Low-Dose Niacin Supplementation Improves Motor Function in US Veterans with Parkinson’s Disease: A Single-Center, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Trial
Abstract
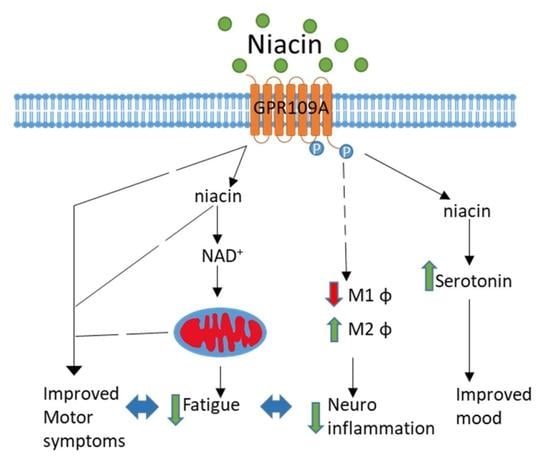
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Intervention
2.3. Outcomes of the Study
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Subjects
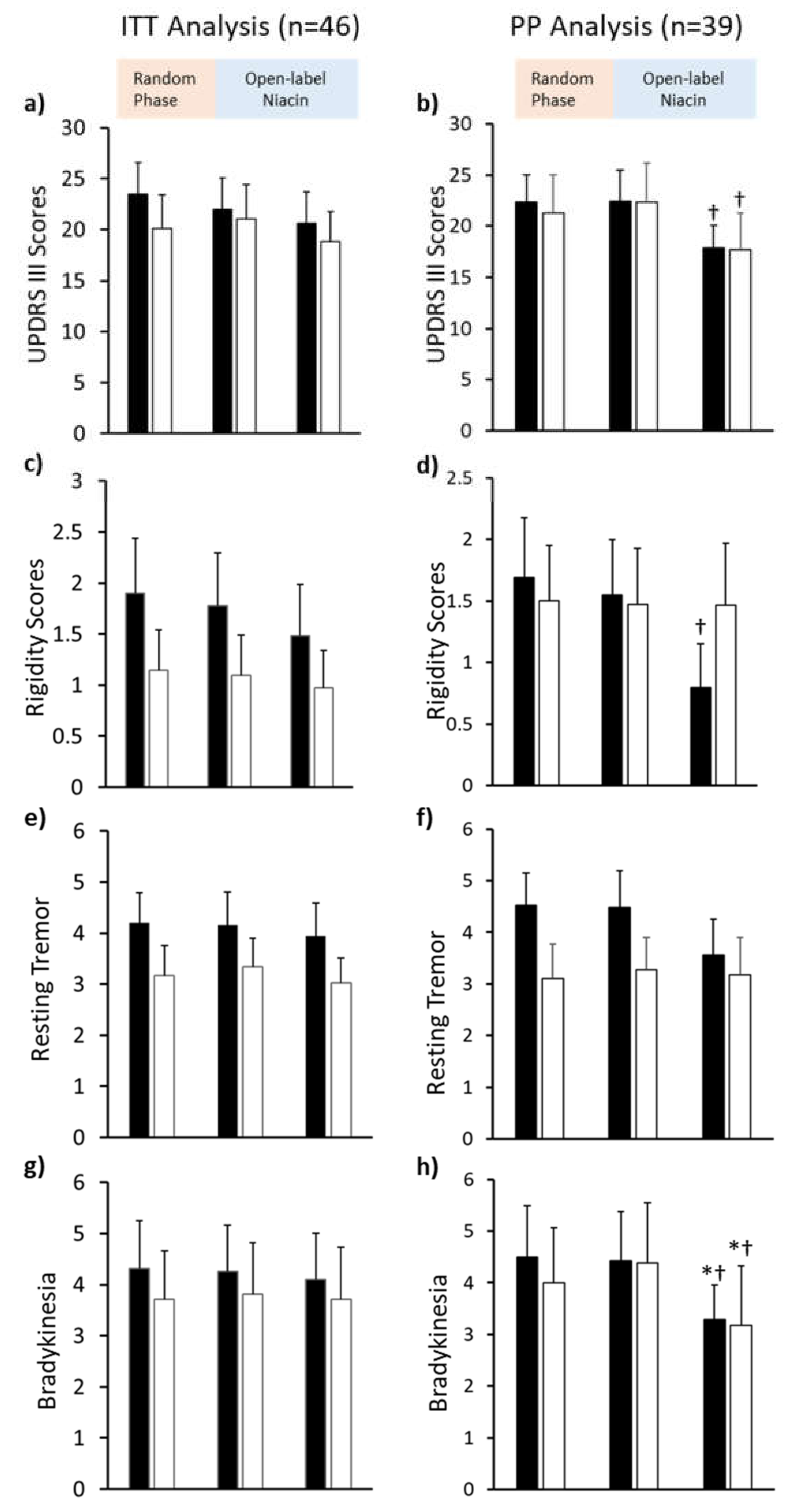
3.2. Primary Outcome: UPDRS III
3.2.1. Six Months of 250 mg Niacin vs. Placebo
3.2.2. Six to Twelve Months of 250 mg Niacin
3.2.3. Baseline to Twelve Months
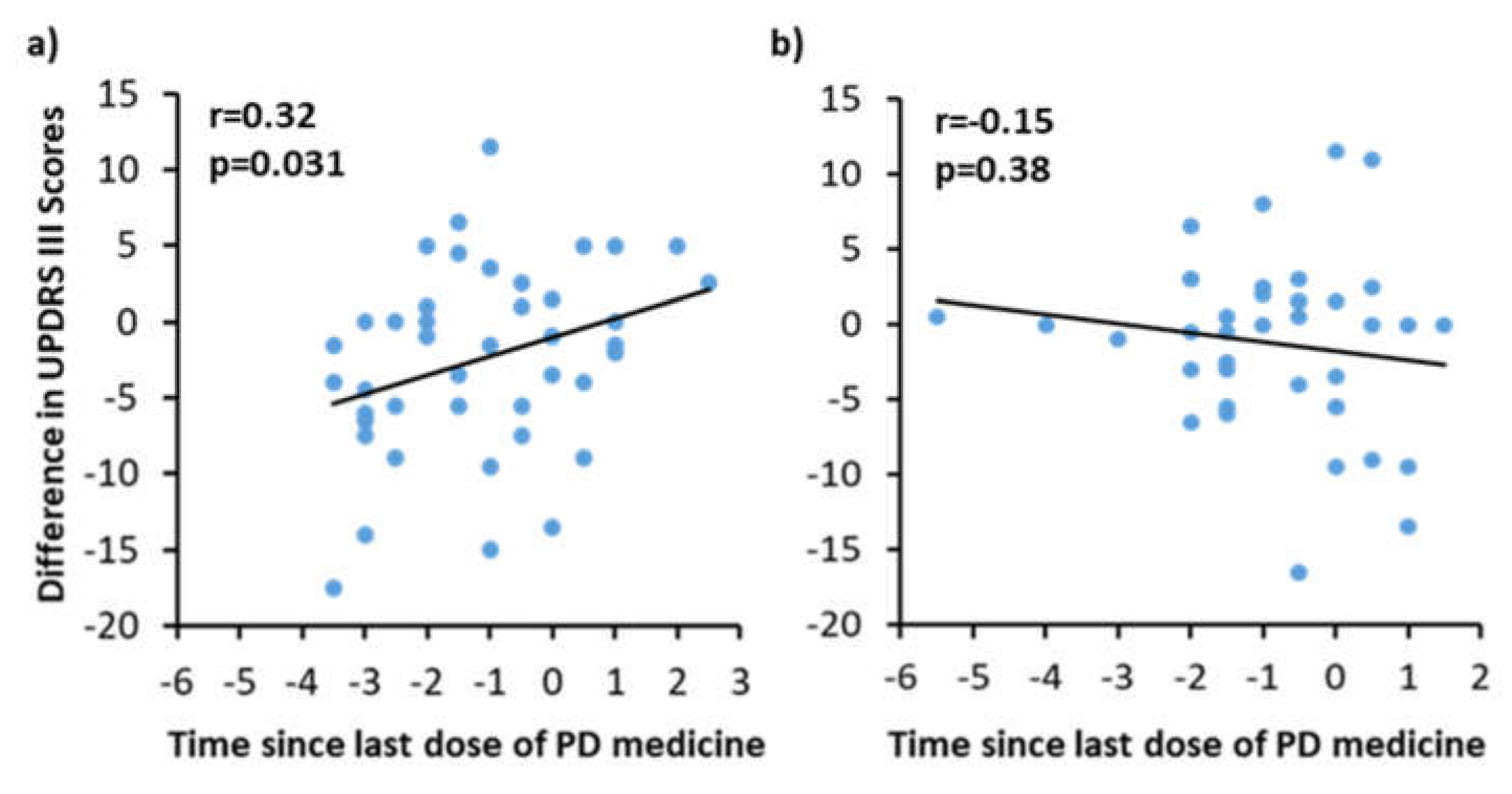
3.3. Correlation with on/off Phenomenon with UPDRS III Scores
3.4. Secondary Outcomes
3.5. Adverse Events
4. Discussion
4.1. Study Strengths
4.2. Study Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dorsey, E.R.; Elbaz, A.; Nichols, E.; Abbasi, N.; Abd-Allah, F.; Abdelalim, A.; Adsuar, J.C.; Ansha, M.G.; Brayne, C.; Choi, J.Y.J.; et al. Global, regional, and national burden of Parkinson’s disease, 1990–2016: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet Neurol. 2018, 17, 939–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schrag, A.; Quinn, N. Dyskinesias and motor fluctuations in Parkinson’s disease. A community-based study. Brain 2000, 123, 2297–2305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rocha, E.M.; De Miranda, B.; Sanders, L.H. Alpha-synuclein: Pathology, mitochondrial dysfunction and neuroinflammation in Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol. Dis. 2018, 109, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Turnbull, D.M.; Reeve, A.K. Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Parkinson’s Disease-Cause or Consequence? Biology 2019, 8, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Giri, B.; Belanger, K.; Seamon, M.; Bradley, E.; Purohit, S.; Chong, R.; Morgan, J.C.; Baban, B.; Wakade, C. Niacin Ameliorates Neuro-Inflammation in Parkinson’s Disease via GPR109A. Int. J. Mol. Sci 2019, 20, 4559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hellenbrand, W.; Boeing, H.; Robra, B.P.; Seidler, A.; Vieregge, P.; Nischan, P.; Joerg, J.; Oertel, W.H.; Schneider, E.; Ulm, G. Diet and Parkinson’s disease. II: A possible role for the past intake of specific nutrients. Results from a self-administered food-frequency questionnaire in a case-control study. Neurology 1996, 47, 644–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barone, P.; Antonini, A.; Colosimo, C.; Marconi, R.; Morgante, L.; Avarello, T.P.; Bottacchi, E.; Cannas, A.; Ceravolo, G.; Ceravolo, R.; et al. The PRIAMO study: A multicenter assessment of nonmotor symptoms and their impact on quality of life in Parkinson’s disease. Mov. Disord. 2009, 24, 1641–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalia, L.V.; Lang, A.E. Parkinson’s disease. Lancet 2015, 386, 896–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, R.; Albor, L.; Wakade, C.; Morgan, J. The dimensionality of fatigue in Parkinson’s disease. J. Transl. Med. 2018, 16, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schaeffer, E.; Vaterrodt, T.; Zaunbrecher, L.; Liepelt-Scarfone, I.; Emmert, K.; Roeben, B.; Elshehabi, M.; Hansen, C.; Becker, S.; Nussbaum, S.; et al. Effects of Levodopa on quality of sleep and nocturnal movements in Parkinson’s Disease. J. Neurol. 2021, 268, 2506–2514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bender, D.A.; Earl, C.J.; Lees, A.J. Niacin depletion in Parkinsonian patients treated with L-dopa, benserazide and carbidopa. Clin. Sci. 1979, 56, 89–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chong, R.; Wakade, C.; Seamon, M.; Giri, B.; Morgan, J.C.; Purohit, S. Niacin Enhancement for Parkinson’s Disease: An Effectiveness Trial. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2021, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wakade, C.; Chong, R.; Bradley, E.; Morgan, J.C. Low-dose niacin supplementation modulates GPR109A, niacin index and ameliorates Parkinson’s disease symptoms without side effects. Clin. Case Rep. 2015, 3, 635–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hughes, A.J.; Daniel, S.E.; Kilford, L.; Lees, A.J. Accuracy of clinical diagnosis of idiopathic Parkinson’s disease: A clinico-pathological study of 100 cases. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1992, 55, 181–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Evans, J.R.; Mason, S.L.; Williams-Gray, C.H.; Foltynie, T.; Brayne, C.; Robbins, T.W.; Barker, R.A. The natural history of treated Parkinson’s disease in an incident, community based cohort. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2011, 82, 1112–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Poewe, W. The natural history of Parkinson’s disease. J. Neurol. 2006, 253, VII2-6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kortte, K.B.; Horner, M.D.; Windham, W.K. The trail making test, part B: Cognitive flexibility or ability to maintain set? Appl. Neuropsychol. 2002, 9, 106–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alisky, J.M. Niacin improved rigidity and bradykinesia in a Parkinson’s disease patient but also caused unacceptable nightmares and skin rash—A case report. Nutr. Neurosci. 2005, 8, 327–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schöndorf, D.C.; Ivanyuk, D.; Baden, P.; Sanchez-Martinez, A.; De Cicco, S.; Yu, C.; Giunta, I.; Schwarz, L.K.; Di Napoli, G.; Panagiotakopoulou, V.; et al. The NAD+ Precursor Nicotinamide Riboside Rescues Mitochondrial Defects and Neuronal Loss in iPSC and Fly Models of Parkinson’s Disease. Cell Rep. 2018, 23, 2976–2988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, D.W.; Bradbury, K.A.; Schneider, J.S. Broad neuroprotective profile of nicotinamide in different mouse models of MPTP-induced parkinsonism. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 610–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, H.; Li, X.; Gao, H.; Feng, Z.; Li, X.; Zhao, L.; Jia, X.; Zhang, H.; Liu, J. High doses of nicotinamide prevent oxidative mitochondrial dysfunction in a cellular model and improve motor deficit in a Drosophila model of Parkinson’s disease. J. Neurosci. Res. 2008, 86, 2083–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wise, A.; Foord, S.M.; Fraser, N.J.; Barnes, A.A.; Elshourbagy, N.; Eilert, M.; Ignar, D.M.; Murdock, P.R.; Steplewski, K.; Green, A.; et al. Molecular identification of high and low affinity receptors for nicotinic acid. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 9869–9874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wakade, C.; Giri, B.; Malik, A.; Khodadadi, H.; Morgan, J.C.; Chong, R.K.; Baban, B. Niacin modulates macrophage polarization in Parkinson’s disease. J. Neuroimmunol. 2018, 320, 76–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chai, J.T.; Digby, J.E.; Ruparelia, N.; Jefferson, A.; Handa, A.; Choudhury, R.P. Nicotinic Acid Receptor GPR109A Is Down-Regulated in Human Macrophage-Derived Foam Cells. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e62934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gyoneva, S.; Shapiro, L.; Lazo, C.; Garnier-Amblard, E.; Smith, Y.; Miller, G.W.; Traynelis, S.F. Adenosine A2A receptor antagonism reverses inflammation-induced impairment of microglial process extension in a model of Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol. Dis. 2014, 67, 191–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hirsch, E.C.; Hunot, S.; Damier, P.; Faucheux, B. Glial cells and inflammation in Parkinson’s disease: A role in neurodegeneration? Ann. Neurol. 1998, 44, S115–S120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bohannon, R.W. Grip Strength: An Indispensable Biomarker For Older Adults. Clin. Interv. Aging 2019, 14, 1681–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
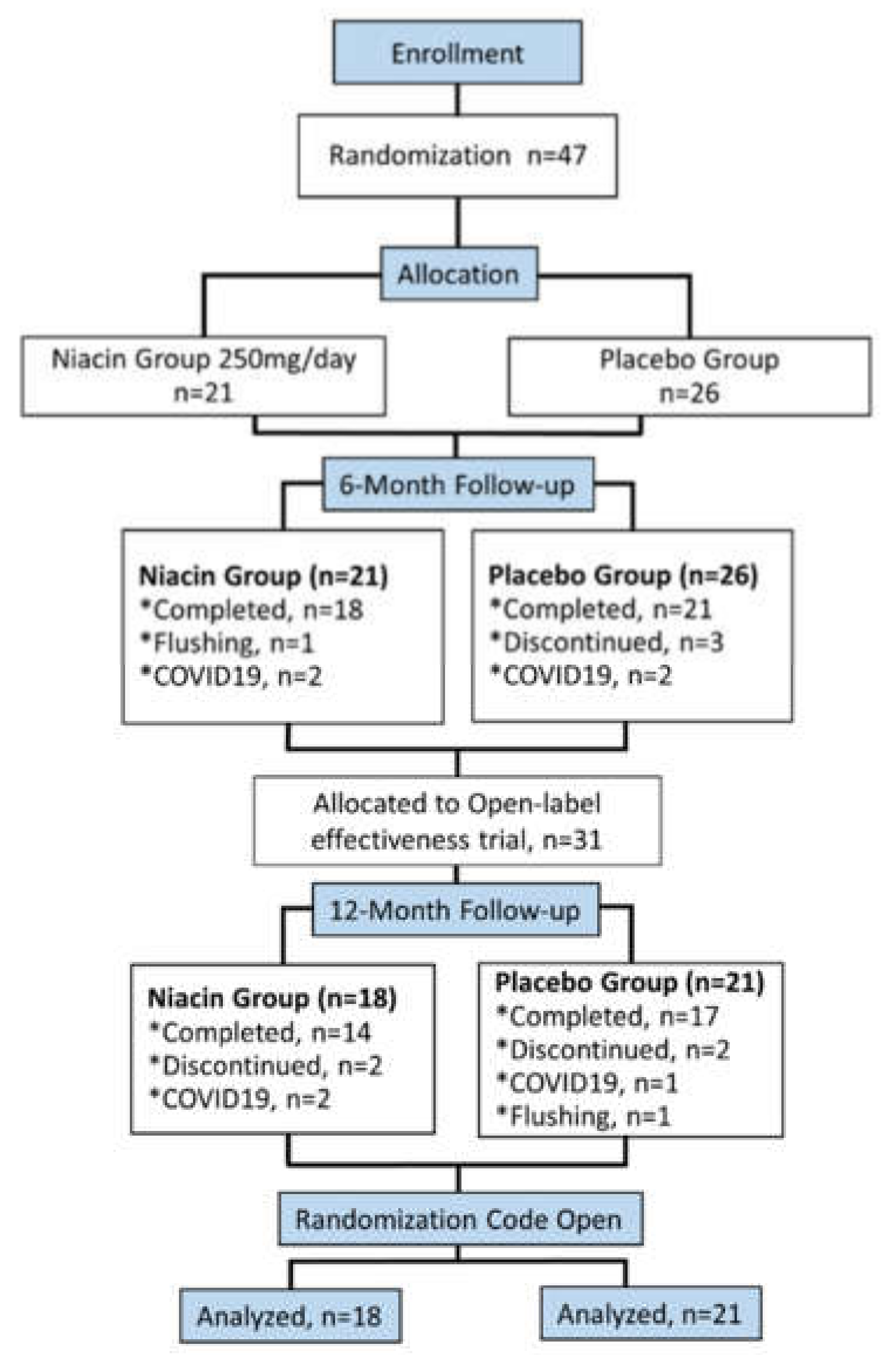
| Treatment Groups | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Characteristics | Placebo (n = 21) | Niacin (n = 18) | p-Value |
| Sex, N (%) | |||
| Men | 19 (90.5) | 16 (88.9) | 1 a |
| Women | 2 (9.5) | 2 (11.1) | |
| Race/ethnicity, N (%) | |||
| Non-Hispanic White | 18 (85.7) | 18 (100) | 0.29 a |
| Non-Hispanic Black | 3 (14.3) | 0 (0) | |
| Veteran status, N (%) | |||
| Veterans | 15 (71.4) | 10 (55.6) | 0.5 a |
| Non-Veterans | 6 (28.6) | 8 (44.4) | |
| Age, mean (SD), y | 68.0 (10.7) | 68.2 (6.0) | |
| Duration of PD, mean (SD), y | 5.6 (4.2) | 6.0 (6.0) | |
| Age of Onset, mean (SD), y | 61.6 (10.9) | 63.3 (7.2) | |
| Disease Stage, N (%) | |||
| Early (H&Y < 2.5) | 14 (66.7) | 14 (77.8) | 0.68 a |
| Late (H&Y ≥ 2.5) | 7 (33.3) | 4 (22.2) | |
| Medications, mg/day | |||
| Sinemet intake, N (%) | 20 (95.2) | 15 (83.3) | 0.5 a |
| Levodopa dosage, mean (range) | 488.9 (300–1000) | 480.8 (200–800) | |
| H&Y staging, mean (range) | 2.2 (1.5–4) | 1.8 (0.5–4) | |
| UPDRS III Scores, mean (SD) | 22.4 (11.8) | 21.3 (15.8) | 0.99 b |
| Rigidity | 1.69 (2.23) | 1.5 (1.92) | 0.99 b |
| Resting Tremor | 4.52 (2.87) | 3.11 (2.82) | 0.34 b |
| Bradykinesia | 4.5 (4.6) | 4 (4.5) | 0.98 b |
| Cognitive flexibility | 73.38 (57.11) | 79.42 (62.46) | 0.99 b |
| Grip Strength, PSI | |||
| First affected hand | 305.09 (105.26) | 297.04 (125.68) | 0.99 b |
| Non (or later) affected hand | 300.43 (80.49) | 284.1 (123.09) | 0.98 b |
| FSS | 36.65 (13.02) | 40.28 (11.99) | 0.76 b |
| VAFS | 5.4 (2.23) | 5.17 (2.23) | 0.96 b |
| REM sleep, % | 15.19 (12.1) | 22.5 (13.36) | 0.32 b |
| GDS | 6.2 (5.87) | 7.89 (7.31) | 0.66 b |
| Stroop 3 trial | 8.13 (6.64) | 6.18 (7.92) | 0.81 b |
| Walk and Turn, s | 11.47 (3.46) | 10.33 (3.16) | 0.66 b |
| Valine, mg/dL | 229.33 (51.78) | 245.64 (33.42) | 0.69 b |
| Tyrosine, mg/dL | 73.93 (14.77) | 64.93 (16.28) | 0.35 b |
| Tryptophan, mg/dL | 60.87 (11.39) | 53.5 (10.81) | 0.23 b |
| Serotonin, mg/dL | 89.56 (60.5) | 84.21 (68.17) | 0.99 b |
| Phenylalanine, mg/dL | 74.47 (12.59) | 73.07 (9.74) | 0.98 b |
| Leucine, mg/dL | 136.87 (38.75) | 143.07 (27.71) | 0.95 b |
| Isoleucine, mg/dL | 72.14 (24.2) | 73.36 (15) | 0.99 b |
| Clinical | Baseline Values, Mean ±SD | 6-Month Change (Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Trial) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable, Units | Placebo Group | Niacin Group | Placebo Group Change | Niacin Group Change | Between Group Difference |
| UPDRS III Scores | 22.4 ± 11.8 | 21.3 ± 15.8 | −0.05 (−2.4–2.32) | −1.06 (−3.68–1.57) | 1.13 (−10.40–12.65) |
| Rigidity | 1.69 ± 2.23 | 1.5 ± 1.92 | 0.14 (−0.14–0.42) | 0.03 (−0.26–0.31) | 0.19 (−1.47–1.85) |
| Resting Tremor | 4.52 ± 2.87 | 3.11 ± 2.82 | 0.05 (−0.54–0.64) | −0.17 (−0.49–0.16) | 1.4 (−0.87–3.7) |
| Bradykinesia | 4.5 ± 4.6 | 4 ± 4.5 | 0.07 (−0.35–0.49) | −0.39 (−1.42–0.65) | 0.5 (−3.15–3.7) |
| Cognitive flexibility | 73.38 ± 57.11 | 79.42 ± 62.46 | −3.04 (−28.04–21.96) | 5.44 (−30.78–41.67) | −6.04 (−54.93–42.85) |
| Grip Strength, PSI | |||||
| First affected hand | 305.09 ± 105.26 | 297.04 ± 125.68 | 5.88 (−14.19–25.94) | −22.56 (−53.54–8.43) | 8.05 (−132.3–148.4) |
| Non (or later) affected hand | 300.43 ± 80.49 | 284.1 ± 123.09 | 3.73 (−35.11–42.56) | −31.67 (−63.74–0.39) | 16.33 (−110–142.7) |
| FSS | 36.65 ± 13.02 | 40.28 ± 11.99 | −0.06 (−2.5–2.37) | 1.78 (−5.5–9.05) | −3.63 (−13.79–6.53) |
| VAFS | 5.4 ± 2.23 | 5.17 ± 2.23 | −0.22 (−0.97–0.53) | −0.44 (−1.74–0.85) | 0.23 (−1.58–2.05) |
| REM sleep, % | 15.19 ± 12.1 | 22.5 ± 13.36 | −6.26 (−11.05–1.47) * | 1.39 (−5.42–8.2) | −7.31 (−17.62–3.0) |
| GDS | 6.2 ± 5.87 | 7.89 ± 7.31 | 0.25 (−0.53–1.03) | 1.17 (−1.75–4.08) | −1.69 (−7.14–3.76) |
| Stroop 3 trial | 8.13 ± 6.64 | 6.18 ± 7.92 | −0.59 (−3.17–1.99) | −2.19 (−5.93–1.54) | 1.96 (−4.16–8.08) |
| Walk and Turn, s | 11.47 ± 3.46 | 10.33 ± 3.16 | 0.44 (−1.08–1.96) | 0.18 (−0.61–0.96) | 1.14 (−1.61–3.88) |
| Valine, mg/dL | 229.33 ± 51.78 | 245.64 ± 33.42 | 1.83 (−27.05–30.72) | −0.71 (−35.17–33.74) | −16.31 (−57.55–24.93) |
| Tyrosine, mg/dL | 73.93 ± 14.77 | 64.93 ± 16.28 | 8.82 (−2.2–19.84) | −0.5 (−10.82–9.82) | 9.01 (−5.75–23.76) |
| Tryptophan, mg/dL | 60.87 ± 11.39 | 53.5 ± 10.81 | 7.48 (−0.39–15.34) | −0.07 (−6.1–5.96) | 7.37 (−3.13–17.86) |
| Serotonin, mg/dL | 89.56 ± 60.5 | 84.21 ± 68.17 | 25.34 (5.79–44.89) * | 1.21 (−17.82–20.25) | 5.35 (−55.03–65.72) |
| Phenylalanine, mg/dL | 74.47 ± 12.59 | 73.07 ± 9.74 | 3.74 (−8.48–15.97) | −1.64 (−8.62–5.33) | 1.40 (−9.23–12.02) |
| Leucine, mg/dL | 136.87 ± 38.75 | 143.07 ± 27.71 | 9.26 (−15.26–33.77) | −4.64 (−28.45–19.16) | −6.21 (−38.02–25.61) |
| Isoleucine, mg/dL | 72.14 ± 24.2 | 73.36 ± 15 | 4.03 (−14.21–22.26) | −4.79 (−19.34–9.77) | −1.21 (−20.89–18.47) |
| Clinical | 6-Month Values (Mean ±SD) | 6–12 Month Change (Open-Label Niacin Treatment) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable, Units | Placebo Group | Niacin Group | Placebo Group Change | Niacin Group Change | Between Group Difference |
| UPDRS III Scores | 22.4 ± 14 | 22.3 ± 16.4 | 4.58 (0.85–8.30) * | 4.63 (1.42–7.83) * | 0.12 (−12.29–12.53) |
| Rigidity | 1.5 ± 2.1 | 1.5 ± 1.9 | 0.75 (−0.01–1.51) * | 0.008 (−0.47–0.49) | 0.08 (−1.522–1.673) |
| Resting Tremor | 4.5 ± 3.3 | 3.3 ± 2.7 | 0.92 (−0.12–1.96) | 0.1 (−0.56–0.76) | 1.20 (−1.17–3.57) |
| Bradykinesia | 4.4 ± 4.4 | 4.4 ± 4.9 | 1.13 (0.25–2.02) * | 1.21 (0.36–2.06) * | 0.04 (−3.74–3.82) |
| Cognitive flexibility | 76.4 ± 63.1 | 74 ± 54.7 | −15.18 (−40.6–10.24) | 4.9 (−27.8–37.6) | 2.44 (−47.02–51.91) |
| Grip Strength, Newtons | |||||
| First affected hand | 299.2 ± 107.5 | 319.6 ± 118.2 | −23.58 (−79.14–31.98) | −80.3 (−176.2–15.65) | −20.38 (−167.4–126.7) |
| Non (or later) affected hand | 296.7 ± 89.4 | 315.8 ± 119.4 | −11.84 (−56.59–32.92) | −54.72 (−128.8–19.38) | −19.07 (−152.8–114.7) |
| FSS | 36.7 ± 14.2 | 38.5 ± 11 | 2.89 (−1.62–7.4) | 4.36 (1.59–7.13) * | −1.79 (−11.91–8.34) |
| VAFS | 5.6 + 2.5 | 5.6 ± 2.2 | −0.76 (−1.75–0.24) | −0.39 (−0.92–0.14) | 0.008 (−1.88–1.89) |
| REM sleep, % | 6 ± 5.9 | 6.7 ± 5.9 | 1.92 (−7.2–11.03) | −4.32 (−10.32–1.68) | 0.34 (−11.09–11.77) |
| GDS | 21.5 ±16.3 | 21.1 ± 11.6 | 1.08 (−1.12–3.28) | 1.37 (−0.5–3.23) | −0.77 (−5.53–3.99) |
| Stroop 3 trial average | 8.7 ± 6.9 | 8.4 ± 5.6 | −0.78 (−5.47–3.91) | −0.78 (−2.85–1.28) | 0.35 (−4.9–5.61) |
| Walk and Turn, s | 11 ± 3.2 | 10.2 ± 3.4 | 0.75 (−0.53–2.02) | 1.72 (0.59–2.84) * | 0.87 (−1.95–3.69) |
| Valine, mg/dL | 227.5 ± 45 | 246.4 ± 29.7 | 4.29 (−32.51–41.08) | 21.07 (−16.01–58.15) | −18.86 (−52.4–14.69) |
| Tyrosine, mg/dL | 65.1 ± 15.5 | 65.4 ± 14.4 | 1.83 (−11.66–15.31) | 4.57 (−5.33–14.47) | −0.32 (−13.74–13.11) |
| Tryptophan, mg/dL | 53.4 ± 11.6 | 53.6 ± 10.9 | −4.11 (−12.97–4.75) | 4.29 (−4.75–13.32) | −0.18 (−10.28–9.92) |
| Serotonin, mg/dL | 64.2 ± 44.5 | 83 ± 75.2 | −18.11 (−37.97–1.75) | −13.36 (−58.77–32.06) | −18.78 (−77.83–40.27) |
| Phenylalanine, mg/dL | 70.7 ± 20.6 | 74.7 ± 9.8 | −0.85 (−12–10.3) | 2.43 (−9.35–14.21) | −3.99 (−18.11–10.12) |
| Leucine, mg/dL | 127.6 ± 32.5 | 147.7 ± 21.7 | −1.75 (−29.99–26.5) | 14.86 (−9.31–39.02) | −20.1 (−44.43–4.23) |
| Isoleucine, mg/dL | 68.1 ± 20.4 | 78.1 ± 15.2 | 1.26 (−14.45–16.97) | 8.64 (−4.48–21.77) | −10.03 (−26.28–6.230) |
| 12-Month Values (Mean ±SD) | 12- Month Change | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clinical Variable, Units | Placebo Group | Niacin Group | Placebo Group Change | Niacin Group Change | Between Group Difference |
| UPDRS III Scores | 17.9 ± 9.2 | 17.7 ± 13.3 | 4.52 (−0.16–9.21) | 3.57 (−1.019–8.16) | 0.17 (−10.66–11.01) |
| Rigidity | 0.8 ± 1.5 | 1.5 ± 1.9 | 0.90 (−0.05–1.84) | 0.04 (−0.43–0.5) | −0.67 (−2.25–0.91) |
| Resting Tremor | 3.6 ± 2.9 | 3.2 ± 2.7 | 0.97 (−0.16–2.09) | −0.07 (−0.94–0.81) | 0.38 (−2.18–2.94) |
| Bradykinesia | 3.3 ± 2.8 | 3.2 ± 4.3 | 1.21 (0.19–2.23) * | 0.82 (−0.004–1.65) * | 0.12 (−3.34–3.57) |
| Cognitive flexibility | 91.6 ± 72 | 69.1 ± 55.5 | 18.22 (−42.79–6.35) | 10.35 (−17.7–38.39) | 22.52 (−36.72–81.77) |
| Grip Strength, Newtons | |||||
| First affected hand | 322.8 ± 91.7 | 399.9 ± 54.1 | −17.71 (−62.17–26.75) | −102.9 (−218.8–13.14) | −77.1 (−186.4–32.22) |
| Non (or later) affected hand | 308.5 ± 84.6 | 370.5 ± 75.3 | −8.12 (−56.34–40.13) | −86.4 (−187.8–15.05) | −61.96 (−181.5–57.59) |
| FSS | 33.8 ± 13.6 | 34.1 ± 12 | 2.83 (−2.15–7.81) | 6.14 (−1.59–13.86) | −0.32 (−12–11.37) |
| VAFS | 6.4 ± 2.2 | 6 ± 2.5 | −0.98 (−2.2–0.25) | −0.83 (−2.16–0.49) | 0.38 (−1.84–2.59) |
| REM sleep, % | 4.9 ± 4.9 | 5.4 ± 5.3 | −4.34 (−11.45–2.76) | −2.93 (−11.11–5.26) | −5.9 (−20.57–8.78) |
| GDS | 19.5 ± 16.8 | 25.4 ± 14.1 | 1.33 (−1.01–3.66) | 2.53 (−1.56–6.62) | −0.48 (−5.24–4.28) |
| Stroop 3 trial average | 9.5 ± 7.5 | 9.2 ± 6.3 | −1.37 (−5.41–2.67) | −2.98 (−7.73–1.78) | 0.35 (−6.45–7.14) |
| Walk and Turn, s | 10.3 ± 2.8 | 8.4 ± 1.7 | 1.19 (−0.38–2.76) | 1.89 (0.55–3.23) * | 1.84 (−0.39–4.07) |
| Valine, mg/dL | 223.2 ± 37.7 | 225.3 ± 37.9 | 6.12 (−29.16–41.4) | 20.36 (−17.62–58.33) | −2.07 (−38.5–34.35) |
| Tyrosine, mg/dL | 63.3 ± 12.1 | 60.9 ± 9.2 | 10.65 (1.19–20.1) * | 4.07 (−8.28–16.42) | 2.43 (−7.98–12.84) |
| Tryptophan, mg/dL | 57.5 ± 9.3 | 49.3 ± 10.8 | 3.37 (−5.21–11.94) | 4.21 (−3.69–12.12) | 8.21 (−1.54–17.97) |
| Serotonin, mg/dL | 82.3 ± 31.6 | 96.4 ± 56.3 | 7.23 (−24.06–38.51) | −12.14 (−49.59–25.31) | −14.02 (−58.56–30.51) |
| Phenylalanine, mg/dL | 71.6 ± 11 | 72.3 ± 13.5 | 2.9 (−6.82–12.61) | 0.79 (−10.03–11.6) | −0.71 (−12.62–11.19) |
| Leucine, mg/dL | 129.4 ± 24.6 | 132.9 ± 28.9 | 7.51 (−18.63–33.65) | 10.21 (−21.1–41.53) | −3.5 (−29.45–22.45) |
| Isoleucine, mg/dL | 66.9 ± 11.2 | 69.5 ± 16 | 5.29 (−8.82–19.39) | 3.86 (−10.4–18.12) | −2.64 (−16.11–10.82) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wakade, C.; Chong, R.; Seamon, M.; Purohit, S.; Giri, B.; Morgan, J.C. Low-Dose Niacin Supplementation Improves Motor Function in US Veterans with Parkinson’s Disease: A Single-Center, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1881. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9121881
Wakade C, Chong R, Seamon M, Purohit S, Giri B, Morgan JC. Low-Dose Niacin Supplementation Improves Motor Function in US Veterans with Parkinson’s Disease: A Single-Center, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Biomedicines. 2021; 9(12):1881. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9121881
Chicago/Turabian StyleWakade, Chandramohan, Raymond Chong, Marissa Seamon, Sharad Purohit, Banabihari Giri, and John C. Morgan. 2021. "Low-Dose Niacin Supplementation Improves Motor Function in US Veterans with Parkinson’s Disease: A Single-Center, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Trial" Biomedicines 9, no. 12: 1881. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9121881
APA StyleWakade, C., Chong, R., Seamon, M., Purohit, S., Giri, B., & Morgan, J. C. (2021). Low-Dose Niacin Supplementation Improves Motor Function in US Veterans with Parkinson’s Disease: A Single-Center, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Biomedicines, 9(12), 1881. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9121881