Y.; Kim, W.Y.; Ryu, J.H. Tussilagone suppresses colon cancer cell proliferation by promoting the degradation of β-catenin. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2014, 443, 132–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.; Ryu, H.S.; Lee, H.K.; Kim, J.S.; Yun, J.; Kang, J.S.; Hwang, B.Y.; Hong, J.T.; Kim, Y.; Han, S.B. Tussilagone inhibits dendritic cell functions via induction of heme oxygenase-1. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2014, 22, 400–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, H.J.; Lee, H.S.; Ryu, J.H. Suppression of inducible nitric oxide synthase and cyclooxygenase-2 expression by tussilagone from Farfarae flos in BV-2 microglial cells. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2008, 31, 645–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, K.S.; Sethi, G.; Aggarwal, B.B. Nuclear factor-kappa B: From clone to clinic. Curr. Mol. Med. 2007, 7, 619–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Concetti, J.; Wilson, C.L. NF-κB and cancer: Friend or Foe? Cells 2018, 7, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kensler, T.W.; Wakabayashi, N.; Biswal, S. Cell survival responses to environmental stresses via the Keap1-Nrf2-ARE pathway. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2007, 47, 89–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayan, V.; Wagener, F.A.D.T.G.; Immenschuh, S. The macrophage heme-heme oxygenase-1 system and its role in inflammation. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2018, 153, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khor, T.O.; Huang, M.T.; Kwon, K.H.; Chan, J.Y.; Reddy, B.S.; Kong, A.N. Nrf2-deficient mice have an increased susceptibility to dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 11580–11584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Clevers, H.; Nusse, R. Wnt/β-catenin signaling and disease. Cell 2012, 149, 1192–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shang, S.; Hua, F.; Hu, Z.W. The regulation of β-catenin activity and function in cancer: Therapeutic opportunitie. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 33972–33989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, D.; Chen, L.; Zhao, H.; Vaziri, N.D.; Ma, S.C.; Zhao, Y.Y. Small molecules from natural products targeting the Wnt/β-catenin pathway as a therapeutic strategy. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 117, 108990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, R.S. Apoptosis in cancer: From pathogenesis to treatment. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 30, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khan, K.H.; Blanco-Codesido, M.; Molife, L.R. Cancer therapeutics: Targeting the apoptotic pathway. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2014, 90, 200–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Hu, X.; Zuo, X.; Wang, M. Chemopreventive effects of some popular phytochemicals on human colon cancer: A review. Food Funct. 2018, 9, 4548–4568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nam, S.-H.; Kim, J.-K. Tussilagone Reduces Tumorigenesis by Diminishing Inflammation in Experimental Colitis-Associated Colon Cancer. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 86. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines8040086
Nam S-H, Kim J-K. Tussilagone Reduces Tumorigenesis by Diminishing Inflammation in Experimental Colitis-Associated Colon Cancer. Biomedicines. 2020; 8(4):86. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines8040086
Chicago/Turabian StyleNam, Sang-Hyeon, and Jin-Kyung Kim. 2020. "Tussilagone Reduces Tumorigenesis by Diminishing Inflammation in Experimental Colitis-Associated Colon Cancer" Biomedicines 8, no. 4: 86. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines8040086
APA StyleNam, S.-H., & Kim, J.-K. (2020). Tussilagone Reduces Tumorigenesis by Diminishing Inflammation in Experimental Colitis-Associated Colon Cancer. Biomedicines, 8(4), 86. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines8040086