Oxidized LDL Increase the Proinflammatory Profile of Human Visceral Adipocytes Produced by Hypoxia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects
2.2. Laboratory Measurements
2.3. Mature Adipocyte Isolation
2.4. In Vitro-Differentiated Visceral Adipocyte Culture
2.5. RNA Extraction and Real-Time Quantitative PCR
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
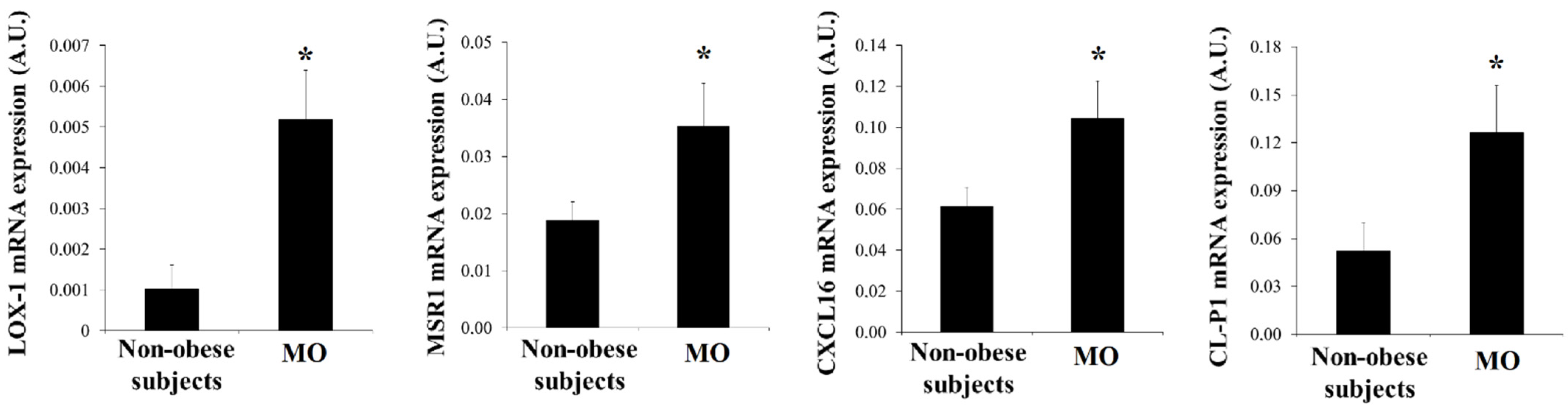
3.1. HIF-1α and Inflammation Markers Are Increased in Visceral Adipocytes from MO
3.2. SRs Levels Are Increased in Visceral Adipocytes from MO
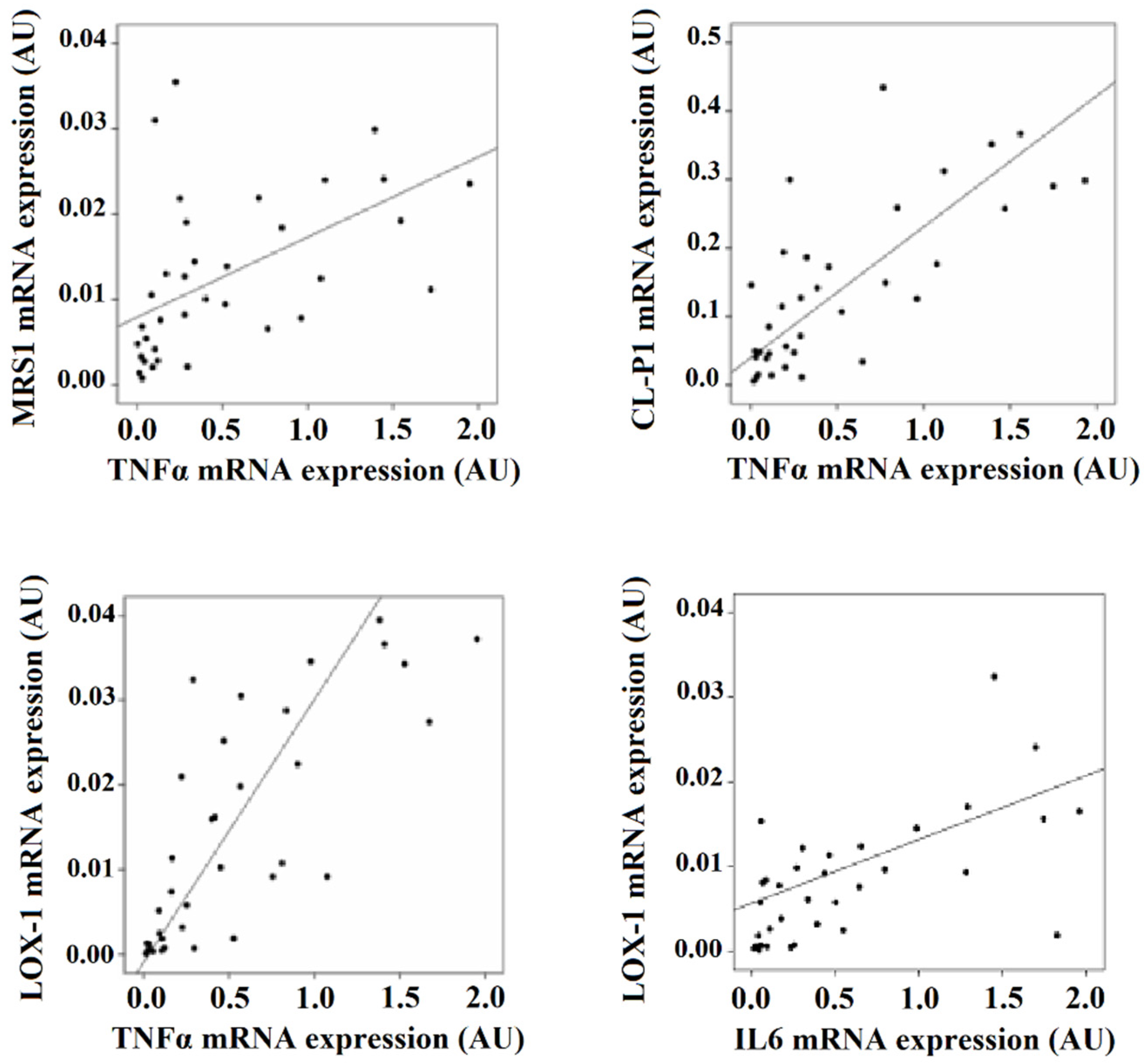
3.3. SRs Levels Are Associated with Inflammation Markers
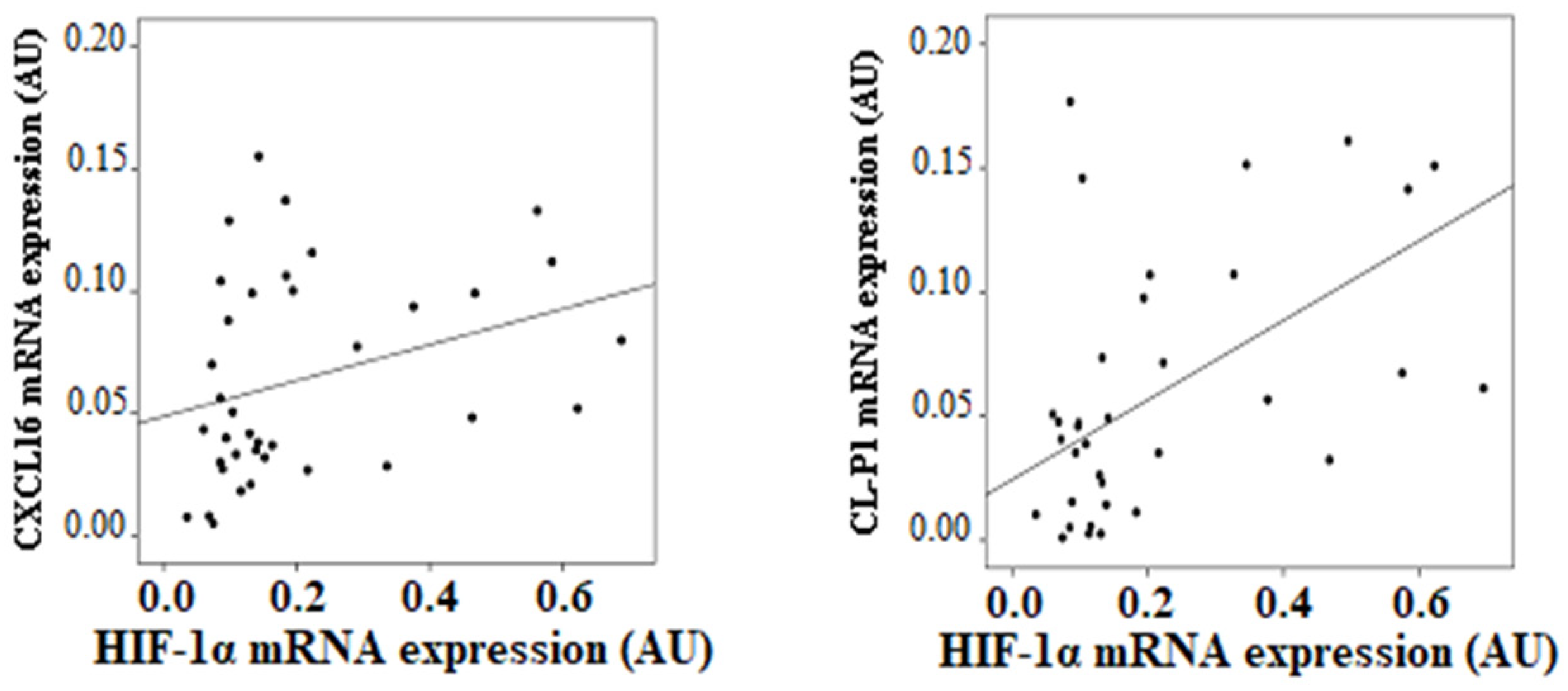
3.4. SRs Levels Are Associated with HIF-1α
3.5. Hypoxia Modifies SRs Expression of In Vitro-Differentiated Visceral Adipocytes
3.6. Silencing HIF-1α Counteracts the Effects of Hypoxia on SRs Expression Levels
3.7. Combined Effects of Hypoxia and Ox-LDL on Inflammation Marker Levels of In Vitro-Differentiated Visceral Adipocytes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- García-Fuentes, E.; Santiago-Fernández, C.; Gutiérrez-Repiso, C.; Mayas, M.D.; Oliva-Olivera, W.; Coín-Aragüez, L.; Alcaide, J.; Ocaña-Wilhelmi, L.; Vendrell, J.; Tinahones, F.J.; et al. Hypoxia is associated with a lower expression of genes involved in lipogenesis in visceral adipose tissue. J. Transl. Med. 2015, 13, 373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Sánchez, A.; Madrigal-Santillán, E.; Bautista, M.; Esquivel-Soto, J.; Morales-González, A.; Esquivel-Chirino, C.; Durante-Montiel, I.; Sánchez-Rivera, G.; Valadez-Vega, C.; Morales-González, J.A. Inflammation, oxidative stress, and obesity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2011, 12, 3117–3132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, F.; Guo, Z.Z.; Ji, W.J.; Ma, Y.Q.; Zhang, Z.; Zhou, X.; Li, Y.M. BOLD-MRI evaluation of subcutaneous and visceral adipose tissue oxygenation status: Effect of dietary salt intake. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2015, 7, 598–606. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Trayhurn, P.; Wang, B.; Wood, I.S. Hypoxia in adipose tissue: A basis for the dysregulation of tissue function in obesity? Br. J. Nutr. 2008, 100, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trayhurn, P.; Wang, B.; Wood, I.S. Hypoxia and the endocrine and signalling role of white adipose tissue. Arch. Physiol. Biochem. 2008, 114, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Wood, I.S.; Trayhurn, P. Dysregulation of the expression and secretion of inflammation-related adipokines by hypoxia in human adipocytes. Pflug. Arch. 2007, 455, 479–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Q.; Gao, Z.; Yin, J.; Zhang, J.; Yun, Z.; Ye, J. Regulation of HIF-1 activity in adipose tissue by obesity-associated factors: Adipogenesis, insulin, and hypoxia. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 300, E877–E885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, K.P.; Ganju, L.; Singh, S.B. Hypoxia modulates innate immune factors: A review. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2015, 28, 425–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, C.P.; Dandapat, A.; Liu, Y.; Hermonat, P.L.; Mehta, J.L. Blockade of hypoxia-reoxygenation-mediated collagen type I expression and MMP activity by overexpression of TGF-beta1 delivered by AAV in mouse cardiomyocytes. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2007, 293, H1833–H1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prabhudas, M.; Bowdish, D.; Drickamer, K.; Febbraio, M.; Herz, J.; Kobzik, L.; Krieger, M.; Loike, J.; Means, T.K.; Moestrup, S.K.; et al. Standardizing scavenger receptor nomenclature. J. Immunol. 2014, 192, 1997–2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holvoet, P.; Mertens, A.; Verhamme, P.; Bogaerts, K.; Beyens, G.; Verhaeghe, R.; Collen, D.; Muls, E.; Van de Werf, F. Circulating oxidized LDL is a useful marker for identifying patients with coronary artery disease. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2001, 21, 844–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Fuentes, P.; Civeira, F.; Recalde, D.; García-Otín, A.L.; Jarauta, E.; Marzo, I.; Cenarro, A. Individual variation of scavenger receptor expression in human macrophages with oxidized low-density lipoprotein is associated with a differential inflammatory response. J. Immunol. 2007, 179, 3242–3248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zingg, J.M.; Vlad, A.; Ricciarelli, R. Oxidized LDLs as Signaling Molecules. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rhoads, J.P.; Major, A.S. How Oxidized Low-Density Lipoprotein Activates Inflammatory Responses. Crit. Rev. Immunol. 2018, 38, 333–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuniyasu, A.; Ohgami, N.; Hayashi, S.; Miyazaki, A.; Horiuchi, S.; Nakayama, H. CD36-mediated endocytic uptake of advanced glycation end products (AGE) in mouse 3T3-L1 and human subcutaneous adipocytes. FEBS Lett. 2003, 537, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasouli, N.; Yao-Borengasser, A.; Varma, V.; Spencer, H.J.; McGehee, R.E., Jr.; Peterson, C.A.; Mehta, J.L.; Kern, P.A. Association of scavenger receptors in adipose tissue with insulin resistance in nondiabetic humans. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2009, 29, 1328–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varghese, D.S.; Ali, B.R. Pathological Crosstalk between Oxidized LDL and ER Stress in Human Diseases: A Comprehensive Review. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 674103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santiago-Fernandez, C.; Martin-Reyes, F.; Tome, M.; Ocana-Wilhelmi, L.; Rivas-Becerra, J.; Tatzber, F.; Tinahones, F.J.; García-Fuentes, E.; Garrido-Sánchez, L. Oxidized LDL modify the human adipocyte phenotype to an insulin resistant, proinflamatory and proapoptotic profile. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farkhondeh, T.; Llorens, S.; Pourbagher-Shahri, A.M.; Ashrafizadeh, M.; Talebi, M.; Shakibaei, M.; Samarghandian, S. An Overview of the Role of Adipokines in Cardiometabolic Diseases. Molecules 2020, 25, 5218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsch, E.; Sluimer, J.C.; Daemen, M.J. Hypoxia in atherosclerosis and inflammation. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 2013, 24, 393–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexopoulos, N.; Katritsis, D.; Raggi, P. Visceral adipose tissue as a source of inflammation and promoter of atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis 2014, 233, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tinahones, F.J.; Garrido-Sanchez, L.; Miranda, M.; García-Almeida, J.M.; Macias-Gonzalez, M.; Ceperuelo, V.; Gluckmann, E.; Rivas-Marin, J.; Vendrell, J.; García-Fuentes, E. Obesity and insulin resistance-related changes in the expression of lipogenic and lipolytic genes in morbidly obese subjects. Obes. Surg. 2010, 20, 1559–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garrido-Sánchez, L.; Vendrell, J.; Fernández-García, D.; Ceperuelo-Mallafré, V.; Chacón, M.R.; Ocaña-Wilhelmi, L.; Alcaide, J.; Tinahones, F.J.; García-Fuentes, E. De novo lipogenesis in adipose tissue is associated with course of morbid obesity after bariatric surgery. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e31280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garrido-Sánchez, L.; García-Almeida, J.M.; García-Serrano, S.; Cardona, I.; García-Arnes, J.; Soriguer, F.; Tinahones, F.J.; García-Fuentes, E. Improved carbohydrate metabolism after bariatric surgery raises antioxidized LDL antibody levels in morbidly obese patients. Diabetes Care 2008, 31, 2258–2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- García-Serrano, S.; Moreno-Santos, I.; Garrido-Sánchez, L.; Gutierrez-Repiso, C.; García-Almeida, J.M.; García-Arnés, J.; Tinahones, F.J.; García-Fuentes, E. Stearoyl-CoA desaturase-1 is associated with insulin resistance in morbidly obese subjects. Mol. Med. 2011, 17, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-Pacheco, F.; Garcia-Serrano, S.; Garcia-Escobar, E.; Gutierrez-Repiso, C.; Garcia-Arnes, J.; Valdes, S.; Gonzalo, M.; Soriguer, F.; Moreno-Ruiz, F.J.; Rodriguez-Cañete, A.; et al. Effects of obesity/fatty acids on the expression of GPR120. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2014, 58, 1852–1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Pacheco, F.; Gutierrez-Repiso, C.; García-Serrano, S.; Ho-Plagaro, A.; Gómez-Zumaquero, J.M.; Valdes, S.; Garcia-Arnes, J.; Gonzalo, M.; Andrade, R.J.; Moreno-Ruiz, F.J.; et al. The pro-/anti-inflammatory effects of different fatty acids on visceral adipocytes are partially mediated by GPR120. Eur. J. Nutr. 2017, 56, 1743–1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Chen, J.; Tao, Q.; Zhu, J.; Shang, Y. Effects of ox-LDL on number and activity of circulating endothelial progenitor cells. Drug Chem. Toxicol. 2004, 27, 243–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garrido-Sánchez, L.; Tomé, M.; Santiago-Fernández, C.; García-Serrano, S.; García-Fuentes, E.; Tinahones, F.J. Adipose tissue biomarkers involved in early resolution of type 2 diabetes after bariatric surgery. Surg. Obes. Relat. Dis. 2017, 13, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, A.; Gupta, S.S.; Sabharwal, N.; Meghrajani, V.; Sharma, S.; Kamholz, S.; Kupfer, Y. A comprehensive review of obstructive sleep apnea. Sleep Sci. 2021, 14, 142–154. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gabryelska, A.; Szmyd, B.; Szemraj, J.; Stawski, R.; Sochal, M.; Białasiewicz, P. Patients with obstructive sleep apnea present with chronic upregulation of serum HIF-1α protein. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2020, 16, 1761–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, D.; Li, N.; Yao, X.; Zhou, L. Potential inflammatory markers in obstructive sleep apnea-hypopnea syndrome. Bosn. J. Basic Med. Sci. 2017, 17, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trayhurn, P. Hypoxia and adipose tissue function and dysfunction in obesity. Physiol. Rev. 2013, 93, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosogai, N.; Fukuhara, A.; Oshima, K.; Miyata, Y.; Tanaka, S.; Segawa, K.; Furukawa, S.; Tochino, Y.; Komuro, R.; Matsuda, M.; et al. Adipose tissue hypoxia in obesity and its impact on adipocytokine dysregulation. Diabetes 2007, 56, 901–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halberg, N.; Khan, T.; Trujillo, M.E.; Wernstedt-Asterholm, I.; Attie, A.D.; Sherwani, S.; Wang, Z.V.; Landskroner-Eiger, S.; Dineen, S.; Magalang, U.J.; et al. Hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha induces fibrosis and insulin resistance in white adipose tissue. Mol. Cell Biol. 2009, 29, 4467–4483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.S.; Kim, J.W.; Osborne, O.; Oh, D.Y.; Sasik, R.; Schenk, S.; Chen, A.; Chung, H.; Murphy, A.; Watkins, S.M.; et al. Increased adipocyte O2 consumption triggers HIF-1alpha, causing inflammation and insulin resistance in obesity. Cell 2014, 157, 1339–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, L.; Wang, Z.; Ji, A.; Meyer, J.M.; Van der Westhuyzen, D.R. Scavenger receptor CD36 expression contributes to adipose tissue inflammation and cell death in diet-induced obesity. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e36785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abumrad, N.A.; el-Maghrabi, M.R.; Amri, E.Z.; Lopez, E.; Grimaldi, P.A. Cloning of a rat adipocyte membrane protein implicated in binding or transport of long-chain fatty acids that is induced during preadipocyte differentiation. Homology with human CD36. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 17665–17668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Febbraio, M.; Silverstein, R.L. CD36, Implications in cardiovascular disease. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2007, 39, 2012–2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viola, M.; Bartolini, B.; Vigetti, D.; Karousou, E.; Moretto, P.; Deleonibus, S.; Sawamura, T.; Wight, T.N.; Hascall, V.C.; De Luca, G.; et al. Oxidized low density lipoprotein (LDL) affects hyaluronan synthesis in human aortic smooth muscle cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 29595–29603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Masaki, T.; Sawamura, T. LOX-1, the receptor for oxidized low-density lipoprotein identified from endothelial cells: Implications in endothelial dysfunction and atherosclerosis. Pharmacol. Ther. 2002, 95, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogura, S.; Kakino, A.; Sato, Y.; Fujita, Y.; Iwamoto, S.; Otsui, K.; Yoshimoto, R.; Sawamura, T. LOX-1, the multifunctional receptor underlying cardiovascular dysfunction. Circ. J. 2009, 73, 1993–1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crucet, M.; Wüst, S.J.; Spielmann, P.; Lüscher, T.F.; Wenger, R.H.; Matter, C.M. Hypoxia enhances lipid uptake in macrophages: Role of the scavenger receptors LOX1, SRA, and CD36. Atherosclerosis 2013, 229, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tinahones, F.J.; Murri-Pierri, M.; Garrido-Sánchez, L.; García-Almeida, J.M.; García-Serrano, S.; García-Arnés, J.; García-Fuentes, E. Oxidative stress in severely obese persons is greater in those with insulin resistance. Obes. Silver Spring 2009, 17, 240–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirato, K.; Kizaki, T.; Sakurai, T.; Ogasawara, J.E.; Ishibashi, Y.; Iijima, T.; Okada, C.; Noguchi, I.; Imaizumi, K.; Taniguchi, N.; et al. Hypoxia-inducible factor-1a suppresses the expression of macrophage scavenger receptor 1. Eur. J. Physiol. 2009, 459, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirillo, A.; Norata, G.D.; Catapano, A.L. LOX-1, OxLDL, and atherosclerosis. Mediat. Inflamm. 2013, 2013, 152786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Liang, C.P.; DeVries-Seimon, T.; Ranalletta, M.; Welch, C.L.; Collins-Fletcher, K.; Accili, D.; Tabas, I.; Tall, A.R. Macrophage insulin receptor deficiency increases ER stress-induced apoptosis and necrotic core formation in advanced atherosclerotic lesions. Cell Metab. 2006, 3, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Netzer, N.; Gatterer, H.; Faulhaber, M.; Burtscher, M.; Pramsohler, S.; Pesta, D. Hypoxia, Oxidative Stress and Fat. Biomolecules 2015, 5, 1143–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pachón-Peña, G.; Serena, C.; Ejarque, M.; Petriz, J.; Duran, X.; Oliva-Olivera, W.; Simó, R.; Tinahones, F.J.; Fernández-Veledo, S.; Vendrell, J. Obesity Determines the Immunophenotypic Profile and Functional Characteristics of Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells From Adipose Tissue. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2016, 5, 464–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holvoet, P.; Jenny, N.S.; Schreiner, P.J.; Tracy, R.P.; Jacobs, D.R. Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis. The relationship between oxidized LDL and other cardiovascular risk factors and subclinical CVD in different ethnic groups: The Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis (MESA). Atherosclerosis 2007, 194, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hulthe, J.; Fagerberg, B. Circulating oxidized LDL is associated with subclinical atherosclerosis development and inflammatory cytokines (AIR Study). Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2002, 22, 1162–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Non-Obese Subjects (n = 21) | Patients with Morbid Obesity (n = 26) | |
|---|---|---|
| Sex (male/female) | 9/12 | 9/17 |
| Age (years) | 44.6 ± 16.1 | 38.9 ± 10.5 |
| Weight (Kg) | 63.2 ± 9.5 | 148.2 ± 28.3 2 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 22.5 ± 1.7 | 56.1 ± 8.6 2 |
| Waist (cm) | 82.1 ± 9.9 | 141.9 ± 17.4 2 |
| Hip (cm) | 96.5 ± 5.4 | 155.6 ± 14.8 |
| Glucose (mg/dL) | 89.4 ± 14.0 | 94.1 ± 11.7 |
| Cholesterol (mg/dL) | 202.8 ± 34.4 | 195.2 ± 41.7 |
| Triglycerides (mg/dL) | 124.1 ± 100.2 | 136.6 ± 78.5 |
| HDL-c (mg/dL) | 55.8 ± 13.5 | 43.4 ± 11.0 1 |
| LDL-c (mg/dL) | 121.4 ± 26.9 | 122.4 ± 29.6 |
| Insulin (μIU/mL) | 13.5 ± 9.5 | 23.2 ± 14.1 1 |
| HOMA-IR | 2.0 ± 2.1 | 5.5 ± 3.4 1 |
| Leptin (ng/mL) | 14.8 ± 15.5 | 68.6 ± 35.0 2 |
| Adiponectin (µg/mL) | 25.4 ± 16.0 | 9.6 ± 4.4 2 |
| Oxidized LDL (mU/L) | 52,977 ± 13,722 | 73,598 ± 26,506 1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Santiago-Fernández, C.; Martín-Reyes, F.; Tome, M.; Gutierrez-Repiso, C.; Fernandez-Garcia, D.; Ocaña-Wilhelmi, L.; Rivas-Becerra, J.; Tatzber, F.; Pursch, E.; Tinahones, F.J.; et al. Oxidized LDL Increase the Proinflammatory Profile of Human Visceral Adipocytes Produced by Hypoxia. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1715. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9111715
Santiago-Fernández C, Martín-Reyes F, Tome M, Gutierrez-Repiso C, Fernandez-Garcia D, Ocaña-Wilhelmi L, Rivas-Becerra J, Tatzber F, Pursch E, Tinahones FJ, et al. Oxidized LDL Increase the Proinflammatory Profile of Human Visceral Adipocytes Produced by Hypoxia. Biomedicines. 2021; 9(11):1715. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9111715
Chicago/Turabian StyleSantiago-Fernández, Concepción, Flores Martín-Reyes, Monica Tome, Carolina Gutierrez-Repiso, Diego Fernandez-Garcia, Luis Ocaña-Wilhelmi, Jose Rivas-Becerra, Franz Tatzber, Edith Pursch, Francisco J. Tinahones, and et al. 2021. "Oxidized LDL Increase the Proinflammatory Profile of Human Visceral Adipocytes Produced by Hypoxia" Biomedicines 9, no. 11: 1715. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9111715
APA StyleSantiago-Fernández, C., Martín-Reyes, F., Tome, M., Gutierrez-Repiso, C., Fernandez-Garcia, D., Ocaña-Wilhelmi, L., Rivas-Becerra, J., Tatzber, F., Pursch, E., Tinahones, F. J., García-Fuentes, E., & Garrido-Sánchez, L. (2021). Oxidized LDL Increase the Proinflammatory Profile of Human Visceral Adipocytes Produced by Hypoxia. Biomedicines, 9(11), 1715. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9111715






