Studying the Pathophysiology of Parkinson’s Disease Using Zebrafish
Abstract
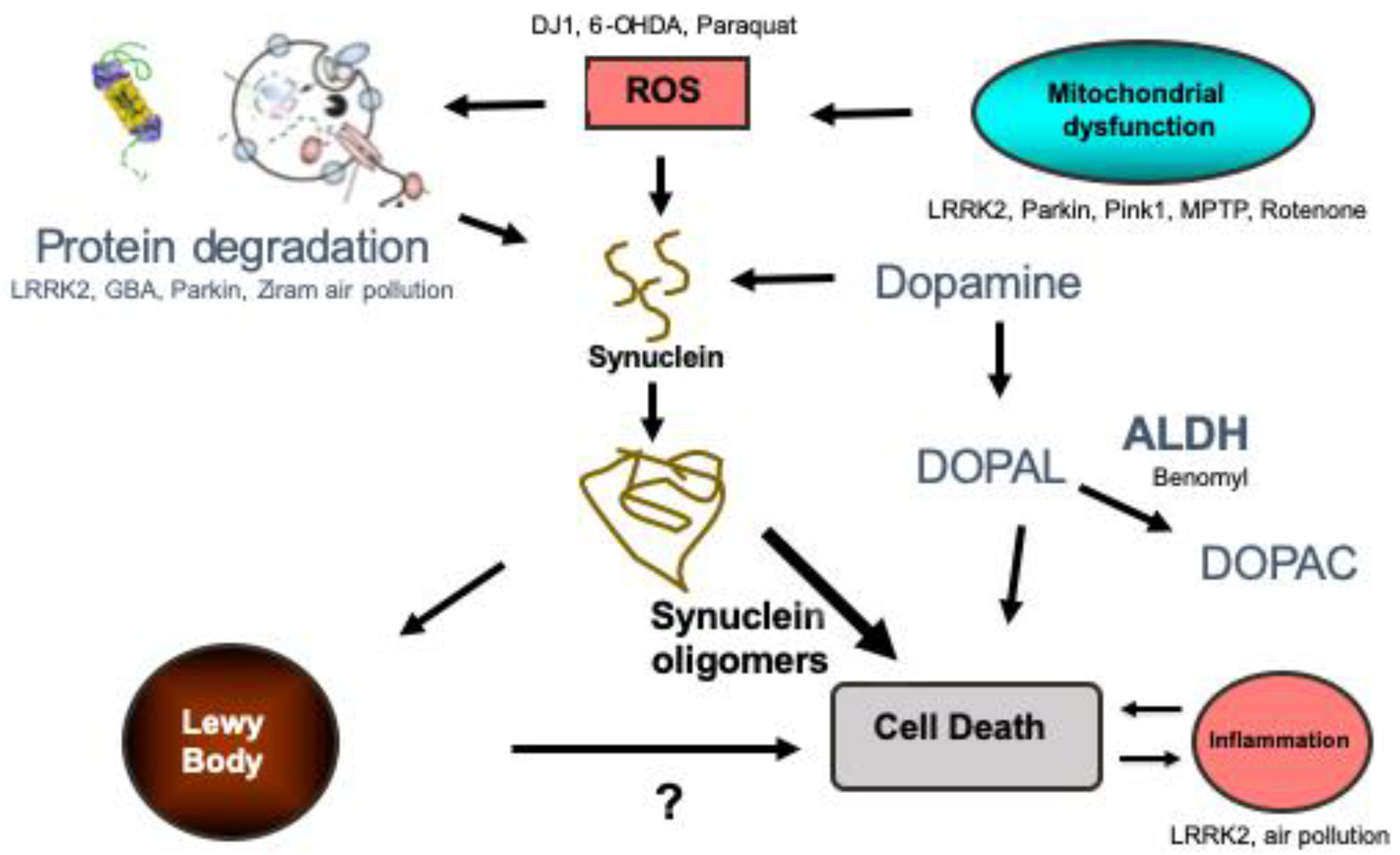
:1. Introduction
2. What Is Known About the Pathophysiology of PD
3. Zebrafish as a Model Organism to Study PD
4. Genetic Models Used to Study PD
4.1. Synuclein
4.2. LRRK2
4.3. GBA
4.4. Parkin
4.5. (PTEN)-Induced Putative Kinase 1 (Pink1)
4.6. DJ1
5. Toxins and the Study of PD
5.1. Toxins That Kill Dopamine Neurons
5.2. Toxins Associated With the Pathogenesis of PD
5.2.1. Rotenone Is a Mitochondrial Complex I Inhibitor and Is Associated With an Increased Risk of PD
5.2.2. Paraquat Is Another Pesticide Associated With an Increased Risk of Developing PD
5.2.3. Ziram Is a Dithiocarbamate Fungicide, and Is an E1 Ligase Inhibitor of the UPS
5.2.4. Benomyl Is Another Fungicide Found to Be Associated With an Increased Risk of Developing PD
5.2.5. Air Pollution Has Recently Been Found to Be Associated With an Increased Risk of PD and Alzheimer’s Disease, Although the Mechanisms Remain Largely Unknown
6. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dorsey, E.R.; Constantinescu, R.; Thompson, J.P.; Biglan, K.M.; Holloway, R.G.; Kieburtz, K.; Marshall, F.J.; Ravina, B.M.; Schifitto, G.; Siderowf, A.; et al. Projected Number of People with Parkinson Disease in the Most Populous Nations, 2005 through 2030. Neurology 2007, 68, 384–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braak, H.; Del Tredici, K. Invited Article: Nervous System Pathology in Sporadic Parkinson Disease. Neurology 2008, 70, 1916–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polymeropoulos, M.H.; Lavedan, C.; Leroy, E.; Ide, S.E.; Dehejia, A.; Dutra, A.; Pike, B.; Root, H.; Rubenstein, J.; Boyer, R.; et al. Mutation in the Alpha-Synuclein Gene Identified in Families with Parkinson’s Disease [See Comments]. Science 1997, 276, 2045–2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Spillantini, M.G.; Schmidt, M.L.; Lee, V.M.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; Jakes, R.; Goedert, M. Alpha-Synuclein in Lewy Bodies. Nature 1997, 388, 839–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jucker, M.; Walker, L.C. Self-Propagation of Pathogenic Protein Aggregates in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Nature 2013, 501, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Q.; Liu, Y.; Sun, M. Autophagy and Alzheimer’s Disease. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2017, 37, 377–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luk, K.C.; Lee, V.M. Modeling Lewy Pathology Propagation in Parkinson’s Disease. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2014, 20, S85–S87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prusiner, S.B.; Scott, M.R.; DeArmond, S.J.; Cohen, F.E. Prion Protein Biology. Cell 1998, 93, 337–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miller, D.W.; Hague, S.M.; Clarimon, J.; Baptista, M.; Gwinn-Hardy, K.; Cookson, M.R.; Singleton, A.B. Alpha-Synuclein in Blood and Brain from Familial Parkinson Disease with Snca Locus Triplication. Neurology 2004, 62, 1835–1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chartier-Harlin, M.C.; Kachergus, J.; Roumier, C.; Mouroux, V.; Douay, X.; Lincoln, S.; Levecque, C.; Larvor, L.; Andrieux, J.; Hulihan, M.; et al. Alpha-Synuclein Locus Duplication as a Cause of Familial Parkinson’s Disease. Lancet 2004, 364, 1167–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sibon, I.; Larrieu, D.; El Hadri, K.; Mercier, N.; Feve, B.; Lacolley, P.; Labat, C.; Daret, D.; Bonnet, J.; Lamaziere, J.M. Semicarbazide-Sensitive Amine Oxidase in Annulo-Aortic Ectasia Disease: Relation to Elastic Lamellae-Associated Proteins. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2004, 52, 1459–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ibanez, P.; Bonnet, A.M.; Debarges, B.; Lohmann, E.; Tison, F.; Pollak, P.; Agid, Y.; Durr, A.; Brice, A. Causal Relation between Alpha-Synuclein Gene Duplication and Familial Parkinson’s Disease. Lancet 2004, 364, 1169–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maraganore, D.M.; de Andrade, M.; Elbaz, A.; Farrer, M.J.; Ioannidis, J.P.; Kruger, R.; Rocca, W.A.; Schneider, N.K.; Lesnick, T.G.; Lincoln, S.J.; et al. Collaborative Analysis of Alpha-Synuclein Gene Promoter Variability and Parkinson Disease. JAMA J. Am. Med Assoc. 2006, 296, 661–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ebrahimi-Fakhari, D.; Cantuti-Castelvetri, I.; Fan, Z.; Rockenstein, E.; Masliah, E.; Hyman, B.T.; McLean, P.J.; Unni, V.K. Distinct Roles in Vivo for the Ubiquitin-Proteasome System and the Autophagy-Lysosomal Pathway in the Degradation of Alpha-Synuclein. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 14508–14520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuervo, A.M.; Stefanis, L.; Fredenburg, R.; Lansbury, P.T.; Sulzer, D. Impaired Degradation of Mutant Alpha-Synuclein by Chaperone-Mediated Autophagy. Science 2004, 305, 1292–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.W.; Giasson, B.I.; Lewis, K.A.; Lee, V.M.; Demartino, G.N.; Thomas, P.J. A Precipitating Role for Truncated Alpha-Synuclein and the Proteasome in Alpha-Synuclein Aggregation: Implications for Pathogenesis of Parkinson Disease. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 22670–22678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mak, S.K.; McCormack, A.L.; Manning-Bog, A.B.; Cuervo, A.M.; Di Monte, D.A. Lysosomal Degradation of -Synuclein in Vivo. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 13621–13629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, N.Y.; Tang, Z.; Liu, C.W. Alpha-Synuclein Protofibrils Inhibit 26 S Proteasome-Mediated Protein Degradation: Understanding the Cytotoxicity of Protein Protofibrils in Neurodegenerative Disease Pathogenesis. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 20288–20298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, H.J.; Khoshaghideh, F.; Patel, S.; Lee, S.J. Clearance of Alpha-Synuclein Oligomeric Intermediates Via the Lysosomal Degradation Pathway. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 2004, 24, 1888–1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitcairn, C.; Wani, W.Y.; Mazzulli, J.R. Dysregulation of the Autophagic-Lysosomal Pathway in Gaucher and Parkinson’s Disease. Neurobiol. Dis. 2019, 122, 72–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berwick, D.C.; Heaton, G.R.; Azeggagh, S.; Harvey, K. Lrrk2 Biology from Structure to Dysfunction: Research Progresses, but the Themes Remain the Same. Mol. Neurodegener. 2019, 14, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dupuis, L. Mitochondrial Quality Control in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Biochimie 2013, 100, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gautier, C.A.; Corti, O.; Brice, A. Mitochondrial Dysfunctions in Parkinson’s Disease. Revue Neurol. 2013, 170, 339–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swerdlow, R.H.; Burns, J.M.; Khan, S.M. The Alzheimer’s Disease Mitochondrial Cascade Hypothesis: Progress and Perspectives. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1842, 1219–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Swomley, A.M.; Forster, S.; Keeney, J.T.; Triplett, J.; Zhang, Z.; Sultana, R.; Butterfield, D.A. Abeta, Oxidative Stress in Alzheimer Disease: Evidence Based on Proteomics Studies. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1842, 1248–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tanner, C.M.; Kamel, F.; Ross, G.W.; Hoppin, J.A.; Goldman, S.M.; Korell, M.; Marras, C.; Bhudhikanok, G.S.; Kasten, M.; Chade, A.R.; et al. Rotenone, Paraquat, and Parkinson’s Disease. Environ. Health Perspect. 2011, 119, 866–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gash, D.M.; Rutland, K.; Hudson, N.L.; Sullivan, P.G.; Bing, G.; Cass, W.A.; Pandya, J.D.; Liu, M.; Choi, D.Y.; Hunter, R.L.; et al. Trichloroethylene: Parkinsonism and Complex 1 Mitochondrial Neurotoxicity. Ann. Neurol. 2008, 63, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Choi, D.Y.; Hunter, R.L.; Pandya, J.D.; Cass, W.A.; Sullivan, P.G.; Kim, H.C.; Gash, D.M.; Bing, G. Trichloroethylene Induces Dopaminergic Neurodegeneration in Fisher 344 Rats. J. Neurochem. 2010, 112, 773–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goldman, S.M.; Quinlan, P.J.; Ross, G.W.; Marras, C.; Meng, C.; Bhudhikanok, G.S.; Comyns, K.; Korell, M.; Chade, A.R.; Kasten, M.; et al. Solvent Exposures and Parkinson Disease Risk in Twins. Ann. Neurol. 2011, 71, 776–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dryanovski, D.I.; Guzman, J.N.; Xie, Z.; Galteri, D.J.; Volpicelli-Daley, L.A.; Lee, V.M.; Miller, R.J.; Schumacker, P.T.; Surmeier, D.J. Calcium Entry and Alpha-Synuclein Inclusions Elevate Dendritic Mitochondrial Oxidant Stress in Dopaminergic Neurons. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 2013, 33, 10154–10164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Subramaniam, S.R.; Vergnes, L.; Franich, N.R.; Reue, K.; Chesselet, M.F. Region Specific Mitochondrial Impairment in Mice with Widespread Overexpression of Alpha-Synuclein. Neurobiol. Dis. 2014, 70, 204–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guardia-Laguarta, C.; Area-Gomez, E.; Rub, C.; Liu, Y.; Magrane, J.; Becker, D.; Voos, W.; Schon, E.A.; Przedborski, S. Alpha-Synuclein Is Localized to Mitochondria-Associated Er Membranes. J. Neurosci. 2014, 34, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenamyre, J.T.; Betarbet, R.; Sherer, T.B. The Rotenone Model of Parkinson’s Disease: Genes, Environment and Mitochondria. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2003, 9, S59–S64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Maio, R.; Barrett, P.J.; Hoffman, E.K.; Barrett, C.W.; Zharikov, A.; Borah, A.; Hu, X.; McCoy, J.; Chu, C.T.; Burton, E.A.; et al. Alpha-Synuclein Binds to Tom20 and Inhibits Mitochondrial Protein Import in Parkinson’s Disease. Sci. Transl. Med. 2016, 8, 342ra78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lull, M.E.; Block, M.L. Microglial Activation and Chronic Neurodegeneration. Neurotherapeutics 2010, 7, 354–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kannarkat, G.T.; Boss, J.M.; Tansey, M.G. The Role of Innate and Adaptive Immunity in Parkinson’s Disease. J. Parkinsons Dis. 2013, 3, 493–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Booth, H.D.E.; Hirst, W.D.; Wade-Martins, R. The Role of Astrocyte Dysfunction in Parkinson’s Disease Pathogenesis. Trends Neurosci. 2017, 40, 358–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aguzzi, A.; Barres, B.A.; Bennett, M.L. Microglia: Scapegoat, Saboteur, or Something Else? Science 2013, 339, 156–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Butchart, J.; Holmes, C. Systemic and Central Immunity in Alzheimer’s Disease: Therapeutic Implications. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2012, 18, 64–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deleidi, M.; Gasser, T. The Role of Inflammation in Sporadic and Familial Parkinson’s Disease. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. CMLS 2013, 70, 4259–4273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, N.; Singh, S. Updates on Immunity and Inflammation in Parkinson Disease Pathology. J. Neurosci. Res. 2018, 96, 379–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullett, S.J.; Di Maio, R.; Greenamyre, J.T.; Hinkle, D.A. Dj-1 Expression Modulates Astrocyte-Mediated Protection against Neuronal Oxidative Stress. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2013, 49, 507–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tan, Y.M.; Leonard, J.A.; Edwards, S.; Teeguarden, J.; Paini, A.; Egeghy, P. Aggregate Exposure Pathways in Support of Risk Assessment. Curr. Opin. Toxicol. 2018, 9, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, S. Linking Genes to Brain, Behavior and Neurological Diseases: What Can We Learn from Zebrafish? Genes Brain Behav. 2004, 3, 63–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, A. Phylogenetic Relationships and Evolutionary Processes in East African Cichlid Fishes. Trends Ecol. Evol. 1993, 8, 279–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Westerfield, M. The Zebrafish Book: A Guide for the Laboratory Use of Zebrafish (Danio Rerio), 4th ed.; University of Oregon Press: Eugene, Oregon, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.L.J.; Horsfield, J.A.; Black, M.A.; Rutherford, K.; Gemmell, N.J. Identification of Sex Differences in Zebrafish (Danio Rerio) Brains During Early Sexual Differentiation and Masculinization Using 17alpha-Methyltestoterone. Biol. Reprod. 2018, 99, 446–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiba-Falek, O.; Nussbaum, R.L. Effect of Allelic Variation at the Nacp-Rep1 Repeat Upstream of the Alpha-Synuclein Gene (Snca) on Transcription in a Cell Culture Luciferase Reporter System. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2001, 10, 3101–3109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ritz, B.; Rhodes, S.L.; Bordelon, Y.; Bronstein, J. A-Synuclein Genetic Variants Predict Faster Motor Symptom Progression in Idiopathic Parkinson Disease. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e36199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, Z.; Gitler, A.D. Discovery and Characterization of Three Novel Synuclein Genes in Zebrafish. Dev. Dyn. Off. Publ. Am. Assoc. Anat. 2008, 237, 2490–2495. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.C.; Cheng, C.H.; Chen, G.D.; Hung, C.C.; Yang, C.H.; Hwang, S.P.; Kawakami, K.; Wu, B.K.; Huang, C.J. Recapitulation of Zebrafish Sncga Expression Pattern and Labeling the Habenular Complex in Transgenic Zebrafish Using Green Fluorescent Protein Reporter Gene. Dev. Dyn. Off. Publ. Am. Assoc. Anat. 2009, 238, 746–754. [Google Scholar]
- Milanese, C.; Sager, J.J.; Bai, Q.; Farrell, T.C.; Cannon, J.R.; Greenamyre, J.T.; Burton, E.A. Hypokinesia and Reduced Dopamine Levels in Zebrafish Lacking Beta- and Gamma1-Synucleins. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 2971–2983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lulla, A.; Barnhill, L.; Bitan, G.; Ivanova, M.I.; Nguyen, B.; O’Donnell, K.C.; Stahl, M.; Yamaashiro, C.; Klärner, F.G.; Schrader, T.; et al. Neurotoxicity of the Parkinson’s Disease-Associated Pesticide Ziram Is Synuclein- Dependent in Zebrafish Embryos. Environ. Health Perspect. 2016, 124, 1766–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prabhudesai, S.; Sinha, S.; Attar, A.; Kotagiri, A.; Fitzmaurice, A.G.; Lakshmanan, R.; Ivanova, M.I.; Loo, J.A.; Klarner, F.G.; Schrader, T.; et al. A Novel “Molecular Tweezer” Inhibitor of Alpha-Synuclein Neurotoxicity in Vitro and in Vivo. Neurother. J. Am. Soc. Exp. Neurother. 2012, 9, 464–476. [Google Scholar]
- Trinh, J.; Farrer, M. Advances in the Genetics of Parkinson Disease. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2013, 9, 445–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tolosa, E.; Vila, M.; Klein, C.; Rascol, O. Lrrk2 in Parkinson Disease: Challenges of Clinical Trials. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2020, 16, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheng, D.; Qu, D.; Kwok, K.H.; Ng, S.S.; Lim, A.Y.; Aw, S.S.; Lee, C.W.; Sung, W.K.; Tan, E.K.; Lufkin, T.; et al. Deletion of the Wd40 Domain of Lrrk2 in Zebrafish Causes Parkinsonism-Like Loss of Neurons and Locomotive Defect. PLoS Genet. 2010, 6, e1000914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ren, G.; Xin, S.; Li, S.; Zhong, H.; Lin, S. Disruption of Lrrk2 Does Not Cause Specific Loss of Dopaminergic Neurons in Zebrafish. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e20630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhudesai, S.; Bensabeur, F.Z.; Abdullah, R.; Basak, I.; Baez, S.; Alves, G.; Holtzman, N.G.; Larsen, J.P.; Moller, S.G. Lrrk2 Knockdown in Zebrafish Causes Developmental Defects, Neuronal Loss, and Synuclein Aggregation. J. Neurosci. Res. 2016, 94, 717–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, D.; See, K.; Hu, X.; Yu, D.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Li, F.; Lu, M.; Zhao, J.; Liu, J. Disruption of Lrrk2 in Zebrafish Leads to Hyperactivity and Weakened Antibacterial Response. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 497, 1104–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidransky, E.; Lopez, G. The Link between the Gba Gene and Parkinsonism. Lancet Neurol. 2012, 11, 986–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Keatinge, M.; Bui, H.; Menke, A.; Chen, Y.C.; Sokol, A.M.; Bai, Q.; Ellett, F.; Da Costa, M.; Burke, D.; Gegg, M.; et al. Glucocerebrosidase 1 Deficient Danio Rerio Mirror Key Pathological Aspects of Human Gaucher Disease and Provide Evidence of Early Microglial Activation Preceding Alpha-Synuclein-Independent Neuronal Cell Death. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2015, 24, 6640–6652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Watson, L.; Keatinge, M.; Gegg, M.; Bai, Q.; Sandulescu, M.C.; Vardi, A.; Futerman, A.H.; Schapira, A.H.V.; Burton, E.A.; Bandmann, O. Ablation of the Pro-Inflammatory Master Regulator Mir-155 Does Not Mitigate Neuroinflammation or Neurodegeneration in a Vertebrate Model of Gaucher’s Disease. Neurobiol. Dis. 2019, 127, 563–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Uemura, N.; Koike, M.; Ansai, S.; Kinoshita, M.; Ishikawa-Fujiwara, T.; Matsui, H.; Naruse, K.; Sakamoto, N.; Uchiyama, Y.; Todo, T.; et al. Viable Neuronopathic Gaucher Disease Model in Medaka (Oryzias Latipes) Displays Axonal Accumulation of Alpha-Synuclein. PLoS Genet. 2015, 11, e1005065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernandez, D.G.; Reed, X.; Singleton, A.B. Genetics in Parkinson Disease: Mendelian Versus Non-Mendelian Inheritance. J. Neurochem. 2016, 139, 59–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flinn, L.; Mortiboys, H.; Volkmann, K.; Koster, R.W.; Ingham, P.W.; Bandmann, O. Complex I Deficiency and Dopaminergic Neuronal Cell Loss in Parkin-Deficient Zebrafish (Danio Rerio). Brain 2009, 132, 1613–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fett, M.E.; Pilsl, A.; Paquet, D.; van Bebber, F.; Haass, C.; Tatzelt, J.; Schmid, B.; Winklhofer, K.F. Parkin Is Protective against Proteotoxic Stress in a Transgenic Zebrafish Model. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e11783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samaranch, L.; Lorenzo-Betancor, O.; Arbelo, J.M.; Ferrer, I.; Lorenzo, E.; Irigoyen, J.; Pastor, M.A.; Marrero, C.; Isla, C.; Herrera-Henriquez, J.; et al. Pink1-Linked Parkinsonism Is Associated with Lewy Body Pathology. Brain 2010, 133, 1128–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Corti, O.; Brice, A. Mitochondrial Quality Control Turns out to Be the Principal Suspect in Parkin and Pink1-Related Autosomal Recessive Parkinson’s Disease. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2013, 23, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anichtchik, O.; Diekmann, H.; Fleming, A.; Roach, A.; Goldsmith, P.; Rubinsztein, D.C. Loss of Pink1 Function Affects Development and Results in Neurodegeneration in Zebrafish. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 8199–8207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xi, Y.; Ryan, J.; Noble, S.; Yu, M.; Yilbas, A.E.; Ekker, M. Impaired Dopaminergic Neuron Development and Locomotor Function in Zebrafish with Loss of Pink1 Function. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2010, 31, 623–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sallinen, V.; Kolehmainen, J.; Priyadarshini, M.; Toleikyte, G.; Chen, Y.C.; Panula, P. Dopaminergic Cell Damage and Vulnerability to Mptp in Pink1 Knockdown Zebrafish. Neurobiol. Dis. 2010, 40, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flinn, L.J.; Keatinge, M.; Bretaud, S.; Mortiboys, H.; Matsui, H.; De Felice, E.; Woodroof, H.I.; Brown, L.; McTighe, A.; Soellner, R.; et al. Tigarb Causes Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Neuronal Loss in Pink1 Deficiency. Ann. Neurol. 2013, 74, 837–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bai, Q.; Mullett, S.J.; Garver, J.A.; Hinkle, D.A.; Burton, E.A. Zebrafish Dj-1 Is Evolutionarily Conserved and Expressed in Dopaminergic Neurons. Brain Res. 2006, 1113, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bretaud, S.; Allen, C.; Ingham, P.W.; Bandmann, O. P53-Dependent Neuronal Cell Death in a Dj-1-Deficient Zebrafish Model of Parkinson’s Disease. J. Neurochem. 2007, 100, 1626–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Froyset, A.K.; Edson, A.J.; Gharbi, N.; Khan, E.A.; Dondorp, D.; Bai, Q.; Tiraboschi, E.; Suster, M.L.; Connolly, J.B.; Burton, E.A.; et al. Astroglial Dj-1 over-Expression up-Regulates Proteins Involved in Redox Regulation and Is Neuroprotective in Vivo. Redox Biol. 2018, 16, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, Y.; Yu, M.; Godoy, R.; Hatch, G.; Poitras, L.; Ekker, M. Transgenic Zebrafish Expressing Green Fluorescent Protein in Dopaminergic Neurons of the Ventral Diencephalon. Dev. Dyn. 2011, 240, 2539–2547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, L.; Wei, W.; Wenchao, G.; Peng, H.; Xi, R.; Zheng, Z.; Zuoyan, Z.; Shuo, L.; Bo, Z. Visualization of Monoaminergic Neurons and Neurotoxicity of Mptp in Live Transgenic Zebrafish. Dev. Biol. 2008, 314, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Langston, J.W. The Etiology of Parkinson’s Disease with Emphasis on the Mptp Story. Neurology 1996, 47, S153–S160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langston, J.W.; Ballard, P.; Tetrud, J.W.; Irwin, I. Chronic Parkinsonism in Humans Due to a Product of Meperidine-Analog Synthesis. Science 1983, 219, 979–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anichtchik, O.V.; Kaslin, J.; Peitsaro, N.; Scheinin, M.; Panula, P. Neurochemical and Behavioural Changes in Zebrafish Danio Rerio after Systemic Administration of 6-Hydroxydopamine and 1-Methyl-4-Phenyl-1,2,3,6-Tetrahydropyridine. J. Neurochem. 2004, 88, 443–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bretaud, S.; Lee, S.; Guo, S. Sensitivity of Zebrafish to Environmental Toxins Implicated in Parkinson’s Disease. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2004, 26, 857–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, C.S.; Korzh, V.; Strahle, U. Zebrafish Embryos Are Susceptible to the Dopaminergic Neurotoxin Mptp. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2005, 21, 1758–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKinley, E.T.; Baranowski, T.C.; Blavo, D.O.; Cato, C.; Doan, T.N.; Rubinstein, A.L. Neuroprotection of Mptp-Induced Toxicity in Zebrafish Dopaminergic Neurons. Brain Res. Mol. Brain Res. 2005, 141, 128–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalyn, M.; Hua, K.; Mohd Noor, S.; Wong, C.E.D.; Ekker, M. Comprehensive Analysis of Neurotoxin-Induced Ablation of Dopaminergic Neurons in Zebrafish Larvae. Biomedicines 2019, 8, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, W.; Yang, J.; Wang, F.; Sima, Y.; Zhong, Z.M.; Wang, H.; Hu, L.F.; Liu, C.F. Parkinson’s Disease-Like Motor and Non-Motor Symptoms in Rotenone-Treated Zebrafish. NeuroToxicology 2017, 58, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unal, I.; Caliskan-Ak, E.; Ustundag, U.V.; Ates, P.S.; Alturfan, A.A.; Altinoz, M.A.; Elmaci, I.; Emekli-Alturfan, E. Neuroprotective Effects of Mitoquinone and Oleandrin on Parkinson’s Disease Model in Zebrafish. Int. J. Neurosci. 2019, 130, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Bus, J.S.; Gibson, J.E. Paraquat: Model for Oxidant-Initiated Toxicity. Environ. Health Perspect. 1984, 55, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manning-Bog, A.B.; McCormack, A.L.; Li, J.; Uversky, V.N.; Fink, A.L.; Di Monte, D.A. The Herbicide Paraquat Causes up-Regulation and Aggregation of Alpha-Synuclein in Mice: Paraquat and Alpha-Synuclein. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 1641–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thiruchelvam, M.; Richfield, E.K.; Baggs, R.B.; Tank, A.W.; Cory-Slechta, D.A. The Nigrostriatal Dopaminergic System as a Preferential Target of Repeated Exposures to Combined Paraquat and Maneb: Implications for Parkinson’s Disease. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 2000, 20, 9207–9214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Costello, S.; Cockburn, M.; Zhang, X.; Bronstein, J.; Ritz, B. Parkinson’s Disease Risk from Ambient Exposure to Pesticides. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2011, 26, 547–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nellore, J.; Nandita, P. Paraquat Exposure Induces Behavioral Deficits in Larval Zebrafish During the Window of Dopamine Neurogenesis. Toxicol. Rep. 2015, 2, 950–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bortolotto, J.W.; Cognato, G.P.; Christoff, R.R.; Roesler, L.N.; Leite, C.E.; Kist, L.W.; Bogo, M.R.; Vianna, M.R.; Bonan, C.D. Long-Term Exposure to Paraquat Alters Behavioral Parameters and Dopamine Levels in Adult Zebrafish (Danio Rerio). Zebrafish 2014, 11, 142–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, A.P.; Maidment, N.; Klintenberg, R.; Casida, J.E.; Li, S.; Fitzmaurice, A.G.; Fernagut, P.O.; Mortazavi, F.; Chesselet, M.F.; Bronstein, J.M. Ziram Causes Dopaminergic Cell Damage by Inhibiting E1 Ligase of the Proteasome. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 34696–34703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fitzmaurice, A.G.; Rhodes, S.L.; Cockburn, M.; Ritz, B.; Bronstein, J.M. Aldehyde Dehydrogenase Variation Enhances Effect of Pesticides Associated with Parkinson Disease. Neurology 2014, 82, 419–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fitzmaurice, A.G.; Rhodes, S.L.; Lulla, A.; Murphy, N.; Lam, H.A.; O’Donnell, K.C.; Barnhill, L.; Casida, J.E.; Cockburn, M.; Sagasti, A.; et al. Aldehyde Dehydrogenase as a Potential Target for Toxicant-Induced Parkinson’s Disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 636–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ritz, B.; P-Lee, C.; Hansen, J.; Lassen, C.F.; Ketzel, M.; Sorensen, M.; Raaschou-Nielsen, O. Traffic-Related Air Pollution Is a Risk Factor for Parkinson’s Disease in Denmark. Environ. Health Perspect. 2016, 124, 351–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Barnhill, L.M.; Khuansuwan, S.; Juarez, D.; Murata, H.; Araujo, J.A.; Bronstein, J.M. Diesel Exhaust Extract Exposure Induces Neuronal Toxicity by Disrupting Autophagy. Toxicol. Sci. Off. J. Soc. Toxicol. (in press). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khuansuwan, S.; Barnhill, L.M.; Cheng, S.; Bronstein, J.M. A Novel Transgenic Zebrafish Line Allows for in Vivo Quantification of Autophagic Activity in Neurons. Autophagy 2019, 15, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Barnhill, L.M.; Murata, H.; Bronstein, J.M. Studying the Pathophysiology of Parkinson’s Disease Using Zebrafish. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 197. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines8070197
Barnhill LM, Murata H, Bronstein JM. Studying the Pathophysiology of Parkinson’s Disease Using Zebrafish. Biomedicines. 2020; 8(7):197. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines8070197
Chicago/Turabian StyleBarnhill, Lisa M., Hiromi Murata, and Jeff M. Bronstein. 2020. "Studying the Pathophysiology of Parkinson’s Disease Using Zebrafish" Biomedicines 8, no. 7: 197. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines8070197
APA StyleBarnhill, L. M., Murata, H., & Bronstein, J. M. (2020). Studying the Pathophysiology of Parkinson’s Disease Using Zebrafish. Biomedicines, 8(7), 197. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines8070197



