Biomedicines 2021, 9(11), 1549; https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9111549 - 27 Oct 2021
Cited by 2 | Viewed by 2739
Abstract
Visceral obesity may be a driving factor in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) development. Previous studies have shown that the omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid, eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), ameliorates obesity in high-fat (HF) fed male, C57Bl/6 mice at thermoneutral conditions, independent of uncoupling protein
[...] Read more.
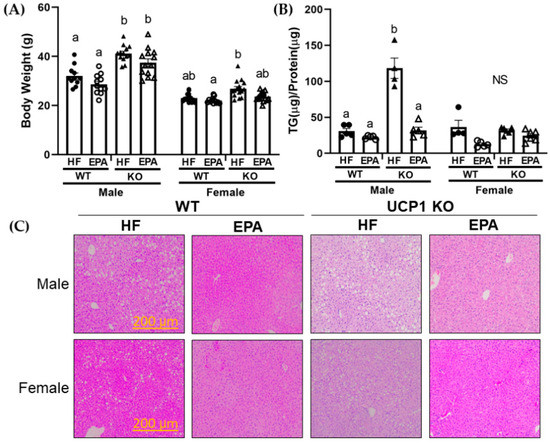
Visceral obesity may be a driving factor in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) development. Previous studies have shown that the omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid, eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), ameliorates obesity in high-fat (HF) fed male, C57Bl/6 mice at thermoneutral conditions, independent of uncoupling protein 1 (UCP1). Our goals herein were to investigate sex-dependent mechanisms of EPA in the livers of wild type (WT) and UCP1 knockout (KO) male and female mice fed a HF diet (45% kcal fat; WT-HF, KO-HF) with or without supplementation of 36 g/kg EPA (WT-EPA, KO-EPA). KO significantly increased body weight in males, with no significant reductions with EPA in the WT or KO groups. In females, there were no significant differences in body weight among KO groups and no effects of EPA. In males, liver TGs were significantly higher in the KO-HF group and reduced with EPA, which was not observed in females. Accordingly, gene and protein markers of mitochondrial oxidation, peroxisomal biogenesis and oxidation, as well as metabolic futile cycles were sex-dependently impacted by KO and EPA supplementation. These findings suggest a genotypic difference in response to dietary EPA supplementation on the livers of male and female mice with diet-induced obesity and housed at thermoneutrality.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue NAFLD: From Mechanisms to Therapeutic Approaches)
►
Show Figures