The Quest to Enhance the Efficacy of Berberine for Type-2 Diabetes and Associated Diseases: Physicochemical Modification Approaches
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Chemical Synthesis of Berberine
3. General Pharmacokinetics Approach
3.1. Improving Berberine Bioavailability
3.2. Berberine Improving the Pharmacokinetics of Other Drugs
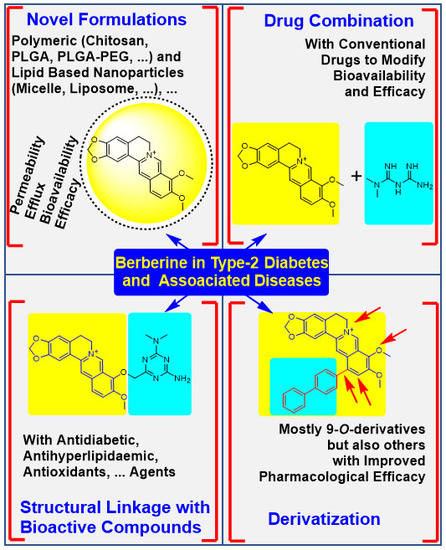
4. The Physicochemical Modification Approaches
4.1. Potency Enhancement Using Novel Formulations
4.2. From Drug Combination to Structural Linkage with Other Bioactive Compounds
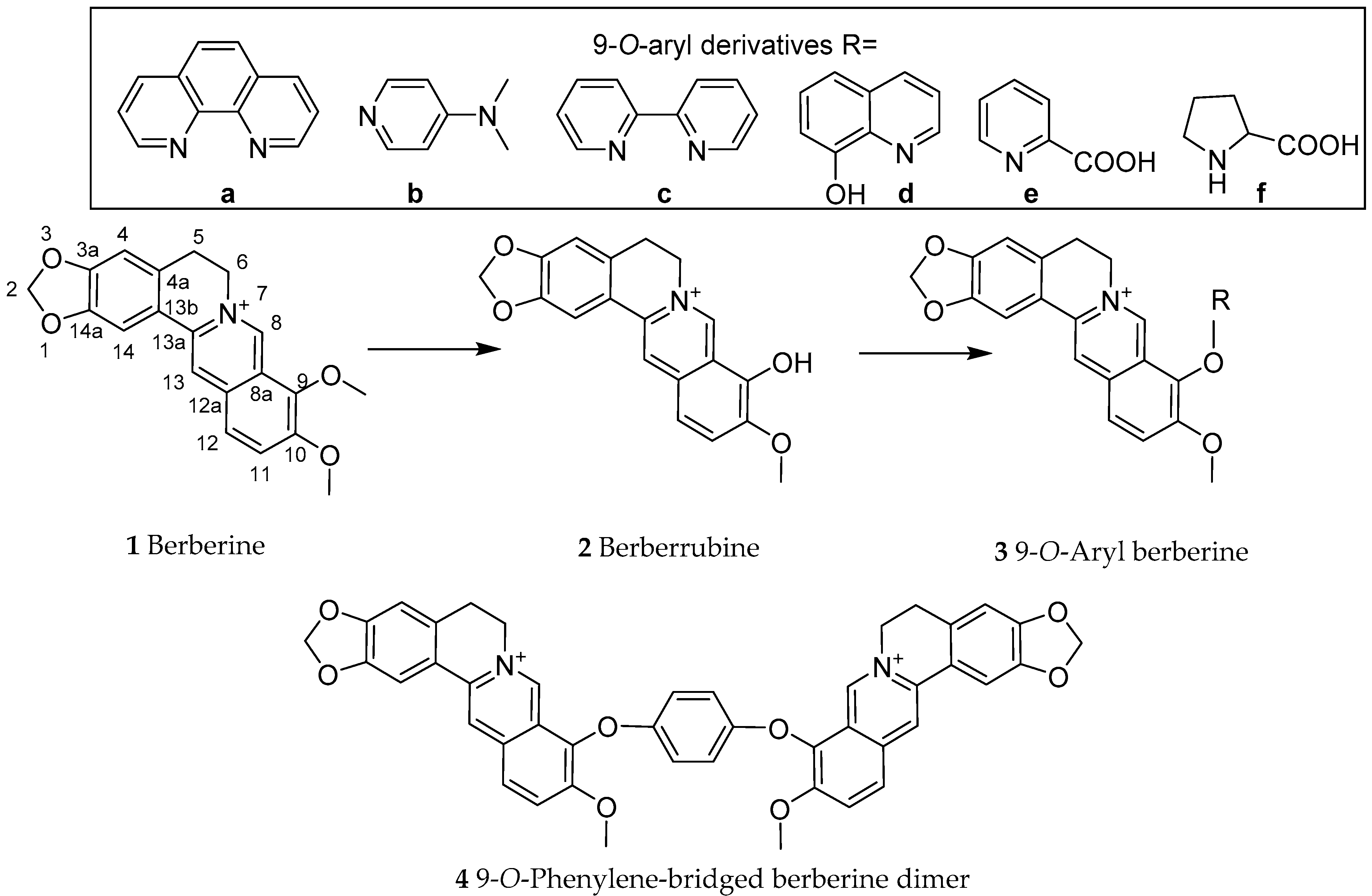
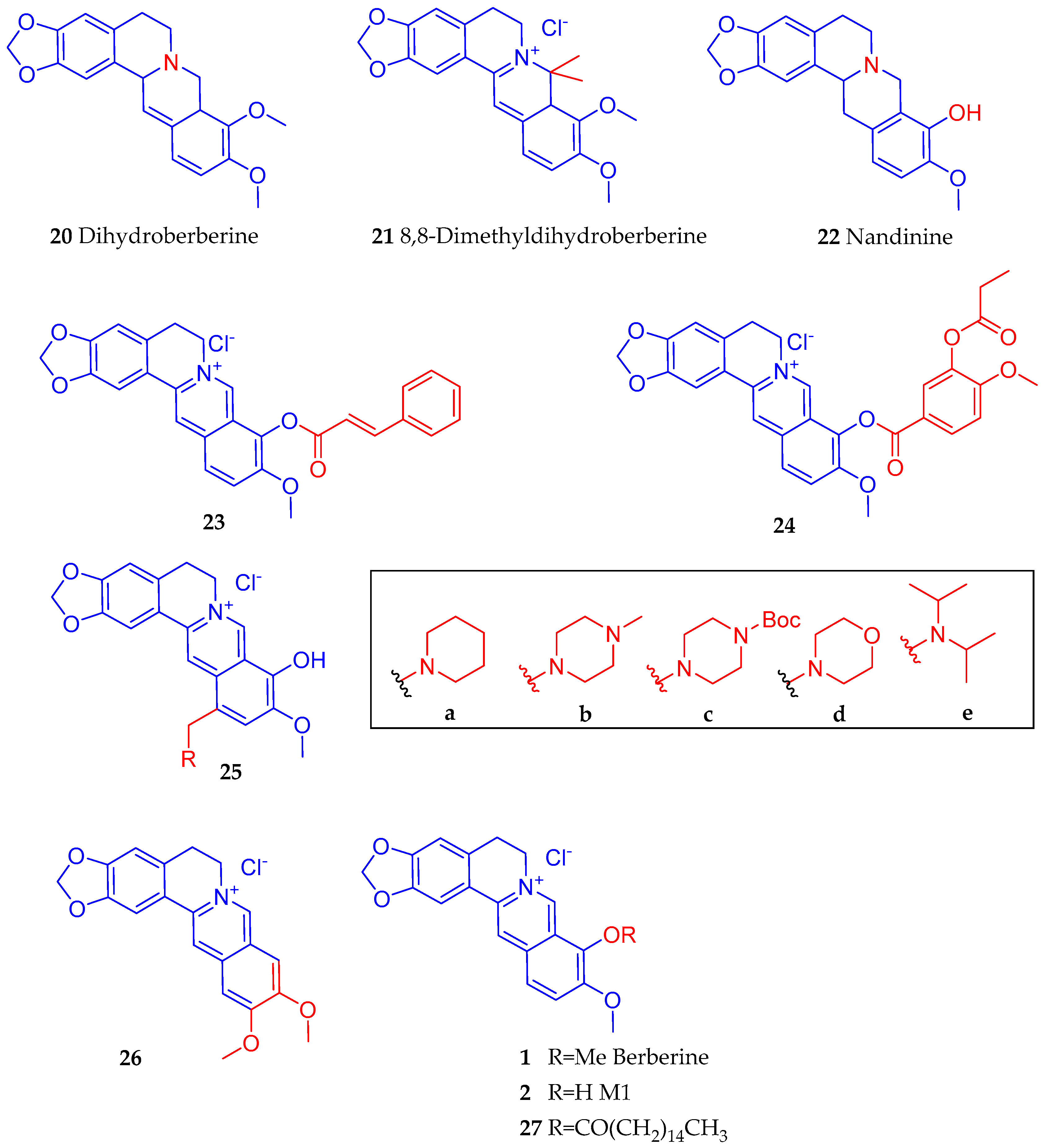
4.3. Synthesis of Berberine Derivatives
5. General Summary and Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO. Diabetes. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/diabetes (accessed on 26 March 2020).
- IDF (International Diabetes Federation). Diabetes Facts & Figures. Available online: https://www.idf.org/aboutdiabetes/what-is-diabetes/facts-figures.html (accessed on 26 March 2020).
- WHO. Obesity and Overweight. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight (accessed on 26 March 2020).
- Habtemariam, S. Chapter 26—Antidiabetic herbal medicines rebranded as dietary supplements. In Medicinal Foods as Potential Therapies for Type-2 Diabetes and Associated Diseases—The Chemical and Pharmacological Basis of Their Action; Academic Press (Elsevier): London, UK, 2019; pp. 1049–1134. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, C.; Hu, X.; Xu, Y.; Yang, J.; Zong, L.; Wang, C.; Zhu, J.; Li, Z.; Lu, D. Berberine inhibits proliferation and migration of colorectal cancer cells by downregulation of GRP78. Anticancer Drugs 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, F.; Xie, T.; Huang, X.; Zhao, X. Berberine inhibits angiogenesis in glioblastoma xenografts by targeting the VEGFR2/ERK pathway. Pharm Biol. 2018, 56, 665–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, S. Berberine suppresses growth and metastasis of endometrial cancer cells via miR-101/COX-2. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 103, 1287–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.G.; Choi, J.W.; Jo, I.J.; Kim, M.J.; Lee, H.S.; Hong, S.H.; Song, H.J.; Bae, G.S.; Park, S.J. Berberine ameliorates lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory responses in mouse inner medullary collecting duct-3 cells by downregulation of NF-κB pathway. Mol. Med. Rep. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Habtemariam, S. Berberine and inflammatory bowel disease: A concise review. Pharmacol. Res. 2016, 113, 592–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derosa, G.; Maffioli, P.; Cicero, A.F. Berberine on metabolic and cardiovascular risk factors: An analysis from preclinical evidences to clinical trials. Expert. Opin. Biol. Ther. 2012, 12, 1113–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.; Zhang, M.; Hu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Teng, F.; Lv, X.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Hatch, G.M.; Chen, L. Increased Bioavailable Berberine Protects Against Myocardial Ischemia Reperfusion Injury Through Attenuation of NFκB and JNK Signaling Pathways. Int. Heart J. 2018, 59, 1378–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, K.; Chen, Q.; Wu, N.; Li, Y.; Zhang, R.; Wang, J.; Gong, D.; Zou, X.; Liu, C.; Chen, J. Berberine ameliorates spatial learning memory impairment and modulates cholinergic anti-Inflammatory pathway in diabetic rats. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghotbi-Ravandi, S.; Shabani, M.; Bashiri, H.; Saeedi Goraghani, M.; Khodamoradi, M.; Nozari, M. Ameliorating effects of berberine on MK-801-induced cognitive and motor impairments in a neonatal rat model of schizophrenia. Neurosci. Lett. 2019, 706, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadraie, S.; Kiasalari, Z.; Razavian, M.; Azimi, S.; Sedighnejad, L.; Afshin-Majd, S.; Baluchnejadmojarad, T.; Roghani, M. Berberine ameliorates lipopolysaccharide-induced learning and memory deficit in the rat: Insights into underlying molecular mechanisms. Metab. Brain Dis. 2019, 34, 245–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Liu, L.; Wang, X.; Liu, X.; Liu, X.; Xie, L.; Wang, G. Modulation of glucagon-like peptide-1 release by berberine: In vivo and in vitro studies. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2010, 79, 1000–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Zou, D.; Liu, W.; Yang, J.; Zhu, N.; Huo, L.; Wang, M.; Hong, J.; Wu, P.; et al. Treatment of type 2 diabetes and dyslipidemia with the natural plant alkaloid berberine. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2008, 93, 2559–2565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, H.; Wei, J.; Xue, R.; Wu, J.D.; Zhao, W.; Wang, Z.Z.; Wang, S.K.; Zhou, Z.X.; Song, D.Q.; Wang, Y.M.; et al. Berberine lowers blood glucose in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients through increasing insulin receptor expression. Metabolism 2010, 59, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.S.; Lee, Y.S.; Cha, S.H.; Jeong, H.W.; Choe, S.S.; Lee, M.R.; Oh, G.T.; Park, H.S.; Lee, K.U.; Lane, M.D.; et al. Berberine improves lipid dysregulation in obesity by controlling central and peripheral AMPK activity. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2009, 296, E812–E819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wei, S.; Zhang, M.; Yu, Y.; Lan, X.; Yao, F.; Yan, X.; Chen, L.; Hatch, G.M. Berberine attenuates development of the hepatic gluconeogenesis and lipid metabolism disorder in type 2 diabetic mice and in palmitate-incubated HepG2 cells through suppression of the HNF-4α miR122 pathway. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0152097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Potdar, D.; Hirwani, R.R.; Dhulap, S. Phyto-chemical and pharmacological applications of Berberis aristate. Fitoterapia 2012, 83, 817–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Duggal, S.; Kaur, N.; Singh, J. Berberine: Alkaloid with wide spectrum of pharmacological activities. J. Nat. Prod. 2010, 3, 64–75. [Google Scholar]
- Habtemariam, S. The hidden treasure in Europe’s garden plants: Case examples; Berberis darwinni and Bergenia cordifolia. Med. Aromat. Plants 2013, 2, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Habtemariam, S. The therapeutic potential of Berberis darwinii stem-bark: Quantification of berberine and in vitro evidence for Alzheimer’s disease therapy. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2011, 6, 1089–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, A.; Bajpai, V.; Srivastava, M.; Arya, K.R.; Kumar, B. Rapid screening and distribution of bioactive compounds in different parts of Berberis petiolaris using direct analysis in real time mass spectrometry. J. Pharm. Anal. 2015, 5, 332–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suau, R.; Rico, R.; López-Romero, J.M.; Nájera, F.; Cuevas, A. Isoquinoline alkaloids from Berberis Vulgaris subsp. Aust. Phytochem. 1998, 49, 2545–2549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habtemariam, S. Going back to the good old days: The merit of crude plant drug mixtures in the 21st century. Int. J. Complement. Altern. Med. 2017, 6, 00182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Habtemariam, S. Berberine pharmacology and the gut Microbiota: A hidden therapeutic link. Pharmacol. Res. 2020, 155, 104722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Habtemariam, S. Recent advances in berberine inspired anticancer approaches: From drug combination to novel formulation technology and dererivatization. Molecules 2020, 25, 1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kametani, T.; Noguchi, I.J. Studies on the syntheses of heterocyclic compounds. CCCII. Alternative total syntheses of (+/−)-nandinine, (+/−)-canadine, and berberine iodide. Chem. Soc. C 1969, 2036–2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatland, A.E.; Pilgrim, B.S.; Procopiou, P.A.; Donohoe, T.J. Short and efficient syntheses of protoberberine alkaloids using palladium-catalyzed enolate arylation. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 14555–14558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, V.; Jadhav, A.S.; Anand, R.V. A room-temperature protocol to access isoquinolines through Ag(I) catalysed annulation of o-(1-alkynyl)arylaldehydes and ketones with NH4OAc: Elaboration to berberine and palmatine. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2015, 13, 3732–3741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Tong, R. A general, concise strategy that enables collective total syntheses of over 50 protoberberine and five aporhoeadane alkaloids within four to eight steps. Chem. Eur. J. 2016, 22, 7084–7089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori-Quiroz, L.M.; Hedrick, S.L.; De Los Santos, A.R.; Clift, M.D. A Unified strategy for the syntheses of the isoquinolinium alkaloids berberine, coptisine, and jatrorrhizine. Org. Lett. 2018, 20, 4281–4284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.M.; Liang, J.Q.; Wang, H.T.; Zhao, S.H.; Zhang, H.; Tu, P.F. Total synthesis of epiberberine. J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 2012, 14, 873–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, Q.; Zhu, X.; Guo, Q.; Jiang, W.; Liu, J.; Meng, Q. Synthesis of 9-O-arylated berberines via copper-catalyzed CAr-O coupling reactions. Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 1575–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tera, M.; Hirokawa, T.; Okabe, S.; Sugahara, K.; Seimiya, H.; Shimamoto, K. Design and synthesis of a berberine dimer: A fluorescent ligand with high affinity towards G-quadruplexes. Chem. Eur. J. 2015, 21, 14519–14528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nechepurenko, I.V.; Salakhutdinov, N.F.; Tolstikov, G.A. Berberine: Chemistry and Biological Activity. Chem. Sustain. Dev. 2010, 18, 1–23. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.T.; Hao, H.P.; Xie, H.G.; Lai, L.; Wang, Q.; Liu, C.X.; Wang, G.J. Extensive intestinal first-pass elimination and predominant hepatic distribution of berberine explain its low plasma levels in rats. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2010, 38, 1779–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, Y.; Li, F.; Ma, X.; Cheng, X.; Zhou, H.; Klaassen, C.D. CYP2D plays a major role in berberine metabolism in liver of mice and humans. Xenobiotica 2011, 41, 996–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Ren, G.; Wang, Y.X.; Kong, W.J.; Yang, P.; Wang, Y.M.; Li, Y.H.; Yi, H.; Li, Z.R.; Song, D.Q.; et al. Bioactivities of berberine metabolites after transformation through CYP450 isoenzymes. J. Transl. Med. 2011, 9, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Hao, H.; Xie, H.; Lv, H.; Liu, C.; Wang, G. Oxidative demethylenation and subsequent glucuronidation are the major metabolic pathways of berberine in rats. J. Pharm. Sci. 2009, 98, 4391–4401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeng, H.; Yoo, H.; Kim, I.; Song, I.; Chung, S.; Shim, C. P-glycoprotein-mediated transport of berberine across Caco-2 cell monolayers. J. Pharm. Sci. 2002, 91, 2614–2621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Qiu, F.; Jiang, J.; Gao, C.; Tan, Y. Intestinal absorption mechanisms of berberine, palmatine, jateorhizine, and coptisine: Involvement of P-glycoprotein. Xenobiotica 2011, 41, 290–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, I.; Joshi, G.; Nakhate, K.T.; Ajazuddin Kumar, R.; Gupta, U. Nano-co-delivery of berberine and anticancer drug using PLGA nanoparticles: Exploration of better anticancer activity and in vivo Kinetics. Pharm. Res. 2019, 36, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochin, C.C.; Garelnabi, M. Berberine Encapsulated PLGA-PEG Nanoparticles Modulate PCSK-9 in HepG2 Cells. Cardiovasc. Hematol. Disord. Drug Targets 2018, 18, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.J.; Hu, X.B.; Lu, X.L.; Liao, D.H.; Tang, T.T.; Wu, J.Y.; Xiang, D.X. Nanoemulsion-based delivery system for enhanced oral bioavailability and caco-2 cell monolayers permeability of berberine hydrochloride. Drug Deliv. 2017, 24, 1868–1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xie, D.; Xu, Y.; Jing, W.; Juxiang, Z.; Hailun, L.; Yu, H.; Zheng, D.H.; Lin, Y.T. Berberine nanoparticles protects tubular epithelial cells from renal ischemia-reperfusion injury. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 24154–24162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xiong, W.; Sang, W.; Linghu, K.G.; Zhong, Z.F.; Cheang, W.S.; Li, J.; Li, J.; Hu, Y.J.; Yu, H.; Wang, Y.T. Dual-functional Brij-S20-modified nanocrystal formulation enhances the intestinal transport and oral bioavailability of berberine. Int. J. Nanomed. 2018, 13, 3781–3793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Elsheikh, M.A.; Elnaggar, Y.S.R.; Hamdy, D.A.; Abdallah, O.Y. Novel cremochylomicrons for improved oral bioavailability of the antineoplastic phytomedicine berberine chloride: Optimization and pharmacokinetics. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 535, 316–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsheikh, M.A.; Elnaggar, Y.S.R.; Otify, D.Y.; Abdallah, O.Y. Bioactive-chylomicrons for oral lymphatic targeting of berberine chloride: Novel flow-blockage assay in tissue-based and caco-2 cell line models. Pharm. Res. 2018, 35, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Liu, S.; Ming, J.; Li, Y.; Deng, M.; He, B. Sustained release effects of berberine-loaded chitosan microspheres on in vitro chondrocyte culture. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2017, 43, 1703–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.J.; Don, T.M.; Lin, C.W.; Mi, F.L. Delivery of berberine using chitosan/fucoidan-taurine conjugate nanoparticles for treatment of defective intestinal epithelial tight junction barrier. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 5677–5697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, Y.; He, P.; Liu, A.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Y.; Dai, R. Drug-drug interactions between ketoconazole and berberine in rats: Pharmacokinetic effects benefit pharmacodynamic synergism. Phytother. Res. 2012, 26, 772–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Deng, J.; Jia, X.; Zhou, J.; Lv, H. Solid dispersion of berberine-phospholipid complex/TPGS 1000/SiO₂: Preparation, characterization and in vivo studies. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 465, 306–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, K.Y.; Lin, Y.C.; Lu, H.T.; Ho, Y.C.; Weng, S.C.; Tsai, M.L.; Mi, F.L. A novel injectable in situ forming gel based on carboxymethyl hexanoyl chitosan/hyaluronic acid polymer blending for sustained release of berberine. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 206, 664–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torky, A.S.; Freag, M.S.; Nasra, M.M.A.; Abdallah, O.Y. Novel skin penetrating berberine oleate complex capitalizing on hydrophobic ion pairing approach. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 549, 76–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, H.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Q.; Dang, M.; Liu, H.; Dong, Y.; Zhang, L.; Yang, F.; Wu, J.; Tong, X. In vivo and in vitro study on drug-drug interaction of lovastatin and berberine from pharmacokinetic and HepG2 cell metabolism studies. Molecules 2016, 21, 464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xin, H.W.; Tang, X.; Ouyang, M.; Zhong, J.X.; Li, W.L. Effects of berberine on pharmacokinetics of midazolam and rhodamine 123 in rats in vivo. Springerplus 2016, 5, 380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, J.X.; Tang, D.; Feng, L.; Zheng, Z.G.; Wang, R.S.; Wu, A.G.; Duan, T.T.; He, B.; Zhu, Q. Development of self-microemulsifying drug delivery system for oral bioavailability enhancement of berberine hydrochloride. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2013, 39, 499–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, M.; Zhang, L.; Yang, M.X.; Zhang, W.; Li, X.M.; Ou, Z.M.; Li, Z.P.; Liu, S.H.; Li, X.J.; Yang, S.Y. Berberine-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles are concentrated in the liver and ameliorate hepatosteatosis in db/db mice. Int. J. Nanomed. 2015, 10, 5049–5057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Z.; Wu, J.; Zhou, Q.; Wang, Y.; Chen, T. Berberine nanosuspension enhances hypoglycemic efficacy on streptozotocin induced diabetic C57BL/6 mice. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2015, 2015, 239749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, T.; Wang, N.; Song, H.; Xi, X.; Wang, J.; Hao, A. Preparation of an anhydrous reverse micelle delivery system to enhance oral bioavailability and anti-diabetic efficacy of berberine. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2011, 44, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhaojie, M.; Ming, Z.; Shengnan, W.; Xiaojia, B.; Hatch, G.M.; Jingkai, G.; Li, C. Amorphous solid dispersion of berberine with absorption enhancer demonstrates a remarkable hypoglycemic effect via improving its bioavailability. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 467, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.; Li, Y.; Chen, Q.; He, Y.; Wang, H.; Yang, L.; Guo, S.; Meng, Z.; Cui, J.; Xue, M.; et al. Monodisperse microparticles loaded with the self-assembled berberine-phospholipid complex-based phytosomes for improving oral bioavailability and enhancing hypoglycemic efficiency. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2016, 103, 136–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Huang, X.; Yang, M.; Xu, J.; Chen, Z.; Yu, Z.; Liu, J. Ameliorative effect of berberine coated bio-active nanoparticles in acetaminophen induced hepato-renal damage in diabetic rats. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 2018, 189, 250–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, J.; Hou, Y.; Yin, Y.; Song, X. Selenium-coated nanostructured lipid carriers used for oral delivery of berberine to accomplish a synergic hypoglycemic effect. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 8671–8680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xu, H.Y.; Liu, C.S.; Huang, C.L.; Chen, L.; Zheng, Y.R.; Huang, S.H.; Long, X.Y. Nanoemulsion improves hypoglycemic efficacy of berberine by overcoming its gastrointestinal challenge. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2019, 181, 927–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.; Yang, J.; Zhu, W.; Yin, X.; Yang, B.; Wei, Y.; Guo, X. Combination of berberine with resveratrol improves the lipid-lowering efficacy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Price, N.L.; Gomes, A.; Ling, A.Y.; Duarte, F.V.; Martin-Montalvo, A.; North, B.J.; Agarwal, B.; Ye, L.; Ramadori, G.; Teodoro, J.S.; et al. SIRT1 is required for AMPK activation and the beneficial effects of resveratrol on mitochondrial function. Cell Metab. 2012, 15, 675–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, G.; Zhao, X.; Fu, J.; Wang, X. Resveratrol increase myocardial Nrf2 expression in type 2 diabetic rats and alleviate myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury (MIRI). Ann. Palliat. Med. 2019, 8, 565–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagul, P.K.; Middela, H.; Matapally, S.; Padiya, R.; Bastia, T.; Madhusudana, K.; Reddy, B.R.; Chakravarty, S.; Banerjee, S.K. Attenuation of insulin resistance, metabolic syndrome and hepatic oxidative stress by resveratrol in fructose-fed rats. Pharmacol. Res. 2012, 66, 260–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, L.; Guo, S.; Zou, Z. Resveratrol ameliorates metabolic disorders and insulin resistance in high-fat diet-fed mice. Life Sci. 2019, 242, 117212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.J.; Zhao, H.; Dong, L.; Zhen, Y.F.; Xing, H.Y.; Ma, H.J.; Song, G.Y. Resveratrol ameliorates high-fat diet-induced insulin resistance and fatty acid oxidation via ATM-AMPK axis in skeletal muscle. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2019, 23, 9117–9125. [Google Scholar]
- D’avila, L.S.P.; de Oliveira, K.A.; de Abreu, E.S.; Vasconcelos, R.P.; Nascimento, J.F.; Bezerra Pontes, E.O.; Rickli, S.; Coelho de Souza, A.N.; Leal Cardoso, J.H.; Silveira, L.; et al. Hypoglycaemic effect of resveratrol in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats is impaired when supplemented in association with leucine. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 6, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szkudelska, K.; Deniziak, M.; Hertig, I.; Wojciechowicz, T.; Tyczewska, M.; Jaroszewska, M.; Szkudelski, T. Effects of resveratrol in Goto-Kakizaki rat, a model of type 2 diabetes. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Qu, X.; Chen, X.; Shi, Q.; Wang, X.; Wang, D.; Yang, L. Resveratrol alleviates ischemia/reperfusion injury of diabetic myocardium via inducing autophagy. Exp. Ther. Med. 2019, 18, 2719–2725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhou, X.; Ren, F.; Wei, H.; Liu, L.; Shen, T.; Xu, S.; Wei, J.; Ren, J.; Ni, H. Combination of berberine and evodiamine inhibits intestinal cholesterol absorption in high fat diet induced hyperlipidemic rats. Lipids Health Dis. 2017, 16, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shi, R.; Xu, Z.; Xu, X.; Jin, J.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, T.; Li, Y.; Ma, Y. Organic cation transporter and multidrug and toxin extrusion 1 co-mediated interaction between metformin and berberine. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 127, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.H.; Yu, R.Y.; Liu, Y.H.; Tu, X.Y.; Tu, J.; Wang, Y.S.; Xu, G.L. Interaction of baicalin with berberine for glucose uptake in 3T3-L1 adipocytes and HepG2 hepatocytes. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2014, 151, 864–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, C.; Jiang, S.; Chu, C.; Xin, M.; Song, X.; Zhao, B. Baicalin protects human retinal pigment epithelial cell lines against high glucose-induced cell injury by up-regulation of microRNA-145. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2019, 106, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Chen, X.; Niu, C.; Huang, X.; An, N.; Sun, J.; Huang, S.; Ye, W.; Li, S.; Shen, Y.; et al. Baicalin alleviates hyperglycemia-induced endothelial impairment 1 via Nrf2. J. Endocrinol. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, X.; Wang, J.; Guo, J.; Xu, Y.; Jiang, H.; Zheng, C.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Che, H.; Liang, S.; et al. Effects of baicalin on diabetic cardiac autonomic neuropathy mediated by the P2Y12 receptor in rat stellate ganglia. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 46, 986–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, P.; Yu, M.; Min, W.; Han, S.; Shi, M.; Zhang, Z.; Bo, P. Beneficial effect of baicalin on insulin sensitivity in adipocytes of diet-induced obese mice. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2018, 139, 262–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Liang, J.; Gao, L.R.; Si, Z.P.; Zhang, X.T.; Liang, G.; Yan, Y.; Li, K.; Cheng, X.; Bao, Y.; et al. Baicalin administration attenuates hyperglycemia-induced malformation of cardiovascular system. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, T.; Jiang, H.; Cao, S.; Chen, Q.; Cui, M.; Wang, Z.; Li, D.; Zhou, J.; Wang, T.; Qiu, F.; et al. Baicalin and its metabolites suppresses gluconeogenesis through activation of AMPK or AKT in insulin resistant HepG-2 cells. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 141, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, H.; Liao, S.; Zhong, W.; Xiao, X.; Zhu, J.; Li, W.; Wu, X.; Feng, Y. Synthesis, characterization, and biological evaluations of 1,3,5-triazine derivatives of metformin cyclization with berberine and magnolol in the presence of sodium methylate. Molecules 2017, 22, 1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, M.; Li, Y.; Liu, L.; Yuan, X.; Gao, Y.; Guan, Z.; Li, W. The design and synthesis of a novel compound of berberine and baicalein that inhibits the efficacy of lipid accumulation in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2017, 25, 5506–5512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Jiang, J.D.; Wu, W.; Kong, W.J. The Compound of Mangiferin-Berberine Salt Has Potent Activities in Modulating Lipid and Glucose Metabolisms in HepG2 Cells. Biomed. Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 8753436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guo, F.; Huang, C.; Liao, X.; Wang, Y.; He, Y.; Feng, R.; Li, Y.; Sun, C. Beneficial effects of mangiferin on hyperlipidemia in high-fat-fed hamsters. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2011, 55, 1809–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Y.; Li, S.; Na, L.; Feng, R.; Liu, L.; Li, Y.; Sun, C. Mangiferin decreases plasma free fatty acids through promoting its catabolism in liver by activation of AMPK. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e30782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lim, J.; Liu, Z.; Apontes, P.; Feng, D.; Pessin, J.E.; Sauve, A.A.; Angeletti, R.H.; Chi, Y. Dual mode action of mangiferin in mouse liver under high fat diet. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e90137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Na, L.; Zhang, Q.; Jiang, S.; Du, S.; Zheng, W.; Li, Y.; Sun, C.; Niu, Y. Mangiferin supplementation improves serum lipid profiles in overweight patients with hyperlipidemia: A double-blind randomized controlled trial. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 10344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Han, J.; Yi, J.; Liang, F.; Xiao, Y.; Gao, S.; Yang, N.; Hu, H.; Xie, W.F.; Chen, W. X-3, a mangiferin derivative, stimulates AMP-activated protein kinase and reduces hyperglycemia and obesity in db/db mice. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2015, 405, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apontes, P.; Liu, Z.; Su, K.; Benard, O.; Youn, D.Y.; Li, X.; Mirza, R.H.; Bastie, C.C.; Jelicks, L.A.; Pessin, J.E.; et al. Mangiferin stimulates carbohydrate oxidation and protects against metabolic disorders induced by high-fat diets. Diabetes 2014, 63, 3626–3636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sellamuthu, P.S.; Arulselvan, P.; Fakurazi, S.; Kandasamy, M. Beneficial effects of mangiferin isolated from Salacia chinensis on biochemical and hematological parameters in rats with streptozotocininduced diabetes. Pak. J. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 27, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Cui, X.; Sun, X.; Li, X.; Zhu, Q.; Li, W. Mangiferin prevents diabetic nephropathy progression in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Phytother. Res. 2010, 24, 893–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miura, T.; Ichiki, H.; Hashimoto, I.; Iwamoto, N.; Kato, M.; Kubo, M.; Ishihara, E.; Komatsu, Y.; Okada, M.; Ishida, T.; et al. Antidiabetic activity of a xanthone compound, mangiferin. Phytomedicine 2001, 8, 85–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Pan, Y.; Chonan, R.; Batey, R.; Rong, X.; Yamahara, J.; Wang, J.; Li, Y. Mitigation of insulin resistance by mangiferin in a rat model of fructose-induced metabolic syndrome is associated with modulation of CD36 redistribution in the skeletal muscle. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2016, 356, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pal, P.B.; Sinha, K.; Sil, P.C. Mangiferin attenuates diabetic nephropathy by inhibiting oxidative stress mediated signaling cascade, TNFα related and mitochondrial dependent apoptotic pathways in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e107220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sellamuthu, P.S.; Arulselvan, P.; Kamalraj, S.; Fakurazi, S.; Kandasamy, M. Protective nature of mangiferin on oxidative stress and antioxidant status in tissues of streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. ISRN Pharmacol. 2013, 2013, 750109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sellamuthu, P.S.; Arulselvan, P.; Muniappan, B.P.; Fakurazi, S.; Kandasamy, M. Mangiferin from salacia chinensis prevents oxidative stress and protects pancreatic β-cells in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. J. Med. Food 2013, 16, 719–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, J.; Li, J.; Hou, F.; Wang, X.; Liu, B. Mangiferin inhibits endoplasmic reticulum stress-associated thioredoxin-interacting protein/NLRP3 inflammasome activation with regulation of AMPK in endothelial cells. Metabolism 2015, 64, 428–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, D.; Li, Z.W.; Zhou, X.; Gao, Y.; Feng, Y.; Ma, M.; Wu, Z.; Li, W. A novel berberine-metformin hybrid compound exerts therapeutic effects on obese type 2 diabetic rats. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2019, 46, 533–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fogacci, F.; Grassi, D.; Rizzo, M.; Cicero, A.F.G. Metabolic effect of berberine-silymarin association: A meta-analysis of randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trials. Phytother. Res. 2019, 33, 862–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.T.; Peng, J.G.; Zhang, J.Q.; Wang, Z.X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, X.R.; Miao, J.; Tang, L. Novel berberine-based derivatives with potent hypoglycemic activity. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2019, 29, 126709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, L.; Sheng, W.; Li, X.; Sik, A.; Lin, H.; Liu, K.; Wang, L. Novel carbohydrate modified berberine derivatives: Synthesis and in vitro anti-diabetic investigation. MedChemComm 2019, 10, 598–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Chen, M.; Zheng, Z.; Zhu, G.-Y.; Jiang, Z.-H.; Bai, L.-P. Synthesis and evaluation of novel 12-aryl berberine analogues with hypoxia-inducible factor-1 inhibitory activity. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 26921–26929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Gong, W.; Lv, S.; Qu, H.; He, Y. Berberine improves insulin resistance in adipocyte models by regulating the methylation of hypoxia-inducible factor-3α. Biosci. Rep. 2019, 39, 20192059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Ren, X.; Ma, C. Effect of Berberine on ahemia—Reperfusion injury. J. Coll. Physicians Surg. Pak. 2018, 28, 753–757. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Qian, Z.; Pan, L.; Li, H.; Zhu, H. Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 mediates the anti-apoptosis of berberine in neurons during hypoxia/ischemia. Acta Physiol. Hung. 2012, 99, 311–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Bian, H.; Guo, L.; Zhu, H. Berberine Preconditioning protects neurons against ischemia via Ssphingosine-1-phosphate and hypoxia-inducible factor-1. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2016, 44, 927–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhang, C.; Yang, X.; Yang, B.; Wang, J.; Kang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Li, D.; Huang, G.; Ma, Z.; et al. Berberine inhibits the expression of hypoxia induction factor-1alpha and increases the radiosensitivity of prostate cancer. Diagn. Pathol. 2014, 9, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, C.; Yang, X.; Zhang, Q.; Yang, B.; Xu, L.; Qin, Q.; Zhu, H.; Liu, J.; Cai, J.; Tao, G.; et al. Berberine radiosensitizes human nasopharyngeal carcinoma by suppressing hypoxia-inducible factor-1α expression. Acta Otolaryngol. 2014, 134, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, L.; Chen, Q.; Gong, K.; Xu, X.; Xie, Y.; Zhang, W.; Cao, H.; Hu, T.; Hong, X.; Zhan, Y.Y. Berberine decelerates glucose metabolism via suppression of mTOR-dependent HIF-1α protein synthesis in colon cancer cells. Oncol. Rep. 2018, 39, 2436–2442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, S.; Wang, X.; Yin, W.; Liu, Z.; Zhou, M.; Xiao, D.; Liu, Y.; Peng, D. Synthesis and hypoglycemic activity of 9-O-(lipophilic group substituted) berberine derivatives. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2016, 26, 4799–4803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.; Chen, A.F.; Wu, F.; Sheng, L.; Zhang, H.K.; Gu, M.; Li, Y.Y.; Zhang, L.N.; Hu, L.H.; Li, J.Y.; et al. 8,8-Dimethyldihydroberberine with improved bioavailability and oral efficacy on obese and diabetic mouse models. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2010, 18, 5915–5924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Ge, H.; Liu, K.; Chen, X.; Zhang, J.; Liu, B. Nandinine, a derivative of berberine, inhibits inflammation and reduces insulin resistance in adipocytes via regulation of AMP-kinase activity. Planta Med. 2017, 83, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, R.; Wu, J.; He, Y.; Hai, L.; Wu, Y. Synthesis and in vitro evaluation of 12-(substituted aminomethyl) berberrubine derivatives as anti-diabetics. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2014, 24, 1762–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.X.; Kong, W.J.; Li, Y.H.; Tang, S.; Li, Z.; Li, Y.B.; Shan, Y.Q.; Bi, C.W.; Jiang, J.D.; Song, D.Q. Synthesis and structure-activity relationship of berberine analogues in LDLR up-regulation and AMPK activation. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2012, 20, 6552–6558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.H.; Li, Y.; Yang, P.; Kong, W.J.; You, X.F.; Ren, G.; Deng, H.B.; Wang, Y.M.; Wang, Y.X.; Jiang, J.D.; et al. Design, synthesis, and cholesterol-lowering efficacy for prodrugs of berberrubine. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2010, 18, 6422–6428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirhadi, E.; Rezaee, M.; Malaekeh-Nikouei, B. Nano strategies for berberine delivery, a natural alkaloid of Berberis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 104, 465–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


© 2020 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Habtemariam, S. The Quest to Enhance the Efficacy of Berberine for Type-2 Diabetes and Associated Diseases: Physicochemical Modification Approaches. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 90. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines8040090
Habtemariam S. The Quest to Enhance the Efficacy of Berberine for Type-2 Diabetes and Associated Diseases: Physicochemical Modification Approaches. Biomedicines. 2020; 8(4):90. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines8040090
Chicago/Turabian StyleHabtemariam, Solomon. 2020. "The Quest to Enhance the Efficacy of Berberine for Type-2 Diabetes and Associated Diseases: Physicochemical Modification Approaches" Biomedicines 8, no. 4: 90. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines8040090
APA StyleHabtemariam, S. (2020). The Quest to Enhance the Efficacy of Berberine for Type-2 Diabetes and Associated Diseases: Physicochemical Modification Approaches. Biomedicines, 8(4), 90. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines8040090