Brown Spiders’ Phospholipases-D with Potential Therapeutic Applications: Functional Assessment of Mutant Isoforms
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Wild Type and Site-Directed Mutant PLDs
2.2. Recombinant Expression
2.3. Protein Purification
2.4. Circular Dichroism
2.5. Immunoassays
2.6. Structural Analyses
2.7. Sphingomyelinase Activity
2.8. High Performance Thin Layer Chromatography (HPTLC)
2.9. Animals
2.10. Hemolytic Activity
2.11. Vascular Permeability Assay
2.12. In Vivo Dermonecrosis
2.13. Histological Methods for Light Microscopy
2.14. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
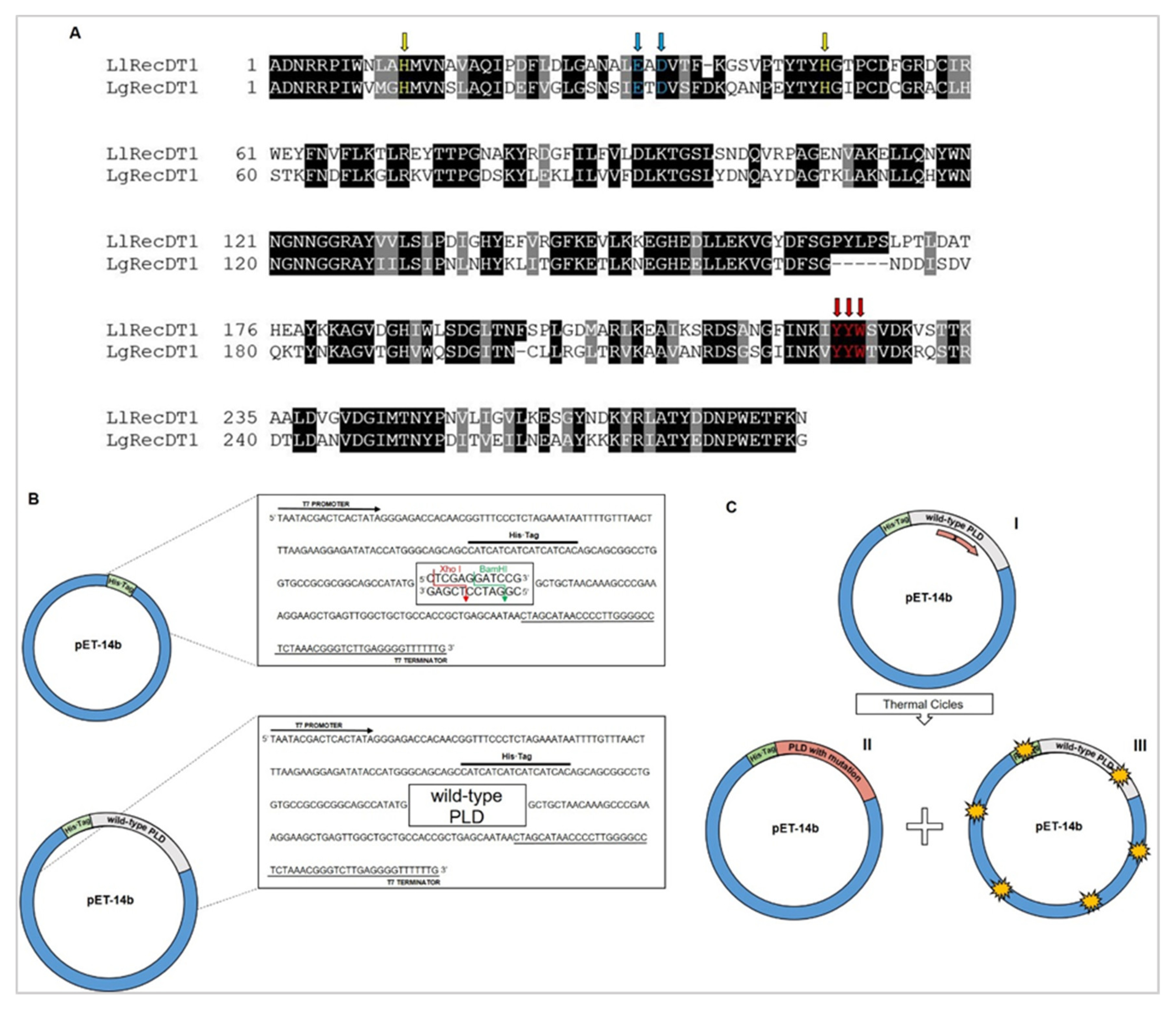
3.1. Analysis of Sequences Encoding Wild type PLDs, Site-Directed Mutagenesis, and Production of Mutant PLDs Isoforms
3.2. Expression and Purification of Recombinant PLD Wild type and Mutant Isoforms
3.3. Circular Dichroism Spectroscopy Analysis
3.4. Molecular Modeling Analysis
3.5. Immunological Cross-Reactivity between Recombinant PLDs and Native Venom Toxins
3.6. Sphingomyelinase Activity
3.7. Hemolytic Activity
3.8. Activity on Blood Vessel Permeability
3.9. Dermonecrotic Activity
3.10. Histopathological Changes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Da Silva, P.H.; da Silveira, R.B.; Appel, M.H.; Mangili, O.C.; Gremski, W.; Veiga, S.S. Brown spiders and loxoscelism. Toxicon 2004, 44, 693–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gremski, L.H.; Trevisan-Silva, D.; Ferrer, V.P.; Matsubara, F.H.; Meissner, G.O.; Wille, A.C.M.; Vuitika, L.; Dias-Lopes, C.; Ullah, A.; De Moraes, F.R.; et al. Recent advances in the understanding of brown spider venoms: From the biology of spiders to the molecular mechanisms of toxins. Toxicon 2014, 83, 91–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ministério da Saúde Acidente por Animais Peçonhentos—Notificações Registradas no Sistema de Informação de Agravos de Notificação—Brasil. Available online: http://tabnet.datasus.gov.br/cgi/deftohtm.exe?sinannet/cnv/animaisbr.def (accessed on 10 December 2020).
- Chaves-Moreira, D.; Senff-Ribeiro, A.; Wille, A.C.M.; Gremski, L.H.; Chaim, O.M.; Veiga, S.S. Highlights in the knowledge of brown spider toxins. J. Venom. Anim. Toxins Incl. Trop. Dis. 2017, 23, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Forrester, L.J.; Barrett, J.T.; Campbell, B.J. Red blood cell lysis induced by the venom of the brown recluse spider. The role of sphingomyelinase D. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1978, 187, 355–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurpiewski, G.; Forrester, L.J.; Barrett, J.T.; Campbell, B.J. Platelet aggregation and sphingomyelinase D activity of a purified toxin from the venom of loxosceles reclusa. BBA Gen. Subj. 1981, 678, 467–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaves-Moreira, D.; Souza, F.N.; Fogaça, R.T.H.; Mangili, O.C.; Gremski, W.; Senff-Ribeiro, A.; Chaim, O.M.; Veiga, S.S. The relationship between calcium and the metabolism of plasma membrane phospholipids in hemolysis induced by brown spider venom phospholipase-D toxin. J. Cell. Biochem. 2011, 112, 2529–2540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Lynch, K.R. Brown recluse spider (Loxosceles reclusa) venom phospholipase D (PLD) generates lysophosphatidic acid (LPA). Biochem. J. 2006, 391, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lajoie, D.M.; Cordes, M.H.J. Spider, bacterial and fungal phospholipase D toxins make cyclic phosphate products. Toxicon 2015, 108, 176–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Fernandes-Pedrosa, M.F.; de Junqueira-de-Azevedo, I.L.M.; Gonçalves-de-Andrade, R.M.; Kobashi, L.S.; Almeida, D.D.; Ho, P.L.; Tambourgi, D.V. Transcriptome analysis of Loxosceles laeta (Araneae, Sicariidae) spider venomous gland using expressed sequence tags. BMC Genom. 2008, 9, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fernandes Pedrosa, M.D.F.; de Azevedo, I.D.L.M.J.; Gonçalves-de-Andrade, R.M.; van Den Berg, C.W.; Ramos, C.R.R.; Lee Ho, P.; Tambourgi, D.V. Molecular cloning and expression of a functional dermonecrotic and haemolytic factor from Loxosceles laeta venom. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2002, 298, 638–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Santi Ferrara, G.I.; de Fernandes-Pedrosa, M.F.; de Junqueira-de-Azevedo, I.L.M.; Gonçalves-de-Andrade, R.M.; Portaro, F.C.V.; Manzoni-de-Almeida, D.; Murakami, M.T.; Arni, R.K.; van den Berg, C.W.; Ho, P.L.; et al. SMase II, a new sphingomyelinase D from Loxosceles laeta venom gland: Molecular cloning, expression, function and structural analysis. Toxicon 2009, 53, 743–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machado, L.F.; Laugesen, S.; Botelho, E.D.; Ricart, C.A.O.; Fontes, W.; Barbaro, K.C.; Roepstorff, P.; de Sousa, M.V. Proteome analysis of brown spider venom: Identification of loxnecrogin isoforms in Loxosceles gaucho venom. Proteomics 2005, 5, 2167–2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magalhães, G.S.; Caporrino, M.C.; Della-Casa, M.S.; Kimura, L.F.; Prezotto-Neto, J.P.; Fukuda, D.A.; Portes-Junior, J.A.; Neves-Ferreira, A.G.C.; Santoro, M.L.; Barbaro, K.C. Cloning, expression and characterization of a phospholipase D from Loxosceles gaucho venom gland. Biochimie 2013, 95, 1773–1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Giuseppe, P.O.; Ullah, A.; Silva, D.T.; Gremski, L.H.; Wille, A.C.M.; Chaves Moreira, D.; Ribeiro, A.S.; Chaim, O.M.; Murakami, M.T.; Veiga, S.S.; et al. Structure of a novel class II phospholipase D: Catalytic cleft is modified by a disulphide bridge. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2011, 409, 622–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ullah, A.; Magalhães, G.S.; Masood, R.; Mariutti, R.B.; Coronado, M.A.; Murakami, M.T.; Barbaro, K.C.; Arni, R.K. Crystallization and preliminary X-ray diffraction analysis of a novel sphingomyelinase D from Loxosceles gaucho venom. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. F Struct. Biol. Commun. 2014, 70, 1418–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Coronado, M.A.; Ullah, A.; Silva, L.S.; Chaves-Moreira, D.; Vuitika, L.; Chaim, O.M.; Veiga, S.S.; Chahine, J.; Murakami, M.T.; Arni, R.K. Structural insights into substrate binding of brown spider venom class II phospholipases D. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 2015, 16, 768–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariutti, R.B.; Chaves-Moreira, D.; Vuitika, L.; Caruso, Í.P.; Coronado, M.A.; Azevedo, V.A.; Murakami, M.T.; Veiga, S.S.; Arni, R.K. Bacterial and arachnid sphingomyelinases D: Comparison of biophysical and pathological activities. J. Cell. Biochem. 2017, 118, 2053–2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masood, R.; Ullah, K.; Ali, H.; Ali, I.; Betzel, C.; Ullah, A. Spider’s venom phospholipases D: A structural review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 107, 1054–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gremski, L.H.; da Justa, H.C.; da Silva, T.P.; Polli, N.L.C.; Antunes, B.C.; Minozzo, J.C.; Wille, A.C.M.; Senff-Ribeiro, A.; Arni, R.K.; Veiga, S.S. Forty years of the description of brown spider venom phospholipases-D. Toxins 2020, 12, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Lima, S.A.; Guerra-Duarte, C.; Costal-Oliveira, F.; Mendes, T.M.; Luís, L.F.; Oliveira, D.; de Avila, R.A.M.; Ferrer, V.P.; Trevisan-Silva, D.; Veiga, S.S.; et al. Recombinant protein containing B-cell epitopes of different Loxosceles spider toxins generates neutralizing antibodies in immunized rabbits. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bermúdez-Méndez, E.; Fuglsang-Madsen, A.; Føns, S.; Lomonte, B.; Gutiérrez, J.M.; Laustsen, A.H. Innovative immunization strategies for antivenom development. Toxins 2018, 10, 452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Da Silveira, R.B.; Pigozzo, R.B.; Chaim, O.M.; Appel, M.H.; Dreyfuss, J.L.; Toma, L.; Mangili, O.C.; Gremski, W.; Dietrich, C.P.; Nader, H.B.; et al. Molecular cloning and functional characterization of two isoforms of dermonecrotic toxin from Loxosceles intermedia (Brown spider) venom gland. Biochimie 2006, 88, 1241–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vuitika, L.; Chaves-Moreira, D.; Caruso, I.; Lima, M.A.; Matsubara, F.H.; Murakami, M.T.; Takahashi, H.K.; Toledo, M.S.; Coronado, M.A.; Nader, H.B.; et al. Active site mapping of Loxosceles phospholipases D: Biochemical and biological features. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2016, 1861, 970–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appel, M.H.; da Silveira, R.B.; Chaim, O.M.; Paludo, K.S.; Silva, D.T.; Chaves, D.M.; da Silva, P.H.; Mangili, O.C.; Senff-Ribeiro, A.; Gremski, W.; et al. Identification, cloning and functional characterization of a novel dermonecrotic toxin (phospholipase D) from brown spider (Loxosceles intermedia) venom. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gen. Subj. 2008, 1780, 167–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buch, D.R.; Souza, F.N.; Meissner, G.O.; Morgon, A.M.; Gremski, L.H.; Ferrer, V.P.; Trevisan-Silva, D.; Matsubara, F.H.; Boia-Ferreira, M.; Sade, Y.B.; et al. Brown spider (Loxosceles genus) venom toxins: Evaluation of biological conservation by immune cross-reactivity. Toxicon 2015, 108, 154–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dolinsky, T.J.; Nielsen, J.E.; McCammon, J.A.; Baker, N.A. PDB2PQR: An automated pipeline for the setup of Poisson-Boltzmann electrostatics calculations. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, W665–W667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrodinger, L.L.C. The PyMOL Molecular Graphics System; Version 2.4; Schrodinger, L.L.C.: New York, NY, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Radu, M.; Chernoff, J. An in vivo assay to test blood vessel permeability. J. Vis. Exp. 2013, 2–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Murakami, M.T.; Fernandes-Pedrosa, M.F.; Tambourgi, D.V.; Arni, R.K. Structural basis for metal ion coordination and the catalytic mechanism of sphingomyelinases D. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 13658–13664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ullah, A.; de Giuseppe, P.O.; Murakami, M.T.; Trevisan-Silva, D.; Wille, A.C.M.; Chaves-Moreira, D.; Gremski, L.H.; da Silveira, R.B.; Sennf-Ribeiro, A.; Chaim, O.M.; et al. Crystallization and preliminary X-ray diffraction analysis of a class II phospholipase D from Loxosceles intermedia venom. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. F Struct. Biol. Cryst. Commun. 2011, 67, 234–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chaves-Moreira, D.; Chaim, O.M.; Sade, Y.B.; Paludo, K.S.; Gremski, L.H.; Donatti, L.; de Moura, J.; Mangili, O.C.; Gremski, W.; Da Silveira, R.B.; et al. Identification of a direct hemolytic effect dependent on the catalytic activity induced by phospholipase-D (dermonecrotic toxin) from brown spider venom. J. Cell. Biochem. 2009, 107, 655–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isbister, G.K.; Fan, H.W. Spider bite. Lancet 2011, 378, 2039–2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malaque, C.M.S.; Santoro, M.L.; Cardoso, J.L.C.; Conde, M.R.; Novaes, C.T.G.; Risk, J.Y.; França, F.O.S.; de Medeiros, C.R.; Fan, H.W. Clinical picture and laboratorial evaluation in human loxoscelism. Toxicon 2011, 58, 664–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manríquez, J.J.; Silva, S. Cutaneous and visceral loxoscelism: A systematic review. Rev. Chil. Infectol. 2009, 26, 420–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vetter, R.S. The distribution of brown recluse spiders in the southeastern quadrant of the United States in relation to loxoscelism diagnoses. South. Med. J. 2009, 102, 518–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schenone, F. Cuadros tóxicos producidos por mordeduras de araña en Chile: Latrodectismo y loxoscelismo. Rev. Méd. Chile 2003, 131, 437–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hogan, C.J.; Barbaro, K.C.; Winkel, K. Loxoscelism: Old obstacles, new directions. Ann. Emerg. Med. 2004, 44, 608–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swanson, D.L.; Vetter, R.S. Medical progress: Bites of brown recluse spiders and suspected necrotic arachnidism. New Engl. J. Med. 2005, 352, 700–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isbister, G.K.; Graudins, A.; White, J.; Warrell, D. Antivenom treatment in arachnidism. J. Toxicol. Clin. Toxicol. 2003, 41, 291–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauli, I.; Minozzo, J.C.; da Silva, P.H.; Chaim, O.M.; Veiga, S.S. Analysis of therapeutic benefits of antivenin at different time intervals after experimental envenomation in rabbits by venom of the brown spider (Loxosceles intermedia). Toxicon 2009, 53, 660–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Futrell, J.M. Loxoscelism. Am. J. Med. Sci. 1992, 304, 261–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, R.O.S.; Chaim, O.M.; da Silveira, R.B.; Gremski, L.H.; Sade, Y.B.; Paludo, K.S.; Senff-Ribeiro, A.; de Moura, J.; Chávez-Olórtegui, C.; Gremski, W.; et al. Biological and structural comparison of recombinant phospholipase D toxins from Loxosceles intermedia (brown spider) venom. Toxicon 2007, 50, 1162–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez-Muñoz, A.; Gangoiti, P.; Arana, L.; Ouro, A.; Rivera, I.G.; Ordoñez, M.; Trueba, M. New insights on the role of ceramide 1-phosphate in inflammation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2013, 1831, 1060–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maceyka, M.; Spiegel, S. Sphingolipid metabolites in inflammatory disease. Nature 2014, 510, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]









| Species | Mutation | Oligonucleotide Sequence (5′-3′ Sense) |
|---|---|---|
| Loxosceles laeta | H12A | GTCCAATTTGGAACCTCGCTGCCATGGTGAACGCTGTTGCACA |
| H47A | GCCTACTTACACTTACGCCGGAACGCCTTGCGACT | |
| Y228A | GGGATTCGGCAAATGGATTTATCAATAAAATTGCCTACTGGTCTGTAGACAA | |
| Y228A-Y229A-W230A | CGGCAAATGGATTTATCAATAAAATTGCCGCCGCCTCTGTAGACAAAGTATCAACAACGAAGGC | |
| E32A-D34A | GGATCTTGGTGCAAACGCATTAGCCGCGGCCGTTACTTTTAAGGGATCAGTGCC | |
| Loxosceles gaucho | H12A | CCTATATGGGTTATGGGTGCCATGGTTAACTCCCTCGCT |
| H47A | AGCTAATCCTGAATACACATACGCCGGAATTCCCTGCGATTGTGGA | |
| Y228A | GCGGGATCATTAACAAAGTGGCCTATTGGACAGTGGACAAACG | |
| Y228A-Y229A-W230A | GAAGCGGGATCATTAACAAAGTGGCCGCCGCCACAGTGGACAAACGCCAATCGACAAG | |
| E32A-D34A | GCCTTGGATCGAATTCAATCGCCACAGCCGTGTCATTCGATAAGCAAGC |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
da Silva, T.P.; de Castro, F.J.; Vuitika, L.; Polli, N.L.C.; Antunes, B.C.; Bóia-Ferreira, M.; Minozzo, J.C.; Mariutti, R.B.; Matsubara, F.H.; Arni, R.K.; et al. Brown Spiders’ Phospholipases-D with Potential Therapeutic Applications: Functional Assessment of Mutant Isoforms. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 320. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9030320
da Silva TP, de Castro FJ, Vuitika L, Polli NLC, Antunes BC, Bóia-Ferreira M, Minozzo JC, Mariutti RB, Matsubara FH, Arni RK, et al. Brown Spiders’ Phospholipases-D with Potential Therapeutic Applications: Functional Assessment of Mutant Isoforms. Biomedicines. 2021; 9(3):320. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9030320
Chicago/Turabian Styleda Silva, Thaís Pereira, Fernando Jacomini de Castro, Larissa Vuitika, Nayanne Louise Costacurta Polli, Bruno César Antunes, Marianna Bóia-Ferreira, João Carlos Minozzo, Ricardo Barros Mariutti, Fernando Hitomi Matsubara, Raghuvir Krishnaswamy Arni, and et al. 2021. "Brown Spiders’ Phospholipases-D with Potential Therapeutic Applications: Functional Assessment of Mutant Isoforms" Biomedicines 9, no. 3: 320. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9030320
APA Styleda Silva, T. P., de Castro, F. J., Vuitika, L., Polli, N. L. C., Antunes, B. C., Bóia-Ferreira, M., Minozzo, J. C., Mariutti, R. B., Matsubara, F. H., Arni, R. K., Wille, A. C. M., Senff-Ribeiro, A., Gremski, L. H., & Veiga, S. S. (2021). Brown Spiders’ Phospholipases-D with Potential Therapeutic Applications: Functional Assessment of Mutant Isoforms. Biomedicines, 9(3), 320. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9030320







